Cell cycle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
History of cell division
Hooke 1665 - organisms are made from cells
Schlegel and Schwann 1857 - plants and animals are made from cells or cell products “cell theory”
Virchow 1858 - cells come from cells, binary fission,
1882 - chromosomes & mitosis, observed elongated threads forming in the nucleus, watched them shorten and thicken during mitosis
Interphase
G1 = growth phase
S = DNA synthesis
G2 = growth phase 2
G0 = cell cycle arrest
Early 1950s, incubated root tips of plants with radioactive phosphorus. Observed that DNA synthesis occurred in S phase.
BrdU stain used to tell if a cell is in S.
Chromosomes to chromatids ….
After duplication, the chromosome now consists of two chromatids, joined copies of the original chromosome (double stranded, two double helices)
Once separated from its sister, each chromatid (single stranded, one double helix) is considered an individual chromosome
N = max number of alleles at any particular locus
2 methods for visualising stages of mitosis
Fluorescent dyes, fluorescently labelled antibodies
Electron microscopy
Late G2 phase
cell has doubled in size, and much of it original contents
Cytoplasm now has 2 centrosomes
Chromosomes have already replicated but cannot be distinguished
The microtubule organising centre (MTOC) is a structure found in eurkaryotic cells from which microtubules emerge
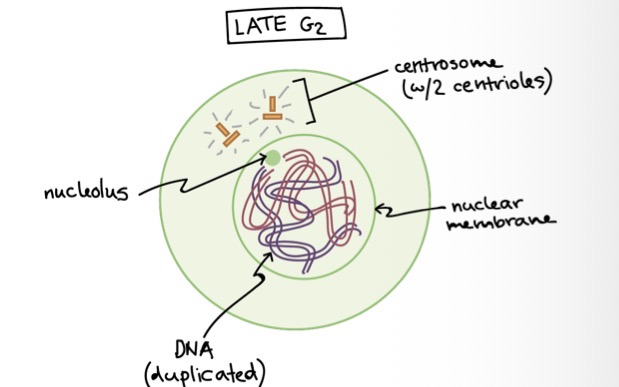
What is a centrosome
Made of 2 centrioles, organise microtubules in the cell
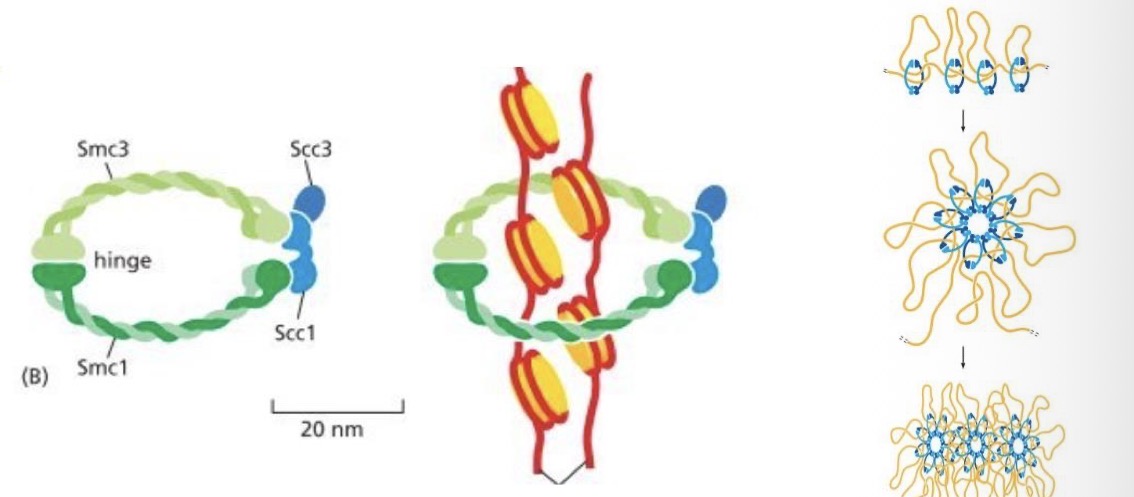
Cohesins
special proteins
Formed after replication
Keep chromatids together
Early prophase
condensation of replicated chromosomes - activated by phosphorylation of condensins
Mitotic spindle begins to form as the microtubules rapidly grow out of the centrosomes, which begin to move away from eachother
nuclear envelope intact

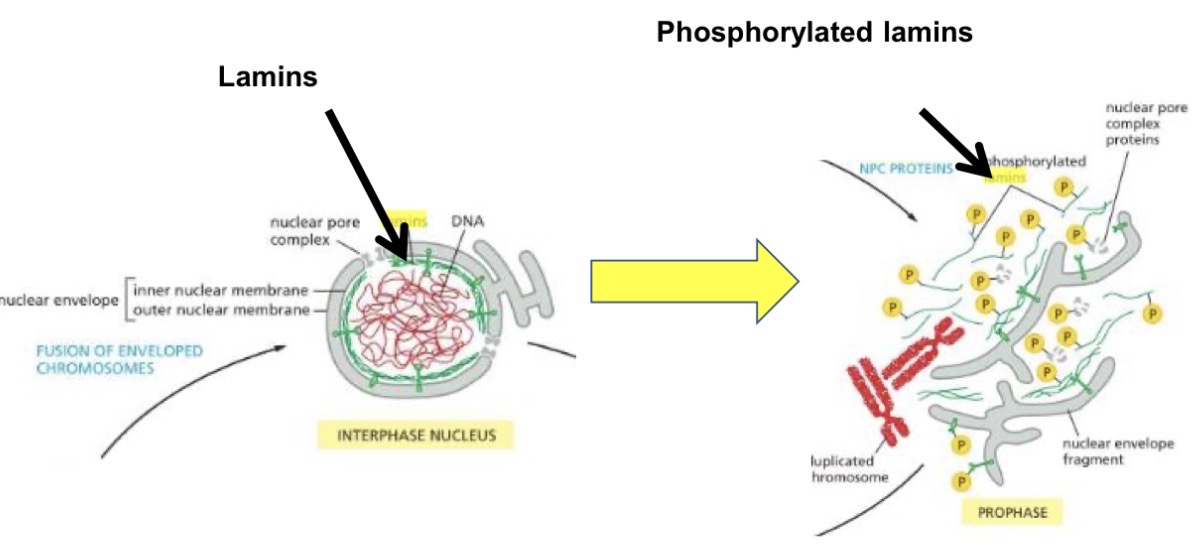
Late prophase
nuclear envelope breaks down, microtubules from the centrosomes at the poles of the mitotic spindle extend into the nuclear region, reaching the chromosomes
Some of the spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores
Other spindle microtubules make contact with microtubules coming from the opposite pole
Lamins phosphorylated = nuclear envelope disintegrates
Moving chromosomes to the cell centre
each chromosome is attached to the spindle
Chromosomes pulled simultaneously toward each pole, leading to a jerky motoring
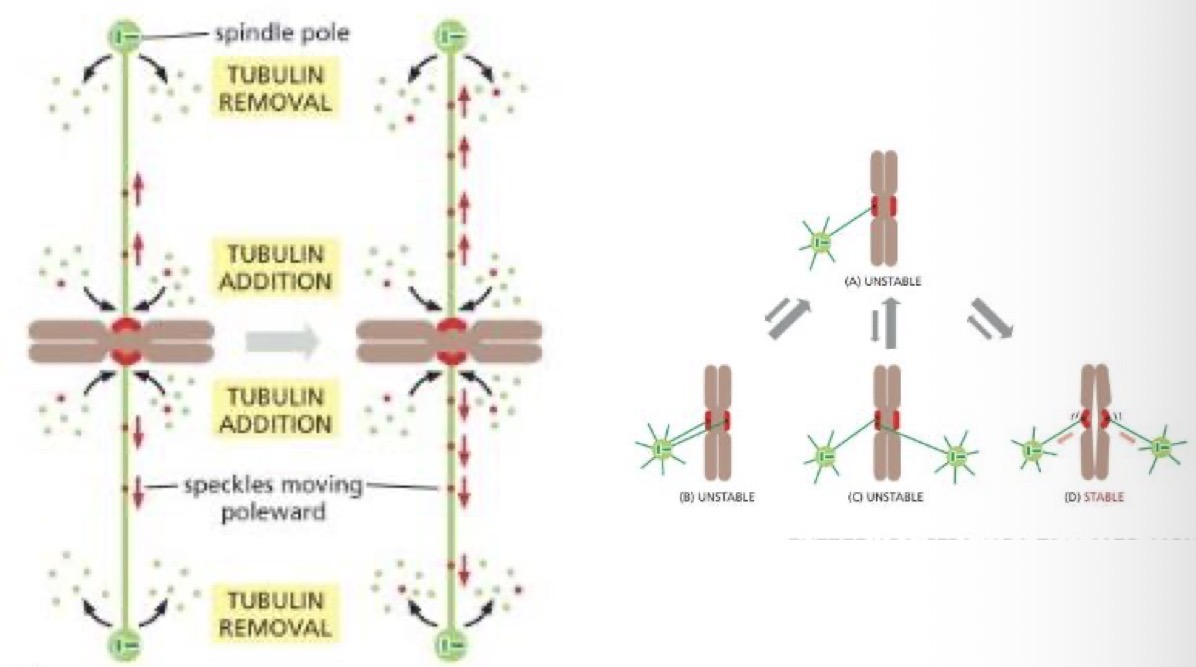
Metaphase
Mitotic spindle is fully formed. Chromosomes midway between the spindle poles
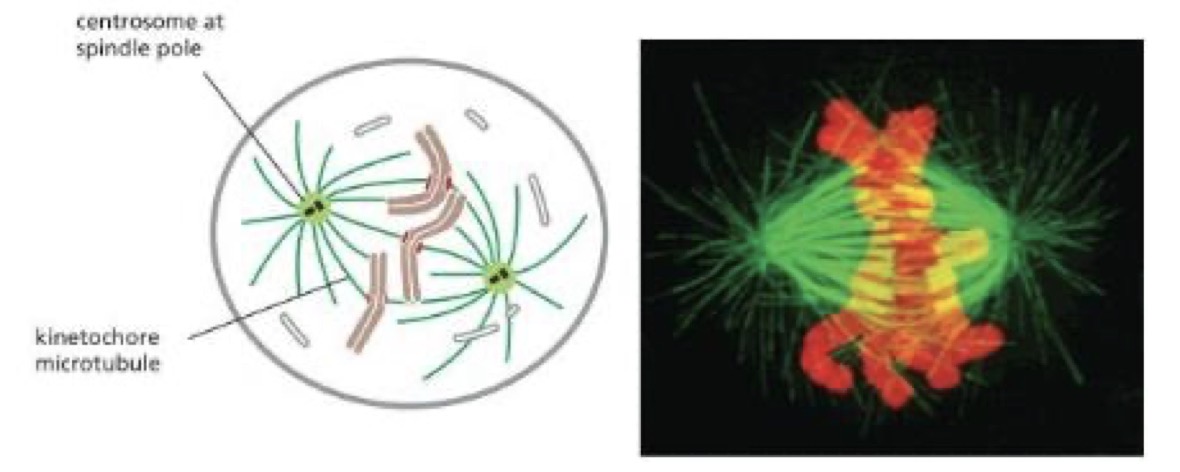
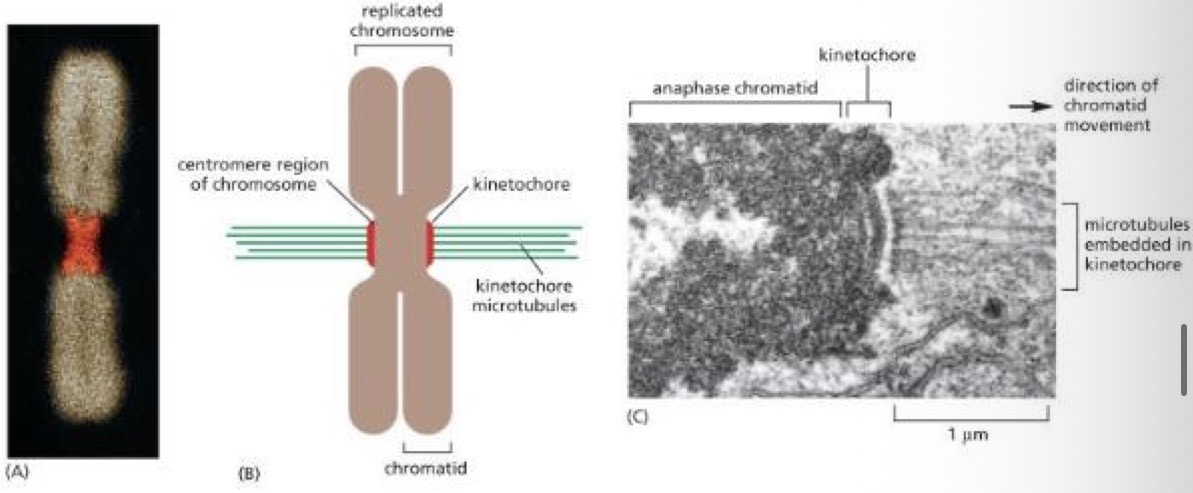
Kinetochores/centromere
Centromere = a point of constriction on the chromosome containing repeated DNA sequences that bind specific proteins
Kinetochores = bunch or proteins attached to centromere, where microtubules bind
proteins make up a disk like structure called the kinetochore
Contains an attachment site for microtubules necessary to separate the chromosomes
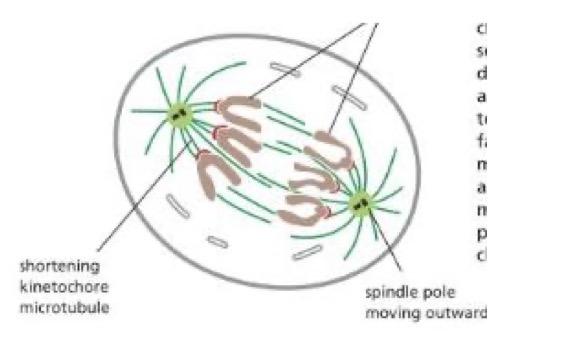
Anaphase
begins when 2 centrosomes of each chromosome come apart, separase (enzyme) cleaves Cohesins
proteins of the kinetochore powered by ATP, walk the newly separated daughter chromosomes along her microtubules towards opposite poles of the cell.
Spindle microtubules attached to the kinetochores shorten, the spindle microtubules not attached lenghten
Poles are moved further apart
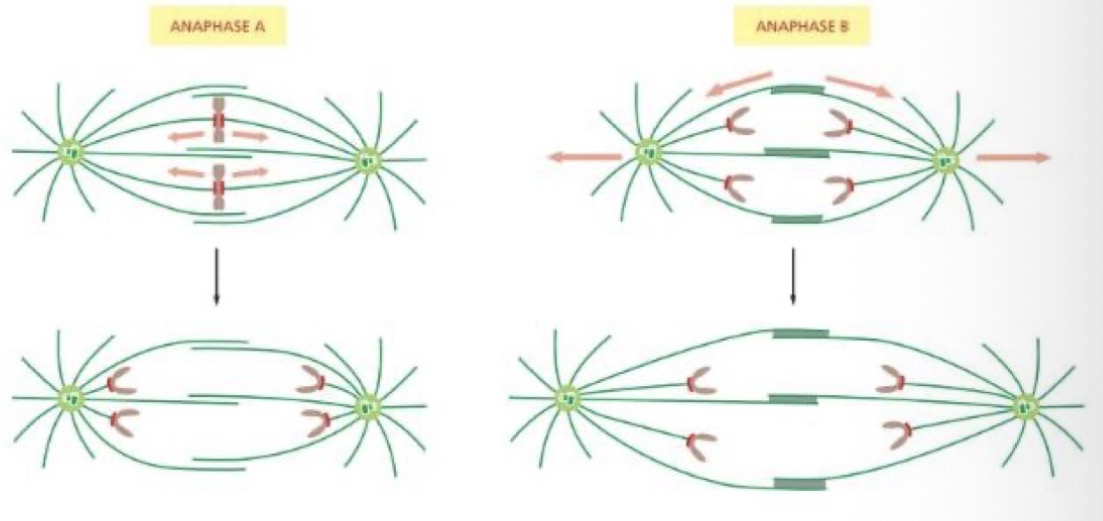
Anaphase A vs B
Anaphase A = chromosomes move towards the centrosome
Anaphase B = spindles move further from eachother
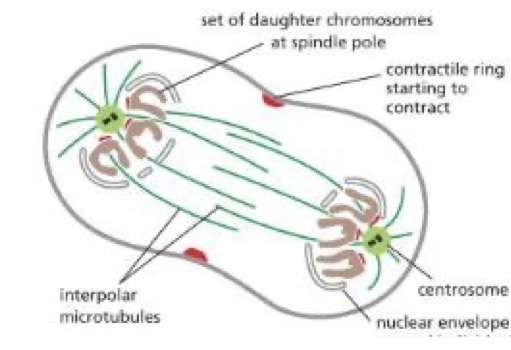
Telophase
nuclear envelope reforms around individual chromosomes
Contractile ring starts to contract
Lamins de-phosphorylated
Cytokinesis
the cleavage furrow
Cytoplasm is divided in two by a contract only end of actin and myosin filaments, which pinches the cell to create two daughters, each with one nucleus
Actin and myosin filaments = contractile ring
Plants = cell plate, animals = cleavage furrow
Diploid dominant life cycle
in animals, sexually reproducing adults form haploid gametes from diploid germ cells
fusion of the gametes = fertilised egg cell or zygote
The zygote will undergo multiple rounds of bursts to produce a multicellular offspring
the germ cells are generated early in the development of the embryo
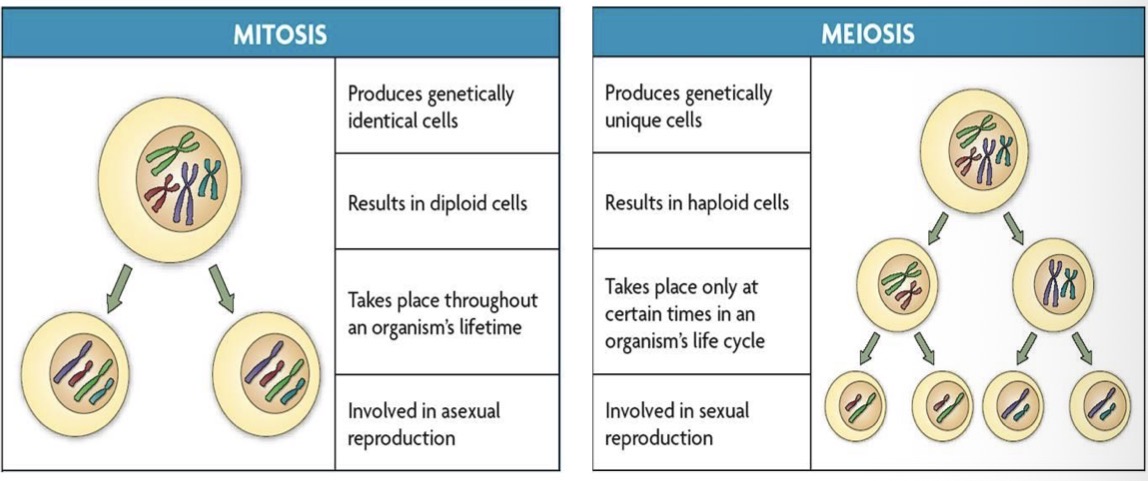
Mitosis meiosis comparison
Mitosis
genetically identical cells
Diploid cells
Throughout an organisms lifetime
Involved in asexual reproduction
Meiosis
genetically unique cells
Haploid cells
Only at certain times in the lift cycle
Involved in sexual reproduction
Stages of meiosis
P1
M1
A1- homologus chromosomes separated
T1
P2
M2
A2 - sister chromosomes separate
T2
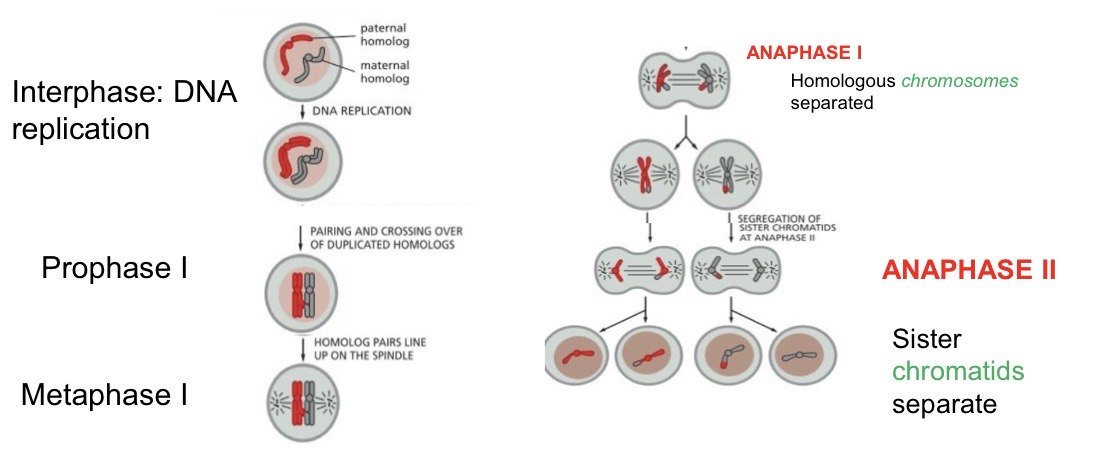
Meiosis 1 vs 2
Meiosis 1 = very distinct, involving homologus chromosomes lining up and exchanging DNA before separating
Meiosis 2 = very similar to mitosis
Meiotic prophase 1
juxtaposition of homologs occurs during a prolonged period of meiotic prophase
Pairing = interactions between complementary DNA sequences in two homologs, held together and in perfect alignment by a protein lattice (synaptonemal complex)
Homologues become more closely juxtaposed, forming 4 four-chromatid structure called a bivalent
Crossing over occur between non-sister chromatids
Cross overs = chiasmata
Meiosis in females after puberty
ovary have 300,000 primary oocytes (in prophase 1) since before birth
Secondary oocytes - egg (in metaphase 2) starts to travel down the fallopian tube
If not fertilised, will never complete meiosis (stay in M2)
Before ovulation, one primary oocyte undergoes asymmetric cell division, to make one polar body, and one secondary oocyte
What happens to the egg at fertilisation
when a sperm (n=1) gets in this causes it to finish meiosis
Another polar body is formed, and the egg becomes an ovum
Nuclear fusion of sperm and egg n=2