AP Bio Midterm
4.3(4)Studied by 257 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:37 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following is not a polysaccharide important to living things?
Cholesterol
2
New cards
The carbohydrates glucose, galactose, and fructose have the same chemical formula (C6H12O6)(C6H12O6) but different structural formulas, as represented in the figure.
Which of the following statements about glucose, galactose, and fructose is most likely true?
Which of the following statements about glucose, galactose, and fructose is most likely true?
The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different arrangements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
3
New cards
Which of the following is responsible for the cohesive property of water?
Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule
4
New cards
Water and ammonia interact to form hydrogen bonds, as represented in the figure.
Which statement best helps explain the formation of the hydrogen bond represented in the figure?
Which statement best helps explain the formation of the hydrogen bond represented in the figure?
The nitrogen has a partial negative charge, and the hydrogen attached to the oxygen has a partial positive charge.
5
New cards
The diagram shows how water can adhere to the xylem in the stems of plants, which contributes to water movement in the plant. Which of the following best explains how water is able to move upward from the roots of a plant, through its xylem in the stem, and out to the leaves?
Water and the xylem are both polar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with the walls of the xylem.
6
New cards
Humans produce sweat as a cooling mechanism to maintain a stable internal temperature. Which of the following best explains how the properties of water contribute to this physiological process?
The high heat of vaporization of water allows the body to remove excess heat through a phase change of water from liquid to gas.
7
New cards
Figure 1 is a diagram of water molecules at the air-water interface at the surface of a pond.
Figure 1. Alignment of water molecules at air-water interface
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes how the properties of water at an air-water interface enable an insect to walk on the water's surface?
Figure 1. Alignment of water molecules at air-water interface
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes how the properties of water at an air-water interface enable an insect to walk on the water's surface?
Hydrogen bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide surface tension, which allows the water surface to deform but not break under the insect.
8
New cards
Which of the following is most directly responsible for water’s unique properties?
It forms hydrogen bonds.
9
New cards
Scientists examined the folded structure of a purified protein resuspended in water and found that amino acids with nonpolar R groups were primarily buried in the middle of the protein, whereas amino acids with polar R groups were primarily on the surface of the protein. Which of the following best explains the location of the amino acids in the folded protein?
Nonpolar R groups that cannot form hydrogen bonds with water are pushed into the middle of the protein.
10
New cards
If 30% of the nucleotides in a single-stranded RNARNA molecule are adenine, then what percent are expected to be thymine?
0% \n
11
New cards
Amylase is an enzyme that converts carbohydrate polymers into monomers. Glycogen synthase is one of the enzymes involved in converting carbohydrate monomers into polymers.
Which of the following best explains the reactions of these enzymes?
Which of the following best explains the reactions of these enzymes?
Amylase aids in the addition of a water molecule to break covalent bonds whereas glycogen synthase aids in the removal of a water molecule to form covalent bonds.
12
New cards
Which of the following correctly illustrates a dipeptide and an amino acid in the optimal position to form a tripeptide?
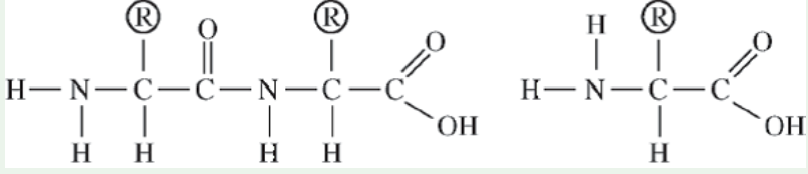
13
New cards
DNADNA and RNARNA are nucleic acids that can store biological information based on the sequence of their nucleotide monomers. Figure 1 shows a short segment of each of the two types of nucleic acids.
Which of the following best describes a structural difference between DNA and RNA?
Which of the following best describes a structural difference between DNA and RNA?
The backbone of DNA contains deoxyribose, whereas the backbone of RNA contains ribose.
14
New cards
The molecular structures of linoleic acid and palmitic acid, two naturally occurring substances, are shown in the figure.
Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature?
Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature?
Palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together.
15
New cards
This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
\
This group of questions refers to the following groups of biological compounds.
\n (A) Proteins \n (B) Carbohydrates \n (C) Nucleic acids \n (D) Lipids \n (E) Steroids
Used to carry the genetic code
\
This group of questions refers to the following groups of biological compounds.
\n (A) Proteins \n (B) Carbohydrates \n (C) Nucleic acids \n (D) Lipids \n (E) Steroids
Used to carry the genetic code
Nucleic acids
16
New cards
This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
\
This group of questions refers to the following groups of biological compounds.
\n (A) Proteins \n (B) Carbohydrates \n (C) Nucleic acids \n (D) Lipids \n (E) Steroids
Synthesized at the ribosome
\
This group of questions refers to the following groups of biological compounds.
\n (A) Proteins \n (B) Carbohydrates \n (C) Nucleic acids \n (D) Lipids \n (E) Steroids
Synthesized at the ribosome
Proteins
17
New cards
Which of the following best describes the hydrolysis of carbohydrates?
The addition of a water molecule breaks a covalent bond between sugar monomers
18
New cards
A small protein is composed of 110 amino acids linked together in a chain. As shown in Figure 1, the first and last five amino acids in the chain are hydrophobic (have nonpolar and uncharged RR-groups), whereas the remaining 100 amino acids are hydrophilic (have charged or polar RR-groups). The nature of the RR-group determines if the amino acid is hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
A mutation results in the production of a version of the small protein that is only 105 amino acids long, as shown in Figure 2. Five of the hydrophobic amino acids are missing from one end of the chain.
Which of the following best depicts the tertiary structures of the two proteins in water? The diagrams in the options are not drawn to the same scale as those in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
A mutation results in the production of a version of the small protein that is only 105 amino acids long, as shown in Figure 2. Five of the hydrophobic amino acids are missing from one end of the chain.
Which of the following best depicts the tertiary structures of the two proteins in water? The diagrams in the options are not drawn to the same scale as those in Figure 1 and Figure 2.

19
New cards
Which of the following best explains why a cell’s plasma membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipids rather than just a single layer?
Having two oppositely oriented layers of phospholipids allows only the hydrophilic heads to interact with water inside and outside of the cell.
\
\
20
New cards
Figure 1. An amino acid
The amino acid in Figure 1 is found in a region of a polypeptide that folds away from water. Which part of the amino acid most likely contributes to the hydrophobic behavior of this region of the polypeptide?
The amino acid in Figure 1 is found in a region of a polypeptide that folds away from water. Which part of the amino acid most likely contributes to the hydrophobic behavior of this region of the polypeptide?
Methyl (CH3CH3) group
21
New cards
Figure 1 represents a common process that occurs in organisms.
\
Which of the following is an accurate description of the process shown in Figure 1 ?
\
Which of the following is an accurate description of the process shown in Figure 1 ?
The formation of a covalent peptide bond in a dehydration synthesis reaction
22
New cards
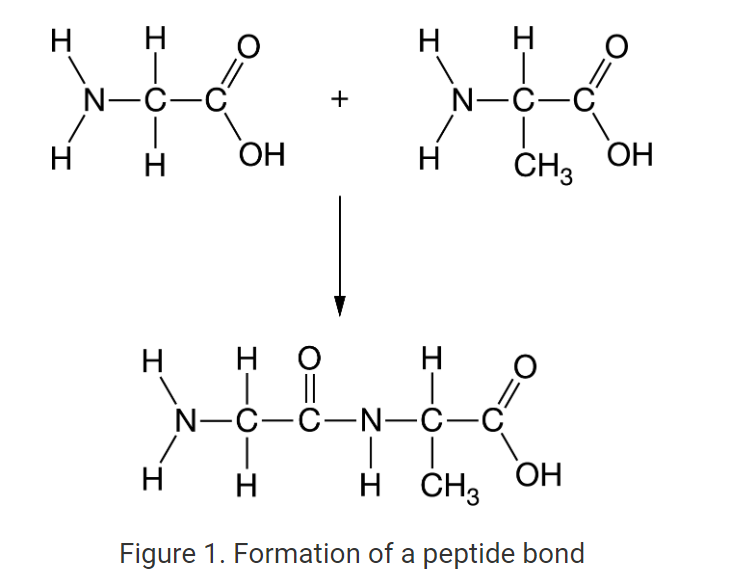
Which of the following best describes the formation of the bond shown in Figure 1 ?
A covalent bond is formed between a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom along with the formation of H2O
23
New cards
Which of the following best describes the structures of carbohydrates?
They occur as monomers, chains of monomers, and branched structures.
24
New cards
The synthesis of protein or carbohydrate polymers always produces which of the following as a byproduct?
Water
25
New cards
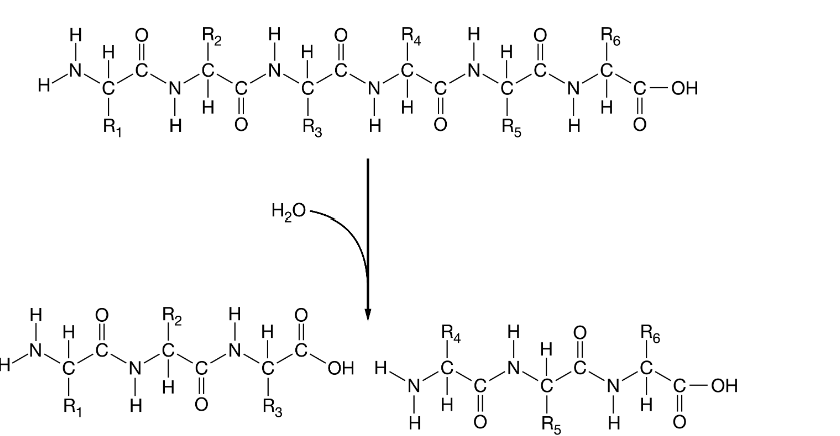
Polypeptides are continuously being formed and degraded. One of these processes is shown.
Figure 1. Polypeptide reaction
Which statement is the most accurate description of the reaction shown in Figure 1?
Figure 1. Polypeptide reaction
Which statement is the most accurate description of the reaction shown in Figure 1?
It represents a polypeptide chain that is broken down through a hydrolysis reaction.
26
New cards
Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein?
The interactions of the different RR-groups with other RR-groups and with their environment determine the tertiary structure of the protein.
27
New cards
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can damage DNA by breaking weak bonds. Which of the following best explains how this occurs?
UV radiation disrupts the double helix structure by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs.
28
New cards
Which two cellular organelles in eukaryotes have both electron transport systems and chemiosmotic mechanisms?
Chloroplasts and mitochondria
29
New cards
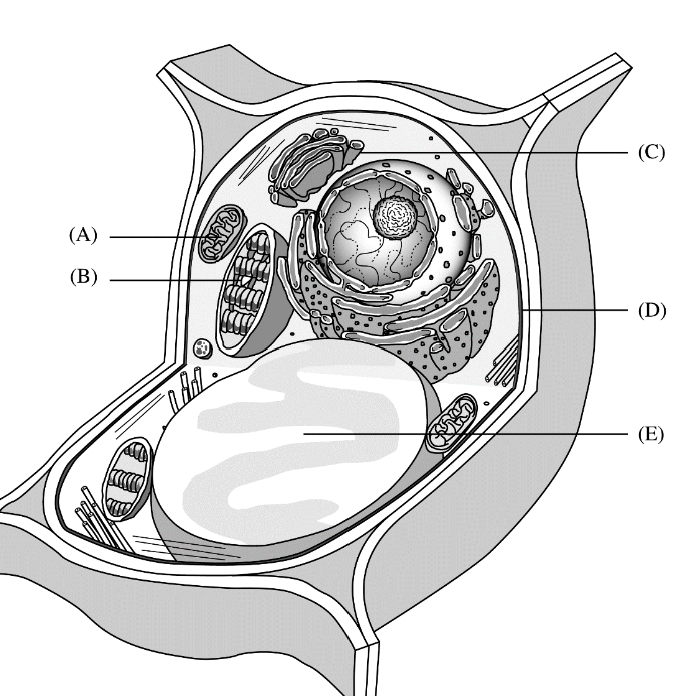
The following questions refer to the following diagram. For each phrase or sentence, select the labeled part to which it is most closely related. Each option may be used once, more than once, or not at all for each group.
Site of glucose synthesis
Site of glucose synthesis
B
30
New cards
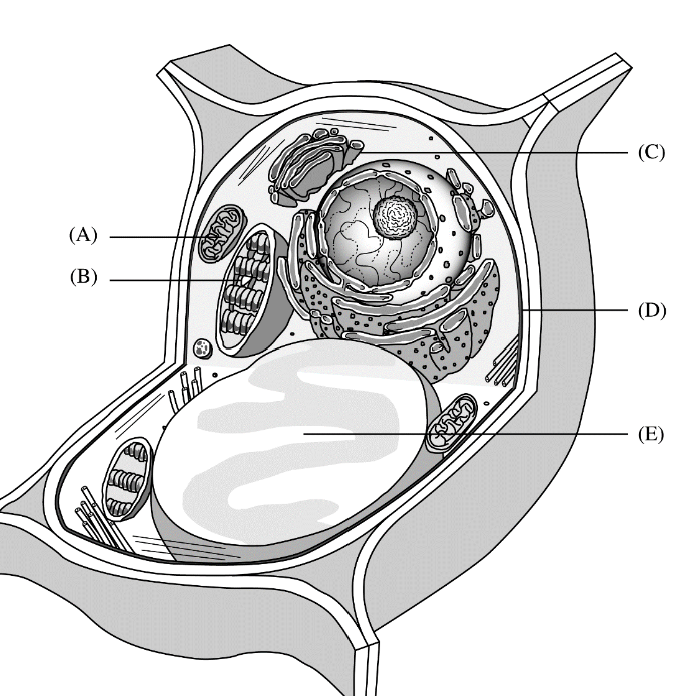
Site of conversion of chemical energy of glucose to ATP
A
31
New cards
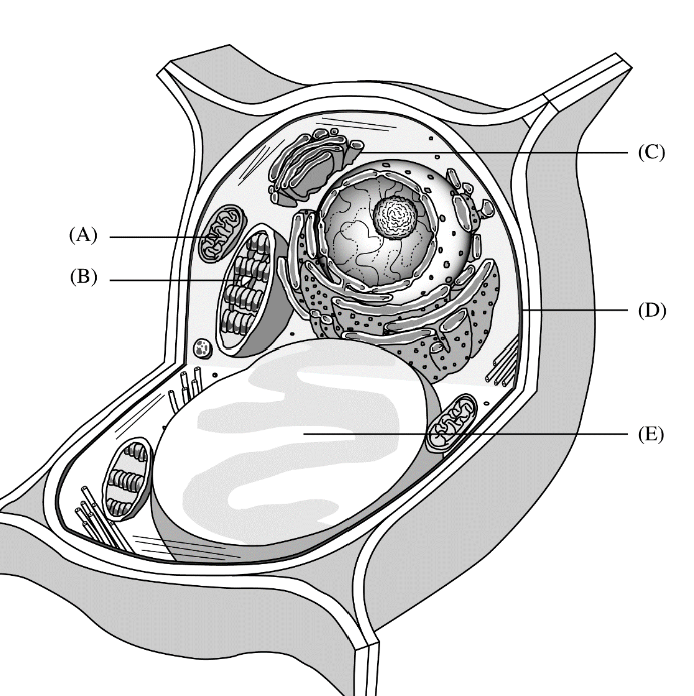
Site of modification and packaging of proteins and lipids prior to export from the cell
C
32
New cards
Which of the following is evidence that eukaryotes and prokaryotes share a common ancestor?
All eukaryotes and prokaryotes contain ribosomes.
33
New cards
Organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum have membranes that compartmentalize reactions and other metabolic processes. To function properly, the organelles must move substances across their membranes.
Which of the following statements describes a feature shared by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum that increases the efficiency of their basic functions?
Which of the following statements describes a feature shared by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum that increases the efficiency of their basic functions?
They have highly folded membranes.
34
New cards
All eukaryotic cells contain at least one Golgi complex, typically located in the cytoplasm and near the endoplasmic reticulum.
Which of the following best describes a process that occurs within the Golgi complex?
Which of the following best describes a process that occurs within the Golgi complex?
Enzymatic modification of newly synthesized integral membrane proteins
35
New cards
Which of the following organelles modifies and packages for secretion the materials produced by the ribosomes?
The Golgi apparatus
36
New cards
Individuals with an inherited autosomal recessive disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) often have severe respiratory problems due to defective cilia. Males with PCD are often sterile because they produce sperm with defective flagella. Which of the following most likely explains the effect of the recessive allele?
The cells do not produce functional motor proteins in flagella and cilia.
37
New cards
Which of the following statements is true about the Krebs (citric acid) cycle and the Calvin (light-independent) cycle?
They both are carried out by enzymes located within an organelle matrix.
38
New cards
Contains hydrolytic enzymes associated with the intracellular digestion of macromolecules
Lysosome
39
New cards
The organelle that is a major producer of ATP and is found in both heterotrophs and autotrophs is the
mitochondrion
40
New cards
In a mesophyll cell of a leaf, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following?
I. Ribosomes \n II. Mitochondria \n III. Chloroplasts
I. Ribosomes \n II. Mitochondria \n III. Chloroplasts
II and III only
41
New cards
Muscle cells have high ATPATP demands. Which of the following is a scientific claim about how the structure of the mitochondria in muscle cells should be different than it is in other cells because of the high energy demands of mitochondria?
The inner membrane of the mitochondria in muscle cells should have more folds to increase the surface area, allowing more ATPATP to be synthesized.
42
New cards
The function of which of the following organelles directly requires oxygen?
Mitochondrion
43
New cards
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the following features in common?
Ribosomes
44
New cards
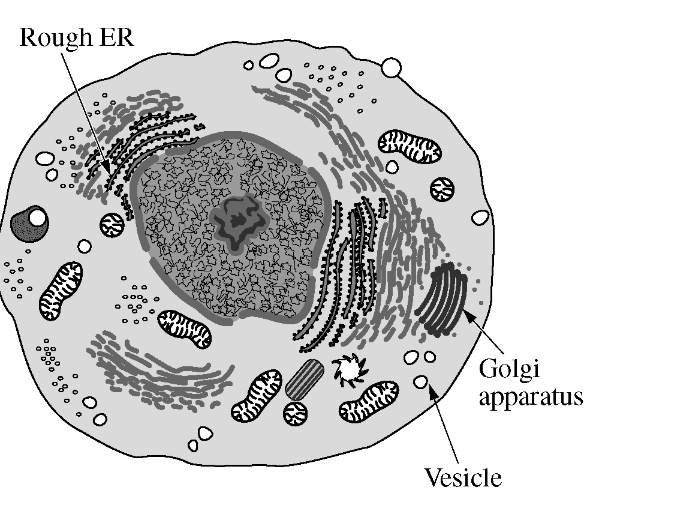
The figure below illustrates a eukaryotic cell. Which of the following best describes how the three structures indicated by the arrows work together?
\
\
To synthesize and isolate proteins for secretion or for use in the cell
\n
\n
45
New cards
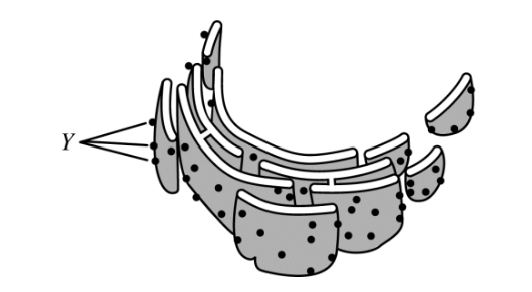
The figure above represents a rough endoplasmic reticulum. Which of the following best describes the role of the structure labeled *Y*?
Structure *Y* is the location where proteins are synthesized.
46
New cards
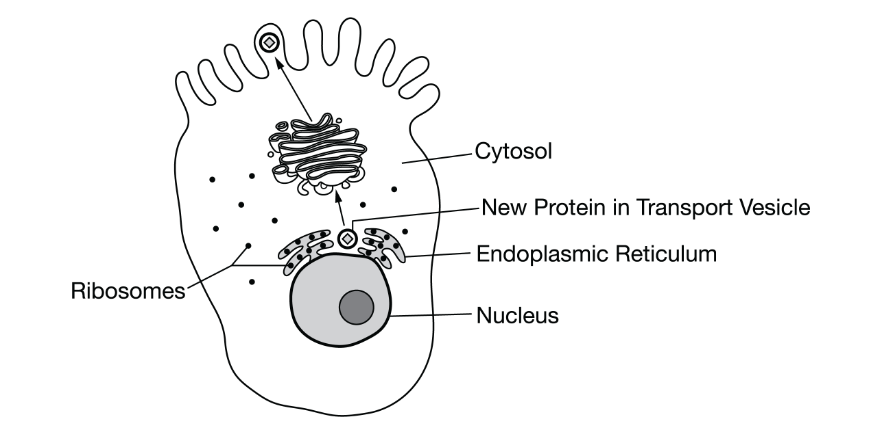
Researchers have proposed a model of the process by which a newly synthesized protein is transported to the plasma membrane and secreted into the extracellular space. The model is represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1. A model of the intracellular transport of a newly synthesized secreted protein
Based on the model, the newly synthesized protein is transported directly from the endoplasmic reticulum to which of the following?
Figure 1. A model of the intracellular transport of a newly synthesized secreted protein
Based on the model, the newly synthesized protein is transported directly from the endoplasmic reticulum to which of the following?
The Golgi complex
47
New cards
The manner in which several different ions and molecules move through a cell membrane is shown in the diagram above. For each ion or molecule, the relative concentration on each side of the membrane is indicated. Which of the following accurately describes one of the movements taking place?
\n Na+ transport out of the cell requires ATP hydrolysis.
48
New cards
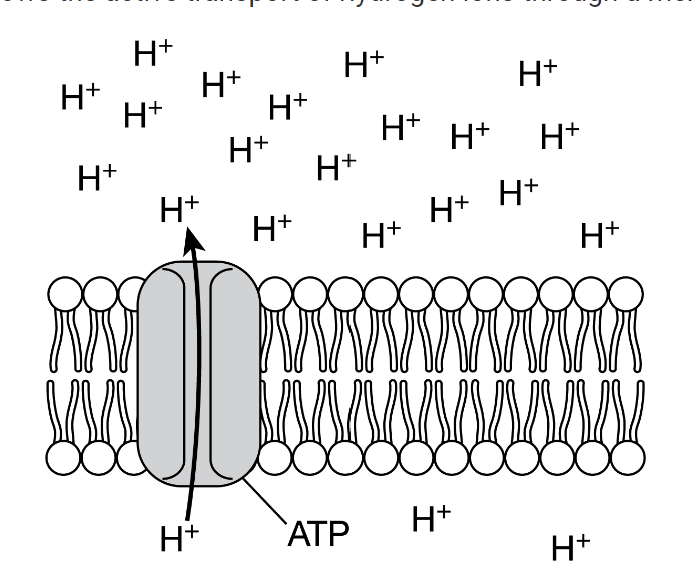
The illustration shows the active transport of hydrogen ions through a membrane protein.
Which of the following best predicts the effect of not having ATPATP available to supply energy to this process?
Which of the following best predicts the effect of not having ATPATP available to supply energy to this process?
H+ ions will stop moving through the protein.
49
New cards
Which statement best describes the effect on water transport across the cell membrane if the aquaporin in the figure ceases to function?
Water molecules will still be able to move across the cell membrane but at a slower rate.
50
New cards
If ATP breakdown (hydrolysis) is inhibited, which of the following types of movement across cell membranes is also inhibited?
Passage of a solute against its concentration gradient
51
New cards
Which of the following components of the cell membrane is responsible for active transport?
Protein
52
New cards
Which of the following describes the most likely location of cholesterol in an animal cell?
Embedded in the plasma membrane
53
New cards
When a substance moves across the plasma membrane along a concentration gradient at a rate faster than would be expected by simple diffusion alone but without the expenditure of metabolic energy, the process is best described as
\n facilitated diffusion
54
New cards
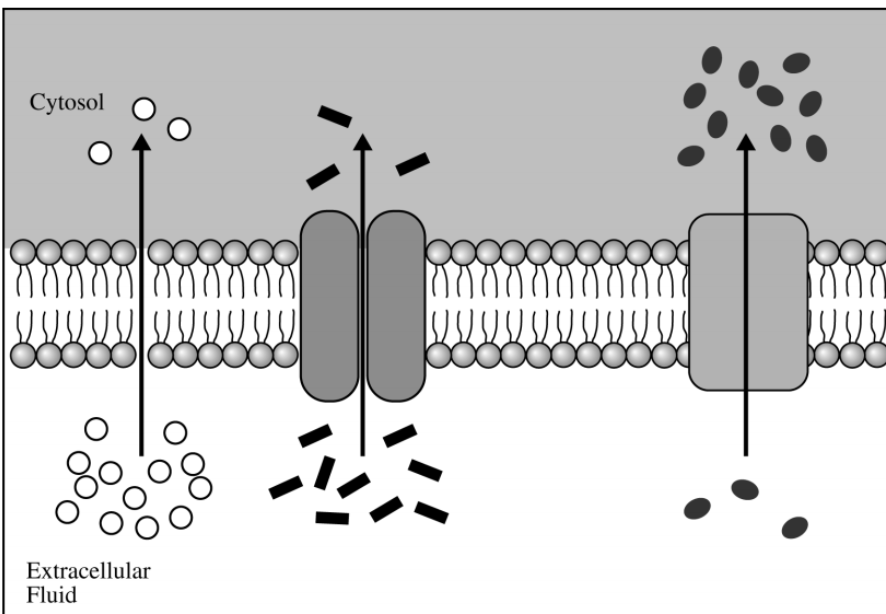
Which of the following scientific questions is most relevant to the model represented in the figure above?
Which molecular substance is actively transported across the plasma membrane?
55
New cards
Carbon dioxide most likely enters a cell through which of the following processes?
Simple diffusion through the membrane
56
New cards
Which of the following best explains how molecules such as O2 and CO2 can move across the membrane of a cell?
The majority of the cell membrane is nonpolar, which allows small, nonpolar molecules to freely cross.
57
New cards
Which of the following statements is true regarding the movement of substances across cell membranes?
Ions are unable to move through the phospholipid bilayer because the nonpolar tail regions of the phospholipids are hydrophobic.
58
New cards
A team of biologists develop a new drug, and one team member hypothesizes that the drug is incapable of freely passing across the plasma membrane and requires the help of membrane proteins to enter cells. Alternatively, another biologist on the team hypothesizes that the drug can diffuse passively across the plasma membrane like O2O2 and CO2CO2 can.
Which of the following, if true about the drug, best supports the alternative hypothesis that the new drug will exhibit simple diffusion across plasma membranes?
Which of the following, if true about the drug, best supports the alternative hypothesis that the new drug will exhibit simple diffusion across plasma membranes?
The drug is a small nonpolar molecule.
59
New cards
The drug is a small nonpolar molecule.
Passive transport is the net movement of substances down a concentration gradient that does not require metabolic energy. Active transport is the movement of substances up a concentration gradient that requires energy.
60
New cards
A pathogenic bacterium has been engulfed by a phagocytic cell as part of the nonspecific (innate) immune response. Which of the following illustrations best represents the response?
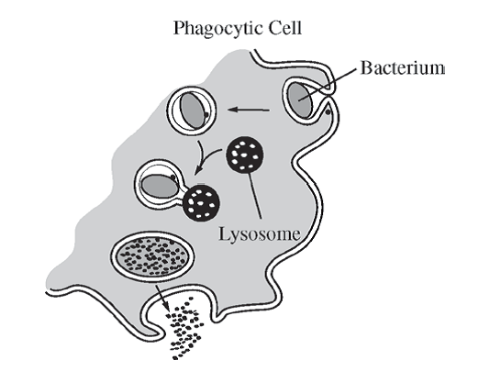
61
New cards
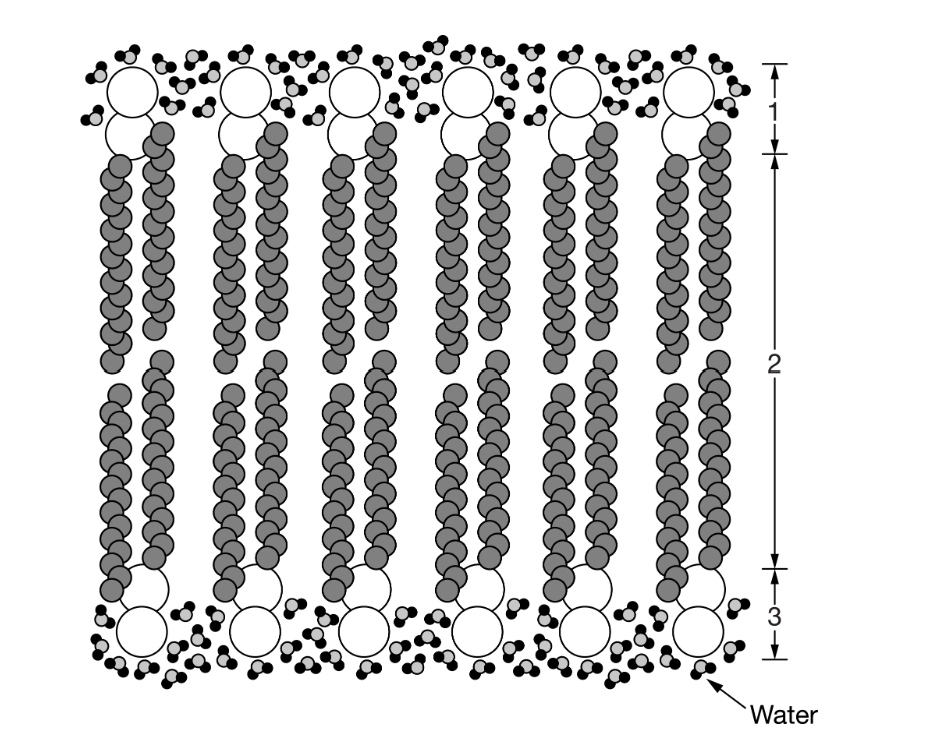
Which of the following best describes the numbered areas?
Areas 1 and 3 are polar, since the membrane molecules are aligned with water molecules
62
New cards
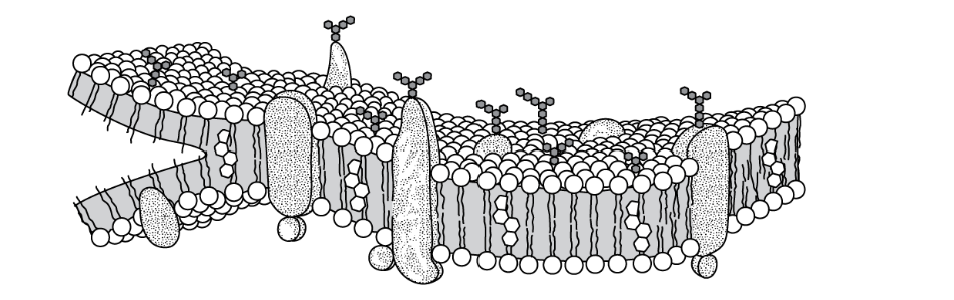
The model below shows the structure of a portion of a plasma membrane in an animal cell.
Which statement best explains the orientation of the phospholipid molecules in this model?
Which statement best explains the orientation of the phospholipid molecules in this model?
The hydrophilic phosphate groups of the phospholipid molecules are attracted to the aqueous internal and external environments.
63
New cards
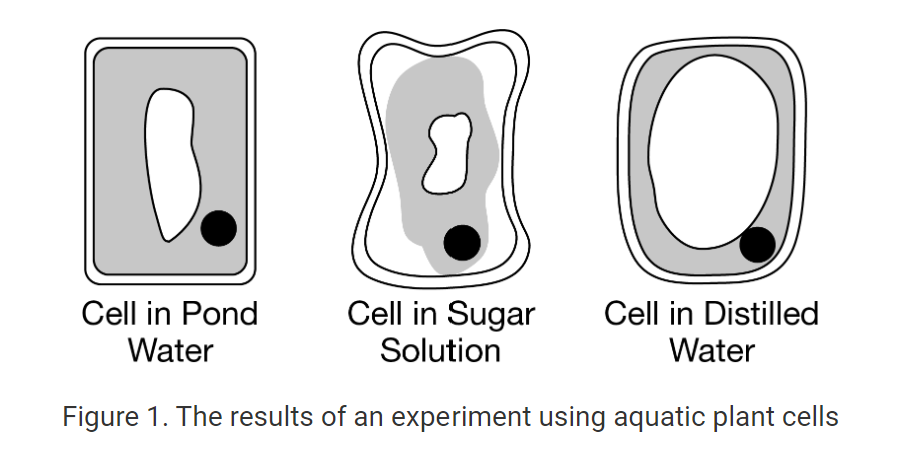
In an experiment, cells were isolated from an aquatic plant and suspended in pond water, a sucrose sugar solution, or distilled water. All of the cells were then viewed under a microscope. Compared with the cell in the pond water, the cell in the sugar solution appeared shriveled, and the cell in the distilled water appeared inflated. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following statements best explains the observations represented in Figure 1 ?
Which of the following statements best explains the observations represented in Figure 1 ?
There was a net movement of water out of the cell suspended in the sugar solution and a net movement of water into the cell suspended in the distilled water.
64
New cards
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are related in that both
depend on a concentration gradient
65
New cards
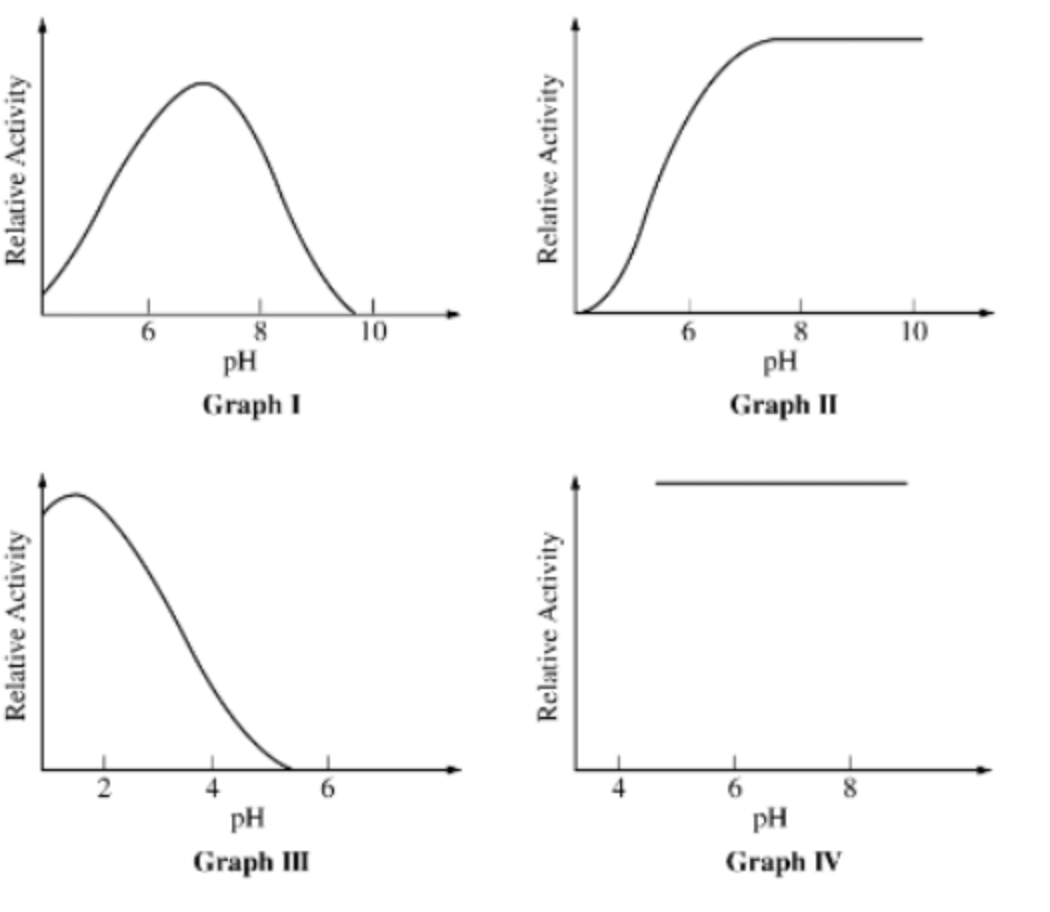
For the following questions: Graphs I-IV depict the effect of pH on the activity of four different hydrolytic enzymes.
\
\
Enzymes with their highest activity at an alkaline (basic) pH are represented by which of the following graphs?
\
\
Enzymes with their highest activity at an alkaline (basic) pH are represented by which of the following graphs?
II only
66
New cards
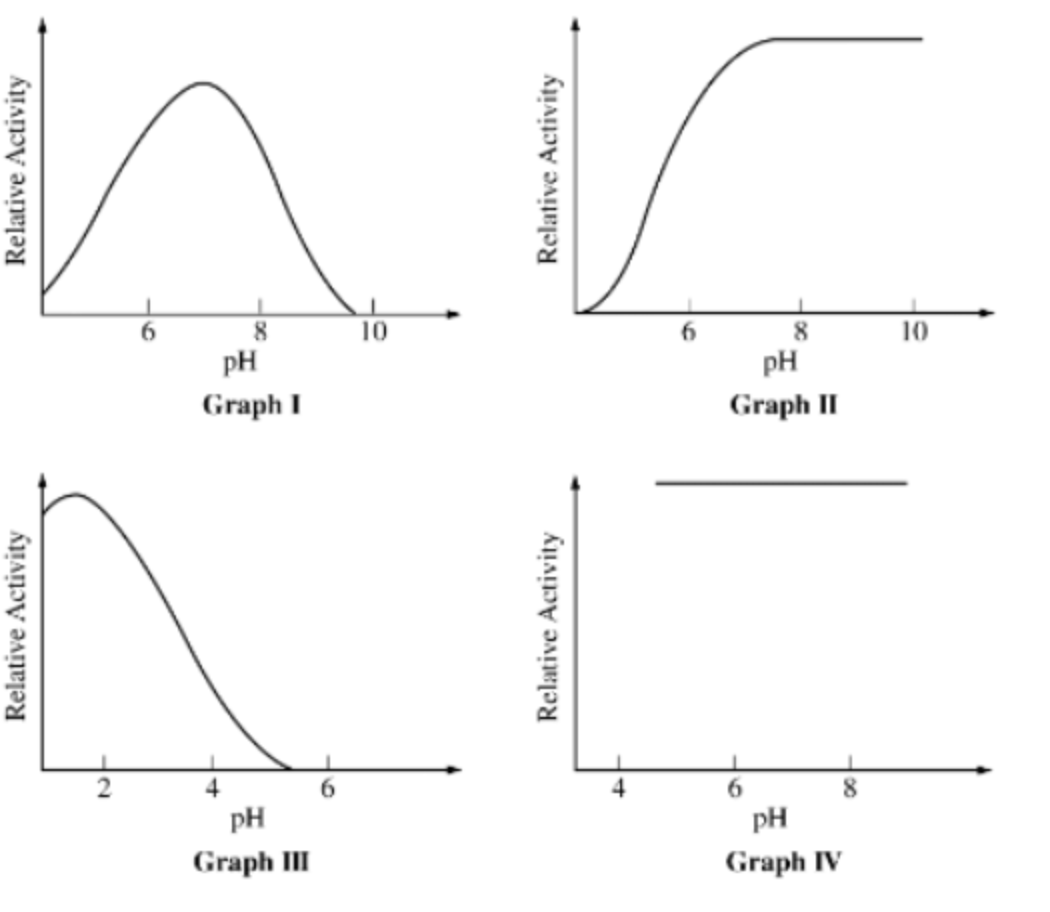
For the following questions: Graphs I-IV depict the effect of pH on the activity of four different hydrolytic enzymes.
\
\
Graphs representing enzymes sensitive to changes in pH include which of the following?
\
\
Graphs representing enzymes sensitive to changes in pH include which of the following?
I, II, and III only
67
New cards
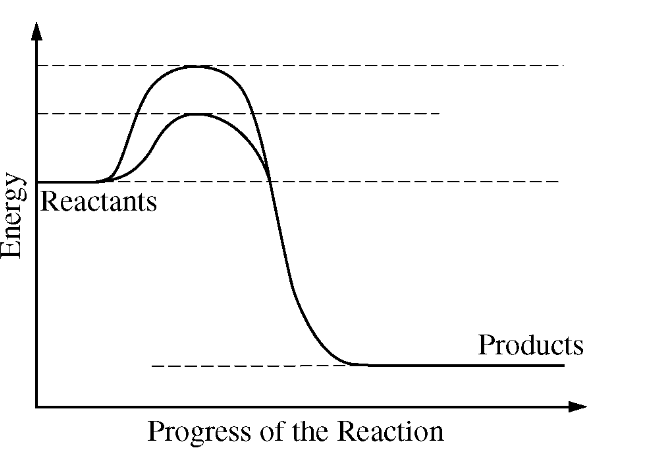
The diagram below shows energy changes in a specific chemical reaction with and without the addition of an enzyme to the reaction.
\
Which of the following questions can best be answered by the diagram?
\
Which of the following questions can best be answered by the diagram?
Does the addition of an enzyme reduce the activation energy required for a reaction?
68
New cards
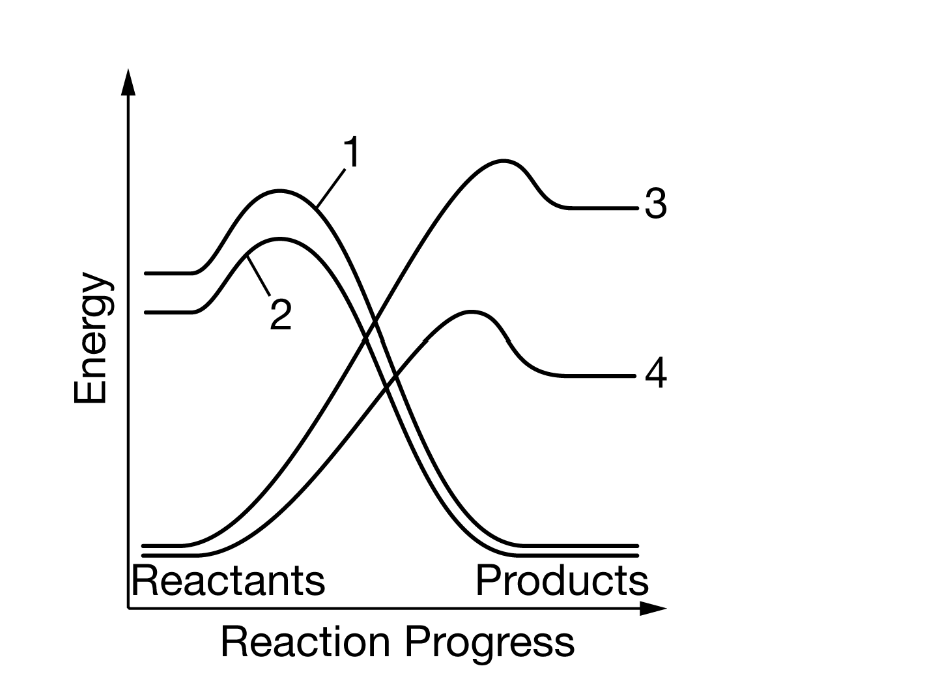
Figure 1. Change in energy over the course of four chemical reactions
Based on the data in Figure 1, which of the following most likely represents the change in energy that occurs when ATPATP hydrolysis is coupled with the phosphorylation of a substrate?
Based on the data in Figure 1, which of the following most likely represents the change in energy that occurs when ATPATP hydrolysis is coupled with the phosphorylation of a substrate?
Line 1 represents ATP hydrolysis, and line 4 represents phosphorylation of a substrate.
69
New cards
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of an enzyme?
The shape and charge of the substrates are compatible with the active site of the enzyme.
70
New cards
The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, which is an important step in glycolysis. The reaction involves the transfer of a phosphate group from ATPATP to glucose.
Either a glucose molecule or a water molecule can fit in the active site of hexokinase. The presence of a water molecule in hexokinase’s active site would result in the hydrolysis of ATPATP to ADPADP instead of the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate.
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of hexokinase?
Either a glucose molecule or a water molecule can fit in the active site of hexokinase. The presence of a water molecule in hexokinase’s active site would result in the hydrolysis of ATPATP to ADPADP instead of the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate.
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of hexokinase?
Glucose has the right shape and charge to cause hexokinase to undergo a structural change needed for catalysis, whereas water does not.
71
New cards
Pyruvate kinase, a key enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, is inhibited by the amino acid alanine. The ability of alanine to inhibit the enzyme is not affected by increasing the concentration of substrate.
Which of the following best explains the mechanism by which alanine inhibits pyruvate kinase activity?
Which of the following best explains the mechanism by which alanine inhibits pyruvate kinase activity?
Alanine binds to an allosteric site of the enzyme, changing the shape of the enzyme’s active site.
72
New cards
Trypsin and pepsin are enzymes that function in different areas of the digestive tract. One functions in the stomach, where the pH is between 1.51.5 and 3.53.5, while the other functions in the small intestines, where the pH is between 66 and 88.
Pepsin works in the stomach because the optimal pH for pepsin is acidic.
73
New cards
A researcher claims that different enzymes exhibit maximal function over different pHpH ranges. To test the claim, the researcher carries out an experiment that includes three different enzymes: pepsin, salivary amylase, and arginase. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1. The effect of pHpH on three different enzymes
Which of the following actions will provide the most appropriate negative control for the experiment?
Figure 1. The effect of pHpH on three different enzymes
Which of the following actions will provide the most appropriate negative control for the experiment?
Repeating the experiment with denatured enzymes
74
New cards
The enzyme peroxidase is found in many organisms. It catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. The rate of peroxidase activity at different pH values was assessed by students in the lab. The students’ results are shown in graph 1.
Graph 1. Effect of pH on peroxidase activity
If the experiment is repeated at pH 11, the observed activity level of the enzyme will most likely be
Graph 1. Effect of pH on peroxidase activity
If the experiment is repeated at pH 11, the observed activity level of the enzyme will most likely be
lower than the level at pH 9
75
New cards
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate during glycolysis, as represented in Figure 1.
PFK can be allosterically inhibited by ATP at high concentrations. Which of the following is the benefit of regulating glycolysis by the concentration of ATP?
PFK can be allosterically inhibited by ATP at high concentrations. Which of the following is the benefit of regulating glycolysis by the concentration of ATP?
Glycolysis proceeds when the intracellular concentration of ATP is low, which provides ATP to drive cellular reactions.
76
New cards
A researcher claims that increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels cause increased growth rates in plants.
Which of the following statements best supports the researcher’s claim?
Which of the following statements best supports the researcher’s claim?
Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds.
77
New cards
The energy required to run the Calvin cycle reactions of photosynthesis comes from which two substances produced during the light-dependent reactions?
ATP and NADPH
78
New cards
The carbon 'that makes up organic molecules in plants is derived __directly__ from
carbon fixed in photosynthesis
79
New cards
carbon fixed in photosynthesis
No ATP is synthesized when channel proteins that allow the free passage of protons are inserted into the thylakoid membrane.
80
New cards
Which of the following is an important difference between light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the light-independent reactions use energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
81
New cards
Carbohydrate-synthesizing reactions of photosynthesis directly require
products of the light reactions
82
New cards
It is estimated that oxygen production first evolved in photosynthetic prokaryotes approximately 2.7 billion years ago. The first photosynthetic prokaryotes are presumed to be similar to today’s cyanobacteria.
Which of the following best supports the claim that photosynthetic prokaryotes were responsible for the oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere?
Which of the following best supports the claim that photosynthetic prokaryotes were responsible for the oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere?
The light reactions of photosynthesis split water into hydrogen ions and oxygen.
83
New cards
A scientist claims that *Elysia chlorotica,* a species of sea slug, is capable of photosynthesis.
Which of the following observations provides the best evidence to support the claim?
Which of the following observations provides the best evidence to support the claim?
*Elysia chlorotica* grows when exposed to light in the absence of other food sources.
84
New cards
* This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
(A) Glysolysis \n (B) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) \n (C) Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis) \n (D) Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis \n (E) Chemiosmosis
Process in which O2 is released as a by-product of oxidation-reduction reactions
(A) Glysolysis \n (B) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) \n (C) Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis) \n (D) Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis \n (E) Chemiosmosis
Process in which O2 is released as a by-product of oxidation-reduction reactions
D
85
New cards
* This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
(A) Glycolysis \n (B) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) \n (C) Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis) \n (D) Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis \n (E) Chemiosmosis
Process in which carbon from CO2 is incorporated into organic molecules
(A) Glycolysis \n (B) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) \n (C) Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis) \n (D) Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis \n (E) Chemiosmosis
Process in which carbon from CO2 is incorporated into organic molecules
C
86
New cards
Which of the following questions is most relevant to understanding the Calvin cycle?
How is ATP used in the formation of 3-carbon carbohydrates?
87
New cards
A researcher is investigating the effects of a chemical that makes thylakoid membranes permeable to hydrogen ions (H+H+). Which of the following is the most likely direct effect of adding the chemical to plant cells?
The chloroplasts will generate less ATP.
88
New cards
The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from
H2O
89
New cards
Which of the following best describes the role of water in photosynthesis?
Water molecules donate electrons to the electron transport chain.
90
New cards
This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
\
This group of questions refers to molecules of the following substances.
\n (A) Cytochrome \n (B) FADH2 \n (C) NAD+ \n (D) NADP+ \n (E) Oxygen (O2)
An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations that occur in both glycolysis and in Krebs cycle reactions
\
This group of questions refers to molecules of the following substances.
\n (A) Cytochrome \n (B) FADH2 \n (C) NAD+ \n (D) NADP+ \n (E) Oxygen (O2)
An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations that occur in both glycolysis and in Krebs cycle reactions
NAD+
91
New cards
ATP serves as a common energy source for organisms because
\n its energy can be easily transferred to do cellular work
92
New cards
During respiration, most ATP is formed as a direct result of the net movement of
protons down a concentration gradient
93
New cards
Which of the following statements about mitochondrial chemiosmosis is NOT true?
Heat energy is required to establish the electron transport chain.
94
New cards
Heat energy is required to establish the electron transport chain.
electrons flowing along the electron transport \n chain
95
New cards
Within the cell, many chemical reactions that, by themselves, require energy input (have a positive free-energy change) can occur because the reactions
may be coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP
96
New cards
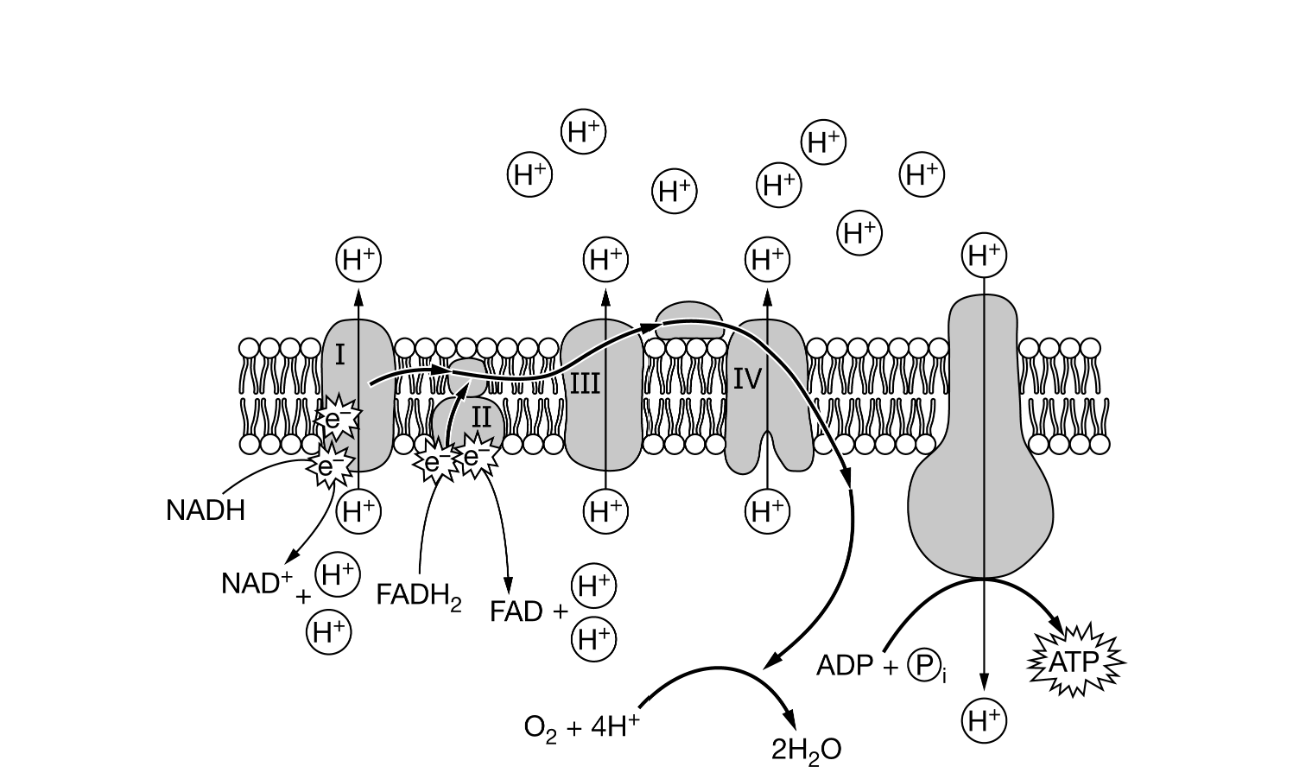
Figure 1. Diagram of the electron transport chain and ATPATP synthase in the membrane of mitochondria
On average, more ATPATP can be produced from an NADH molecule than can be produced from a molecule of FADH2FADH2. Based on Figure 1, which of the following best explains the difference in ATPATP production between these two molecules?
On average, more ATPATP can be produced from an NADH molecule than can be produced from a molecule of FADH2FADH2. Based on Figure 1, which of the following best explains the difference in ATPATP production between these two molecules?
The electrons of FADH2 are transferred through three complexes of the electron transport chain whereas those of NADH are transferred through all four complexes.
97
New cards
Newborn babies and hibernating animals contain a large amount of brown adipose (fat) tissue (BAT). Certain proteins in the BAT cells increase the permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane to protons, disrupting the proton gradient.
Which of the following best predicts the effect of disrupting the proton gradient in BATBAT?
Which of the following best predicts the effect of disrupting the proton gradient in BATBAT?
Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation will be decoupled, generating more heat but less ATP.
98
New cards
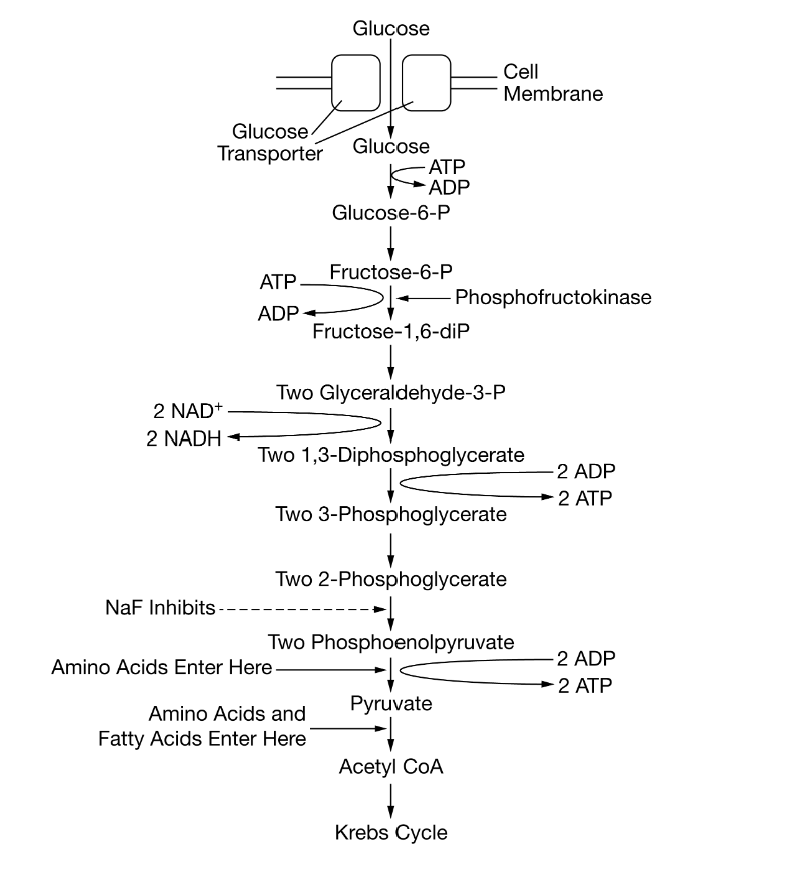
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF.
based on Figure 1, the net number of ATPATP molecules produced during glycolysis from the metabolism of a single glucose molecule is closest to which of the following?
based on Figure 1, the net number of ATPATP molecules produced during glycolysis from the metabolism of a single glucose molecule is closest to which of the following?
2
99
New cards
Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation of the mechanism of ATP synthase?
Is the phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase dependent on the formation of a proton gradient?
100
New cards
When hydrogen ions are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix, across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and into the space between the inner and outer membranes, the result is
the creation of a proton gradient