Anatomy 2320 - Articulations: General Features
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Arthrology
The study of joints
Fibrous Joint
Joints that lack a joint cavity and are held together by dense regular (fibrous) connective tissue
cartilaginous joints
Joints that lack a joint cavity and are joined together by cartilage
Synovial joints
Joints with a joint cavity that seperates the articulating surfaces
Synarthroses
Term for immovable joints
Amphiarthroses
Term for slightly moveable joints
Diarthroses
Term for freely moveable joints
Psuedoarthroses
False joints that occur when a fractured long bone heals in two separate bones
Fibrous joints
Which joints are usually immoveable or slightly moveable
Gomphoses
peg-in-socket fibrous joint, only found where teeth articulate with mandible/maxilla
Periodontal
A tooth is held in place by _____ ligaments
Synarthrotic
functional classification for teeth in their socket
Fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
What are the three structural classifications of joints?
Synarthroses, diarthroses, amphiarthroses
What are the three functional classifications of joints?
Sutures
Immoveable fibrous joints found only between certain bones of the skull
Synostoses
Classification for completely ossified sutures
Syndesmoses
fibrous joints in which articulating bones are joined by long strands of dense regular connective tissue (interosseous membrane)
Amphiarthroses
What functional classification is given to syndesmoses?
Symphyses and Syncondroses
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints?
Synchondroses
Type of cartilaginous joint, joined by hyaline cartilage and are present on the epiphyseal growth plates in children and costochondral articulations
Symphyses
Type of cartilaginous joint that has a pad of fibrocartilage between the articulating bones
Amphiarthrosis
What is the functional classification of symphyses?
Synarthrotic
Functional classification of synchondroses
Symphyses
What type of cartilaginous joint is present between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae and the pubic symphesis?
Marfan's Syndrome
Disease that leads to hypermobile joints, those affected by it tend to be unusually tall with long limbs and long thin fingers
Fibrillin-1, FBN1
Marfan's syndrome is caused by the misfolding of what protein? What gene is it coded by?
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-Beta)
Fibrillin-1, misfolded in Marfan's Syndrome, contributes to cell signaling activity by binding to...
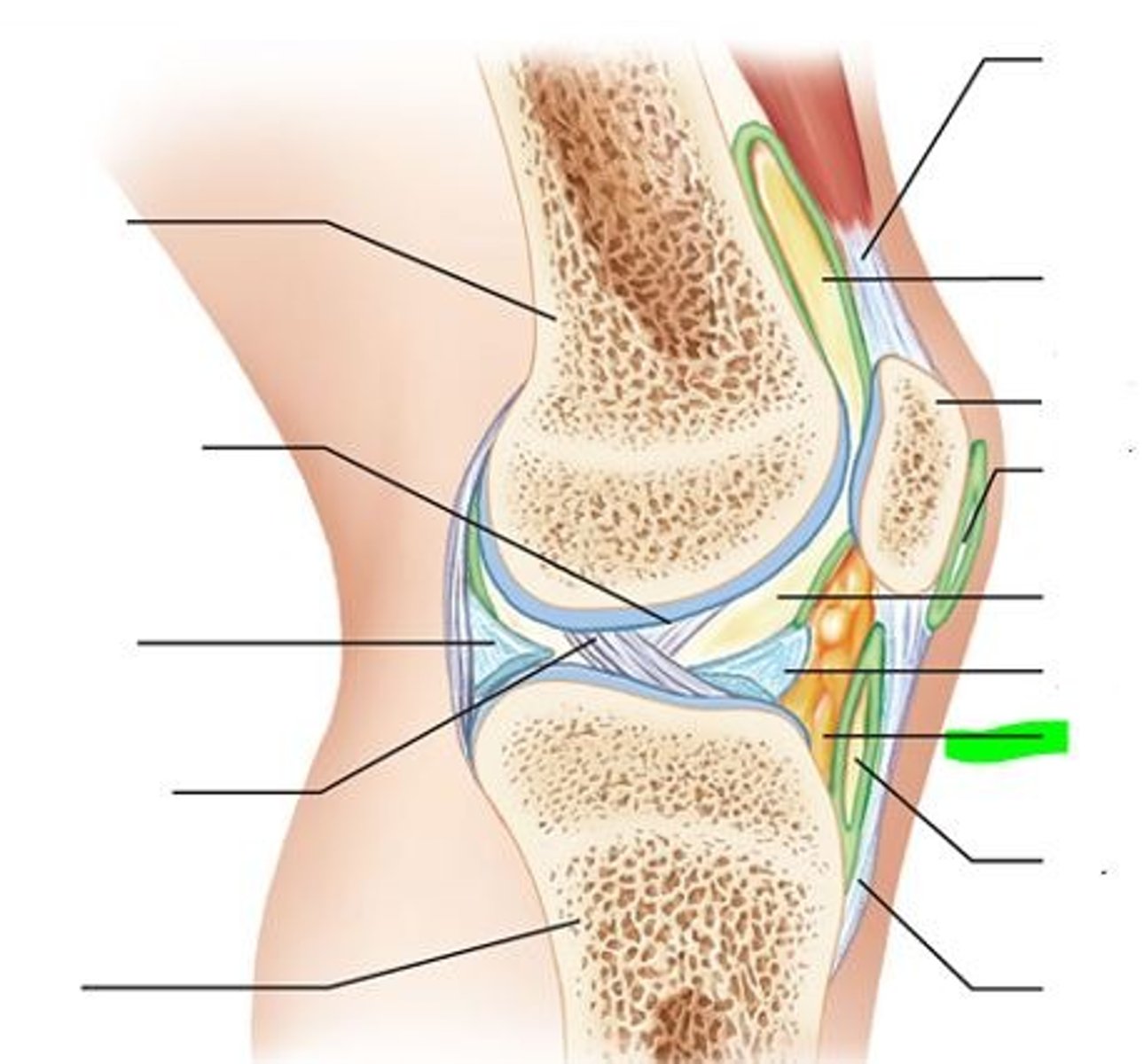
Articular capsule
Name this part of a joint capsule, surrounds synovial joint
Fibrous layer of joint capsule
Name the part of a joint capsule labeled "D"
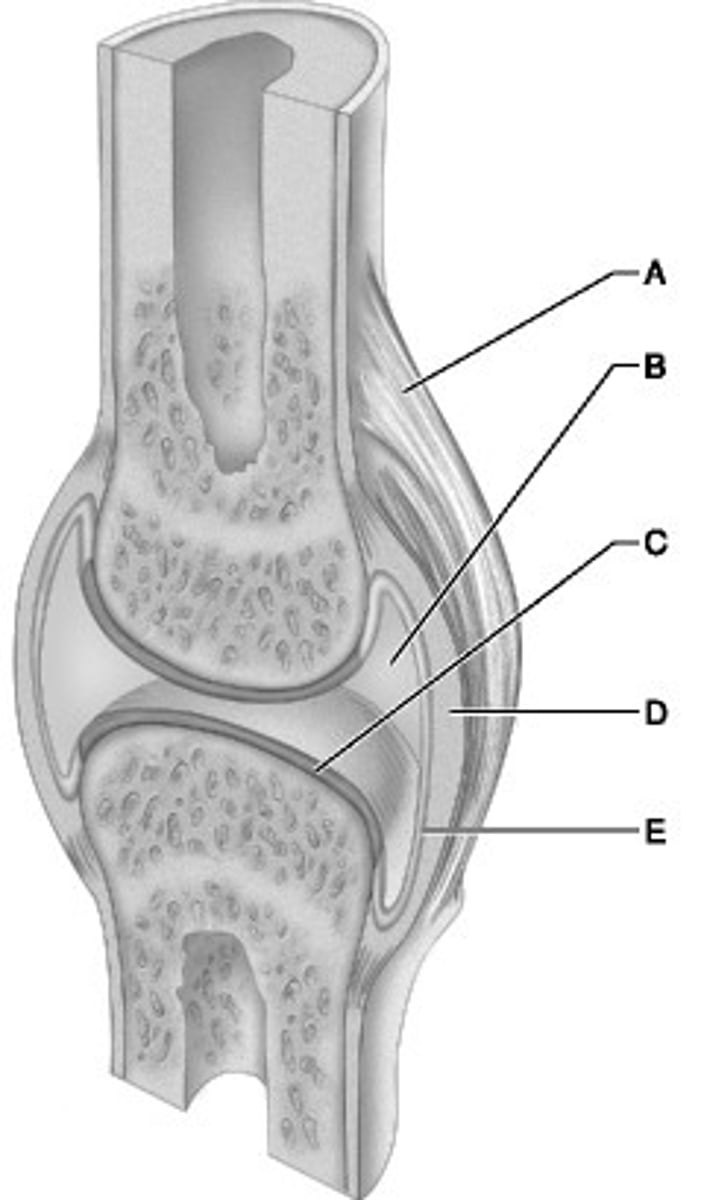
Synovial membrane
Name this part of a joint capsule
Synovial fluid
What nourishes and removes waste from the chondrocytes in the articular cartilage?
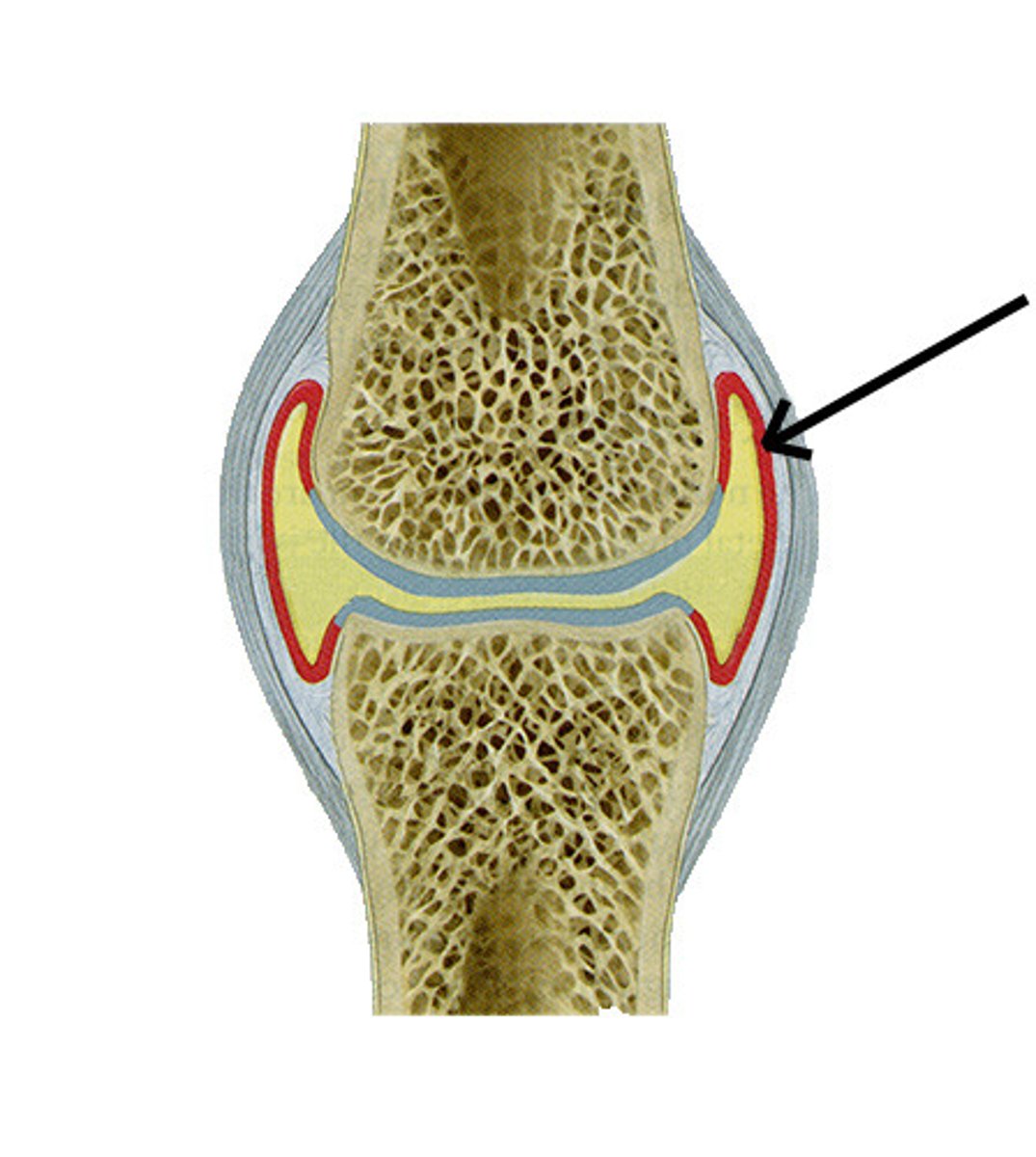
Hyaline articular cartilage
Layer of cartilage that reduces friction in a joint and acts as a cushion to absorb compression
Ligament
Connects bone to bone
Tendon
Connects bone to muscle
Bursae
Fibrous, saclike structures containing synovial fluid
and lined by a synovial membrane
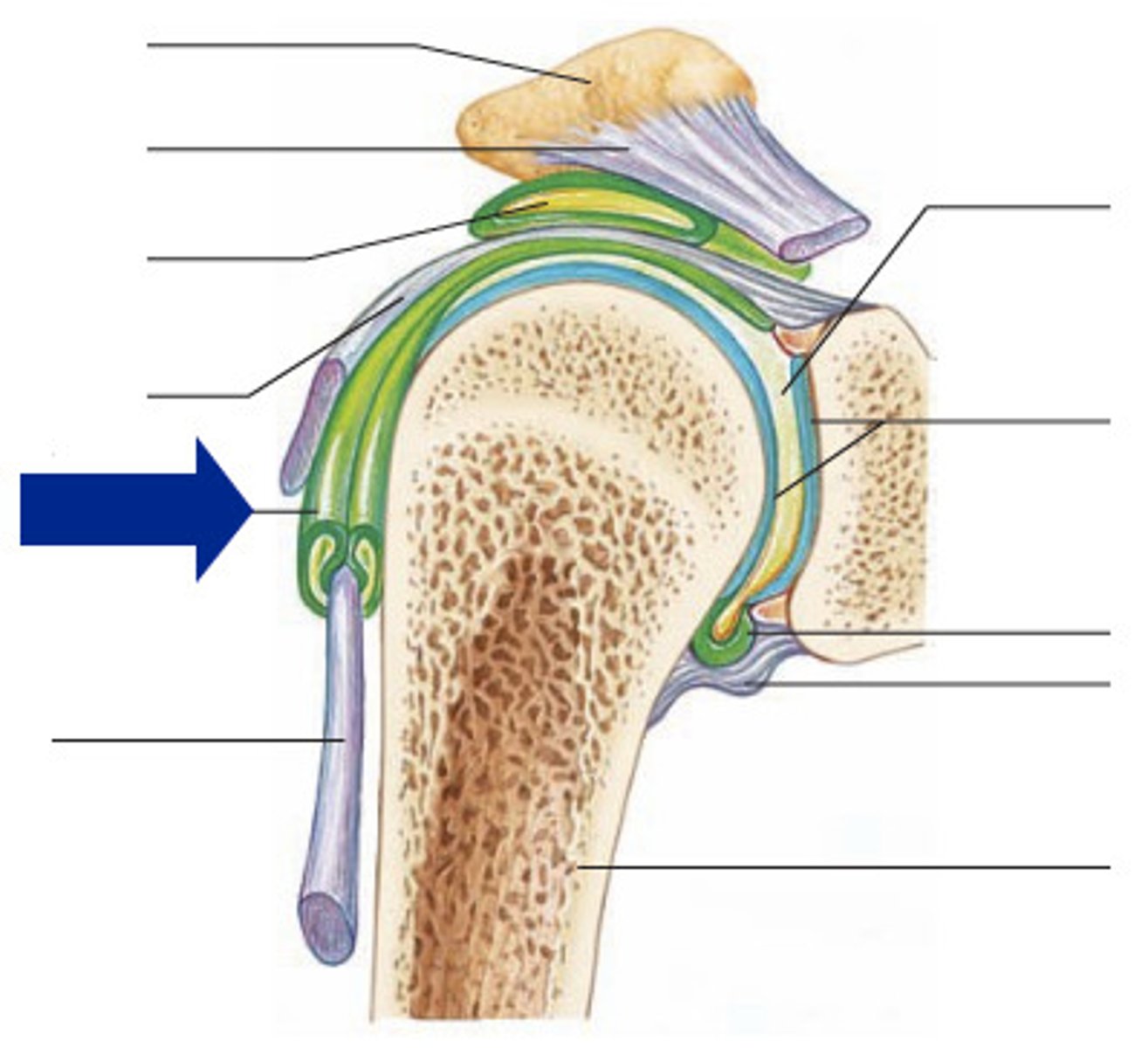
Tendon sheaths
Modified, elongated bursae that wrap around tendons where there may be excessive friction
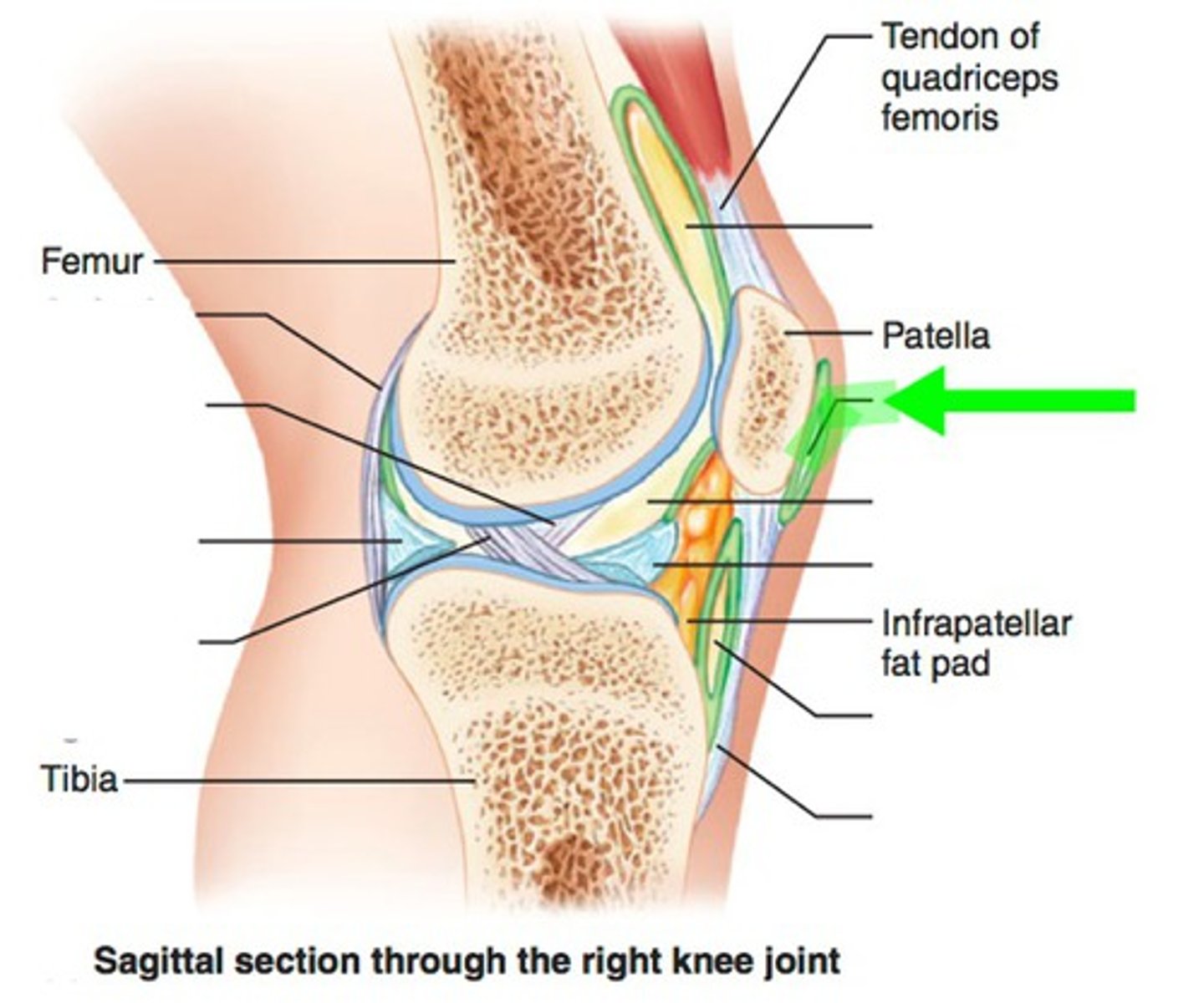
Fat pads
Distributed along the periphery of synovial joints, act as packing material and provide protection
Uniaxial
Term for when a bone moves in just one place or axis
Biaxial
Term for when a bone moves in two planes or axes
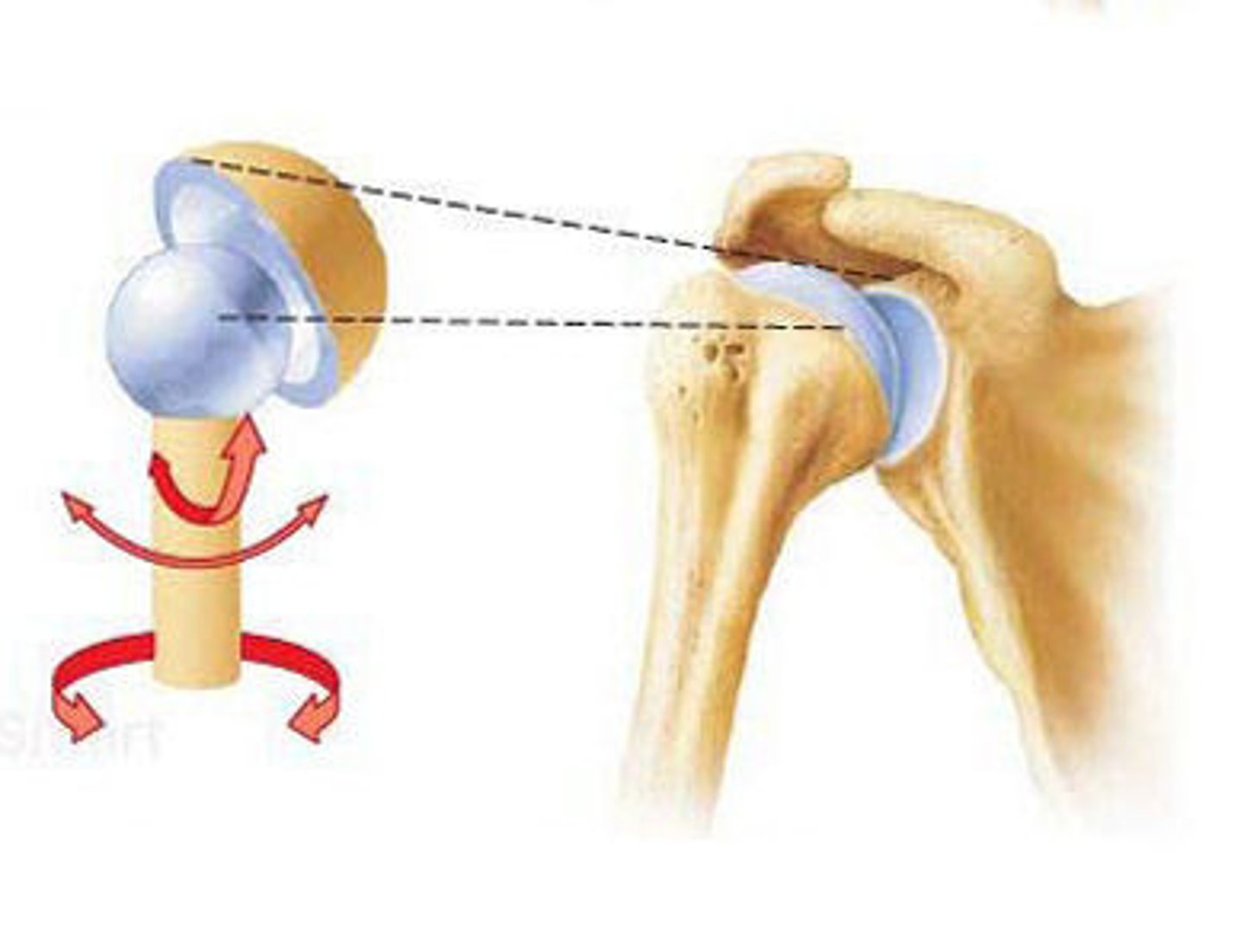
Multiaxial
Term for when a bone moves in multiple planes (only ball and socket)
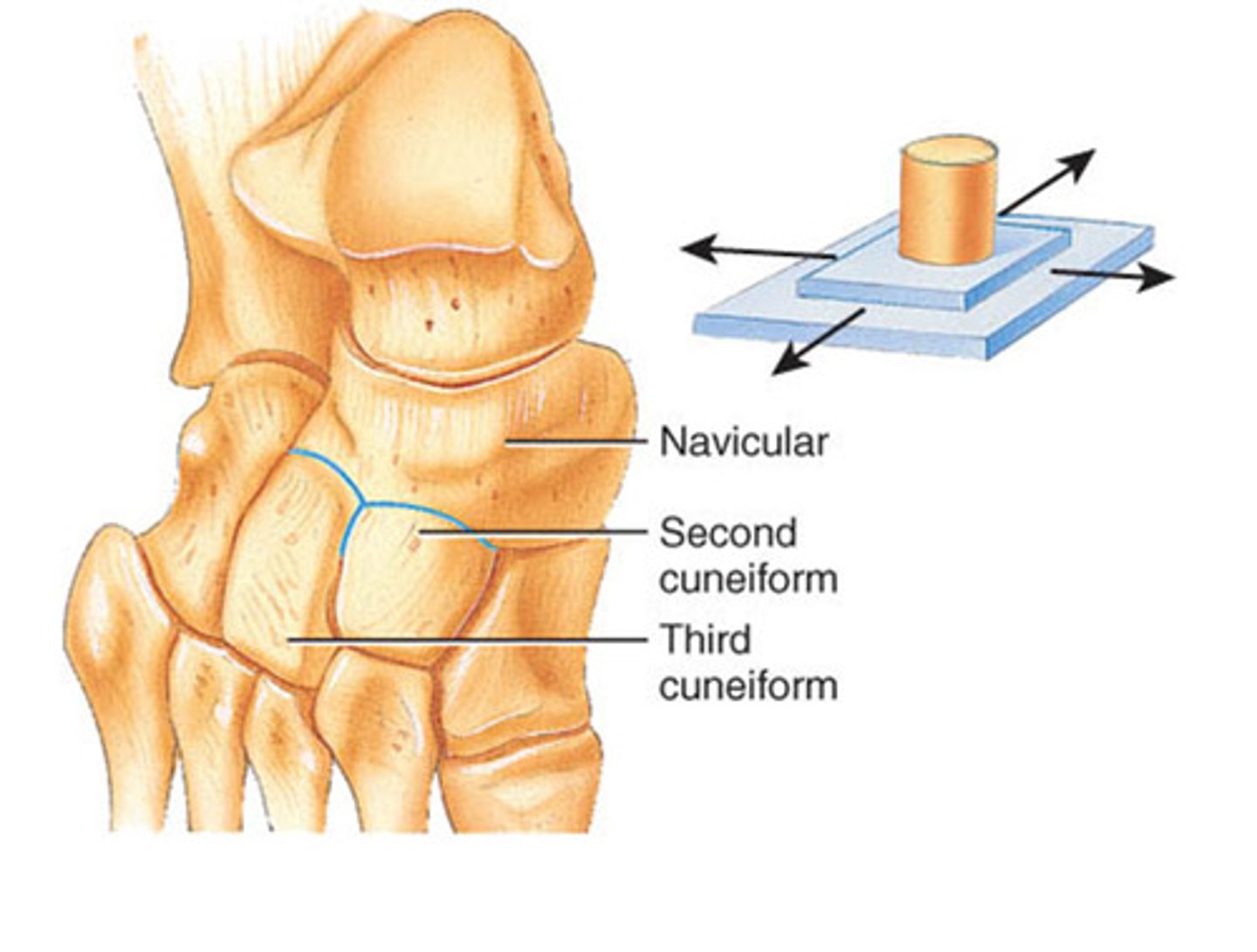
Planar
Another word for gliding joint (can be used interchangeably)
Planar (gliding)
What is the least moveable type of diarthroses?
Uniaxial
What type of movement do planar joints allow?
Intercarpal/intertarsal, joints between articulating processes of adjacent vertebrae, sacroiliac joint, acromioclavicular
What are the examples of planar joints?
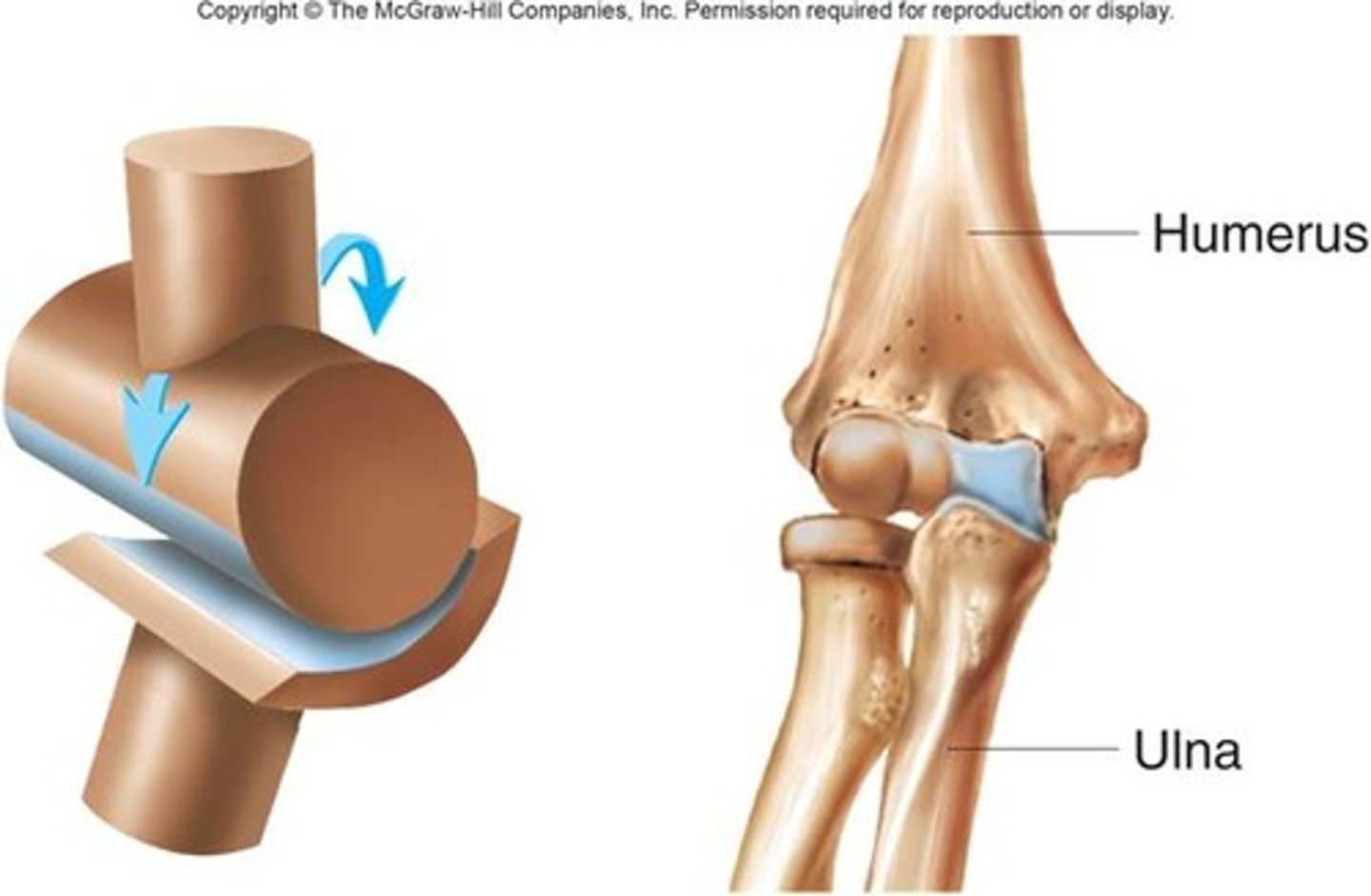
Uniaxial
What type of movement do hinge joints allow?
Humeroulnar articulation, tibiofemoral joint, talocrural joint, interphalangeal joint, metacarpophalangeal joint
What are the examples of hinge joints
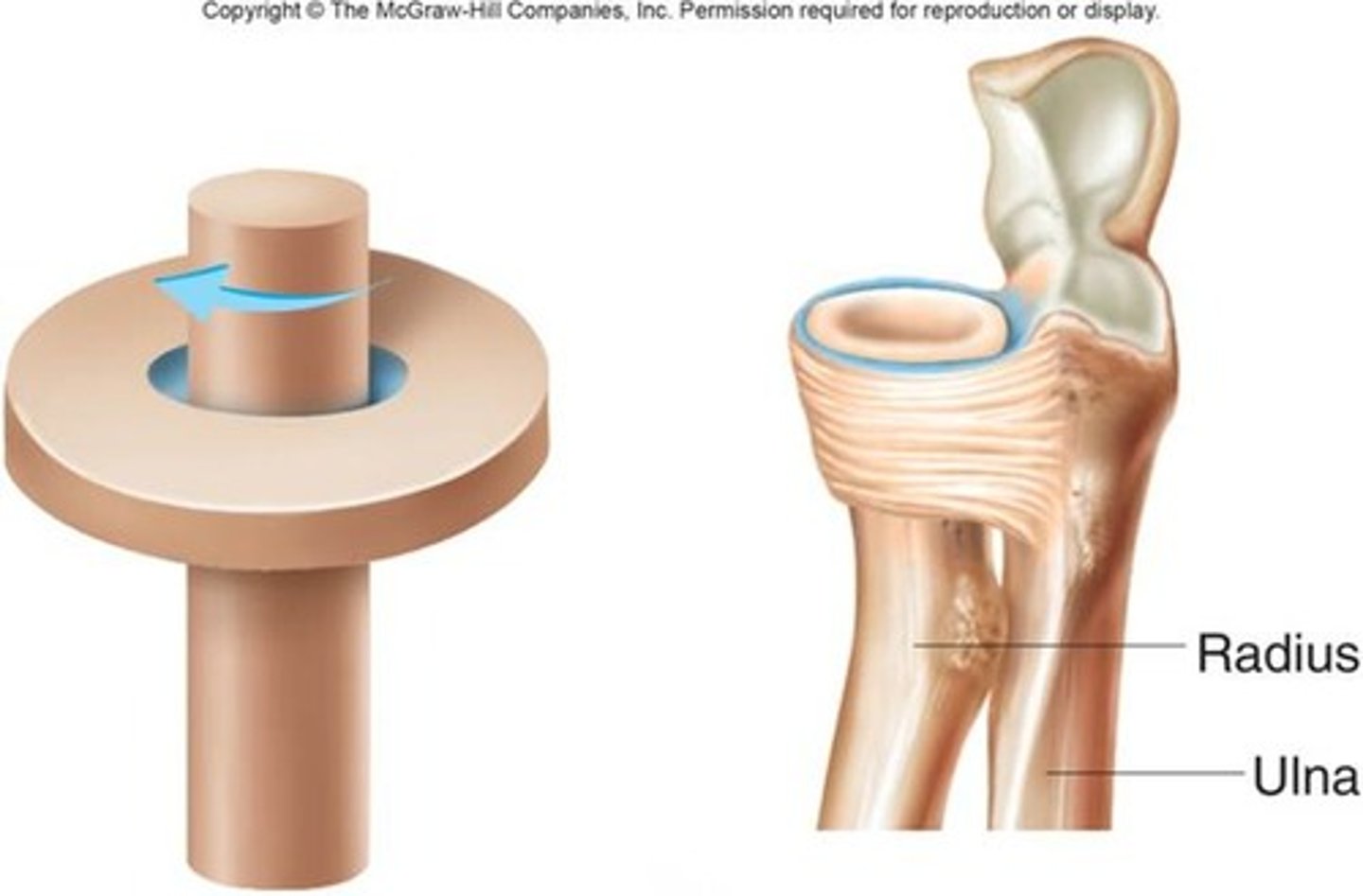
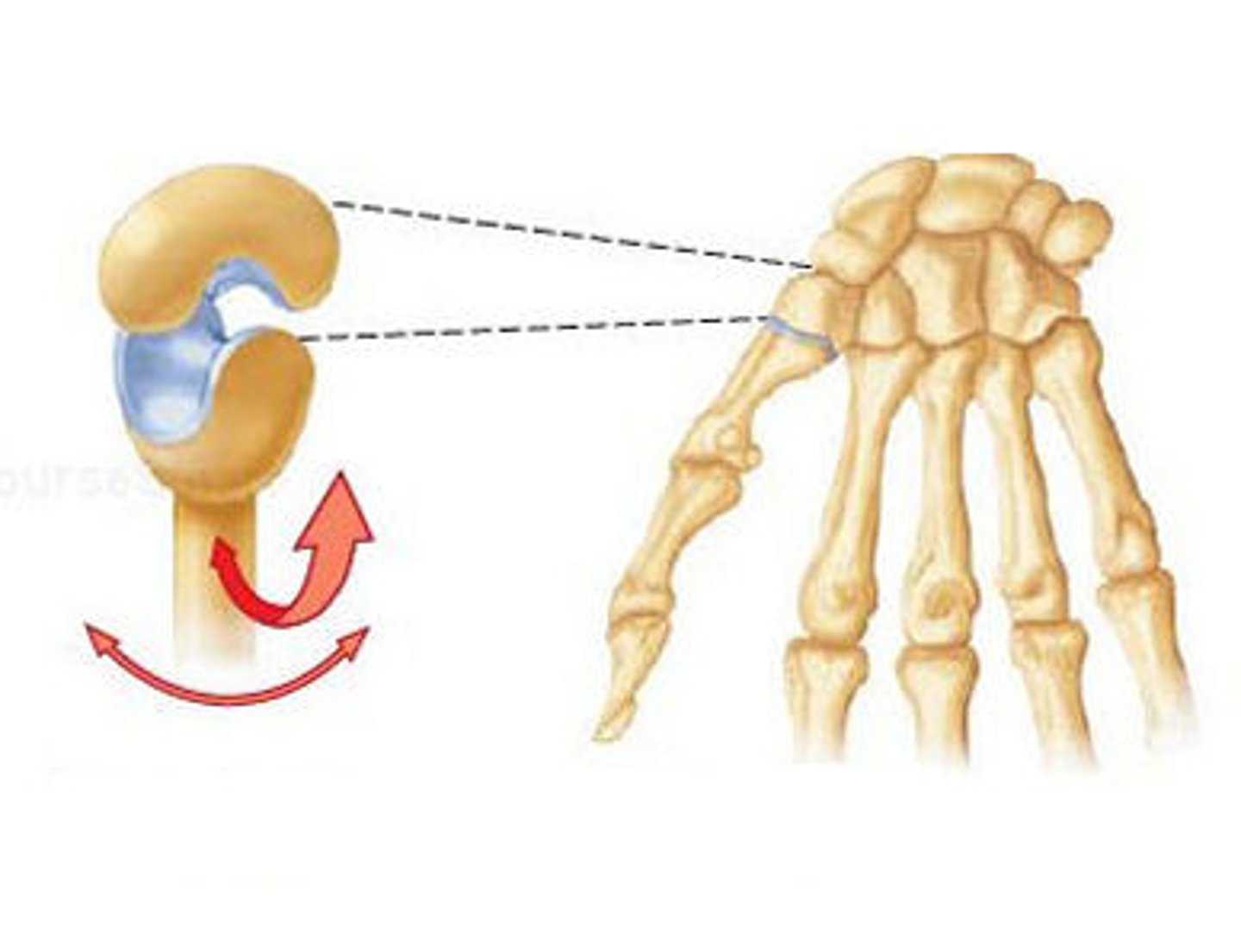
uniaxial
What type of movement do pivot joints allow?
Proximal Radioulnar joint, atlantoaxial joint
What are the examples of pivot joints?
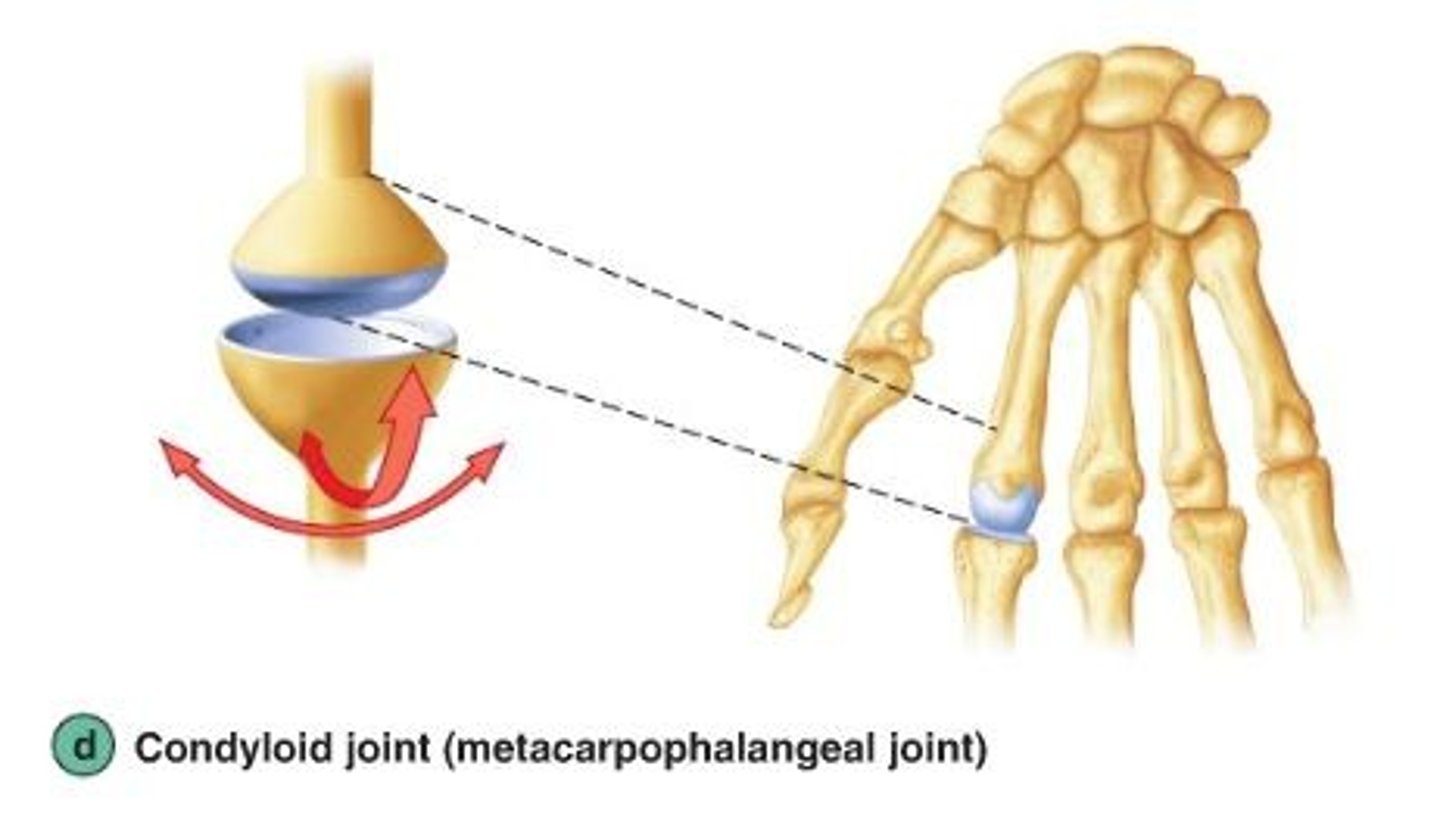
Biaxial
What type of movement do condyloid joints allow?
Metacarpophalangeal joint (2-5) , radiocarpal joint, atlantooccipital joint
What are the examples of condyloid joints?
Pivot joint
Name this type of synovial joint
Hinge joint
Name this type of synovial joint
Planar joint
Name this type of synovial joint
Condyloid joint
Name this type of synovial joint
Saddle joint
Name this type of synovial joint
Biaxial
What type of movement do saddle joints allow?
First carpometacarpal joint, sternoclavicular joint, articulation between malleus and incus
What are the examples of a saddle joint?
Ball-and-socket joint
Name this type of synovial joint
Gliding
Type of movement allowed by planar joints, two surfaces slide back and forth to one another without changing the angle between them
Angular motion
Movement that increases or decreases the angle between two bones
Flexion
Movement in an anterior posterior plane that decreases the angle between two bones
Extension
Movement in an anterior posterior plane that increases the angle between the bones
Hyperextension
Extension of a joint beyond 180 degrees
Optisthotonos
Severe example of hyperextension which occurs in tetanus
Lateral flexion
When the trunk of the body moves in a coronal plane away from the body
Rotational motion
Pivoting motion in which a bone turns on its own longitudinal axis (turning head from side to side)
Depression
Inferior movement of a part of the body (opening the mouth)
Elevation
The opposite of depression (raising mandible)
Dorsiflexion
When the talocrural joint is bent such that superior surface is brought superiorly
Plantarflexion
When the talocrural joint is bent such that superior surface is brought inferiorly
Inversion
Movement of plantar surface of foot inward (medially), only used for the intertarsal joints
Eversion
Movement of plantar surface of foot outward (laterally), only used for the intertarsal joints
Protraction
Movement of a body part anteriorly in a horizontal plane (jaw thrust)
Retraction
Posterior movement of a protracted body part so anatomical position is resumed
Opposition
Movement of thumb toward palmar tips of the fingers as it crosses palms of the hand
Epiphyseal growth plates in children, costochondral articulations
Examples of syncondroses
First carpometacarpal joint, sternoclavicular joint, joint between malleus and incus
Examples of saddle joints
Costochondritis
inflammation and irritation of the costochondral joints, resulting in localized chest pain
Cavitation
Term for when the gases dissolved in synovial fluid become less soluble, and they form bubbles