25 Aromatic compounds
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
molecular formula of benzene
C6H6
characteristics of benzene
colourless, sweet smelling, highly flammable liquid
found in crude oil, is a component of petrol, and also found in cigarette smoke
classified as a carcinogen, can cause cancer
how to name a benzene compound with
an alkyl group
a NO2 group
a halogen
[___] benzene
e.g. chlorobenzene
how to name a benzene compound with
a functional group containing carbon
a phenyl group
e.g. phenyl ethanoate
how to name a benzene compound with
a group attached of 7 carbons or more
phenyl
e.g. 1-phenyl octane
priority in naming
c-acids (highest priority)
esters
acyl chlorides
nitrites
aldehydes
ketones
alcohols
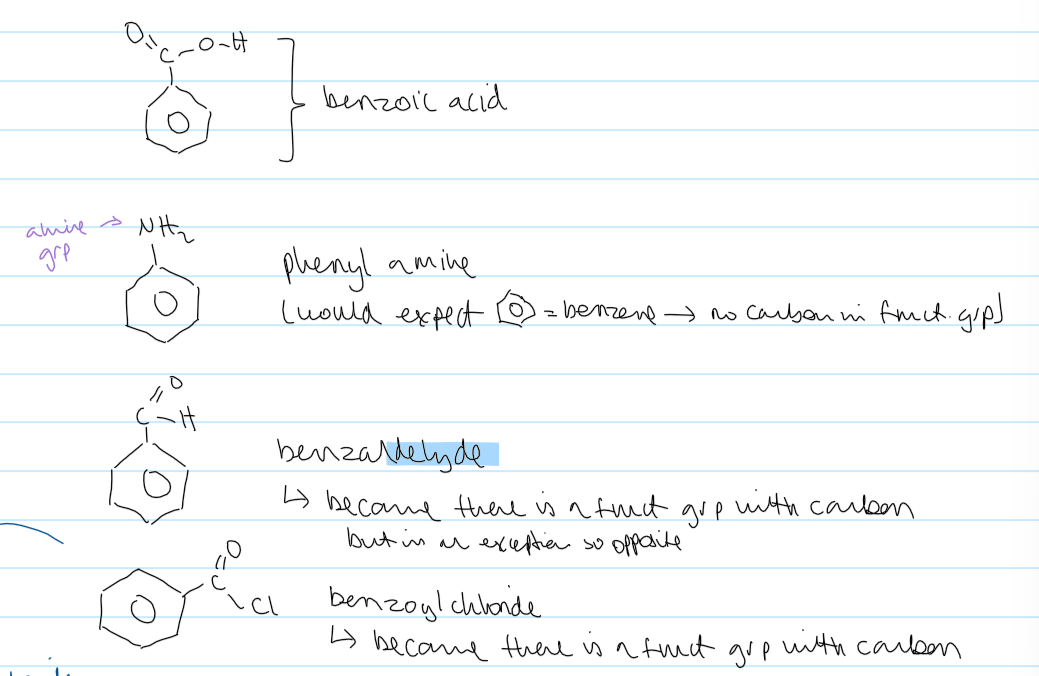
exceptions to naming
benzoic acid
phenyl amine
benzaldehyde
benzoyl chloride
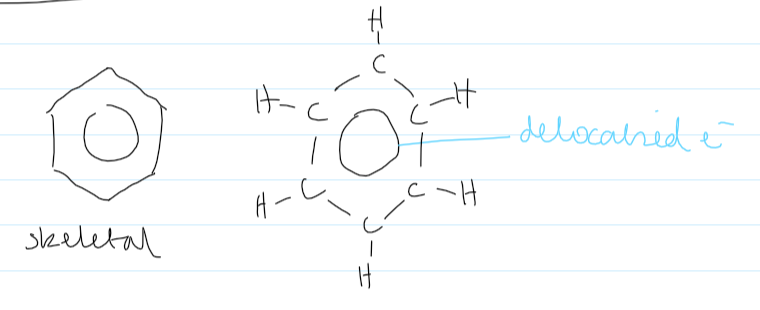
displayed formula of benzene
evidence for kekulé structure being incorrect
all C=C bond lengths in benzene are equal (therefore equal e- density). Use x-ray crystallography to see position of atoms then work out bond lengths.
the C-C bond length in benzene is intermediate between C-C/C=C in length and e- density → therefore sigma σ-bond + some deloc. π e- density)
reactivity: benzene doesn’t undergo electrophilic addition whereas due to presence of double bonds in kekulé model (so e- rich) it would undergo electrophilic addition (electrophile = an e- pair acceptor).
benzene doesn’t decolourise Br2 under normal conditions (needs a halogen carrier) (unlike cyclohexene) so implies no C=C
enthalpy change of hydrogenation: ∆H is less than would be expected of 3 C=C. Benzene is more stable than kekulé so less difference in stability in benzene to cylohexane
structure of bezene
12 σ bonds (the overlap of s-orbitals) (each σ-bond has 2e-)
each carbon is forming 3 bonds
each carbon has 1e- not in a σ bond. forms π bonds
has delocalised π e- above and below the plane of the σ bonds
6 deloc. π e- in total
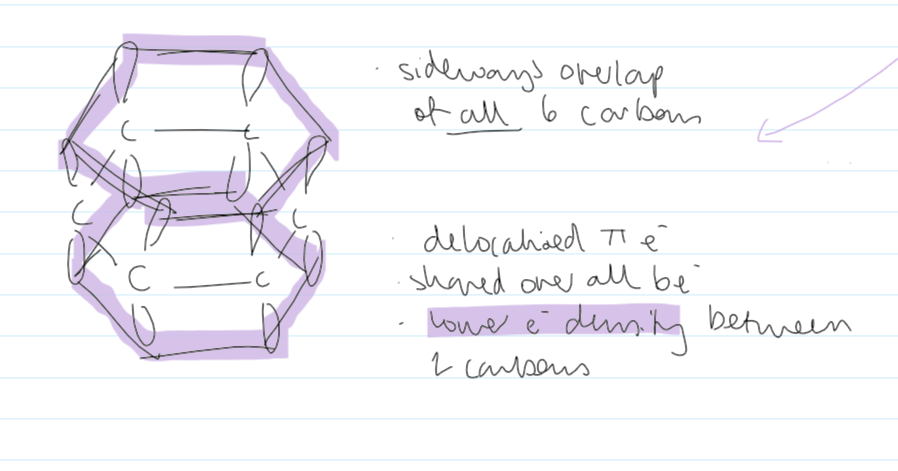
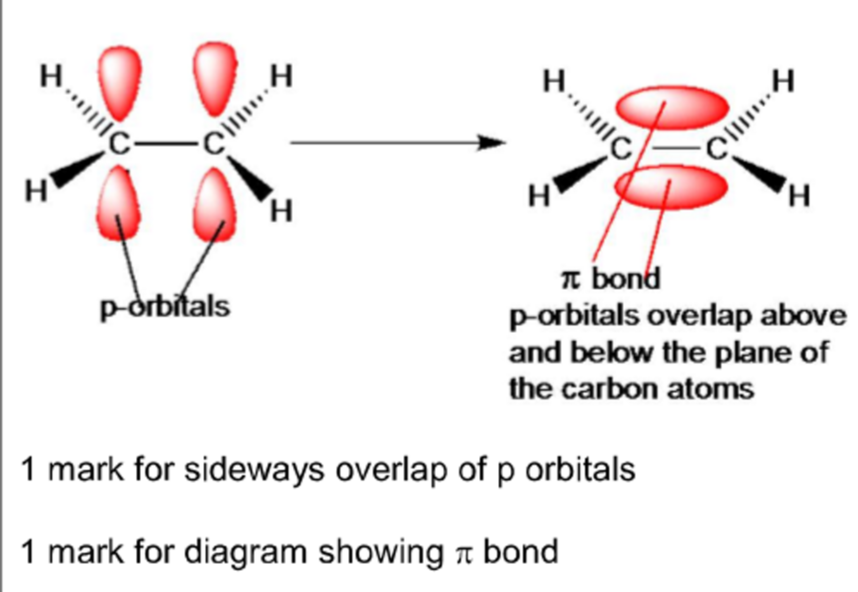
diagram for π bond
π-bond: the sideways overlap of two p-orbitals, one from each C atom of the double bond
what kind of rxn does benzene undergo
electrophilic substitution
list the rxns of benzene u need to know
nitration of benzene
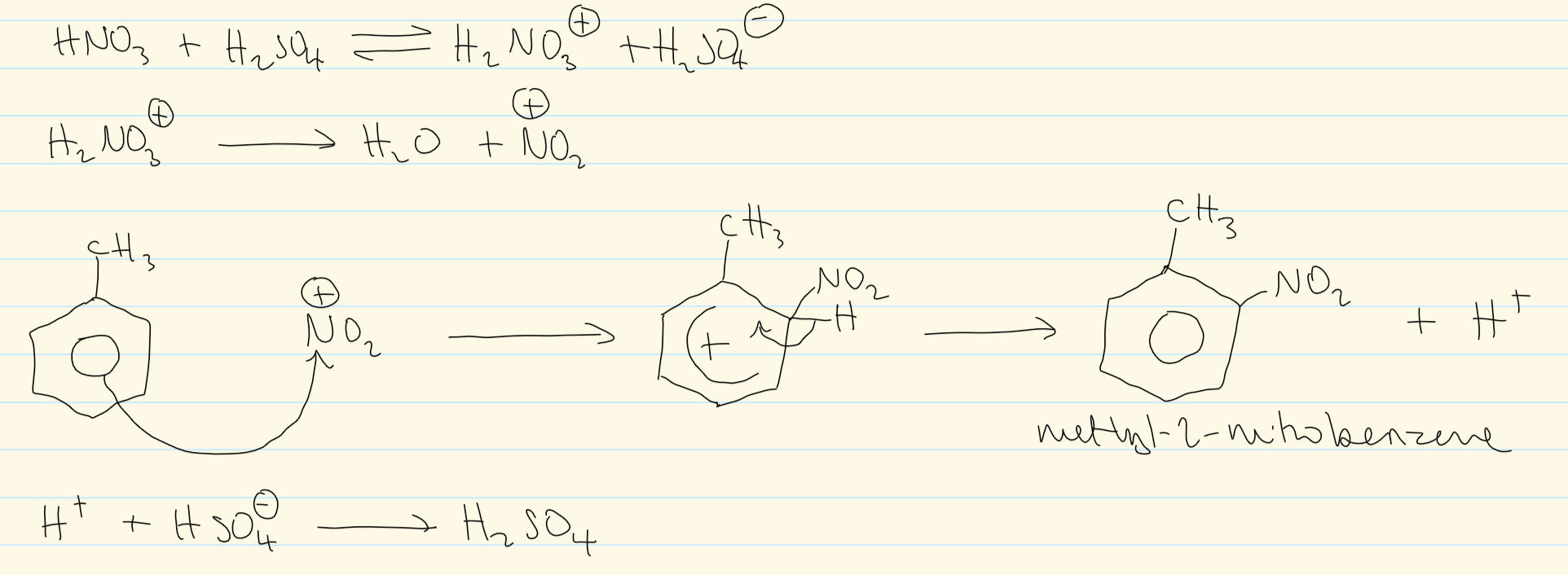
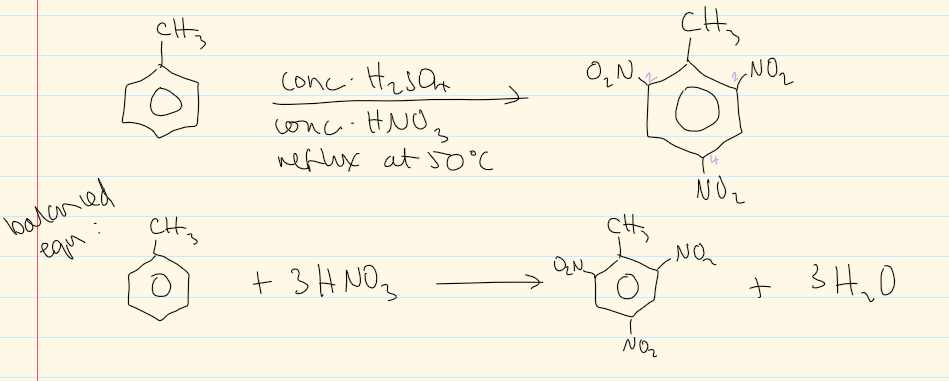
nitration of methyl benzene
rxn of benzene w halogen
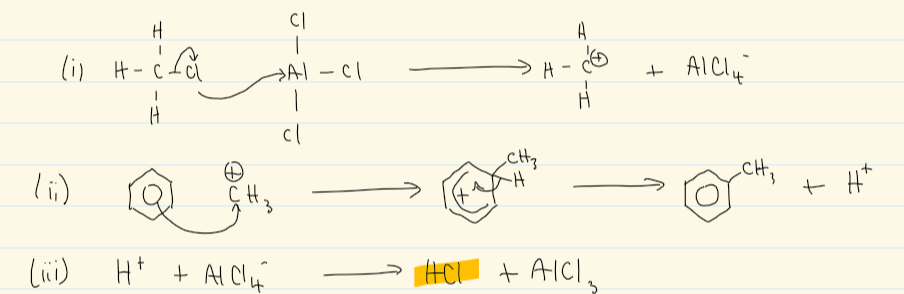
friedel-craft alkylation
friedel-craft acylation
describe the stability of benzene + why
has a high e- density in the delocalised πe- ring (which stabilises it)
benzene is stable due to delocalised πe- ring
with addition rxns, would lose πe- therefore lose stability
but w substitution rxns, keep all 6πe- therefore keep stability
overall equation of nitration of benzene
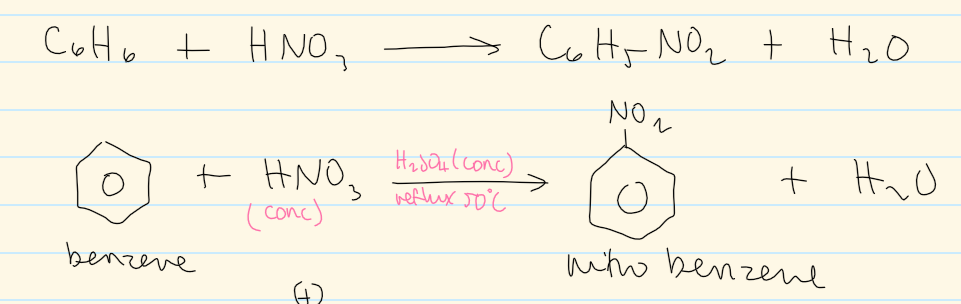
electrophile of nitration of benzene
rxn conditions of nitration of benzene (monosubstitution)
conc. H2SO4
conc. HNO3
room temp
do at reflux 50C for 2,4,6-trinitromethylbenzene
mechanism for nitration of (methyl)benzene
overall equation for nitration of methylbeNzene at reflux 50C
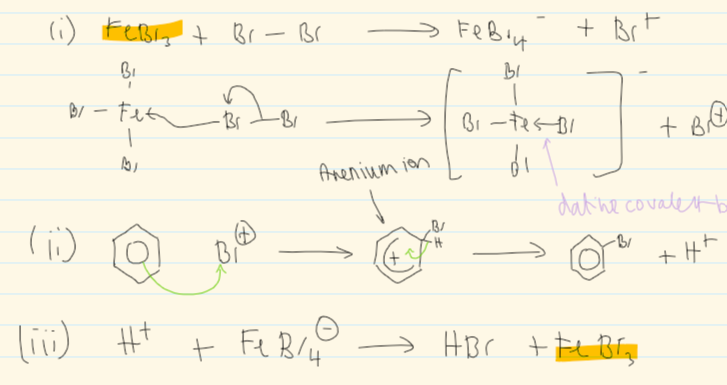
what are some halogen carriers
Fe
FeBR3, FeCl3
AlBr3, AlCl3
mechanism for rxn of benzene w halogen
overall equation of halogenation of benzene
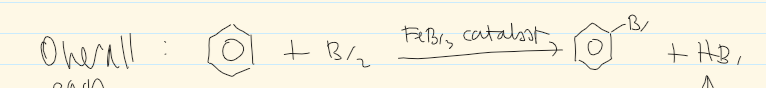
can you get multiple substitution with benzene
no - not reactive enough
how to test HBr
add H2O + AgNO3 → cream ppt
or
HBr(g) + NH3(g) → white smoke
mechanism for friedel-craft alkylation
mechanism for friedel-craft acylation
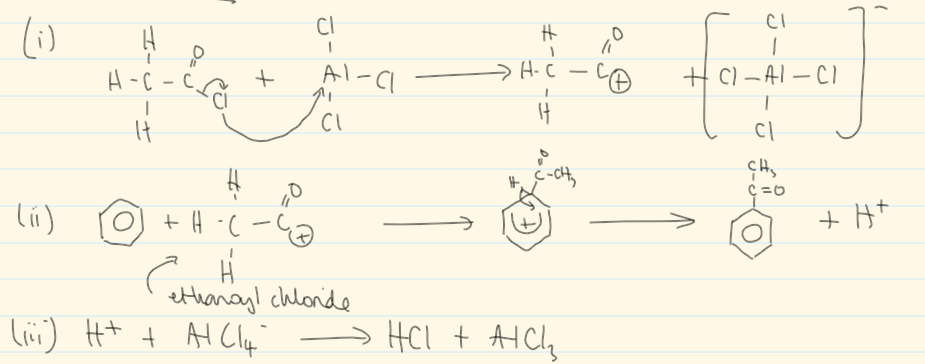
2,4 directing stuff
-NH2 or -NHR
-OH
-OR
-R or -C6H5
-F, -Cl, -Br, -I
they all have a lone pair which donates to the e- density in ring
all increase e- density in ring
3 directing stuff
RCOR
-COOR
-SO3H
-CHO
-COOH
-CN
-NO2 (is slightly e- withdrawing
-NR3+
the compound that reacts w benzene to form this
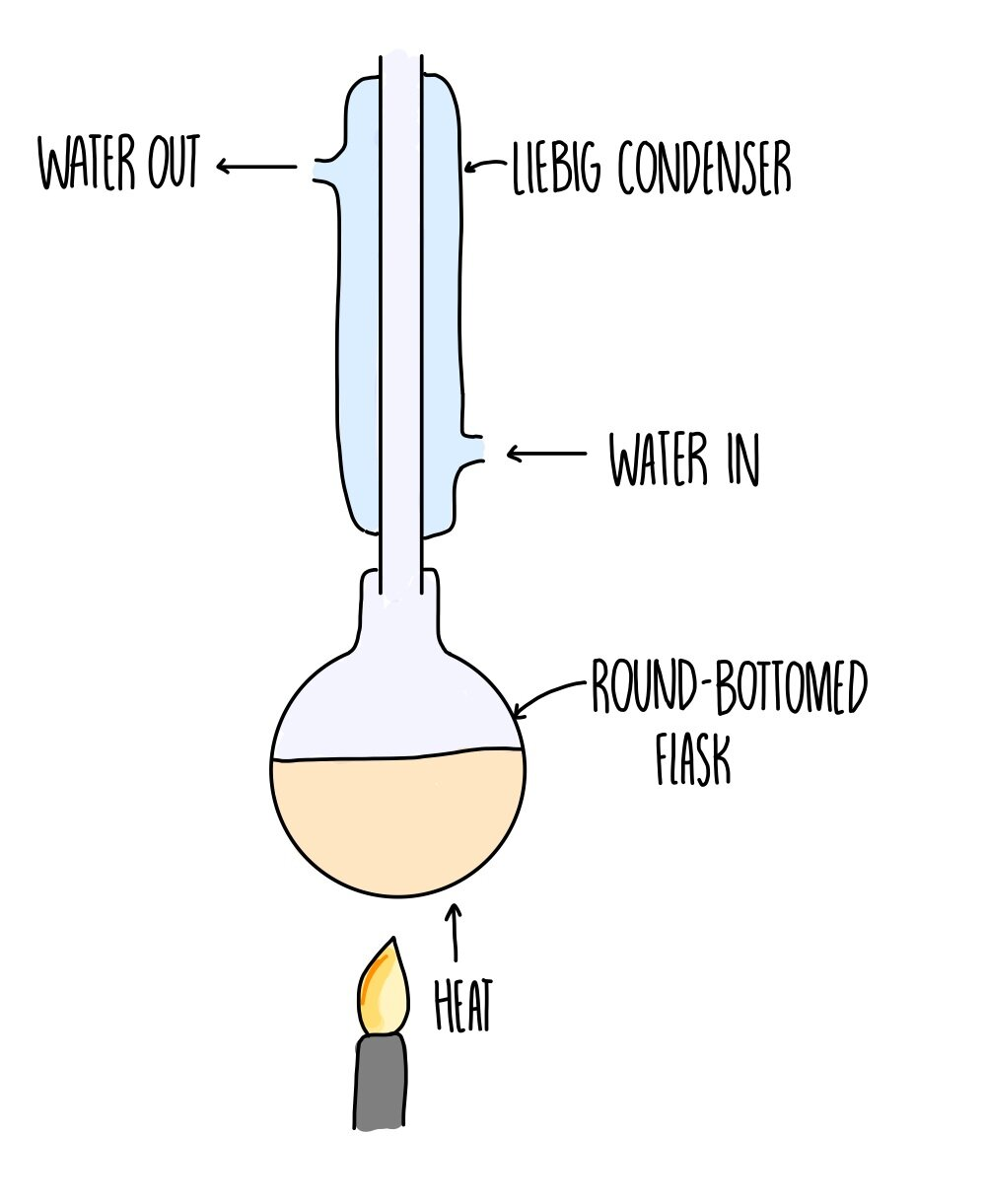
recrystallisation method
filter to collect solid
dissolve in minimum amount of hot solvent
hot filtration under reduced pressure
collect filtrate (contains product)
cool in ice bath (product becomes insoluble in cold solvent)
filtration under reduced pressure
collect residue
rinse with small amount of ice cold solvent
reflux apparatus
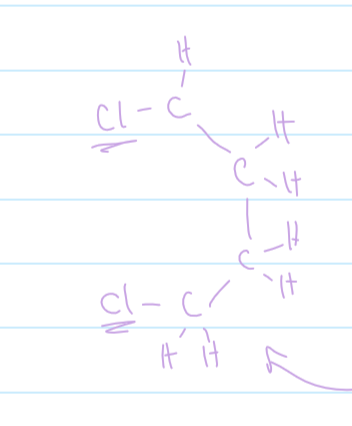
mechanism for electrophilic addition of ethene
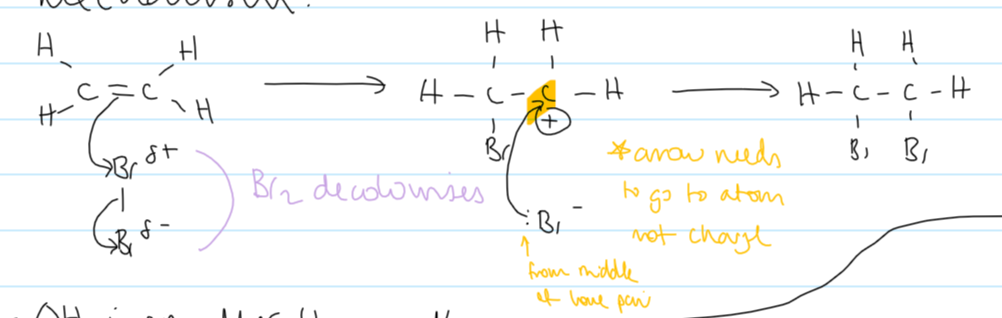
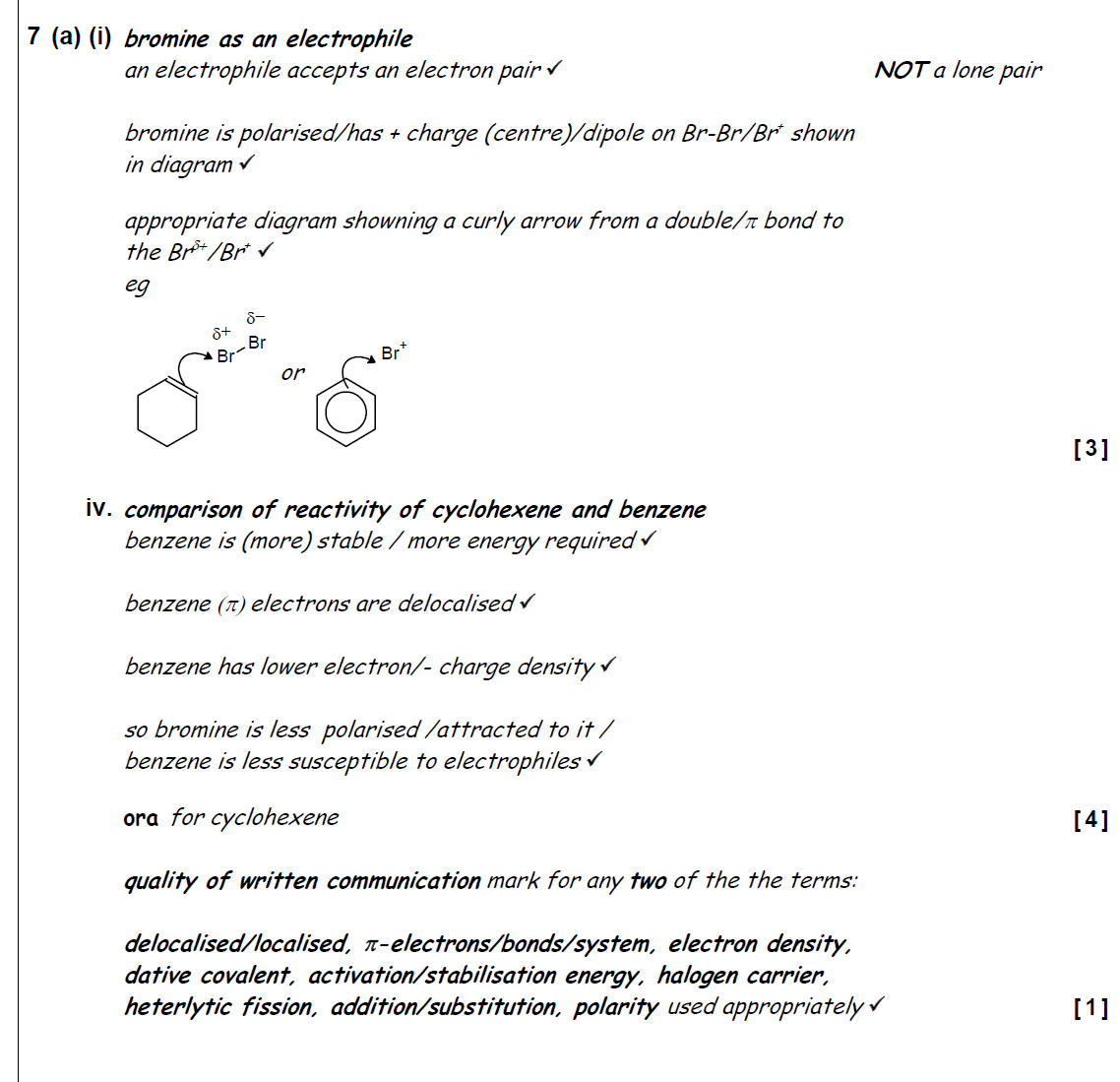
describe and explain the relative reactivity of bromine with cyclohexene and with benzene. include the type of reaction occurring in your answer.
cyclohexene:
undergoes electrophilic addition → presence of C=C → high e- density → susceptible to electrophilic attack
localised e- → more reactive → attracts electrophile more strongly
polarises Br2
benzene:
has no C=C → more stable than cyclohexene
delocalised πe- density → less reactive
requires halogen carrier to make electrophile
undergoes electrophilic substitution (can’t undergo electrophilic addn as no C=C)
only undergoes monobromination (not reactive enough to produce multiple substns)
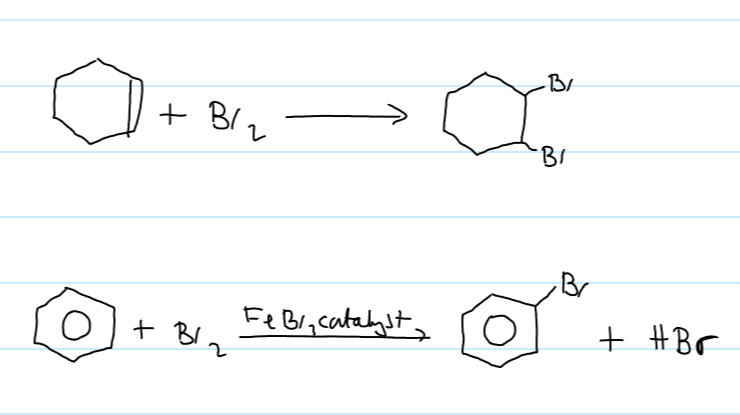
structure of phenol
8 delocalised πe- shared over 7 atoms
e- density between carbons is higher than benzene
phenol more reactive to electrophiles
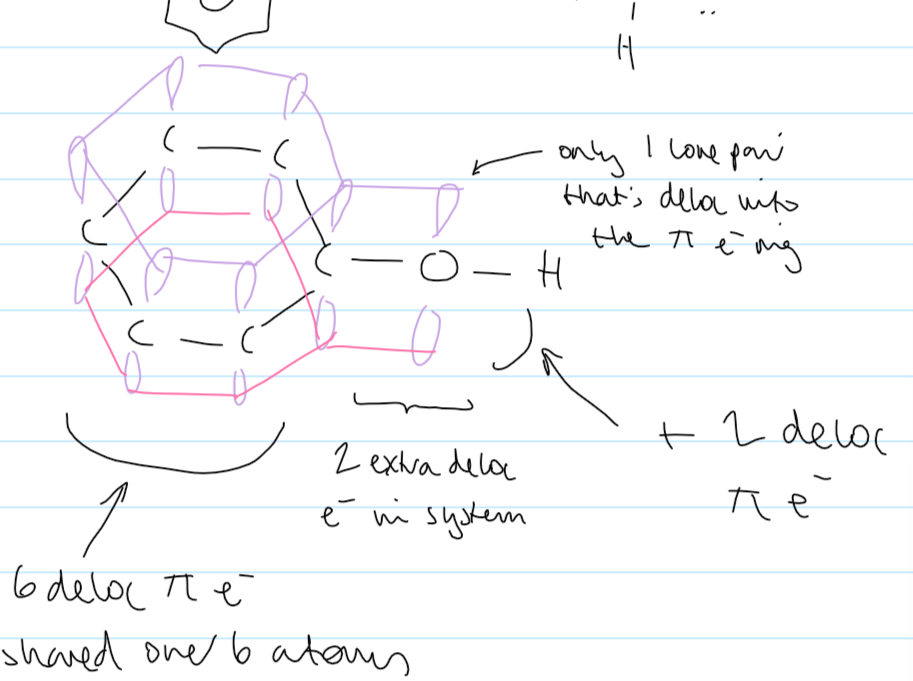
delocalised def
shared across more than 2 atoms
what type of directing is phenol
2,4 (it makes it more reactive)
compare phenol vs alcohols
phenol
shorter C-O bond length
higher e- density in C-O bond
stronger C-O bond
will undergo electrophilic subn. but on the ring (-OH isn’t replaced) (an e- is used in the deloc e- ring)
methanol
longer C-O bond
will undergo nucleophilic substitution & dehydration
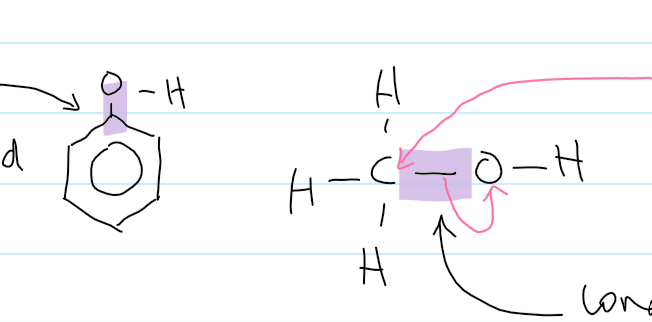
solubility of phenol
sparingly soluble in water (cuz not enough H-bonds to hold phenol and water together)
does form H-bonds
not as strong as other alcohols
large non-polar ring
only forms L.F. with water
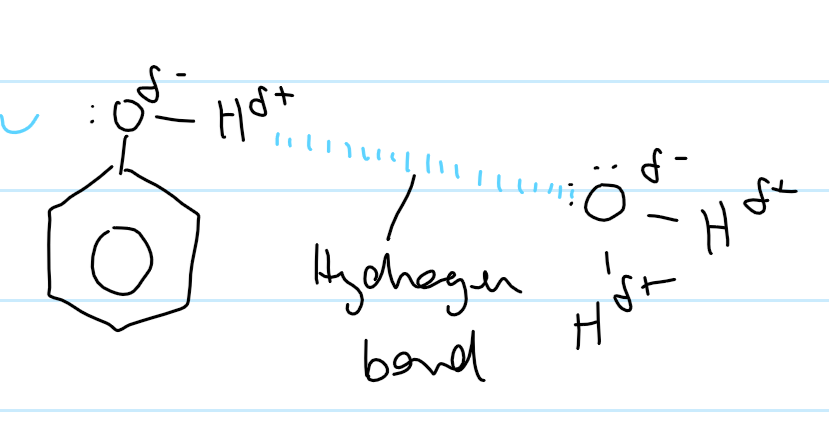
is phenol in water acidic or alkali
acidic
strong C-O, weaker O-H
donates proton

arrange acidity of alcohols, phenol, water
phenol (most acidic) (but is a weak acid)
water
alcohol
bpt of phenol
higher bpt than benzene
O-H group
stronger IMF, has H-bonds
a crystalline solid
colourless/pale pink
smells of antiseptic
highly corrosive
chemical rxns of phenol
as an acid
with Na
w NaOH
w the ring
Br2
HNO3 nitric acid
overall rxn of Na + phenol
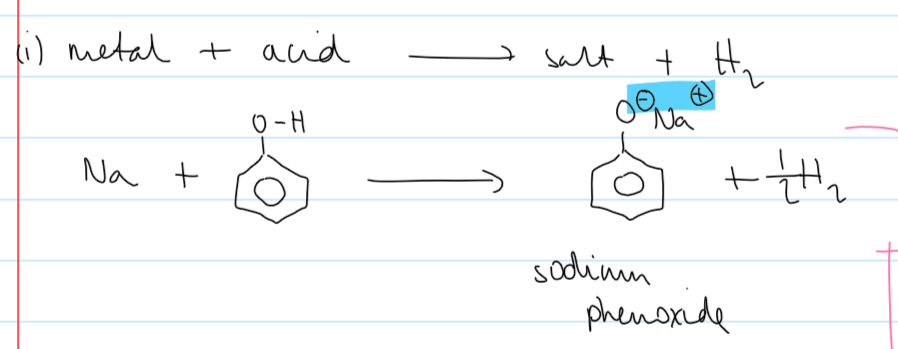
observations of Na + phenol
the product - sodium phenoxide - is a soluble ionic compound so will dissolve

NaOH + phenol eqn

observations of NaOH + phenol
phenol disappears (sparingly soluble phenol → ionic salt which is soluble)
phenol + Na2CO3
no reaction, no fizzing
reactivity table of alcohols, phenols, c-acids w Na, NaOH, Na2CO3
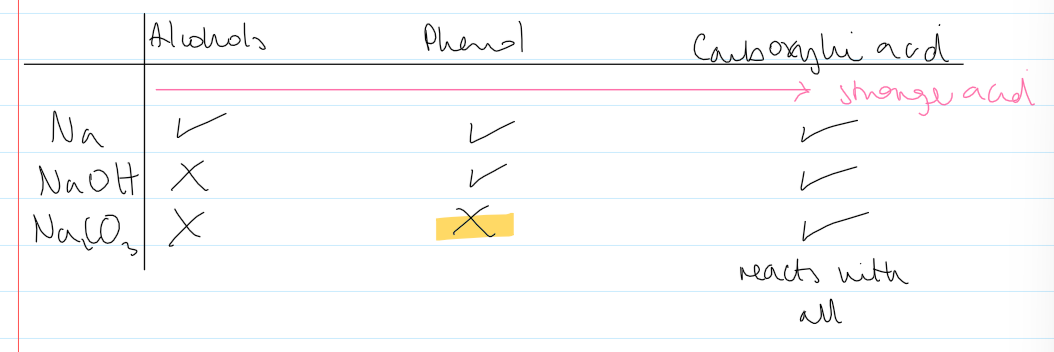
strongest acid out of phenol, c-acids, and phenol
c-acids
alcohols r weakest
phenol in middle
can test which one it is through this

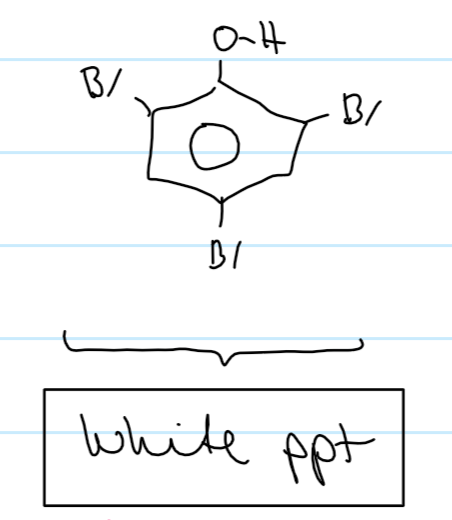
what colour is 2,4,6 - tri bromo phenol
white (can be a test for phenol)
do you need a halogen carrier when halogenation phenol
no
1 lone pair of is delocalised into benzene ring
extra delocalised e-
8 x pi e- delocalised across 7 atoms
more e- density in the ring
enough e- density to polarise Br2
don’t need halogen carrier for electrophilic addition
what observations do you see when phenol reacts with bromine
orange Br2 decolourises
white ppt formed (2,4,6-tribromophenol)
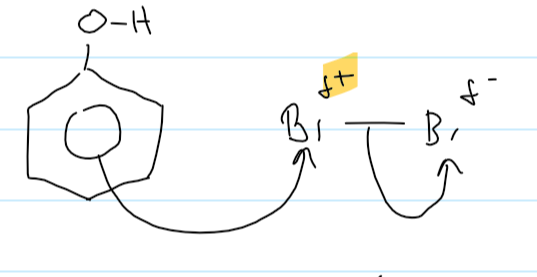
why is benzene + Br2 a substitution reaction
a hydrogen atom is replaced by a Br atom
2 products
1st step of the mechanism for phenol + Br2
what is the electrophile when phenol reacts w HNO3 (nitric acid)
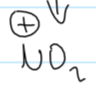
what kind of reaction is phenol + HNO3
electrophilic substitution
do you need H2SO4 to make the electrophile (for benzene + HNO3)
no
phenol is more reactive than benzene so H2SO4 isn’t needed
conditions + equation for monosubstitution of HNO3 + phenol
room temp
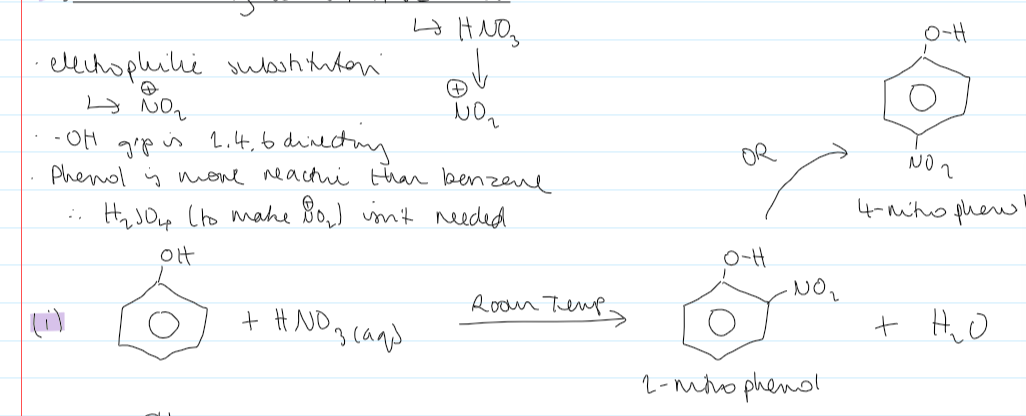
conditions + equation for multiple substitutions of HNO3 + phenol
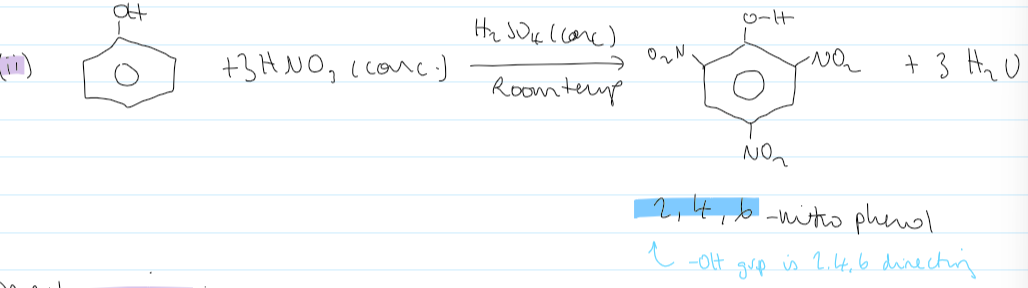
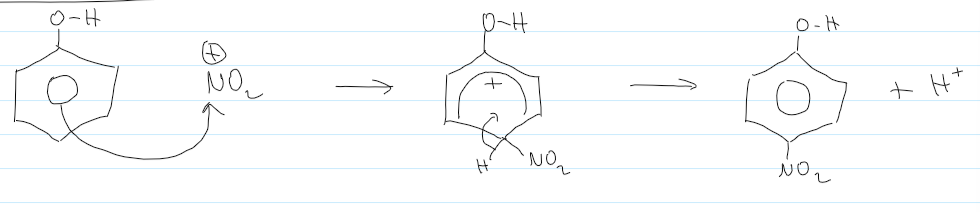
mechanism of phenol and NO2+ electrophile
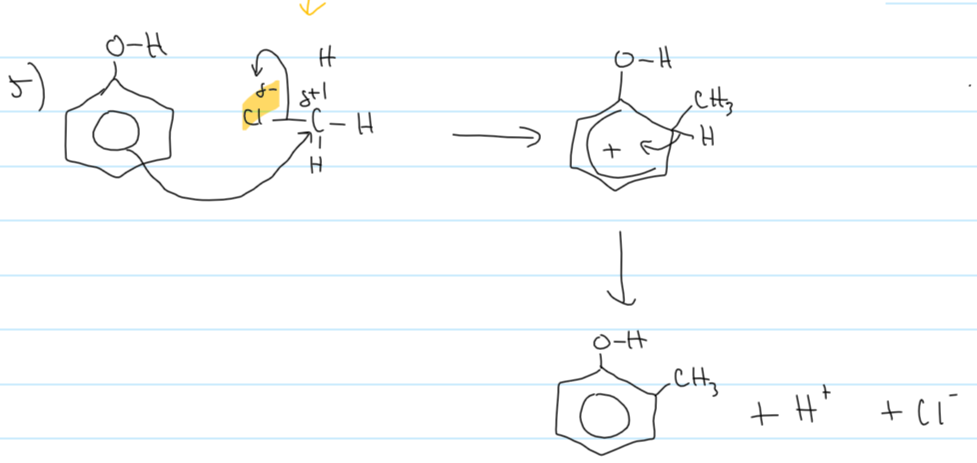
mechanism for phenol + chloromethane
empirical formula of benzene
CH


(and include the reaction)

why is the reaction of benzene + chlorine banned in teaching laboratories in schools?
benzene causes cancer

more effective
Al is smaller than Fe because it has fewer shells
so less e- shielding
so increased nuclear attraction
so polarises Cl2 molecules more readily
why are halogen carriers called halogen carriers
they bind to the halogen and create the electrophile