Chapter 15 - Secondary Assessment
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
First step in Secondary Assessment
Physical Exam
Second step in Secondary Assessment
Pt History
Third step in Secondary Assessment
Vital Signs
A sign
something you can see; objective
A symptom
something the pt tells you; subjective
Pt assessment is a __ process
dynamic
Reassessment
A step within the patient assessment process that is performed at regular intervals to identify and treat changes in a patient's condition, A patient in unstable condition should be reassessed every 5 minutes, whereas a patient in stable condition should be reassessed every 15 minutes
In a conscious pt, obtain your SAMPLE early because
they can become unconscious
Rapid Physical Exam
• Similar to physical exam for trauma patient • Assess head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, extremities, and posterior
Rapid Head-To-Toe Exam
Unresponsive trauma patient
Detailed physical assessment
The part of the assessment process meant to demote in depth exam of one or more body systems, used when more information is needed
DCAP-BTLS
deformities, contusions, abrasions, punctures, burns, tenderness, lacerations, swelling
Deformities
abnormally formed parts of the body
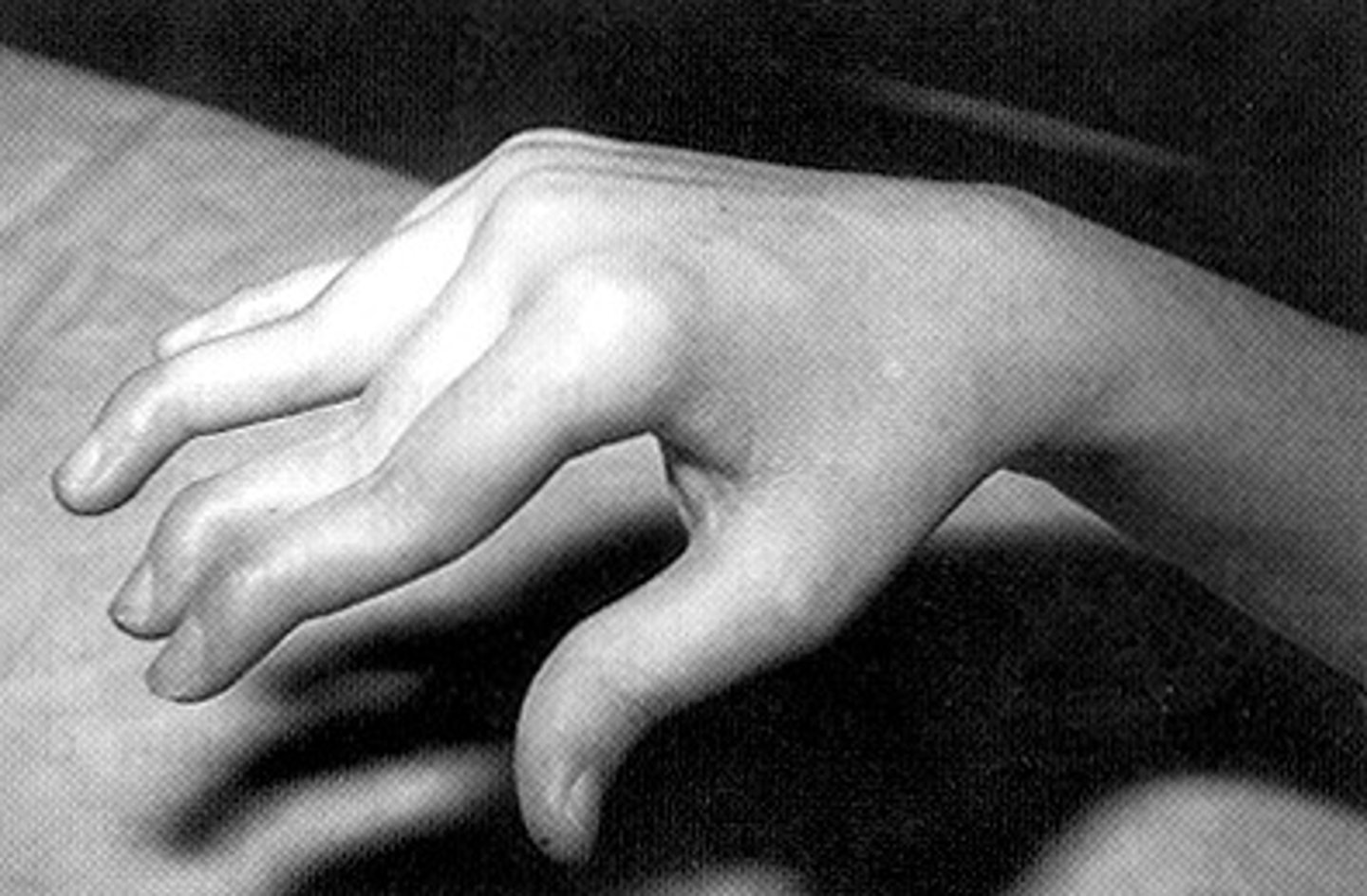
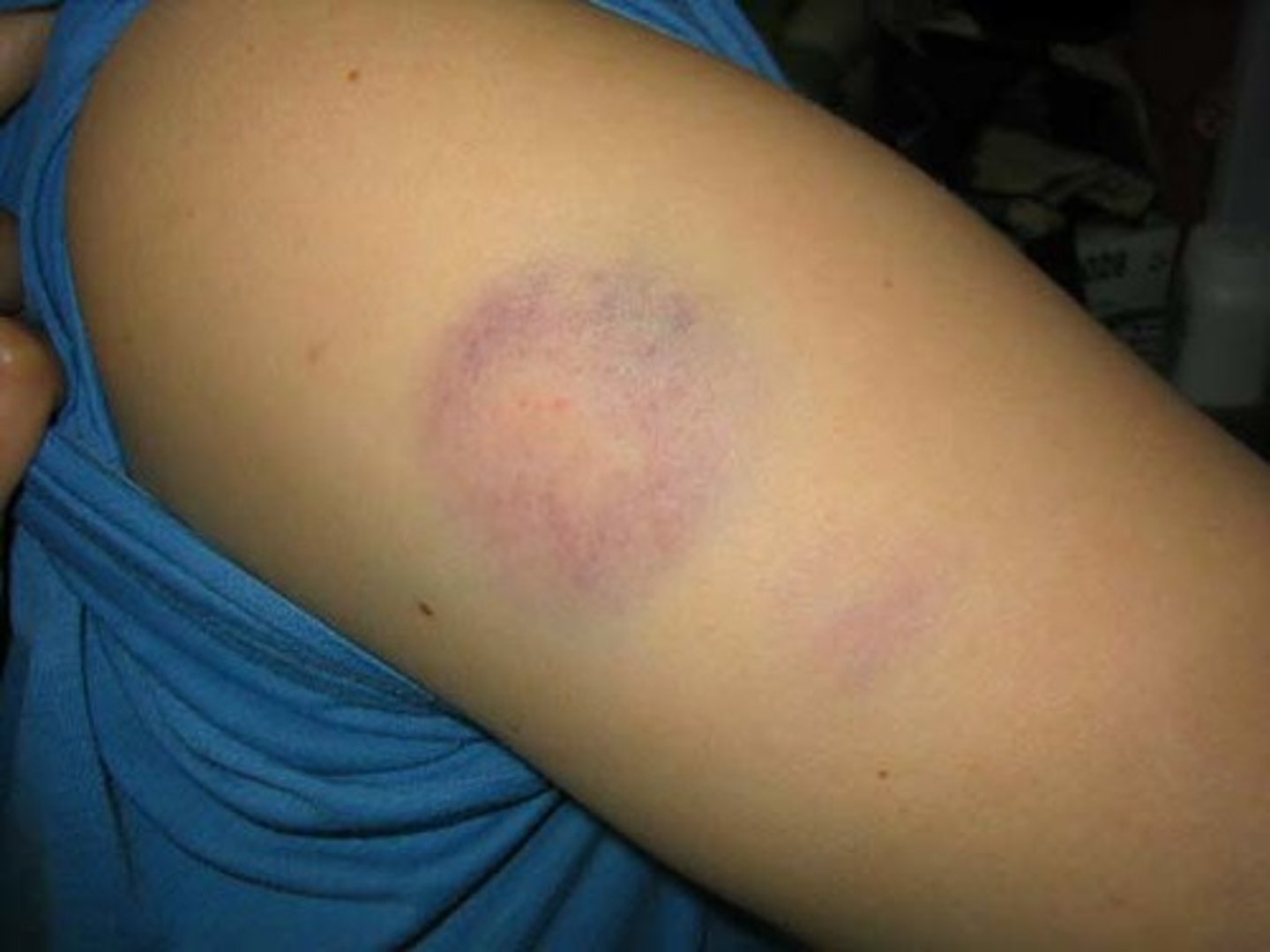
Contusions
bruises
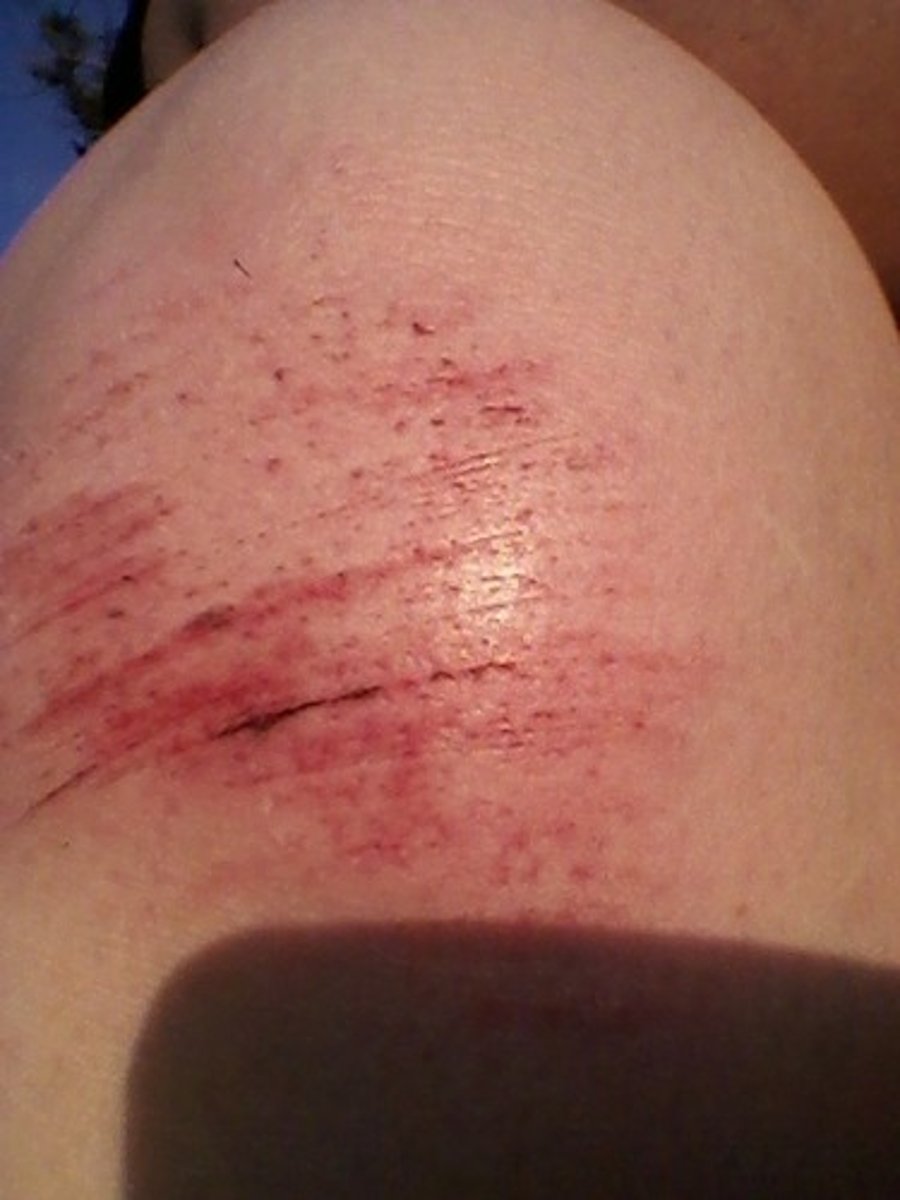
Abrasions
scrapes
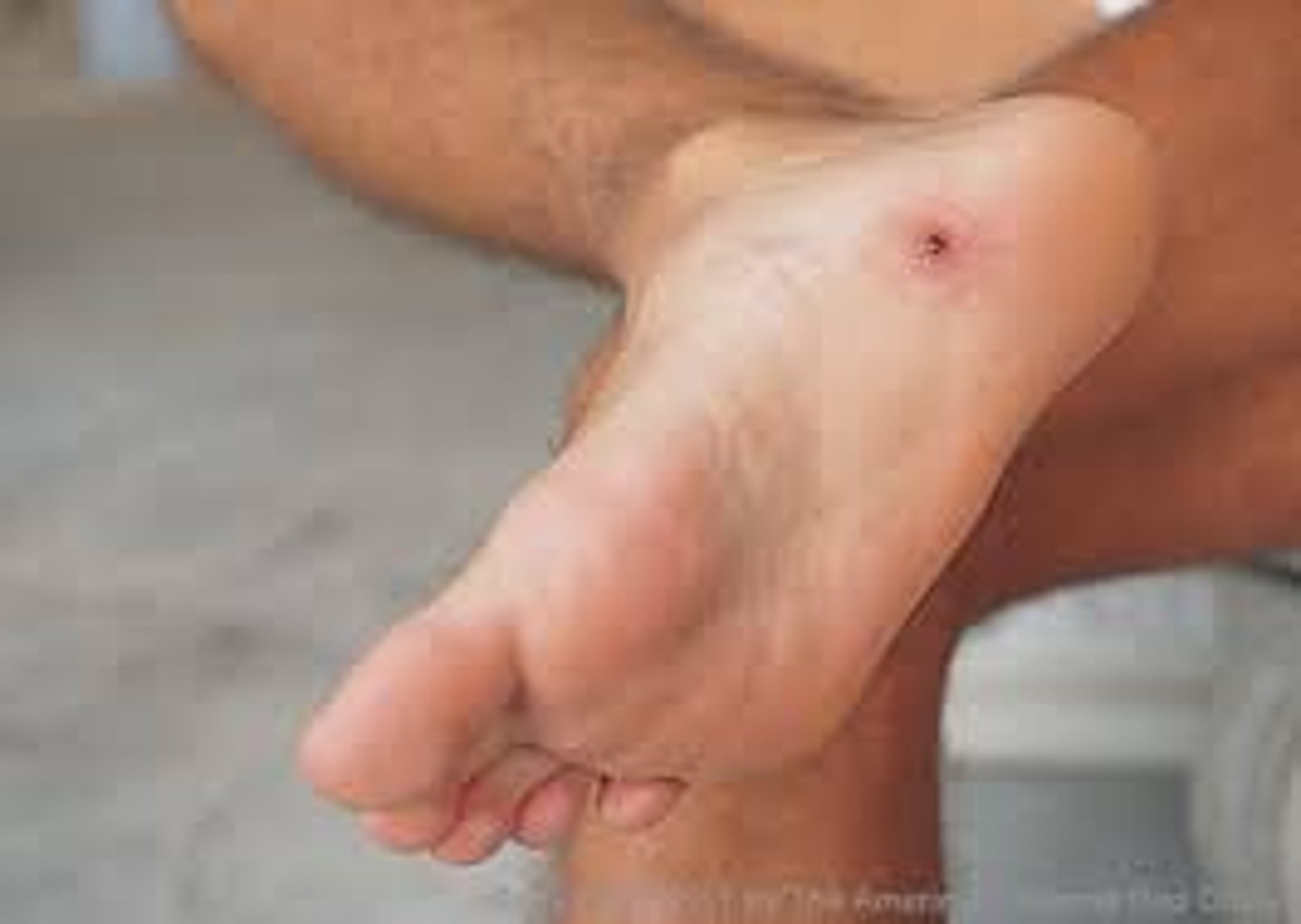
Punctures
result from penetration by small sharp object
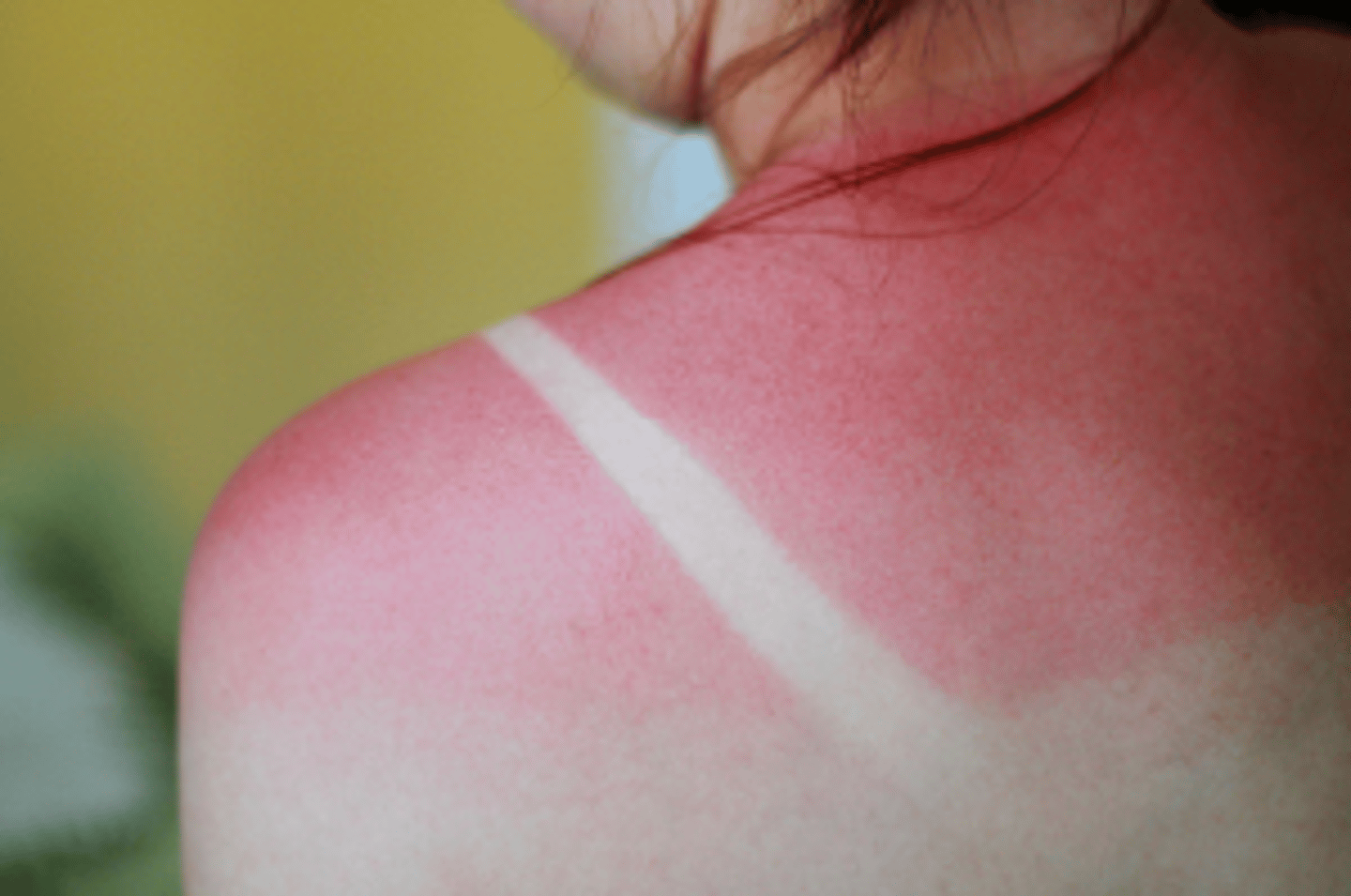
Burns
tissue damage and cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals

Tenderness
pain felt on the release of pressure
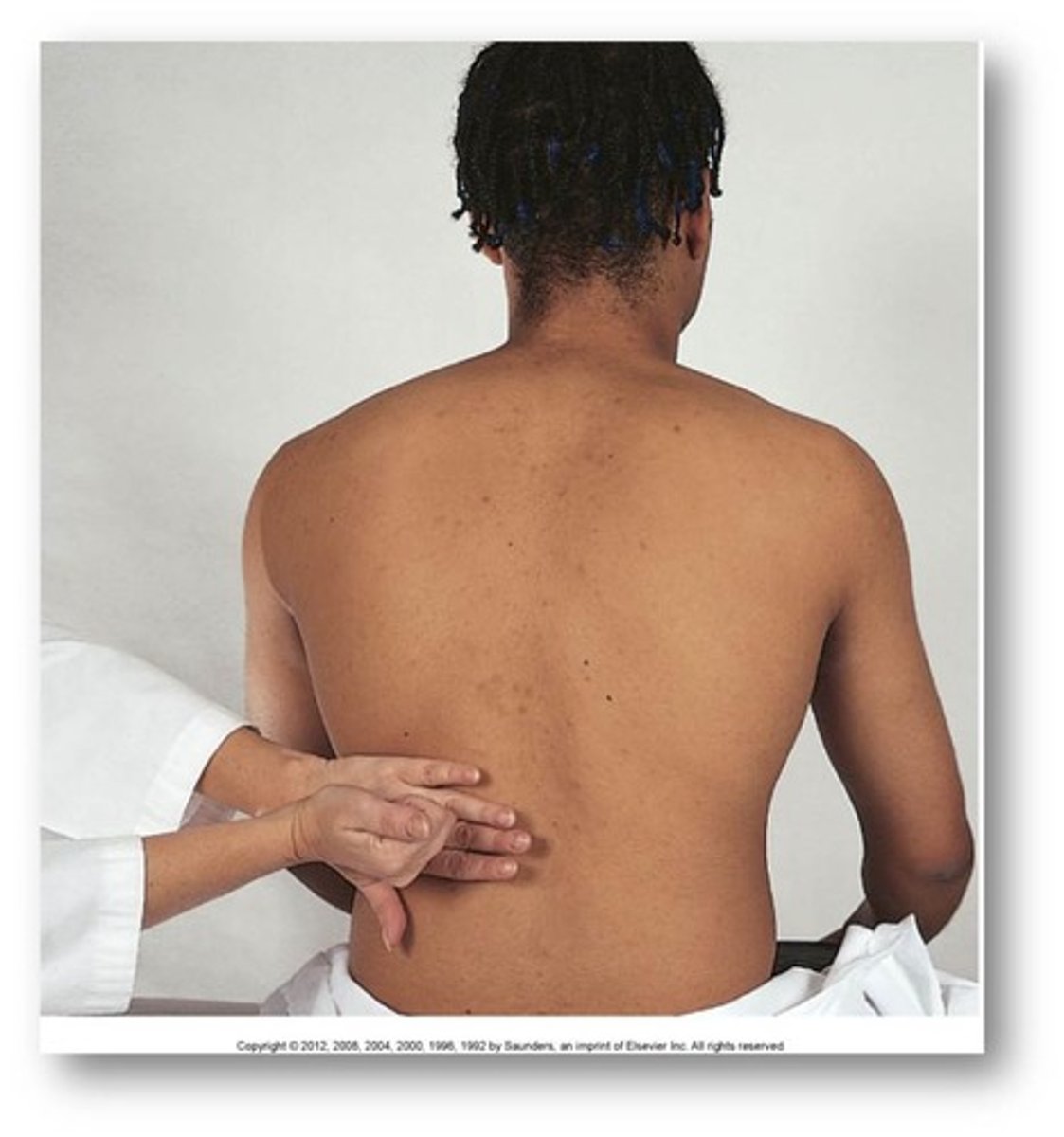
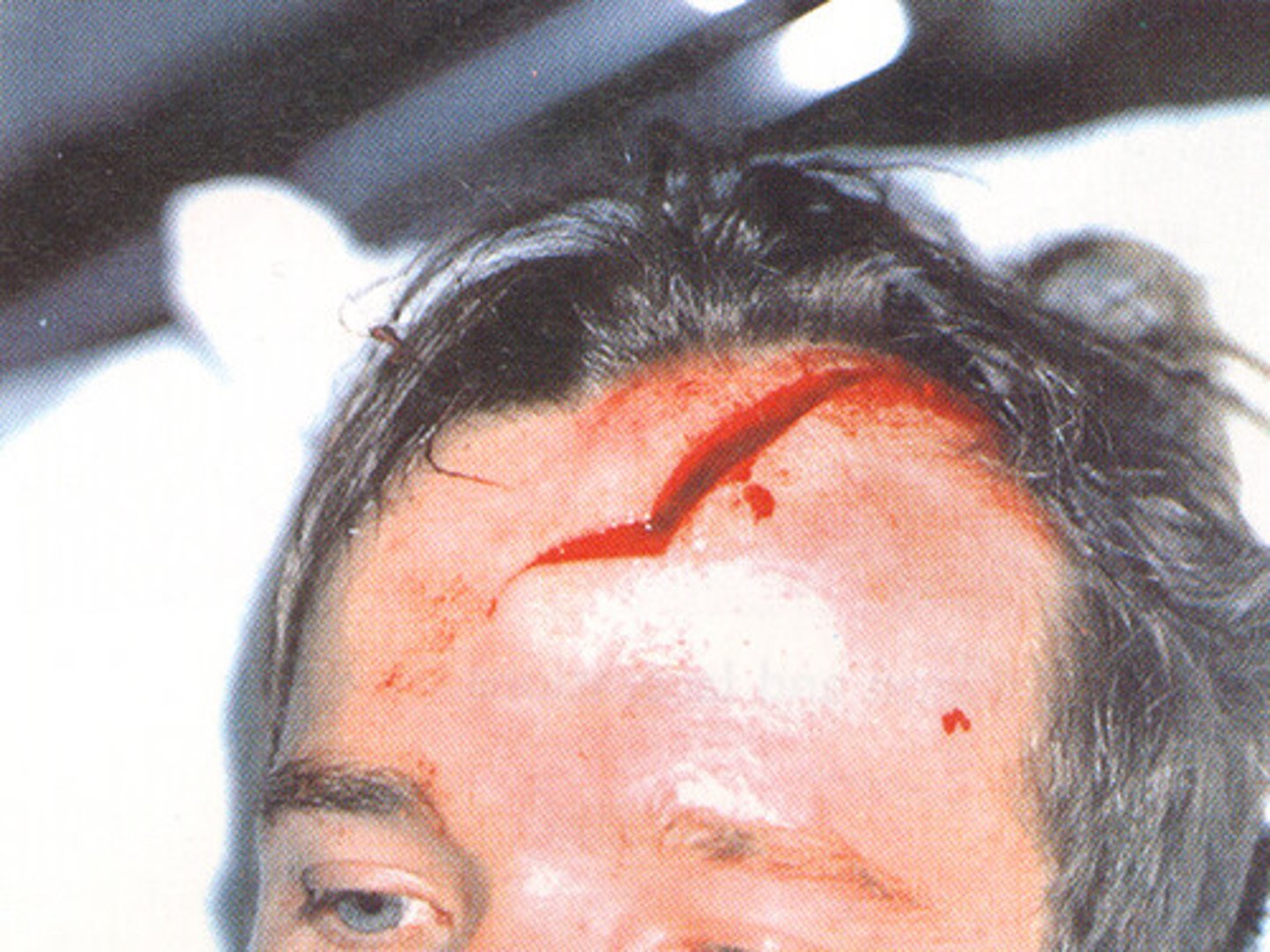
Lacerations
a deep cut or tear in skin or flesh.
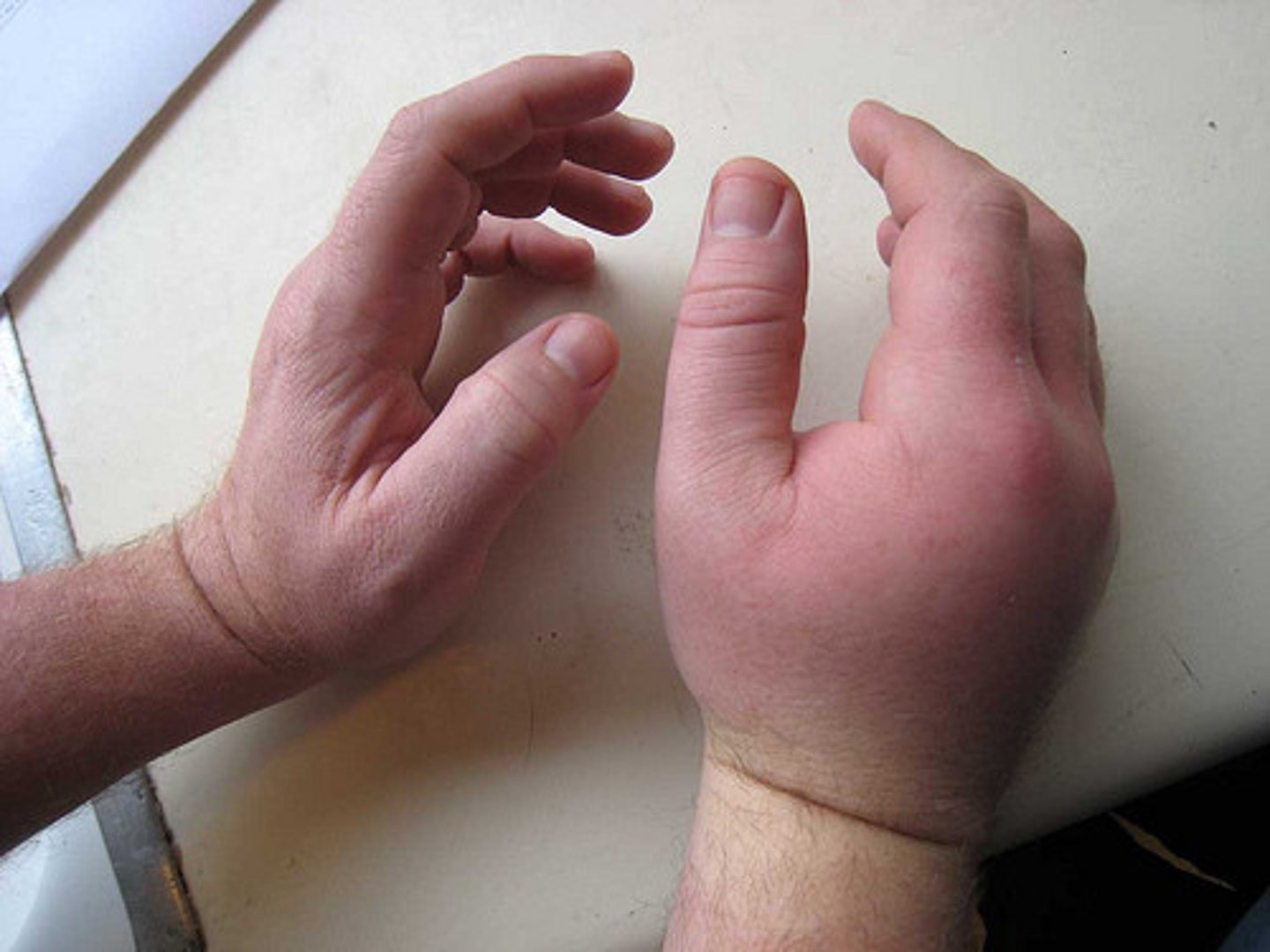
Swelling
a part of your body that has become bigger because of illness or injury
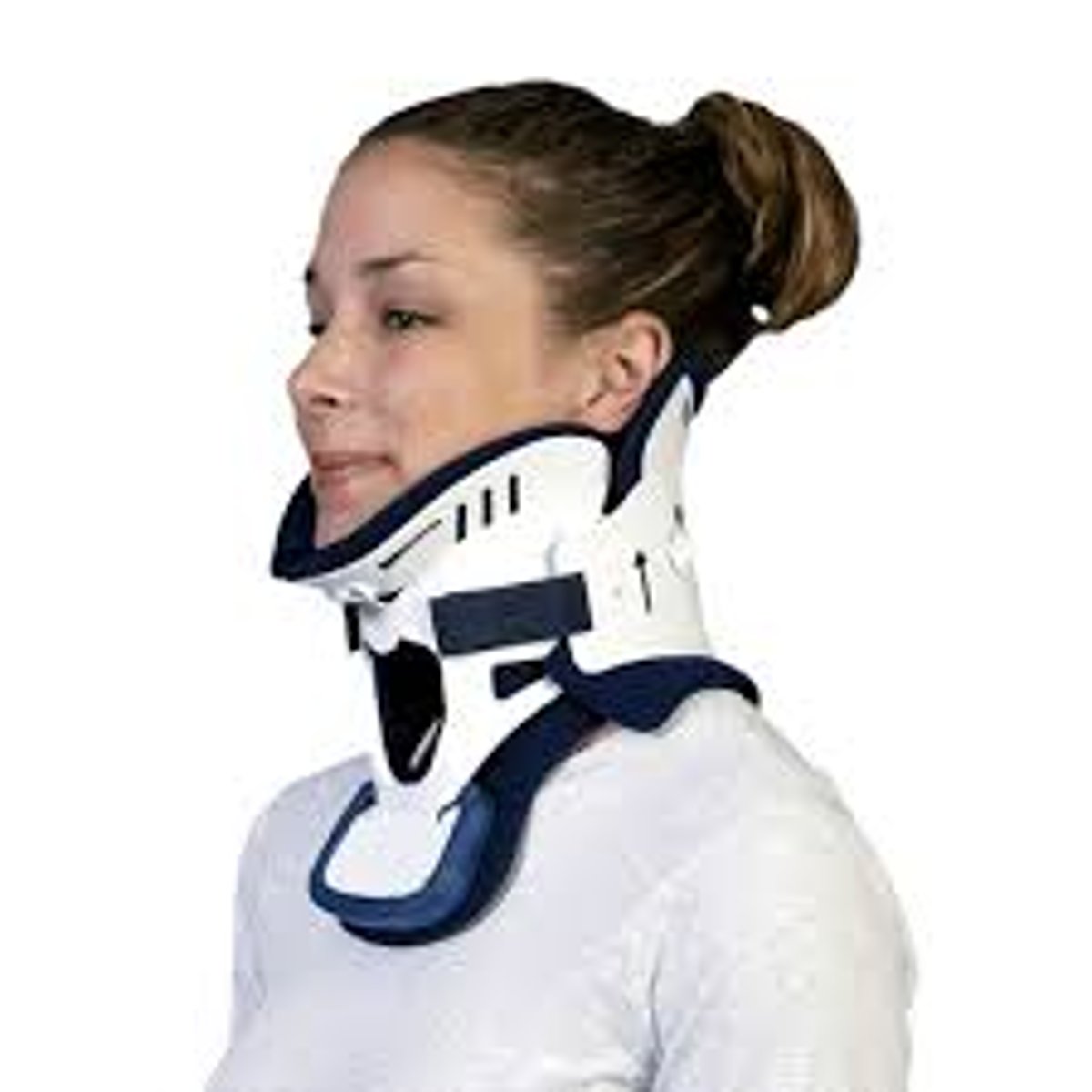
C-Collar
A neck brace that is put in place after a trauma and possible neck injury. It is removed after either exam or radiographic imaging has assured there is no c-spine injury.
Rapid Trauma Assessment
a rapid assessment of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, extremities, and posterior of the body to detect signs and symptoms of injury
Significant fall for adult
>20 feet
Significant fall for pediatric
> 10 feet or 2-3 times their height
High risk auto crashes include
intrusion of >12 inches to occupant side or 18 inches to any locations; ejection; death in same vehicle; auto vs pedestrian; motorcycle crash at 20 mph
CSF
cerebrospinal fluid
Battle signs
Bruising behind the ears, indicative of a basilar skull fracture
pneumothorax
air in the pleural cavity caused by a puncture of the lung or chest wall
cardiac tamponade
pressure on the heart caused by fluid in the pericardial space
Flail chest
fracture of two or more adjacent ribs in two or more places that allows for free movement of the fractured segment
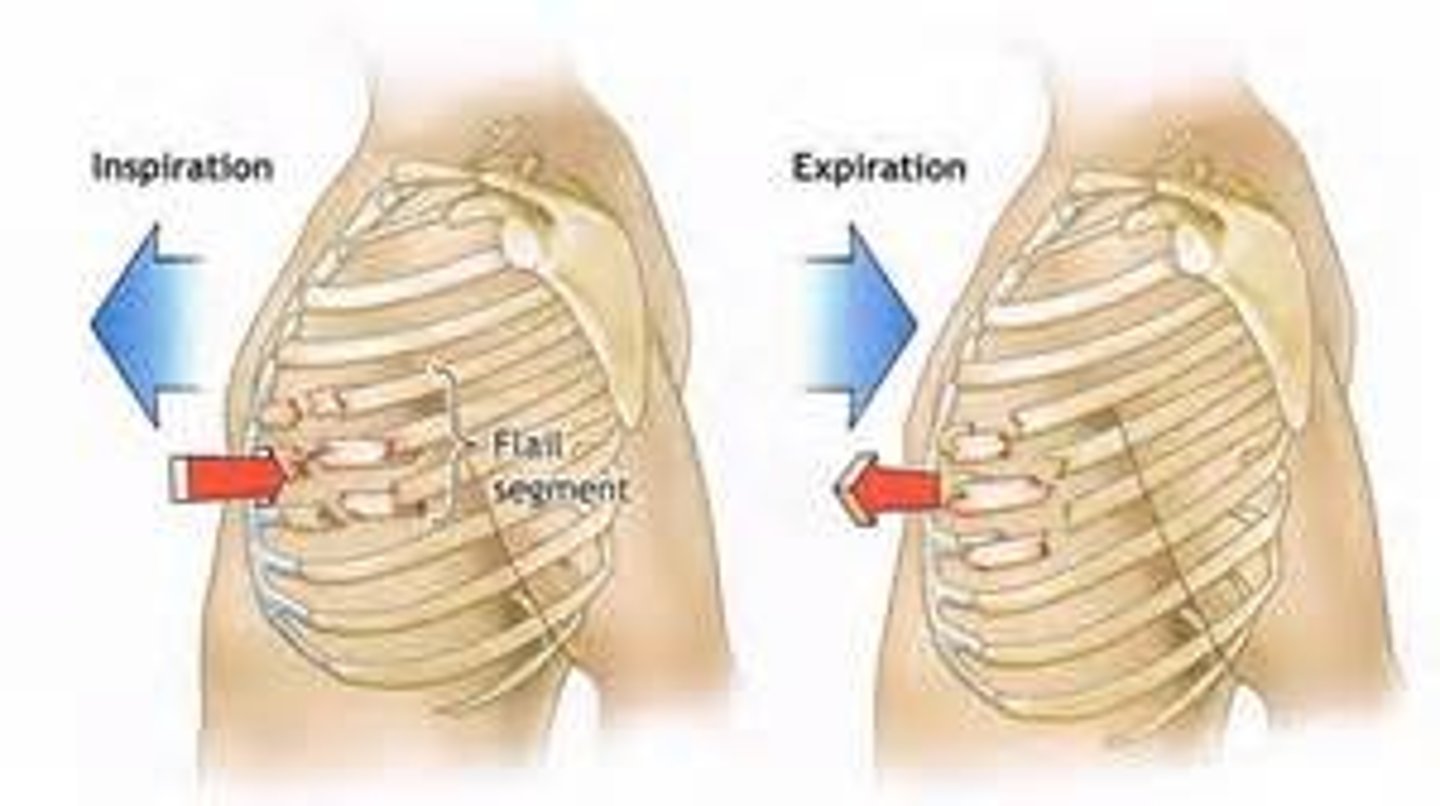
paradoxical motion
movement of a part of the chest in the opposite direction to the rest of the chest during respiration
distention
the state or act of extending or being swollen out of shape
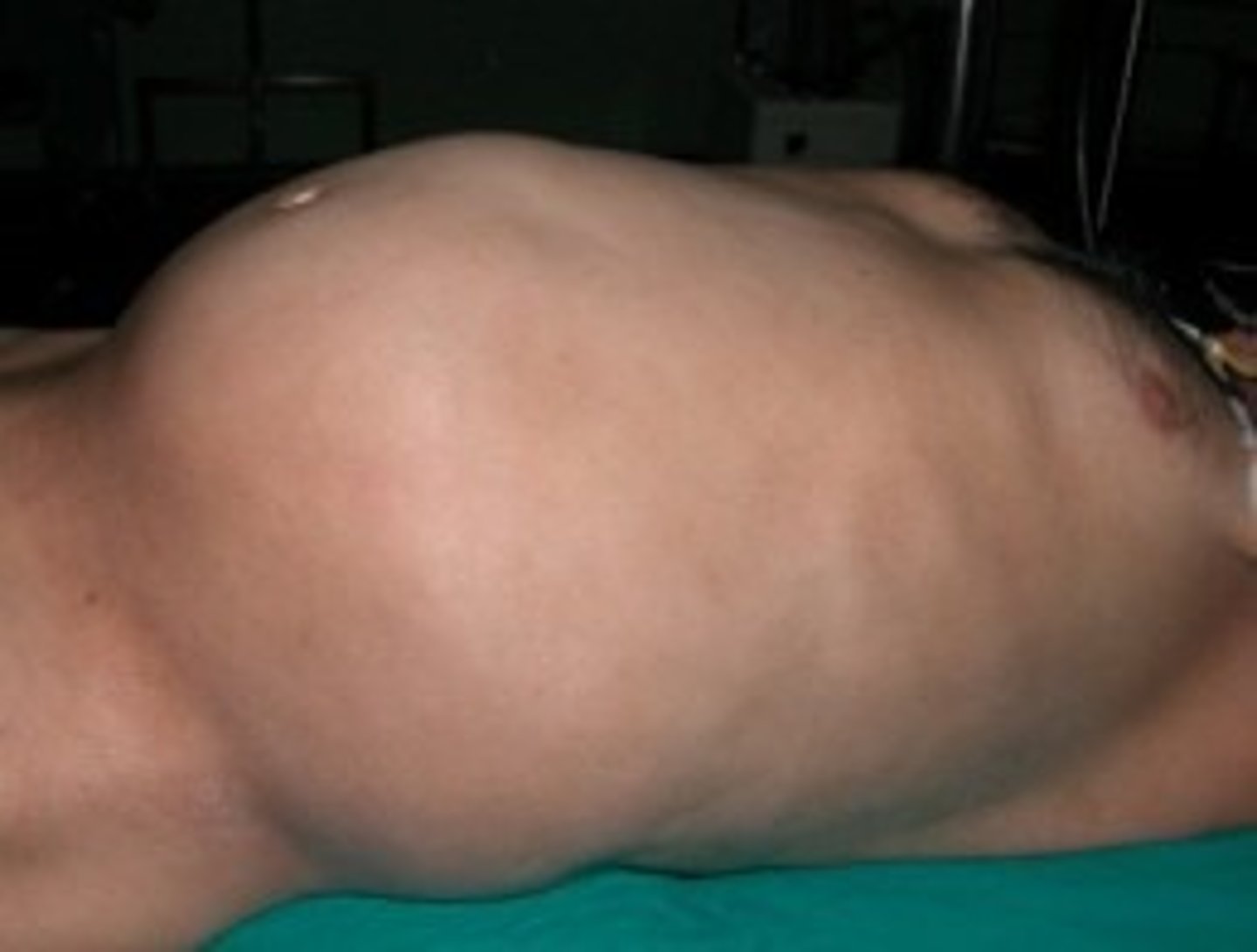
priaprism
persistent and painful erection, often due to trauma
detailed physical exam
An in-depth head-to-toe physical exam; takes more time than the rapid assessment and is only done when time and the patient's condition allow.