2.0 NADHP
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate NADPH
represents an important electron donator that is used in a variety of biological settings
NADPH is formed through the pentose phosphate pathway PPP
an anabolic pathway that runs to parallel to upper glycolysis
that involves the oxidation of glucose
PPP AKA hexose moniphosphate shunt
it occurs virtually in all cells and tissue in the body
PPP primary outputs
NADPH- used in reductive biosynthesis in cells → fatty acid
formed in the oxidative phase
ribose 5 phosphate,→ nucleotides
erythrose 4 phosphate → aromatic amino acids
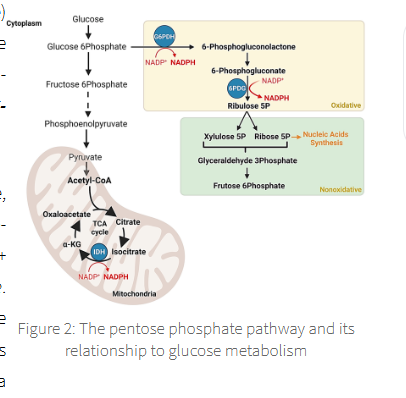
NADPH is generated in the oxidative (irriversible) phase of the PPP
2 molecules of NADP+ are reduced → NADPH
using the energy stored on G6P
regulated by the enzyme glucose 7 phosphate dehydrogenase G6PD
the initial oxidation of G6P →6 phosphogluconate is catalysed by G6PD and is irreversible
this is the rate limiting step if the PPP
the ratio of H to + is the main controling factor of the reaction rate
when H lvls are low → G6PD is activated
G6PD pathway is very efficient:
maintains the ratio of H/+ at -100 in the liver of a normal healthy individual
under conditions where both H + pentose phosphate are needed
the pathway may terminate after the oxidative phase
H acts as a reducing agent in biochemical processes
and acts as a co factor in multiple anabolic reactions
watch video
NADPH is mainly used for
fatty acid synthesis,
reducing the effect of oxidative stress, liver + RBC
CYP450 enzymes-
WBC need H to create superoxide radicals to cause oxidative damage to phagocytosed microbes
glands
50% fatty acid synthesis
all cells rely on H reducing power to produce cholesterol + fatty acids + phospholipids
CYP450 enzymes
the liver needs H to neutralise toxins + hormones using cytochrome P450 pathways
WBC
need H to create superoxide radicals to cause oxidative damage to phagocytosed microbes
Glands
use H to make steroid hormones
PPP activity is minimal in muscles and brain
where almost all of the glucose is used glycolysis for ATP production
PPP activity accounts for a significant portion of the total glucose oxidation in tissues
with active fatty acid + cholesterol synthesis including the liver
around 30% of glucose present in the liver
ends up being metabolised by PPP