RLE 6F - Determining TBSA and Fluid Replacement Computation; Peritoneal Dialysis; Hemodialysis; ABG Analysis; Cystoclysis
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
An artificial device designed to replace a missing body part, potentially lost through trauma, disease, or congenital conditions.
Prosthetic
- Is a measure of the acidity/alkalinity of blood,
normal: 7.35- 7.45
Blood pH
It is a tissue GRAFT taken from one part of a person's body and transplanted to another part of the SAME individual.
Autograft
-Aka XENOGRAFT
- tissue GRAFT obtained FROM a donor of a different SPECIES (animal) than the recipient.
Heterograft
Heterograft AKA....
XENOGRAFT
A GRAFT of tissue or an organ transplanted from a donor of the SAME SPECIES but with different genetic makeup.
Homograft
PRIMARY structural PROTEIN found in connective tissues
Collagen
-provides STRENGTH + STABILITY
Condition: characterized by RIGID TIGHTENING of muscles, tendons, ligaments, or skin
Contracture
Condition: PERMANENT SHORTENING of tissue -> fx impairement
Contracture
Refers to a skin GRAFT created from the patient's OWN KERATINOCYTES, which are grown in a LABORATORY to form cohesive sheets.This
Cultured Epithelial Autograft
A PROCEDURE involving the REMOVAL -> dead, damaged, or infected tissue from a wound.
Debridement
refers to the area of the body from which skin/tissues are HARVESTED for grafting.
Donor Site
A type of dead tissue that forms over a wound due to necrosis
Eschar
A therapeutic practice utilizing water for health benefit
Hydrotherapy
A surgical connection created between an artery +vein to provide an access point for hemodialysis.
Arteriovenous Fistula
Is an abnormal connection between artery and vein
Arteriovenous Shunt
A medical treatment that performs the functions of the kidneys when they are unable to adequately filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood
Dialysis
Is a cleansing fluid composed of water, electrolytes, and salts used during dialysis to filter and clean the blood by removing waste products.
Dialysate
AKA artificial kidney and serves as a medical device used in hemodialysis to filter blood.
Dializer
The process through which solutes move from an area of higher concentration -> area of lower concentration across a semipermeable membrane.
Diffusion
Refers to EXTREME BLOOD LOSS occurring from a site OR DRAINING
Exsanguination
Is a form of dialysis where blood is filtered outside the body using a machine equipped with a dialyzer. This treatment removes waste products and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys can no longer perform these functions.
Hemodialysis
The movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to one of high solute concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis
Ultrafiltration
Tenckhoff catheter
A potential space in the abdomen between the peritoneum's lining and the internal organs.
Peritoneal Cavity:
During peritoneal dialysis, this cavity is filled with dialysate, allowing waste products and excess fluids to be absorbed from the blood through the peritoneal membrane.
A renal replacement therapy that uses the peritoneum as a membrane through which fluids and solutes are exchanged.
Peritoneal Dialysis
The process of removing excess fluid from the blood, employing pressure to drive fluid across a semipermeable membrane
Ultrafiltration
Type of catheter used for peritoneal dialysis
Tenckhoff catheter:
AKA continuous bladder irrigation, is defined as the continuous flushing of the bladder with a sterile saline solution.
Cystoclysis
This process aims to manage various conditions by maintaining bladder hygiene and ensuring the free flow of urine.
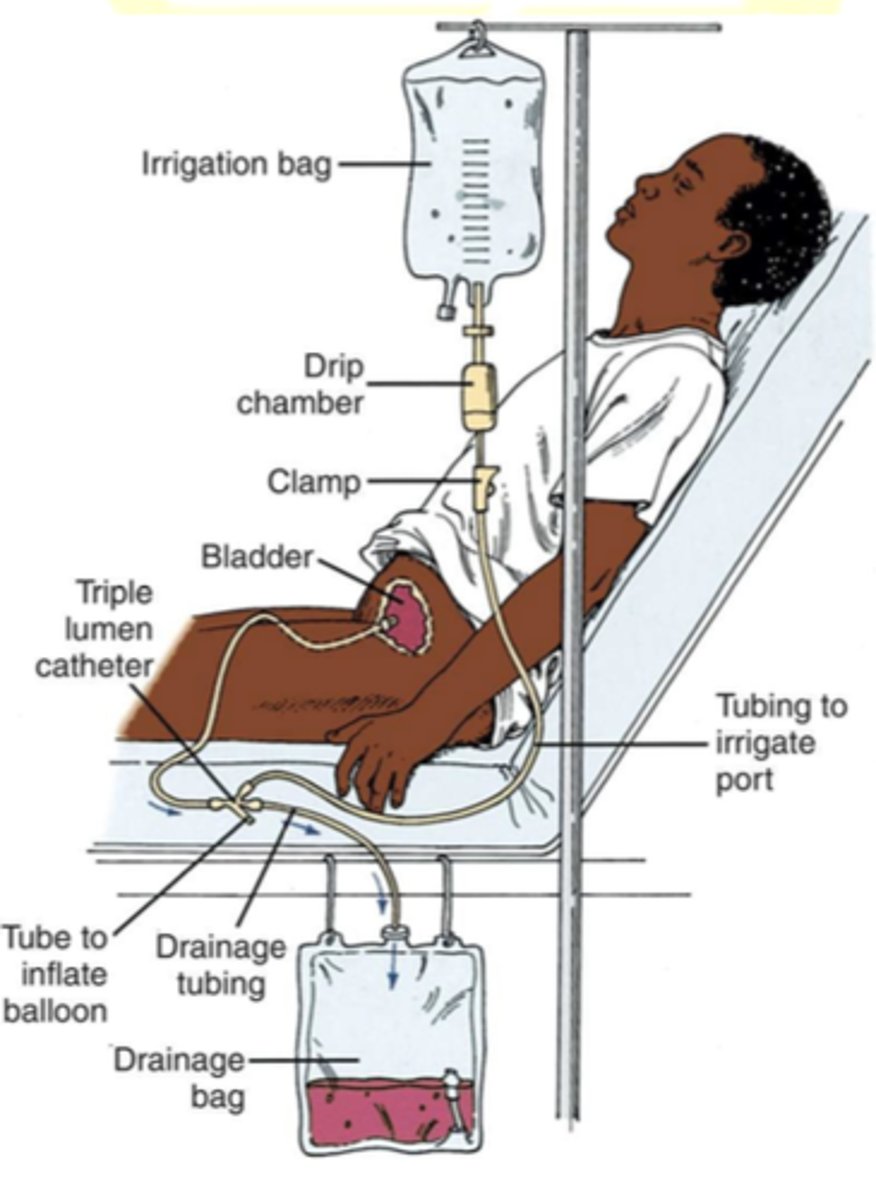
Cystoclysis AKA
CONTINUOUS BLADDER IRRIGATION
What soln used for cystoclysis
Sterile saline soln
clinical procedure used to assess collateral circulation in the arm
Allen's Test
if the color returns within 5-15 seconds, it indicates that the ulnar artery can sufficiently supply blood to the hand
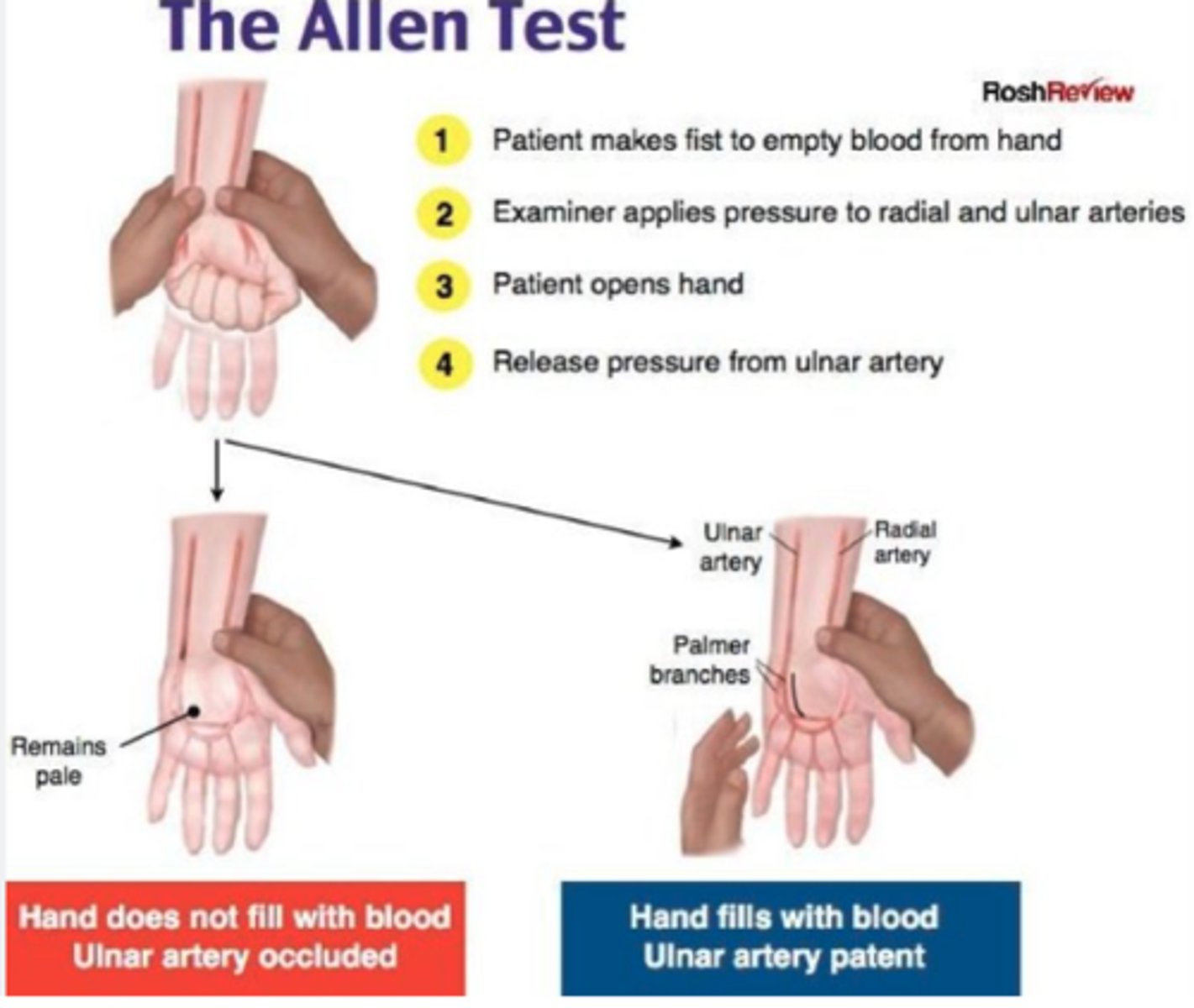
what arteries involved in allens test?
which artery released
how many seconds to return to color
radial + ulnar artery
ulnar artery
5-15sec
List ABG sites:
- Brachial Artery
- Femoral Artery
- Dorsalis Pedis Artery
- Posterior Tibial Artery
-Peripheral Venous Blood Gas (VBG)
It refers to the regulatory processes that maintain the pH level of the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) within a narrow range, typically between 7.35 and 7.45.
Acid base Homeostasis:
A vital electrolyte that plays a significant role in maintaining the body's acid-base balance by acting as a BUFFER
Bicarbonate
A condition marked by an excessive accumulation of acid in the body fluids, resulting from either increased acid production or inadequate acid removal by the kidneys.
Metabolic Acidosis:
It occurs when the body's pH level rises above normal due to:
- excess of bicarbonate
- loss of acid.
Metabolic Alkalosis:
Is the form of hemoglobin that is bound to oxygen, facilitating the transport of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues
Oxyhemoglobin
A condition that arises when the lungs fail = expel carbon dioxide, resulting in increased acidity in the blood (pH <7.35).
Respiratory Acidosis:
It occurs when hyperventilation leads to reduced levels of carbon dioxide in the blood, causing an increase in pH.
Respiratory Alkalosis
TBSA stands for:
total body surface area
pH normal level
7.35 - 7.45
PaCO2 normal
35 - 45 mmHg
PaCO2 > 45 mmHg
Respiratory Acidosis
PaCO2 < 35 mmHg
Respiratory Alkalosis
HCO3 normal
22 - 26 mEq/L
HCO3- < 22 mEq/L
Metabolic Acidosis
HCO3- > 26 mEq/L
Metabolic Alkalosis
type of burn: Burn injury through contact with hot liquids/stea
Scald
type of burn: This type of injury takes place when the electrical current EXCEEDS the skin's resistance and flows through the body.
cONDUCTIVE injury
-This results in the electricity traveling through nerves and vessels and outside bones, generating heat, and damaging tissues/nerves. Muscle contraction may also be evident. Such major effects are often due to high-voltage (>1000 volts).
type of burn Electrical flash which generates heat and light.
Flash injury
type of burnL Also referred to as ‘Frostbite’. Cold/ice burns occur as a result of prolonged exposure to a cold environment or direct contact with an extremely cold material.
Cold Exposure:
What are the phases of burn care: (EAR)
1. Emergent/resuscitative
2. Acute/intermediate
3. Rehabilitation
-Begins when diuresis starts
- Ends when wound closure is complete
- Begins 48-72 hours after the burn
injury
Acute/intermediate
Phase of burn care:
- Begins when injury happens
- Ends with capillary permeability
restoration (fluid restoration)
Emergent/resuscitative
Phase of burn care:
-Starts when there is wound closure
- Ends with patient's return to an
optimal level
Rehabilitation
Burn depths (4)
1. Superficial Burns (First-degree)
2. Partial Thickness Burns (Second-Degree)
3. Full-Thickness Burns (Third-Degree)
4. Full-Thickness burns including Fat, Fascia, Muscles, and/or Bone (Fourth-Degree) (deep burn necrosis)
burn classification: Superficial Burns, AKA
First-degree burns
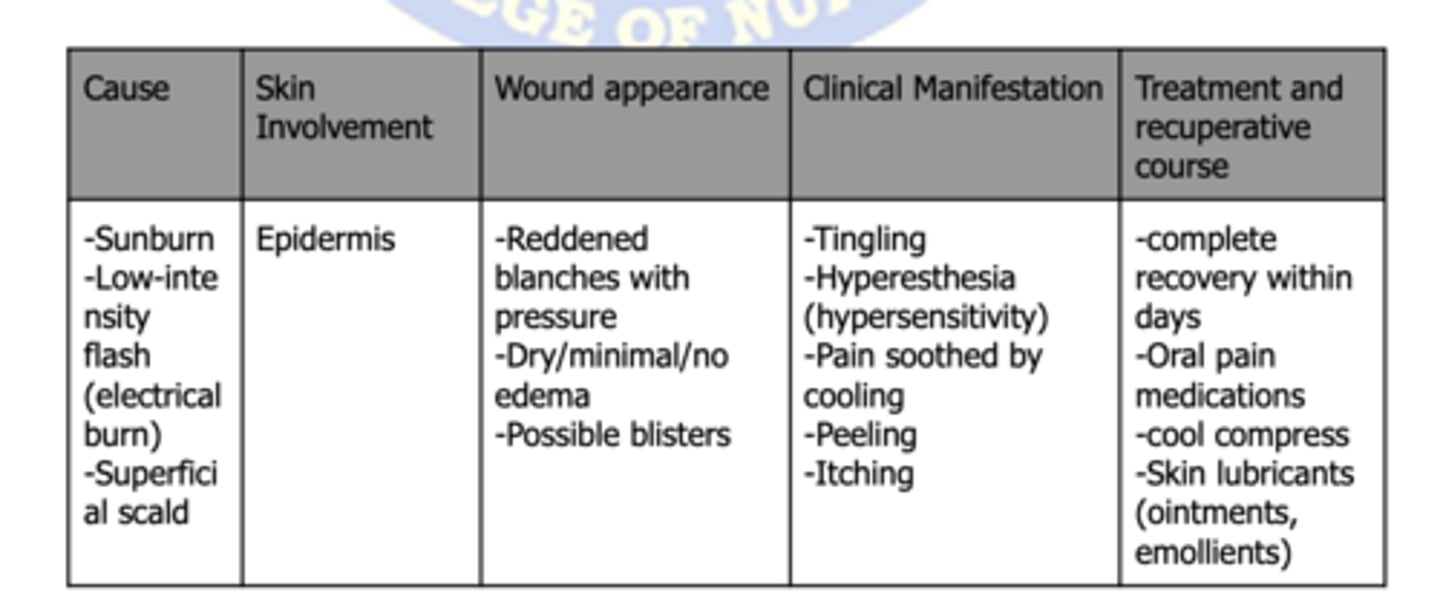
burn classification: second-degree burns
partial thickness burns
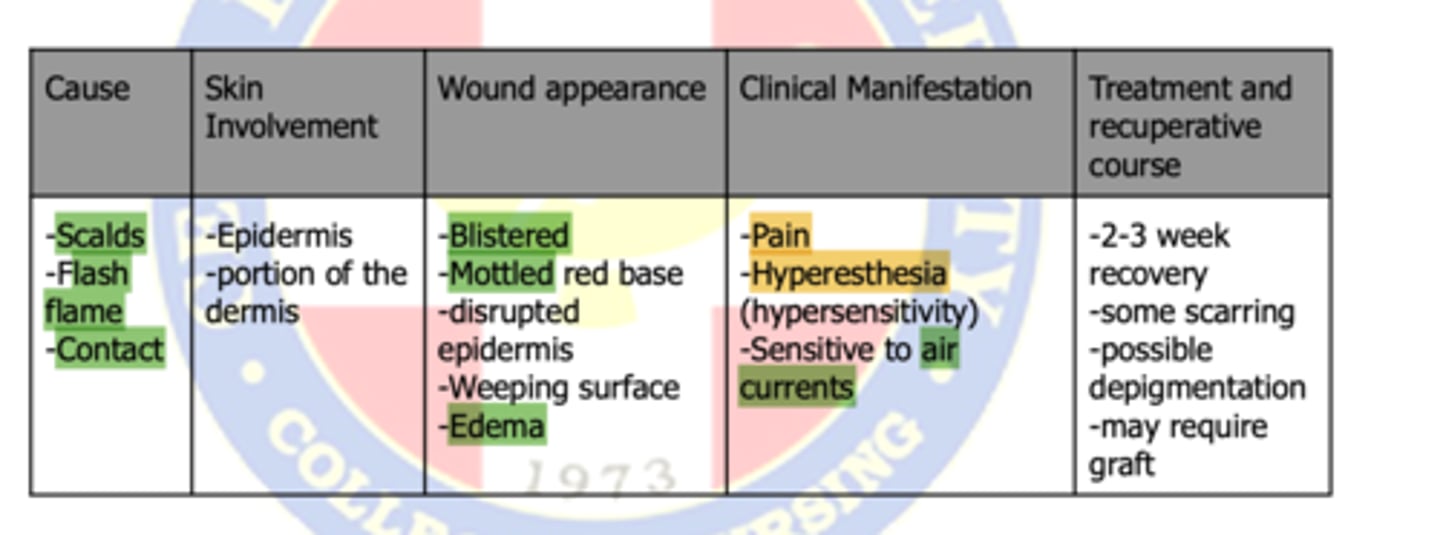
type of burn: !EDEMA! !BLISTER FORMATION!
PARTIAL THICKNESS BURNS (second-degree burns)
type of burn: sensitivity to air currents
PARTIAL THICKNESS BURNS (second-degree burns)
type of burn:
-Tingling
-Hyperesthesia (hypersensitivity)
-Pain soothed by cooling
-Peeling
-Itching
-Reddened blanches with pressure
first-degree burn (superficial burns)
term: Red pigment in urine and possible hemolysis
Myoglobinuria
type of burn: third-degree burn AKA
Full-Thickness Burns
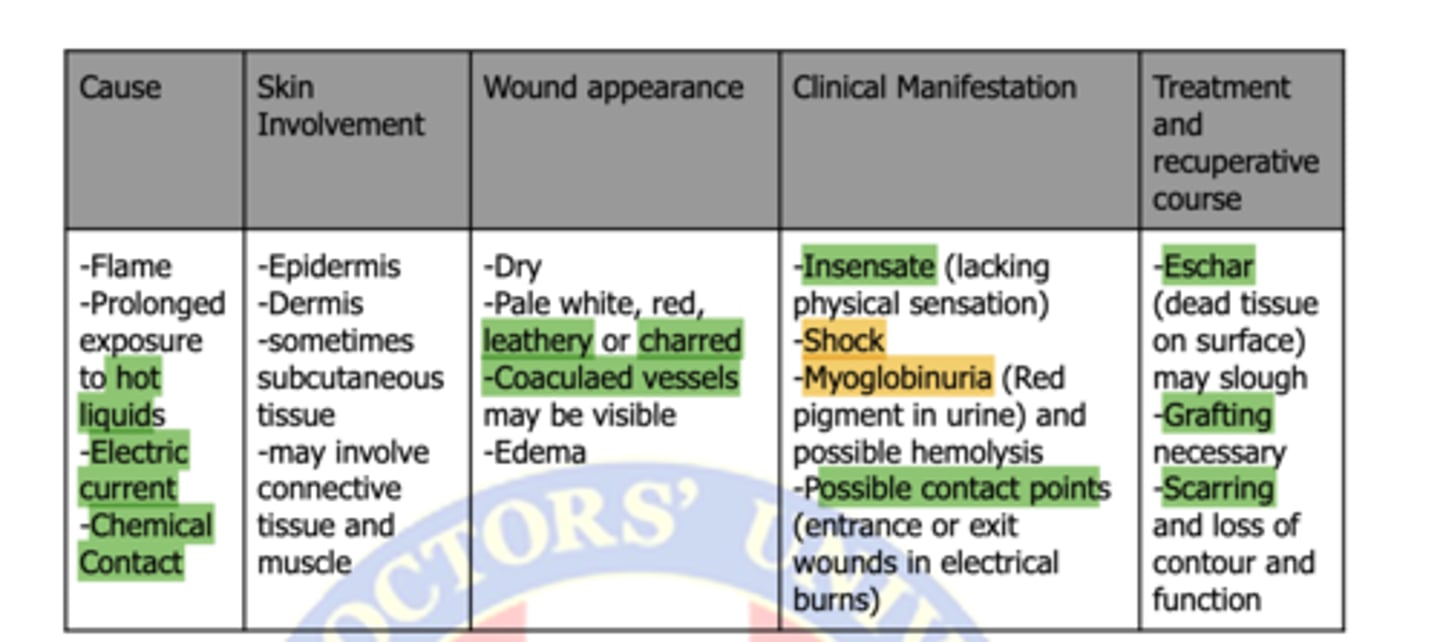
type of burn:
-color change - pale/white/red
-coagulated vessels
-insensate
-possible contact points
third-degree burns
classification of burns: Full-thickness burns including Fat, Fascia, Muscles, and/or Bone (Fourth-Degree) AKA
Deep burn necrosis
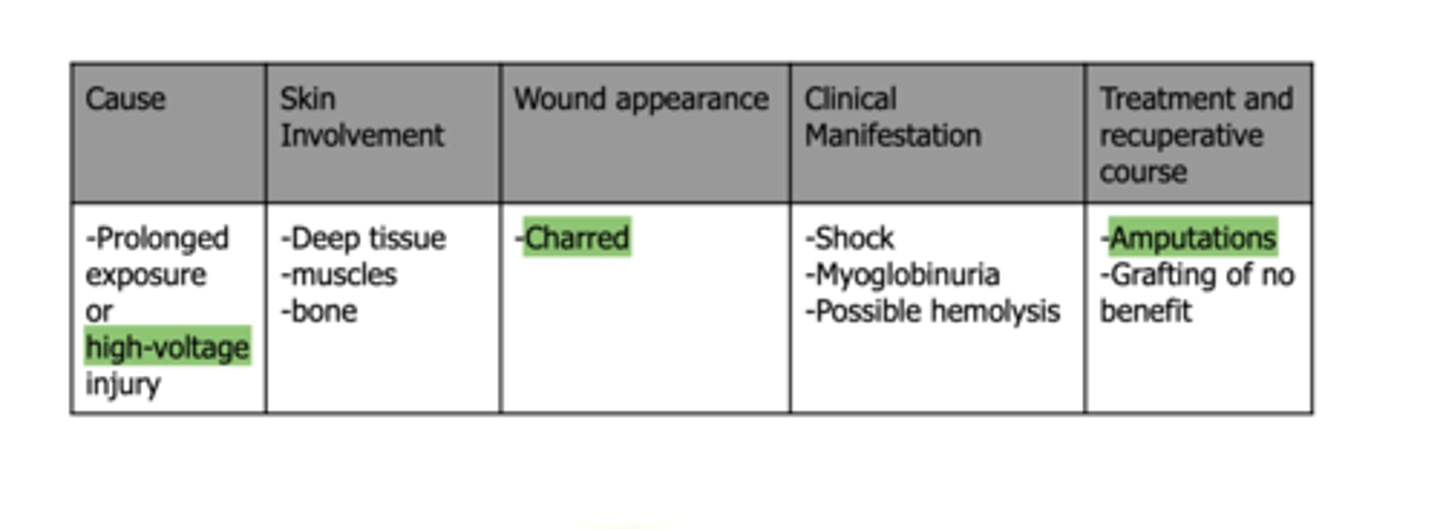
term: hyperesthesia AKA
hypersensitivity
type of burn:
-charred appearance
- requires amputations + hair affected
fourth-degree burns
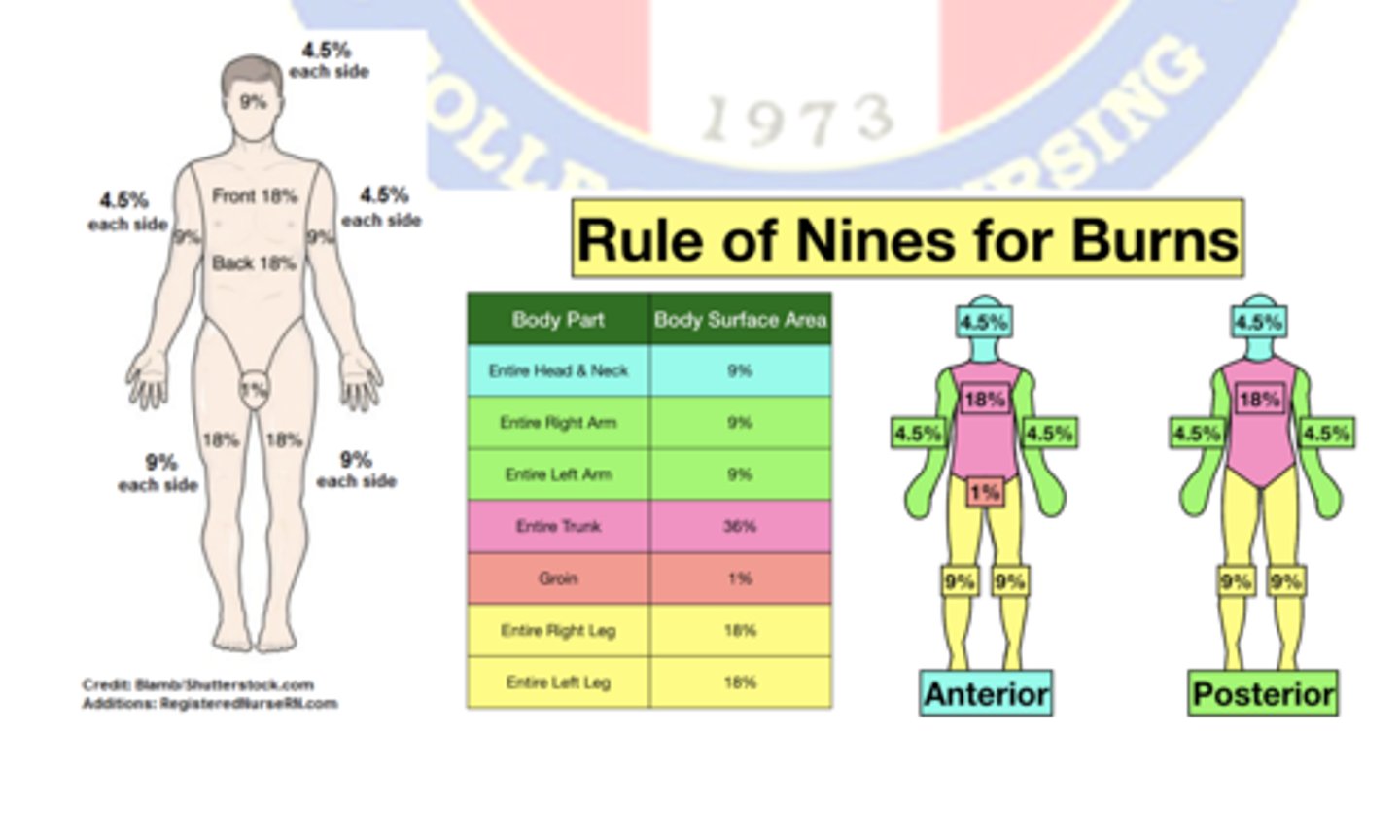
TBSA: Most common method to estimate TBSA
Rules of nine
TBSA: More precise method + considers age
Lund and Browder Method
TBSA: Uses palm + fingers
Palmer method
Rules of nine: Head
Entire:
Anterior/posterior:
9%
4.5%
Rules of nine: Arm
Entire:
Anterior/posterior:
9%
4.5%
Rules of nine: Trunk
Entire:
Anterior/posterior:
inferior/superior:
36%
18%
9%
Rules of nine: groin
Entire:
Anterior/posterior:
1%
Rules of nine: Leg
Entire:
Anterior/posterior:
18%
9%
parkland formula aka
Braxton formula
Most common method to calculate fluid restoration:
Parkland formula
fluid restoration mL:
-thermal/checmial:
-electrical:
-thermal/chemical: 2mL
-electrical: 4mL
colloid or crystalloid: blood/blood products
colloid
colloid or crystalloid: NSS
crystalloid
dialysis: tube inserted to necl/chest//groin
Central venous catheter
FEEL the ____
Hear the ___
thrill
bruit