Chemistry - 1 Atomic Structure
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Atom
Basic unit of matter
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Periodic Table
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
Group
A vertical column of similar elements in the periodic table
Row
The horizontal lines of elements related via their number of electrons and protons
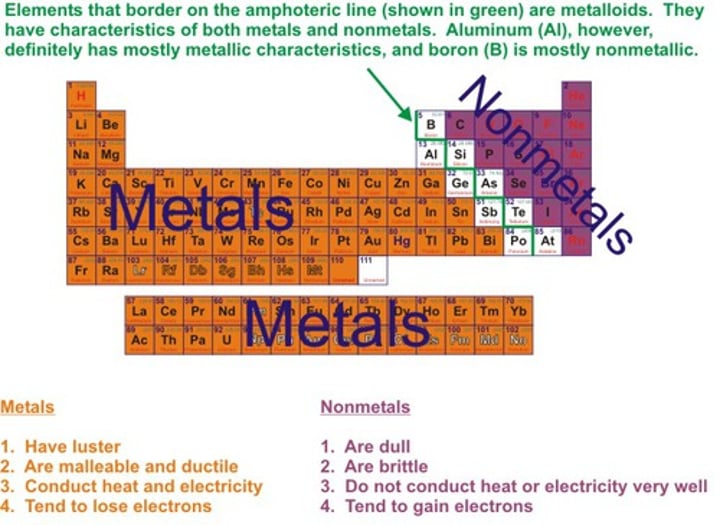
Where is the 'stepped line'?
Begins before boron and after aluminium
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Nucleus
Center of an atom
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
Ion
an atom that has become charged by losing or gaining electrons
Isotope
an atom of the same element with a different number of neutrons
isotopes have different ... properties
physical
isotopes have the same ... properties
chemical
electronic strucutre
atom written as its shells, e.g. 2, 8, 1
What does the number of electrons in the outer shell affect?
the element's Group
John Dalton's model of the atom:
tiny, hard, indivisible spheres - each element's atom has a different mass
Who discovered the electron?
JJ Thomson
How did JJ Thomson discover the electron?
cathode ray tube experiment
cathode ray tube
evacuated glass tube in which a stream of electrons emitted by a cathode strikes a fluorescent material, causing it to glow
Cathode ray tube experiment:
JJ Thompson put positively and negatively charged plates around the cathode ray tube and saw that the ray curved towards the positive plate. He deduced that there must be electrons
JJ Thomson's model of the atom
plum pudding model
Who discovered the nucleus?
Ernest Rutherford
How was the nucleus discovered?
Gold foil experiment
Gold foil experiment [4]:
- gold foil placed in the middle of a fluorescent screen
- alpha particles shot at gold foil
- most particles went through
- some were deflected
conclusions from gold foil experiment [3]:
- atom is mostly empty space
- nucleus has a positive charge
- electrons float around nucleus
Ernest Rutherford's model of the atom:
Nuclear/planetary model
Who discovered that electrons are in shells?
Niels Bohr
Who discovered the neutron?
James Chadwick
How was the neutron discovered? [4]
- alpha particles shot at materials
- emitted rays with no charge
- rays with no charge dislodged protons from paraffin
- deduced that they were neutrons
atomic number
number of protons in an atom
mass number
number of protons + number of neutrons
Miscible
Describes two liquids that are soluble in each other
Why is it difficult to get a pure substance with simple distillation?
Some vapour may be given off before the substance reaches boiling point - the boiling points are too close together.
Fractional distillation
Used to separate liquids with similar boiling points using a fractionating column
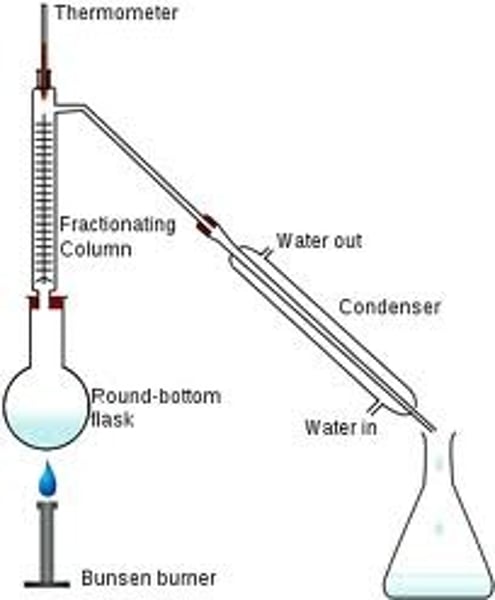
Fractionating column
a glass tube filled with beads
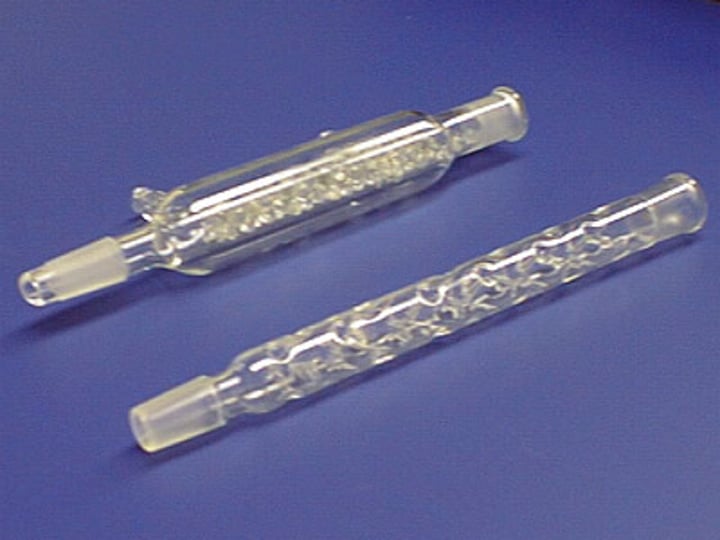

How does a fractionating column work? [3]
- vapours must pass over the beads to reach the condenser
- the substance with the higher boiling point is more likely to condense lower down, where the temperature is higher
- the substance with the lower boiling point will continue to rise through the tube and reach the condenser
The use of fractional distillation [2]
- Use of ethanol as a biofuel
- In oil refineries, to separate crude oil
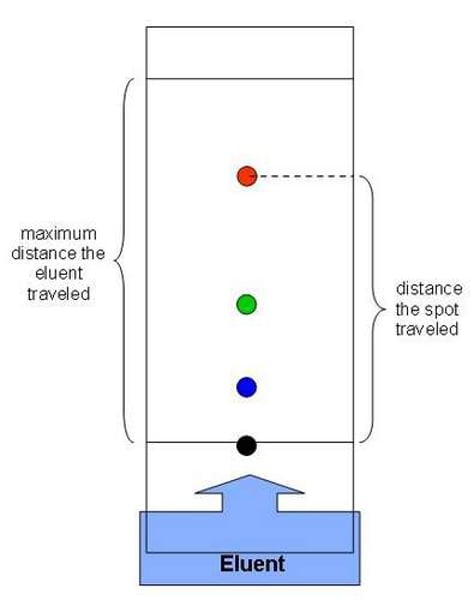
Chromatography
A technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material (solubility)
Paper chromatography [4]
- Draw a pencil line on some absorbent chromatography paper to indicate the starting point
- Use a capillary tube to dab small amounts of solution on the line
- Suspend the paper in a small amount of water (up to the line)
- See which solution travels the furthest
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
Ratios (c vs m)
- Compounds have a fixed composition
- Mixtures have no fixed composition
Separation (c vs m)
- Compounds must be separated by chemical reactions
- Mixtures can be separated by physical means, using the properties of each separate substance
Chemical bonds (c vs m)
- Compounds contain different elements chemically bonded
- There are no chemical bonds between atoms of a different substance in a mixture
Filtration
A process used to separate an insoluble substance from a solvent - usually with filter paper and a funnel
Filtering sand [3]
- The sandy water is poured through filter paper
- The sand collected on the paper is rinsed to remove any remaining soluble solvents
- The sand is dried in a warm oven to evaporate off the water
Crystallisation
The formation of crystals by evaporating a solvent from a saturated solution
Crystallisation process [3]
- Heat an evaporating dish containing the saturated solution (either in a water bath or directly on the gauze and tripod)
- Stop heating at the point of crystallisation
- Leave the rest of the solvent to evaporate at room temp
Filtrate
liquid that has passed through a filter
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
Simple distillation [4]
- solution is heated over Bunsen burner
- a thermometer is placed so that we can record the gas's temperature
- the gas enters a condenser where it is cooled and again becomes liquid
- the liquid enters another glass
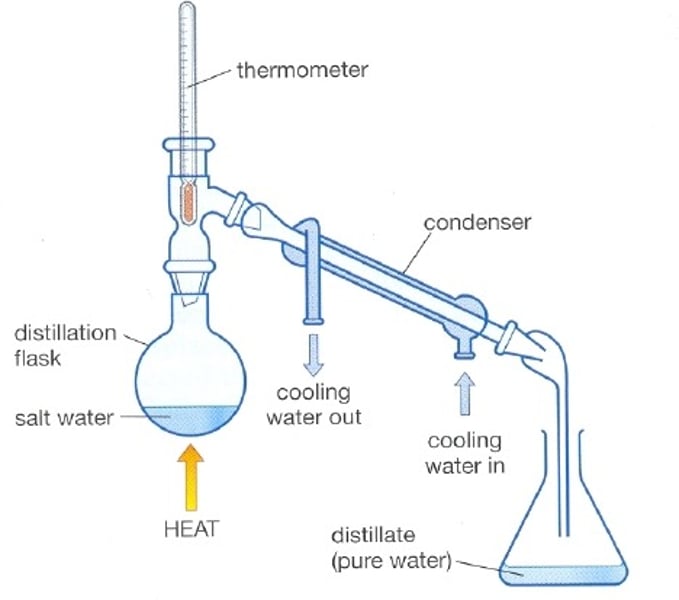
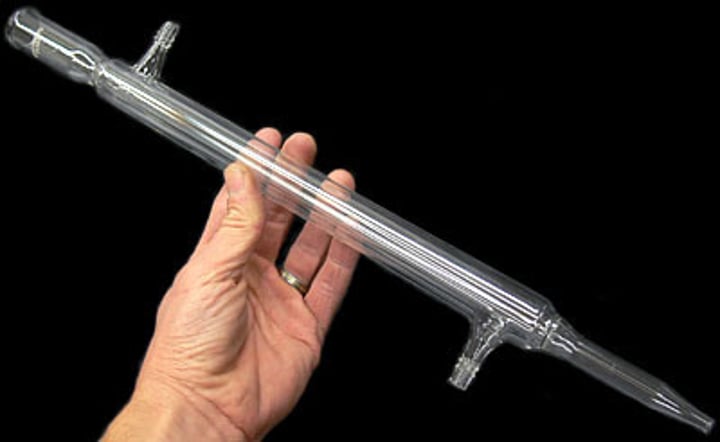
Condenser
A tube with an outer jacket that has water flowing through it, acting as a coolant to condense the vapours inside

Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction
Products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
Word equation
an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words
Symbol equation
equation that shows the chemical symbols and formulae of reactants and products
Law of conservation of mass
Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change
State symbols
Symbols to show the state of a substance - solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g) and aqueous (aq)
Aqueous solutions
solutions with water as the solvent
How do you balance equations? [4]
- Write down all the atoms and the numbers of them on the side of the reactants and of the products
- Change one necessary coefficient
- Rewrite/reevaluate the first step
- Repeat until balanced