Isotopes/ Ions/ Bohr Model and More
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Isotopes
The # of neutrons can be variable for many elements.
Atomic # = number of protons in an atom
Isotopes are atoms that have the same # atomic #, but different mass numbers due to a change in the # of neutrons
Nucleus, the center of an atom, is made of protons & neutrons.
Protons
( + ) charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They determine the atomic number and identity of an element.
Neutrons
( n0 ) neutral particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They contribute to the atomic mass but not to the charge of the atom.
Electrons
( - )charge particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom, playing a key role in chemical bonding and reactions.
Atoms can form….
ions or isotopes by gaining or losing electrons or neutrons.
What are the charge of atoms?
they don’t have a charge
What are elements defined by?
the number of protons in their nucleus
What do metals on the periodic table form?
they form positive ions
What do non- metals on the periodic table form?
they form negative ions
What do you have to do to make a positive ion?
take away an electron
What do you have to do to make a negative ion?
you add an electron
Which group of elements does not form ions?
Noble gases
How many electrons are in the first outer shell?
Two electrons
How many electrons are in the second outer shell?
Eight electrons
When you gain an electron for ex. Li how would you write it out?
You would write it as Li-
When you loose an electron for ex. Li how would you write it out?
You would write it as Li+
Electro - negativity
is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons within a chemical bond.
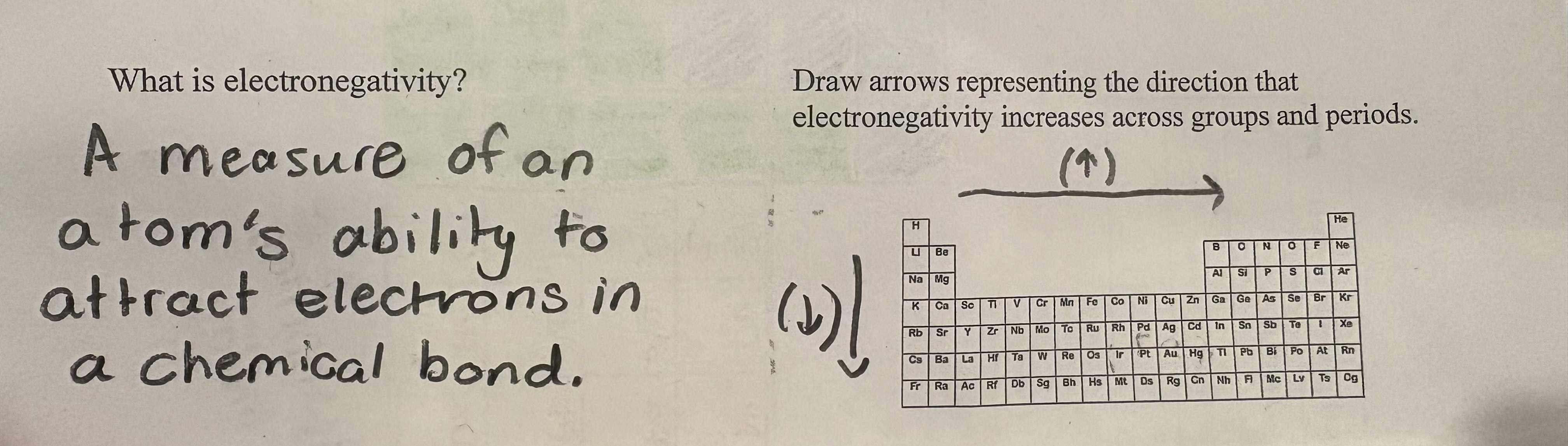
What’s the trend when you across the PT for electronegativity?
Electronegativity increases across a period as the atomic number increases, leading to a stronger attraction for electrons.
What’s the trend when you down the PT for electronegativity?
Electronegativity decreases down a group as atomic size increases, resulting in a weaker attraction for electrons.
Ionization Energy
is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gas phase.
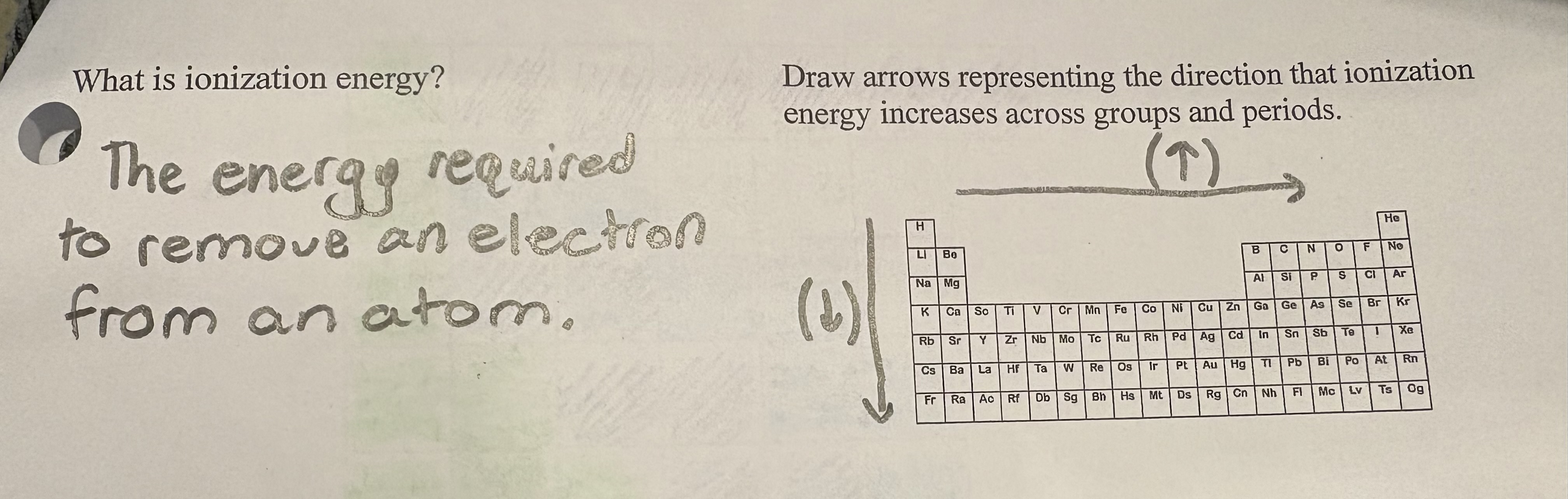
Solve for thus problem answer: P+, N0, and e-
p* = 7. N0 7, e- = 7 =
How do you find the mass #?
Add the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
How do you find the # neutrons?
Subtract the atomic number from the mass number of the atom.
How do you know how many circles you have to draw using Bohr’s model using the periodic table?
Look at the periods of the periodic table
Electronegativity
is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
What’s the trend for electronegativity?
as you go across the PT from left to right, electronegativity increases, while increases as you go up the periodic table
Ionization Energy
is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state.
What’s the trend for ionization?
as you go across the PT from left to right, ionization increases, while it increases while going up the periodic table
How do you find the number of nuetrons?
Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass of the element.
Ground State
is the form that an atom is normally in
Why do electrons get exicted?
b/c of the heat and light will show (ex. color)
Excited State
e- gets excited when it gets energy (sun, heat, fire…) and moves to a higher energy level.
As the wave length increases what happens to the frequency?
The frequency decreases, indicating an inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency.
As the wave length decreases what happens to the frequency?
The frequency increases, demonstrating the inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency.
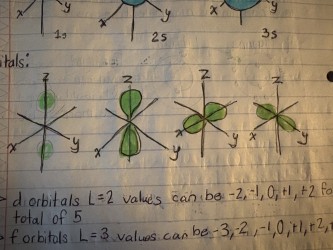
P orbital
Hold’s a max of 6 electrons ( x= 2) (e-) and( z=2 )
Groups 1-2
S orbital
Holds a maximum of 2 electrons (x=1) (e-) and (z=1)
Groups 13 -18
What does the 1 stand for in 1S2?
energy level (period groups)
What does the S stand for in 1S2?
orbital
What does the 2 stand for in 1S2?
Number of electrons
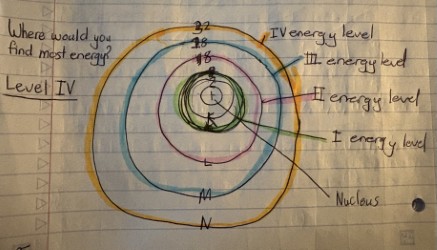
Energy Levels
As you go farther from the nucleus, electrons at higher levels have more energy & their energy.
Electrons can jump from a higher to lower energy level if they absorb this amount of energy.
If electrons jump from higher —- lower energy level, they give off energy, often to form of light.
Which energy level would you find the most energy? (only 4 in the context)
The fourth energy level (4s)
S orbitals are what shape?
spherical
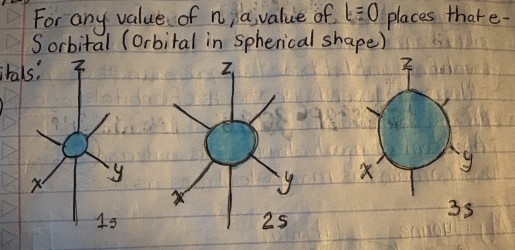
What shape are P orbitals?
dumbbell-shaped
Aufbav Rule
electron configuration energy increases levels as you write them out.
Pavlie Ruler
when you put the arrows into box one goes up on always goes down. (spin)
Hund’s rule
states that electrons will fill degenerate orbitals singly and with the same spin before pairing up in orbitals.
one in each box before you put one arrow orbital box before two goes into any.
Energy levels
in an atom are the fixed distances from the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. Each level corresponds to a specific energy state.
What happens with the energy levels as you get father from the nucleus?
The energy levels increase, allowing electrons to occupy higher energy states.
What energy level would have the most energy?
The outermost energy level, often referred to as the valence shell, contains electrons with the highest energy.
Atomic radius
measurement from the nucleus to the valence electrons

Nuclear charge
is the total charge of the nucleus, determined by the number of protons present in the atom. (GOING DOWN IT INCREASES and going right it also increases)
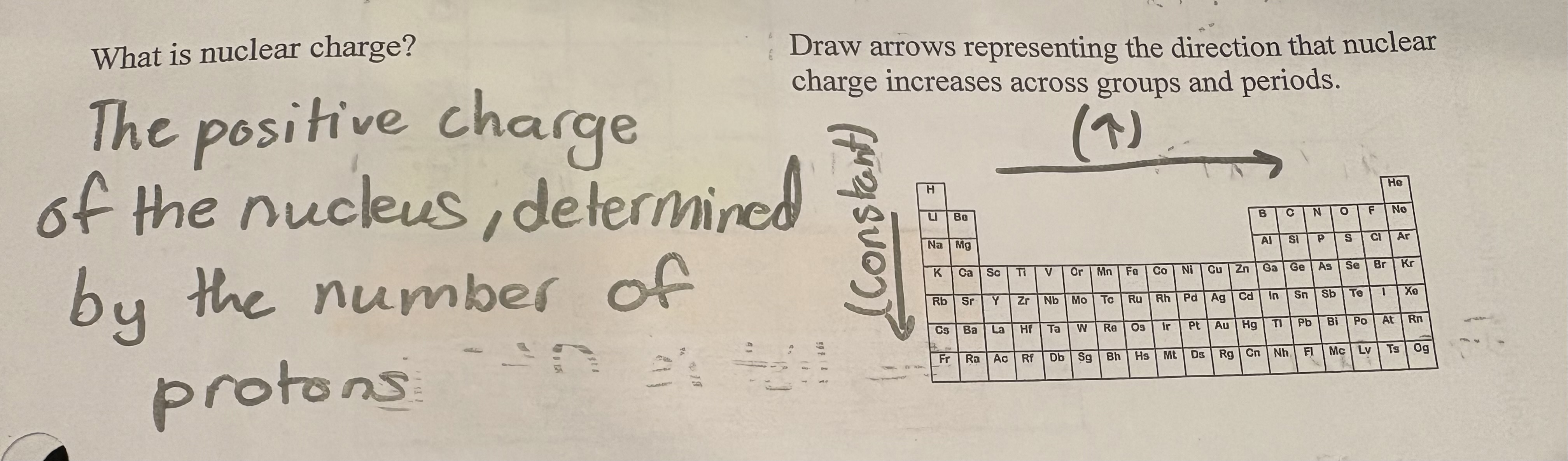
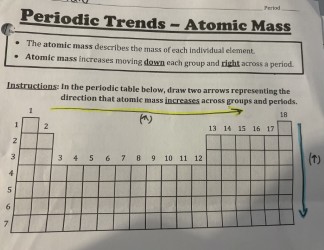
Atomic Mass does what of the periodic table?
increases moving down each group and right across a period
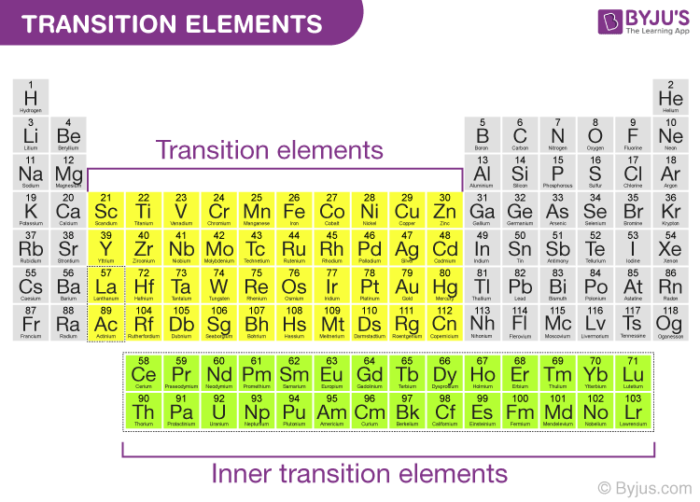
Transition Medals locations
are found in the d-block of the periodic table, consisting of groups 3 to 12.
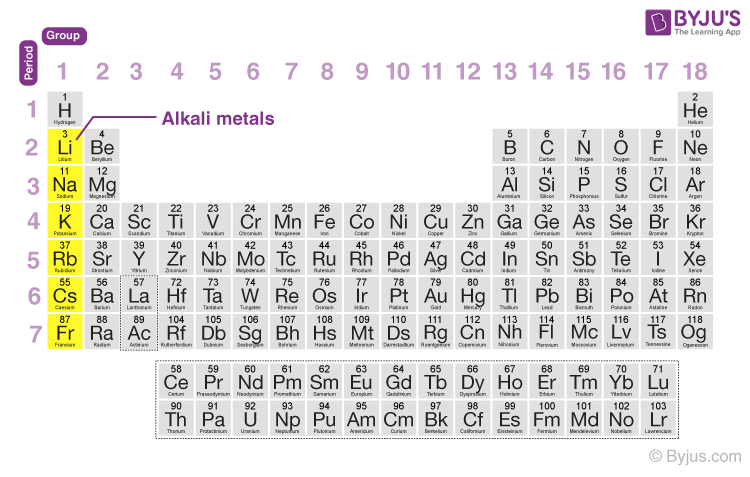
Alkali metals location
are found in group 1 of the periodic table, excluding hydrogen. They are known for their high reactivity and tendency to lose one electron.
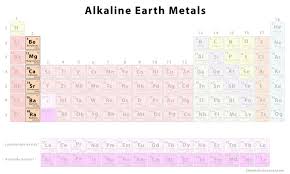
Alkaline earth metals location
are found in group 2 of the periodic table. They are characterized by having two valence electrons and are less reactive than alkali metals.
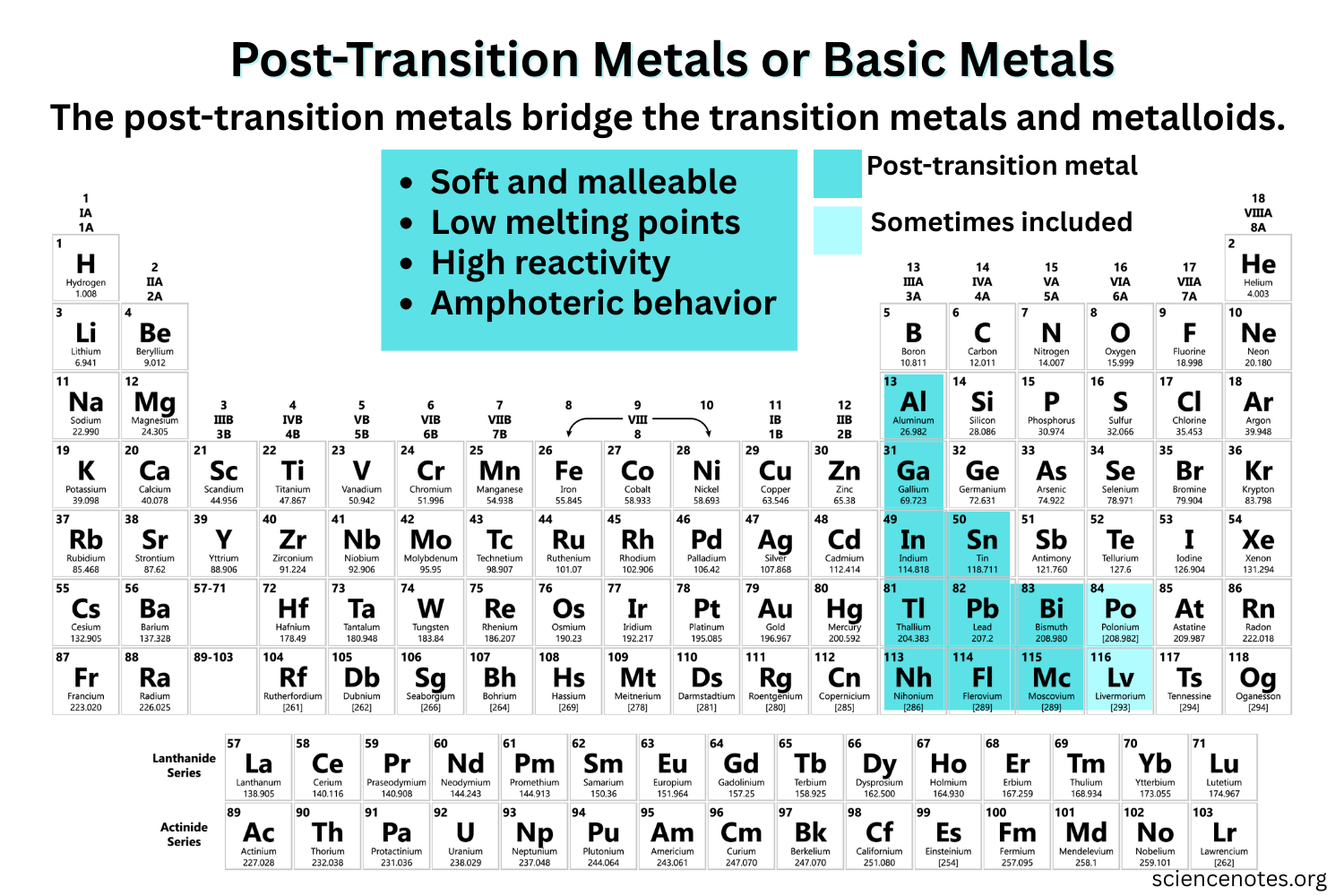
Post - transition metals location
are found in groups 13 to 16 of the periodic table, located to the right of transition metals.
Metalloids location
are found along the zig-zag line on the periodic table, between metals and nonmetals. They exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals.
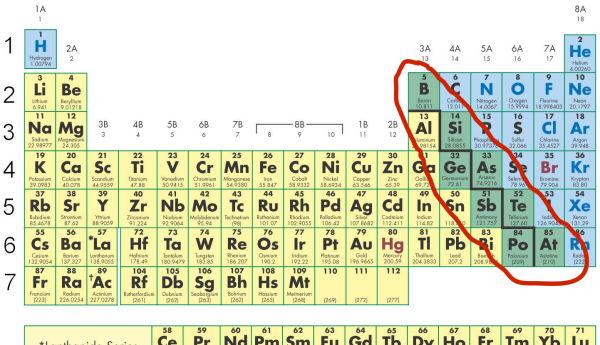
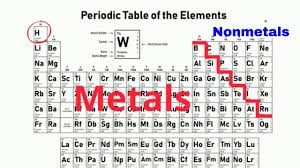
Non-metals location
are found on the right side of the periodic table, primarily in groups 14 to 18. They are characterized by their lack of metallic properties and high electronegativity.
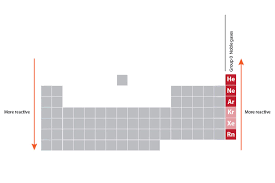
Noble gases location
group 18
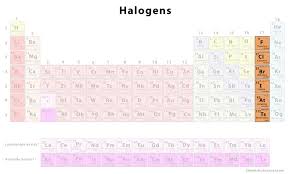
Halogens location
group 17
How many orbitals and electrons are in f orbitals?
There are seven f orbitals, which can hold a total of 14 electrons.
Groups on the periodic table have what in common?
same amount of valence electrons/ same properties
What is a cation?
is an ion with a positive charge, formed when an atom loses one or more electrons.
What is an anion?
an ion with a negative charge, formed by the gain of electrons.