Histology 2 Midterm: A Detailed Guide on How to Eat a Sandwich
1/381
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
382 Terms
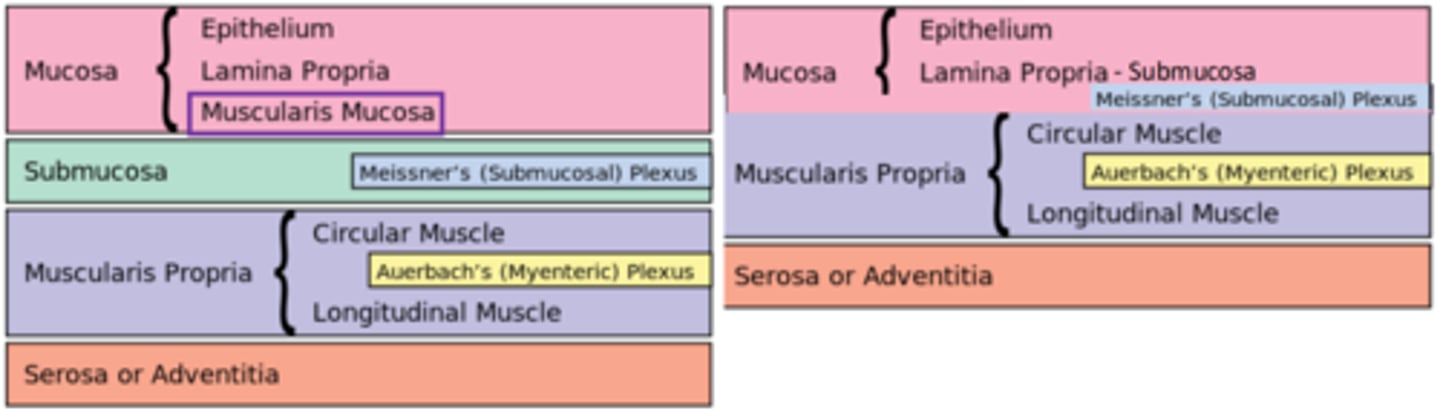
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis Externa
Adventitia or Serosa
(feel free to add "tunica" in front of any of these)
What are the 4 LAYERS of the general organization of the GI tract?
Epithelium
Lamina Propria
Muscularis mucosa
What are the SUBLAYERS of Mucosa?
Inner circular layer
Outer longitudinal layer
What are the SUBLAYERS of Muscularis Externa
Connective tissue
Lamina Propria is the ____ layer underneath/around the epithelium
Independent movement of mucosa
Muscularis mucosa are layers of smooth muscle for what function?
Large blood vessels and nerves (Meissner's plexus)
Submucosa is usually DICT that contains ________ as well as glands
Submucosal (Meissner's) plexus
Myenteric (Auerbach's) plexus
What are the 2 layers of the enteric nervous system?
Secretory functions
What is the main function of the Submucosal plexus?
Motor function (peristalsis)
What is the main function of the Myenteric plexus?
Two layers of smooth muscle (inner circular/outer longitudinal)
Myenteric plexus between muscle layers
What are the layers of Muscularis Externa?
Serosa: Connective tissues covered by Simple Squamous epithelium
Adventitia: Connective tissue continuous with surrounding fascia (It's Adhered)
What are the definitions of Serosa and Adventitia
It's own layer
Else: lamina propria - submucosa or mucosa - submucosa
If muscularis muscosae is present, submucosa is considered ...
Quizzy Pop
FALSE. THIS WILL NOT BE TESTED.
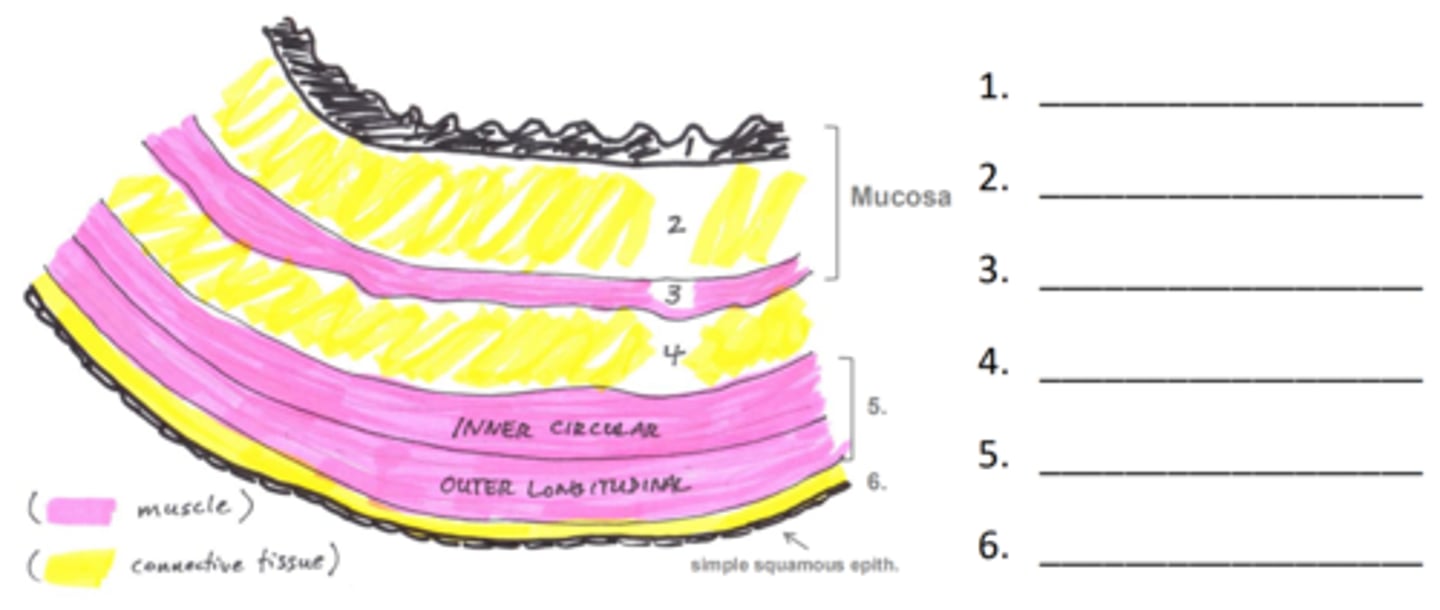
T/F: You should spend time understanding the differences between sections in the villi
Memorize this if you want a 100%
Make this make sense to yourself
Brachydont
- low crown, no further growth
Hypsodont
- high crown, keep growing
What are the two types of teeth?
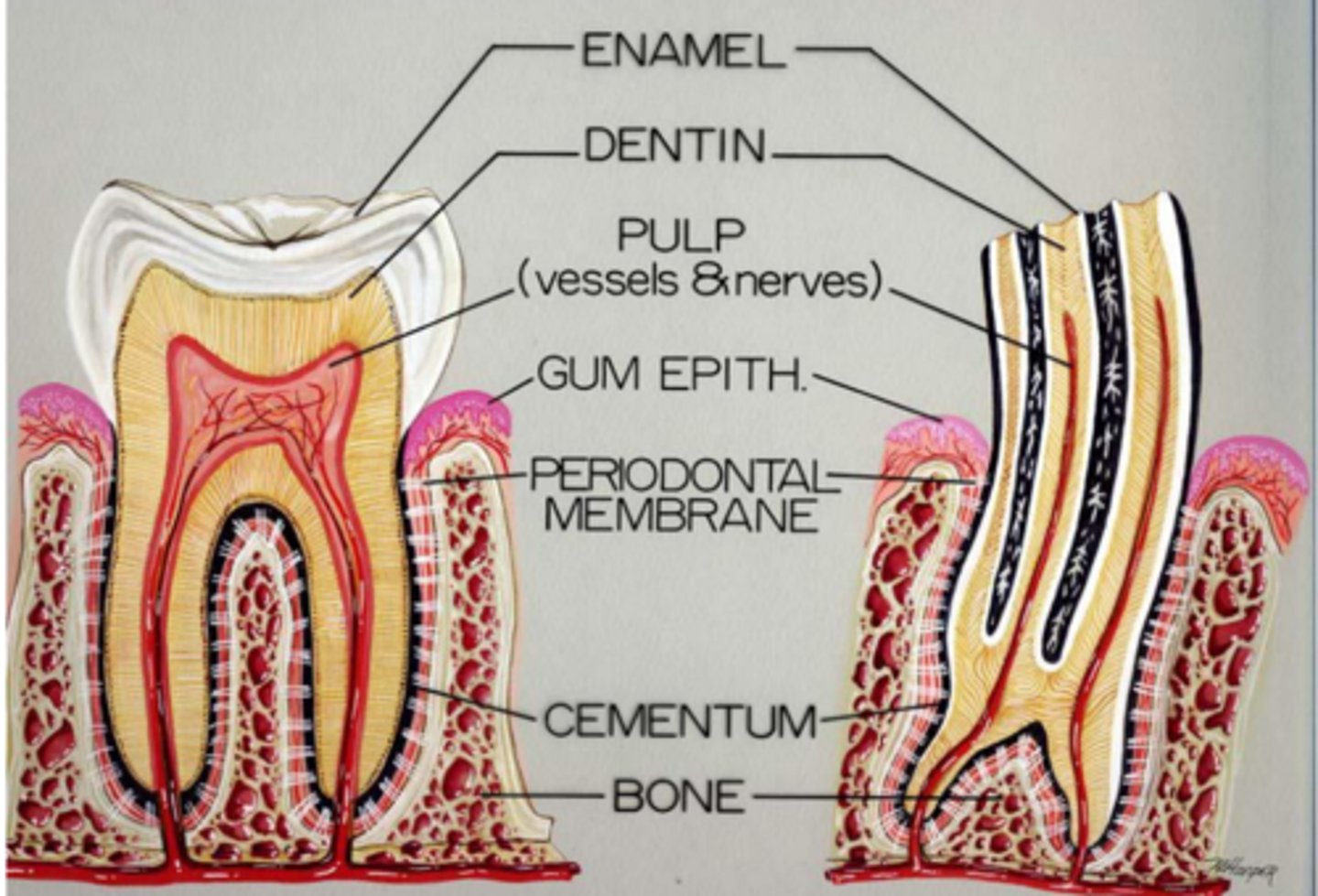
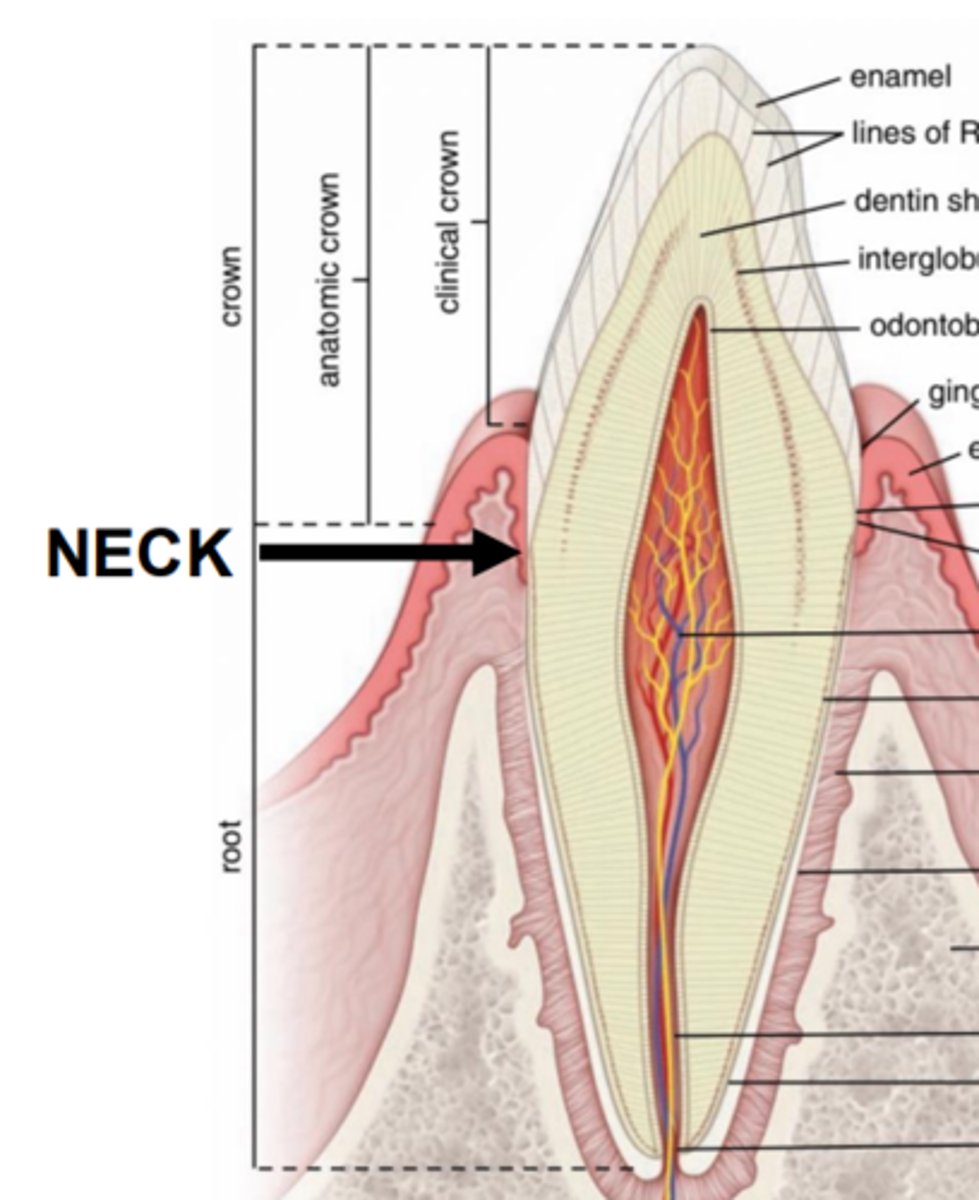
Anatomical crown (covered by enamel)
Clinical crown (visible portion of tooth)
What are the two portions of a crown?
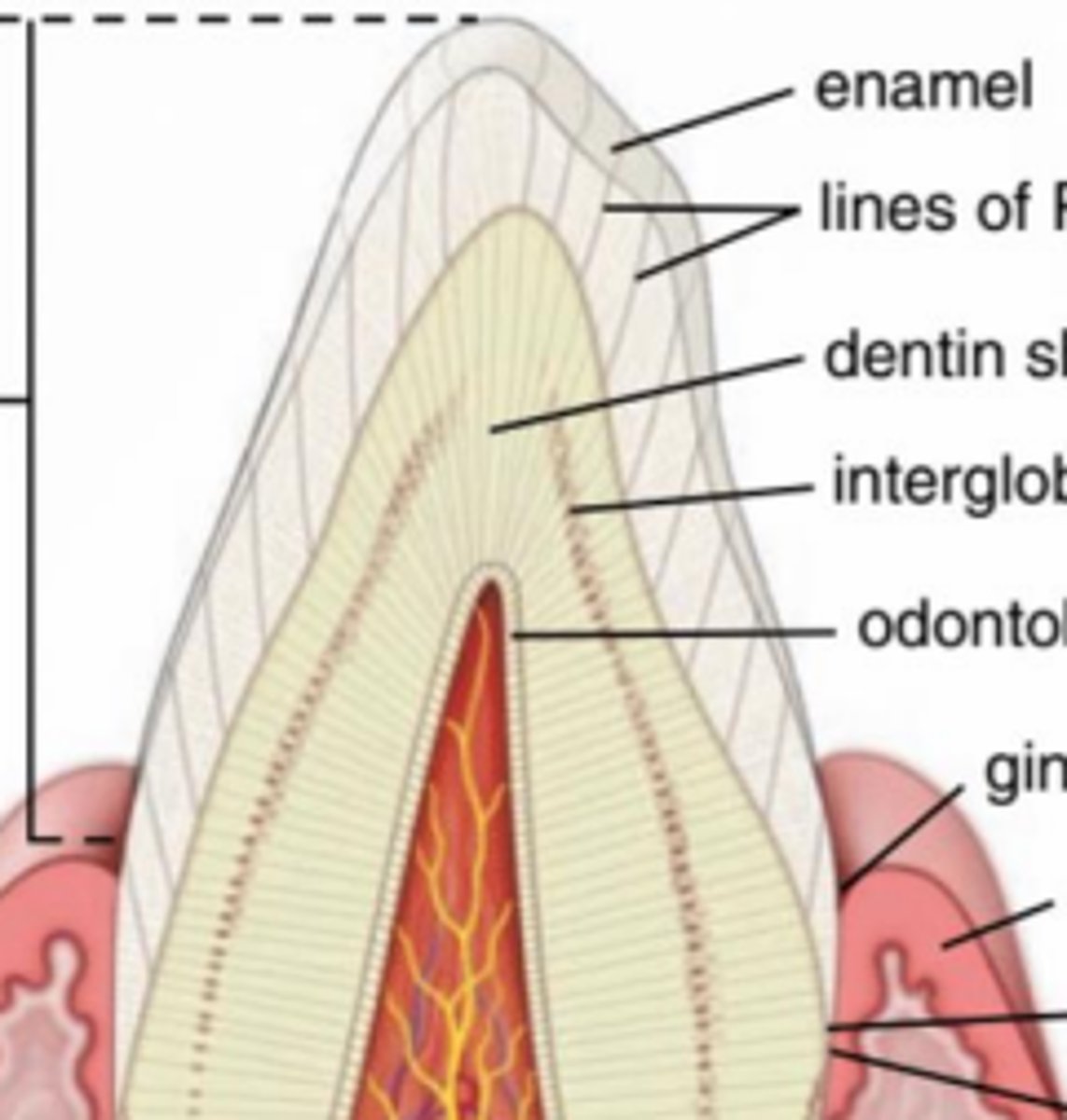
Cementum
Anchor tooth to bone
What is the root covered in?
What is its job?
Junction of crown and root
Enamel ends, cementum begins
Attachment of gingival epithelium to tooth
What is the identifying feature of the neck?
Secreted by ameloblasts
Hardest substance in body
How is enamel made?
What is it's main characteristic?
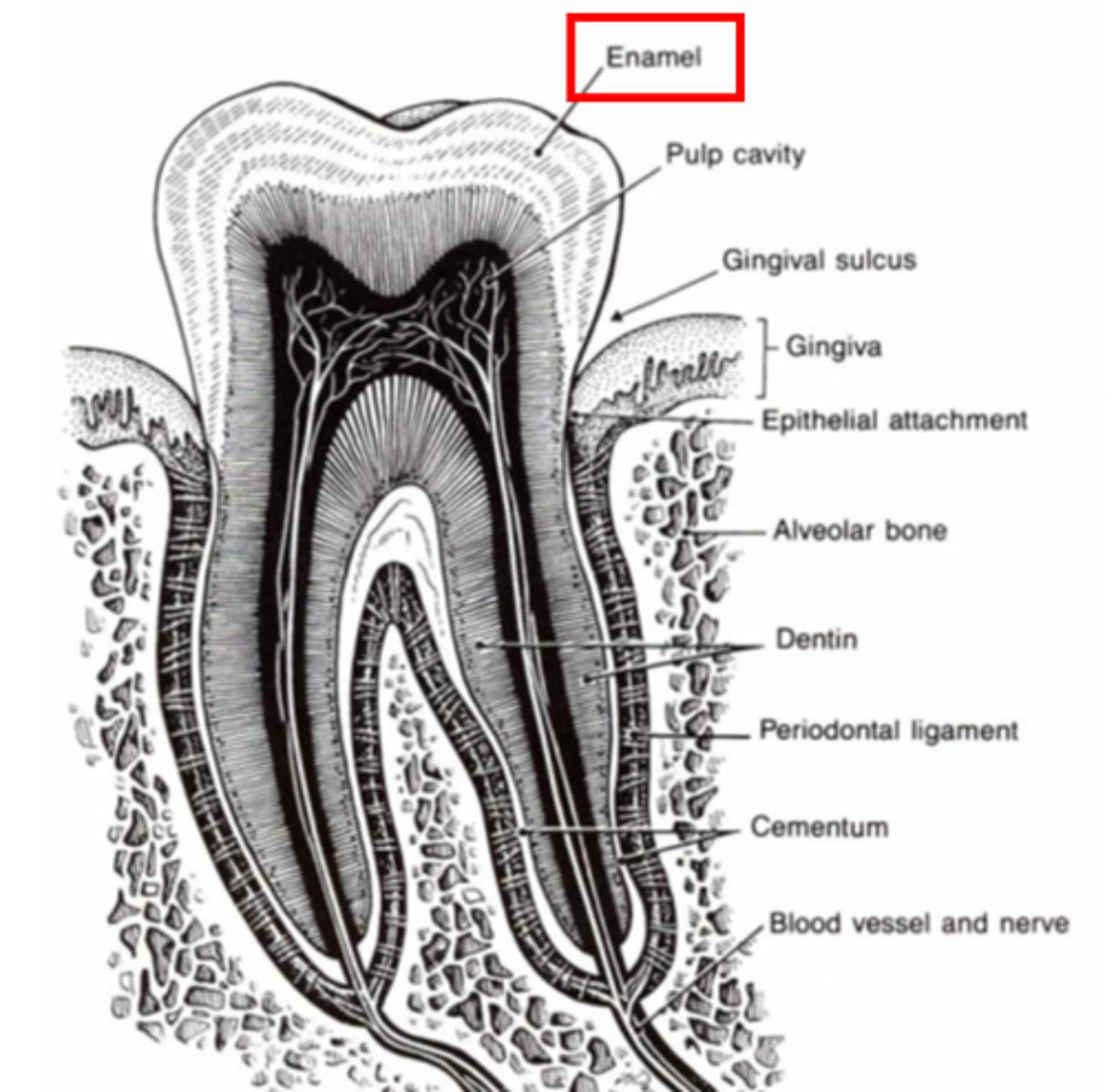
Dentin
Second hardest substance
What is the tooth's internal template?
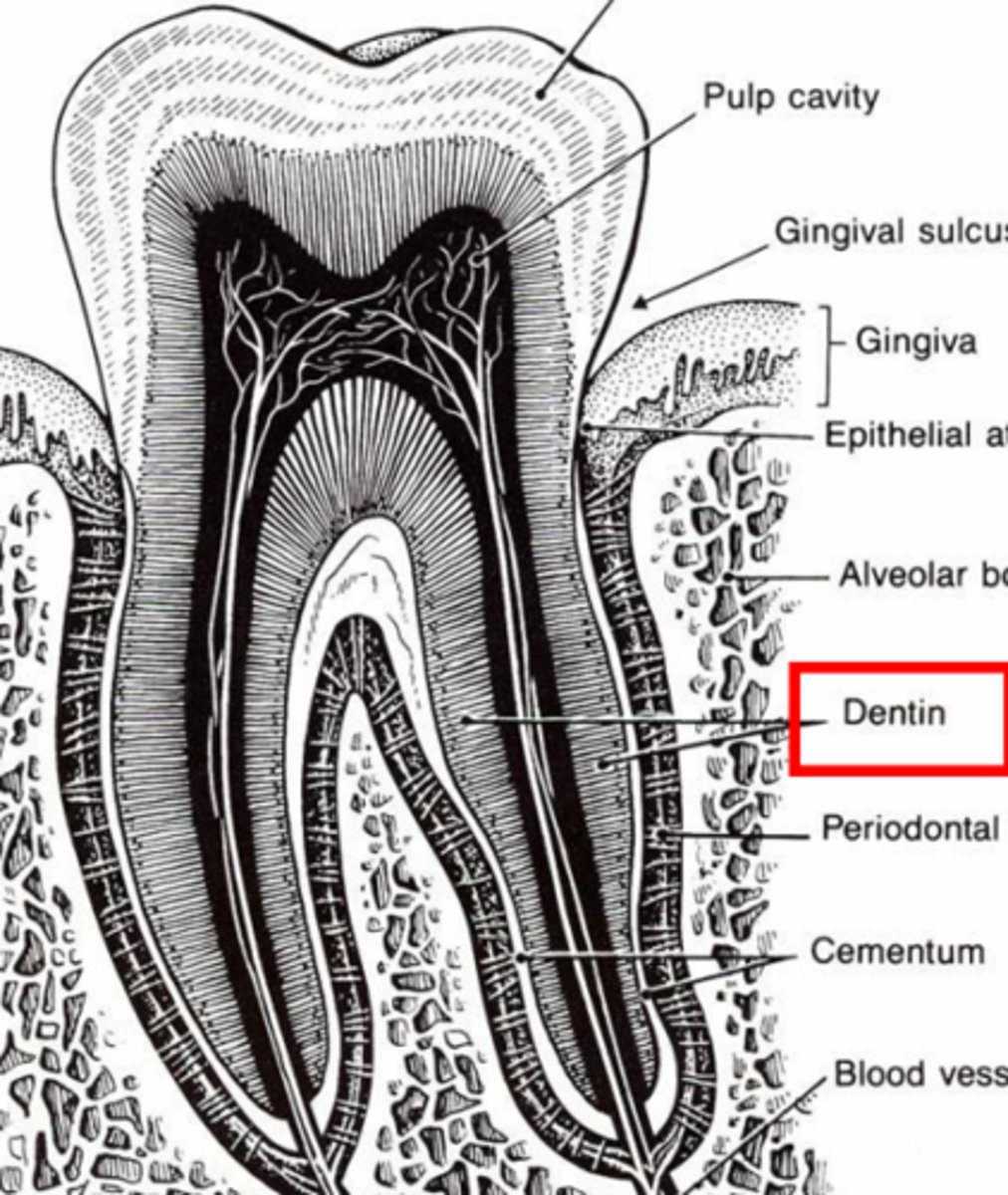
Secreted by odontoblasts
How is dentin made?
Dentinal tubes
Extend the entire length of dentin, with sensory nerve endings
What are the open channels in dentin called?
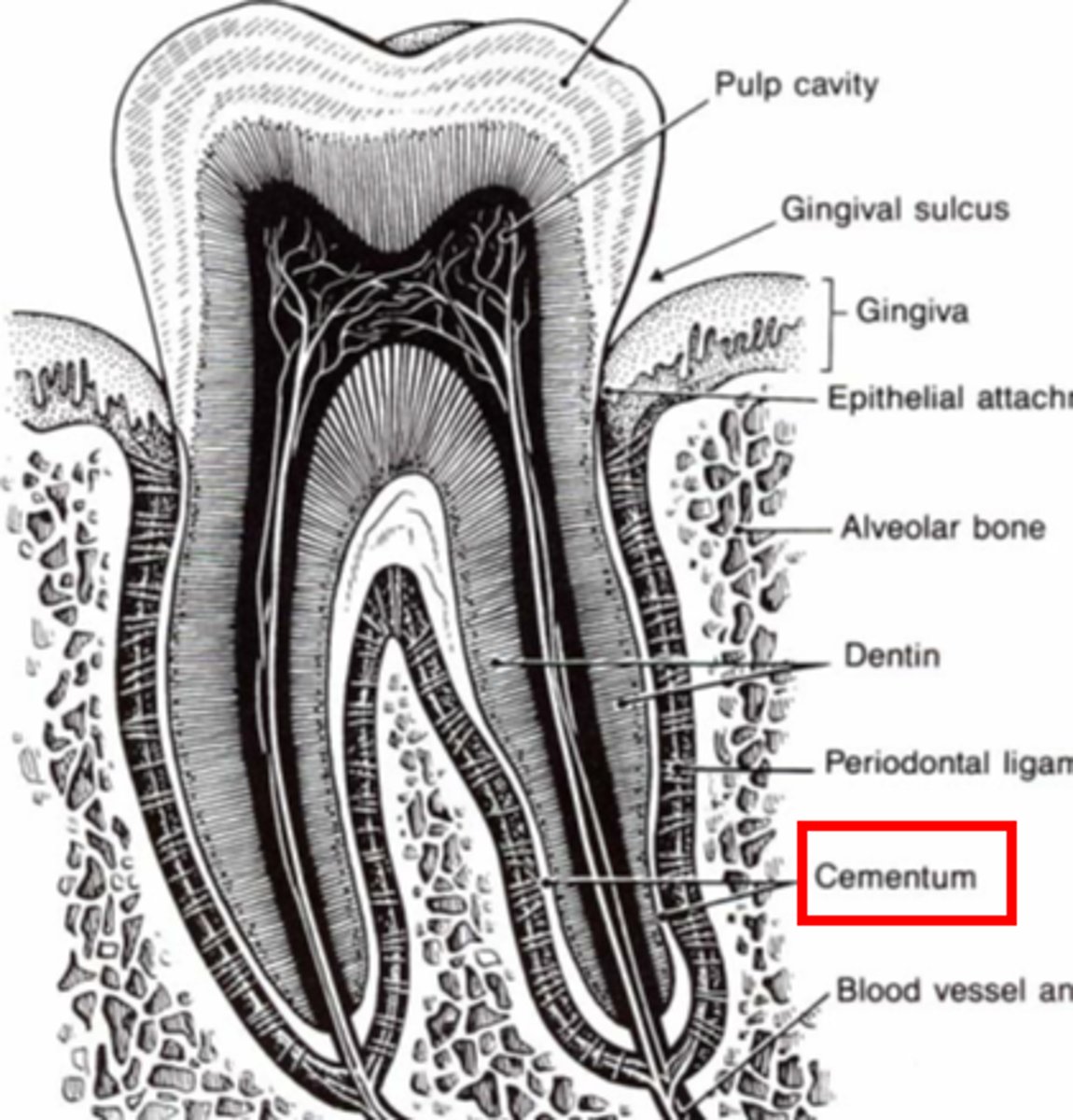
Cementum
Cementoblasts/Cementocytes (Peripheral/central)
Similar hardness to bone
What coats the outer surface of the root?
What secretes and maintain cementum?
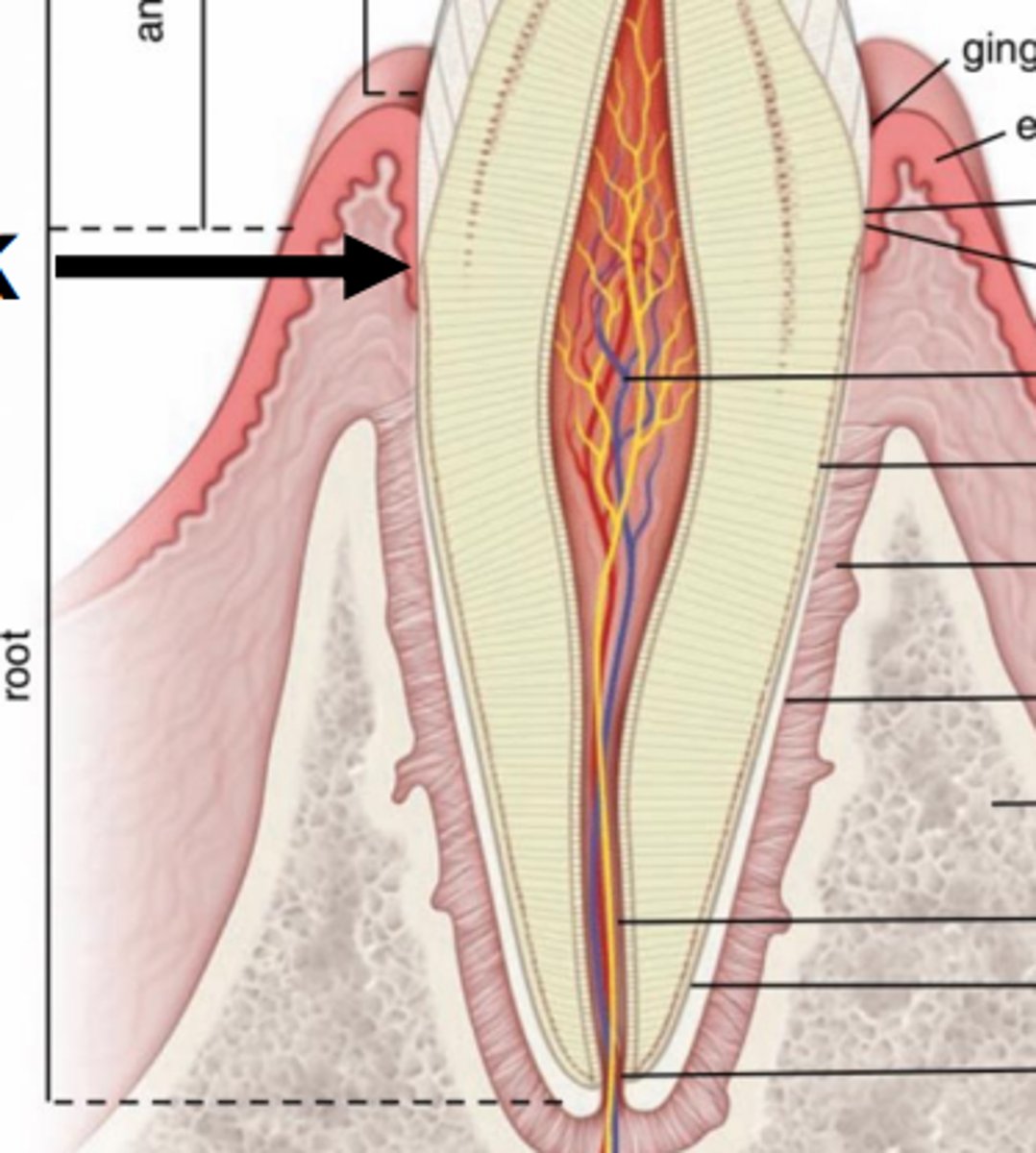
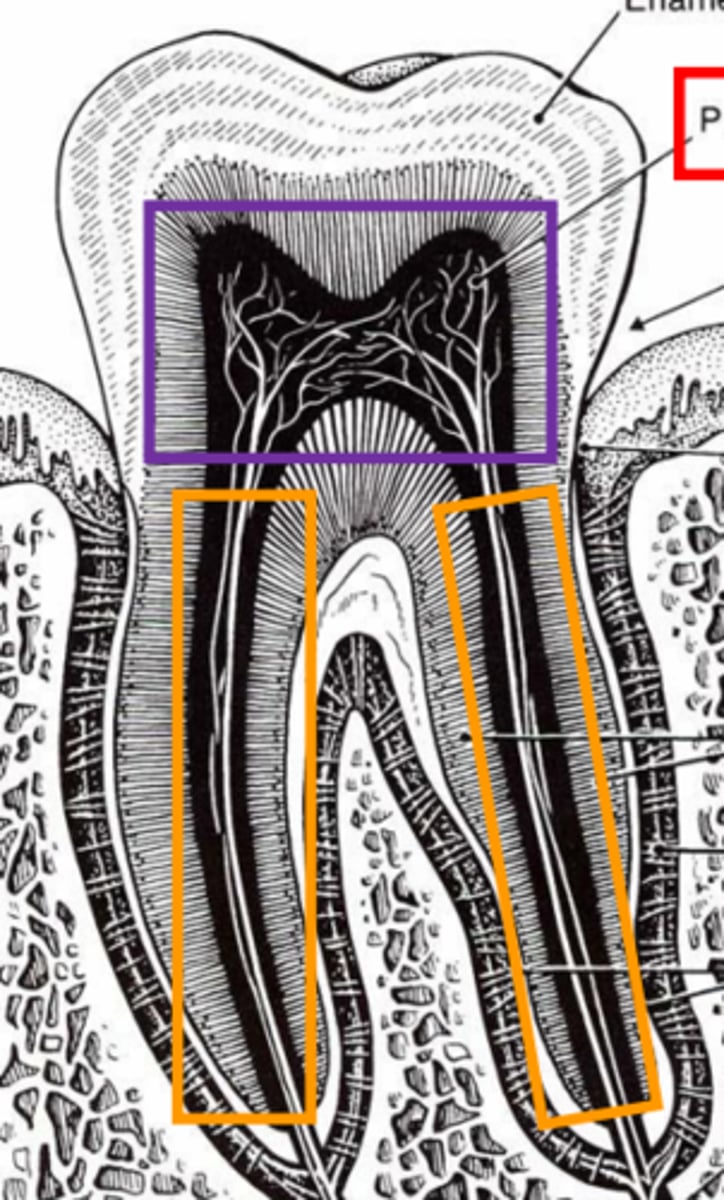
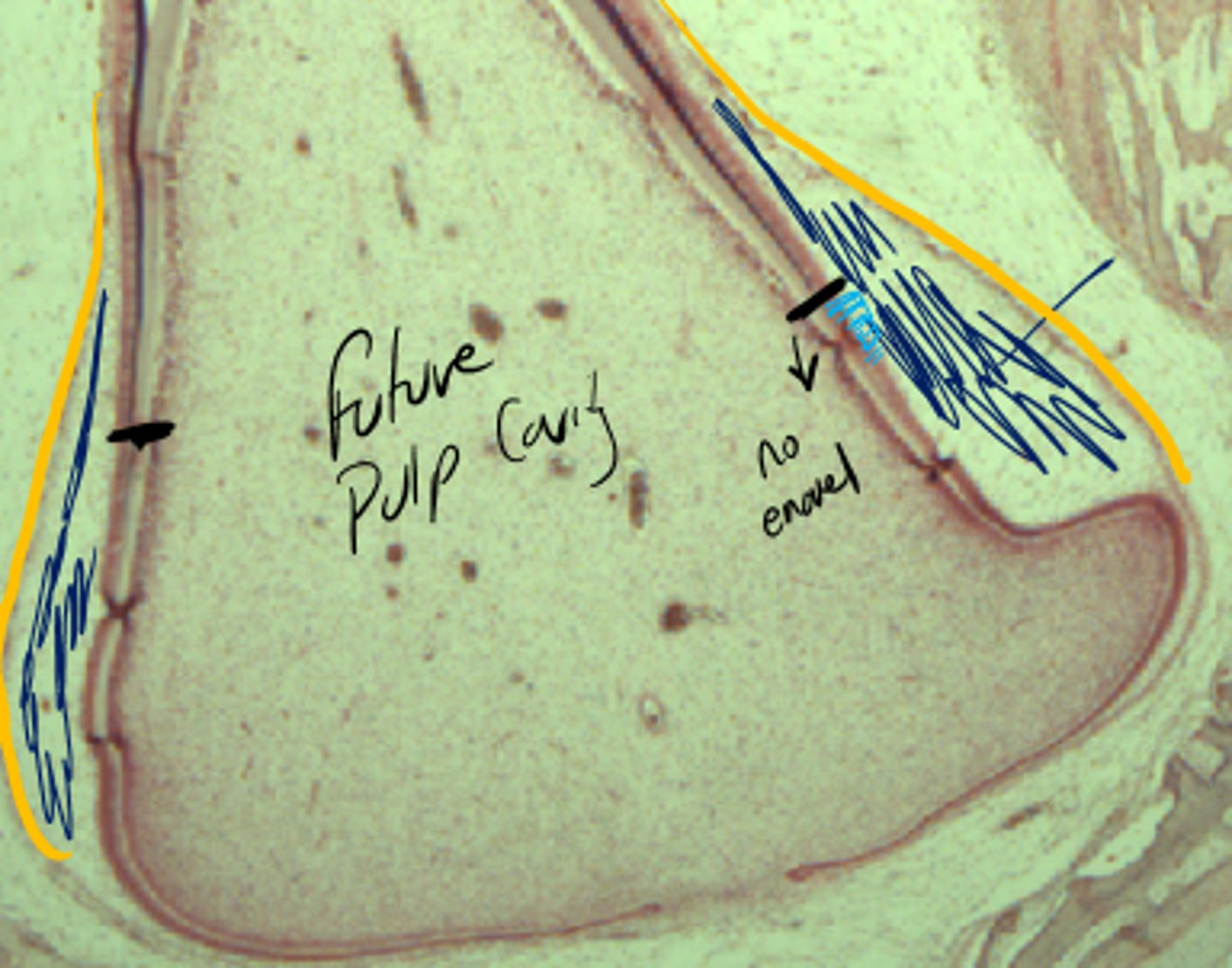
Pulp cavity
What is the space filled with LCT, nerves, and vessels in the tooth?
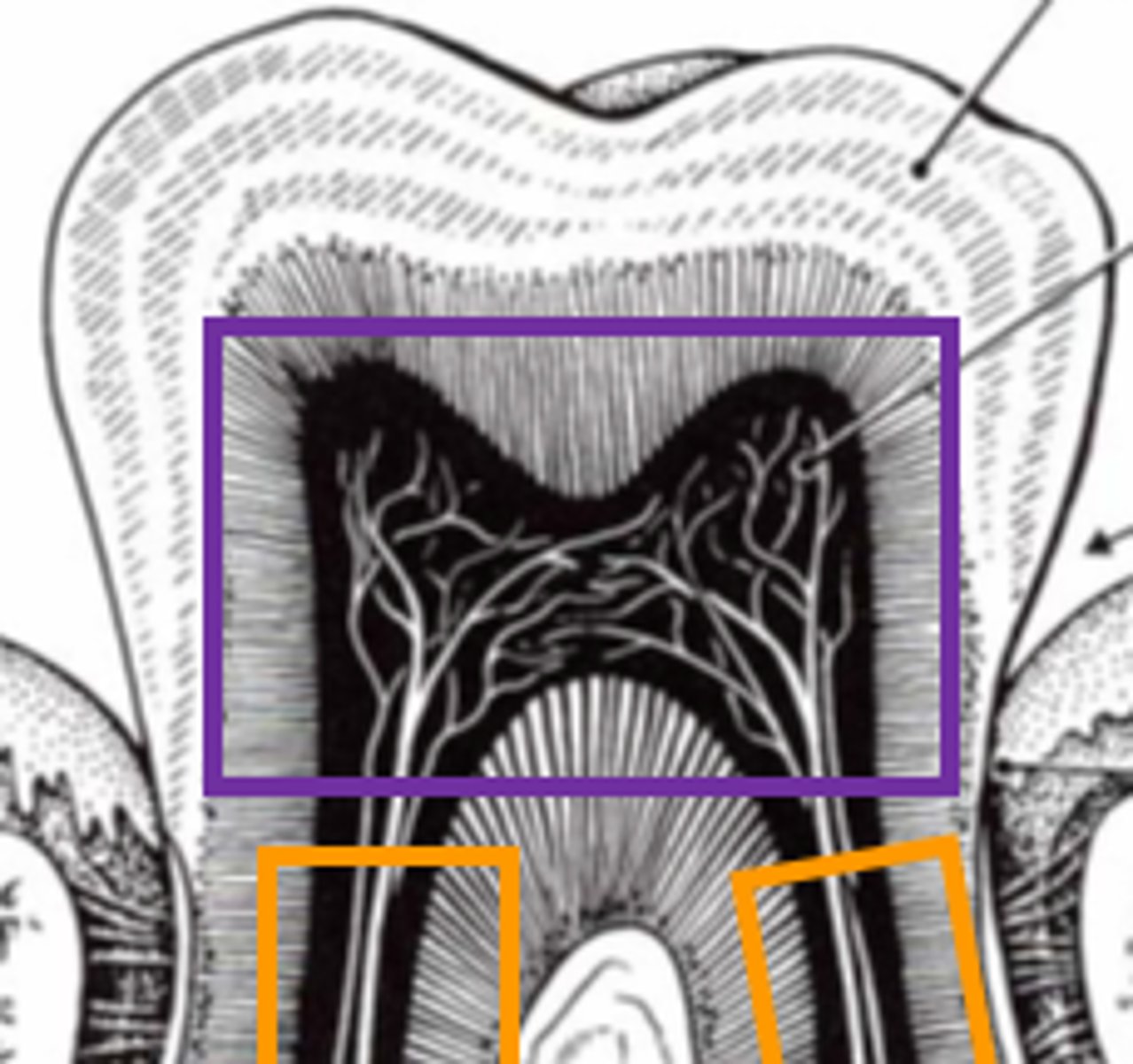
Lined by odontoblasts (that secrete dentin)
Decreases cavity size as dentin is secreted
What lines the pulp cavity?
How do they affect the cavity's size?
Pulp chamber (in crown)
Root canal (in root)
What are the subdivisions of the pulp cavity?
Cutaneous mucous membrane of gingiva (gums)
Mucosa lined by stratified squamous epithelium with supporting DICT is ...
Gingival sulcus
What is the potential space between gingiva and anatomical crown
Periodontal ligament
Made of type I collagen
What ligament suspends the tooth in the alveolus, acting as a shock absorber?
Sharpey's fibers
What are the anchor fibers in the alveolar bone and cementum
Jaw-jerk relflex
Proprioceptive nerve endings sense tooth location, and when you bite too hard, what reflex is involved causing the muscles to relax?
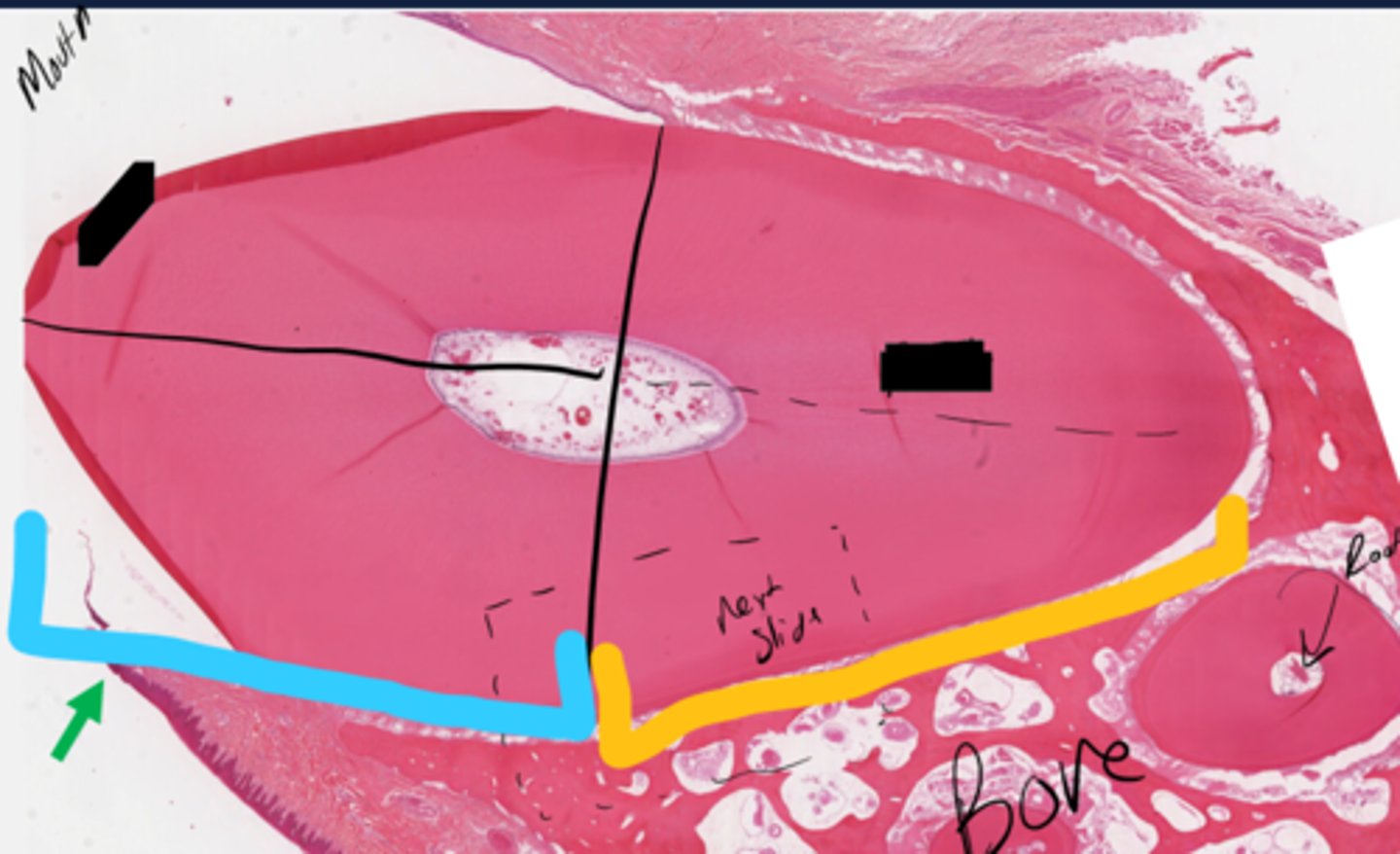
Blue: Crown
Yellow: Root
What are the blue and yellow sections?
Pulp cavity
Dentin
What is outlined in blue in the center of the tooth?
What substance makes up the yellow area?
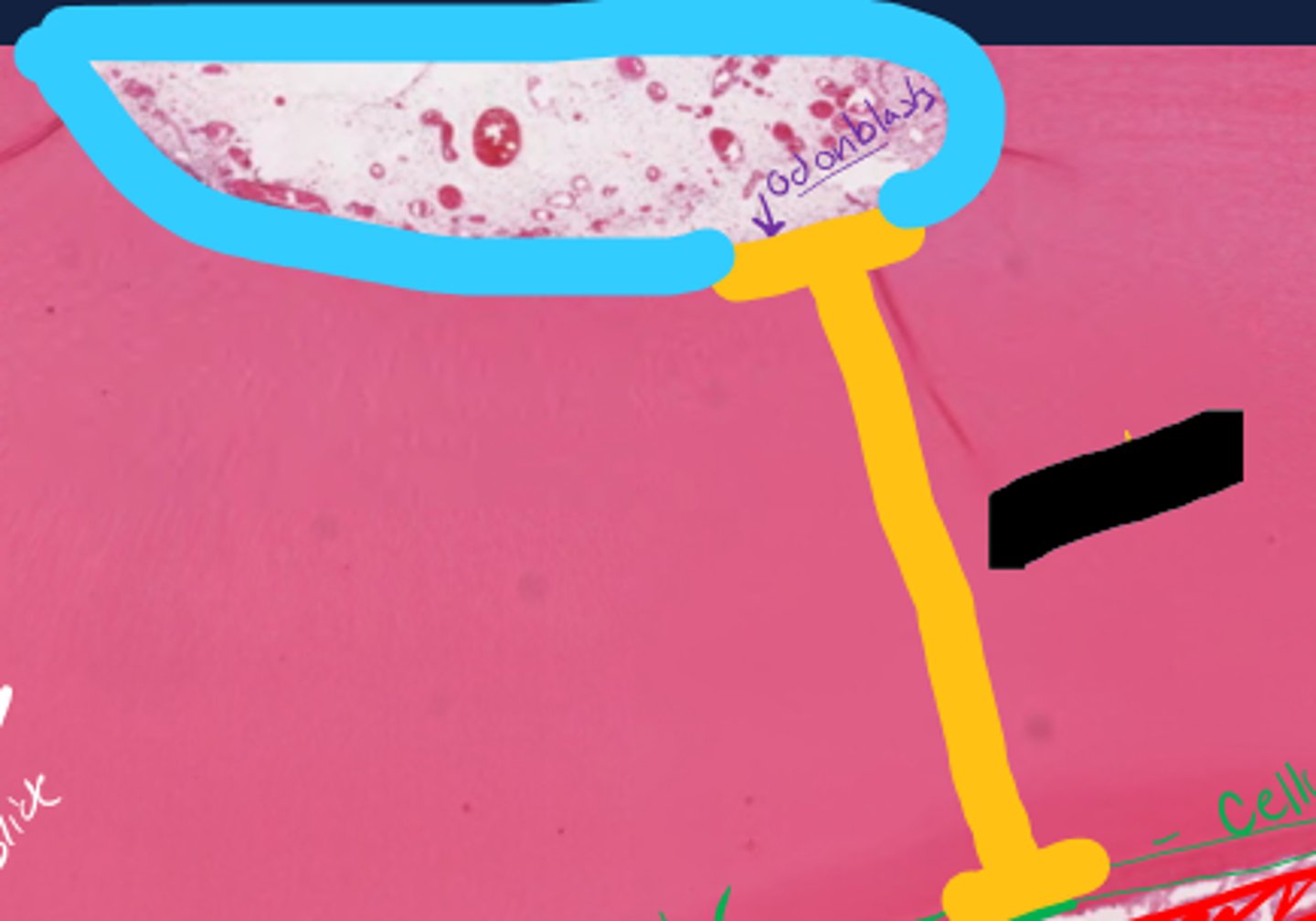

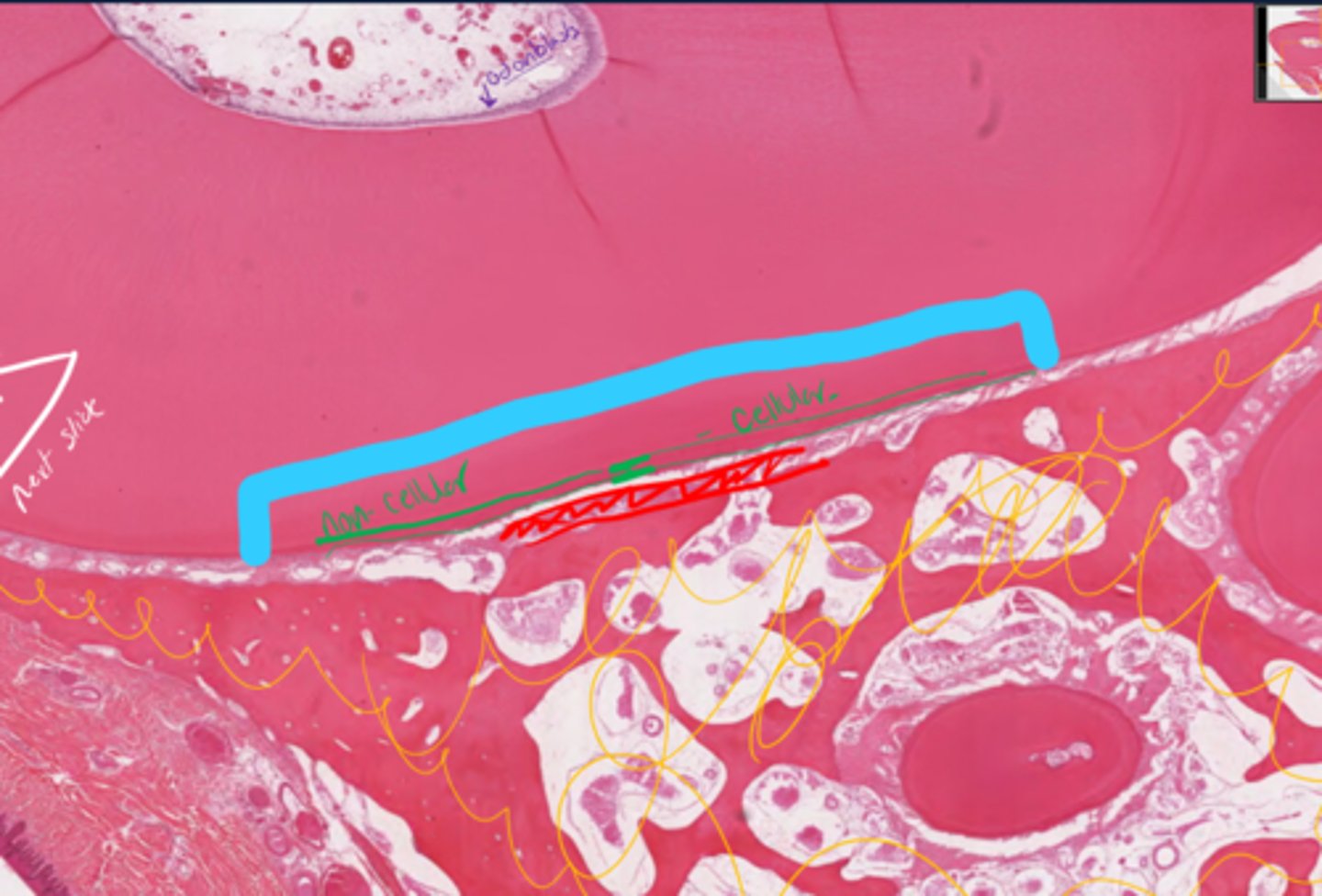
Cementum, divided into cellular and non-cellular
Bone
What is the green layer representing under the blue?
What is scribbled in yellow?
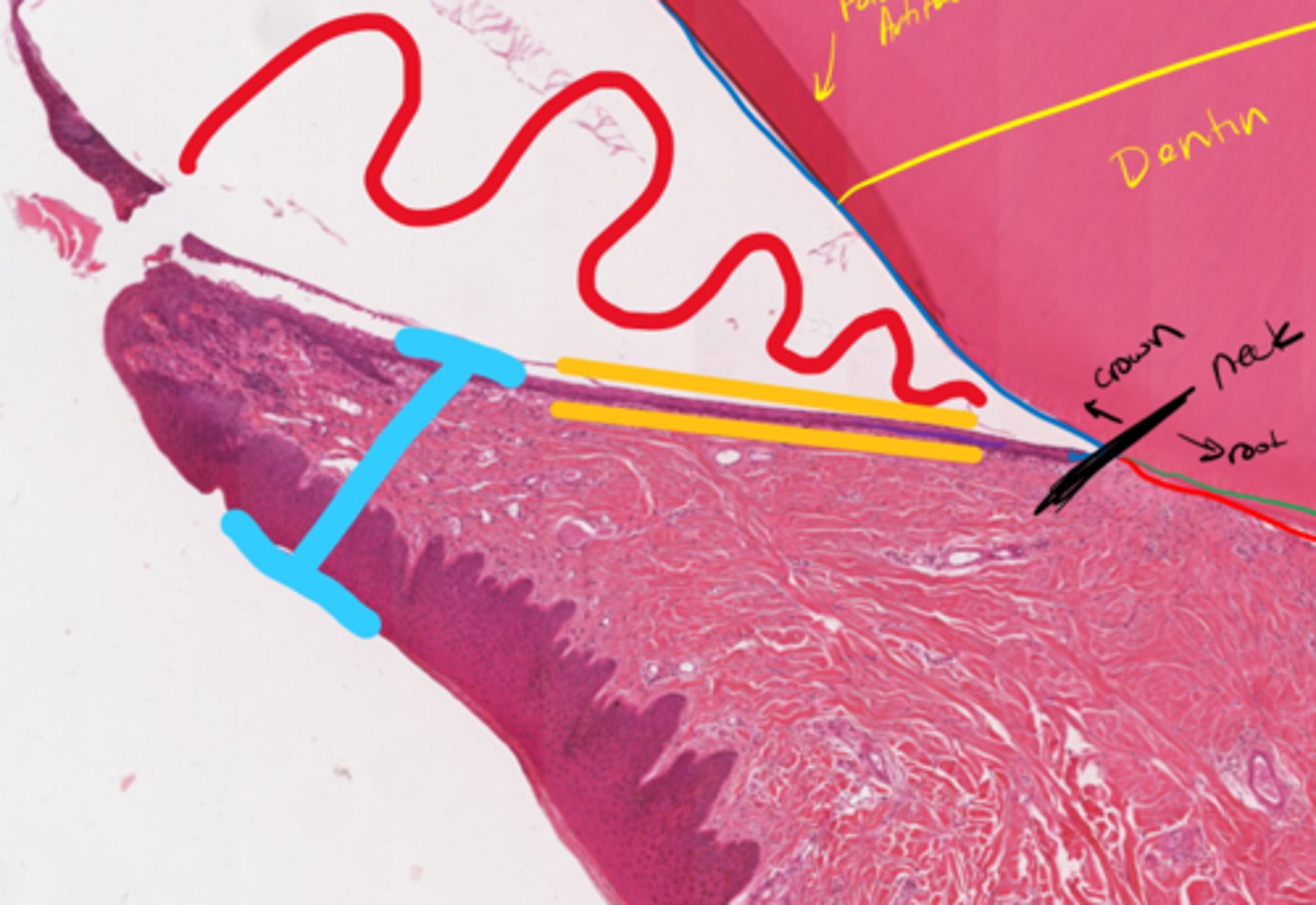
Red: Gingival sulcus
Yellow: Junctional Epithelium
Blue: Cutaneous Mucous Membrane
Red area?
Yellow layer?
Blue structure?
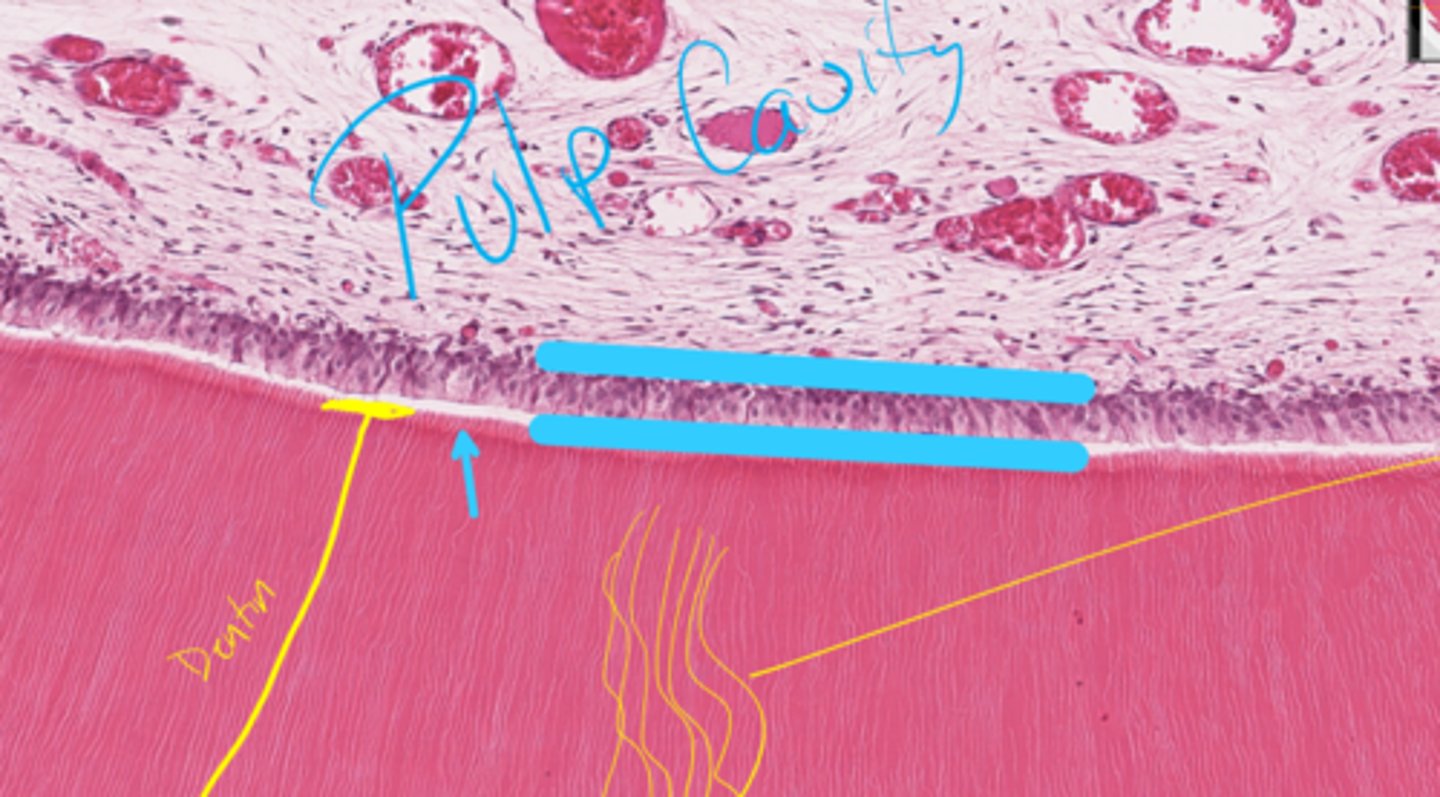
Dentinal tubules
Pre-dentin (will not be asked to ID)
What are the yellow lines indicating?
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
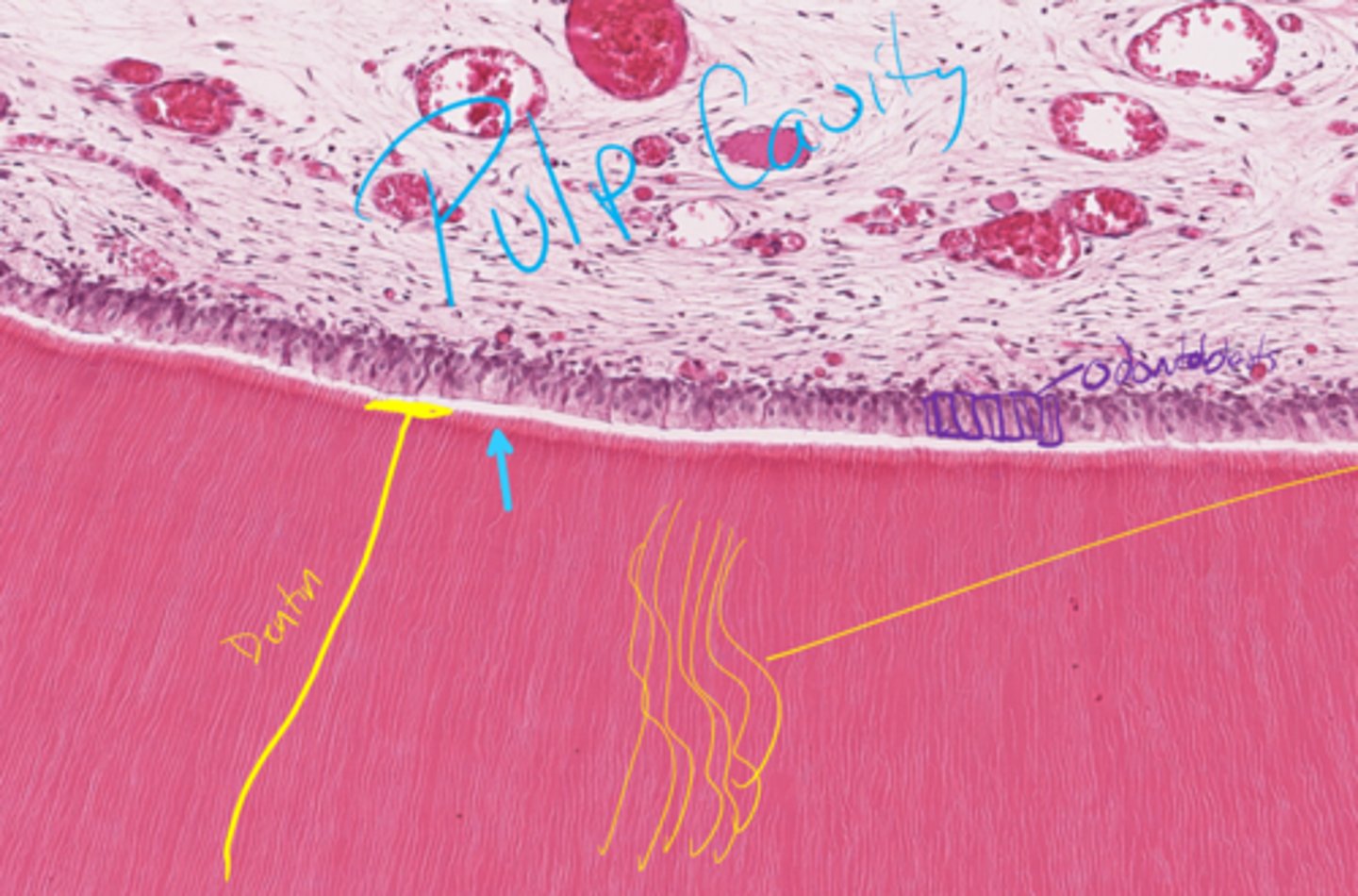
Odontoblast layer
What layer is between the blue lines?
Cementum
Periodontal ligament
What is the layer in blue?
What is the structure in red?
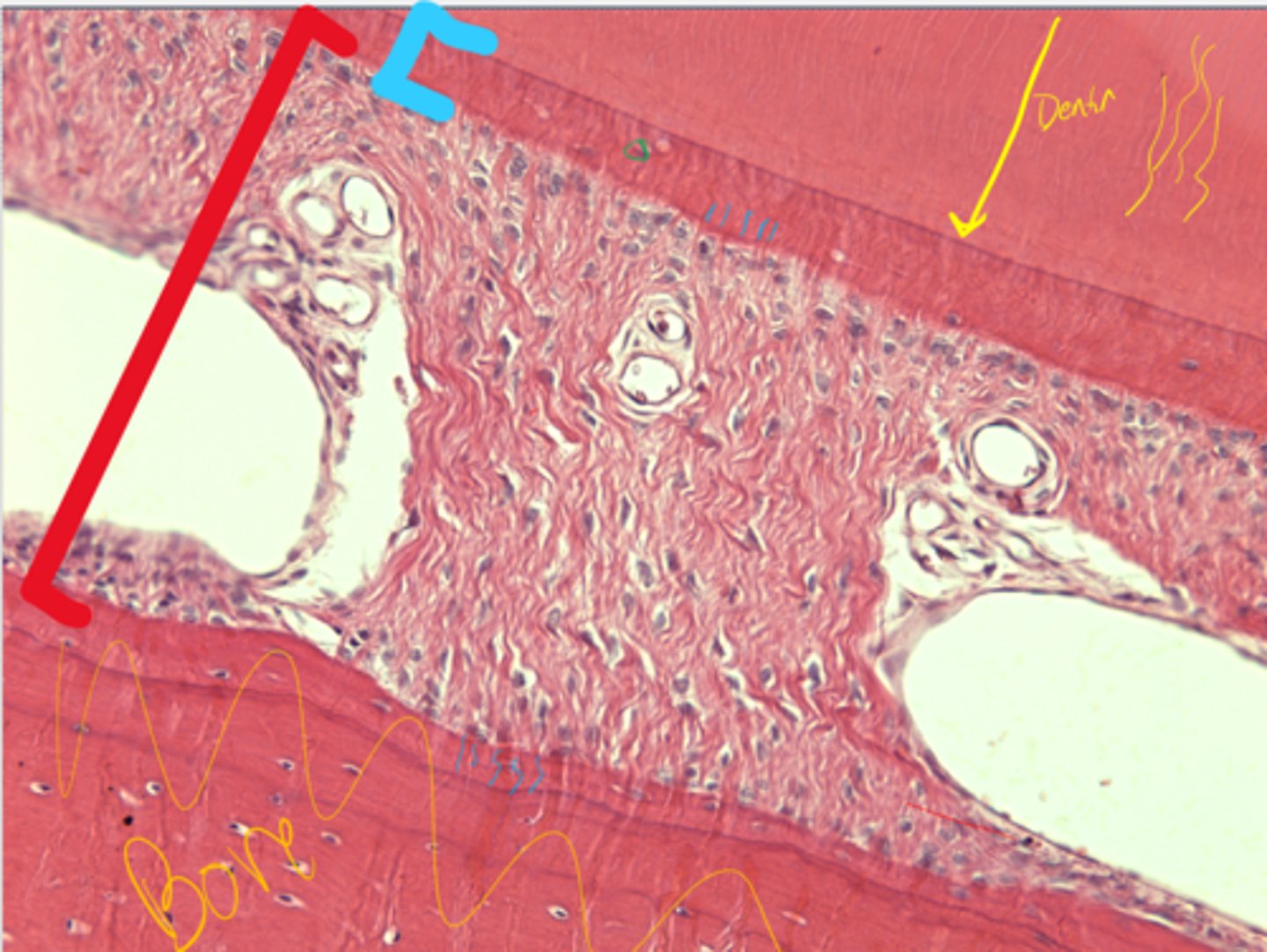
Sharpey's fibers
What are the green lines representing in the periodontal ligament?
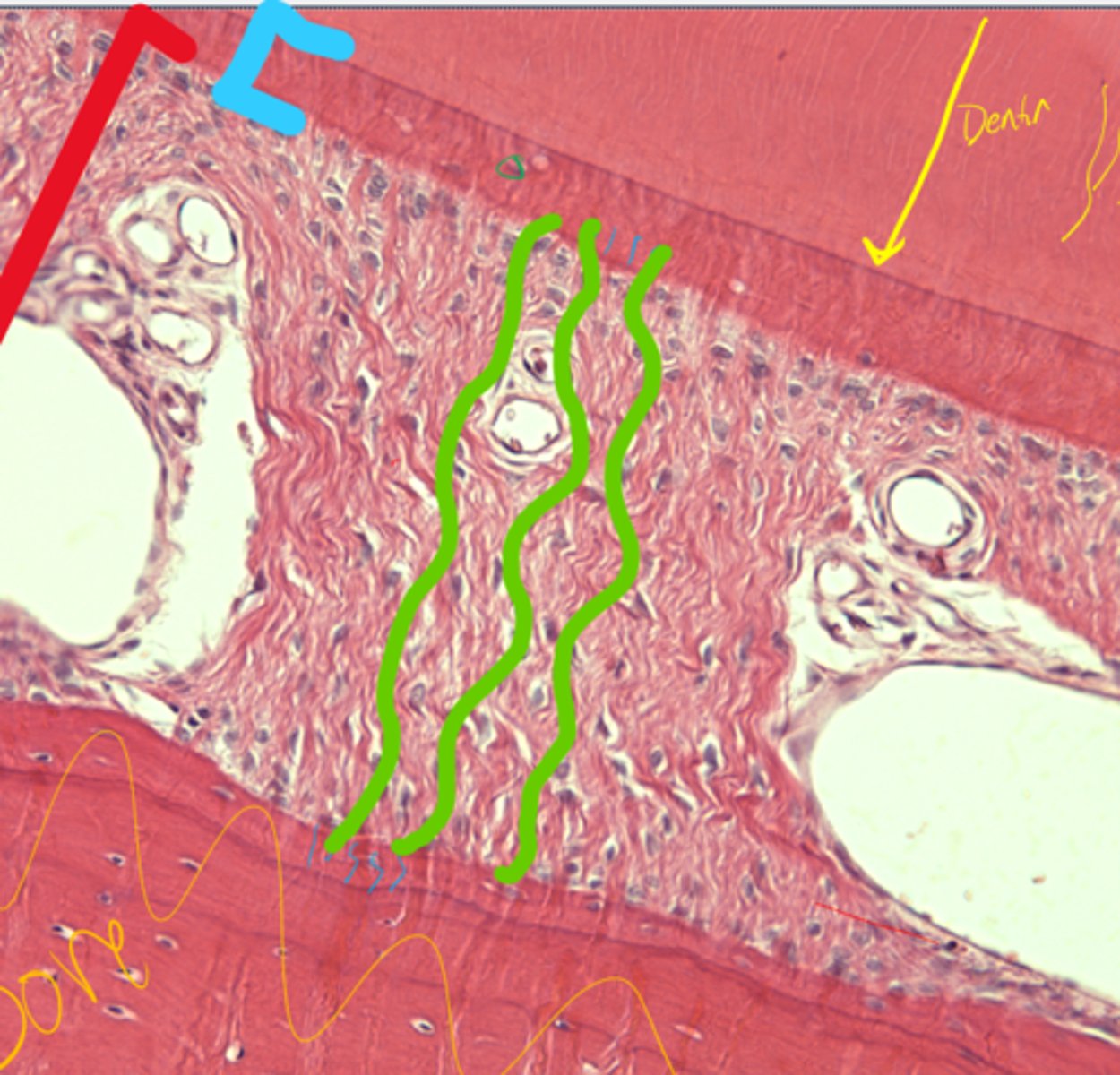
Cementocytes/blasts
Cementum
What are the cells in green?
What are they in?
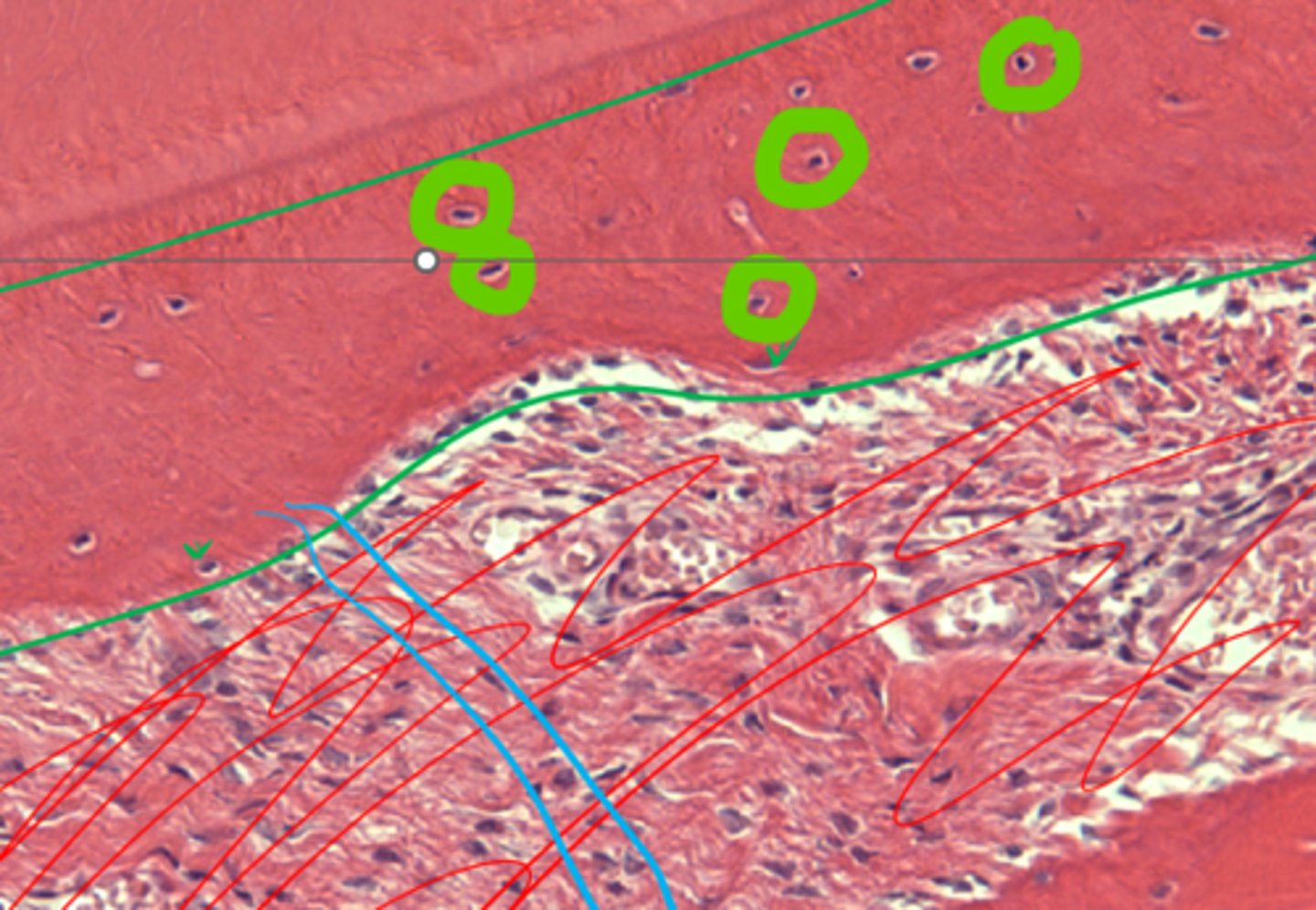
Ameloblasts
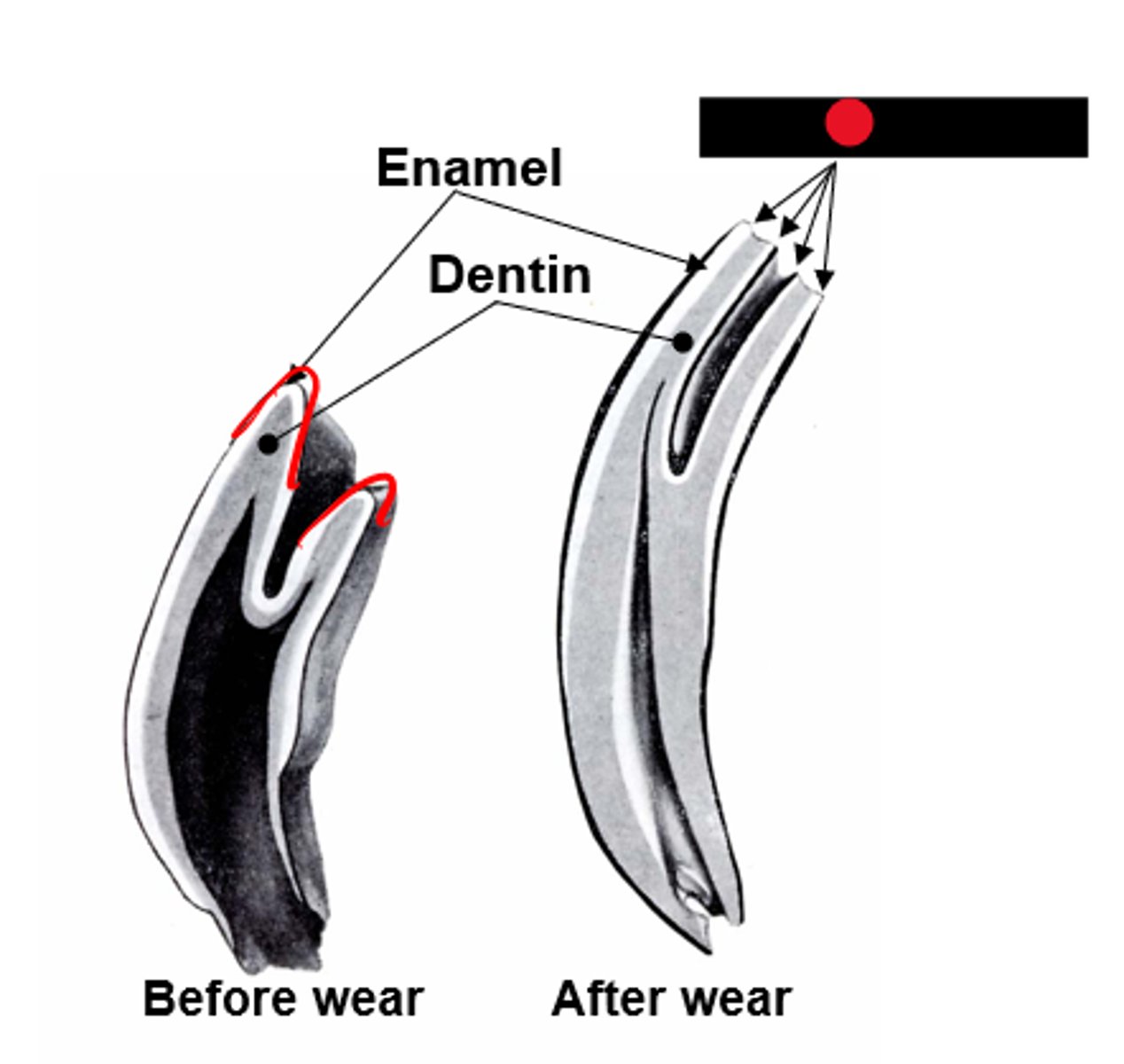
What are destroyed in brachydont teeth but not in hypsodont teeth that allow for continued growth?
The entire surface of the tooth (covers enamel)
Where is cementum deposited on a hypsodont tooth?
Infundibulum
The surface invagination lined by enamel and covered by cementum is called the ...
Enamel crest
When wearing reaches the dentin (which is weaker than enamel), leaving a depression, the projected enamel is called an ...
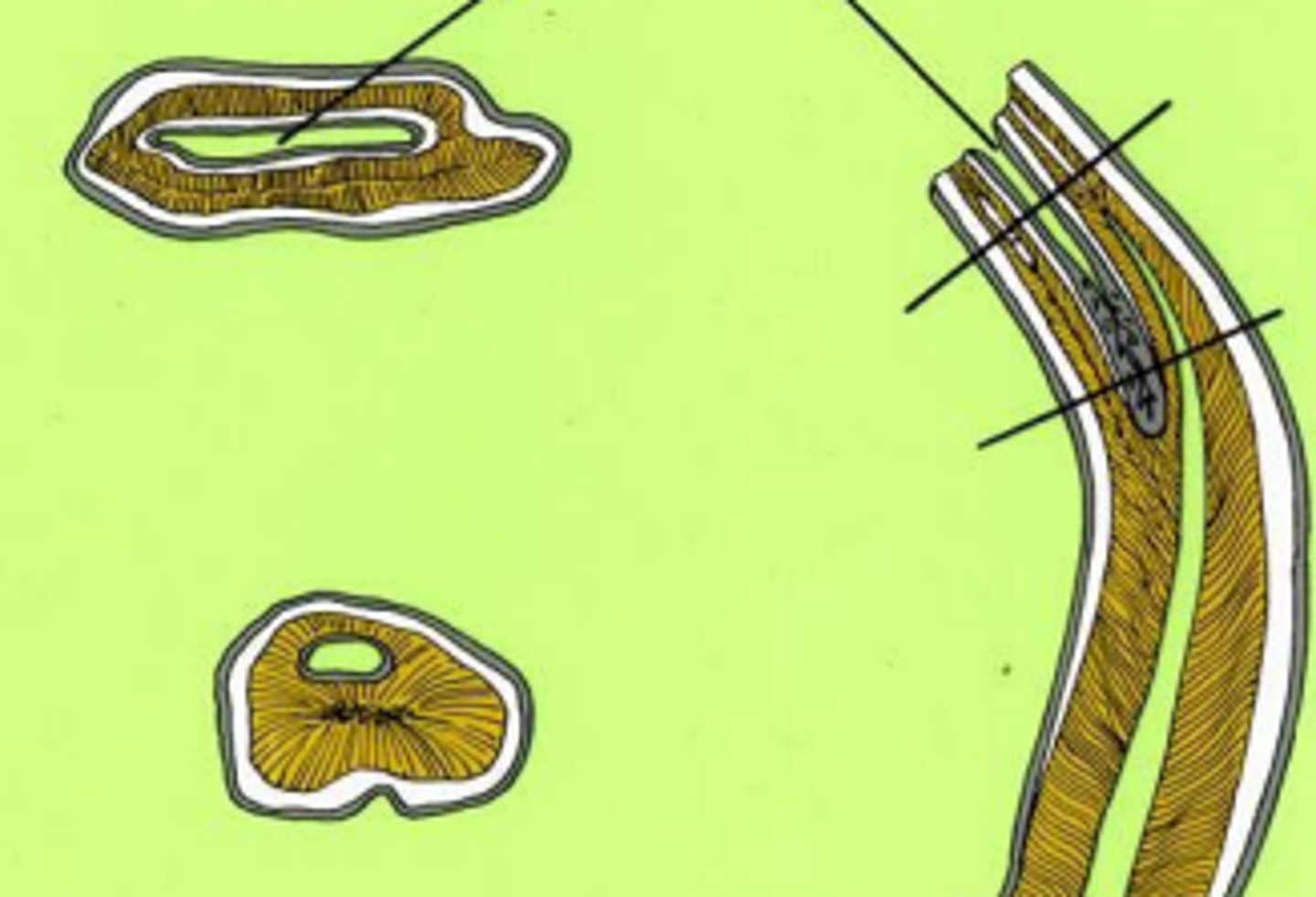
Ectoderm and mesoderm
Where do teeth develop from?
Ameloblasts
Neural crest derived odontoblasts from mesoderm
(whatever that means)
How is enamel produced?
How is dentin produced?
Inner enamel epithelium forms ameloblasts that produce enamel
Stratum intermedium (cause previous to produce ameloblasts)
Stellate reticulum (Cushion to protect ameloblasts)
Outer enamel epithelium (outer boundary of enamel organ)
What are the layers of the enamel organ?
1) Stratum intermedium makes inner enamel epithelium to become ameloblast
2) Ameloblast makes mesenchymal cells on dental papilla to become odontoblasts
3) Odontoblasts secrete dentin first
4) Ameloblasts secrete enamel on top of dentin
What are the steps of enamel and dentin formation?
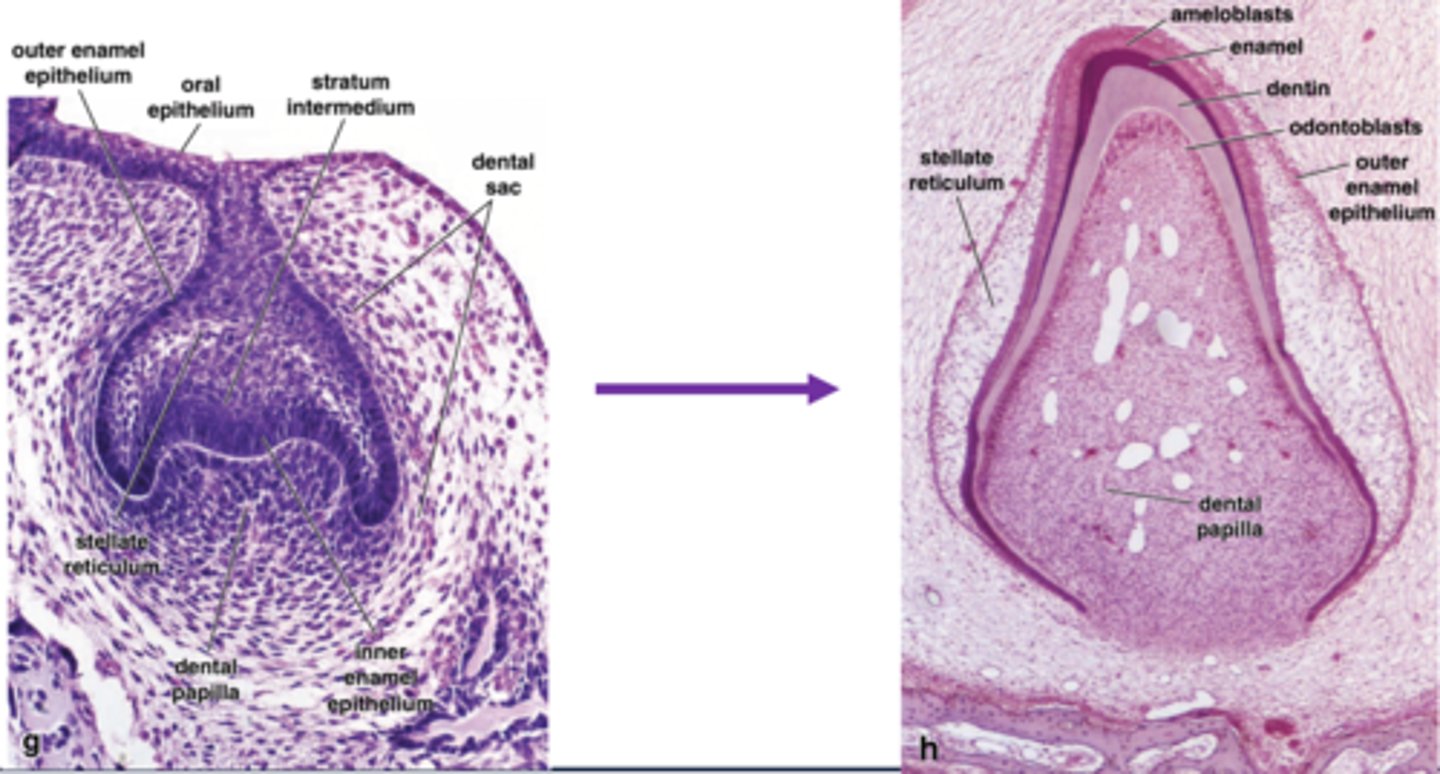
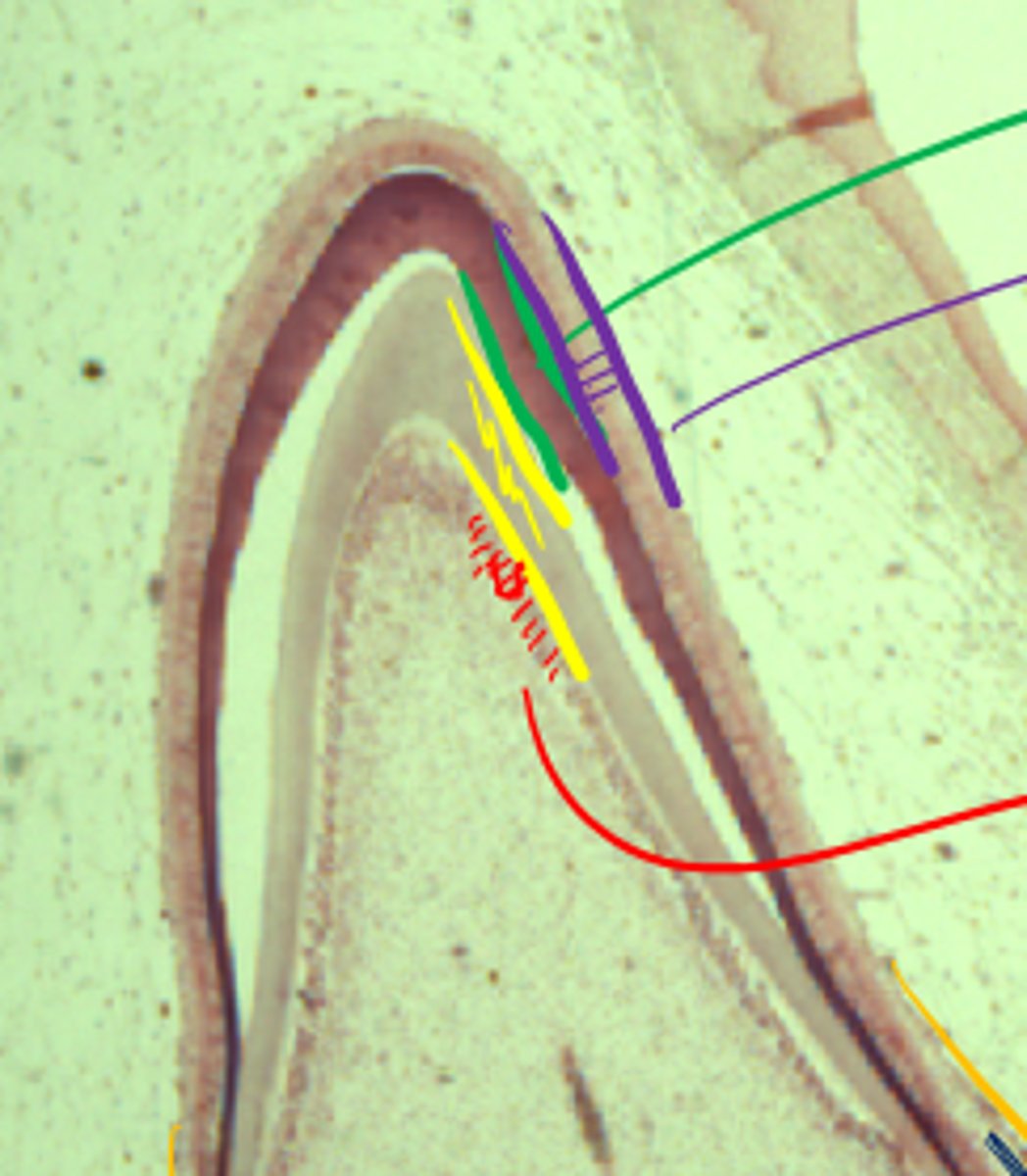
Red: odontoblasts
Yellow: Dentin/pre-dentin
Green: Enamel
Purple: Ameloblasts
Behold, a developing tooth. Label the pretty colors
Stellate reticulum
What is highlighted in blue in this developing tooth?
Purple: Ameloblasts
Green: enamel
Yellow: dentin
Red: odontoblasts
Note, stellate reticulum to left and pulp cavity to right
What are the 4 colored layers?
Secretion goes to mouth by a duct
What is the key characteristic of an exocrine salivary gland?
Don't lose cytoplasm during product release
Recall the key characteristic of a merocrine gland
Major: Gross(ly visible) and away from the mouth
Minor: Glands in the oral cavity
Difference between major and minor glands?
Mucous (highly viscous) and serous (watery)
Recall how to classify glands by nature of the product
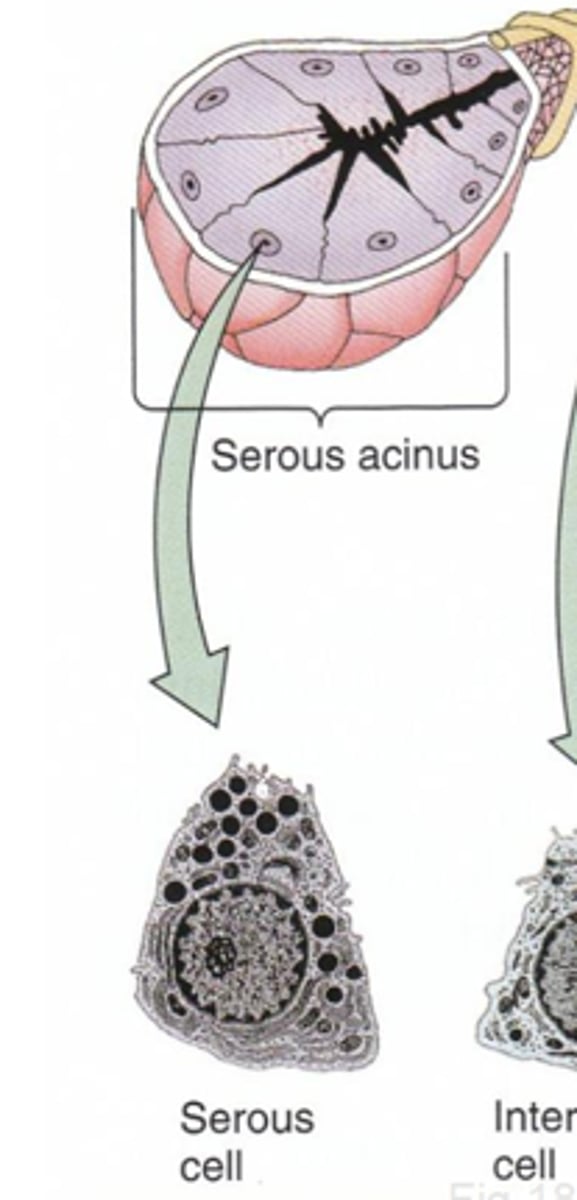
Round nucleus at base of cell, cells arranged in acini
Describe the structure of a serous salivary gland
Flat nucleus at base of cell, may be acinus or "tube-like" arrangement
Cytoplasm does not stain well
Describe a mucous salivary gland
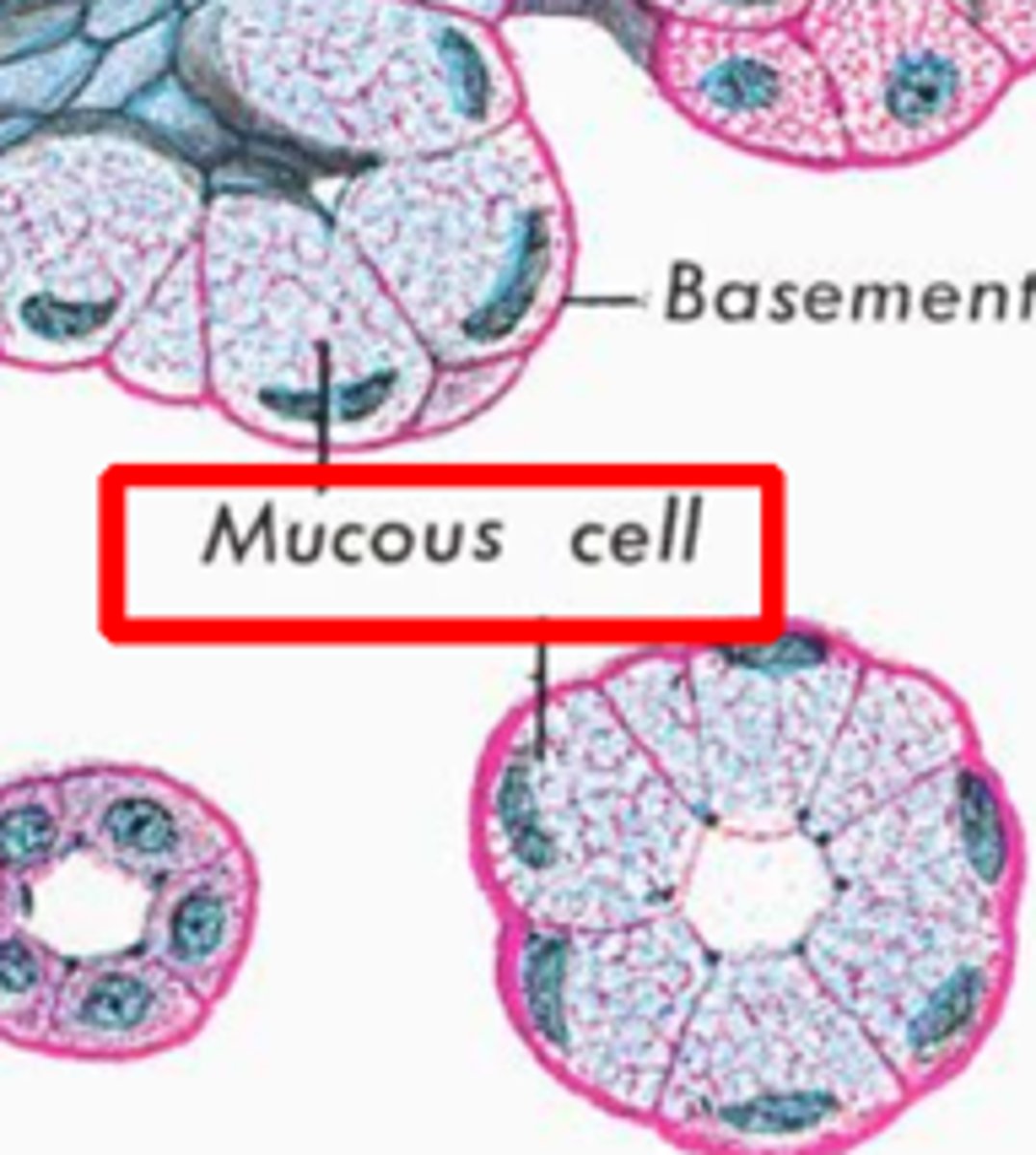
Mucinogen (precursor to mucous)
What is the secretory product of mucous SG?
Mixed SG
Specifically a serous demilune
What's this?
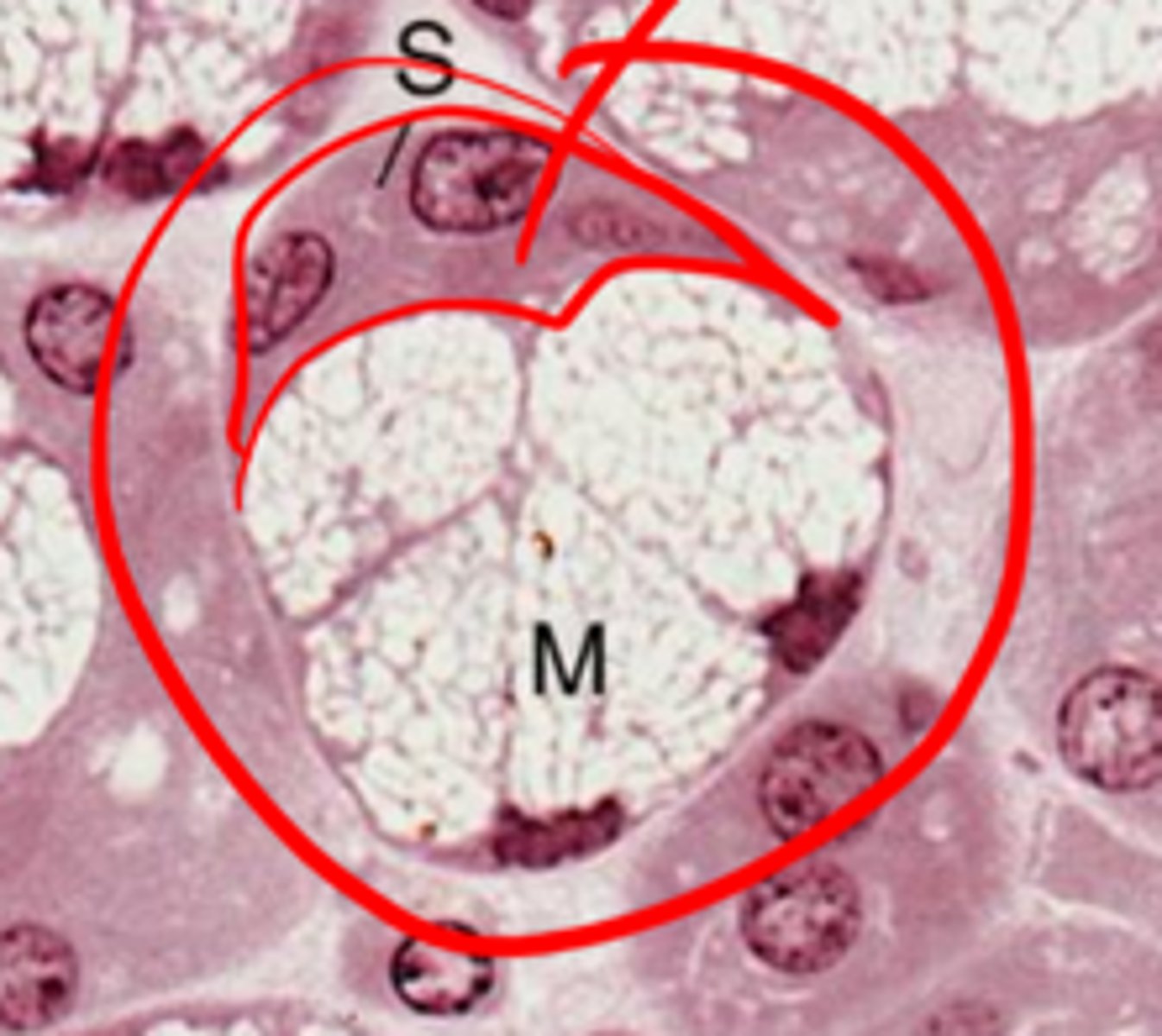
- Individual ends of serous and mucous empty into a common duct
- Integrated end pieces, with a cap of serous cells (demilune)
What are the two arrangements of mixed SG
Myoepithelial (basket) cells
What cells have contractile properties and surround the base of secretory cells to facilitate movement and prevent luminal pressure from damaging the cells?
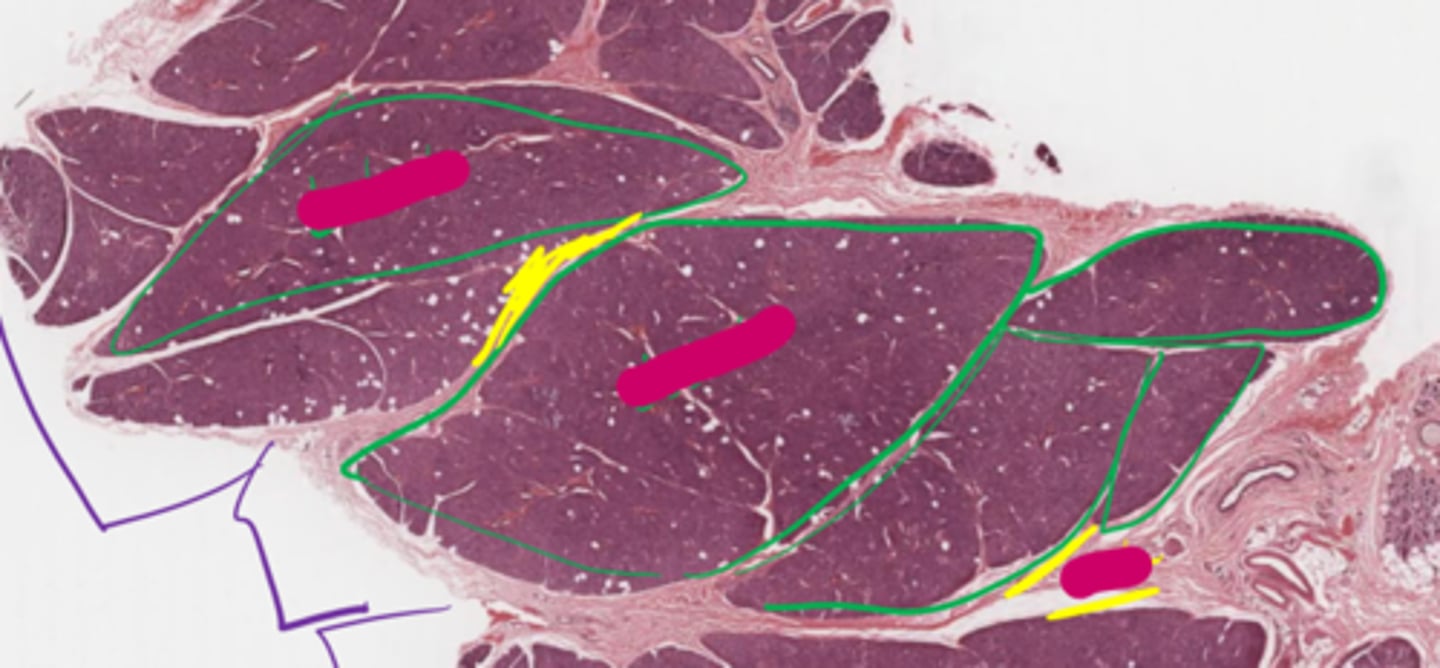
Green: lobules
Yellow: Septa
Purple: Lobe
Outlined in green are individual ____
They are separated by ____
The purple lines are indicated a ____
Salivary gland ducts
The channels transporting secretions from acini lumen to the mouth are ...
Intercalated ducts (in lobules)
Intralobular (striated) ducts (in lobule)
Interlobular duct (between lobules)
Lobar duct (between lobes)
Main duct (opens into body)
What are the duct categories, from small to large?
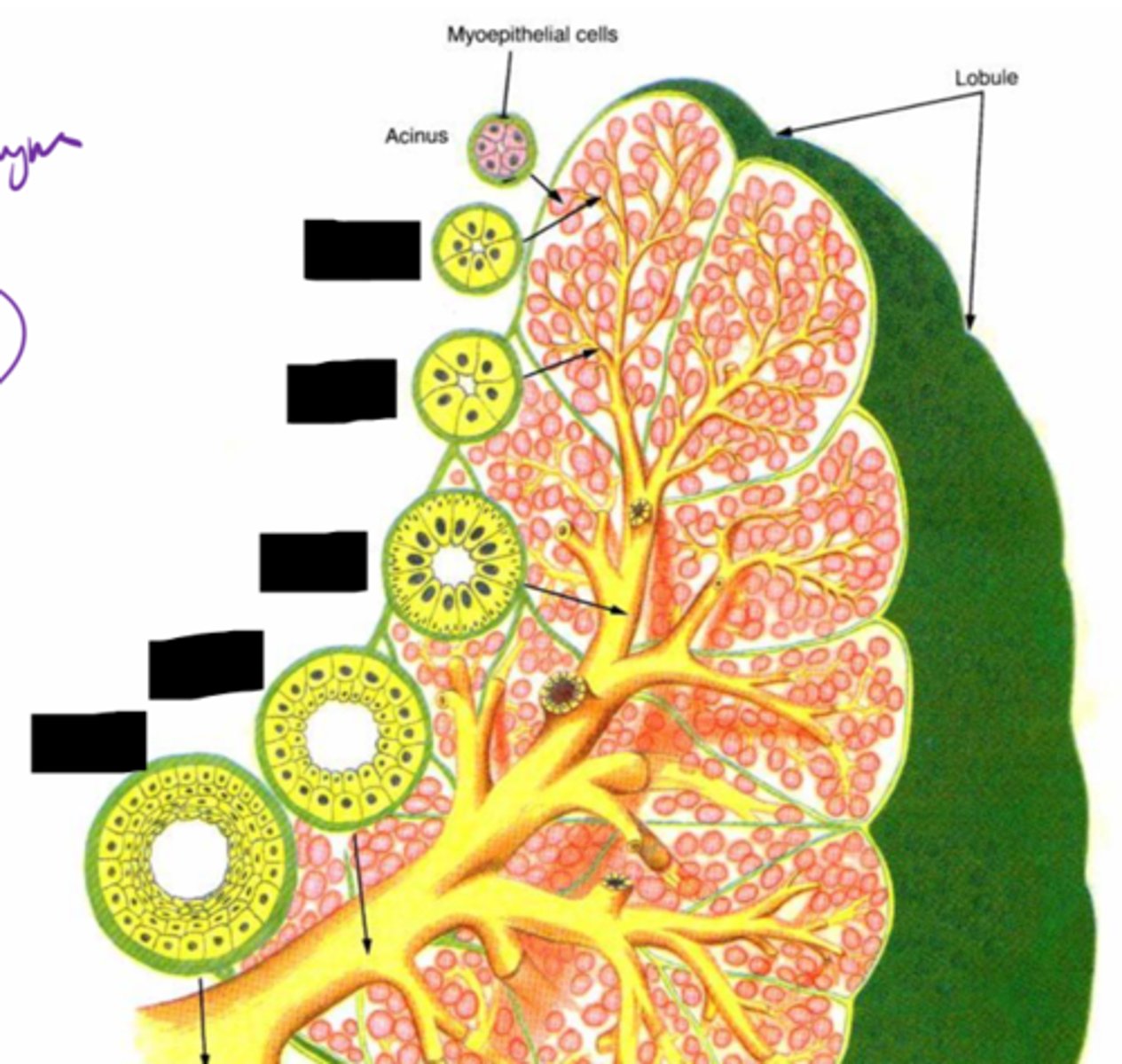
Simple cuboidal
4-8 cells (cross section)
Direct connection to acini
What are the characteristics of an intercalated duct?
Simple columnar
Striated appearance
Buffers saliva pH with bicarbonate
Characteristics of intralobular (striated) ducts
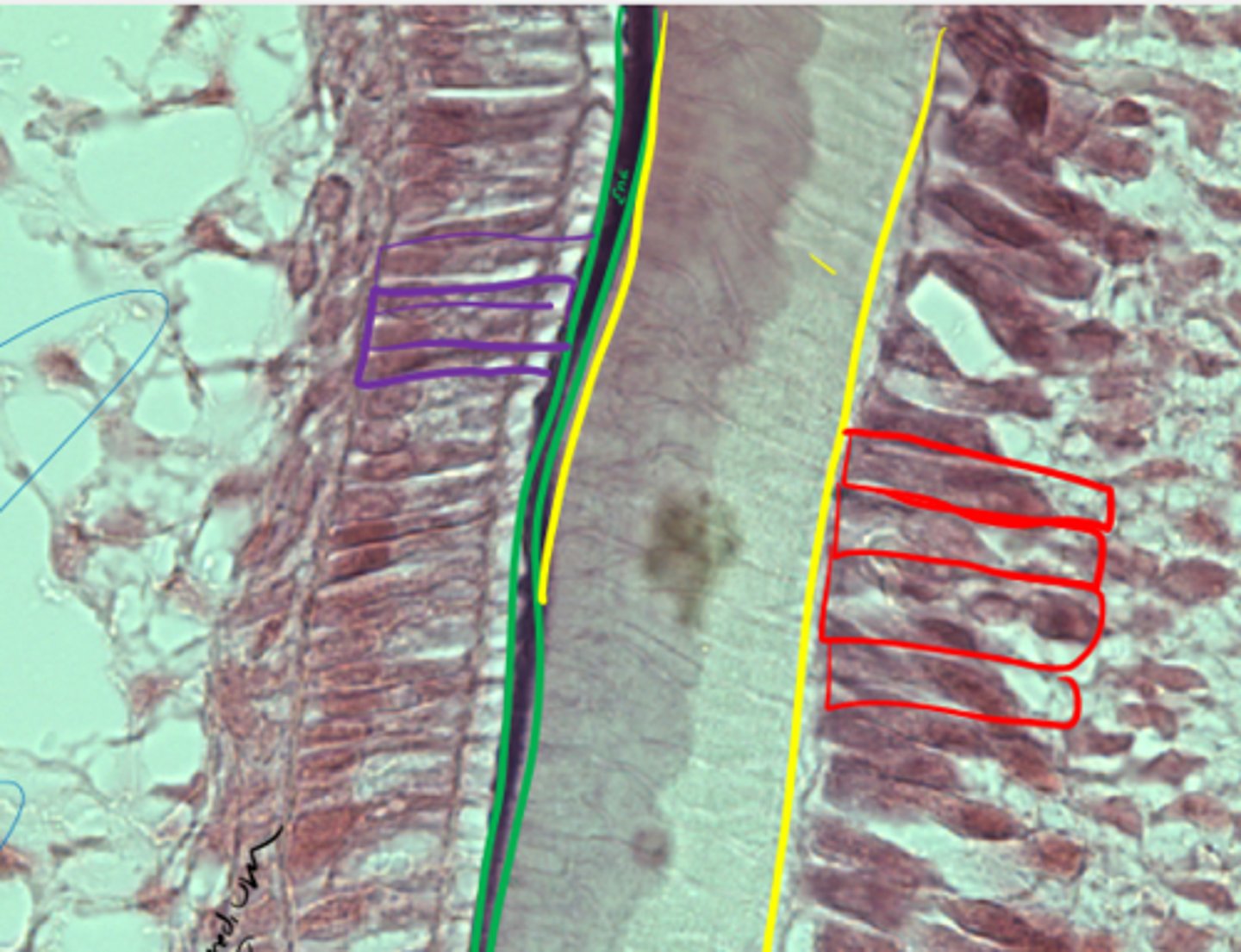
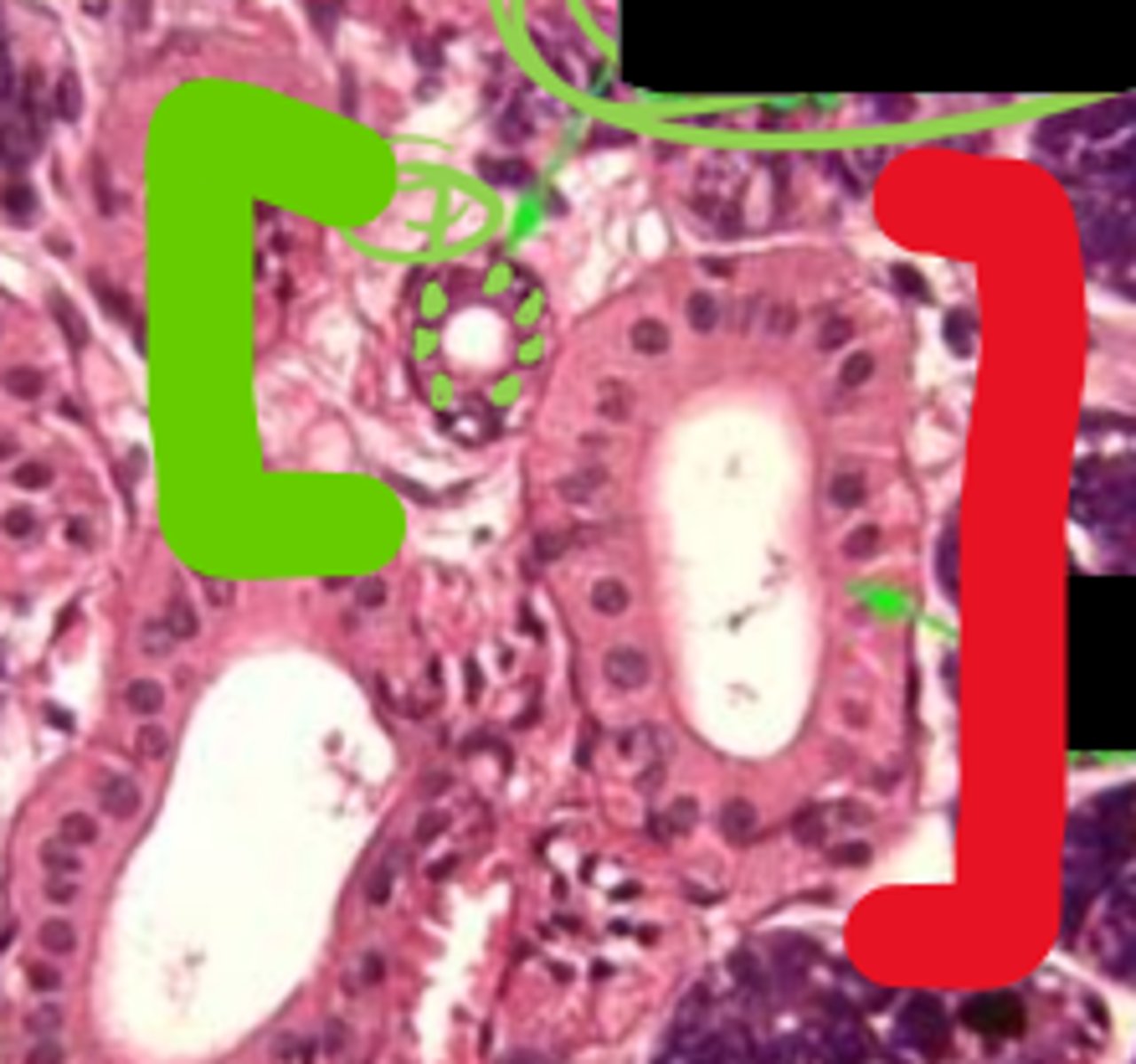
Green: Intercalated duct
Red: Striated duct
ID Ducts
Striated duct
Infoldings of basal membrane
ID duct
What are the green lines representing?
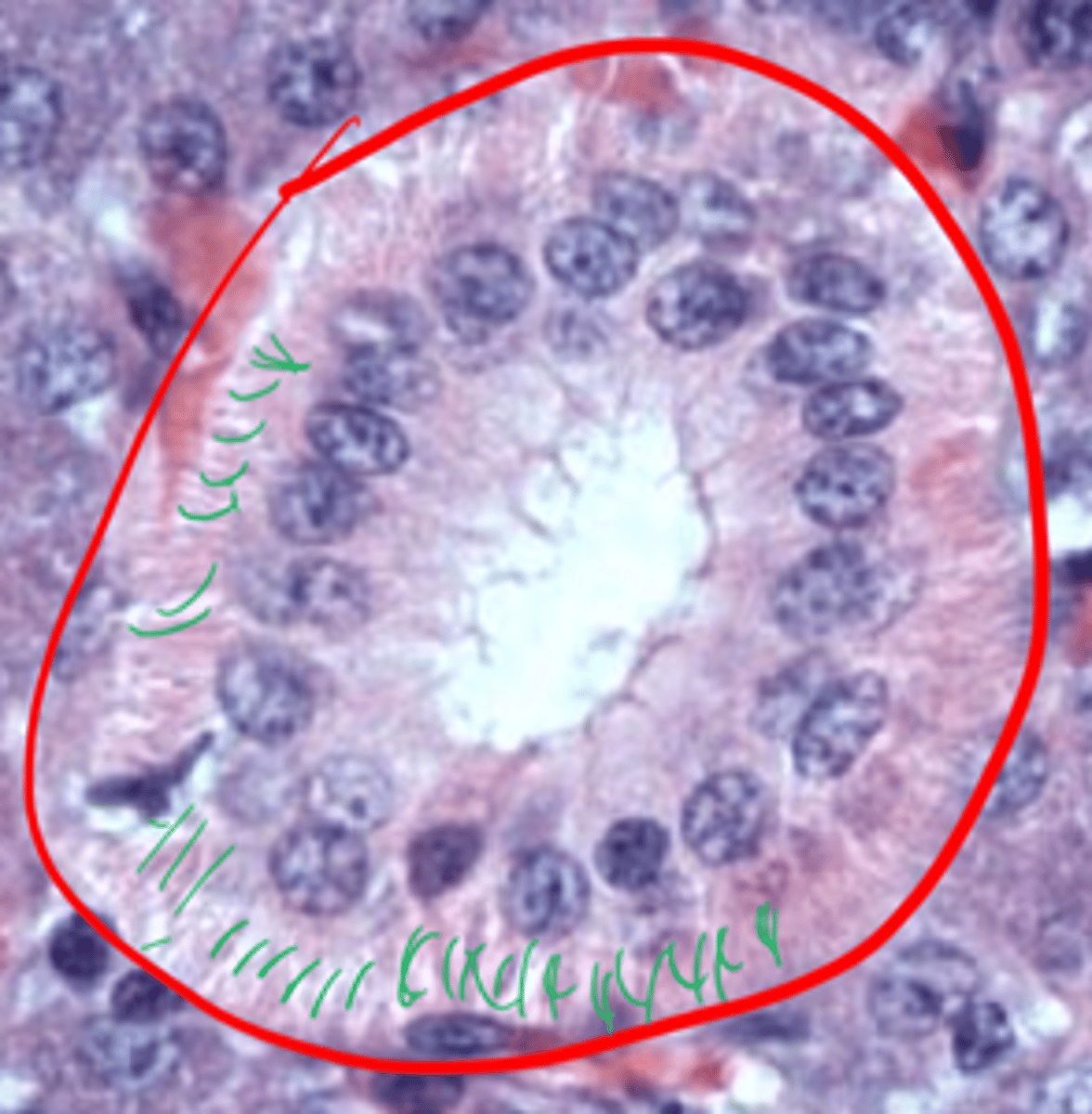
Interlobular: simple columnar or stratified cuboidal
Lobar + Main: Stratified epithelium
What kind of epithelium do the largest three ducts have?
Interlobular duct
Septa
ID duct
What is it surrounded by?
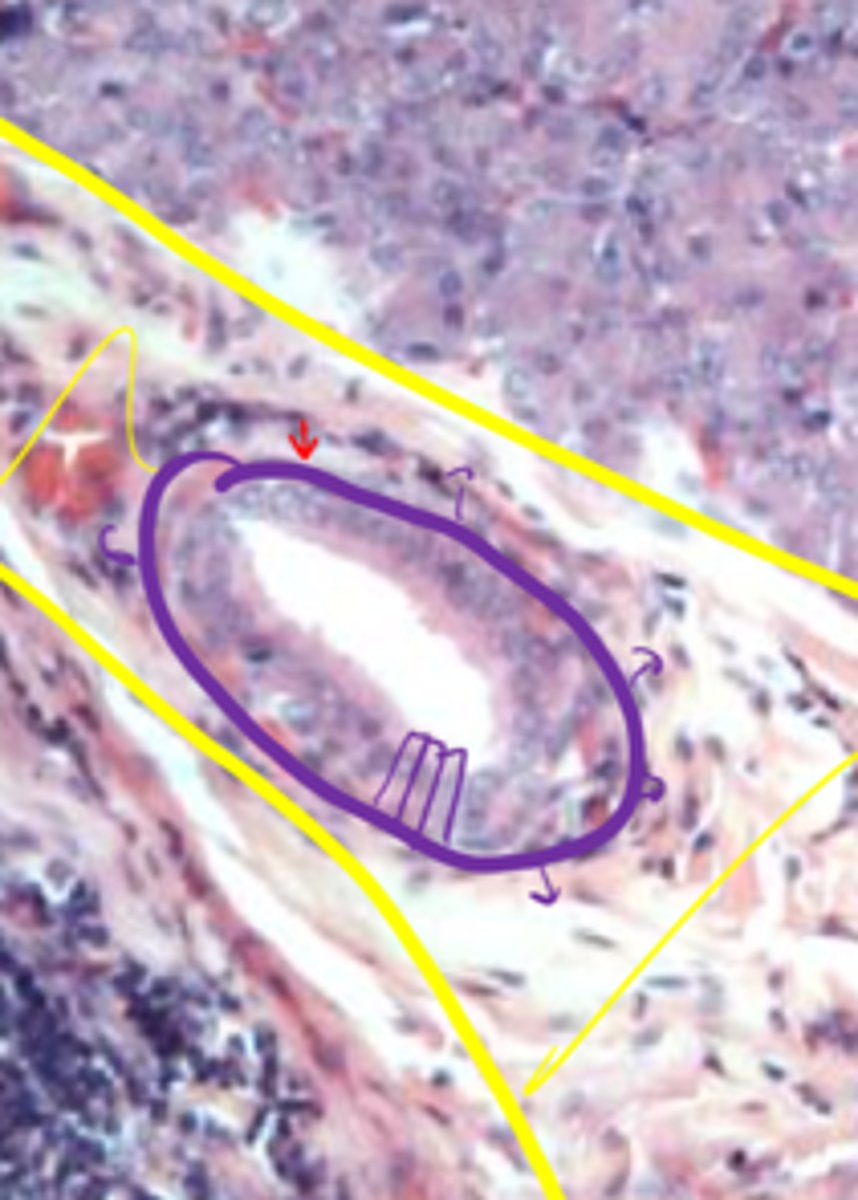
There is no muscularis mucosae
Why are the lamina propria and submucosa combined in the mouth?
Mouth, cheek
Hard/soft palate
Gingiva
Where is cutaneous mucous membrane found?
Mucocutaneous junction
What is the site of transition between epidermis and mucous membrane?
Intrinsic: change shape
Extrinsic: move
What are the roles of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Root
body
Apex
Subdivisions of the tongue?
Papillae
Projections from tongue surface are...
Move food, groom, taste
Functions of papillae
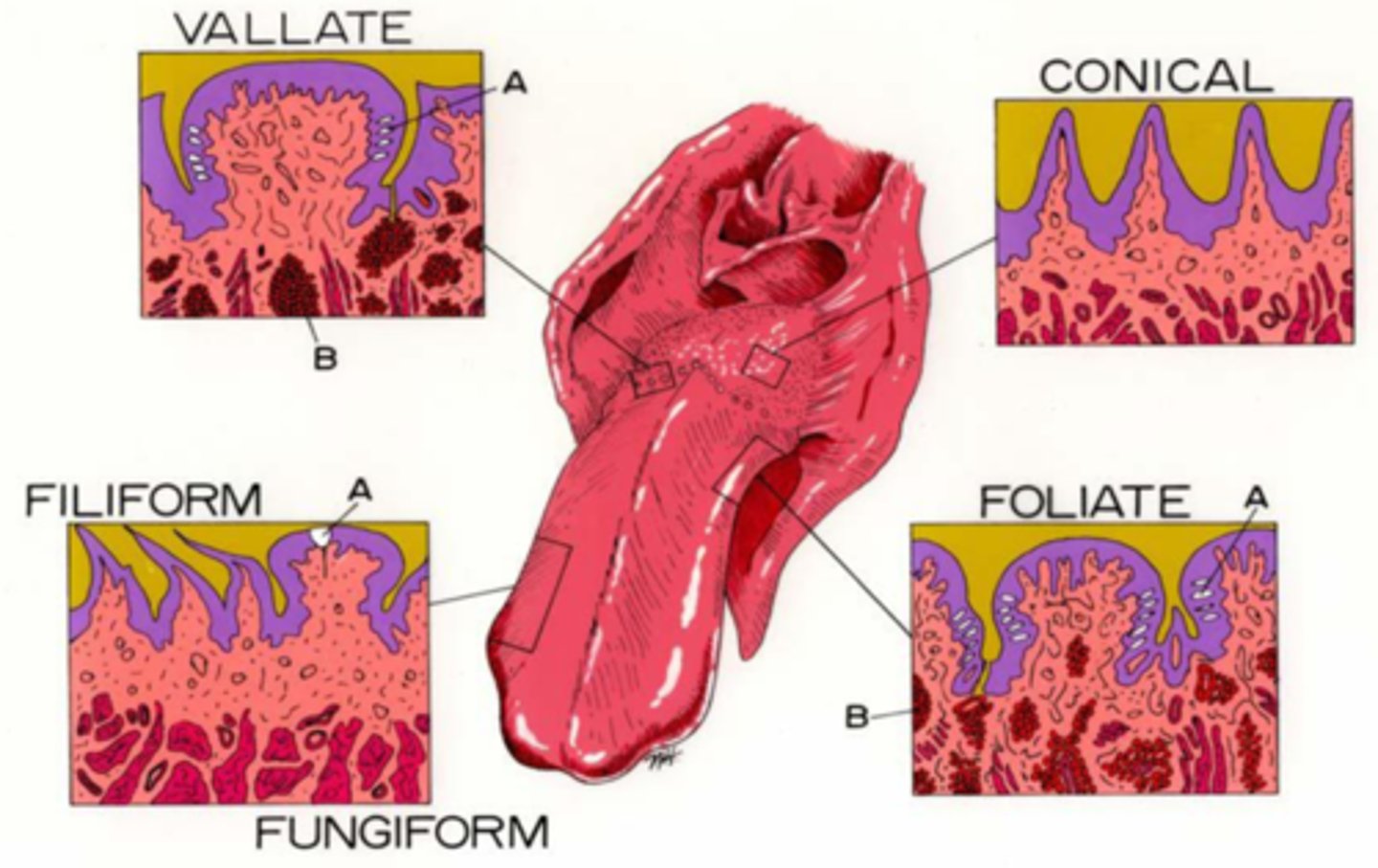
Fungiform
Foliate
Vallate
Chef's love using Fungi, Foliage, and Vegetables!
Which papillae have taste buds?
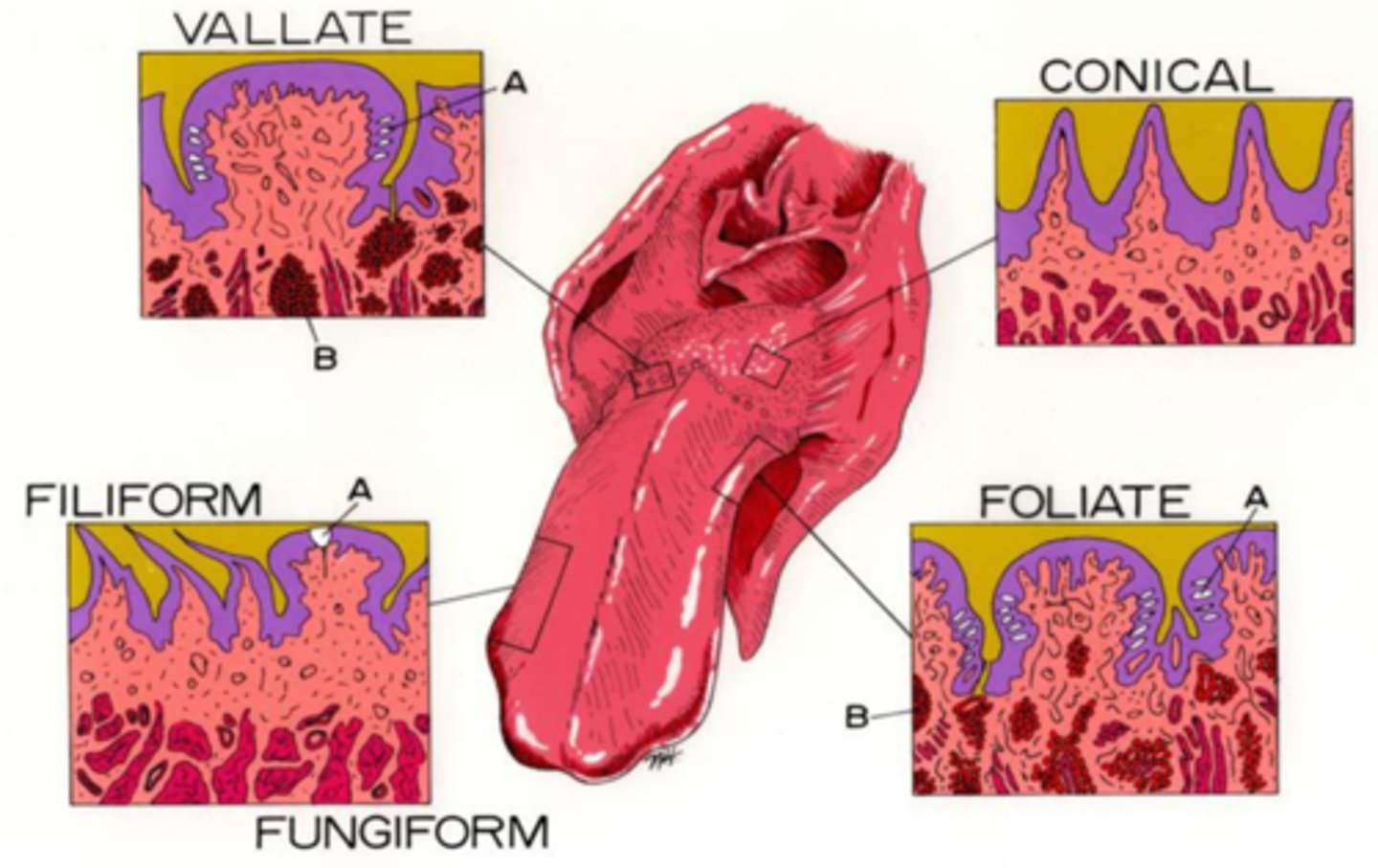
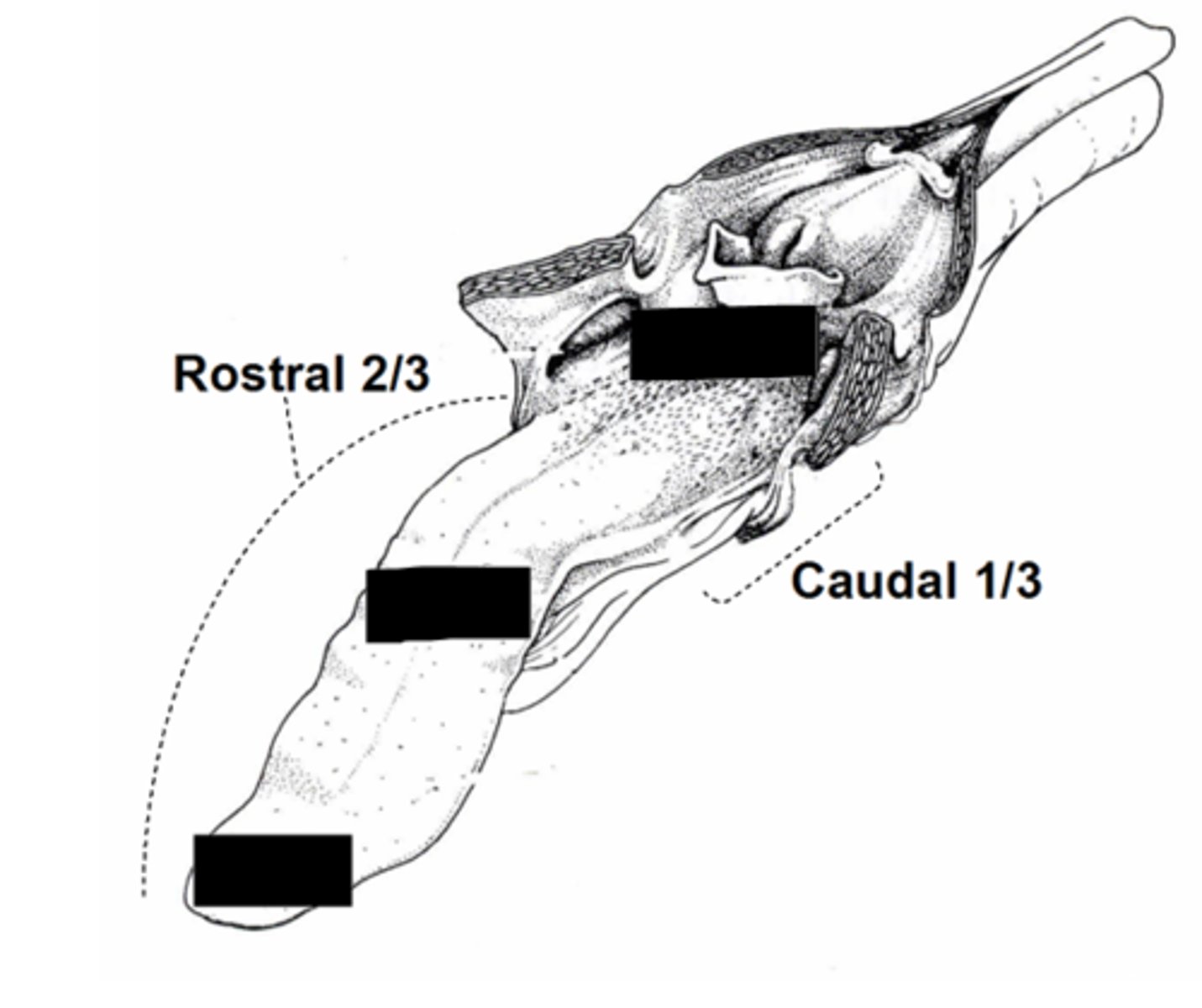
Rostral 2/3,
Filiform keratinized in cat/cow
Fungiform is mushroom shaped
Where are filiform/fungiform papillae?
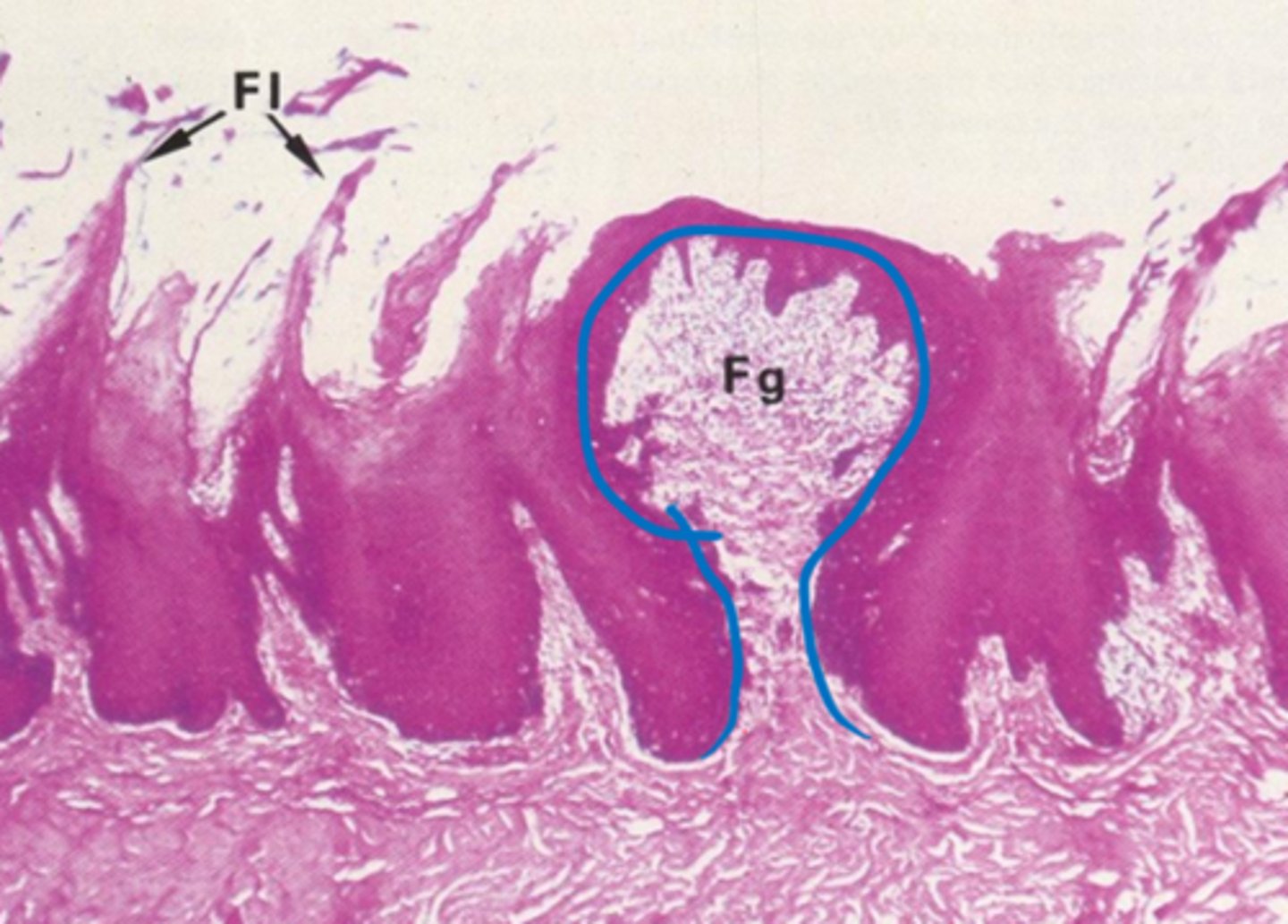
Filiform
Type of papillae?
Fungiform
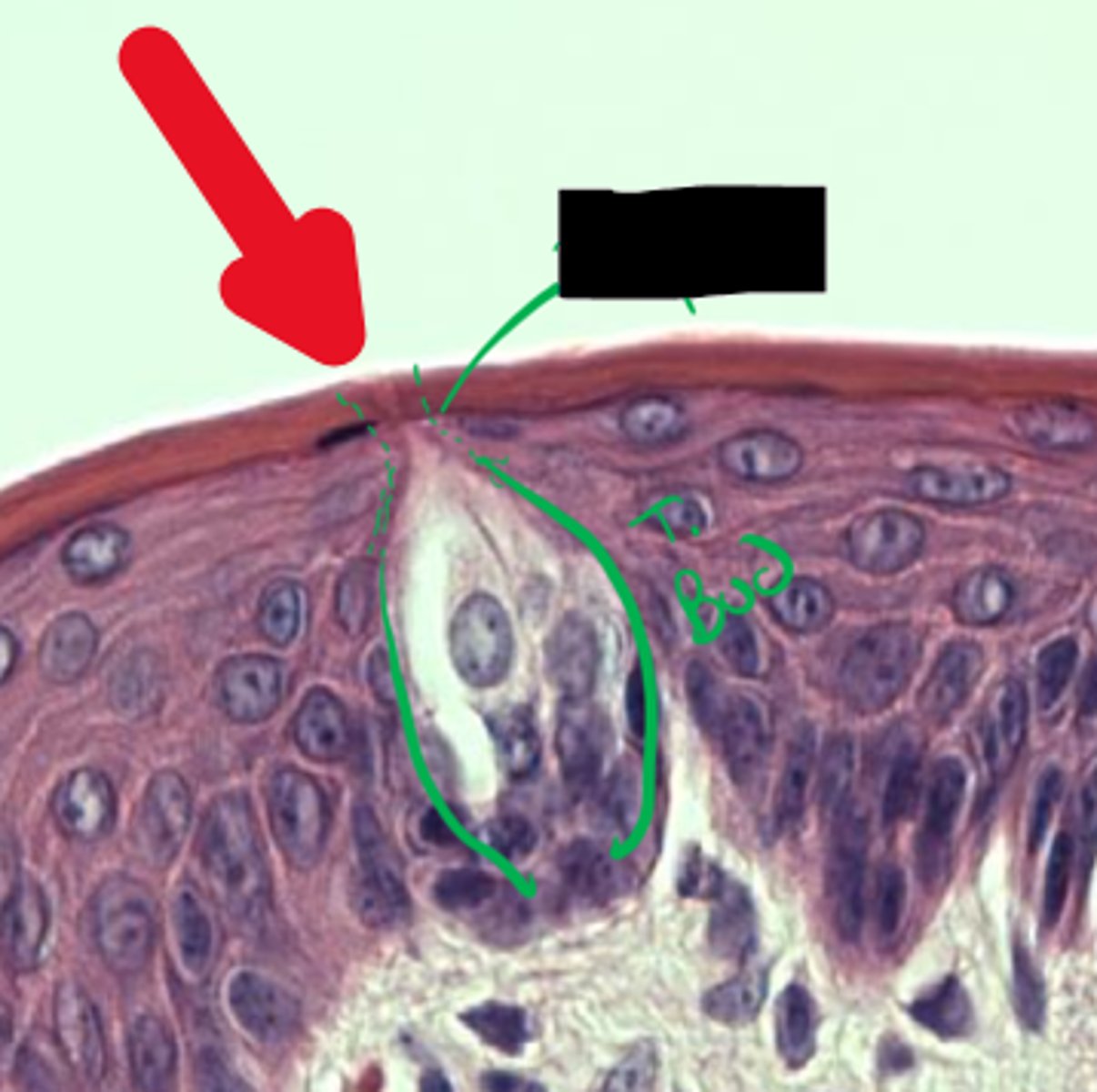
Taste bud
Type of papillae?
What is in green?
Taste bud
Taste pore
What is highlighted in green?
What is the red arrow pointing to?
Horses
What animal are conical papillae NOT in?
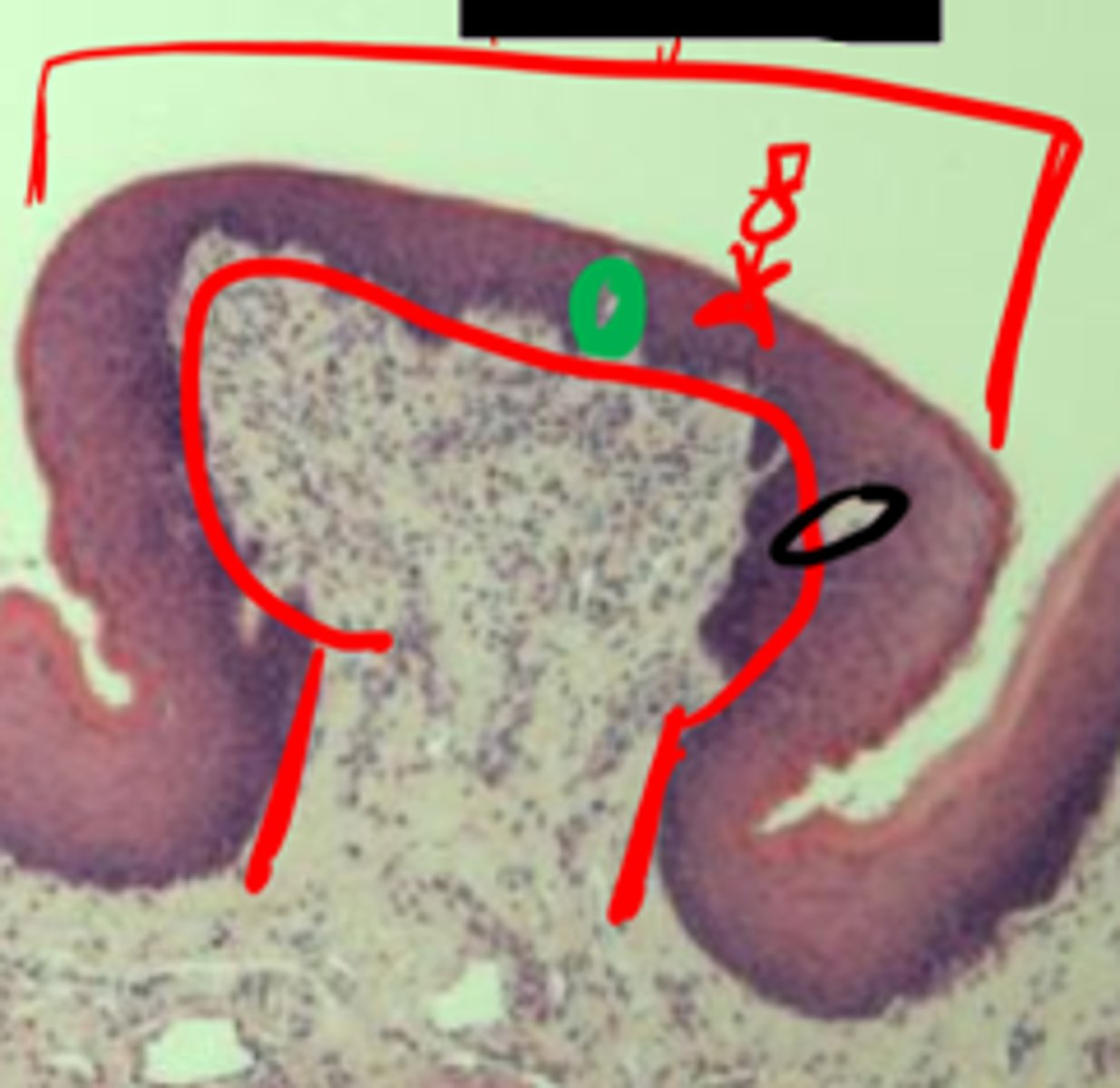
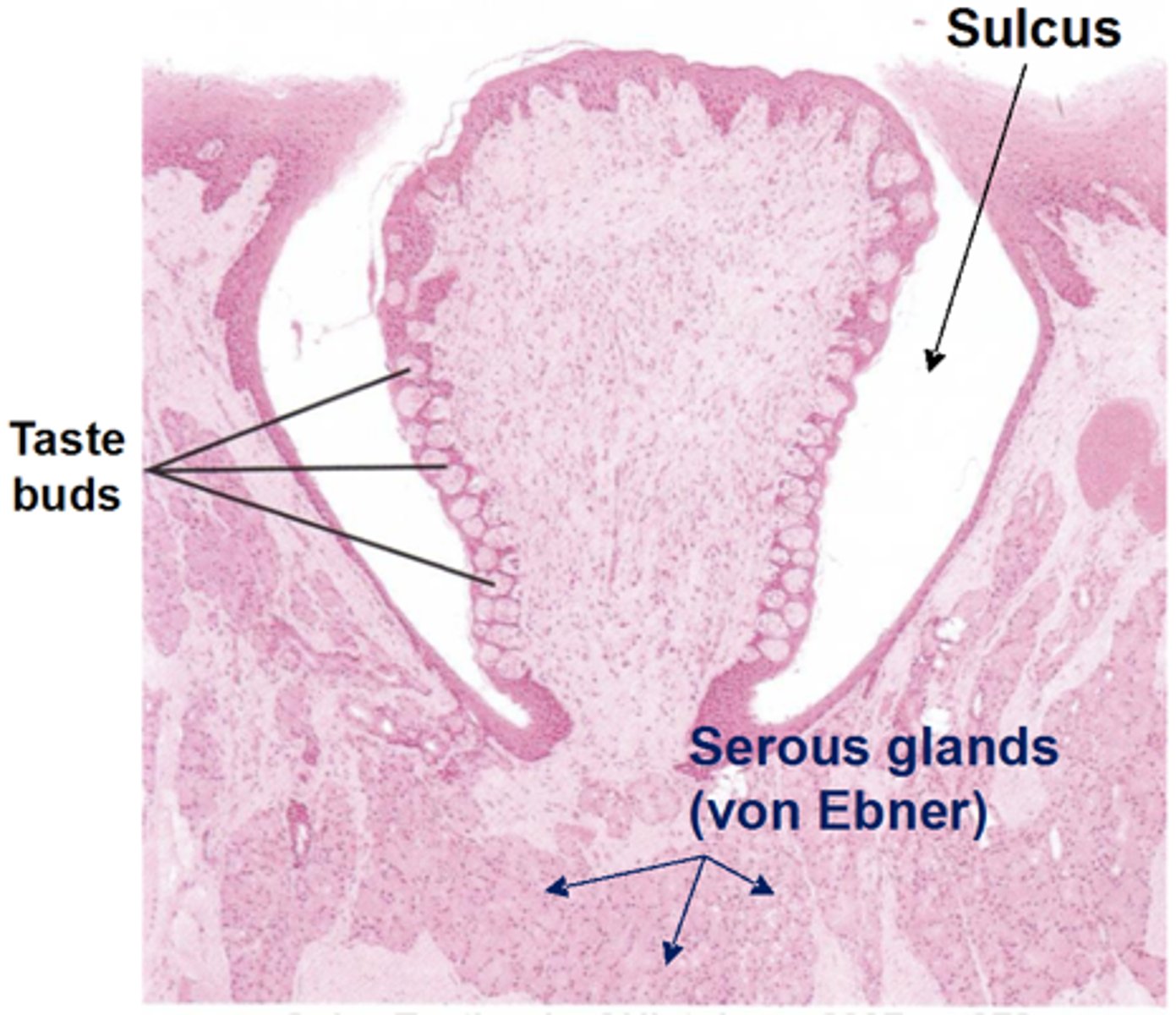
(Circum)Vallate
ID Papillae
Foliate
Cow
ID. Name animal it's absent in
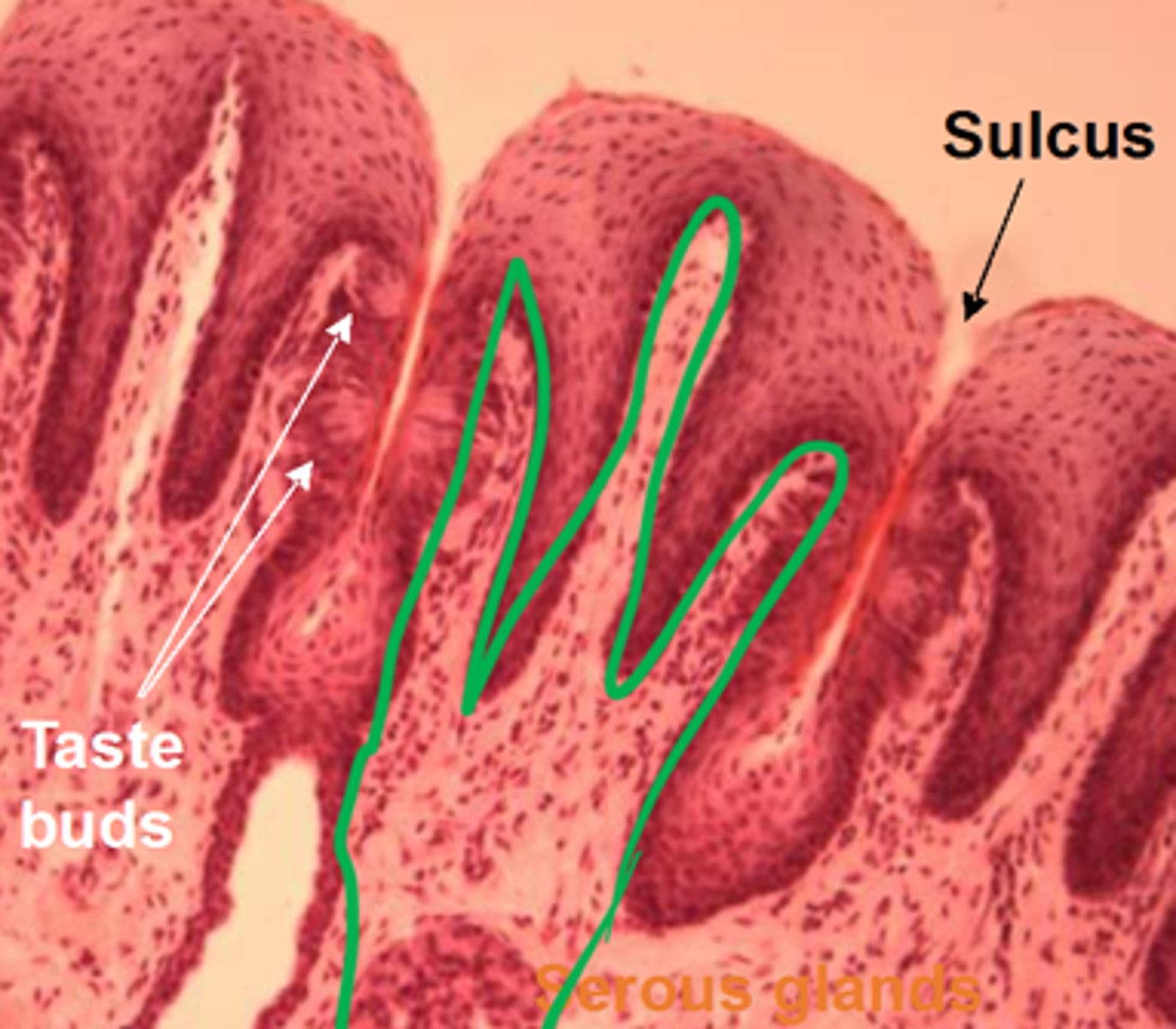
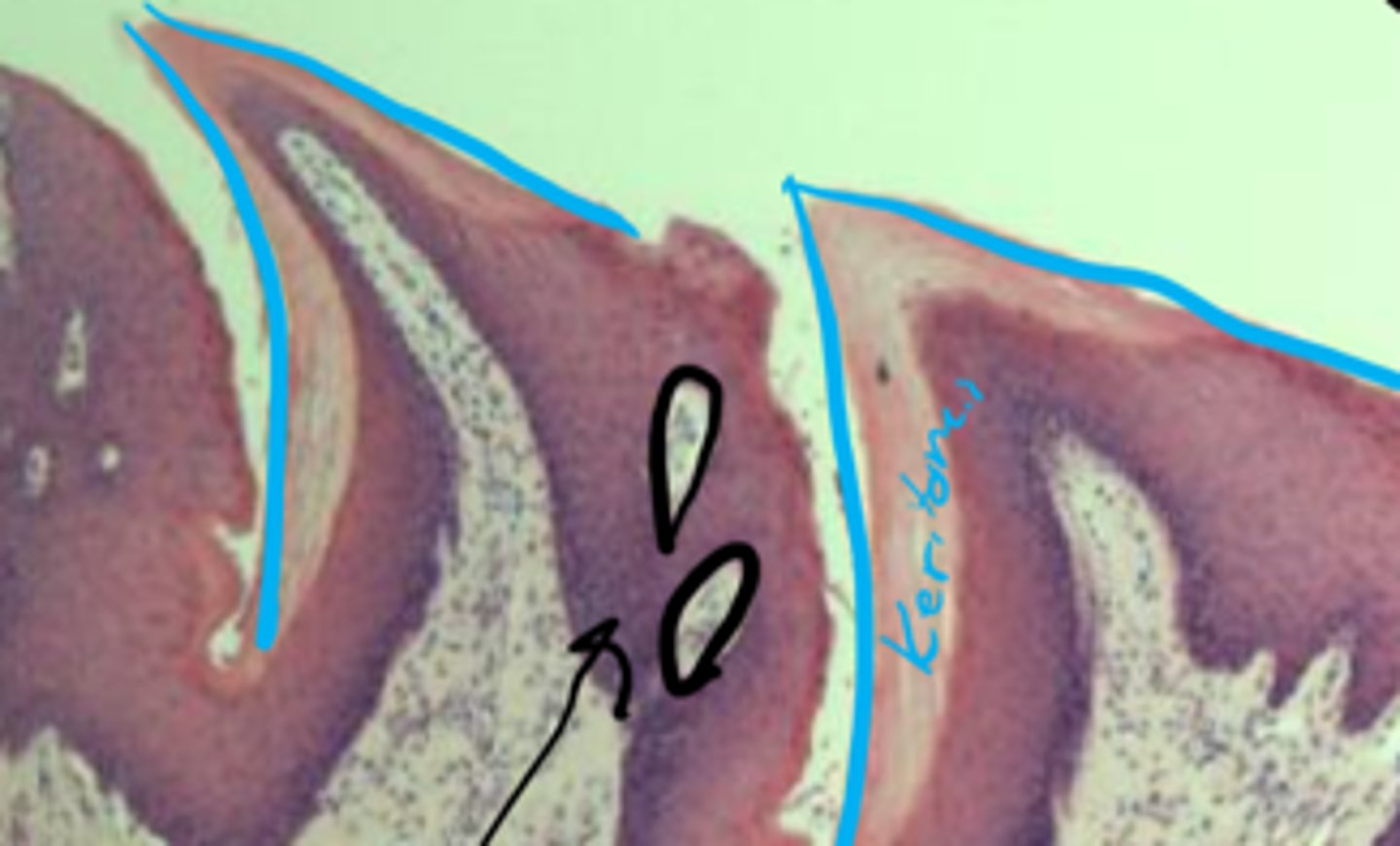
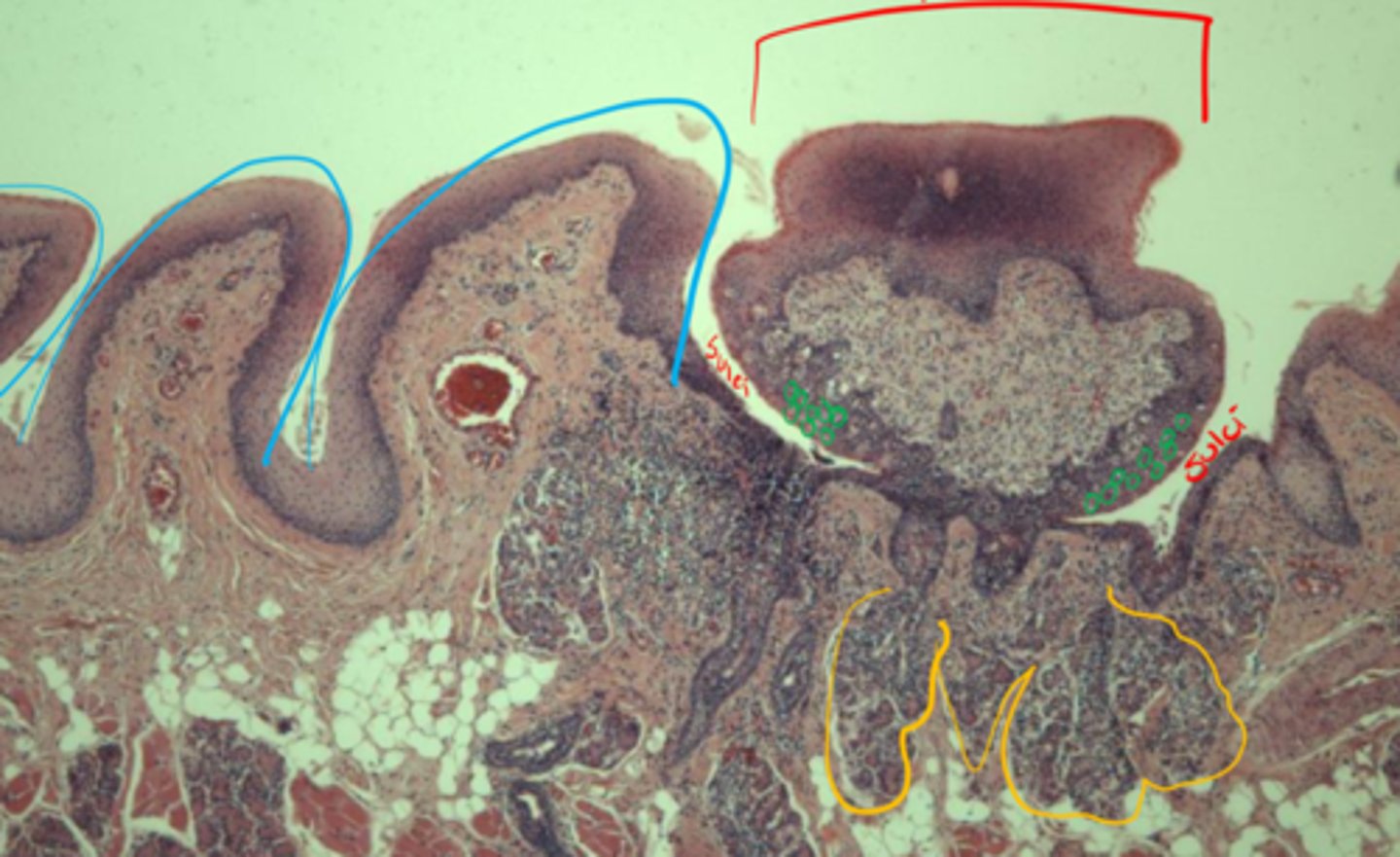
Blue: conical
Red: vallate
Yellow: Von Ebner's glands
ID pretty colors
Papillae on lateral margins of tongue to facilitate nursing
What are marginal papillae for?
10 days
What is the average lifespan of taste buds?
Rugae, allowing for expansion
What are the longitudinal folds/what are they for in the esophagus?
Stratified squamous non-keratinized (carnivores)
Mucosa: What epithelia is present in the esophagus
Pepsinogen
Lysozyme
Mucous
Submucosa: Seromucous glands in the esophagus secrete what?
Dogs (+ cows): entirely skeletal
Cats (+ horses): 2/3 skeletal + 1/3 smooth
Muscularis externa: What is the muscle composition of the esophagus in dog/cats?
Adventitia
The cervical portion of the esophagus is ...
Orange: Mucosa
Red: Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Green: lamina propria
Blue: Muscularis mucosae
Lumen is above
Label the layer (orange)
Label the sublayers (RGB)
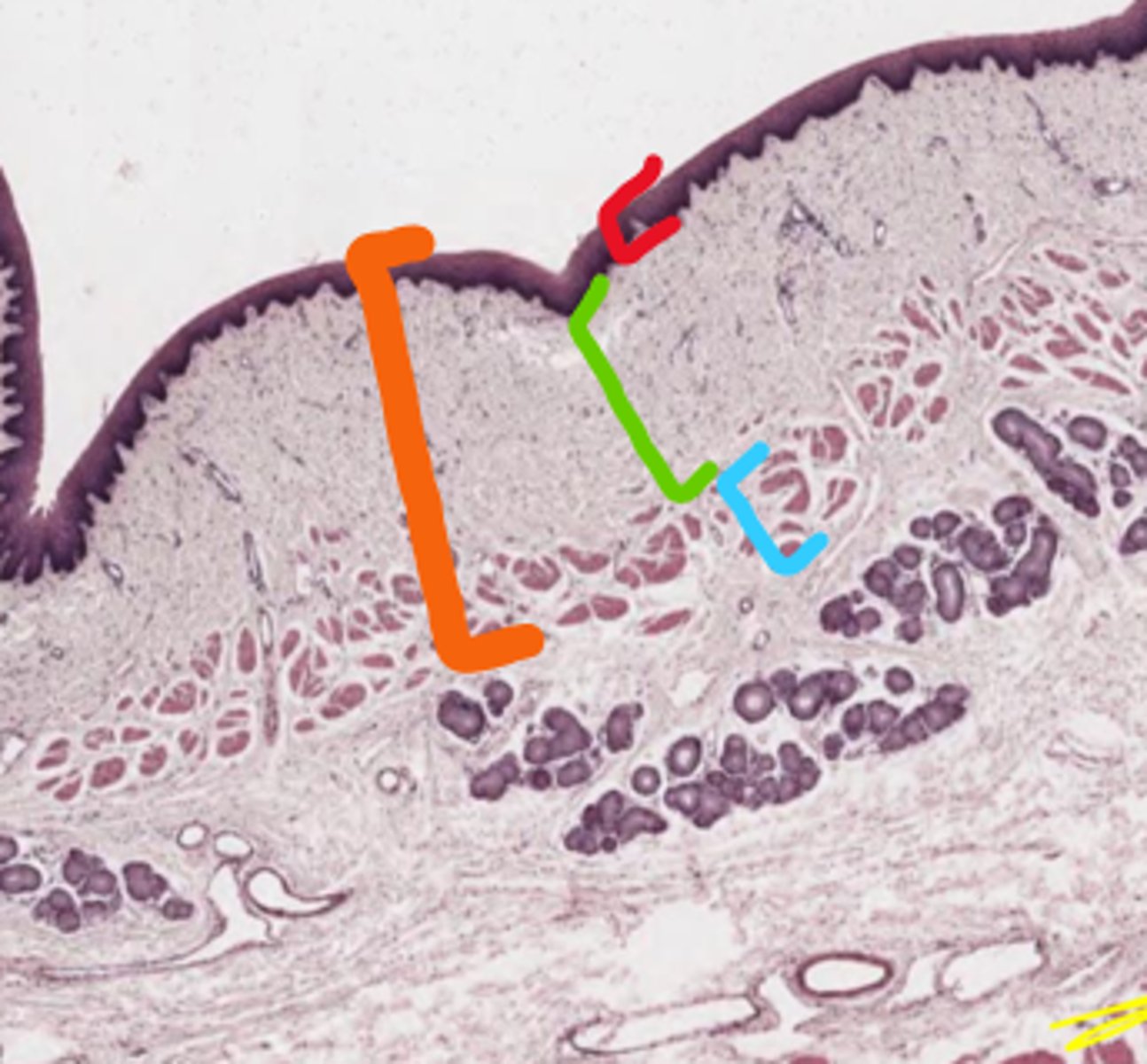
Orange: Submucosa
Blue: Seromucous gland duct
What layer is below the mucosa (orange)
What glands are here (blue)
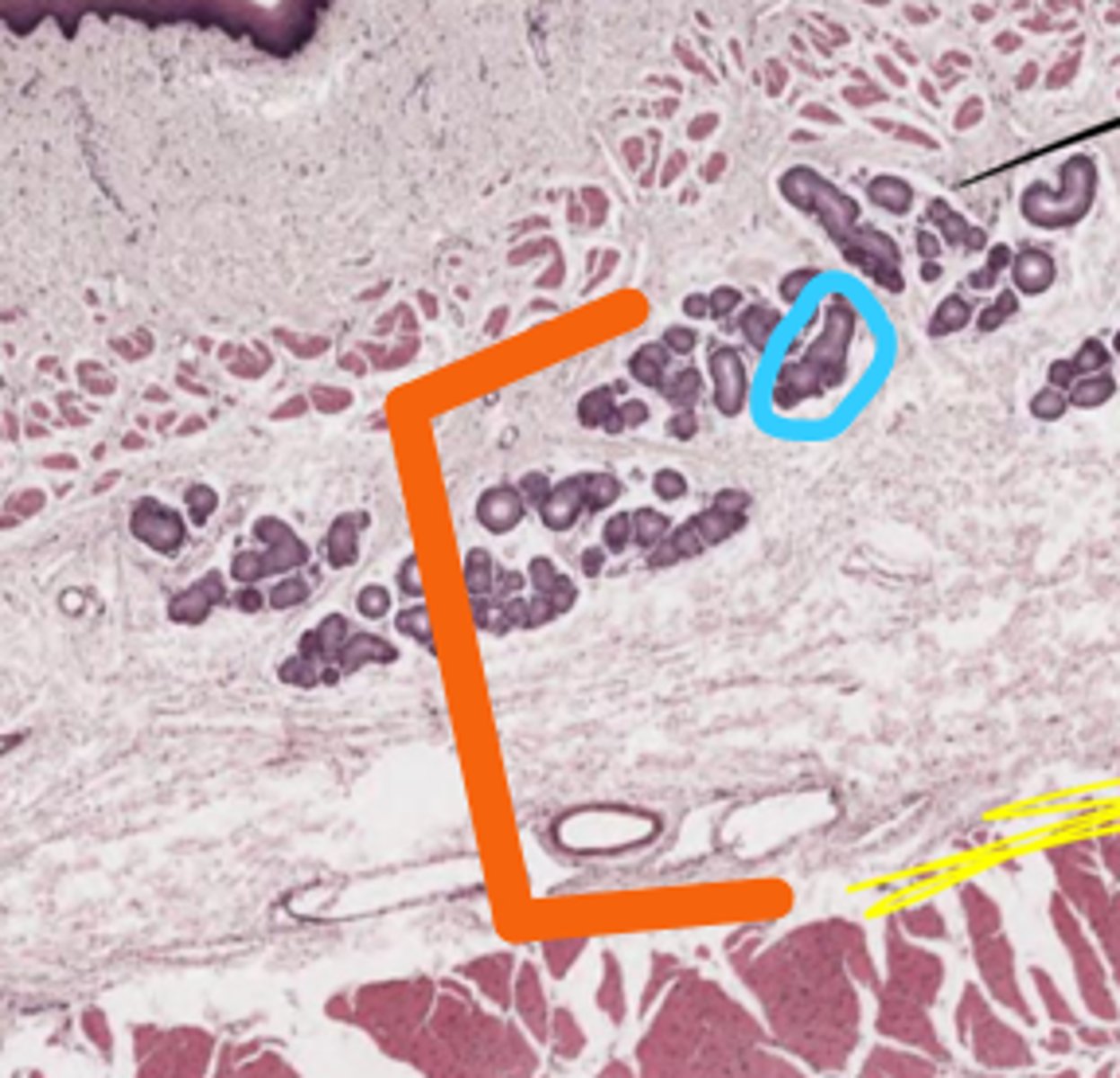
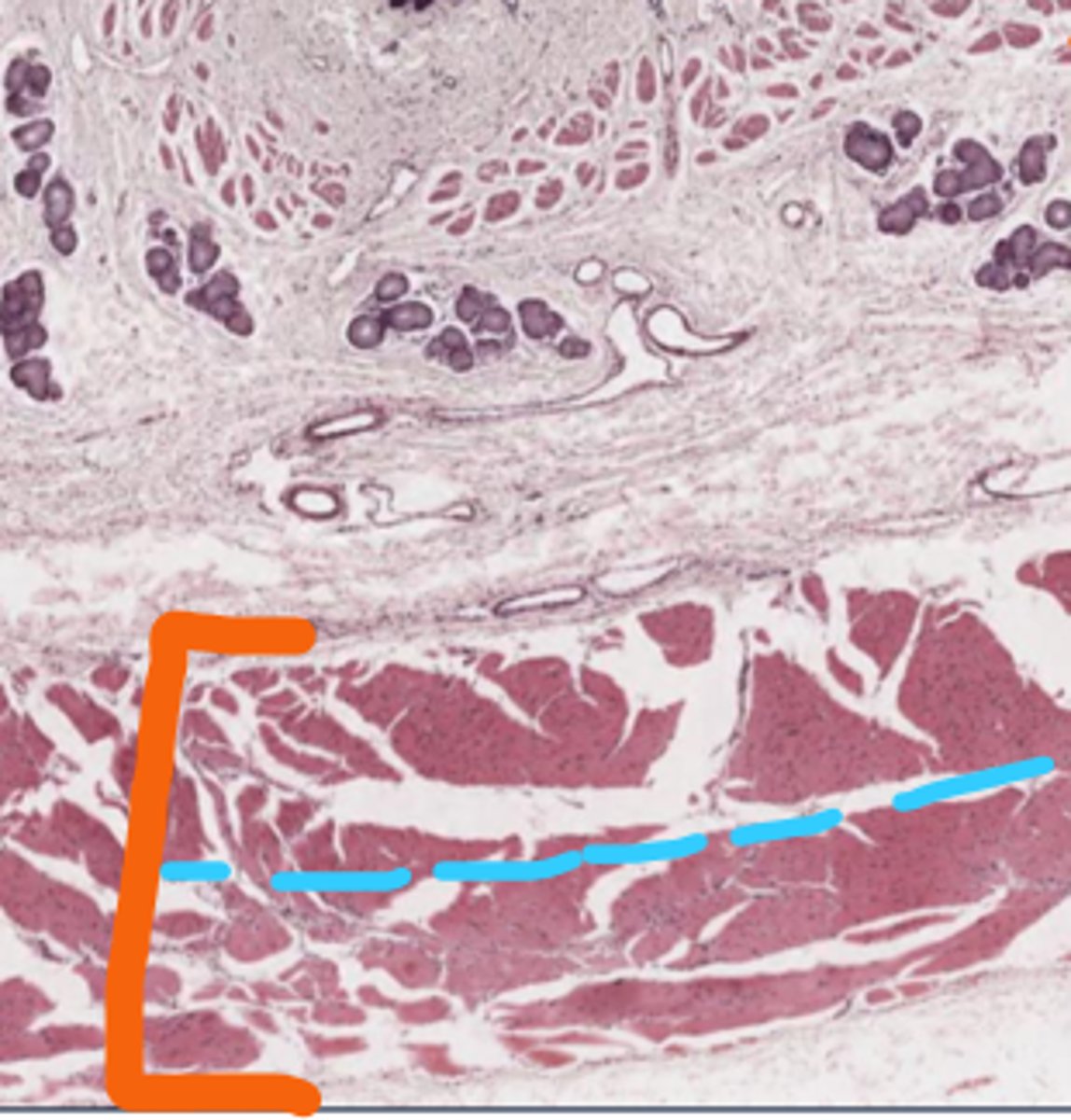
Orange: Muscularis externa
- Top: Inner circular layer
- Bot: Outer longitudinal layer
Serosa/adventitia
What layer is below submucosa (orange)
What sublayers does it have?
What is this layer above?
Cutaneous mucous membrane
What lines the non-glandular region of the stomach?
Cardiac/fundic/pyloric gland regions
What are the glandular regions of the stomach?
Rumen
Reticulum
Omasum
3 parts to the non-glandular stomach of ruminant?