Eukaryotic protein synthesis
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Characteristics of DNA
double stranded, deoxyribose sugar, nitrogen bases ATCG
Characteristics of RNA
single stranded, ribose sugar, nitrogen bases AUCG, three types: mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
name the parts of a nucelotide
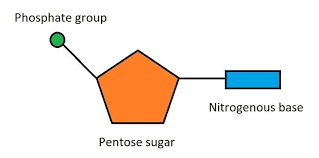
Bond between adjecent nucleotides
phosphodiester bond
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
takes genetic code transcribed from the DNA to the Ribosome
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
located in the ribosome
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
carries specific amino acid to Ribosome to build protein
Gene
a section of DNA that codes for a protein
Gene expression and what it involves
the process by which the information in a gene is used to synthesise a functional product, usually a protein. It involves transcription (DNA → mRNA) and translation (mRNA → protein).
Structural genes
code for proteins invloved in structure and function
Regulatory genes
control the activity of other genes, and often code for repressor proteins, which bind to the promotor region and prevent transcription
A regulatory gene codes for a protein that has a function in the body; true or false?
false, they create proteins that control other gene function (i.e. turning other genes on or off)
Gene expression is the same as __?
protein synthesis, transcription and translation to produce proteins
- make flashcard with diagram of gene expression process*
Triplet
sequence of 3 DNA bases
Codon
sequence of 3 RNA bases
Anticodon
complementary sequence of 3 tRNA bases
Degenerate/redundant code
one amino acid could be coded for by various DNA triplet combinations
Universal DNA/genetic code meaning
one mRNA codon codes for the same amino acid in almost all organisms (but basically the DNA too since the mRNA comes from it)
Promotor region
located at the start of the gene and regulates gene activity. Enzymes bind here to begin transcription
Coding region
contains introns and exons
Introns
non-coding segments of a gene that are spliced out during RNA processing (after transcription but before translation) and so are not translated into a protein (hint: introns go IN the bin)
Exons
coding segments of a gene that is transcribed and joined together in RNA processing. They are translated into proteins during translation (obviously) (hint: exons or EXpressed)
Terminator sequence
section of DNA located at the end of the gene that signals RNA polymerase to stop transcription/that the gene has ended. It causes mRNA to be released
- make card with gene structure image*
Transcription
the process where RNA polymerase reads a gene’s DNA template strand and synthesises a complementary pre-mRNA strand.
It occurs in the
nucleus
and is the
first step
of gene expression.
(RNA processing follows to convert pre-mRNA to mature mRNA)
Transcription factors
regulatory proteins that help control gene expression. They bind to specific DNA sequences, such as the promoter, to help activate or repress transcription.
Transcription complex
formed at the promoter and made up of RNA polymerase and transcription factors.It enables RNA polymerase to bind and start transcription. It’sonly formed when a gene is actively being transcribed, not all the time.
Steps of transcription
The enzyme RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter region of the gene and unzips/unwinds the DNA.
RNA polymerase binds to the template strand (so the mRNA is the same as the coding strand), bringing in free RNA nucleotides which are complementary to the DNA.
Single stranded mRNA forms.
DNA template reads 3' to 5' and mRNA is synthesised 5' to 3'.
End product pre-mRNA!
RNA processing
also known as post-transcription modification and is considered part of transcription, pre-mRNA has introns removed, poly A tail added, and methyl cap (modified guanine) added, which protects the RNA as it travels through the cytoplasm. End product: final-mRNA, which leaves the nucleus and travels to ribosomes
Alternative splicing
splicing occurs to remove introns from pre-mRNA. Exons are joined together after splicing to produce a final/mature mRNA transcript. A primary mRNA transcript can be spliced in multiple ways which will change/result in alternative final/mature mRNA strands
- How will alternative splicing affect the protein?
a gene can produce multiple proteins via alternative splicing
Transfer RNA/tRNA
specific amino acid attatches on one end and anticodon is at the other end
Ribosomal RNA/rRNA
ribosomes are mostly made up of this. Ribosomes are the site of translation.
Translation
the building of a polypeptide chain from amino acids guided by the sequence of codons in the mRNA. Occurs in ribosomes, location: cytoplasm
START codon
AUG (codes for met amino acid), it's at the start of every protein
STOP codon
UAA, UAG, UGA, all code for 'no amino acid' signalling the end of the protein. (so there is one at the end of every protein)
Steps of translation
mRNA feeds into the ribosome.
start codoon AUG starts the process and also codes for the amino acid 'met'.
a tRNA with anticodon UAC is drawn to the mRNA codon AUG
anticodon and codon form hydrogen bonds according to base pair rules (A-U G-C).
these bonds are formed temporarily and broken when
the amino acid 'met' is dropped off.
this process continues as the mRNA moves along the ribosome and peptide bonds form between amino acids to produce a polypeptide
translation stops when STOP codon is reached (no amino acid)
Can mRNA be used multiple times?
yes, one mRNA can feed through many ribosomes to make multiples polypeptides. these could then enter the rough ER to undergo further modificaiton in the process of becoming a funcitonal protein.
Gene expression = ?
protein synthesis

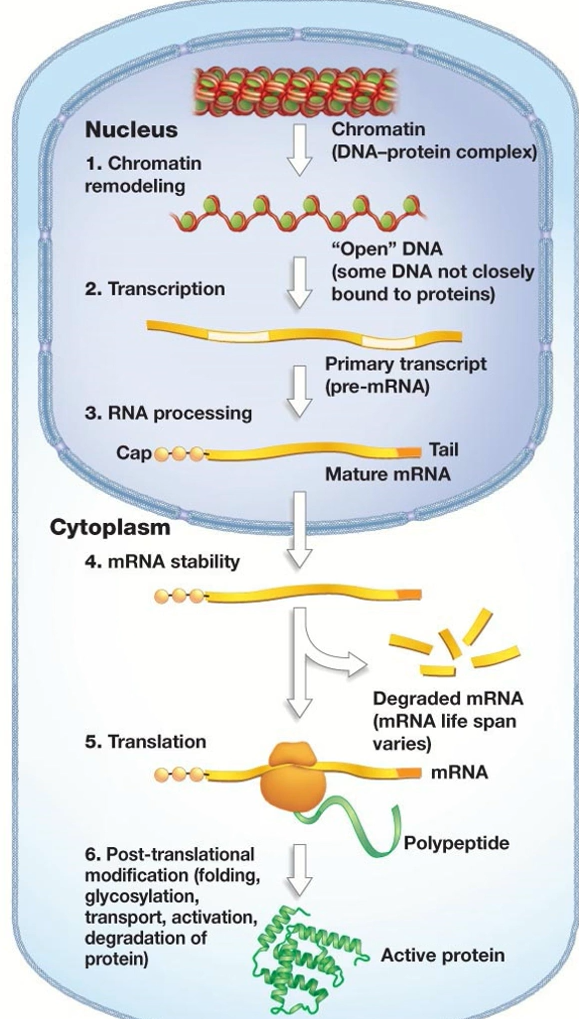
How is it possible for one gene to produce multiple proteins via alternative splicing?
a cell must recieve a signal to initiate transcription. Different signalling molecules can result in the production of different transcription factors, leading to different proteins produced from a single gene. This can occur via alternative splicing of exons during post transcriptional modification resulting in the production of different proteins