Lecture 5: Rumen acidosis, simple indigestion, and rumen drinker
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Normal rumen fluid pH range of animal on grain is?
A. <5
B. >8
C. 5.8-7
D. 7-8
C. 5.8-7
What is the VFA?
Highest amount, fat synthesis by adipose tissues and extra hepatic tissue energy. Decreases with high carb diets.
Acetate
Normal rumen pH of animals on forage diet
7
What is the VFA?
Gluconeogensis by liver, 60% of glucose used by animal
Proprionate
What is the VFA?
Ketone bodies always by extra hepatic tissues
Butyrate
Etiology of rumen acidosis
Excessive consumption of readily fermentable carbs
Increase production of latic acid
Decreased in rumen pH
What is rumen acidosis associated with?
Cereal grains
Potatoes, beets
Fruit
Etiology of rumen acidosis
Glucose and organic acids produced
S. bovis proliferate
Metabolize the CHO and produce lactic acid
VFAs produced as pH decreases, act as buffers
Osmolality increases. Pulls in water.
Lactic acid damages rumen wall. Mycotic rumenitis
Why do grains and other fine compounds increase risk for rumen acidosis?
Decreased fiver, less saliva, less buffering and scratch factor. D lactate produced and not easily metabolized. Histamine results in vasodilation, arterioconstriction, increases vascular permeability leading to laminitis.
CS of acute rumen acidosis
Rumen distension
Diarrhea (discolored by grain)
Dehydration
Recumbency
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Decreased palpebral reflex
CS of long term rumen acidosis
Polioencephalomalacia
Liver abscesses
Rumen hyperkeratosis, mycotic rumenitis
Hoof wall changes and laminitis
Clostridial overgrowth (endotoxemia)
An animal presents with the following CS. What is your diagnosis?
A. Listeria
B. Trauma
C. Polioencephalomalacia
D. Toxin
C. Polioencephalomalacia
Excessive carbs or low forage diets over long times causes high rate of termination (pH 5-5.5) and high VFAs . Observed as low butterfat, increased abomasal disease and decreased DMI
Subacute Rumen Acidosis
How do you diagnose subacute rumen acidosis?
Rumenocentesis of group of cattle
Septic thromboemboli secondary to liver abscesses secondary to rumenitis from SARA.
Caudal Vena Caval Syndrome
Acute rumen acidosis pH
<5.5
How can you diagnose acute rumen acidosis?
Rumen pH
Acid base venous sample
urine pH low
Treatment of rumen acidosis
Empty with large tube or rumenotomy
Magnesium hydroxide to neutralize
Fluids (IV)
Thiamine for q8 hours
CD antitoxin
NSAIDs for acute laminitis if no renal changes
PPG or tylan for liver abscesses
SLOW reintroduction to grain
1 week on forage then slow stepping up
Transfaunate (cud snatching for goats)
How much bicarbonate does he need
• Base deficit = 34 – ECO2
• Bicarb requirement (mEq) = BD x body weight x 0.3
• mEq bicarbonate to grams = /12
• Isotonic bicarb = 1.3%
• Correct half over a few hours, rest in 24 hours
• BD = 24-8 = 16
• Bicarbonate requirement = 16 x 0.6 x 50kg
= 480 mEq
• 480mEq/12 = 40g
• Therefore needs 40/13g/L = 3 liters isotonic
• Replace half initially
• 10% dehydrated
• Fluid deficit = 5L
• On going losses approx. 0.5 liter
• Maintenance 60ml/kg/day = 3 liters • In first 24 hours. 1.5 L Na bicarbonate followed by 0.9% NaCl at 300ml/hour
Why do you use Mg hydroxide over bicarb?
Mg hydroxide is cheaper
Bicarb may make the bloat worse
Making isotonic bicarb calculations
• Isotonic 1.3% = 13g/L
• Commercially available is 8.4%
• V1C1=V2C2 • 1000 1.3 = x 8.4 • X = 154ml
What can magnesium hydroxide cause?
Hypermagnesemia, alkalosis if excessive
A 700lb show heifer that the clients just purchased and
switched feeds rapidly present with bloat, diarrhea. She is
depressed. Bloodwork reveals a base deficit of 8. What is her
TOTAL bicarbonate requirement to correct her acid base
imbalance
• 2545mEq
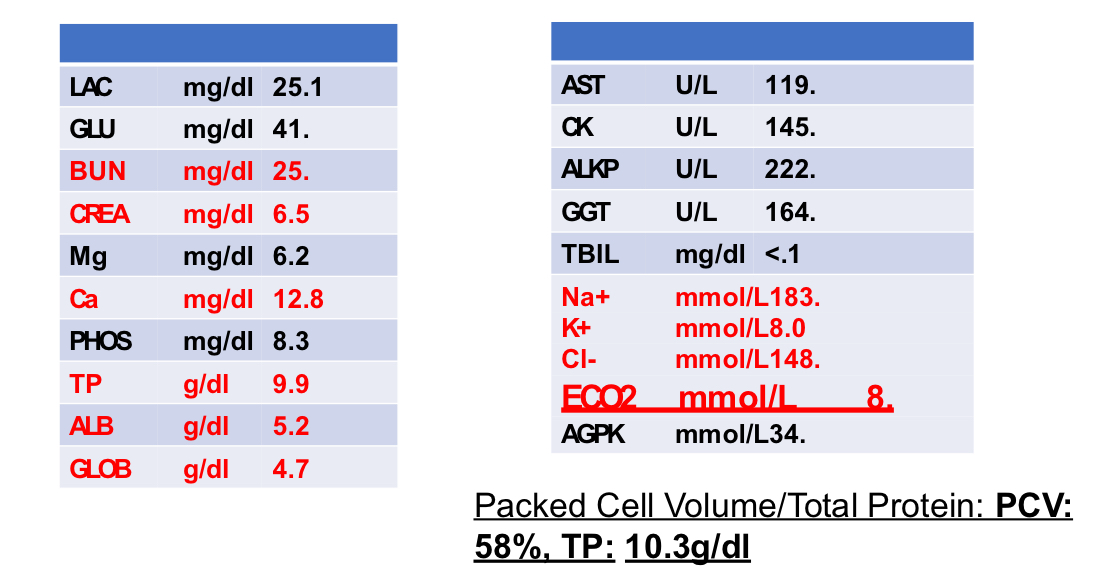
Case 1:
Signalment: 6 month old show lamb Presenting complaint Progressive anorexia of about five days duration.
Diarrhea and bloating
His attitude has not been significantly altered during this time. • No other sheep are showing similar symptoms of disease
Purchased 2 weeks ago at sale
Diet is 2 lb of grain with 1 handful alfalfa in evenings
Wears polowraps as has been known to pick at legs
Housed in barn/dry lot
PE findings:
HR: 180bpm, RR: 70bpm, Temp: 104.7F, Wt: ~101#,
BCS: 3.5/5
Mucous membranes were dark pink
Hydration status was ~5% dehydrated.
Bronchovesicular sounds were increased bilaterally.
Grunting and signs of discomfort were noted during examination
No rumenal contractions were noted and there was obvious distension of the left flank.
Diarrhea passed on digital rectal exam
Passed NG tube
pH of rumen fluid sample was estimated to be 5 and microscopic examination showed no microflora present.
BW results included
Simple indigestion
What causes simple indigestion?
Abrupt changes in feed abruptly causes an imbalance in microflora and its fermentation products. Mouldy feeds, sour silages, frozen fed
CS of simple indigestion in cattle
Mild and self limiting
Decreased intake
Diarrhea
Rumen motility decreased
Mild pH changes
How do calves inoculate microflora?
Environment or reflux from abomasum
What is responsible for rumen mucosal development in calves?
VFAs
What rumen disorders are calves on a finely ground feed without forages?
Chronic rumen acidosis
Parakeratosis
Rumen hypomotility
Poor BCS
What rumen disorders are calves on excessive long stem forage at risk for?
Hay belly
Poor rumen microbes
Firm on palpation
Poor motility
Closes in response to milk suckling and diverts milk to abomasum
Esophageal groove
In calves <12 weeks what stimulates esophageal groove?
Bucket and nipple
In bottle calves >12 weeks what stimulates esophageal groove?
Only nipple
What can cause rumen drinkers?
Failure of groove to close (Non-whey milk)
Calves on milk for >3-4 months
Over feeding neonates large volumes
Increased abomasal emptying times
Abomasal ulcers or inflammation
What kind of rumen bloat often occurs in calves?
Free gas (type 1 vagal)
What is the normal rumen fluid pH range of animals on grain?
a. <5 b. >8
c. 5.8 - 7
d. 7 - 8
c. 5.8 - 7
What kind of milk replacer is more likely to cause rumen drinkers?
Soy based milk replacers
Which of the following is NOT a synonym for rumen acidosis?
a. Lactic acidosis
b. Grain overload
c. Rumen drinker syndrome
d. Carbohydrate overload
c. Rumen drinker syndrome
What is the approximate percentage of feedlot cattle that suffer from digestive disorders?
a. 1-2%
b. 4.4%
c. 10%
d. 20%
b. 4.4%
Which of the following feeds is commonly associated with acute rumen acidosis?
a. Hay
b. Cereal grains
c. Grass silage
d. Straw
b. Cereal grains
What clinical sign is NOT typically associated with acute rumen acidosis?
a. Rumen distension
b. Diarrhea
c. Increased appetite
d. Tachycardia
c. Increased appetite
What is the primary cause of subacute rumen acidosis (SARA)?
a. Excessive fiber intake
b. Low protein diets
c. Excessive carbohydrates or low forage diets
d. Sudden changes in environmental temperature
c. Excessive carbohydrates or low forage diets
Which of the following is an important treatment for rumen acidosis?
a. Increase grain intake
b. Administer magnesium hydroxide
c. Provide only water
d. Feed high amounts of forage
b. Administer magnesium hydroxide
What is the role of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) in the rumen?
a. Decrease rumen motility
b. Act as buffers
c. Decrease absorption
d. Increase lactic acid production
b. Act as buffers
Which clinical sign indicates a longer-term consequence of acute rumen acidosis?
a. Rumen distension
b. Polioencephalomalacia
c. Tachycardia
d. Depression
b. Polioencephalomalacia
What is the main consequence of D-lactate production in the rumen?
a. Improved fiber digestion
b. Increased gluconeogenesis
c. Metabolic acidosis
d. Enhanced microbial growth
c. Metabolic acidosis
Which of the following clinical signs is associated with rumen drinker syndrome?
a. Pot bellies
b. Increased rumen motility
c. Bright red mucous membranes
d. Increased milk fat content
a. Pot bellies
What is the main reason for rumen drinker syndrome in calves?
a. Too much exercise
b. Failure of the esophageal groove to close
c. Insufficient water intake
d. Excessive fiber consumption
b. Failure of the esophageal groove to close
What is the typical pH range for subacute rumen acidosis (SARA)?
a. <5
b. 5 - 5.5
c. 5.5 - 6.5
d. >7
b. 5 - 5.5
c. Decreased intake
Which of the following factors can lead to chronic rumen acidosis in calves?
a. High fiber intake
b. Finely ground feed without forages
c. Increased water consumption
d. Adequate protein levels
b. Finely ground feed without forages
What is the first step in the treatment of acute rumen acidosis?
a. Administer antibiotics
b. Perform a rumenotomy
c. Provide IV fluids
d. Empty the rumen using a large tube
d. Empty the rumen using a large tube
Which bacteria is primarily responsible for the production of lactic acid in the rumen during acidosis?
a. S. bovis
b. E. coli
c. Lactobacillus
d. Clostridium
a. S. bovis
What is the primary diagnostic method for identifying acute rumen acidosis?
a. Fecal analysis
b. Bloodwork
c. Rumen pH measurement
d. Ultrasound imaging
c. Rumen pH measurement
Which of the following is a key prevention strategy for rumen acidosis?
a. Rapid feed changes
b. Adequate fiber in the diet
c. High grain diets
d. Restricting water access
b. Adequate fiber in the diet
What is the expected outcome for an animal diagnosed with severe rumen acidosis if not treated?
a. Rapid recovery
b. No significant effects
c. Increased production
d. High mortality risk
d. High mortality risk