Unit 12: Urinary System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
kidney
this organ filters blood, forms urine, and helps regulate metabolism
ureter
this transports urine
urinary bladder
this is the place where urine is held
urethra
this drains the bladder of urine
sanitation workers
what are the kidneys known as?
erythropoietin
what hormone do the kidneys produce?
stimulates red blood cell production in marrow
what does erythropoietin do?
bean
what is the shape of a kidney?
true
true or false: the kidney is about the size of a bar of soap
T12-L3
around what vertebrae are the kidneys located?
false
true or false: the kidneys are located inside the peritoneum
adipose
what type of tissue are the kidneys surrounded by?
adrenal glands
what are the tops of the kidneys covered by?
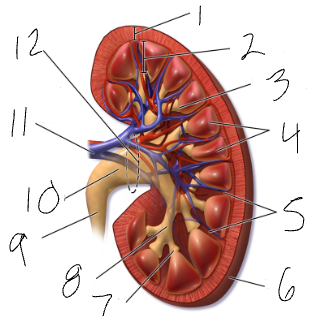
renal hilus
medial indentation (#12)
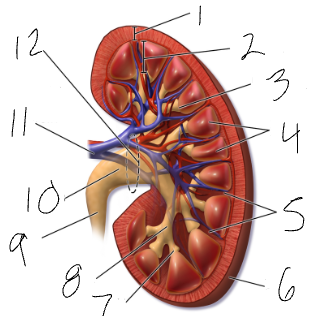
renal pelvis
funnel at superior end of ureter (#10)
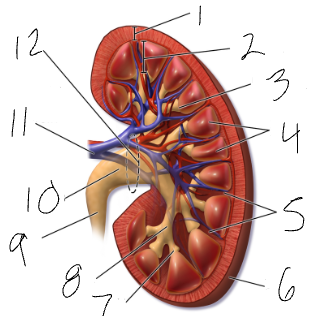
calyx
sections of renal pelvis (7 & 8)
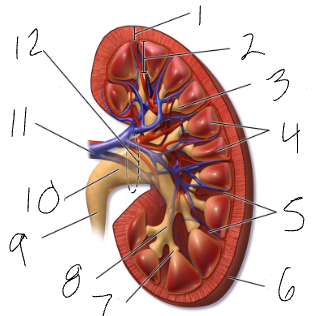
medulla
cone shaped mass of tissue (#2)
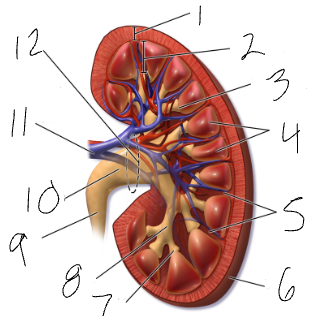
cortex
contains nephrons (#1)
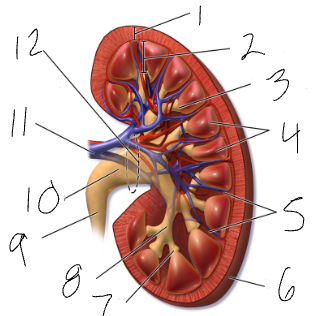
renal columns
regions of cortex that separate the medullary pyramids (#5)
nephron
basic functional unit of a kidney
1 million
how many nephrons does each kidney have?
glomerulus
knot of capillaries under high pressure
bowman’s capsule
surrounds the glomerulus
podocytes
filtrate
filtered materials (water, urea, glucose, salts, amino acids, vitamins)
45
about __ gallons of filtrate pass from blood to renal tubes each day
peritubular capillaries
where is most of the filtrate reabsorbed into the blood?
distal, urine
filtrate that remains in the ___ tube becomes ___
collecting ducts
urine drains into ___ ___ which lead to medulla
renal pelvis
medulla lead to calyces and then to ___ ___
glomerulus
in the first step of filtration, blood collects in a ___ and is under high pressure
podocytes, Bowman’s capsule
after blood collects, ___ absorb filtrates that are being forced out of the glomerulus and into the ___ ___
proximal convoluted
after filtrates go into the bowman’s capsule, filtrates enter the ___ ___ tube
capillaries
filtrates and 99% of water is reabsorbed into the ___
loop of henle, distal convoluted
remaining filtrates after the capillaries are carried through the ___ ___ ___ and to the ___ ___ tube
urine
Filtrates in the distal convoluted tube become ___
renal pelvis
All urine from each nephron is funneled to the ___ ___
urochrome
pigment produced when hemoglobin is broken down
urinalysis
physical & chemical assessment of urine
pyelogram
x-ray image of kidneys
diuretics
drugs that promote fluid loss in the urine
hematuria
blood loss in urine
proteinuria
protein loss in urine
dysuria
painful urination
UTI/urinary tract infection
bacteria colonize bladder, ureters, urethra
ureters
slender tubes that carry urine from kidney to bladder
peristalsis
how do the ureters propel urine?
small folds in the lining
how is urine prevented from backing up?
kidney stones
extremely concentrated urine
renal pelvis
where do crystals precipitate?
intense pain
ureters closing in on the sharp crystals causes…
surgery or lithotripsy
what are the treatment options for kidney stones?
urinary bladder
collapsible sac made of smooth muscle that stores urine temporarily
transitional epithelium
what type of tissue lines the bladder?
posterior to the pubis symphysis
explain the location of the bladder anatomically
ureteral orifices
what are the openings to the bladder from the ureters called?
internal urethral orifice
what is the opening to the bladder from the urethra called?
trigone
smooth, sensitive triangular region, prone to infection
superiorly
which way does the bladder expand as it fills?
4 cups
how much is the bladder capable of holding?
urethra
uses peristalsis to pass urine from bladder to outside of body
internal sphincter
involuntary, junction of bladder & urethra (smooth muscle)
external sphincter
voluntary, surrounds urethra (skeletal muscle)
2 in
how long is the female urethra?
8 in
how long is the male urethra?
micturition/voiding
act of emptying the bladder
200
after ___ mL collect, the bladder stretches, stimulating nerves
incontinence
unable to control the external sphincter
urinary retention
bladder is unable to expel urine