Cellular Respiration Notes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Cell Respiration Equation
C6+ H12+ 6O2 = 6CO2+ 6H2O + ATP
Glycosis Overview
Glucose is broken down in to 2 pyurvates and NADH and ATP are made
Kerbs Cycle Overview
Pyurvates are further broken down and NADH, FADH2 and a small amount of ATP is made
ETC Overview
NADH and FADH2 power the formation of H+ gradient and H+ leading to the formation of many ATP molecules
Glycosis occurs where?
Cytoplasm
Glycosis Input starts with 6 carbon molecules then how many are in the end?
3 carbons
Is oxygen needed in glycosis?
Oxygen is not need in the first step of cellular respiration
Glycosis Inputs?
Glucose and 2 ATP
Outputs of Glycosis?
2 NADH and 4 ATP and 3 Carbons
What is the transitional step of the Kerb’s cycle?
Pyurvates entering the mitochondria
Why are pyurvates further broken down?
To energize NAD+ and FAD
Kerbs Cycle Inputs?
2 pyurvates
Kerbs Cycle Outputs?
6CO2 and 8 NADH and 2 FADH2 and 2ATP
What are the electron carriers in the ETC?
FADH2 and NADH which release electrons into the ETC
High energy electrons pump what into the intermembrane space?
Hydrogen is Pumped
What pass through the ATP synthase while producing many ATP?
H+ ions
What is the final acceptor of cellular respiration?
Oxygen
What does oxygen form with the electrons to get rid of excess electrons?
Water
What cannot function without oxygen?
ETC
Where does NAD and FAD return to once finished in the ETC?
Glycosis and the Kerbs Cycle
Main Idea Of Cellular Respiration?
Cellular Respiration harvests the energy from the food we eat to make ATP.
Since Oxygen is the final electron acceptor what does it take away through water?
Excess H+ and Electrons
Main Idea of Glycosis
Summary: Glucose gets turned into 2 pyurvate acids
Main Idea of the Kerbs Cycle?
Summary: Breaks down pyurvates to energize NADH and FADH2, to release CO2
Main Idea of the ETC?
Summary: Creates an hydrogen gradient to make many ATP
How many ATP are made in the ETC?
38
One glucose is how many pyurvate
2
How much smaller is the pyurvate to the glucose molecule
1/2
Which type of respiration requires oxygen?
Aerobic
Does glycosis occur in both respirations?
Yes
Describe the function of cellular respiration
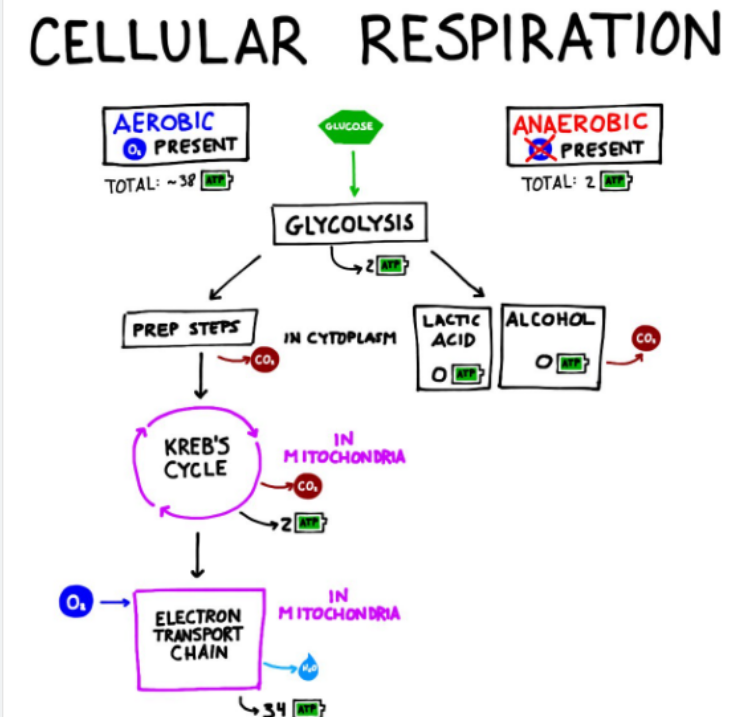
When there is no oxygen for cellular respiraton what path does it take?
Anaerobic Respiration
In Anaerobic Respiration how many ATP are produced?
2 ATP are made in the alternative pathway
What are the two most common fermentation?
Lactic Acids and Alcoholic Fermentation
Where does Anaerobic Respiration take place?
In the cytoplasm