All Ceramic Restorations in Fixed Prosthodontics
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from the lecture on all-ceramic restorations and their applications in fixed prosthodontics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Define Fixed Dental Prosthesis
A prosthesis that is securely fixed to a natural tooth or teeth, or to one or more dental implants; it cannot be removed by the patient.
Define Partial-Coverage Restoration
An artificial replacement that restores missing tooth structure by surrounding part of the remaining structure with materials such as cast metal alloy, ceramics, or resin.
Indications for Complete Ceramic Crown
extensive loss of tooth structure
existing complete crown
major morphological modification
significant shade change
All-Ceramic Restorations Advantages
superior esthetics
good tissue response
digital workflow capability
higher mechanical strength
All-Ceramic Restorations Disadvantages
Critical preparation design
Strict bonding protocols
Opposing tooth wear
Brittleness
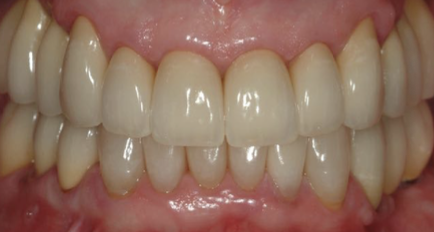
Indications for All-Ceramic Restorations
High esthetic requirements
Favorable distribution of occlusal load
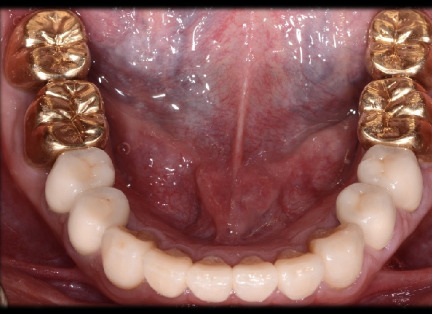
Contraindications for All-Ceramic Restorations
More conservative restorations applicable
Unfavorable distribution of occlusal load
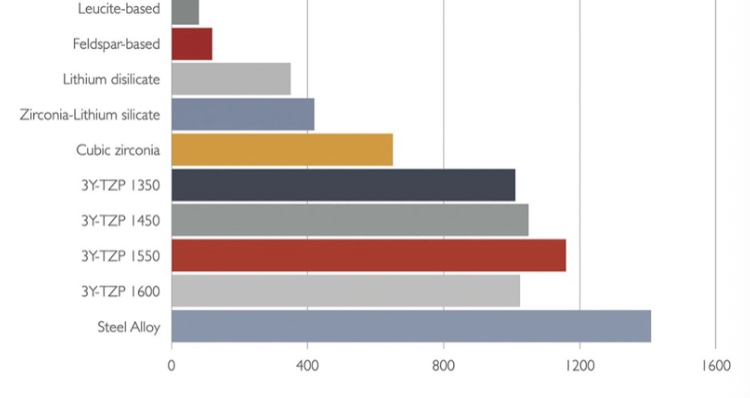
Flexural Strength
The material's ability to withstand bending forces without breaking or deforming.
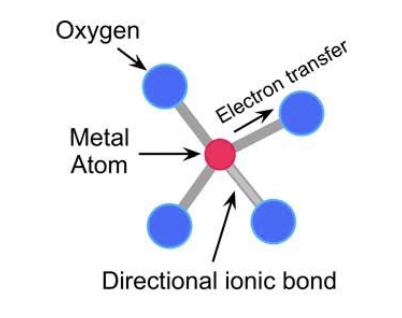
Dental Ceramics
Materials that typically have strong, directional, ionic bonds between metals and oxygen, providing strength but limited tolerance to distortion.
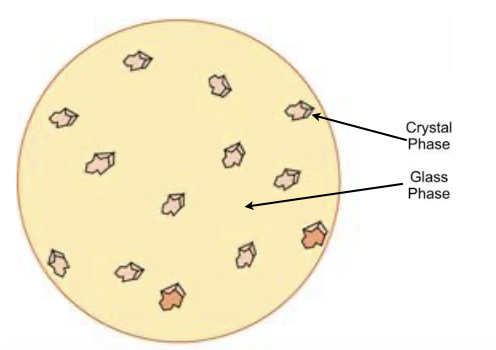
Dental Ceramics composition
Glassy phase
1+ Crystalline phase
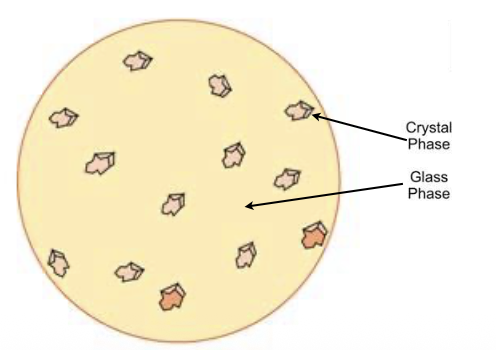
Consequence of Increasing Crystalline phase amount
Crystalline reinforcement
Increase resistance of crack propagation
Decrease translucency
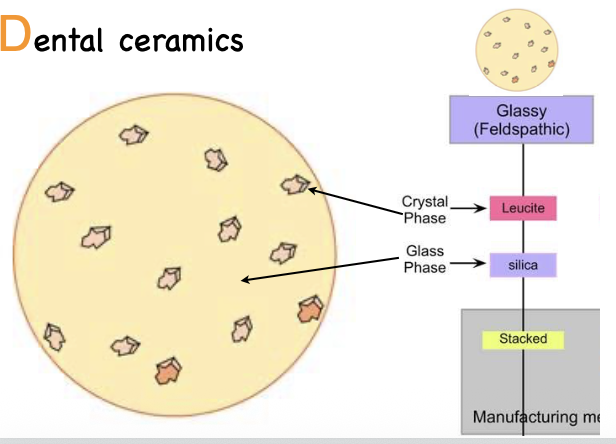
Feldspathic ceramic porcelain composition
Glassy phase
Embedded leucite crystals
Advantages of Feldspathic porcelain
High translucency
Highly esthetic results
Technique sensitivity
Low flexural strength
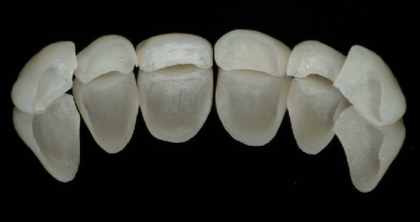
Uses for Feldspathic porcelain
Ceramic veneers
Metal-ceramic restorations
Glass-dominated ceramics
Ceramics with more crystalline phase than glass; crystals are usually fluoroapatite or leucite
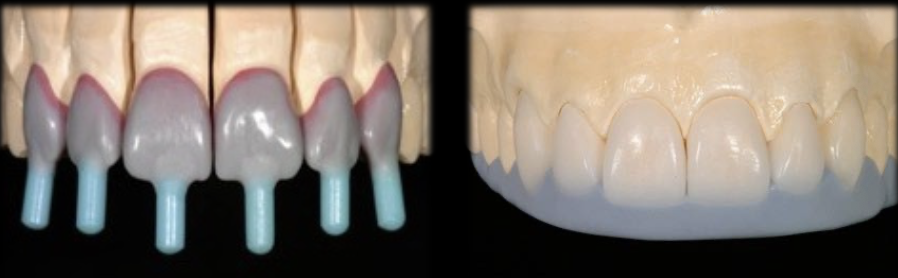
Leucite-Reinforced Glass Properties
Sufficient translucency
Moderate esthetic results
Less technique sensitivity
Higher flexural strength (85-112 MPa)
What are crystalline-dominated ceramics and what are they made of?
Alumina or zirconia, doped with ions (magnesium or yttrium);
they are ~70% crystalline, with crystals such as
spinel
zirconia
alumina
or lithium disilicate
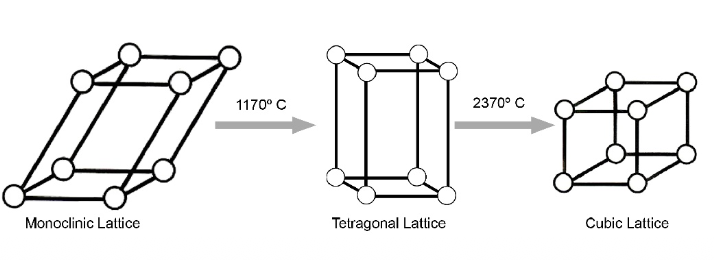
Phases of Zirconia
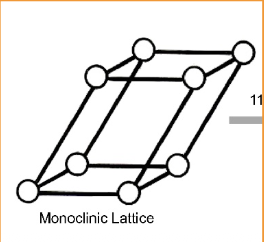
Monoclinic (m)
Tetragonal (t)
Cubic ©
This phase does not possess exceptional mechanial properties
Monoclinic
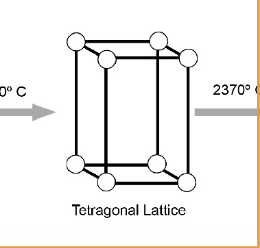
Tetragonal zirconia phase
Superior mechanical properties, unstable at room temp
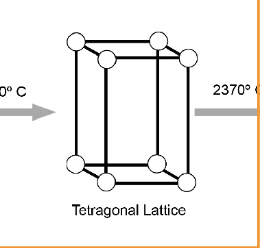
What is added to stable zirconia t-phase at room temp?
Dopants to enhance strength and partially stabilized at room temperature
Lithium Disilicate
A type of glass-ceramic used in dental restorations, known for its translucency and flexural strength.
Zirconia
A high-strength ceramic material used in dentistry, available in multiple phases including monoclinic, tetragonal, and cubic.
Monolithic Ceramics
Ceramic restorations made from a single material without layering, often demonstrating high strength and esthetic qualities.
CAD/CAM Technology
Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing used in creating precise dental restorations.
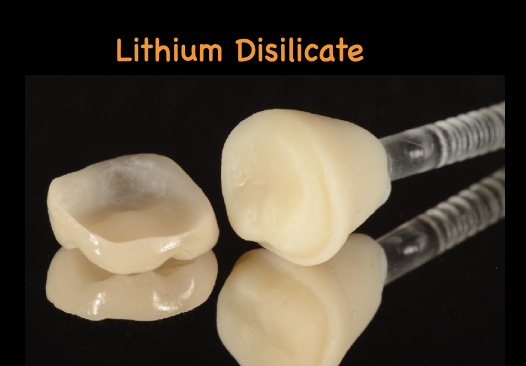
Lithium Disilicate properties
More translucent
Press & CAD/CAM
Laminated / monolithic
Flexural strength 215-400 MPA
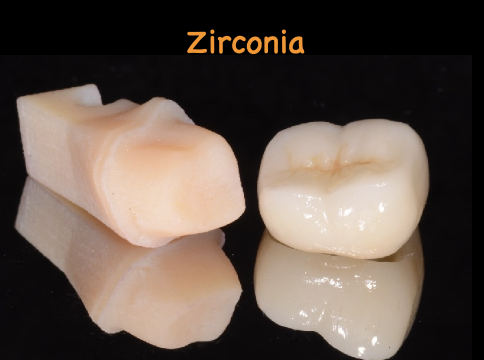
Zirconia properties
More reflective
CAD/CAM
Laminated / monolithic
Flexural strength 900-1200 MPa
Why are monolithic ceramics favorable for crowns and FPDs?
High survival and low complication rates; although monolithic zirconia is stronger than lithium disilicate in lab conditions, clinical survival and complications are similar.
Advantages of supragingival finish lines (5)
Preserve tooth structure
Reduce soft tissue trauma
Improve impression accuracy
Enhance bonding strength
Maintain periodontal health
Disadvantages of supragingival finish lines (1)
Potential visibility of tooth-restoration interface
Advantages of subgingival finish lines
Restore deep caries, cervical erosion, or existing subgingival restorations
Enhance retention/resistance form
Conceal tooth-restoration interface
Disadvantages of subgingival finish lines (5)
Compromise tooth structure
Increase soft tissue trauma
Challenge impression efficacy
Complicated bonding procedures
Difficult to maintain periodontal health
What is the cavosurface angle for rounded shoulder finishing lines?
90 degrees