Cell Adaptation and Necrosis 8/6/25
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary flashcards covering definitions, examples, and distinguishing features of cellular adaptation, dysplasia, anaplasia, necrosis types, gangrene, and pathologic calcifications.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Cellular Adaptation
Reversible functional and structural changes that allow cells to cope with prolonged or abnormal stimulation. Some cells don’t revert which can be detrimental (ex. cancer)
Atrophy
Decrease in the size of a tissue, organ, or entire body due to shrinkage of individual cells.
Physiologic Atrophy
Normal, programmed reduction in tissue size (e.g., thymus involution, post-menopausal uterus/ovaries/breasts, elderly bones/muscles).
Pathologic Atrophy
Shrinkage caused by disease or altered environment (e.g., ischemic kidney, testicular atrophy, Alzheimer brain).
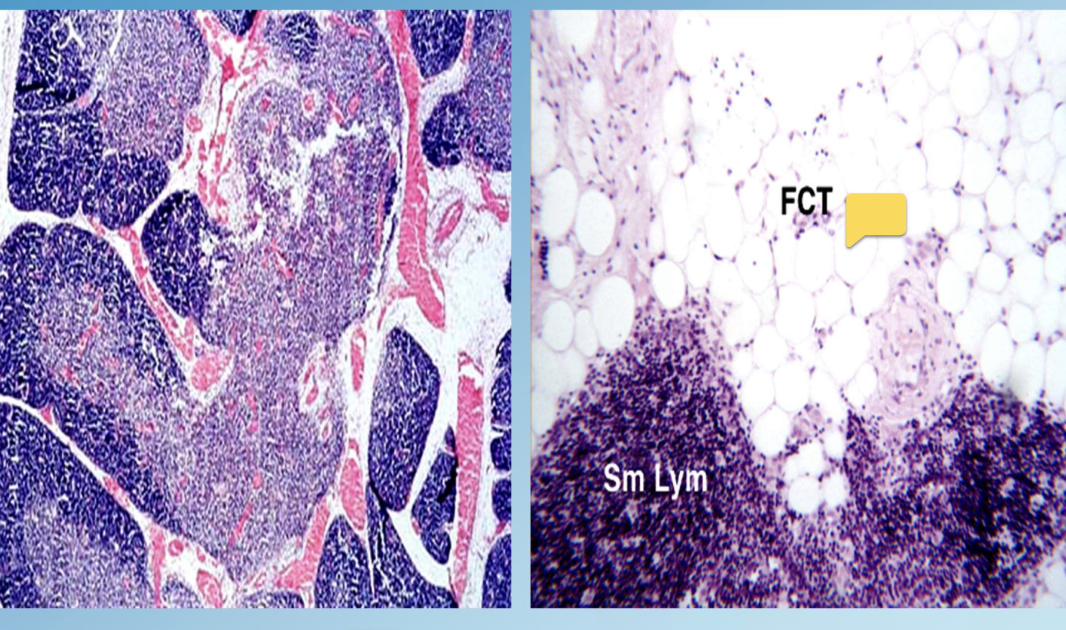
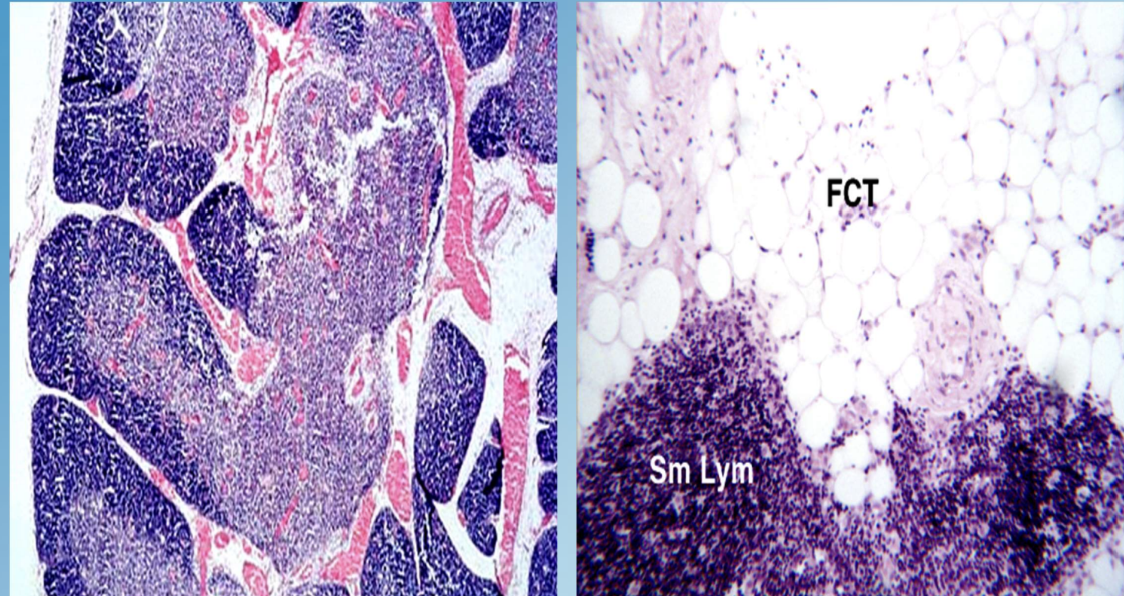
Thymic Involution
Physiologic atrophy of the thymus that occurs with aging ~age 21
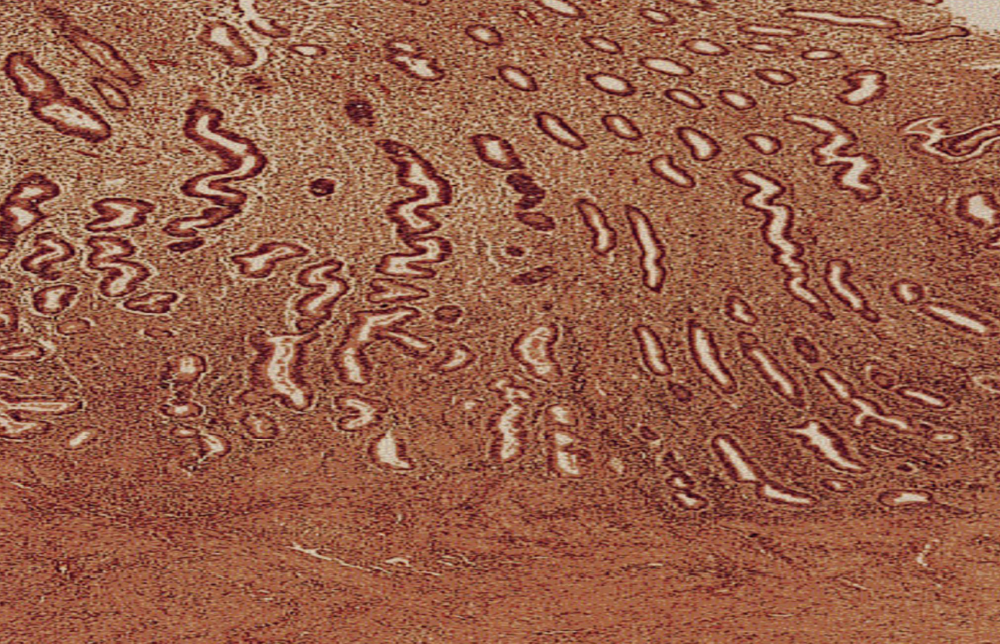
Postmenopausal Endometrial Atrophy
Thinning of the uterine lining after loss of estrogen stimulation.
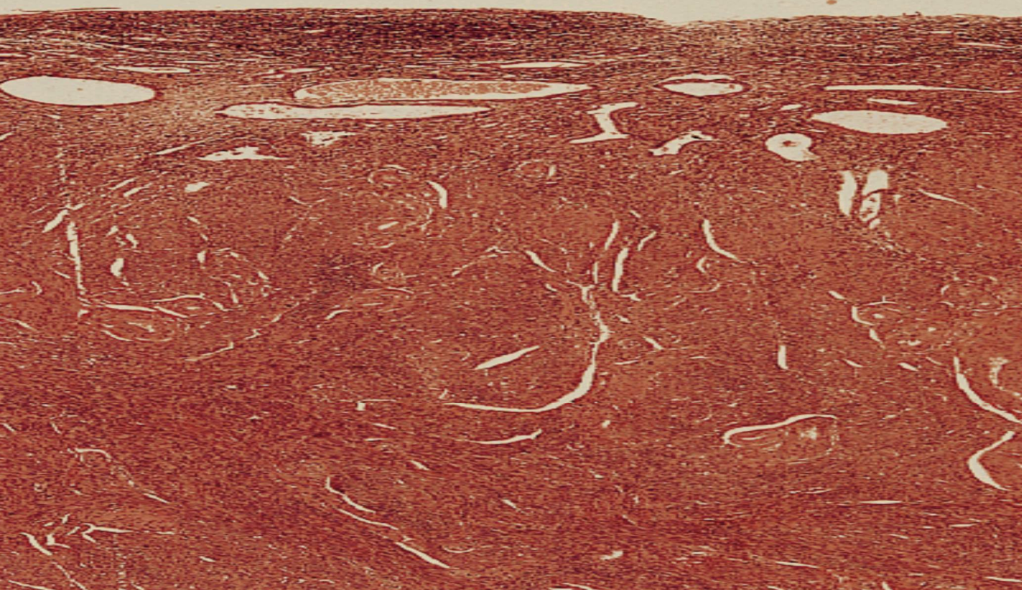
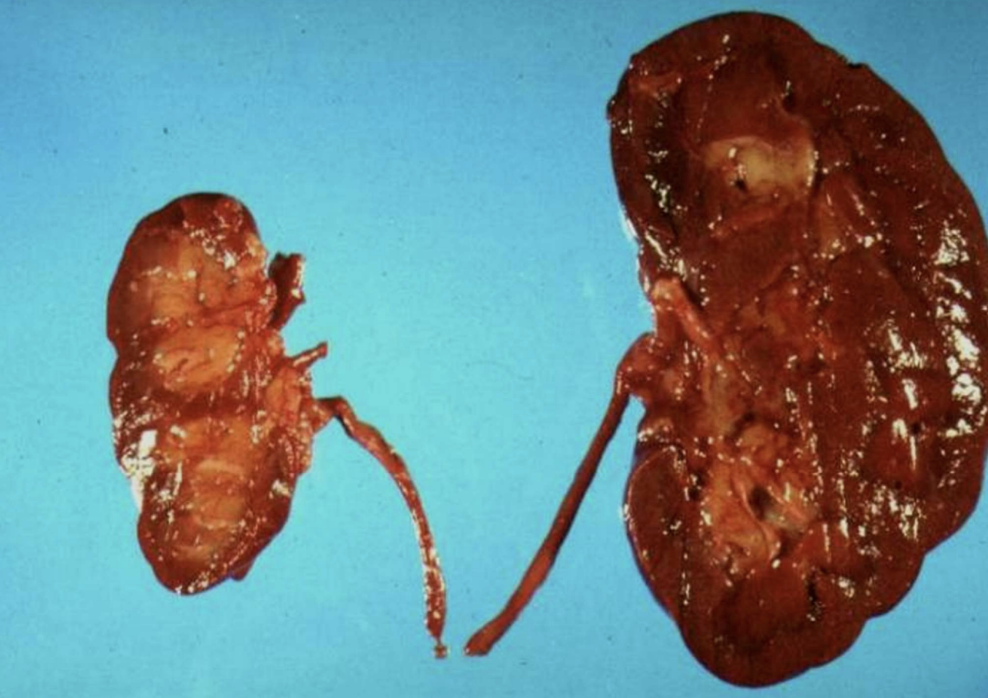
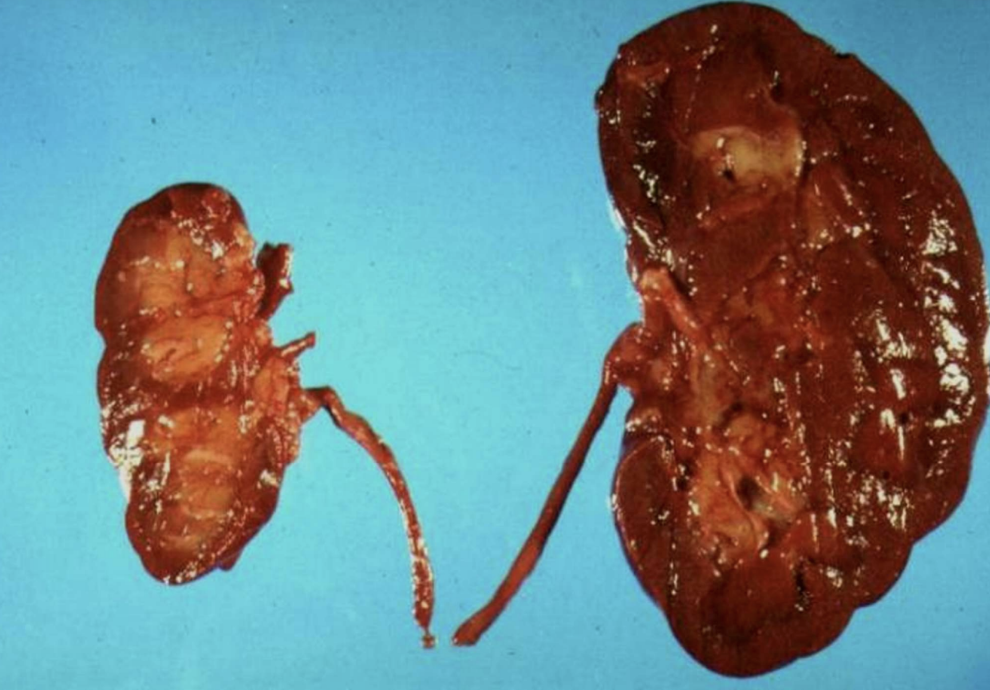
Ischemic Organ Atrophy
Size reduction of organs (e.g., kidney) due to chronic loss of blood flow.
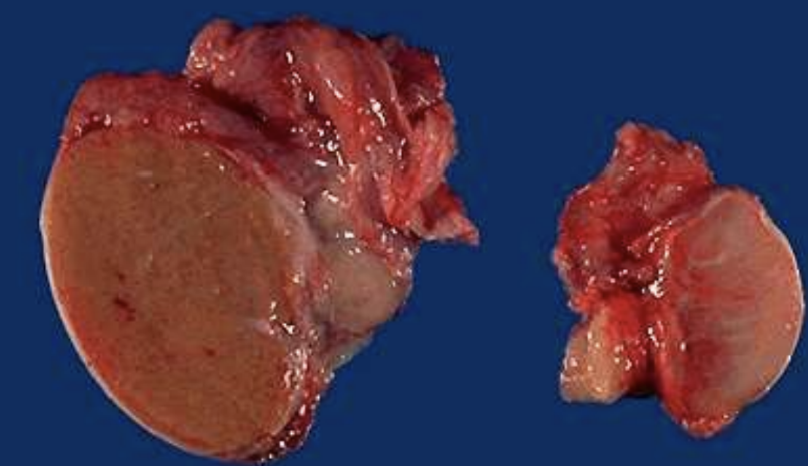
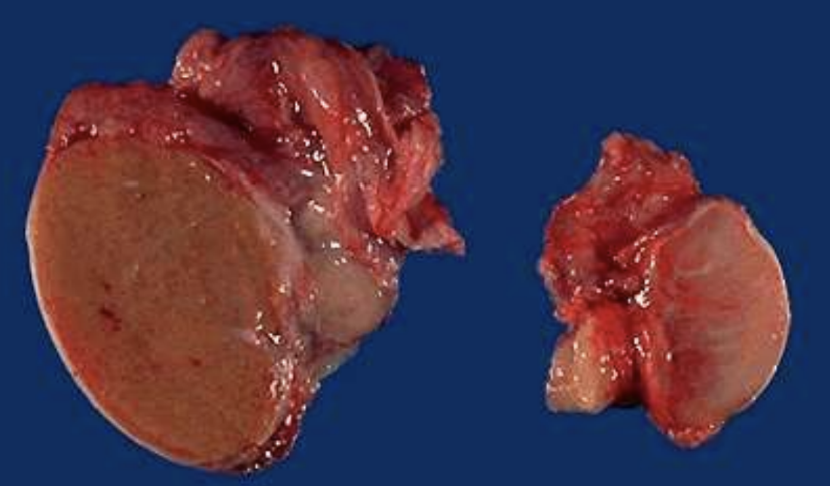
Testicular Atrophy
Pathologic shrinkage of testes often from ischemia, hormonal loss, or illness.
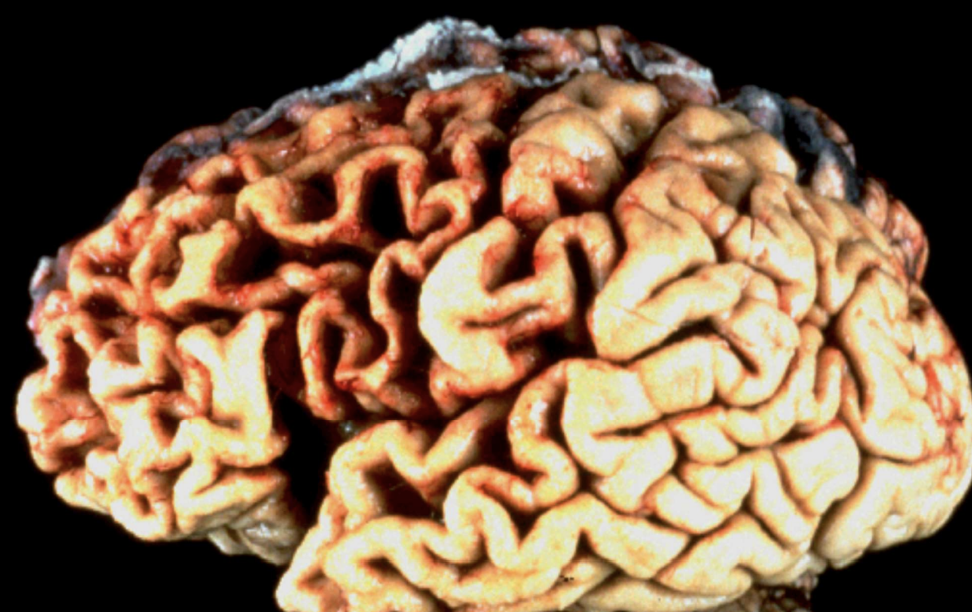
Generalized Cerebral Atrophy
Global brain shrinkage typical of Alzheimer dementia.
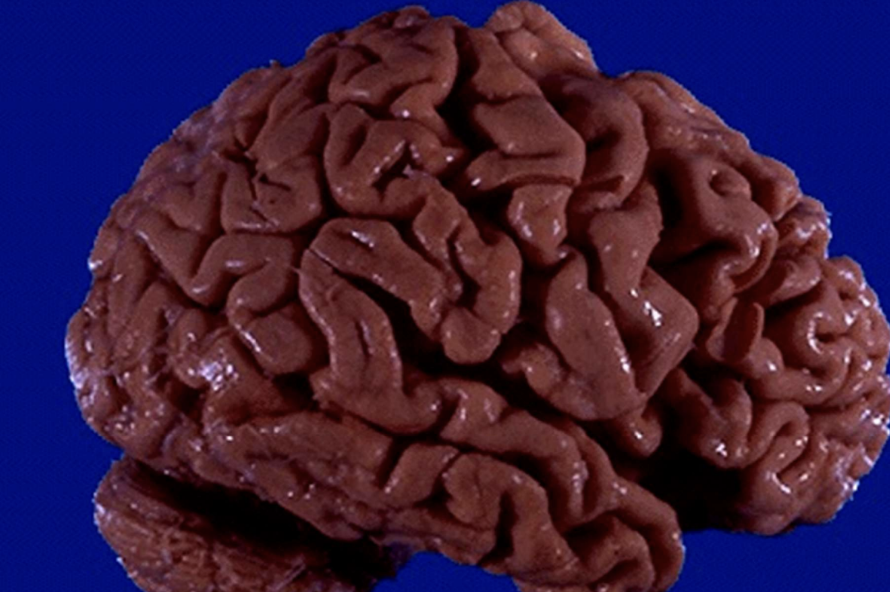
Hypertrophy
Increase in tissue or organ size due to enlargement of individual cells.
Physiologic Hypertrophy
Healthy enlargement from increased demand (e.g., skeletal muscle in weight-lifters, gravid uterus).
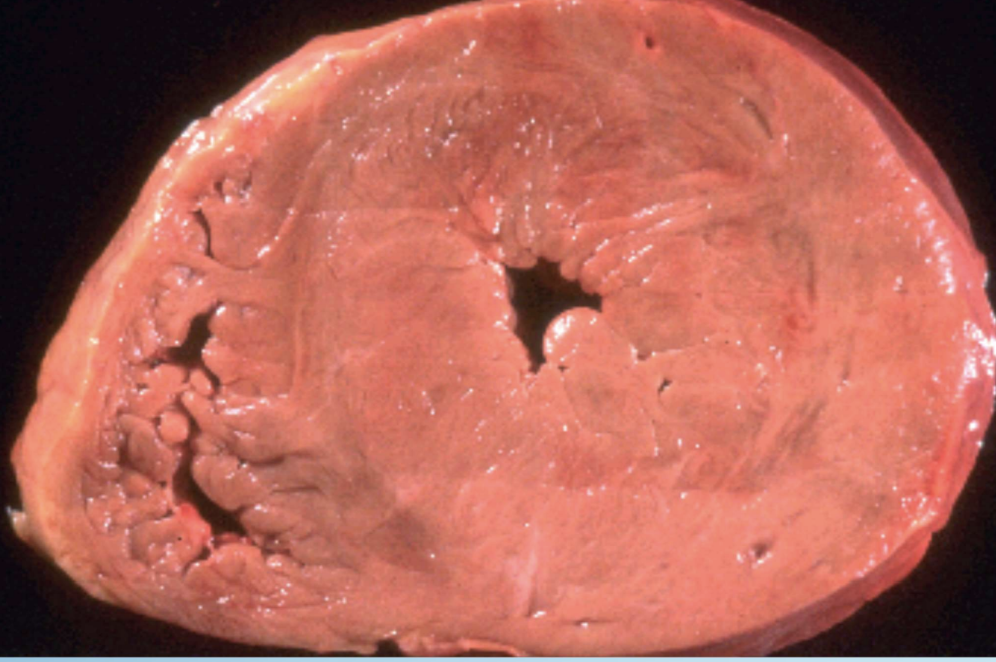
Pathologic Hypertrophy
Maladaptive cell enlargement from disease (e.g., LV hypertrophy in hypertension).
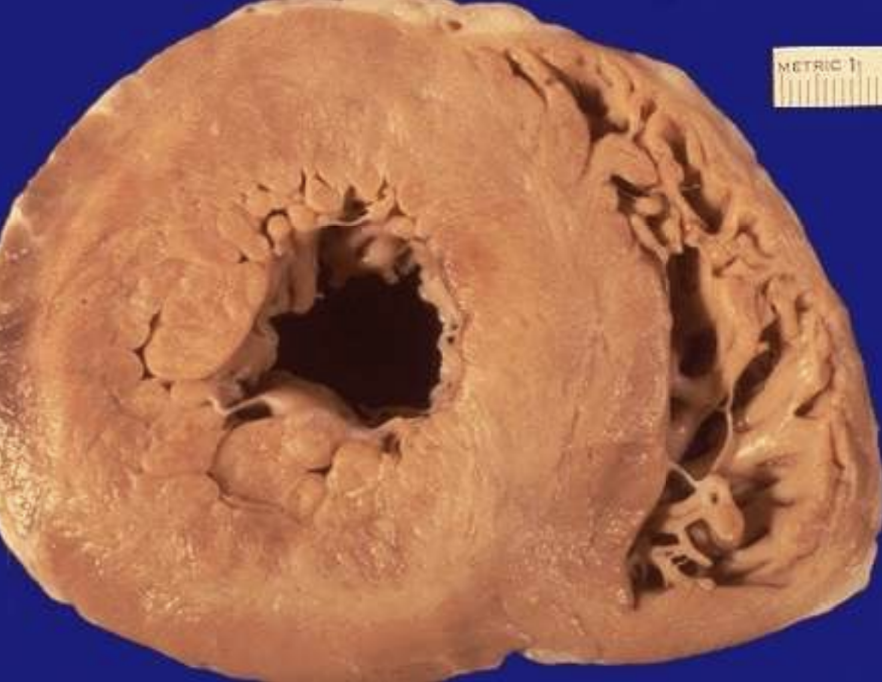

Concentric Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Thickening of LV wall in response to chronic pressure overload, commonly hypertension.
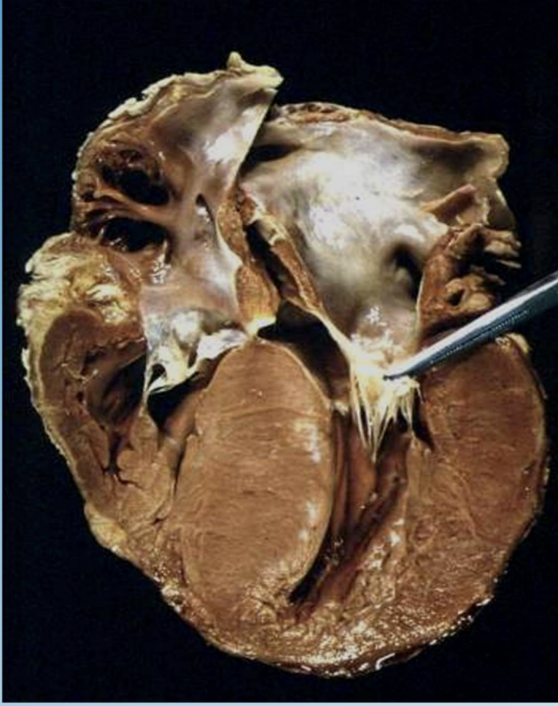
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Genetic myocardial thickening that can obstruct outflow and cause sudden death. (athlete killer)
Hyperplasia
Adaptive increase in the number of cells causing tissue enlargement.
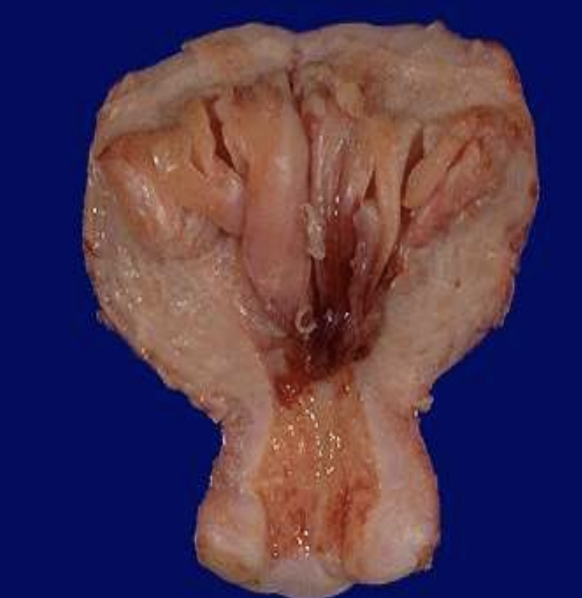
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Excess proliferation of uterine lining driven by unopposed estrogen.
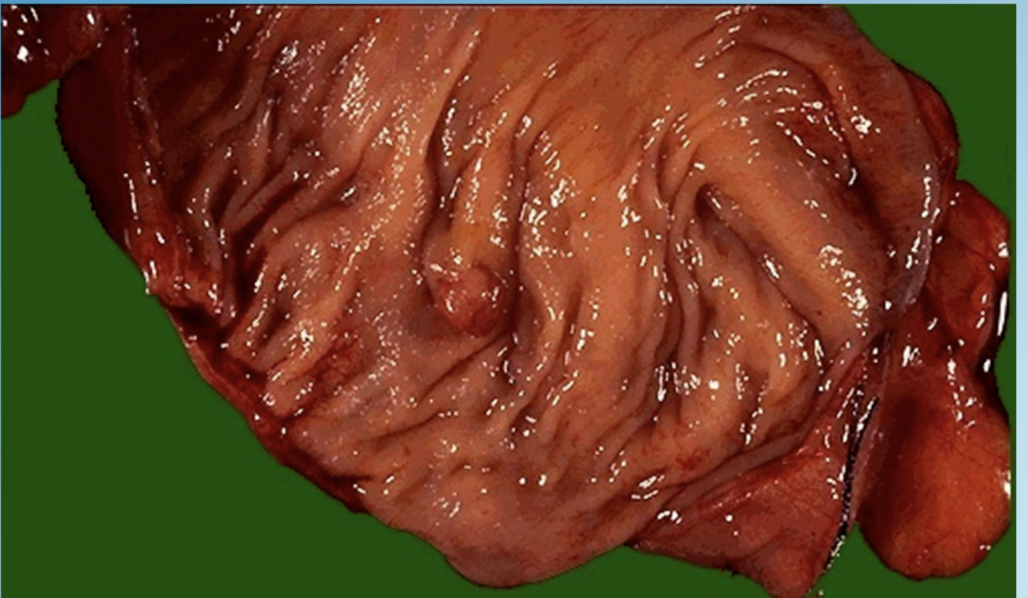
Hyperplastic Polyp
Benign mucosal proliferation in colon or stomach forming a polypoid mass.
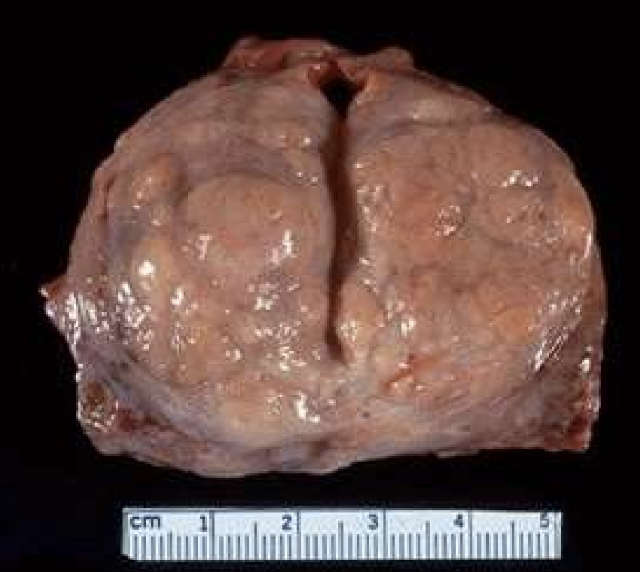
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Combined hyperplasia and hypertrophy of prostate glands and stroma, leading to urinary obstruction.
Hypertrophy with Hyperplasia
Simultaneous cell enlargement and proliferation (e.g., uterine smooth muscle during pregnancy).
Metaplasia
Reversible substitution of one mature cell type by another better suited to the stress of a particular environment.
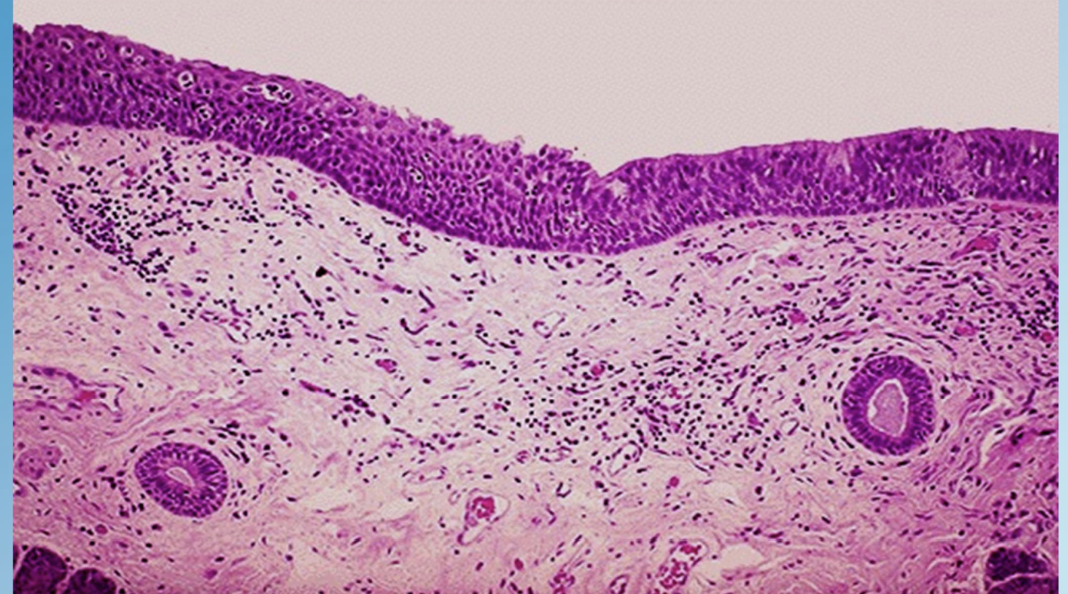
Squamous Metaplasia (Bronchus)
Replacement of ciliated columnar epithelium with stratified squamous cells in smokers.
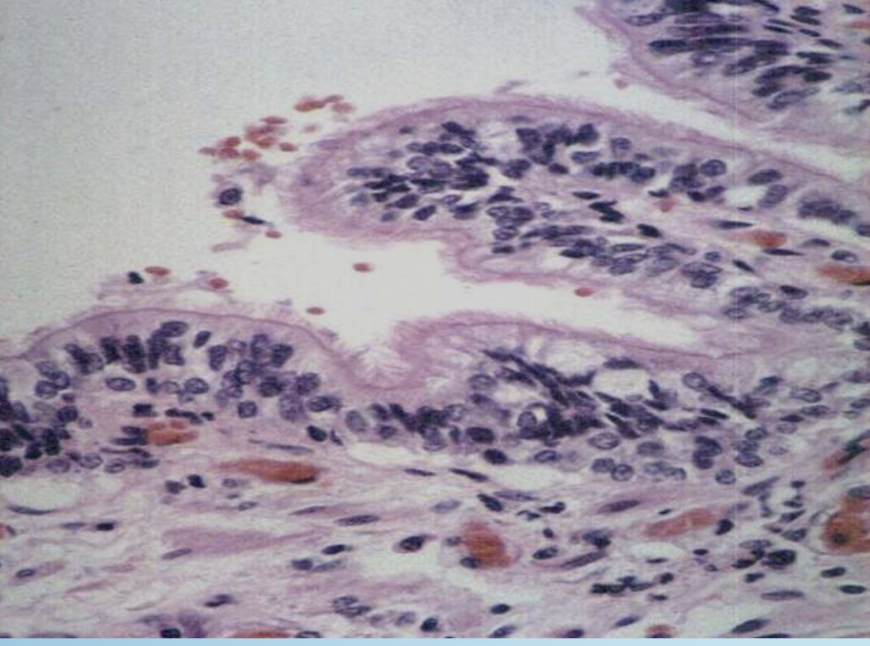
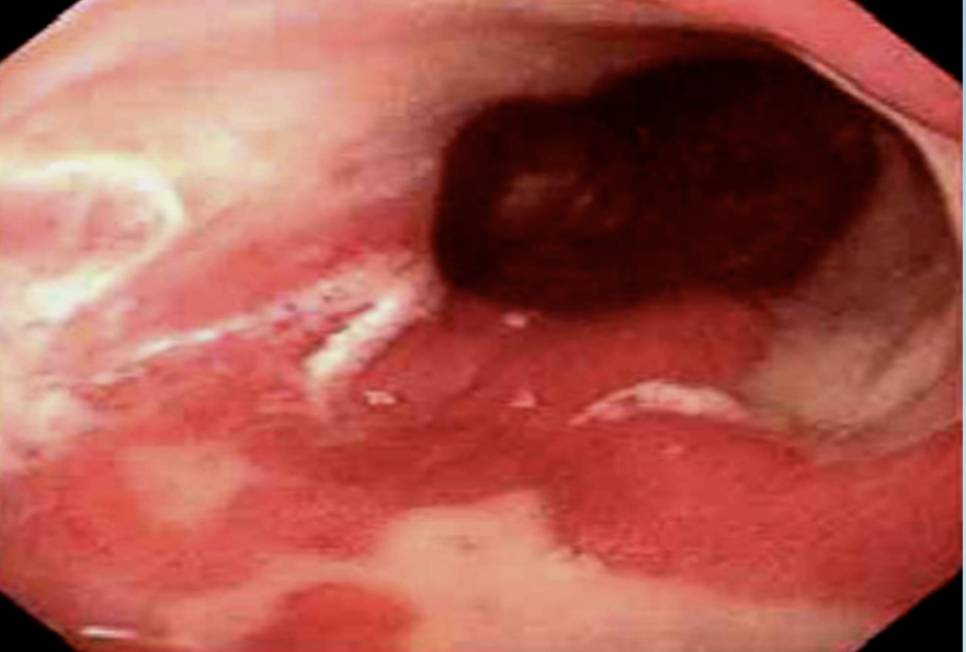
Barrett Esophagus
Glandular (intestinal) metaplasia of distal esophageal squamous epithelium due to chronic reflux.
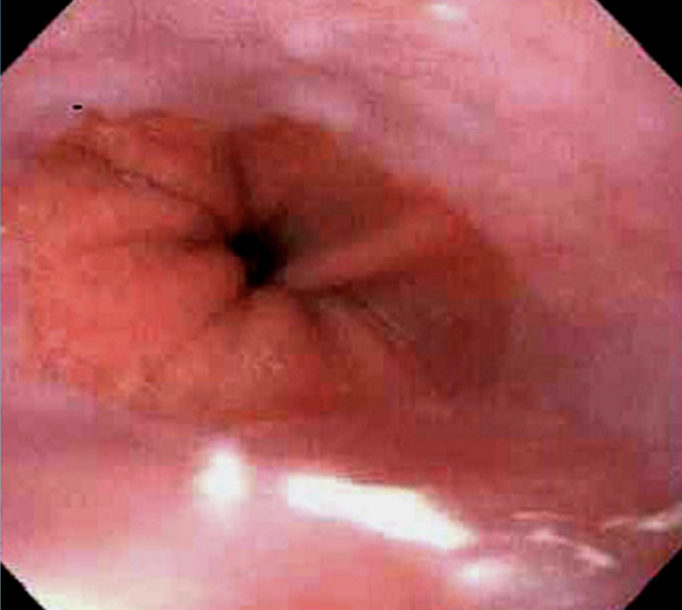
Dysplasia
Disordered, atypical cell growth often arising in metaplastic epithelium with chronic irritation or infection; considered premalignant/precancerous.
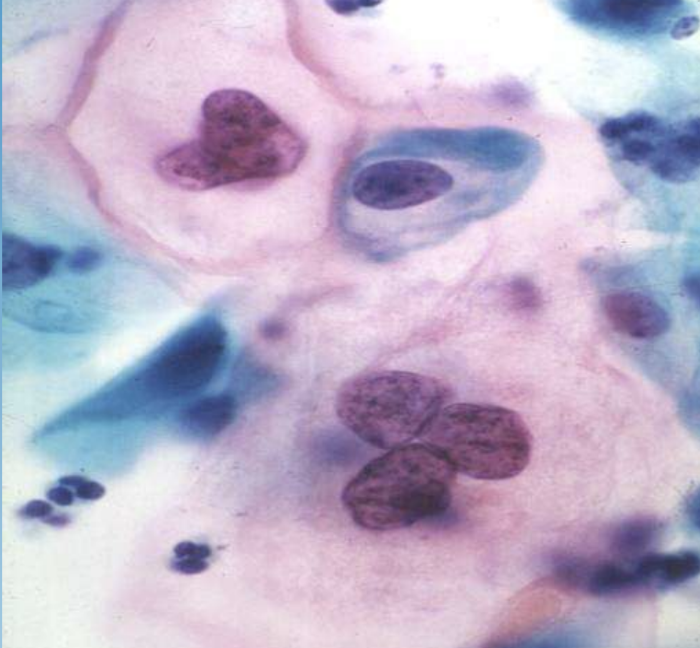
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
Graded dysplasia of cervical squamous epithelium detected by Pap smear; linked to HPV.
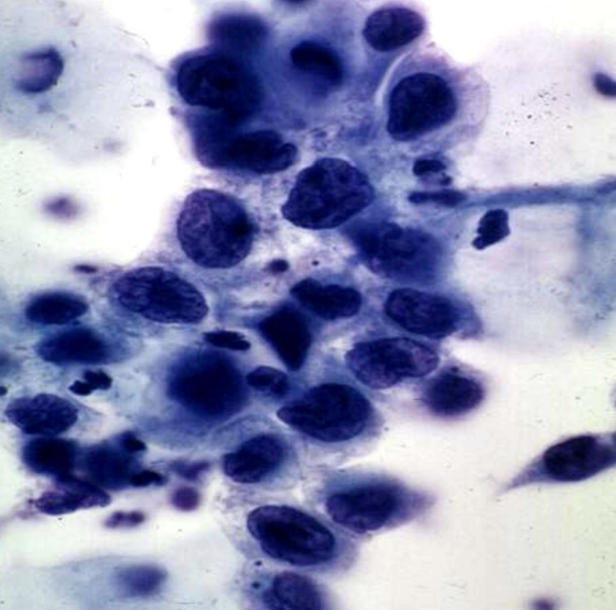
Precancerous Condition
Lesion such as dysplasia that has high risk of progressing to invasive malignancy.
Anaplasia
Undifferentiated, uncontrolled cellular growth—the microscopic hallmark of malignant tumors. Cancer
Microscopic hallmarks of Malignancy
1.marked cellular pleomorphism (variation in size and
shape).
2. The nuclei are irregular and hyperchromatic
3. Extremely high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio
(N/C ratio), about 1:1 instead of 1:4 or 1:6.
4. Large nucleoli present within the nucleus.
5. Large numbers of abnormal mitotic figures.
Other Names for Anaplasia
Malignancy, carcinoma, cancer, neoplasm.
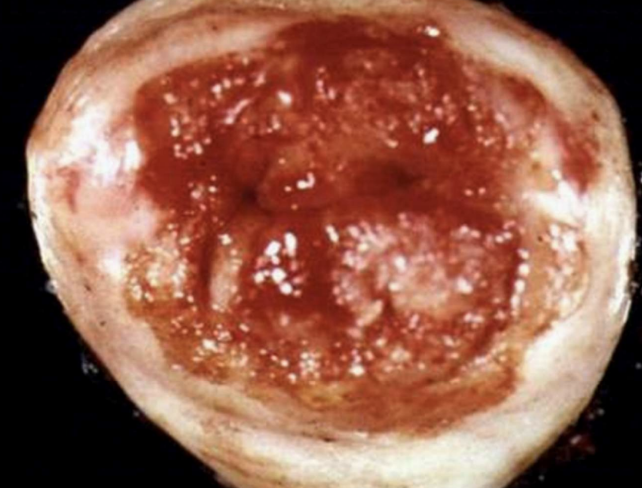
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Malignant tumor of squamous epithelium, e.g., cervix or lung.
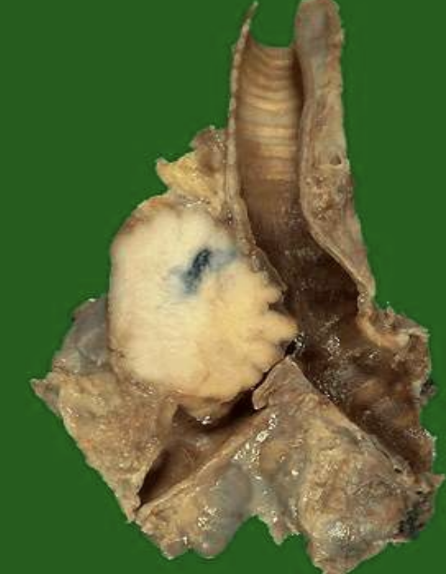
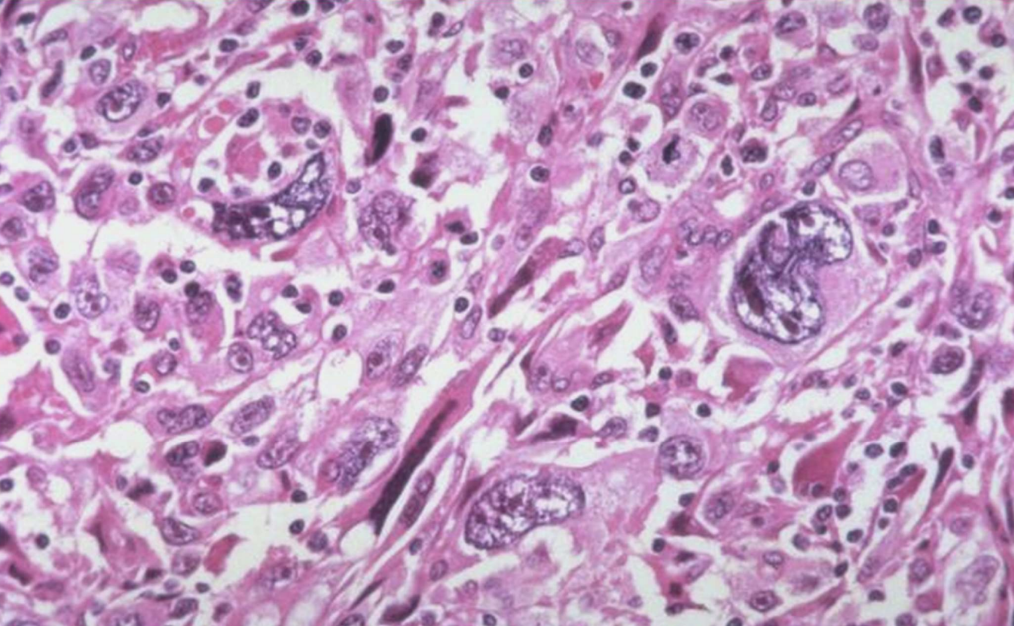
Cellular Pleomorphism
Variation in size and shape of cells and nuclei; key feature of anaplasia.
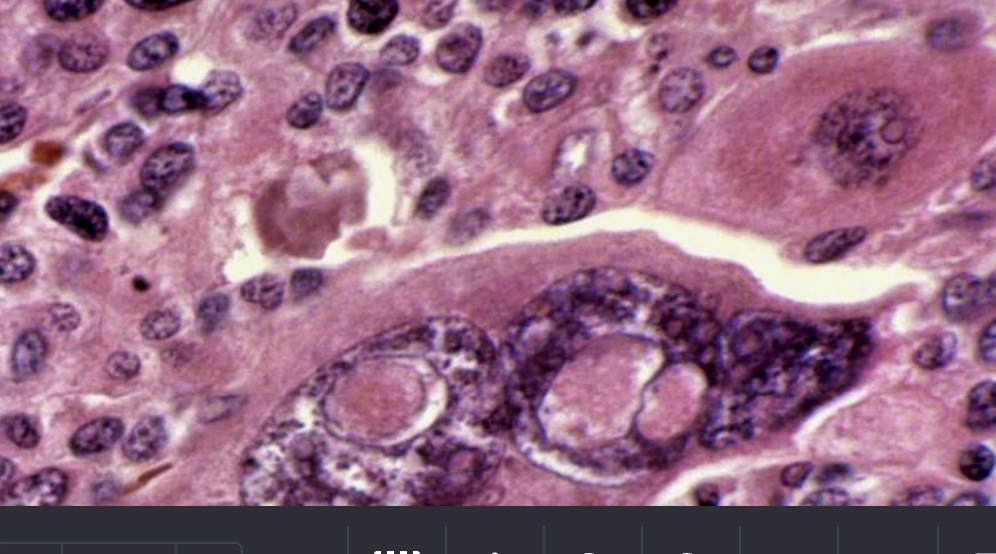
Hyperchromatic Nuclei
Dark-staining, irregular nuclei characteristic of malignant cells.
High Nuclear-to-Cytoplasmic Ratio
Approximately 1:1 N/C ratio seen in anaplastic cells (normal ~1:4–1:6).
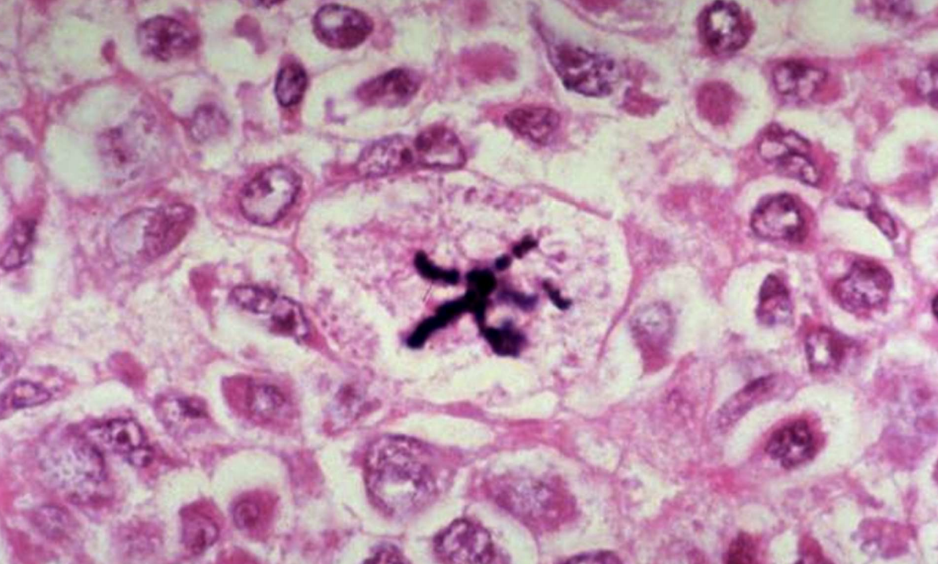
Abnormal Mitotic Figures
Atypical or numerous mitoses indicating uncontrolled proliferation.
Necrosis
Death of cells or tissues within a living organism, usually accompanied by inflammation.
Autolysis
Self-digestion of cells occurring after organismal death without inflammation.
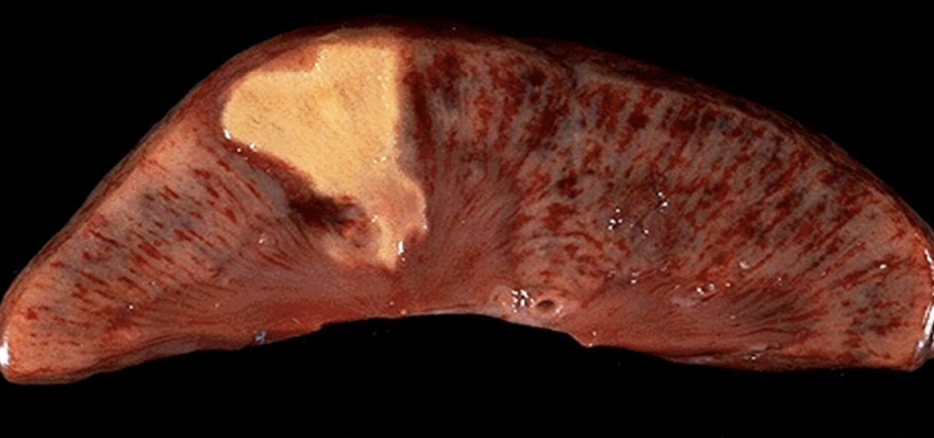
Coagulative Necrosis
Preservation of tissue architecture with protein denaturation; typical of ischemic/anoxic injury to solid organs. Most common necrosis
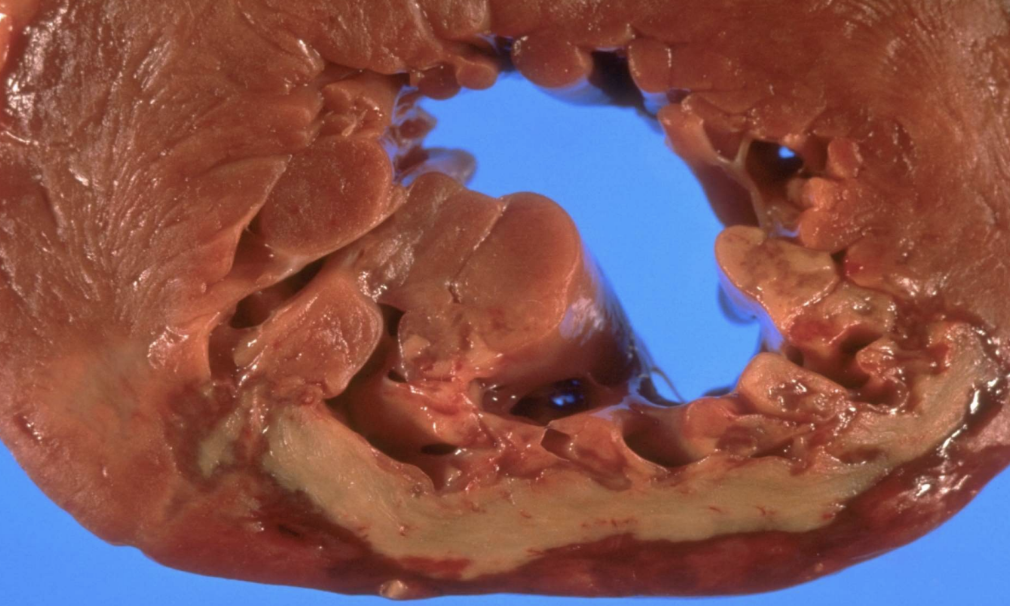
Myocardial Infarction
Acute heart muscle ischemia leading to coagulative necrosis.
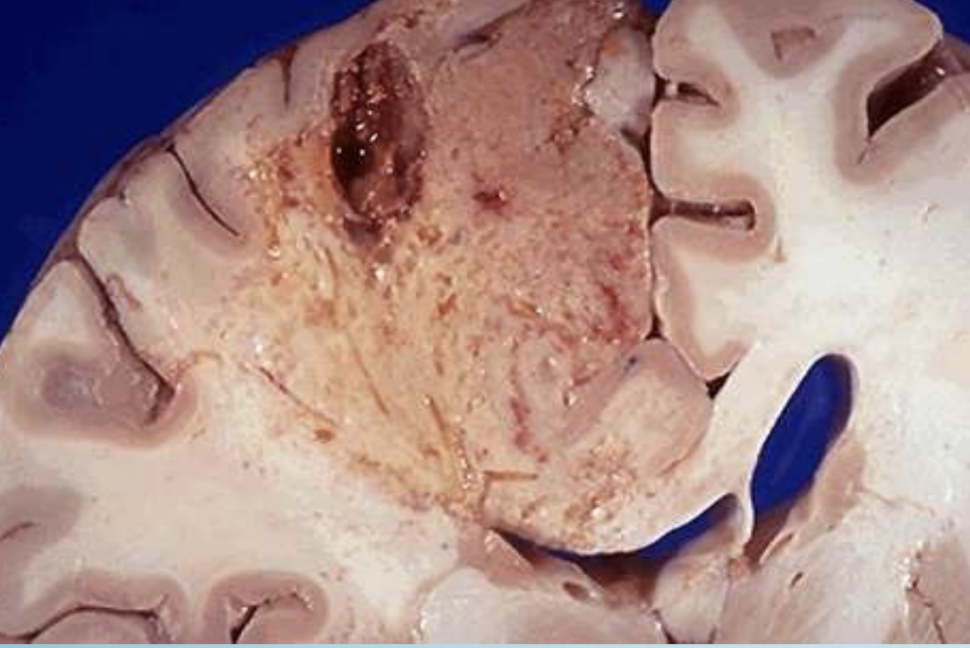
Liquefactive Necrosis
Enzymatic digestion converting tissue to liquid viscous mass; classic in brain infarcts and abscesses. Soft, gel-like
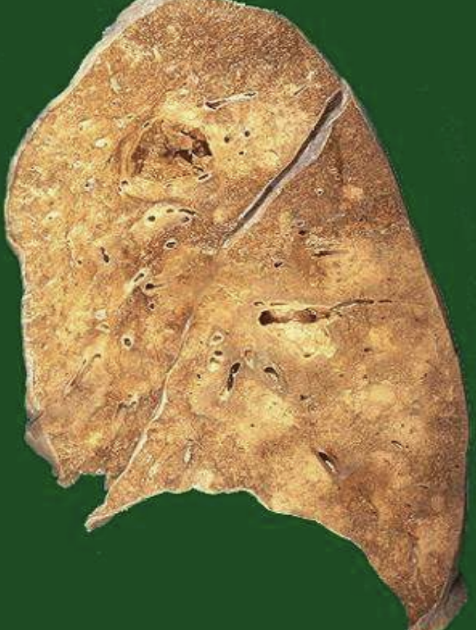

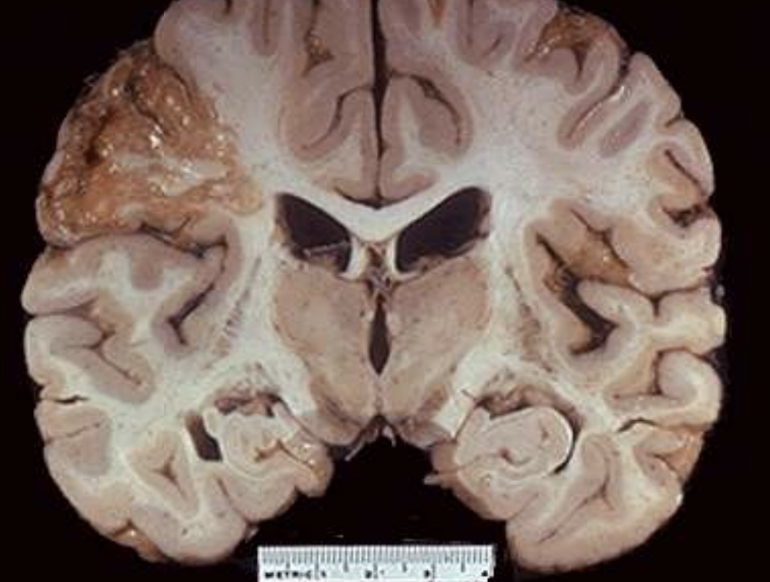
Brain Infarct
Stroke lesion characterized microscopically by liquefactive necrosis.
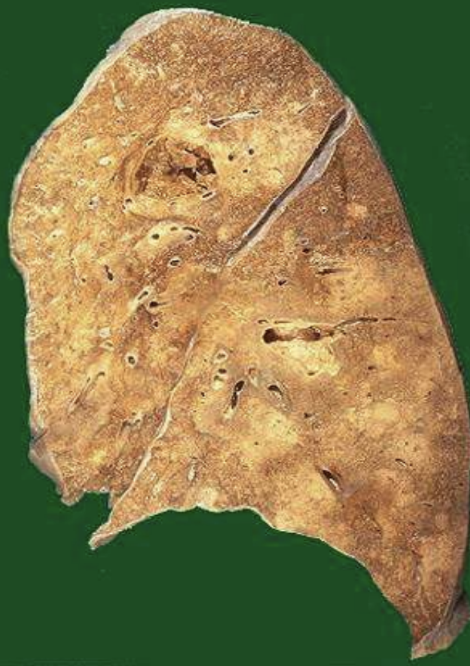

Lung Abscess
Localized pus-filled cavity from infection producing liquefactive necrosis.
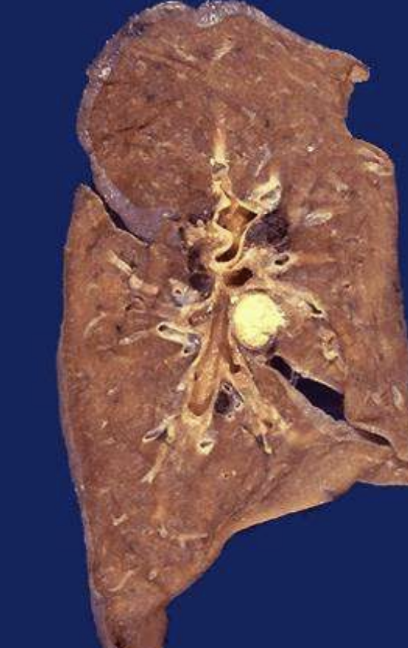
Caseous Necrosis
Cheese-like form of coagulative necrosis seen within granulomas of tuberculosis and some fungi.
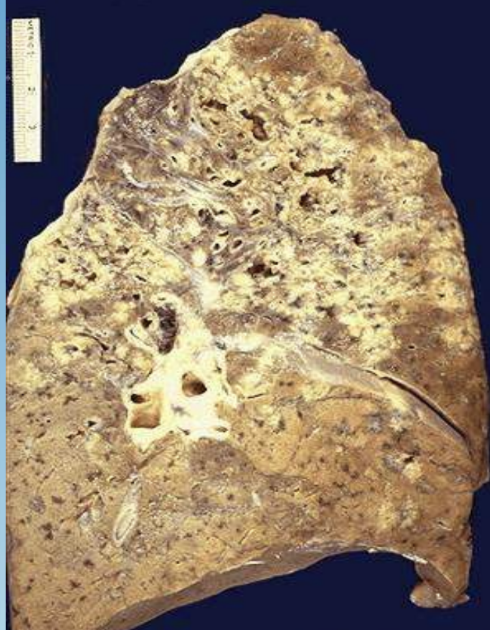
Ghon Complex
Primary TB lesion with caseous necrosis in lung and lymph node.
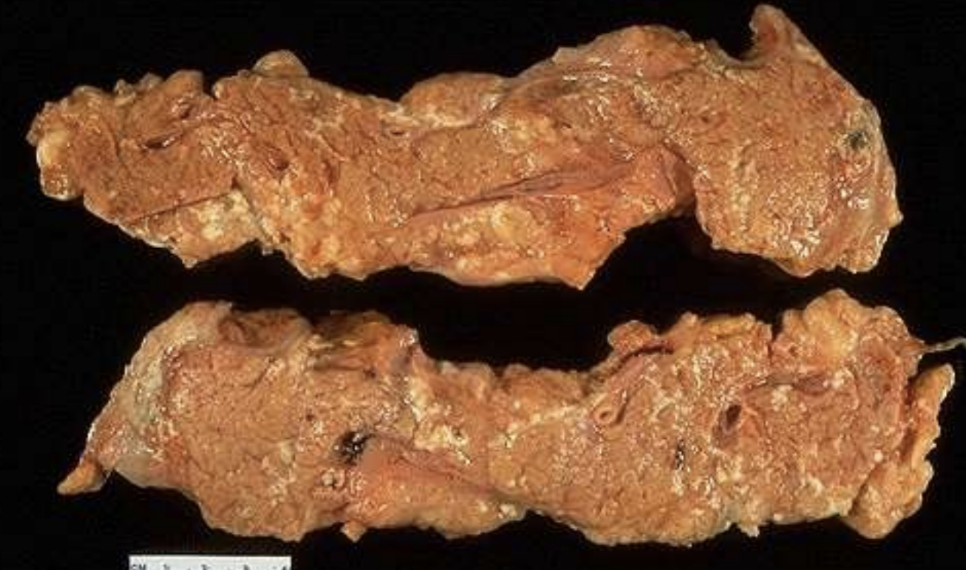
Fat Necrosis
Necrosis of adipose tissue by lipolytic enzymes with soap (calcium) formation; e.g., pancreatitis.
Acute Pancreatitis
Inflammation causing release of enzymes that produce peripancreatic fat necrosis.
Gangrene
Necrosis of tissue with superimposed bacterial infection (wet) or mummification (dry).
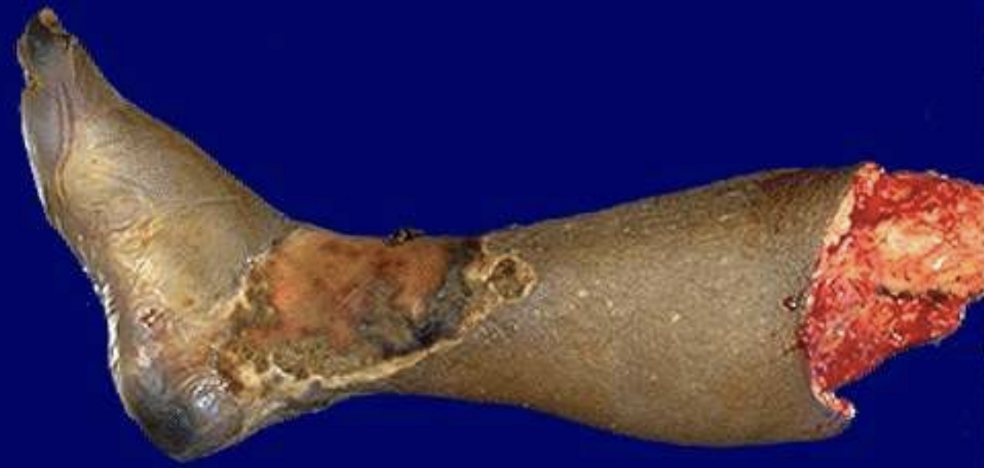
Wet Gangrene
Coagulative necrosis infected and liquefied by bacteria, common in diabetic ulcers or bowel infarct.
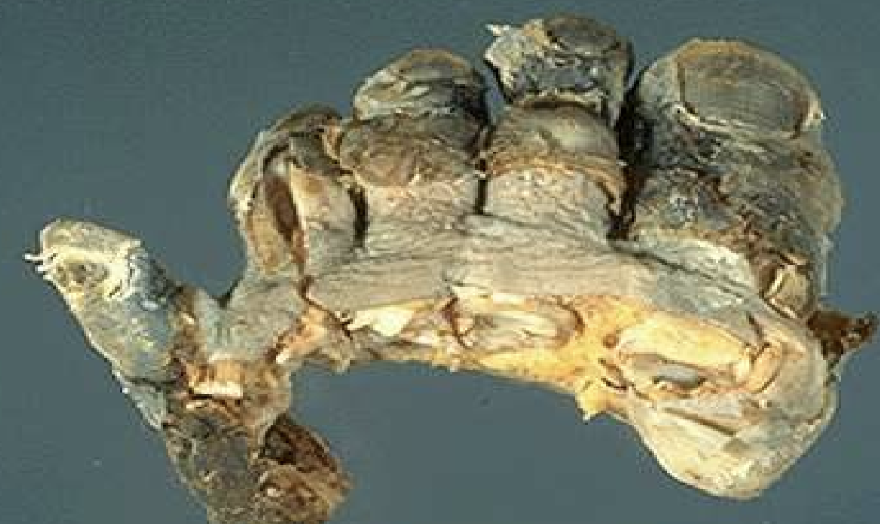

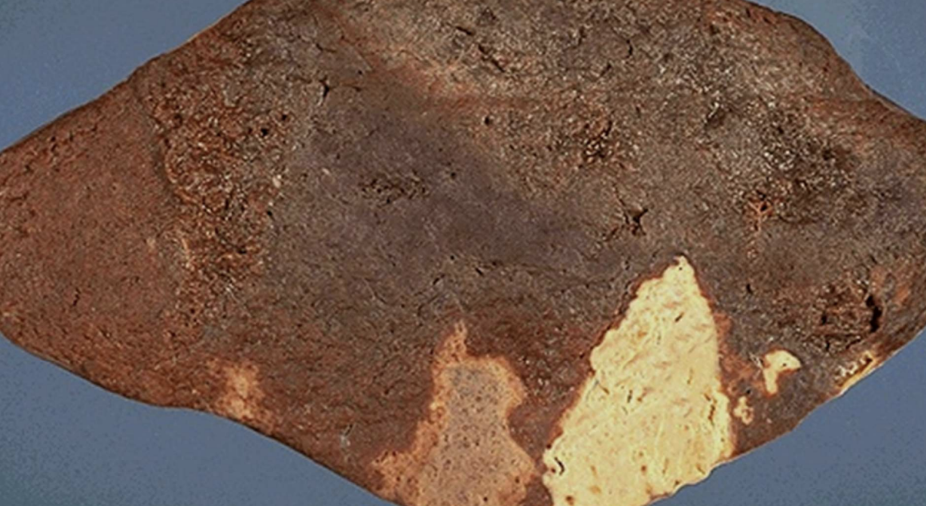
Dry Gangrene
Desiccated, black, mummified necrotic tissue usually from ischemia or frostbite.
Dystrophic Calcification
Deposition of calcium salts in necrotic or damaged tissues despite normal serum calcium.
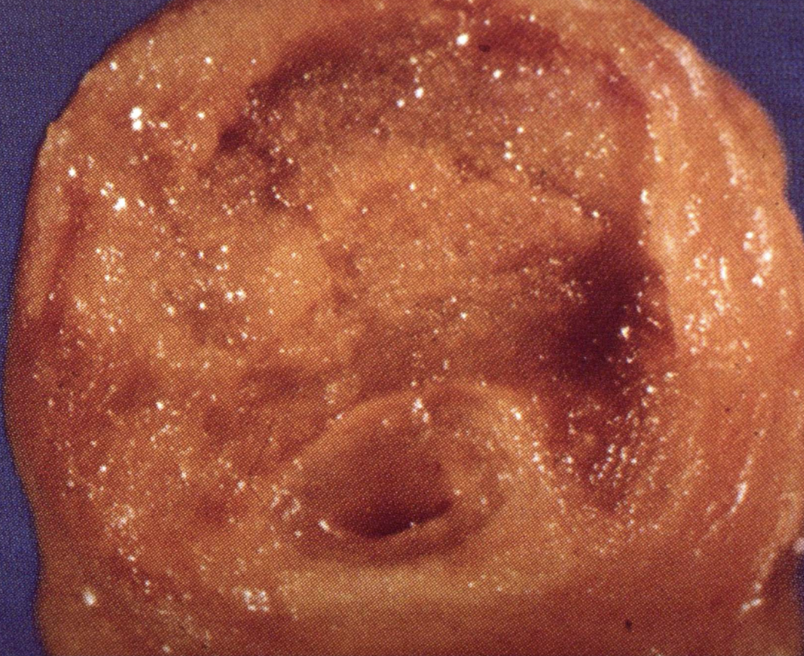

Coronary Artery Calcification
Dystrophic calcification within atherosclerotic plaques that narrows vessels.
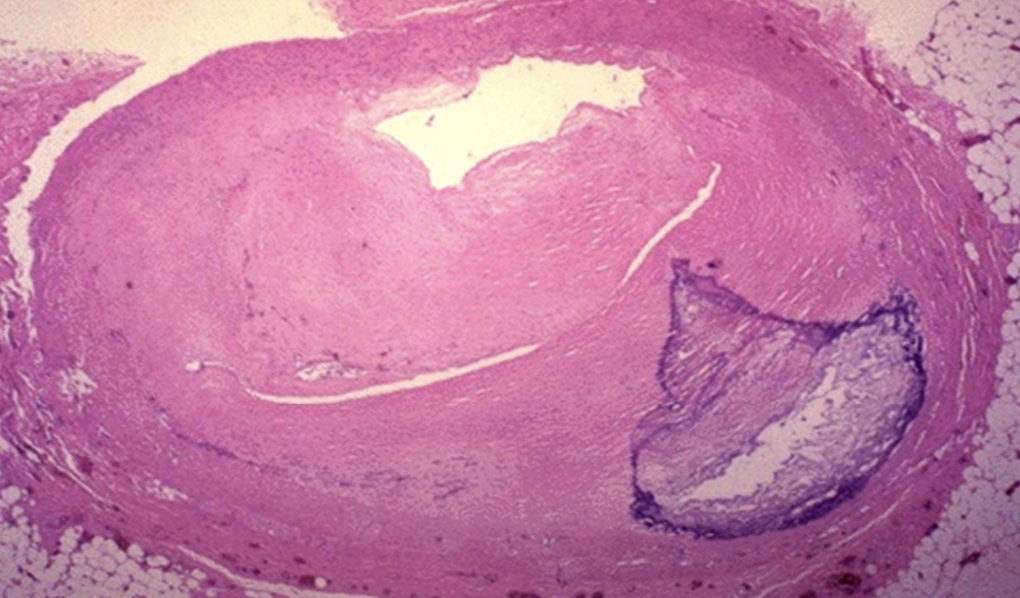
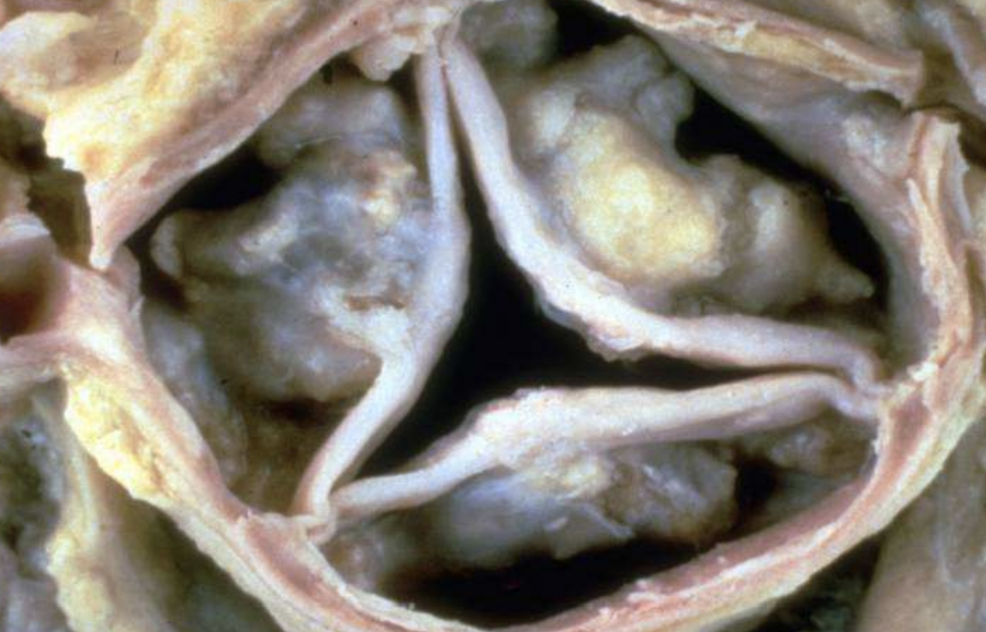
Calcified Aortic/Mitral Stenosis
Valve cusps hardened by dystrophic calcium, impeding blood flow.
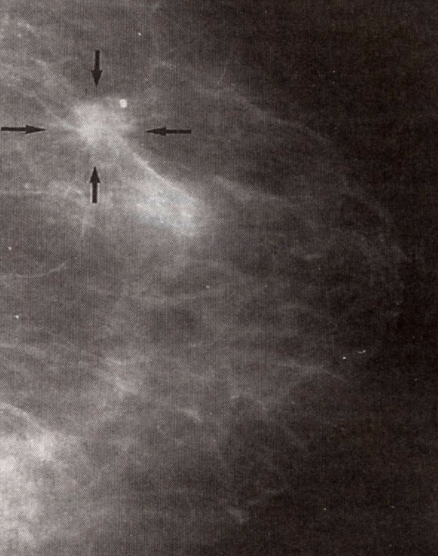
Breast Cancer Microcalcifications
Dystrophic calcium deposits around tumor detectable by mammography.
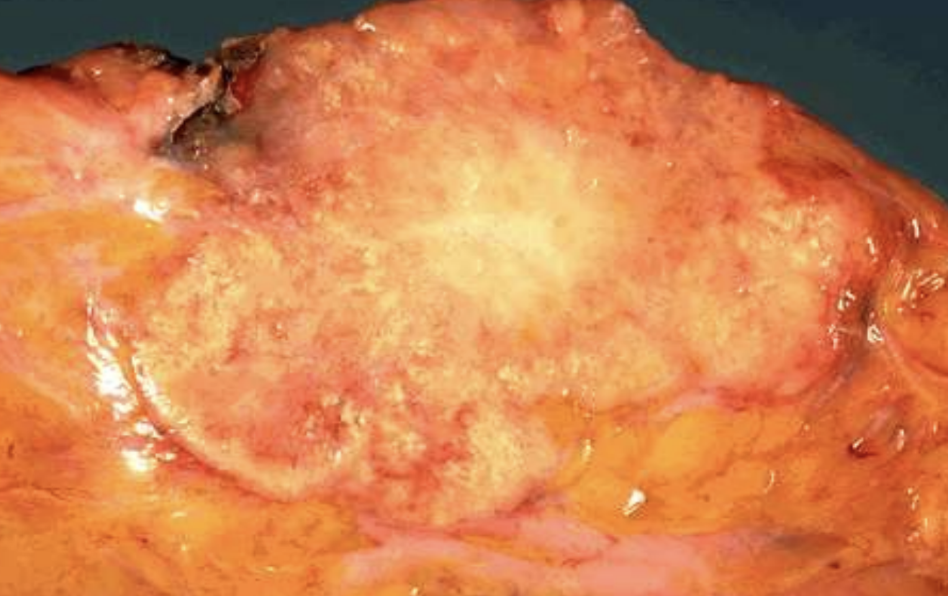
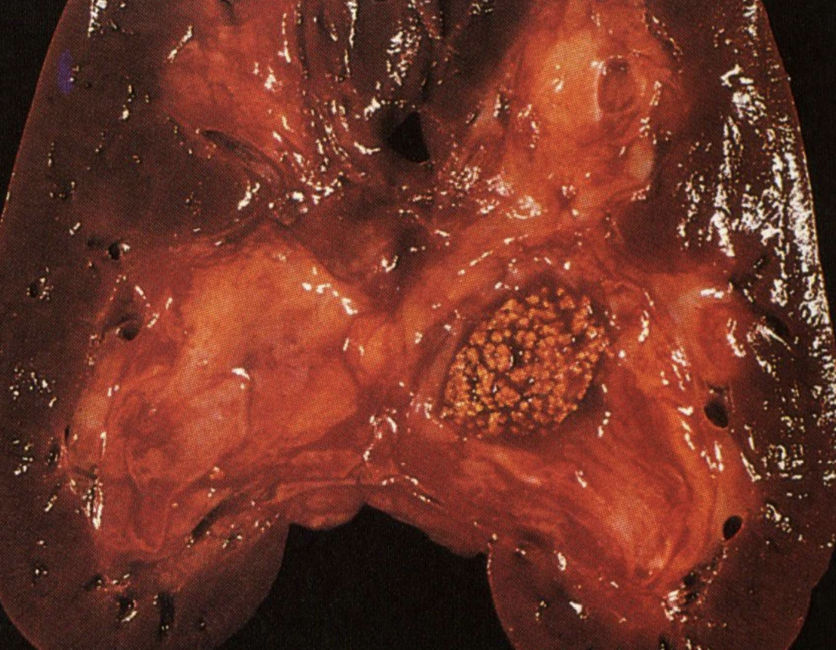
Metastatic Calcification
Calcium deposition in normal tissues due to hypercalcemia and disturbed metabolism.
Hyperparathyroidism
Endocrine disorder elevating serum calcium, leading to metastatic calcifications.
Vitamin D Toxicity
Excess vitamin D causing hypercalcemia and metastatic calcification.
Chronic Renal Failure (Calcification)
Kidney failure leading to phosphate retention and secondary hyperparathyroidism with metastatic calcium deposition.
Calcium Oxalate Stones
Crystalline concretions in kidney, bladder, or gallbladder formed via metastatic calcification processes.
Adaptive vs Maladaptive Response
Physiologic adaptations aid survival and are reversible; pathologic changes may lead to dysfunction or cancer.
Chronic Irritation
Persistent noxious stimulus that can drive metaplasia and progress to dysplasia.
Premalignant Lesion
Altered tissue such as dysplasia that carries significant risk of becoming invasive cancer.
Marked Pleomorphism (Microscopy)
Pronounced variability in cell and nuclear morphology diagnostic of anaplasia.
Living vs Post-mortem Cell Death
Necrosis occurs in living tissue with inflammation, while autolysis occurs after death without inflammation.