Business: 3.1 and 3.2 (Marketing & Market Research)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Product-Oriented businesses focus on…
product development first.
(Early Apple, Dyson, Ferrari)
Market-Orientated businesses focus on…
customer needs through market research.
(McDonald’s, Nike, Netflix)

Market Research definition
The process of gathering, analysing, and interpreting information about a market, including potential customers and competitors.
Benefits of Market Research
Helps businesses make informed decisions
Reduces risk of unsuccessful products
Identifies customer preferences and buying habits
Helps determine pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies
Ways of doing primary research (AKA ___ research) are…
(field research): Surveys, questionnaires, interviews, focus groups, and observations, etc.
A set of written questions to gather information.
Questionnaire
+Can reach a large audience, cheap online.
-Responses may not always be honest.
Interviews (definition, pro’s and con’s)
A face-to-face or phone conversation for detailed responses.
+Provides detailed feedback.
-Time-consuming and expensive.
Watching customer behaviour without an explanation
Observations
+ Provides real customer actions rather than opinions.
- No explanations for customer choices.
Focus group (definition, pro’s and con’s)
A small group of people discuss a product/service.
+ Provides in-depth opinions
- Difficult to organise, small sample size.
Ways of doing secondary research (AKA ___ research) are…
(desk research): Government reports, online articles, market research reports, company sales data, etc.
Data that was collected by the business from its own organisation are…
Internal Secondary Research Sources
Sales records (pro’s and con’s)
+Helps identify best-selling products and customer trends.
-Only reflects past sales, not future demand.
Customer feedback forms (pro’s and con’s)
+Provides direct insights into customer satisfaction and preferences.
-Can be biased if only a small group of customers respond.
Financial statements (pro’s and con’s)
+Helps track profitability and financial performance.
-Does not provide reasons for trends or external market influences.
Loyalty programme data (pro’s and con’s)
+Helps track repeat customers and their buying habits.
-Does not include data on potential new customers.
Website analytics (pro’s and con’s)
+Shows which products/pages attract the most interest.
-Does not explain why customers do/don’t make purchases
Data that was collected outside the business are…
External Secondary Research Sources
External Secondary Research Sources (pro’s and con’s)
+Quick to access, cost-effective, large sample size, useful for market trends.
- May be outdated, not specific to business, available to competitors, possible inaccuracy.
Sampling is…
selecting a smaller group to represent a whole population.
Types of Sampling
Random sampling (selecting names from a database randomly)
Quota sampling (based on characteristics: age, race, etc.)
Factors Influencing Accuracy of Market Research Data
Sample size (may not reflect accurately)
Bias (biased sample = inaccurate answers)
Questionnaire design & clarity (poorly worded questions)
Timing of research (outdated data, trends change rapidly.)
Influence of external factors (ex. inflation, a recession, etc.)
What are the roles of the marketing department?
IDENTIFY
SATISFY
MAINTAIN
BUILD
ANTICIPATE
What must be IDENTIFIED?
Customer needs.
What must be ANTICIPATED?
Changes in customers’ needs and spending patterns.
What must be MAINTAINED?
Customer relations, loyalty, and satisfaction.
What must be BUILT?
Customer loyalty.
What must be SATISFIED?
Customers’ needs.
What are the market research steps?
Identify research objective.
Define target market.
Choose research method (primary or secondary).
Collect data.
Analyse using charts, graphs, and statistical tools.
Draw conclusions and make decisions.
What are the 4P’s of marketing?
PRODUCT
PROMOTION
PLACE
PRICE
Marketing (definition)
The business activity that involves finding out what customers want, using that information to design products and services, and selling them effectively.

Demographics (definition)
Statistical data about a population such as age, gender, or income level.
Customer needs are…
The products, services, or solutions customers require to solve problems or meet desires.
How can a business investigate customer needs?
By doing market research, either primary (field) or secondary (desk) and by analysing customer data: Demographics, trends, and feedback.
Define customer satisfaction.
A measure of how well a business meets or exceeds customer expectations.
How can a business be sure its customers are satisfied?
By providing:
High-quality products (e.g. durable, reliable.)
Appropriate pricing (e.g. competitive, value for money.)
Effective customer service (e.g. after-sales support.)
Regular innovation and updates to meet evolving expectations.
Define customer loyalty.
The likelihood of customers repeatedly choosing a business’s products or services over competitors.

What is the importance of customer loyalty?
Loyal customers cost less to retain than acquiring new ones (they already know what is being offered and don’t need to be convinced.)
They promote the business via word-of-mouth (free advertising.)
How can customer loyalty be built?
Consistent product quality.
Transparent, honest communication.
Personalised rewards (e.g. loyalty cards.)
Define retention.
Keeping existing customers rather than focusing solely on attracting new ones.
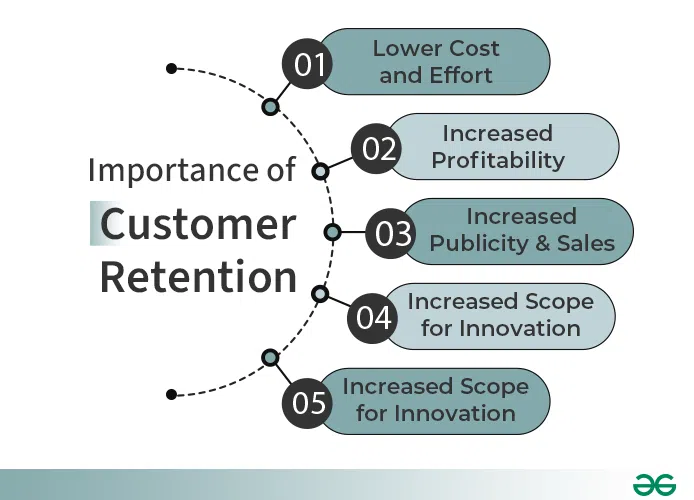
Strong relationships with customers → Loyal customers →
Increased sales
How can a business be prepared for potential changes in customers’ wants/needs?
Being dynamic and staying relevant/up-to-date with trends.
Being proactive with customer service.
Remaining ahead of the game.
Innovating to offer something fresh & exciting.
Being ready to respond to a problem at any moment.
Define a brand.
The unique identity and reputation of a business/product.

What are the benefits of successful marketing?
Increased sales & profitability
Customer loyalty & retention
Improved brand reputation
Reduced risk of becoming out of date/no longer useful
Higher market share
Enter new markets
Develop new products/improve existing products
Define market share.
The percentage of the total market controlled by a business/product.
