NCLEX
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Monitor INR/PT
Warfarin

Warfarin range
2-3
Risk of skin necrosis in first week
warfarin
Warfarin toxicity
stop, give fresh frozen plasma and vitamin K

Oral vit. K preferred if no bleeding
warfarin
Antidote is vitamin K
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Black tarry stools
warfarin
nosebleeds, hematomas, risk of bleeding
warfarin
prophylaxis for venous thrombosis and PEs
warfarin
off label use is preventing stroke and TIA
warfarin
eat leafy greens
warfarin
Avoid Alcohol, Chamomile or green tea, Cranberry juice, Grapefruit juice
warfarin
contraindicated for patients with a bleed or pre/eclampsia
warfarin
Interactions with NSAIDS, fibrinolytics, antiplatelets, antiarrhythmics, and antimicrobials
warfarin
used in emergencies to dissolve blood clots
alteplase (fibrinolytic)
critical in treating: ischemic stroke, acute MI, PE, and occluded central vein catheters
alteplase (fibrinolytics)
contraindicated for bleeds, especially potentially fatal intracranial hemorrhage
alteplase (fibrinolytics)
medications for postpartum hemorrhage
oxytocin, misoprostol, tranexamic acid
Misoprostol (L&D drug)
prostaglandin E1 analog also used to promote contractions
tranexamic acid
Oxytocin (Pitocin)
stimulates uterine contractions, used to induce labor
Methergine (Methylergonovine)
Stimulates uterine contractions and vasoconstriction. It's given IM, and should be avoided in patients with hypertension.
uterine atony
Failure of the uterus to contract effectively, most common cause of uterine hemorrhage
Magnesium Sulfate (labor)
Smooth muscle relaxant. Decreases contractions during preterm labor.
LION PIT (Low fetal heart rate, Low baseline variability
Late decelerations)
Leftside, IV increase, O2, notify doctor, pitocin (if pitocin is running, shut off first)
VEAL CHOP
V- Variable C- Cord Compression
E- Early Decels H- Head Compression
A- Accelerations O - OK
L-Late Decels P - Placenta
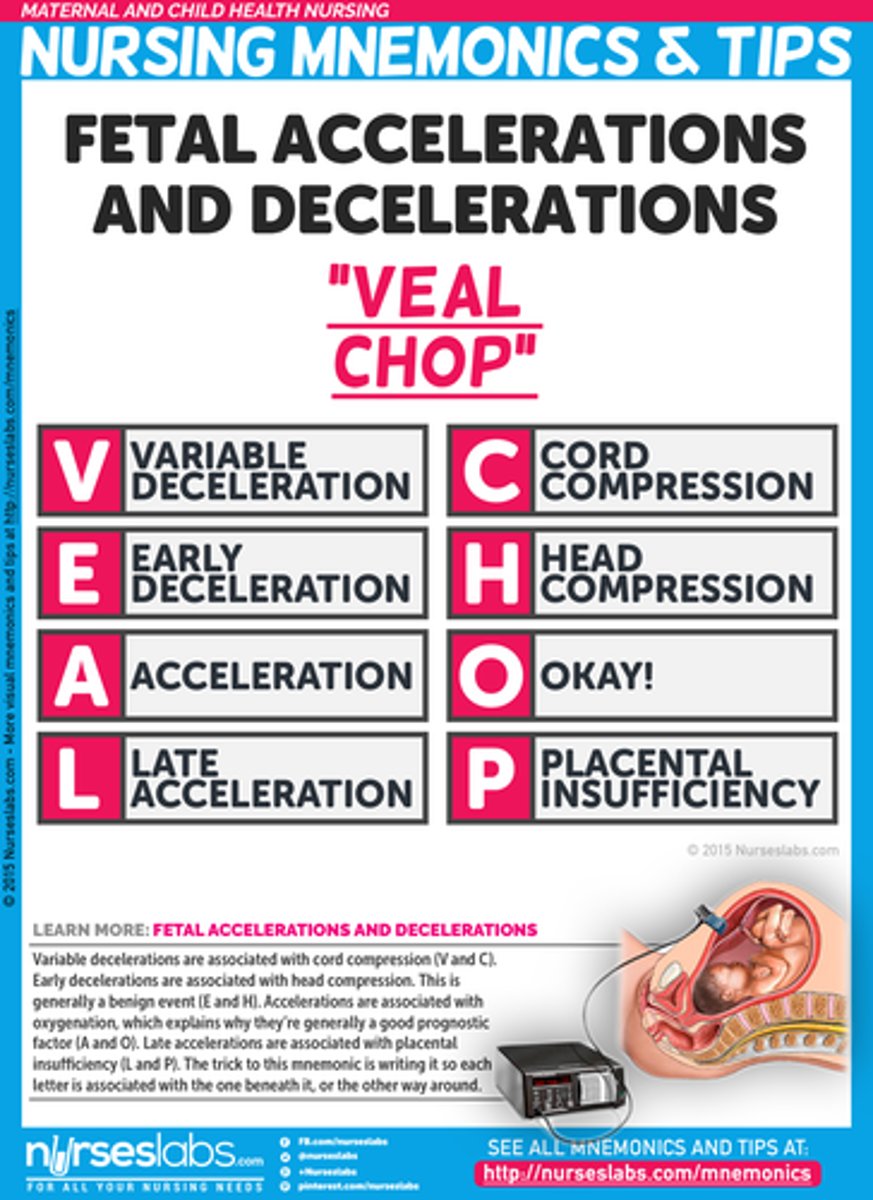
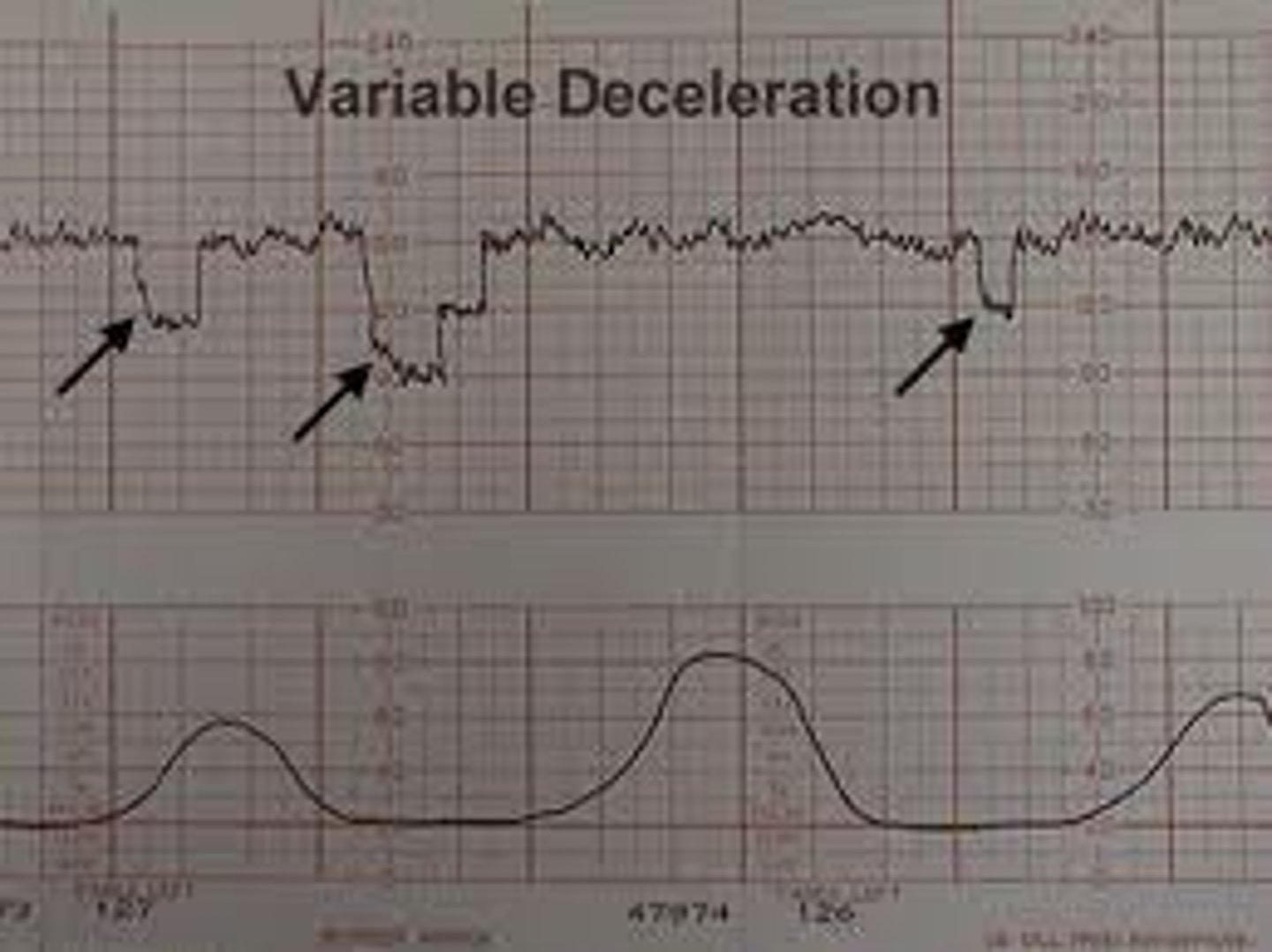
Variable decelerations
HR up or down, cord compression = VERY BAD
Prolapsed cord= push head up, change mom position
Early decelerations
Head pressed on. This is ok.
Late decelerations
Bad (placental insufficiency)
LION
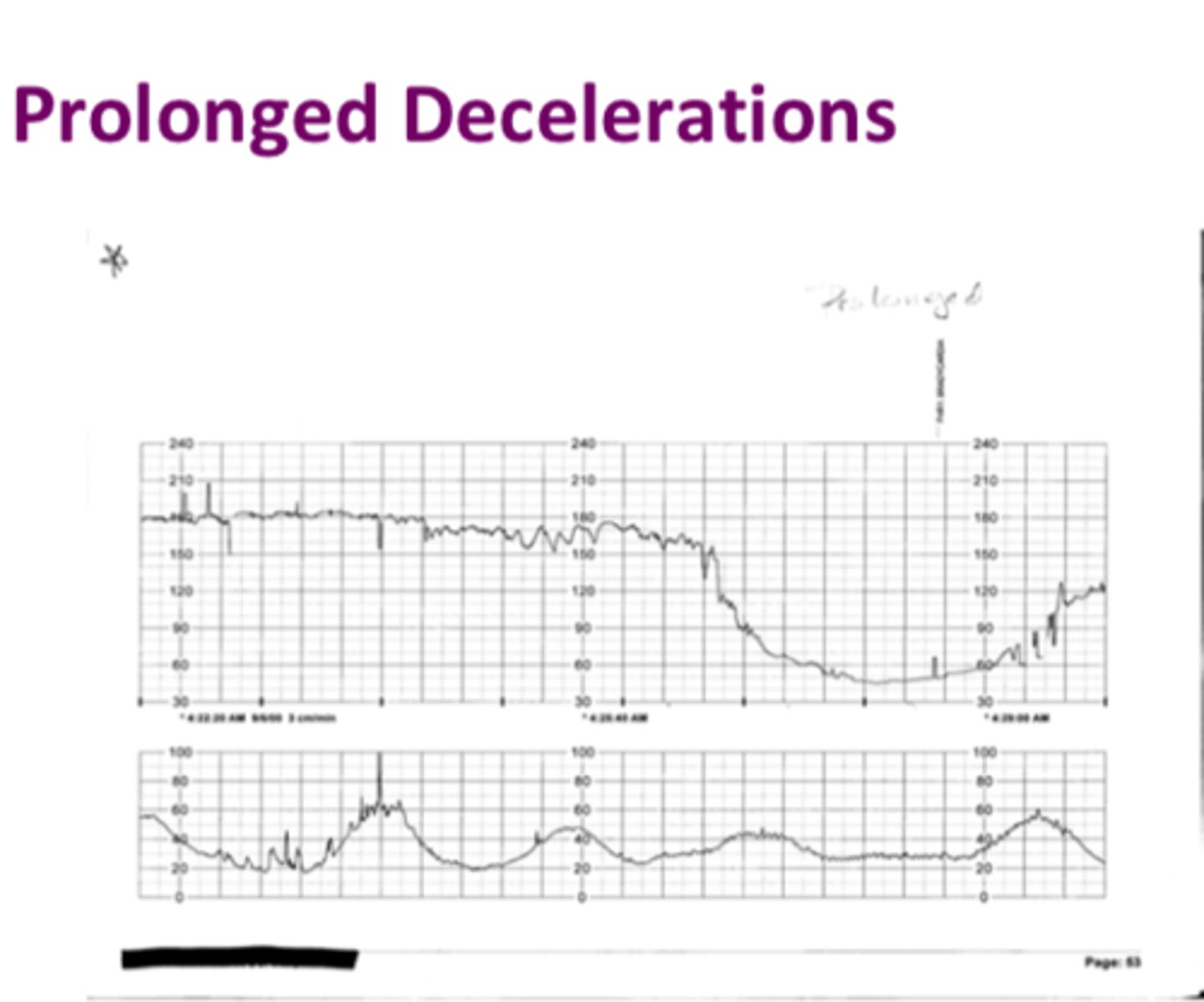
Prolonged decelerations (very bad)
These decelerations are abrupt, FHR decreases of at least 15 bpm from baseline longer than 2 minutes but less than 10 minutes
Excessive bleeding with perineal pads
saturates the pad in less than 15 minutes
Temp. after pregnancy delivery
normally elevated to 100.4 first 24 hours after labor, anything above is reported
to prevent bladder distention
ensure mom pees right after delivery and within 8 hours of catheter removal
bladder distention is cause for
lack of contractions, ergo hemorrhage
every 15 minutes for the first hour
assess mom's vitals, fundus, and lochia
Look for blood loss in mom by
weighing saturated perineal pads
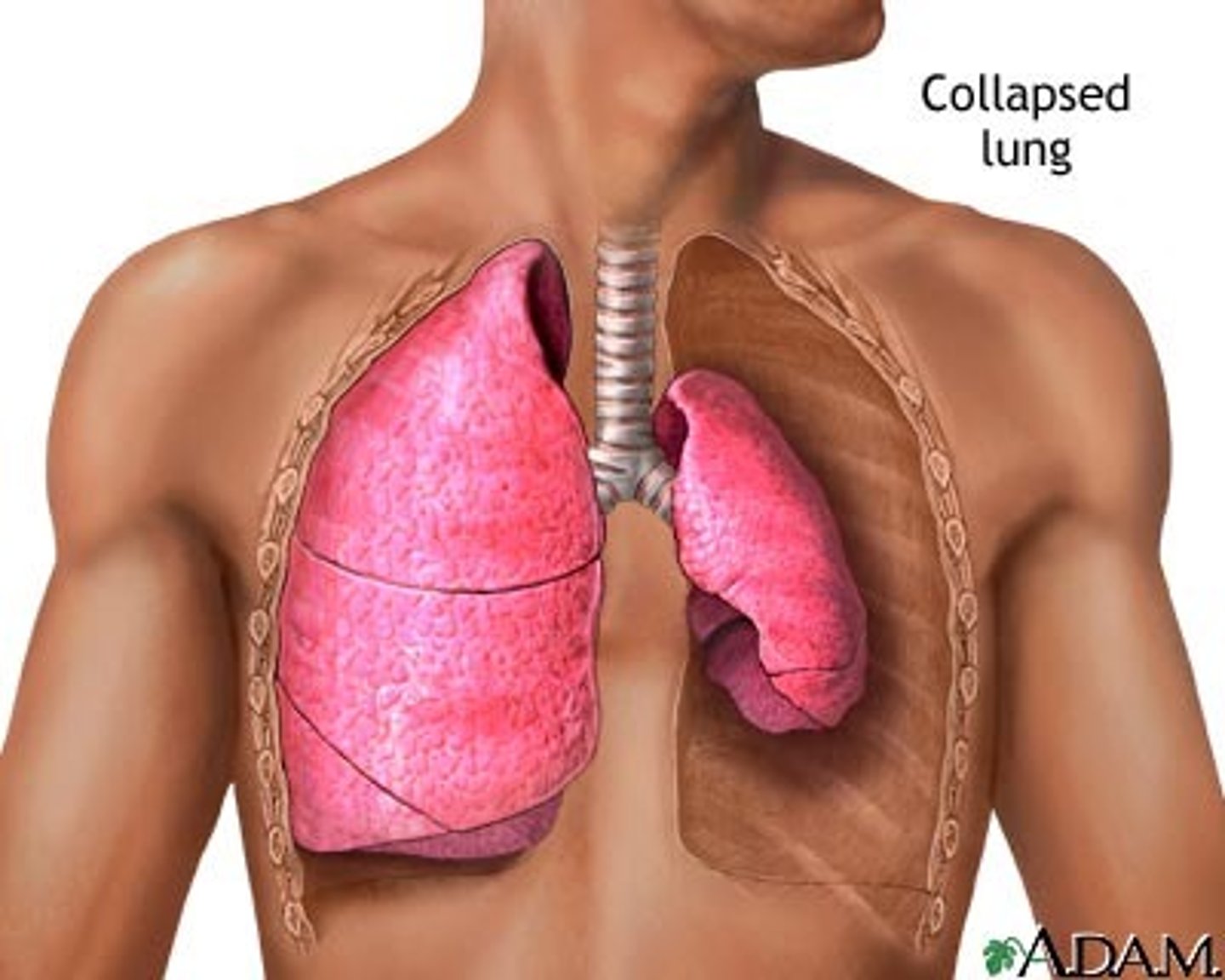
atelectasis
Complete or partial collapse of a lung or a section (lobe) of a lung
common causes of atelectasis
-post surgery
-anesthesia
-complication of:
ARDS, pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, neuromuscular diseases
intervention for atelectasis
breathing exercises, medications, surgery
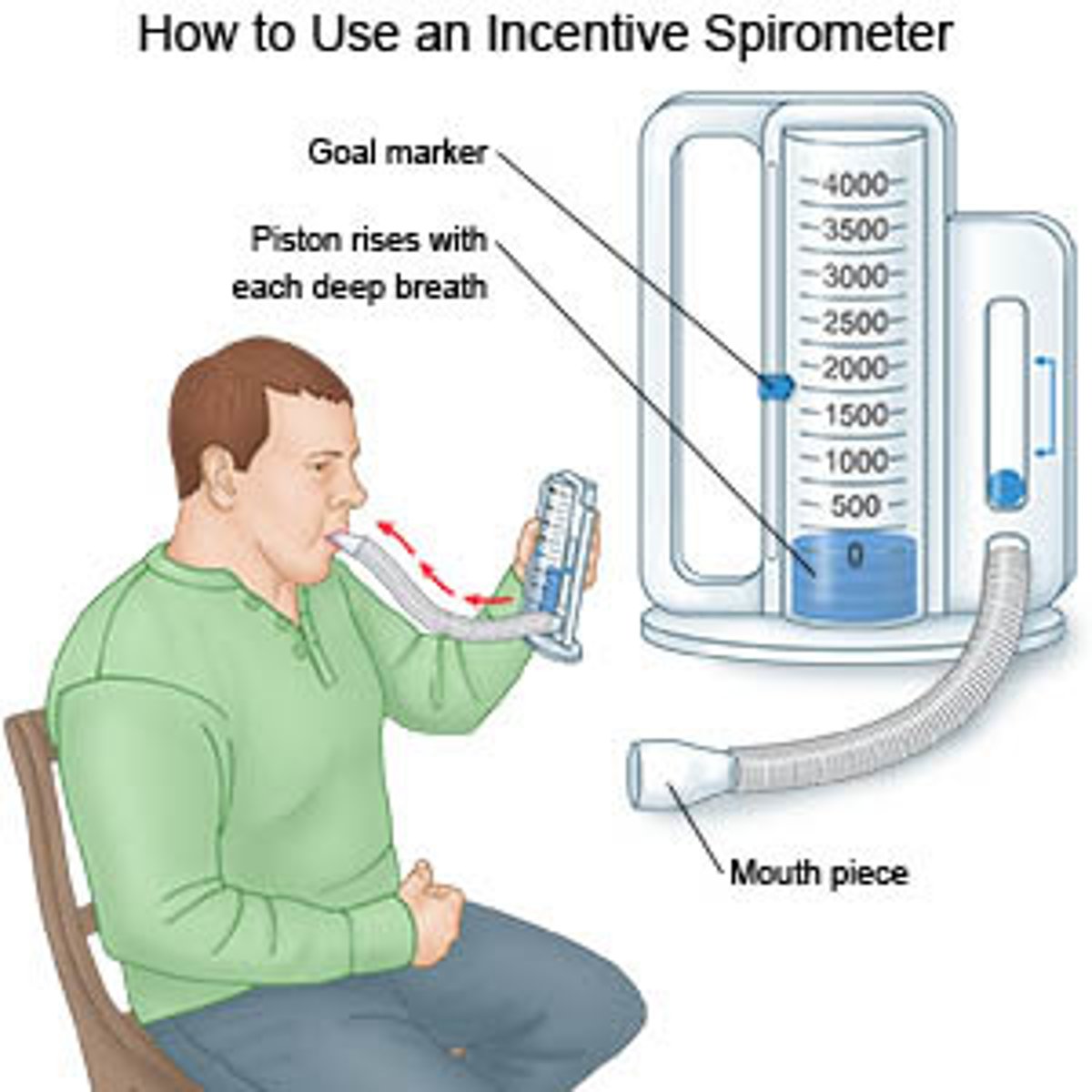
polydipsia
excessive thirst
Polyphagia
excessive hunger/swallowing
if fundus is displaced from midline
have mom pee
Immediately after delivery (fundus)
should be firm and located at or near the level of the umbilicus
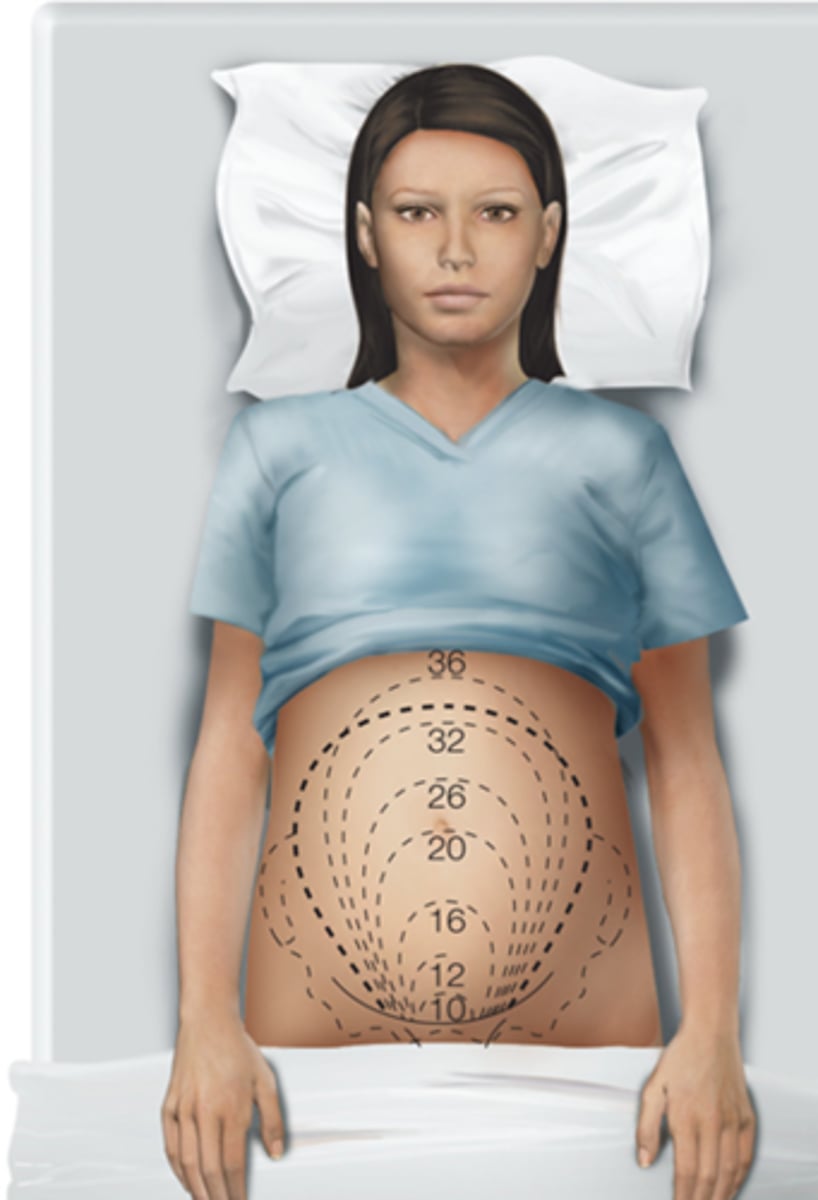
Every 24 hours (fundus)
is expected to descend approximately 1 cm (one finger-breadth) below the umbilicus
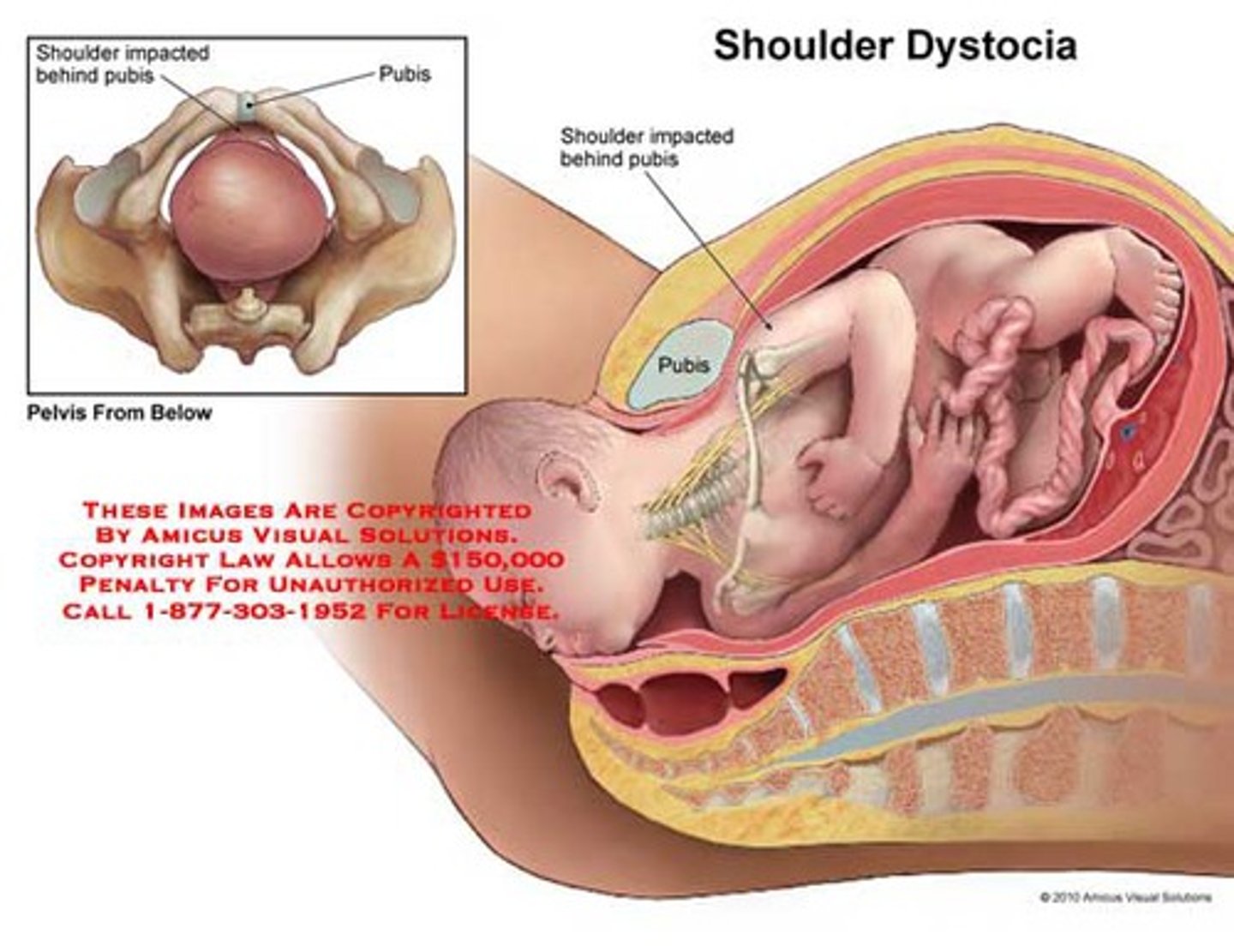
shoulder dystocia
delayed or difficult birth of the fetal shoulders after the head is born
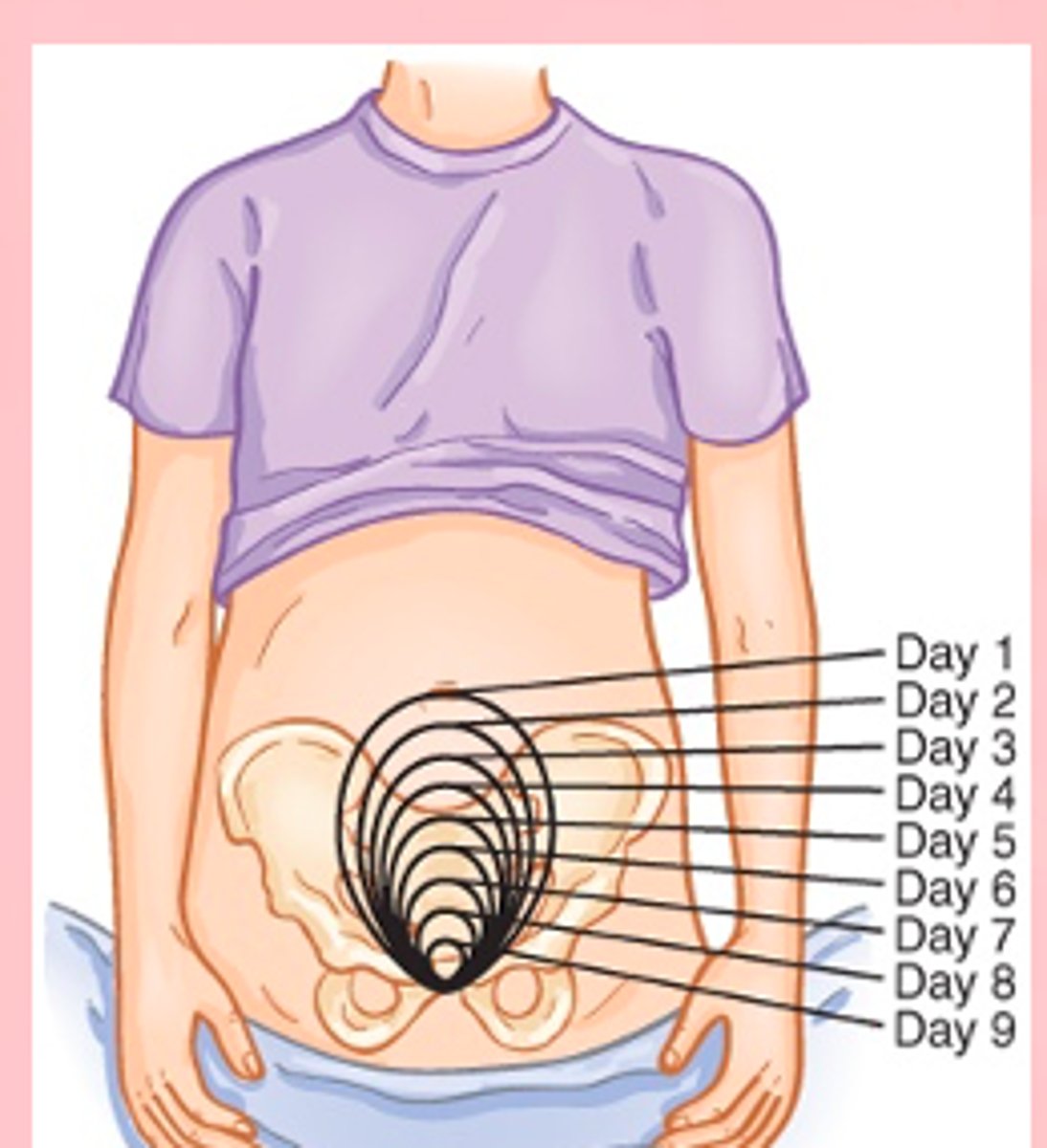
Subinvolution
failure of uterus to return to non-pregnant state
Lochia rubra, serosa, and alba
vaginal discharge after birth
1) _____ = delivery to day 3; dark red, contains mostly blood
2) _____ = day 4-10; pink, contains old blood, serum, leukocytes, tissue debris
3) _____ = day 10-6 weeks; white, leukocytes, epithelial cells serum bacteria
SHOULD NEVER REGRESS
main causes of shoulder dystocia
prior births, overweight, uncontrolled diabetes
amniocentesis
cystic fibrosis, down syndrome, neural tube defects
detected by measuring alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
neural tube defects (spina bifida, anencephaly)
chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
A technique for diagnosing genetic and congenital defects in a fetus
performed between 10 and 13 weeks
chorionic villus sampling
if mom has fever or foul smelling discharge
CBC, blood cultures, antibiotics
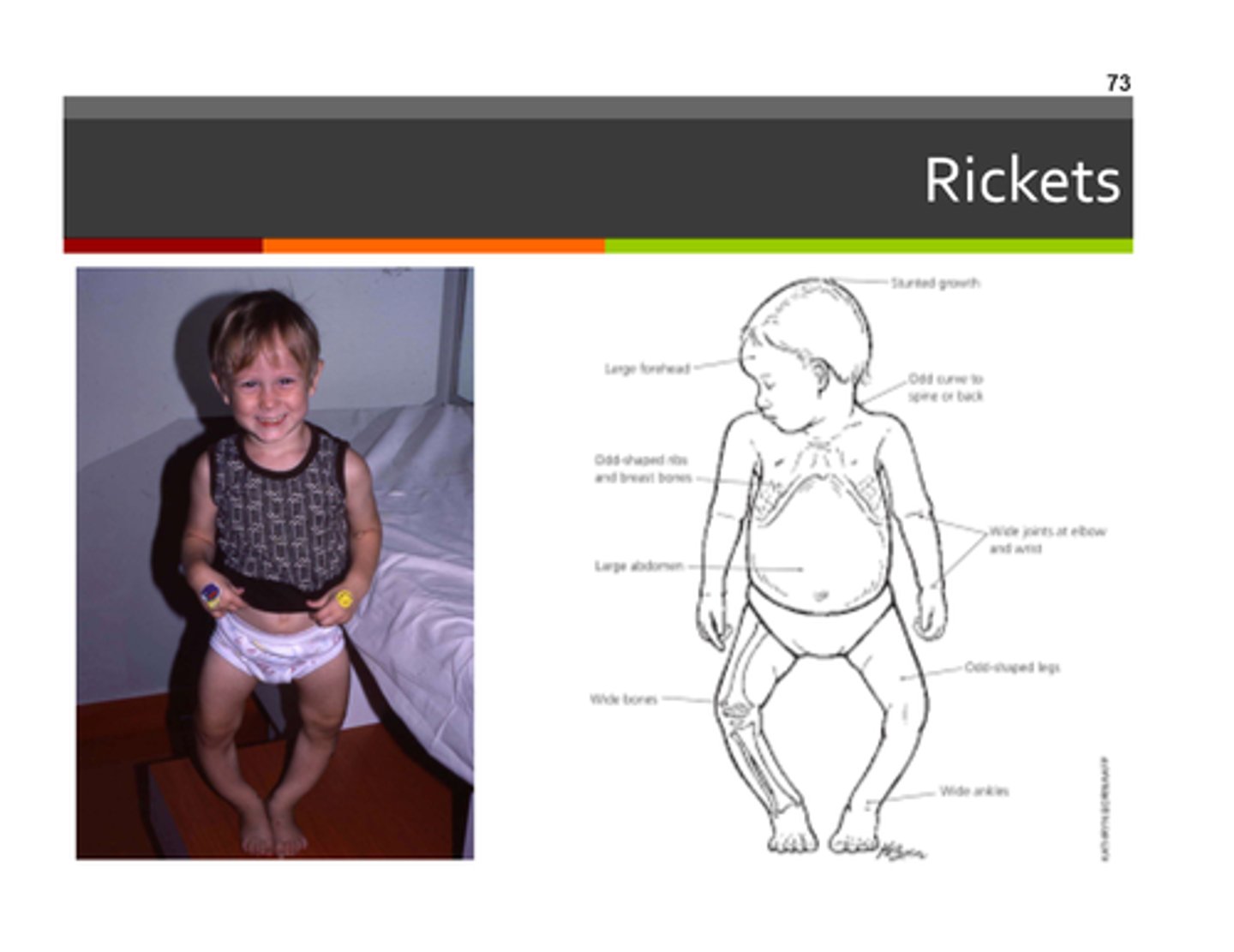
Ricketts
osteomalacia in children; causes bone deformity, take vitamin d
suspected muscular dystrophy
muscle tissue biopsy
polymyositis
a muscle disease characterized by the simultaneous inflammation and weakening of voluntary muscles in many parts of the body
anencephaly
congenital deformity in which some or all of fetal brain is missing
Sarcopenia
age related loss of muscle mass and strength
Dermatomyositis
inflammation of the skin and muscles
avolution
lack of motivation
ataxic
An irregular , unpredictable respiratory rate and tidal volume.
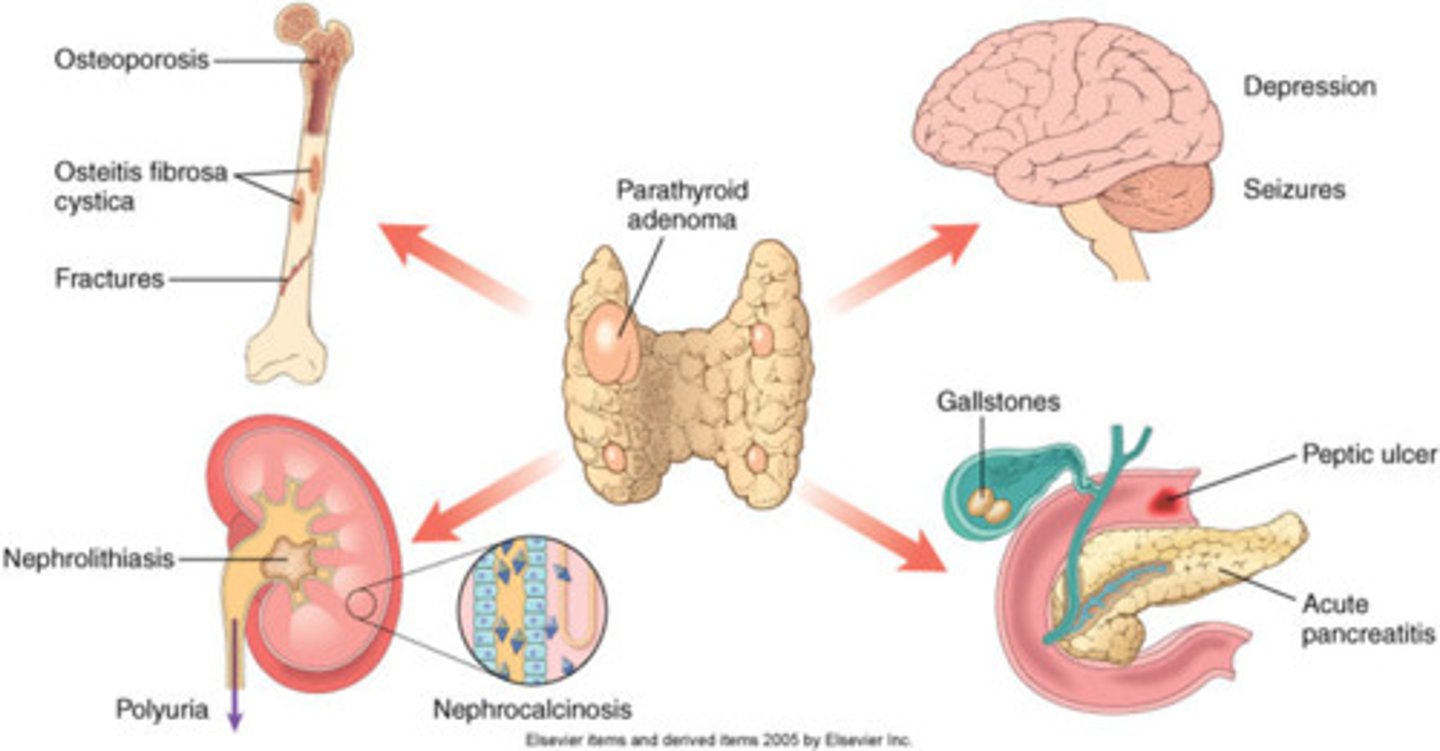
hyperparathyroidism
hypersecretion of the parathyroid glands, usually caused by a tumor
Alogia
A decrease in speech or speech content; a symptom of schizophrenia. Also known as poverty of speech.
Hypokinetic
lack of appropriate level of movement
Addison's disease
A rare, chronic endocrine disorder in which the adrenal glands do not produce sufficient steroid hormones.
Anhedonia
inability to experience pleasure
lithium range
0.6-1.2
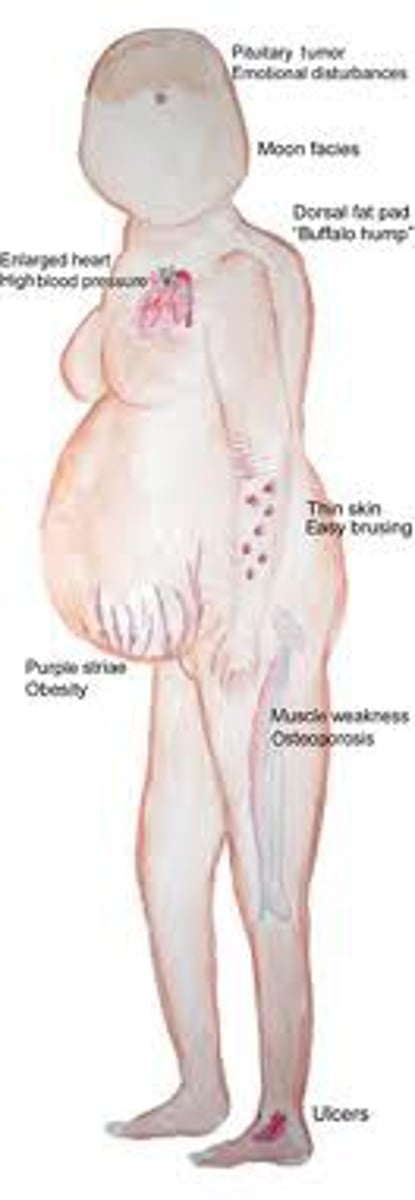
Cushing's syndrome
a condition caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol
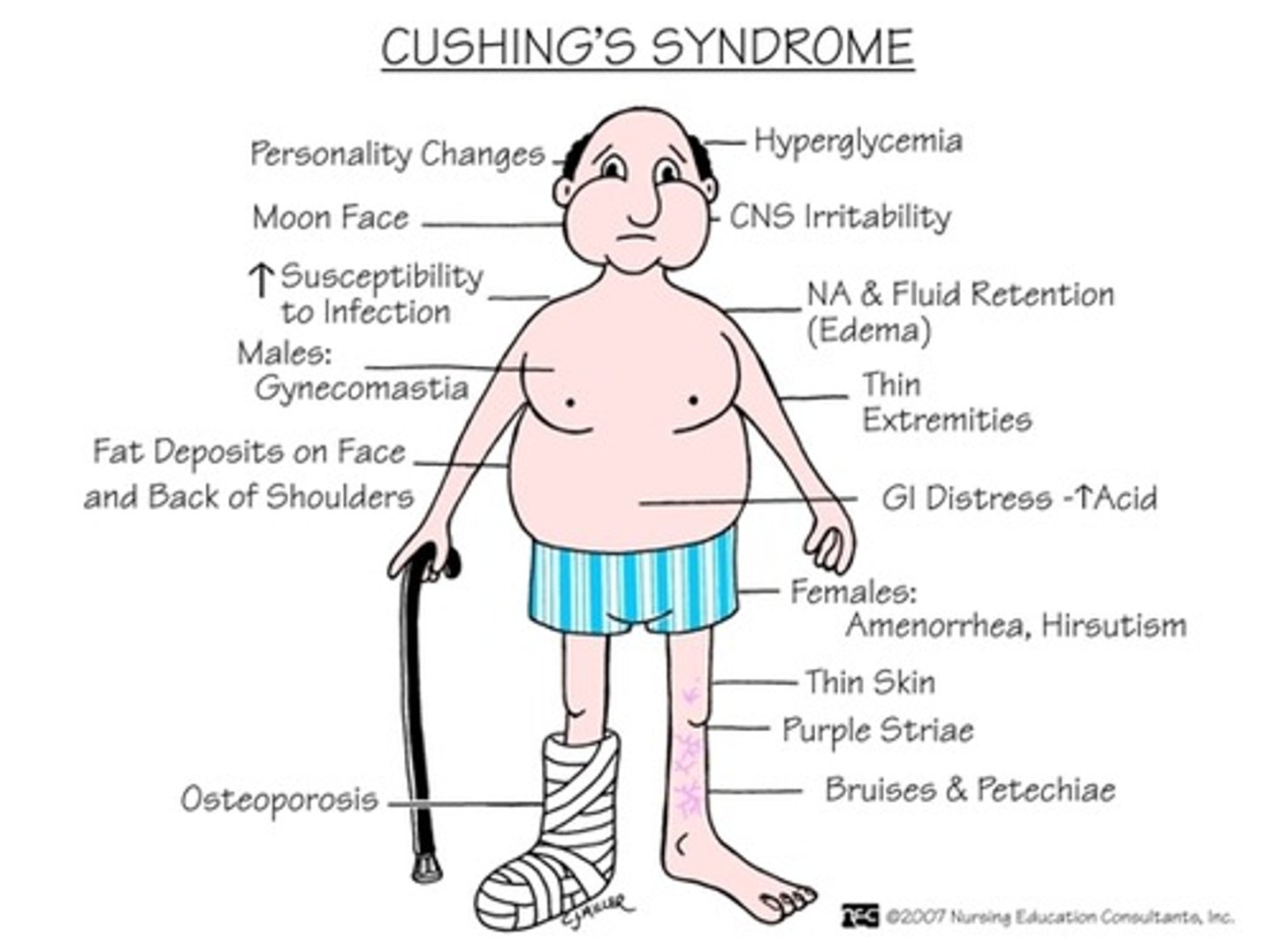
Cushing's syndrome s/s
Moon face, truncal obesity, buffalo hump, peptic ulcers, hypertension, low immune system
S/S of lithium toxicity
vomiting, diarrhea, slurred speech, decreased coordination, drowsiness, muscle weakness, twitching
diabetes insipidus
Condition causing excessive thirst and urination.
Cushings Syndrome treatment?
surgery to remove tumor, drug or radiation therapy, total adrenalectomy
What to do if lithium toxicity is suspected?
Emphasize maintaining consistent sodium intake and adequate fluid intake
lithium
avoid medications that increase lithium levels
NSAIDS, ACE inhibitors
lispro (humalog)
rapid acting insulin
Glargine (Lantus)
Long-acting insulin
Onset 1 hour
Peak (none)
Duration 10-24 hours
Aspart (Novolog)
rapid acting insulin
Detemir (Levemir)
long acting insulin
Glipizide (Glucotrol)
a sulfonylureas, for type 2 diabetes mellitus to lower blood glucose.
- monitor CBC, assess for allergy to sulfonamides
May mask signs of hypoglycemia
beta blockers
may cause aplastic anemias, hypoglycemia, photosensitivity, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, diarrhea
glipizide (glucotrol)
simvastatin
antilipemic, statin
what are the two drug to drug contradictions for sulfonylureas?
Rosuvastatin
antilipemic, statin
Spironolactone
potassium sparing diuretic
contraindicated with: vancomycin, tetracycline, calcium channel blockers, amiodarone
digoxin
treats a-fib
Digoxin
Mannitol
osmotic diuretic, ICP
sign mannitol is working
increased urine output
ventricular catheter
Soft tube put through burr hole. for ICP, drains excess CSF. Increased risk for infection.
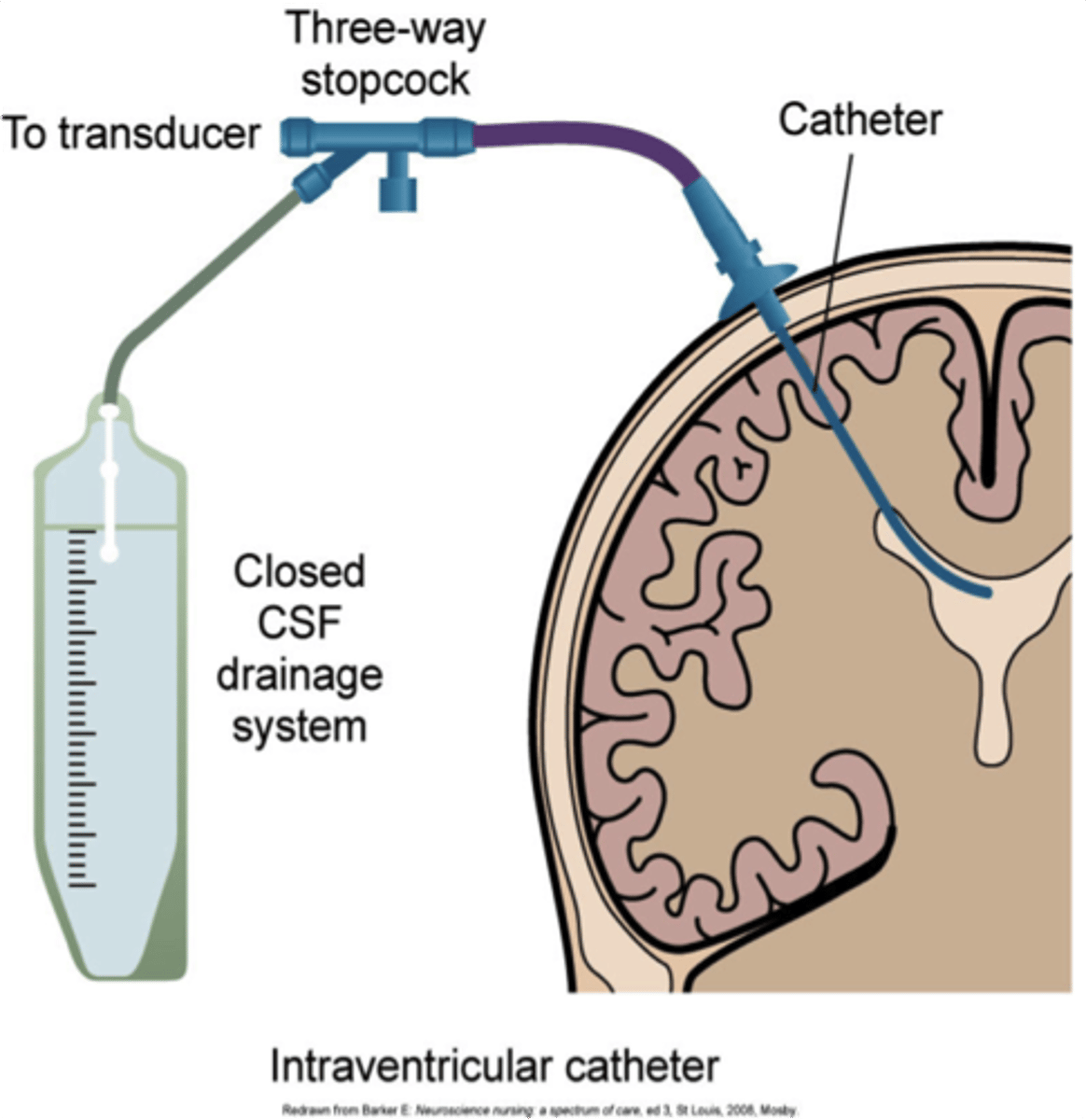
Acetazolamide
- This is a med used for open angle glaucoma
- Adverse effect of this med is tingling of fingers and hyperglycemia
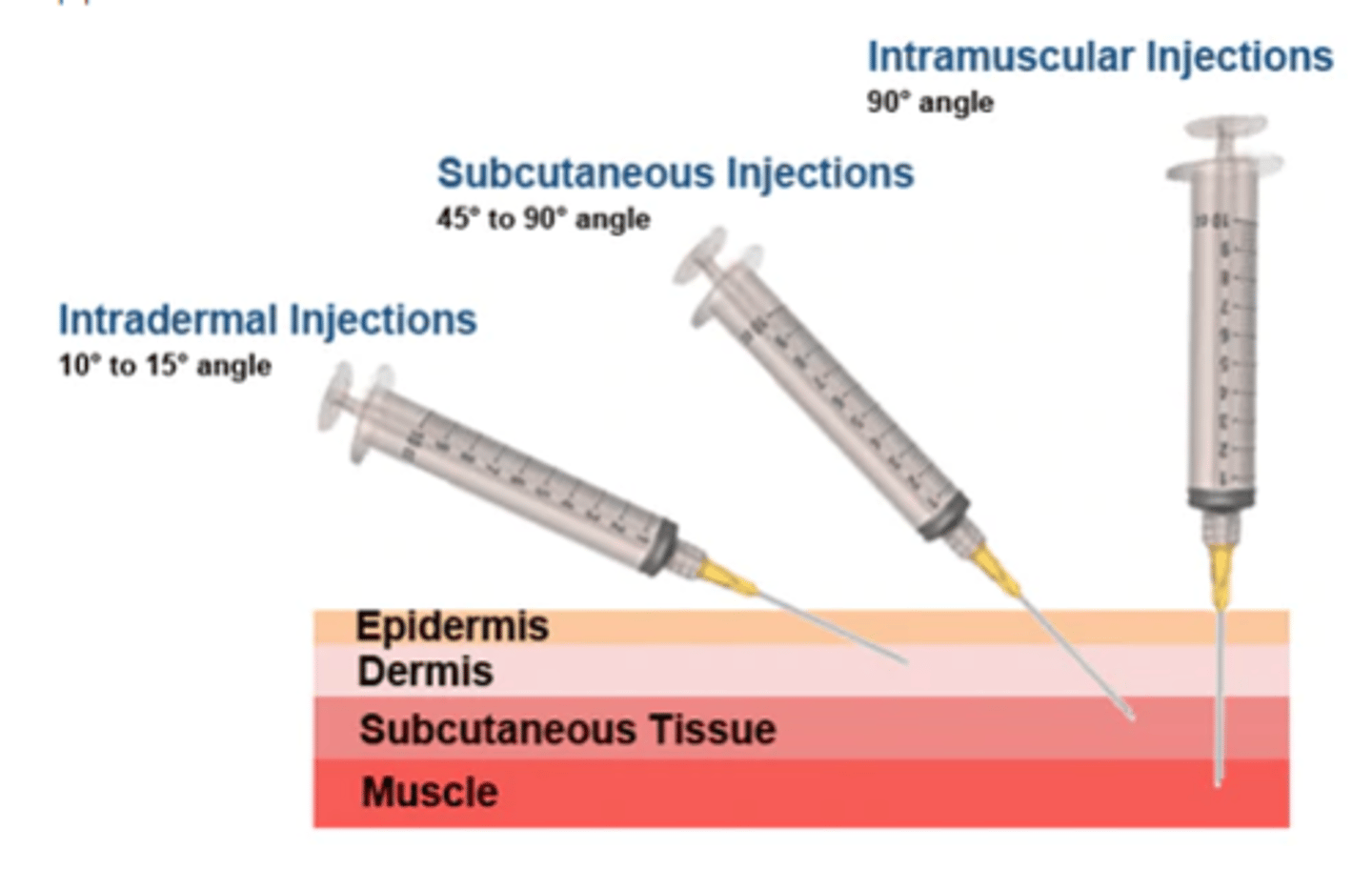
What angle for ID injection?
15 degrees
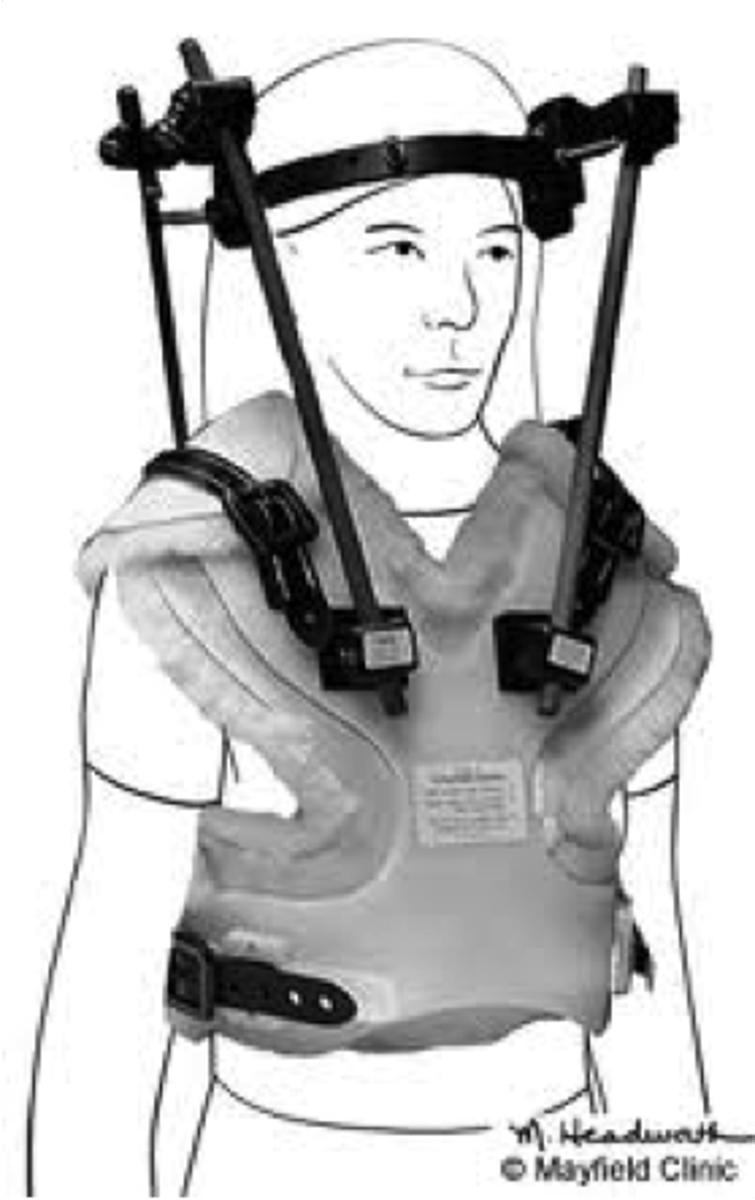
halo traction
Frame apparatus for cervical fractures; four pins inserted in skull attached to metal ring and then to body frames

Furosemide
loop diuretic
foley catheter care
-clean insertion site with soap and water three times a day and after bowel movements
-keep collection bag below level of bladder
-make sure tubing is not kinked (and no dependent loops)
foley catheter (hand washing)
Wash hands before and after touching any part of the catheter system and before and after applying gloves
Hydrochlorothiazide
thiazide diuretic
gloves for foley catheter care
non-sterile
Lisinopril
ACE inhibitor; used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and to improve survival after a heart attack