APAH: Unit 3 - Roman, Early Christian, Byzantine, & Medieval Art
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
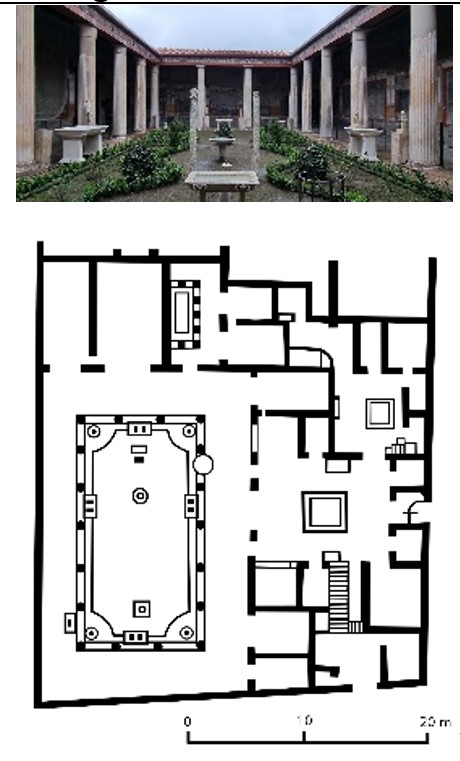
House of Vetti
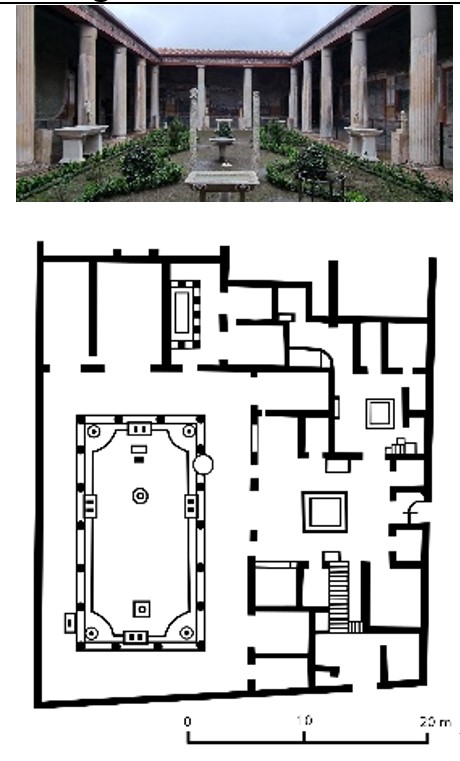
House of Vetti (culture & location)
Roman; Pompeii, Italy
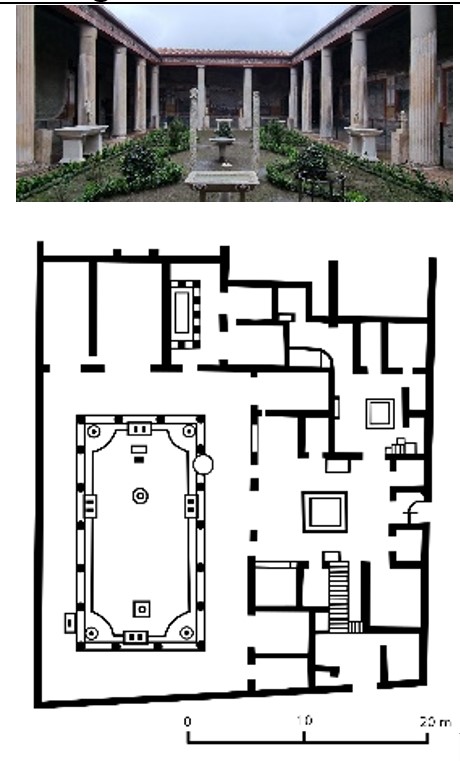
House of Vetti (date & material)
67-79 CE; stone & fresco
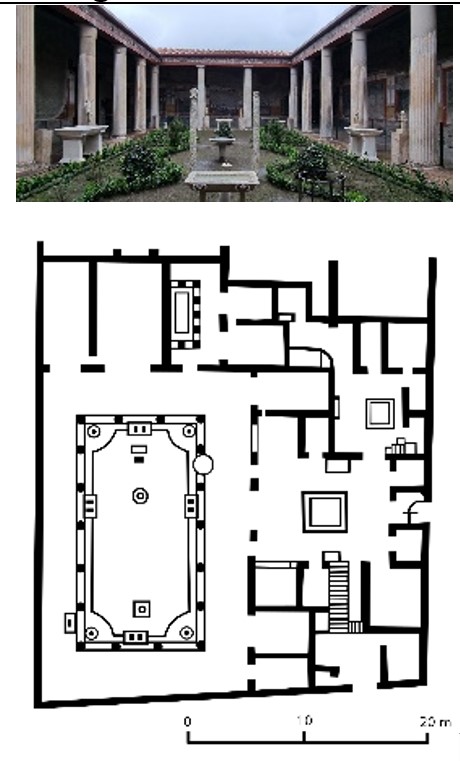
House of Vetti (use & facts)
home of two merchant brothers
destroyed when Mt. Vesuvius (79 CE)
narrow entrance from street leads to open atrium
impluvium (catch basin) collets rainwater
cubicula (bedrooms) radiate from atrium
peristyle garden with sculpture & fountain
no exterior windows
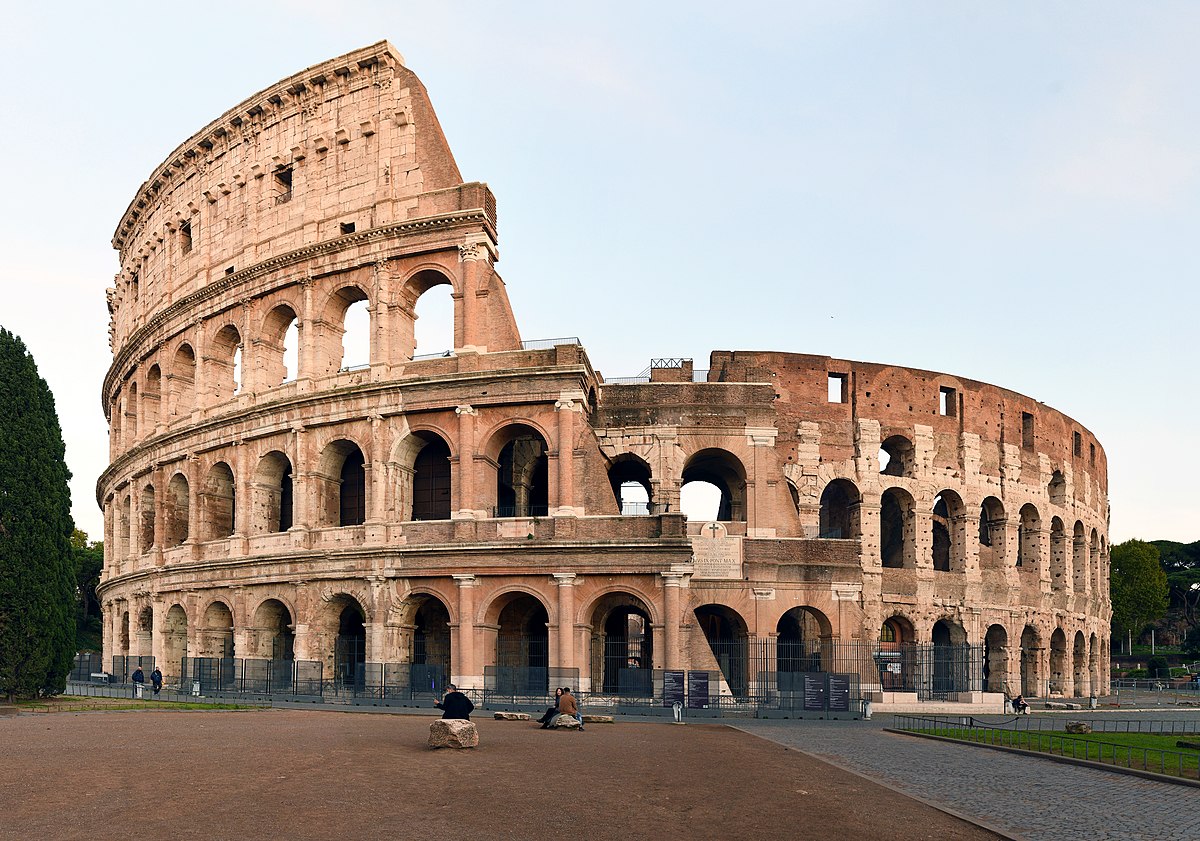

Coliseum (Flavian Ampitheater)
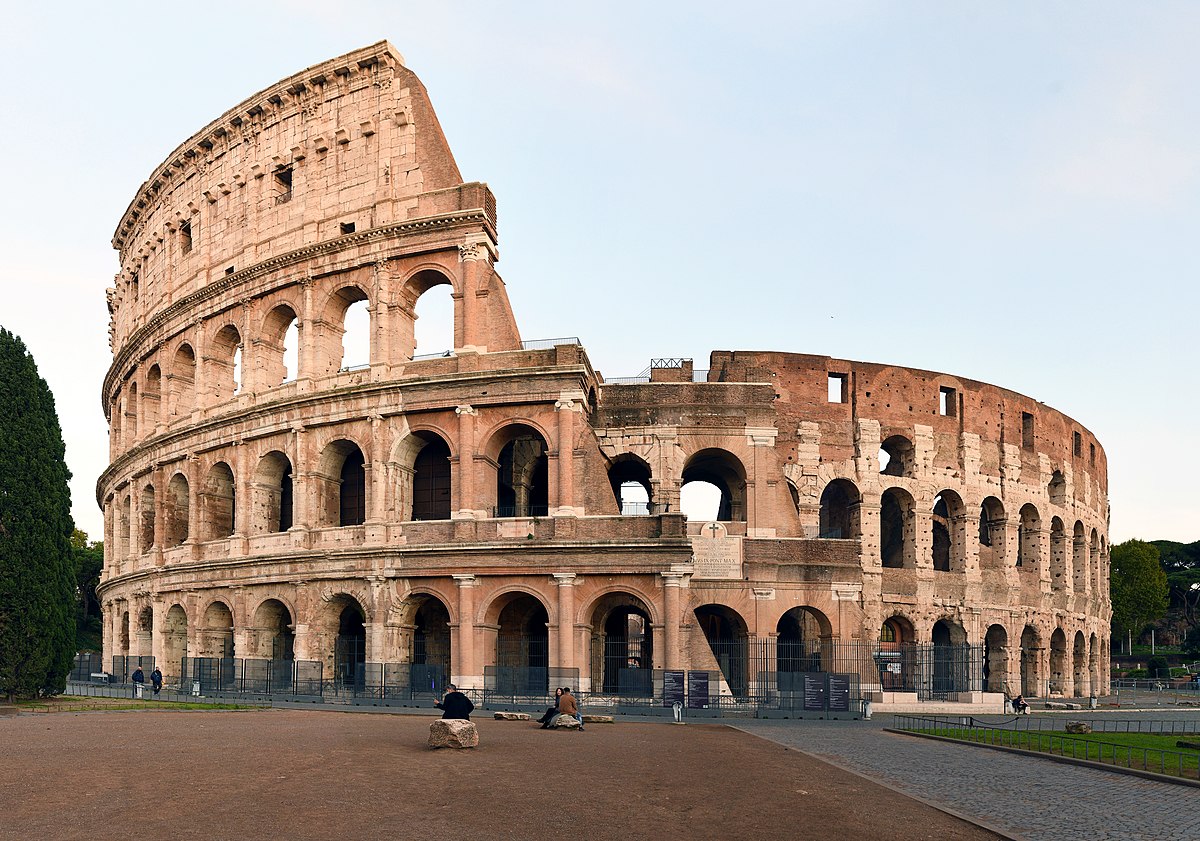

Coliseum (culture & location)
Roman; Rome, Italy
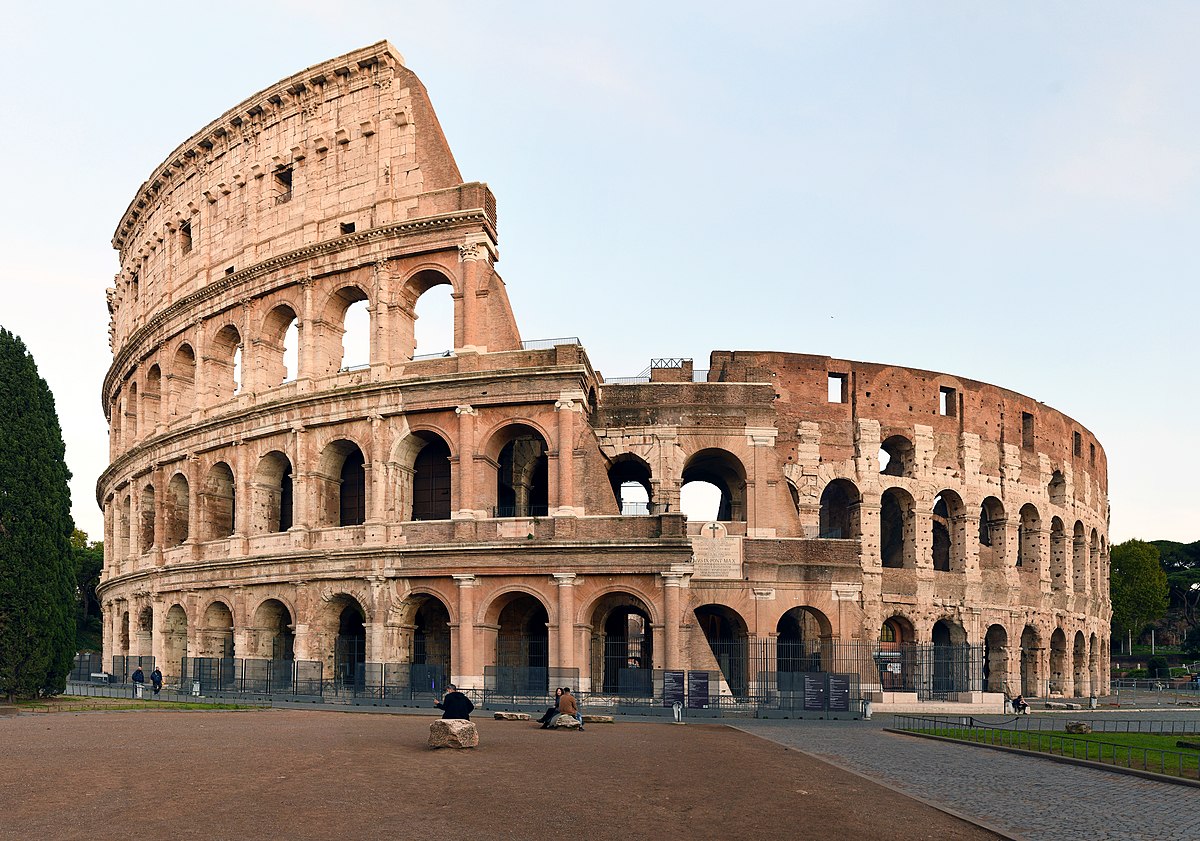

Coliseum (date & material)
70-80 CE; stone & concrete
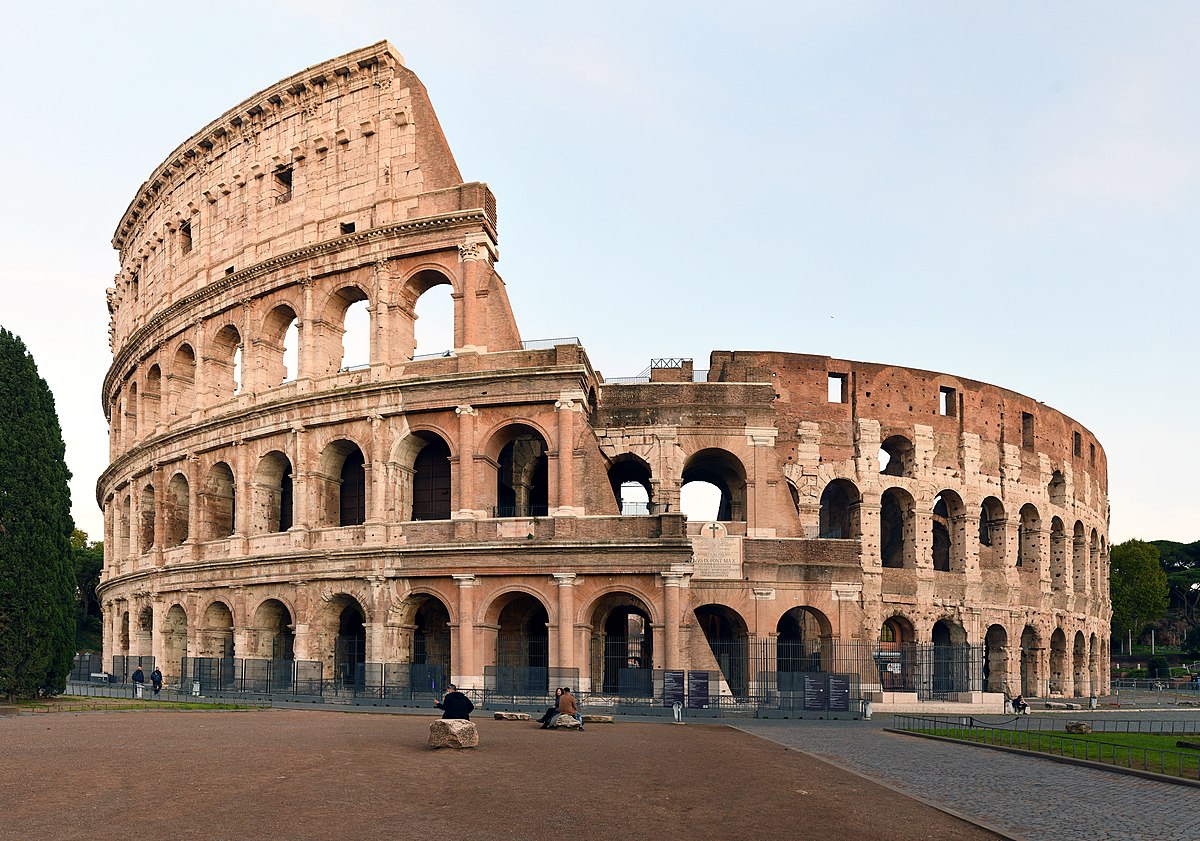

Coliseum (use & facts)
houesd entertainment to prevent rebellion
system of arches
embedded Doric, Ionic, & Corinthian columns
held 10,000 people
site of gladiator games (kept people from rebelling)
could be flooded for mock battles
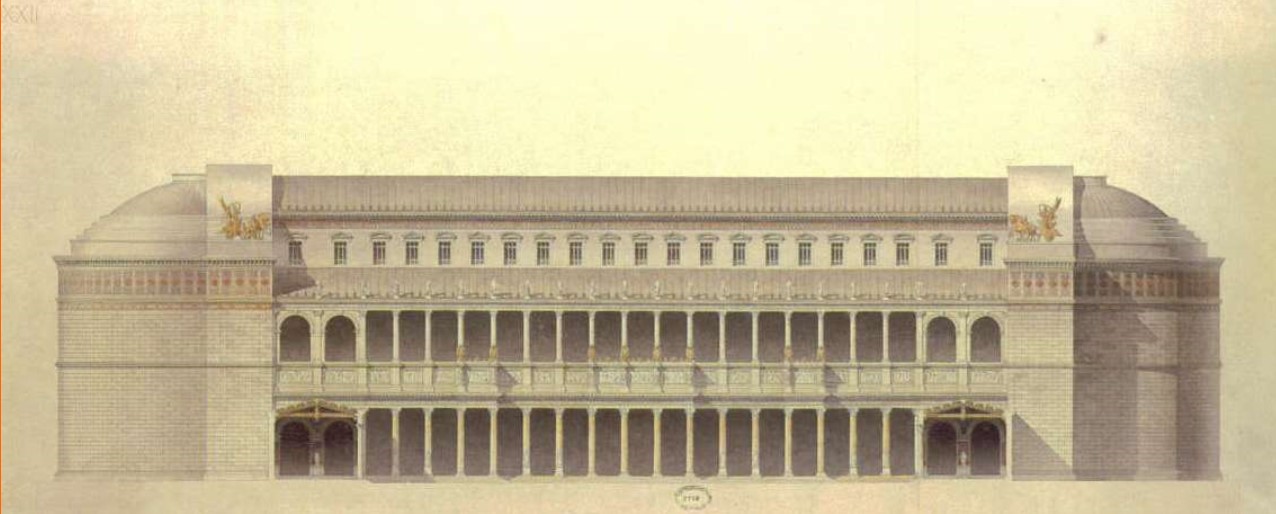
Basilica of Ulpia
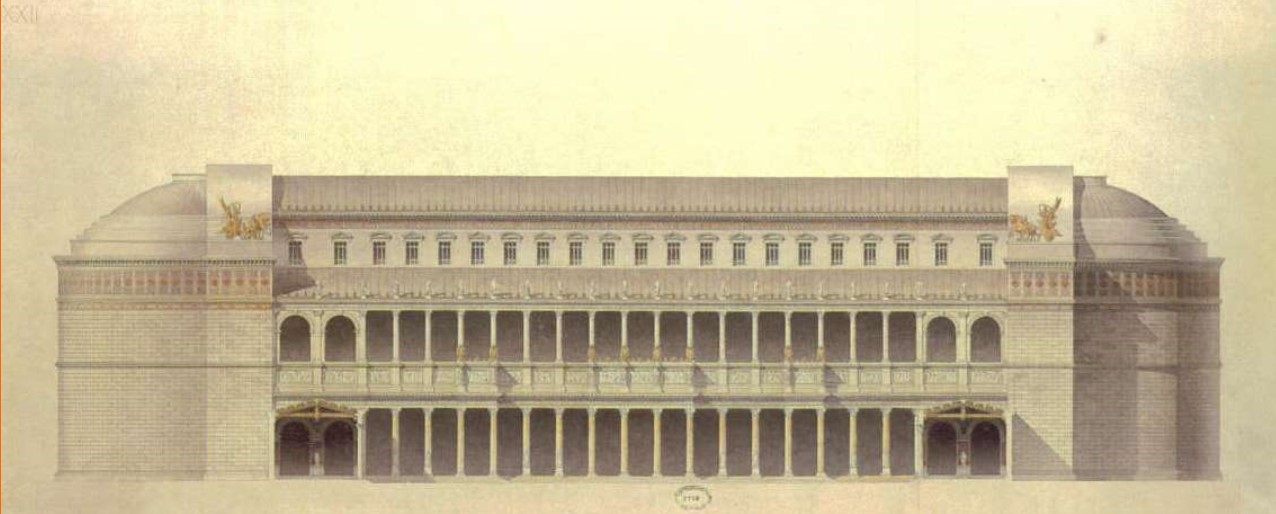
Basilica of Ulpia (culture & location)
Roman; Rome, Italy
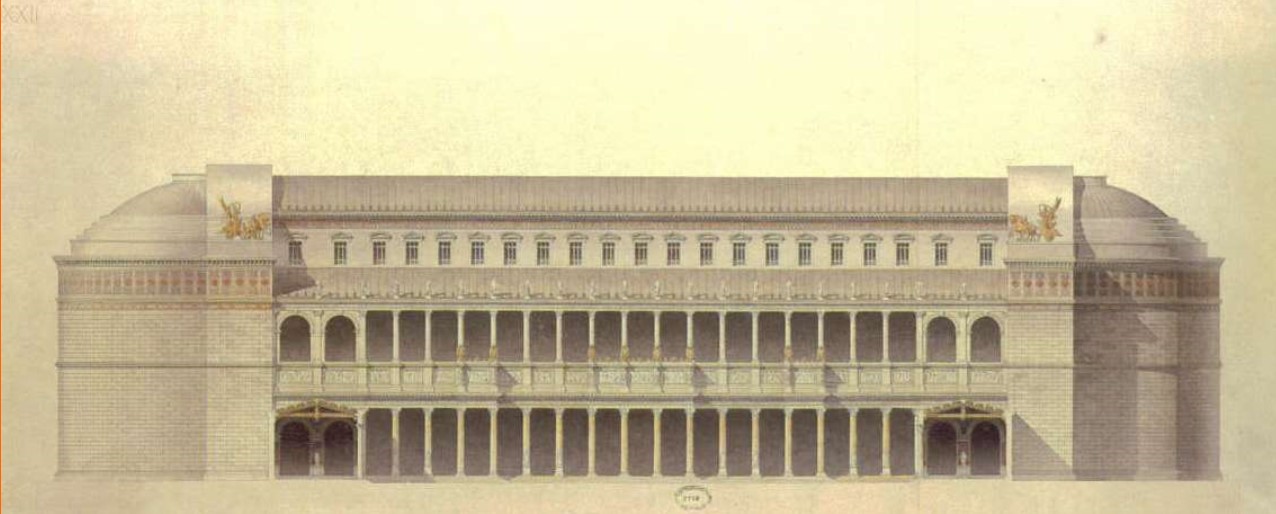
Basilica of Ulpia (date, material, creator)
112 CE; timber; Apollodorus of Damascus
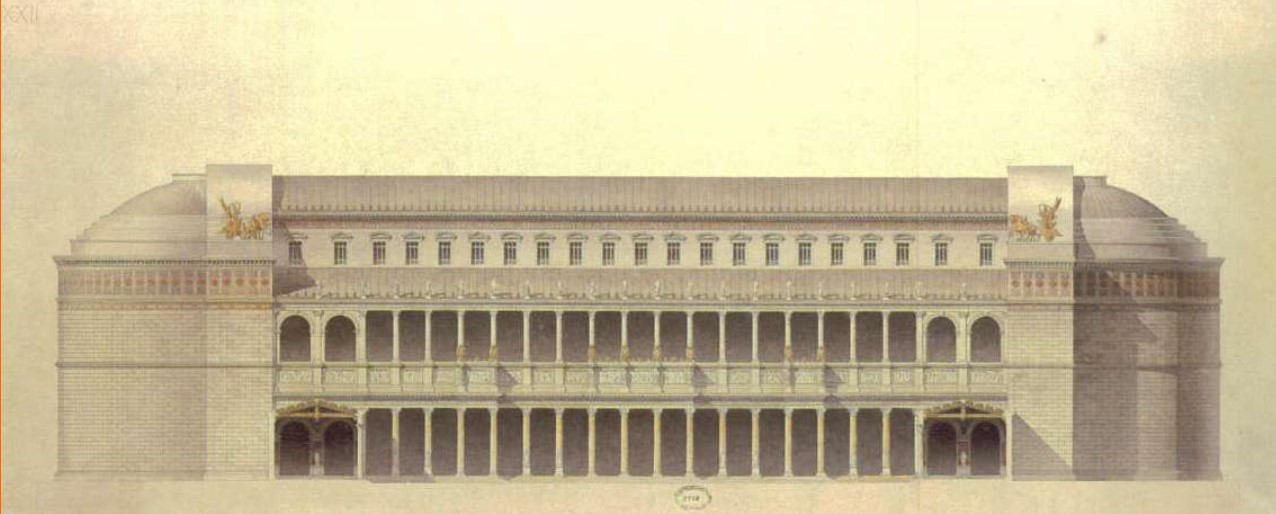
Basilica of Ulpia (use & facts)
housed law courts & markets
part of the complex of Trajan (an emperor)
385 by 182 ft, two apses (large recesses), immense interior space
double colonnaded aisles
second floor had clerestory windows
Ulpia is Trajan’s family name
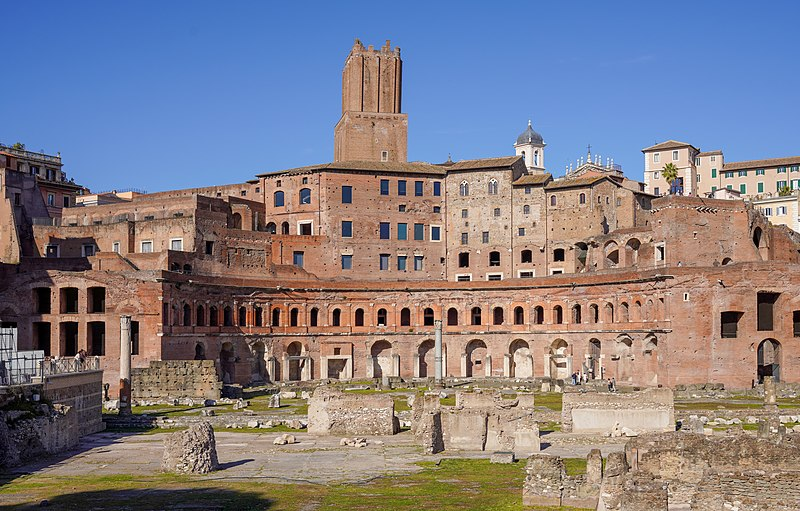

Market of Trajan
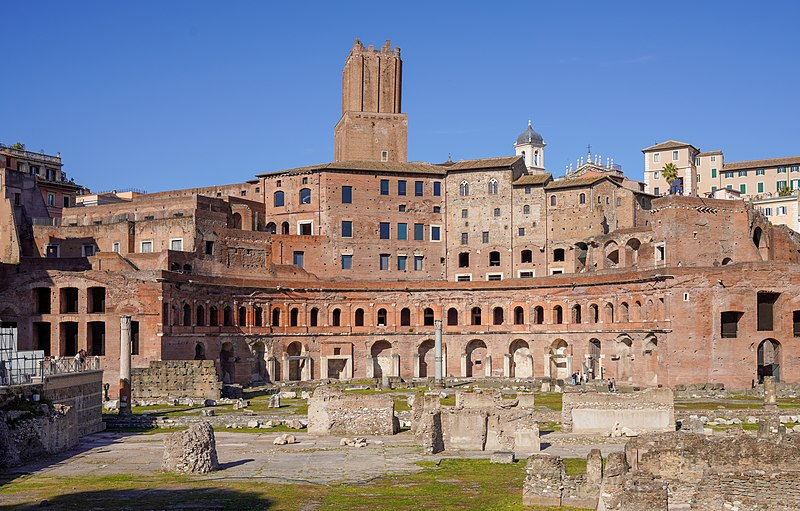

Market of Trajan (culture & location)
Roman; Rome, Italy
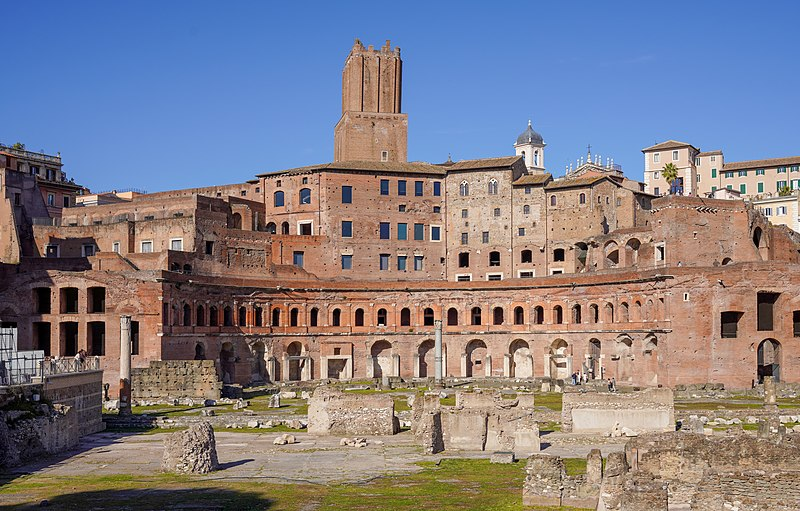

Market of Trajan (date & material)
106-112 CE; brick & concrete
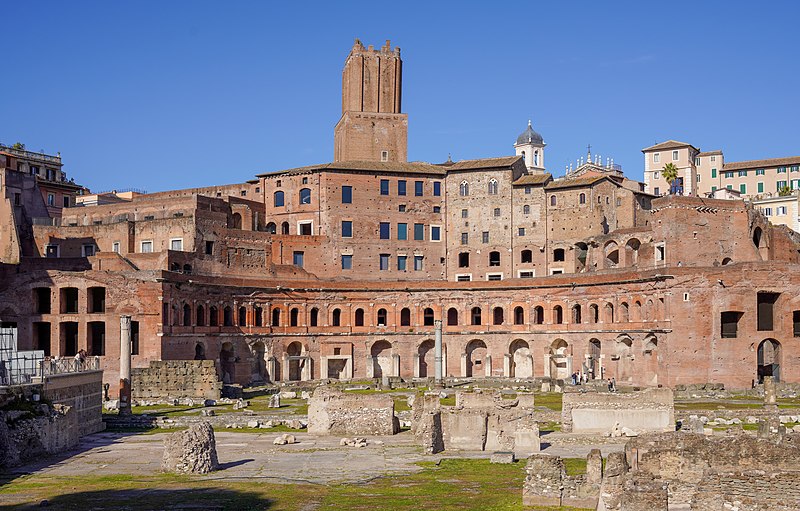

Market of Trajan (use & facts)
housed shops
original market had 150 shops, to form a multilevel mall
semicircular
used groin & barrel vaults
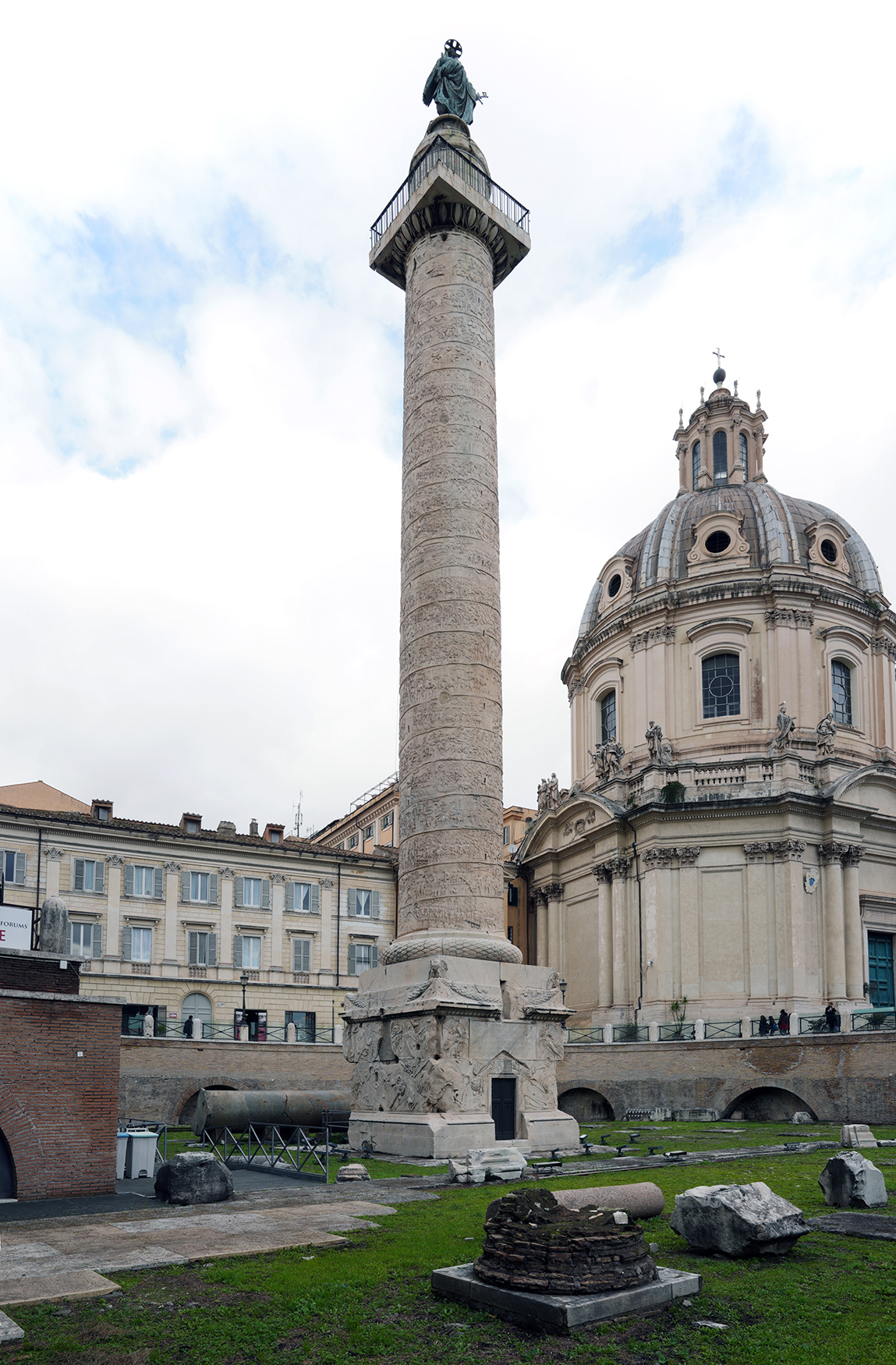

Column of Trajan
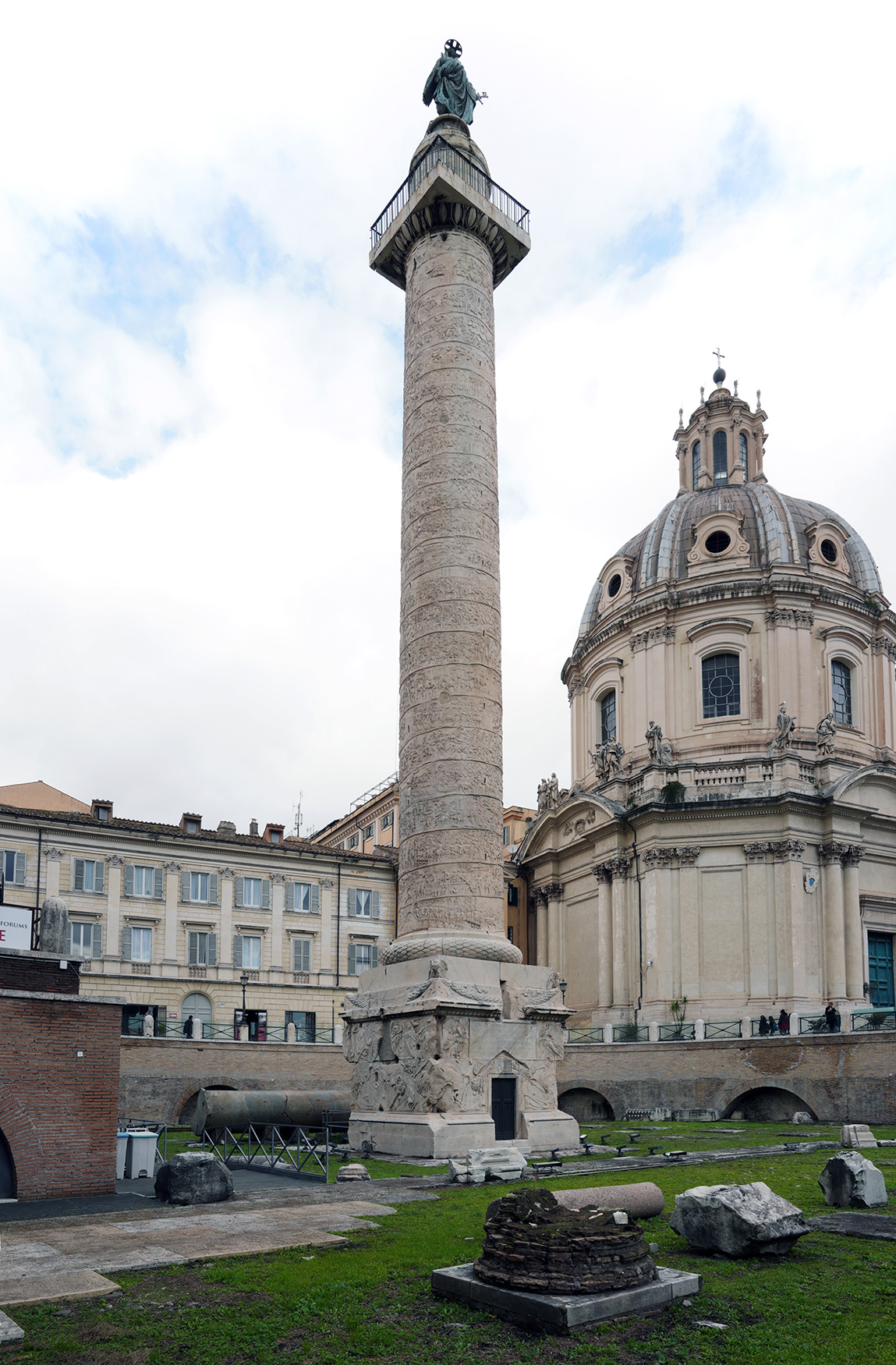

Column of Trajan (culture & location)
Romna; Rome, Italy
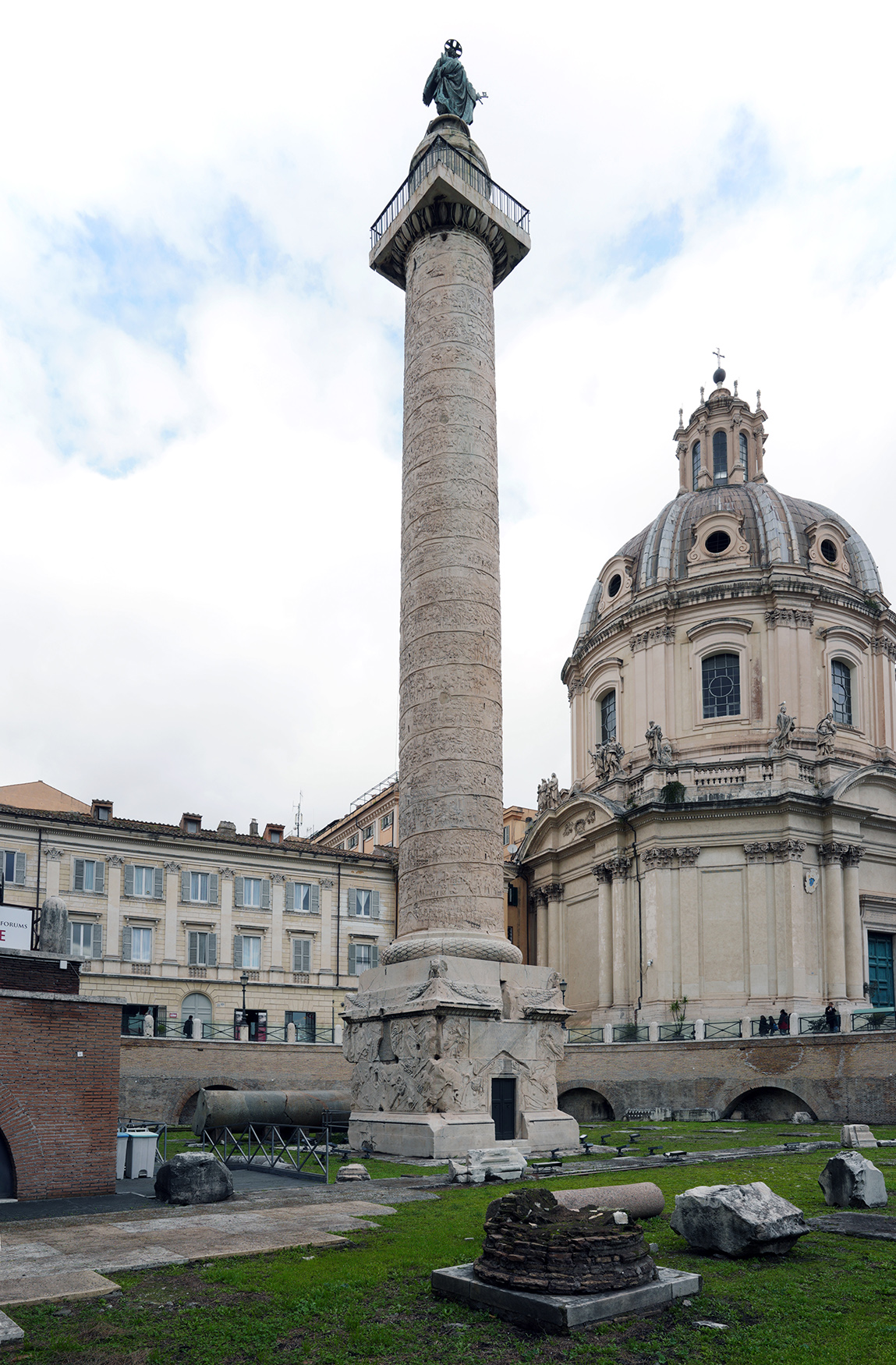

Column of Trajan (date & materials)
113 CE; brick, concrete, & marble
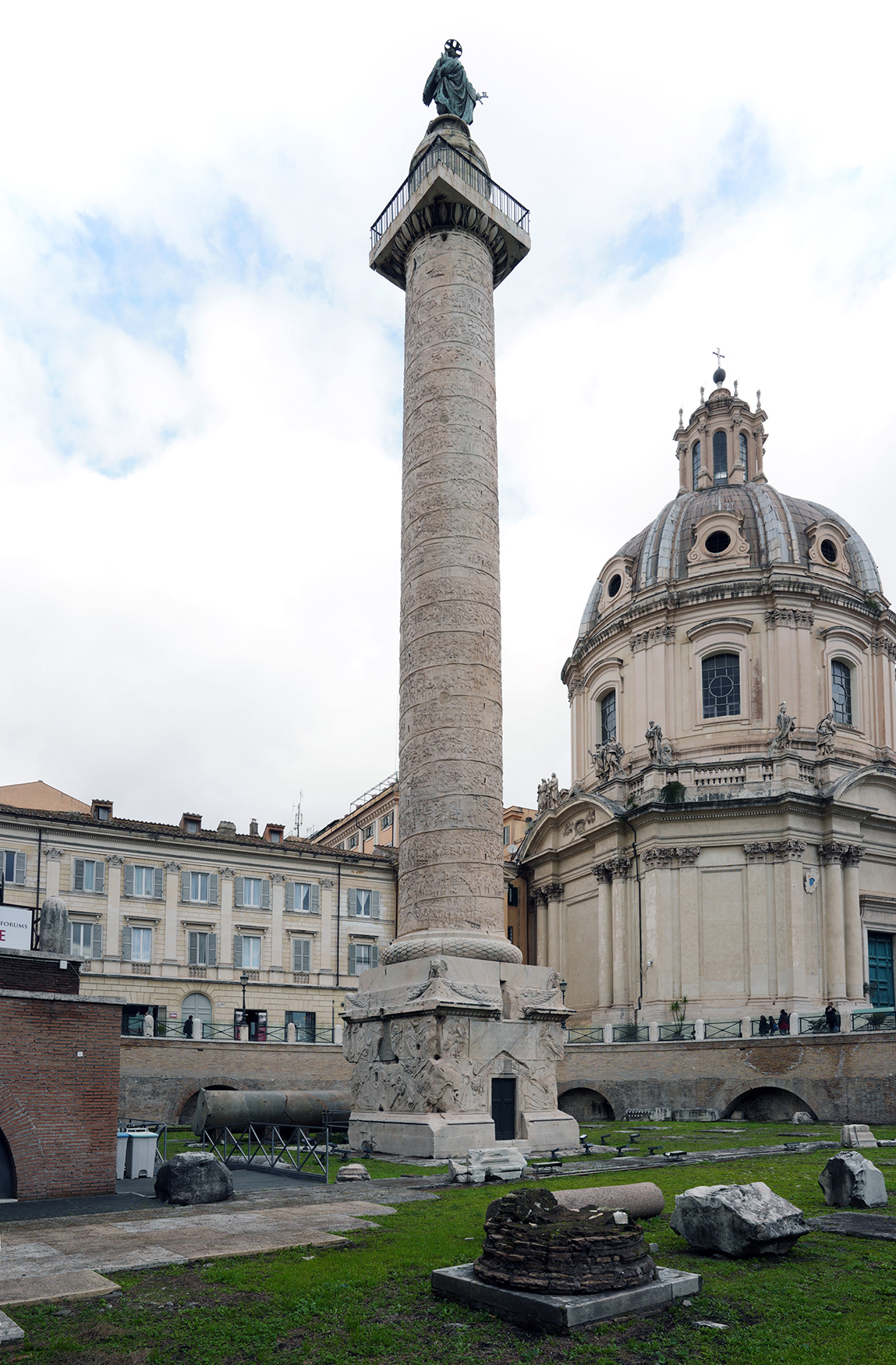

Column of Trajan (use & facts)
burial chamber of Trajan depicting his success in life
narrative or Roman battles
emphasizes methodical planning & imperial leadership
shows battles, Roman army building bridges, forts, training, & making sacrifices to gods
shows theme of Roman power
shows Trajan’s victories blessed by personification of Victory (Nike)
relief sculpture
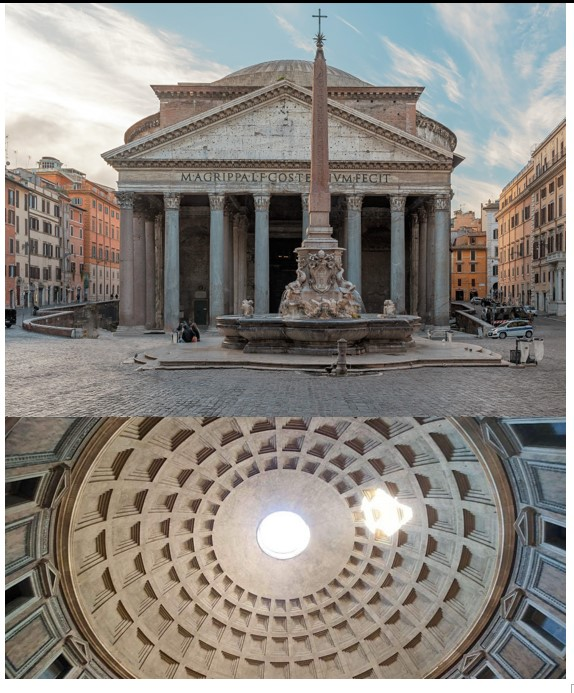

Pantheon
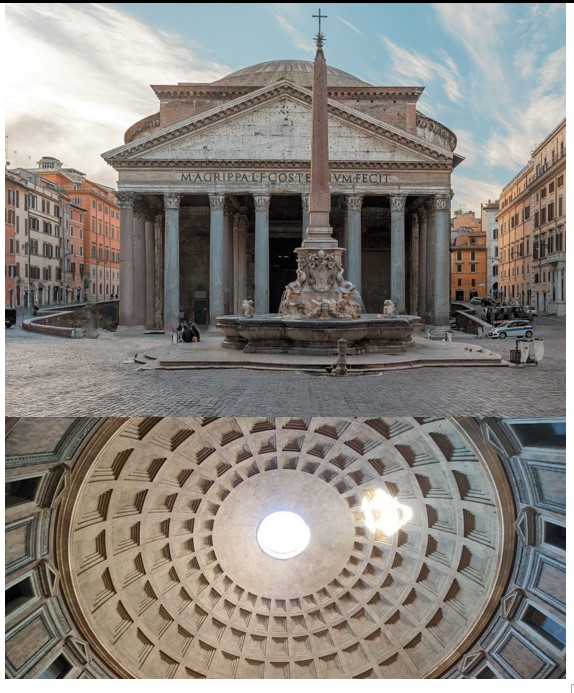

Pantheon (culture & location)
Roman; Rome, Italy
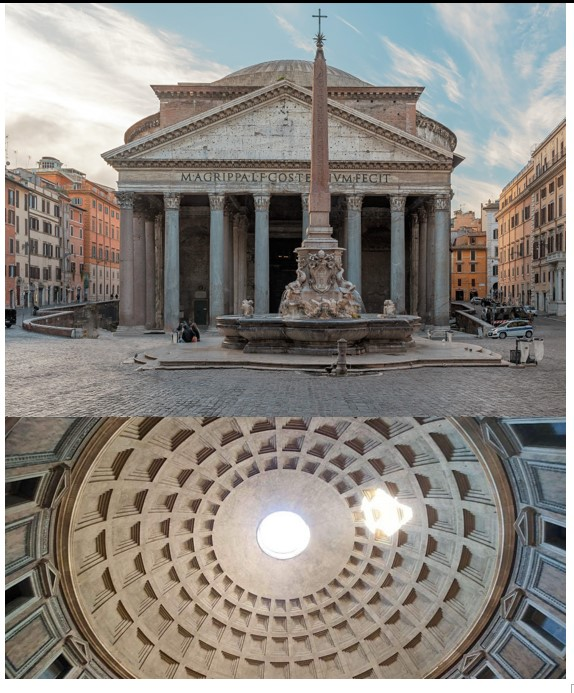

Pantheon (date & material)
118-125 CE; concrete with stone facing
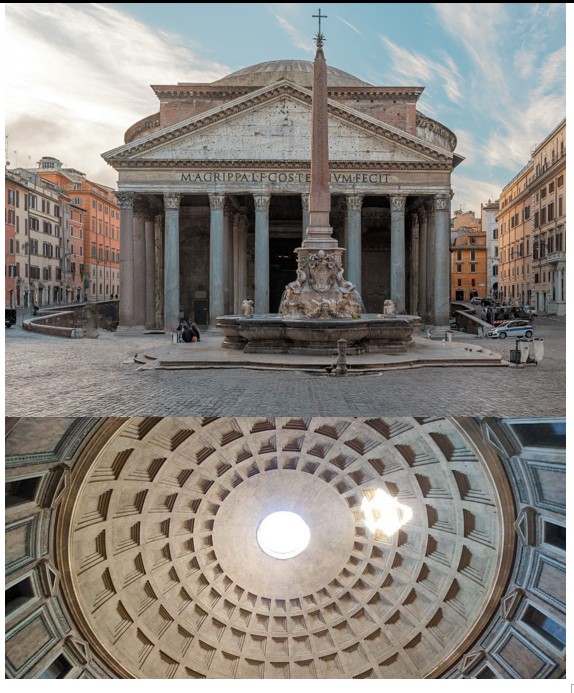

Pantheon (use & facts)
temple to all the Roman gods
Roman engineering, practicality, & style (first dome!)
niches carved out were occupied by statues of all gods (pan = all)
walls are 20ft thick
Corinthian columns
27ft “oculus” provides light
coffered ceiling (makes roof lighter)
height = width
geometry!

Petra

Petra (culture & location)
Roman & Nabataen style; Jordan

Petra (date & material)
400 BCE-100 CE; sandstone

Petra (use & facts)
city
built by Nabataeans & territory annexed by Romans
built as part of trade route
tombs cut into rock, no remains found
Treasury at Petra (most intricate)
entrance is Siq (long thin pathway between rock)
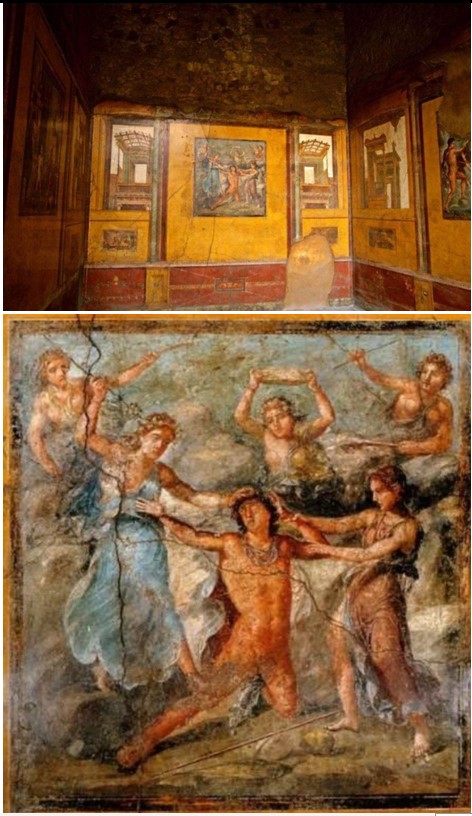

Pentheus Room
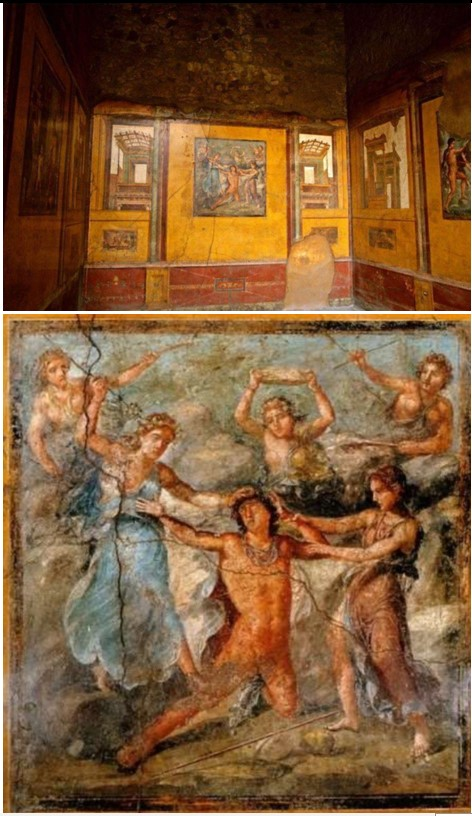

Pentheus Room (culture & location)
Roman; Pompeii, Italy
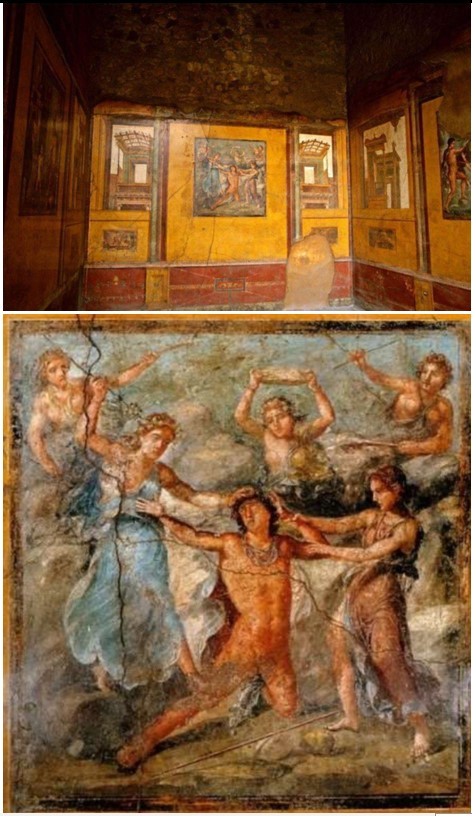

Pentheus Room (date & material)
67-79 CE; paint on plaster
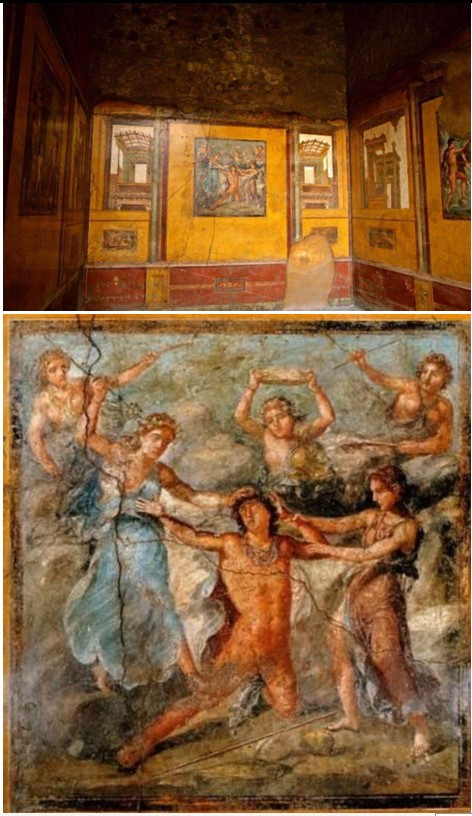

Pentheus Room (ues & facts)
Décor of a house of rich merchants
on the walls of the House of Vettii
fresco = paint on wet plaster that sets when it dries
shows death of Greek hero Pentheus
located in triclinium (dining room)
vistas of “outside” & fake marble “dado”
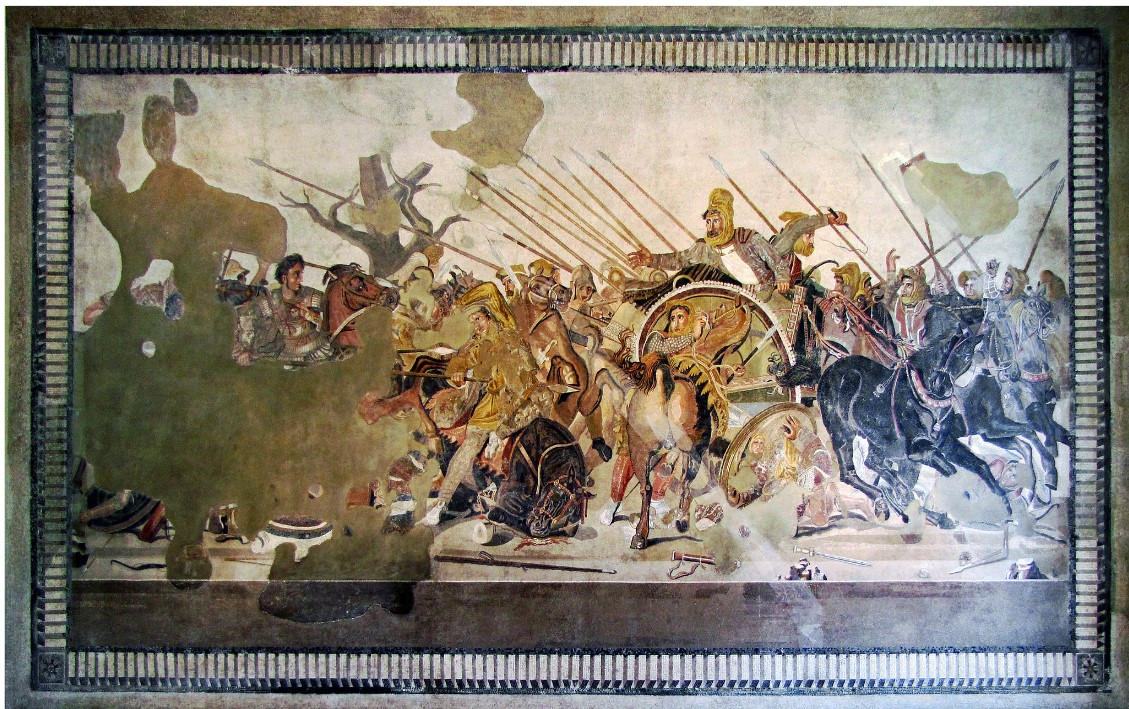

Alexander Mosaic

Alexander Mosaic (culture & location)
Roman; Pompeii Italy

Alexander Mosaic (date & material)
100 BCE; mosiac of tiles (tesserae)

Alexander Mosaic (use & facts)
house decor
8 by 17 ft
found in House of the Faun
arranged in gradual curves called opus vermiculatum
depicts Battle of Issus where Alexander defeats Persian army
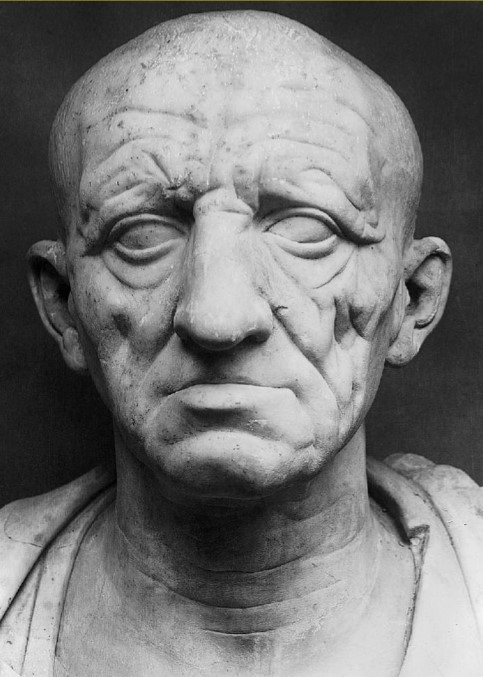

Head of a Roman Patrician
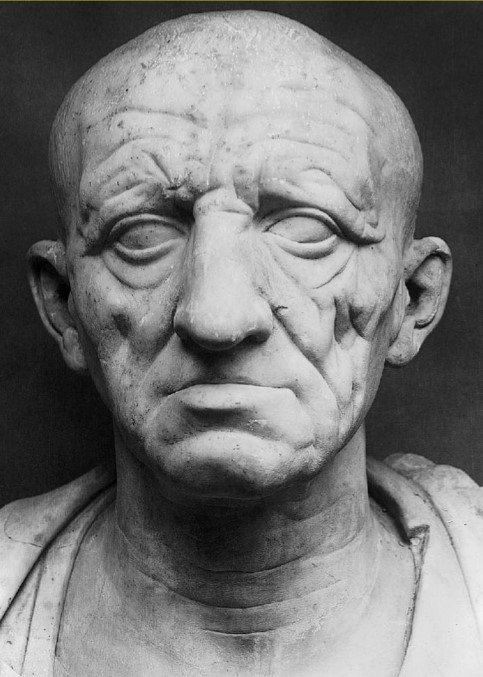

Head of Roman Patrician (culture)
Roman
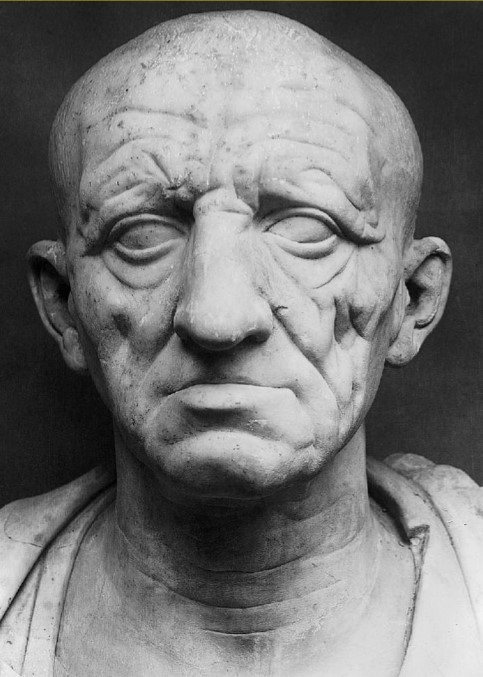

Head of a Roman Patrician (date & material)
75-50 BCE; marble
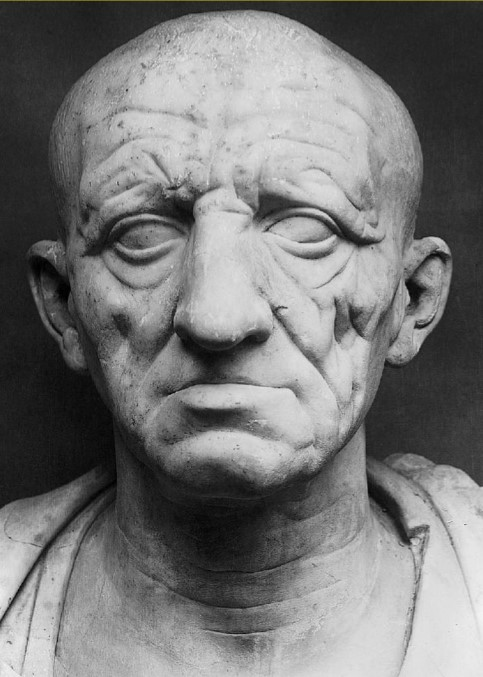

Head of a Roman Patrician (use & facts)
displays Roman values of age & wisdom
veristic portrait = extremely realistic
shows Etruscan & Hellenistic styles
Roman valued experience, wisdom, tenacity = age
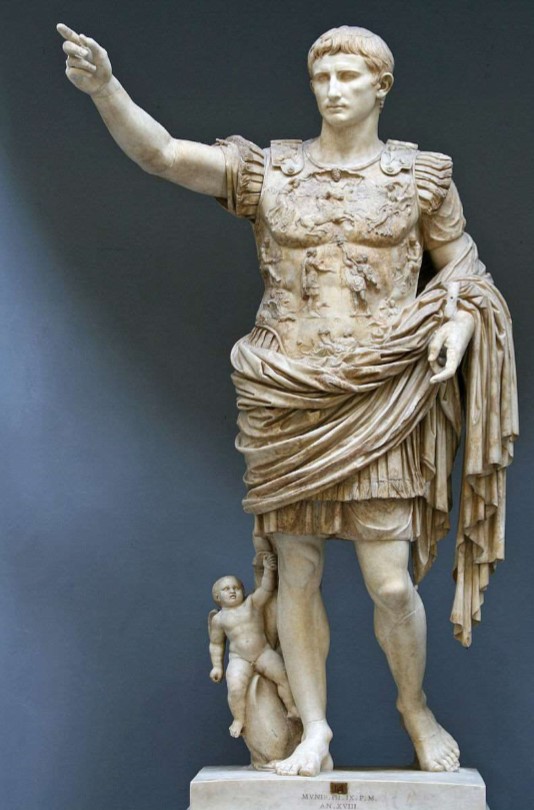

Augustus of Prima Porta
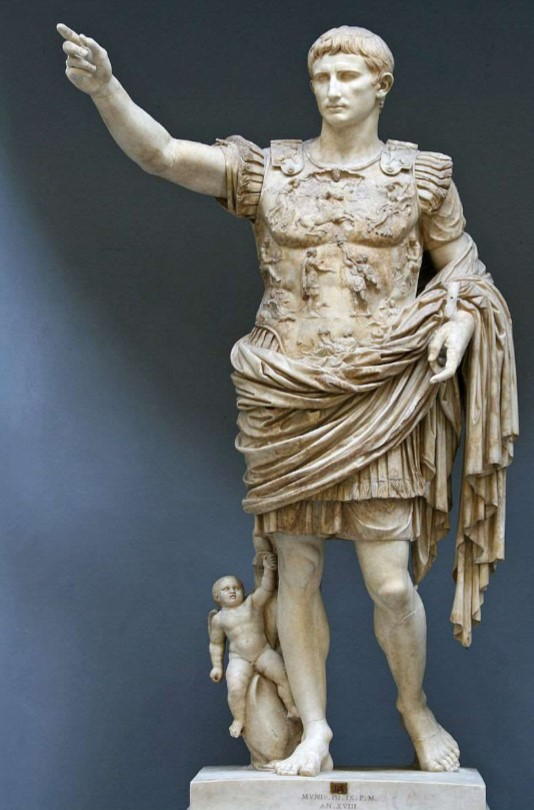

Augustus of Prima Porta (culture & location)
Roman; Prima Porta, Italy
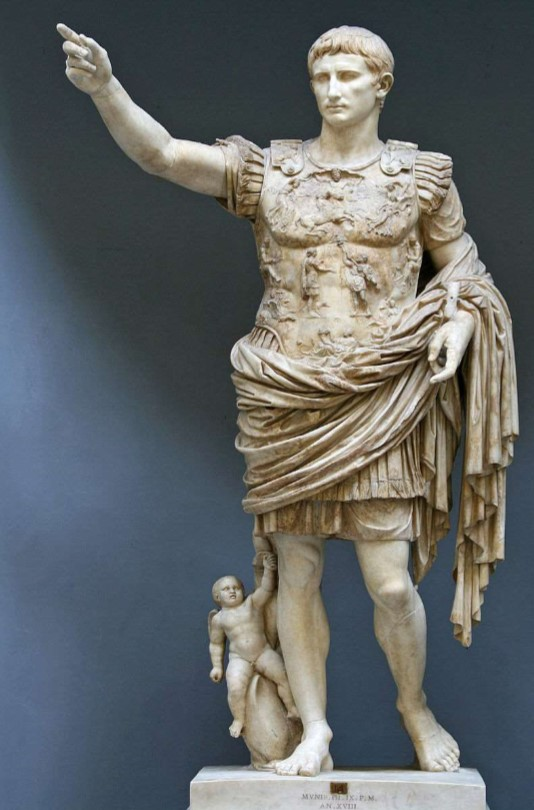

Augustus of Prima Porta (date & material)
1st century CE; marble
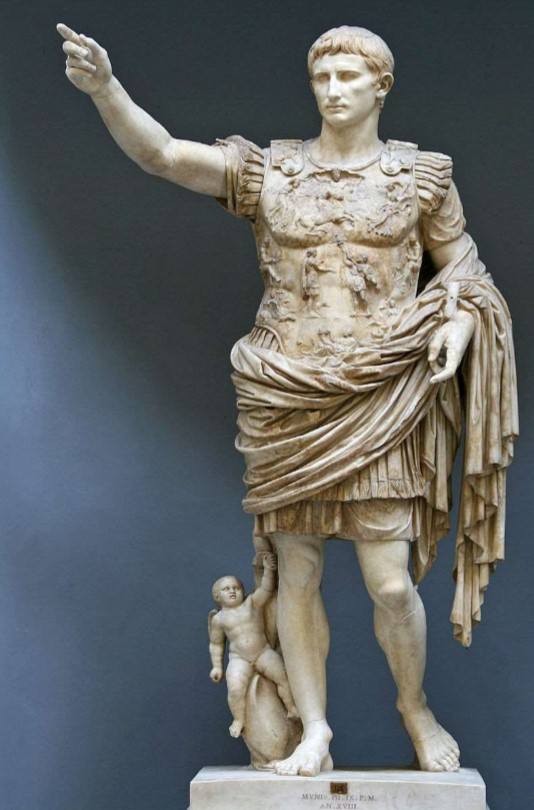

Augustus of Prima Porta (use & facts)
shows Roman ideals: military victory, religious, powerful, ideology
Cupid on dolphin (at bottom) = victory over Mark Antony
son of Julius Caesar
breastplate (cuirass) refers to Pax Romana
idealized, young, vital, contrapposto
warrior, civic ruler, orator
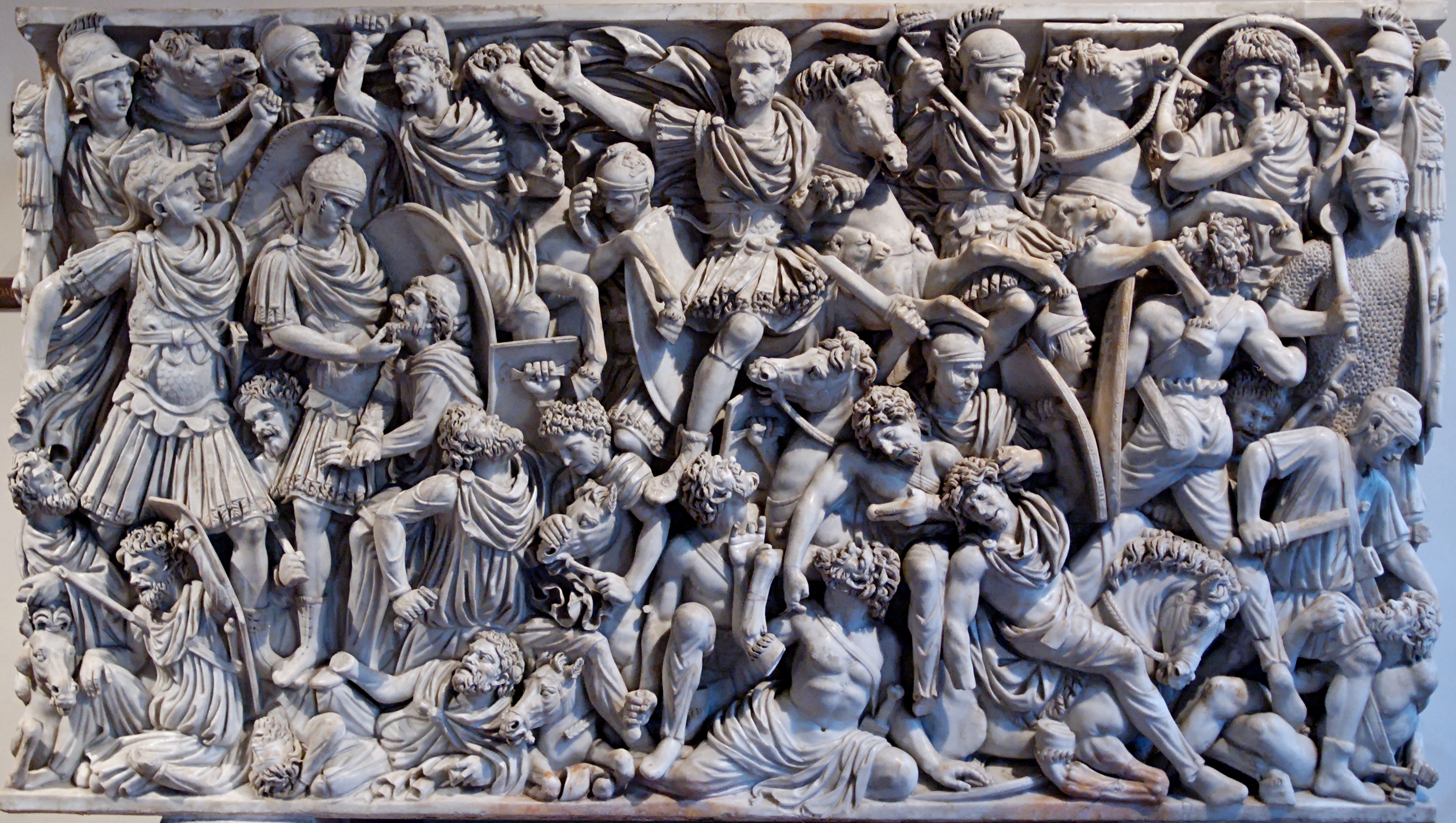

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
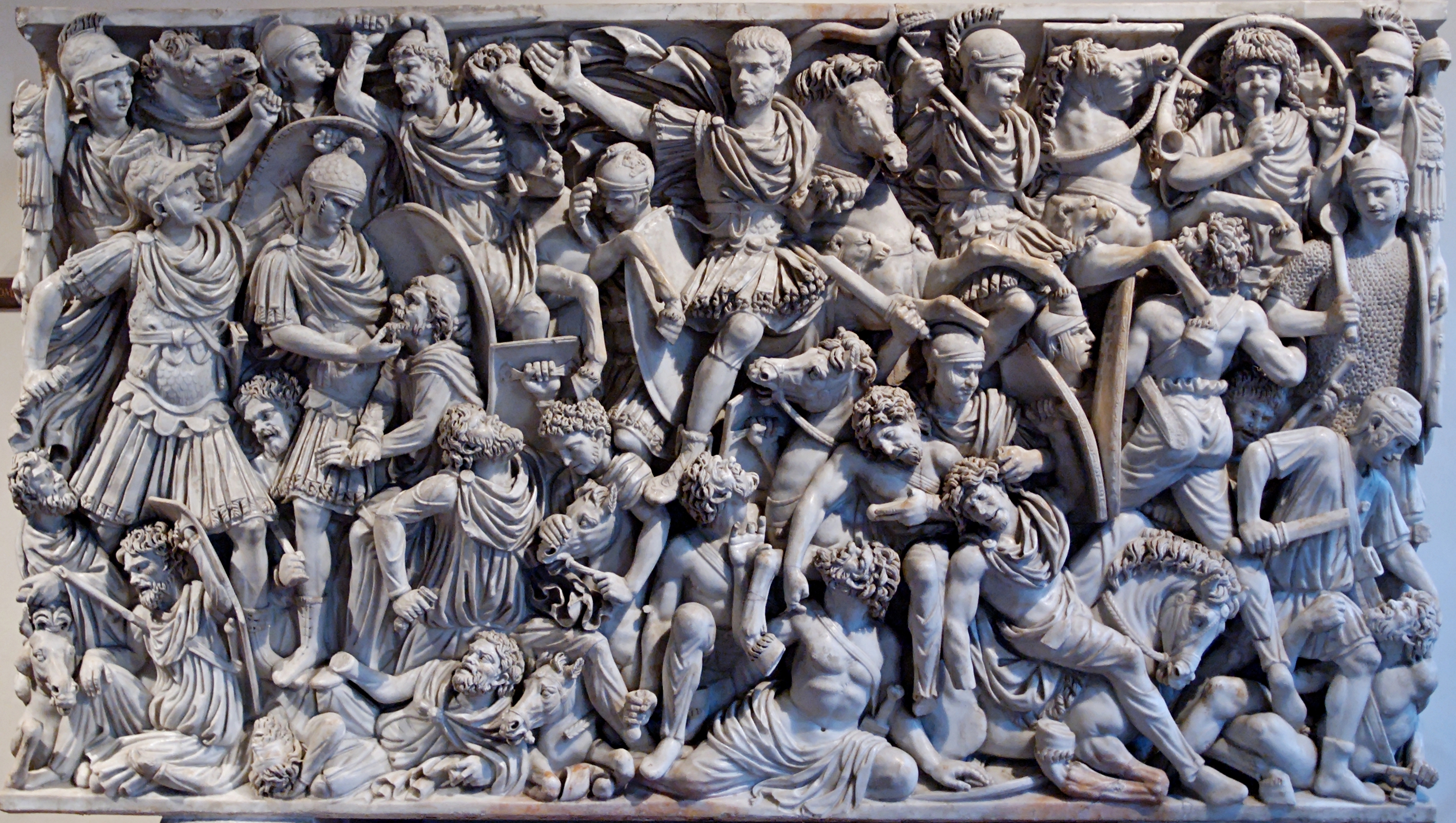

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus (culture & location)
Roman; Via Tiburtina, Italy
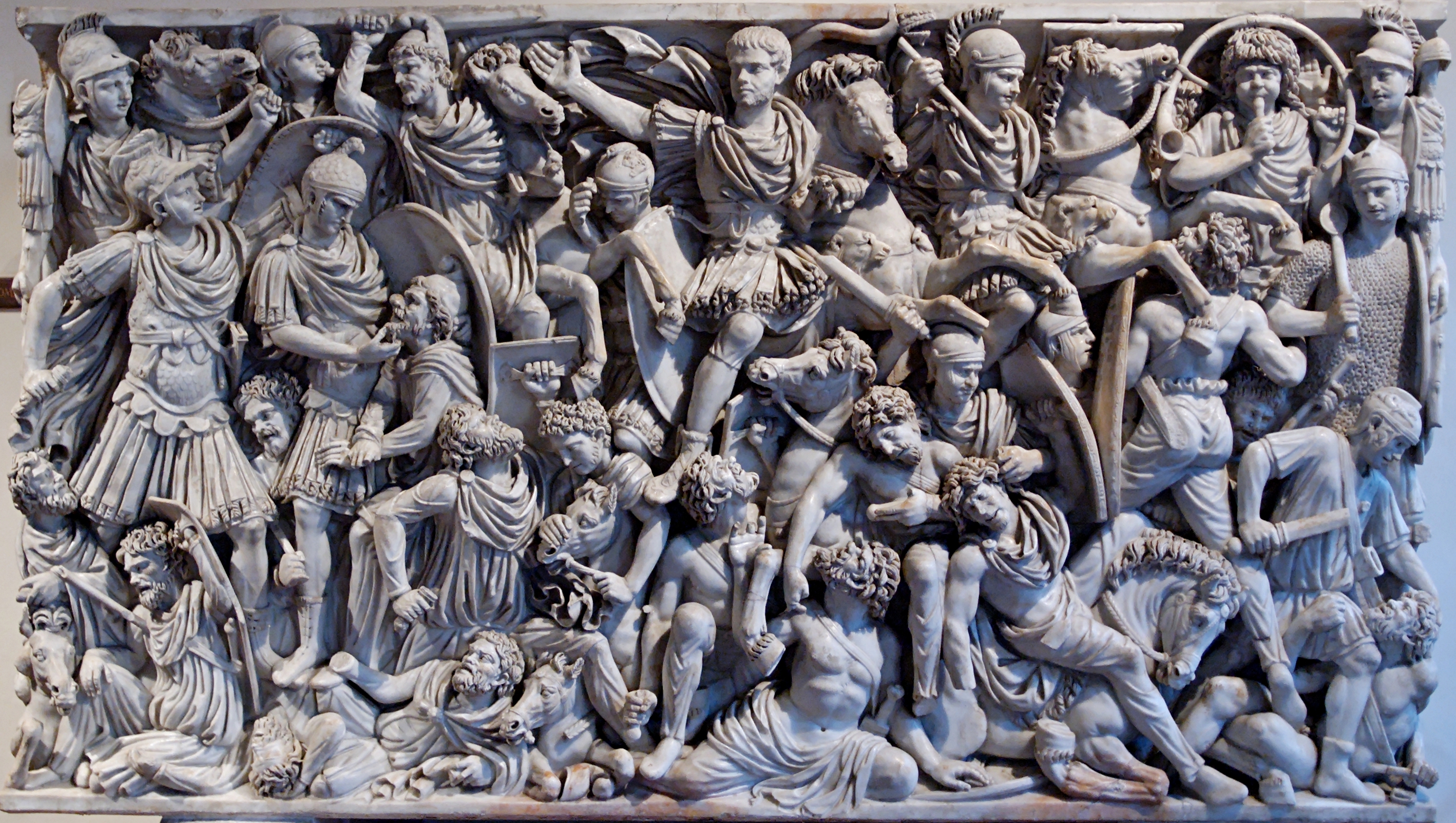

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus (date & material)
250 CE; marble
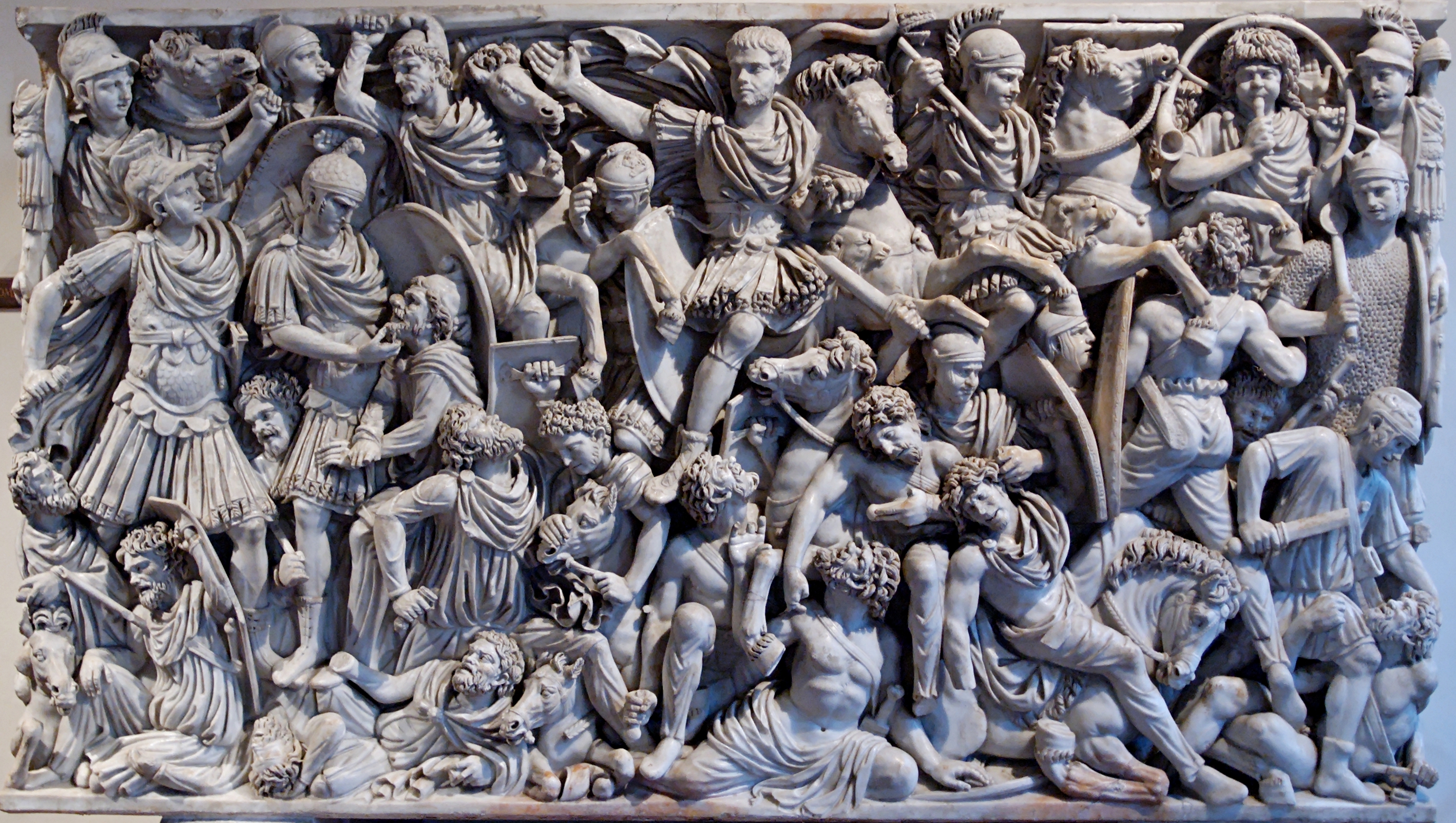

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus (use & facts)
sarcophagus for burial
writhing & emotive people
relief carving
depicts battle between Romans & Goths (France)
no sense of order
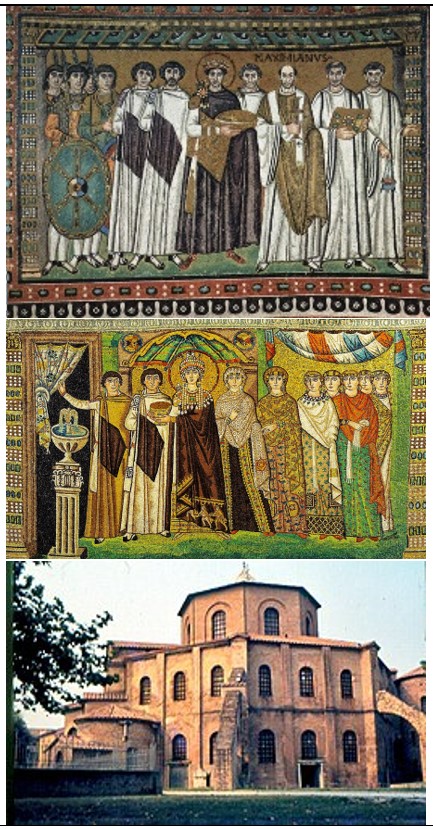

San Vitale
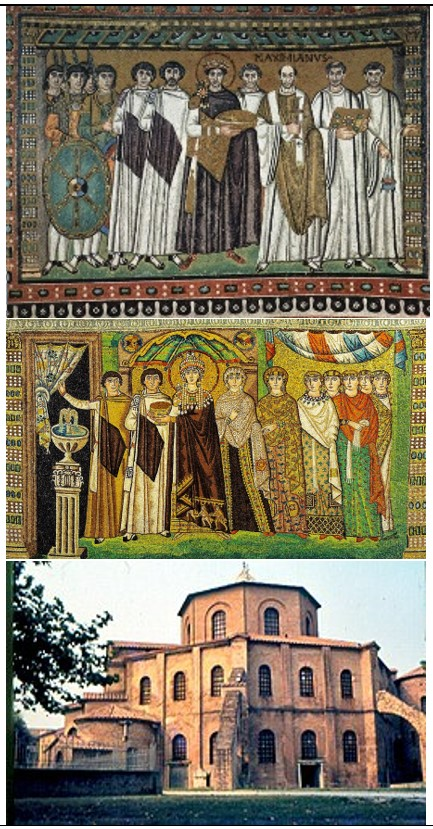

San Vitale (culture & location)
Byzantine; Ravenna, Italy
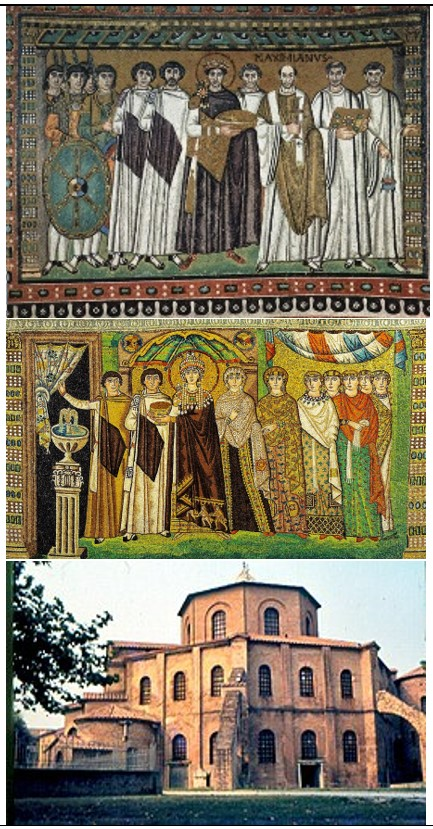

San Vitale (date & material)
536-547 CE; brick, marble, & stone, glass & gold tesserae mosaic
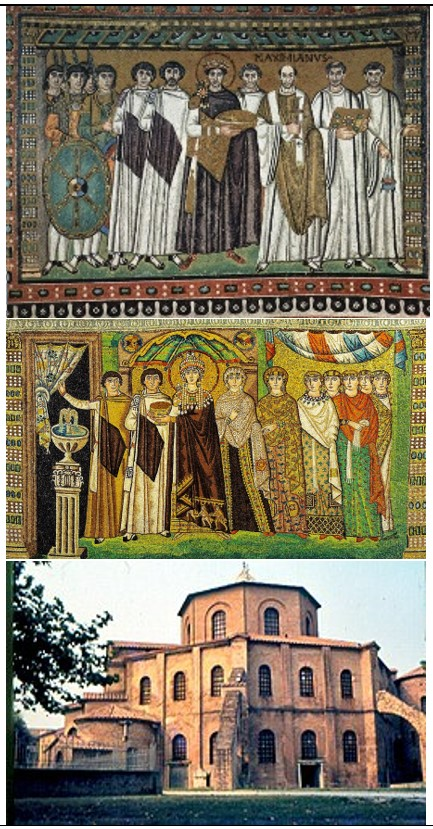

San Vitale (use & facts)
Church mosaic decor
Justinian mosaic (in apse) depicts him uniting the Church & state laws under the emperor
balance between Church, state, & military
elongated figures, not realistic, stiff upright pose, spiritual, ethereal, votive eyes, iconography of religion
Theodora mosaic depicts her entering courtyard & shows her power in Byzantine empire

Hagia Sophia

Hagia Sophia (culture & location)
Byzantine; Constantinople (Istanbul), Turkey

Hagia Sophia (date, material, & creator)
532-537 CE; brick, ceramic, stone, & mosaic; Anthemius of Tralles & Isadorus of Miletus

Hagia Sophia (use & facts)
Christian church (later mosque)
Byzantium’s greatest building & architectural accomplishment
Church that became a Mosque that is now a museum
minarets added & mosaics plastered over when it became a mosque
“floating dome of heaven” covered in windows
mosaics covered all walls & dome
dome built on pendentive = curved vaulted triangle supporting the dome
Theotokos mosaic depicts Virgin & Child
Deesis Mosaic depicts adult Christ
symbol of Byzantium’s religious & cultural mission
beautiful marbles from across Byzantine empire make up walls & floors

Vienna Genesis

Vienna Genesis (culture)
Byzantine

Vienna Genesis (date & material)
early 6th century CE; tempura, gold, & silver on purple vellum

Vienna Genesis (use & facts)
illuminated manuscript for display
Rebecca & Eliezer at the Well and Jacob Wrestling the Angel
vellum = calfskin
purple sheets = royal with silver writing (now tarnished)
Rebecca page is a continuous narrative
Rebecca has a river mermaid/goddess, out of place in Christian narrative
Classical Greek elements (Jacob) = arches, columns, & drapery
part of codex (book with vellum pages)-
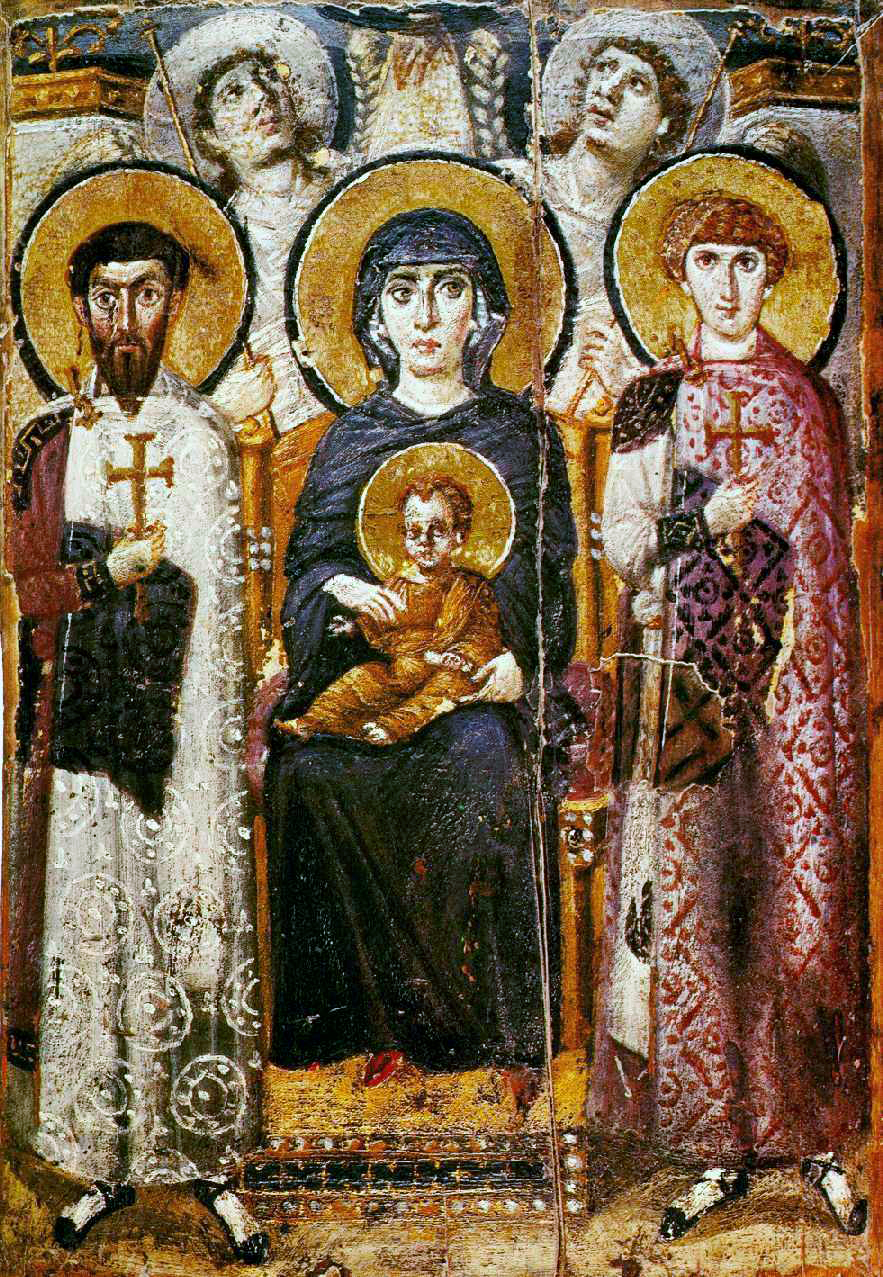

The Virgin & Child Between Saints Theodore & George

The Virgin & Child Between Saints Theodore & George (culture & location)
Byzantine; Egypt

The Virgin & Child Between Saints Theodore & George (date & material)
6th-early 7th century CE; encaustic (pigment & wax) on wood

The Virgin & Child Between Saints Theodore & George (use & facts)
display in a Church
icon
spacial ambiguity (flat)
no expression, Virgin has no eye contact
elongation, floating in another world (ethereal)
Mary = “God bearer” = Theotokos
classicizing Roman style – drapery & value shading
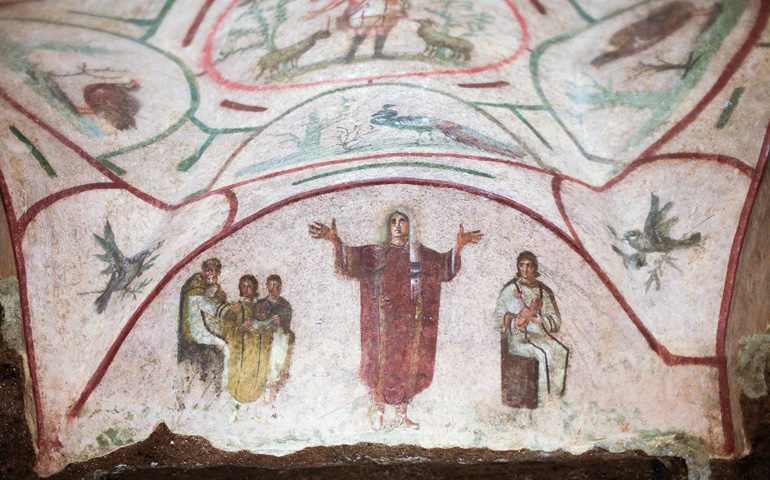

Catacomb of Priscilla
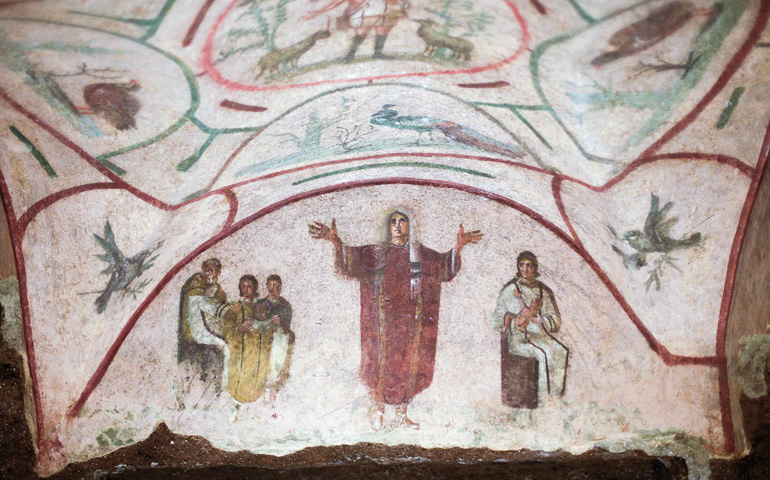

Catacomb of Priscilla (culture & location)
Early Christian; Rome, Italy
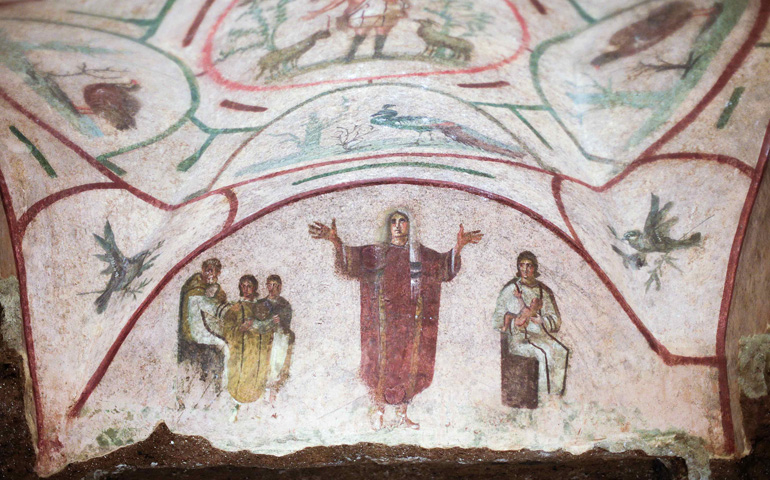

Catacomb of Priscilla (date & material)
200-400 CE; tufa (volcanic rock) & fresco
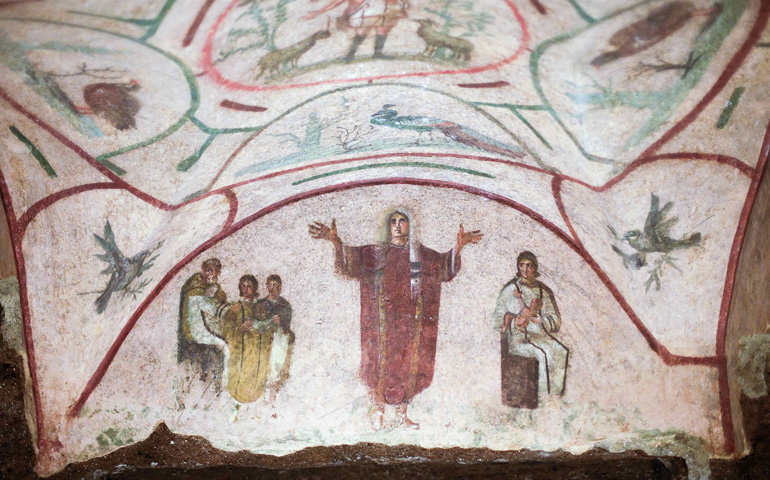

Catacomb of Priscilla (use & facts)
early Christian burial site
not a place of worship
3 niches of sarcophagi
Pompeii-style paintings (realistic fresco)
holds 40,000 dead
burial shelves inside = loculi
chapels here = cubicula
orant = prayer pose
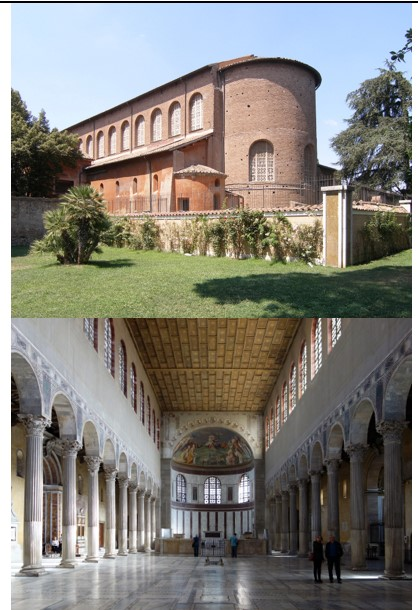

Santa Sabina
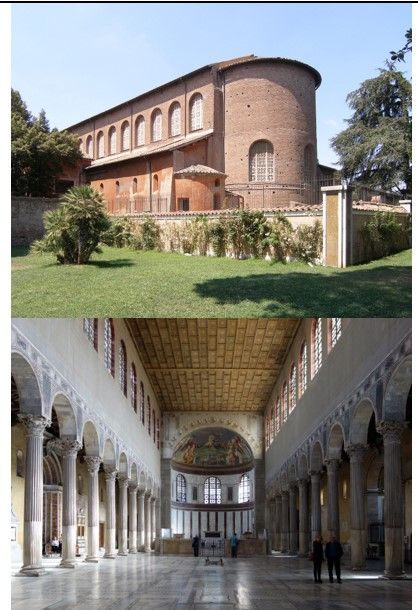

Santa Sabina (culture & location)
Romanesque; Rome, Italy
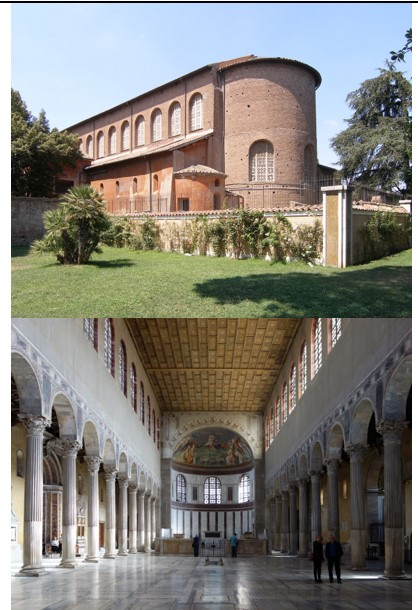

Santa Sabina (date & material)
422-432 CE; brick, stone, & wooden roof
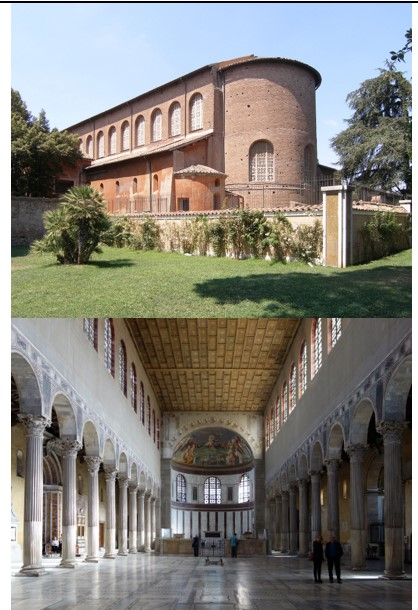

Santa Sabina (use & facts)
basilica church
oldest existing Roman basilica in Rome
colonnaded rectangular plan & architecture
simplistic
5th century carved wood doors with a cycle of Christian scenes
3 isles & no transept (cross part)
spolia - stolen columns from old Roman buildings
axial plan with long nave
coffered roof & thin walls
clerestory windows
light = Christ

Golden Haggadah

Golden Haggadah (culture & location)
Romanesque/Gothic; Spain

Golden Haggadah (date & material)
1320 CE; pigments & gold leaf on vellum

Golden Haggadah (use & facts)
illuminated manuscript for display/religious use
Plagues of Egypt, Scenes of Liberation, & Preparation of Passover
used to tell the story of Passover around the Seder table each year = Haggadah = narration in Hebrew
spiritual item & work of art indicating wealth of owners
one of the best examples of illuminated manuscripts
decorated with gold leaf
ceremonial purpose bc not stained or damaged?
Jewish!
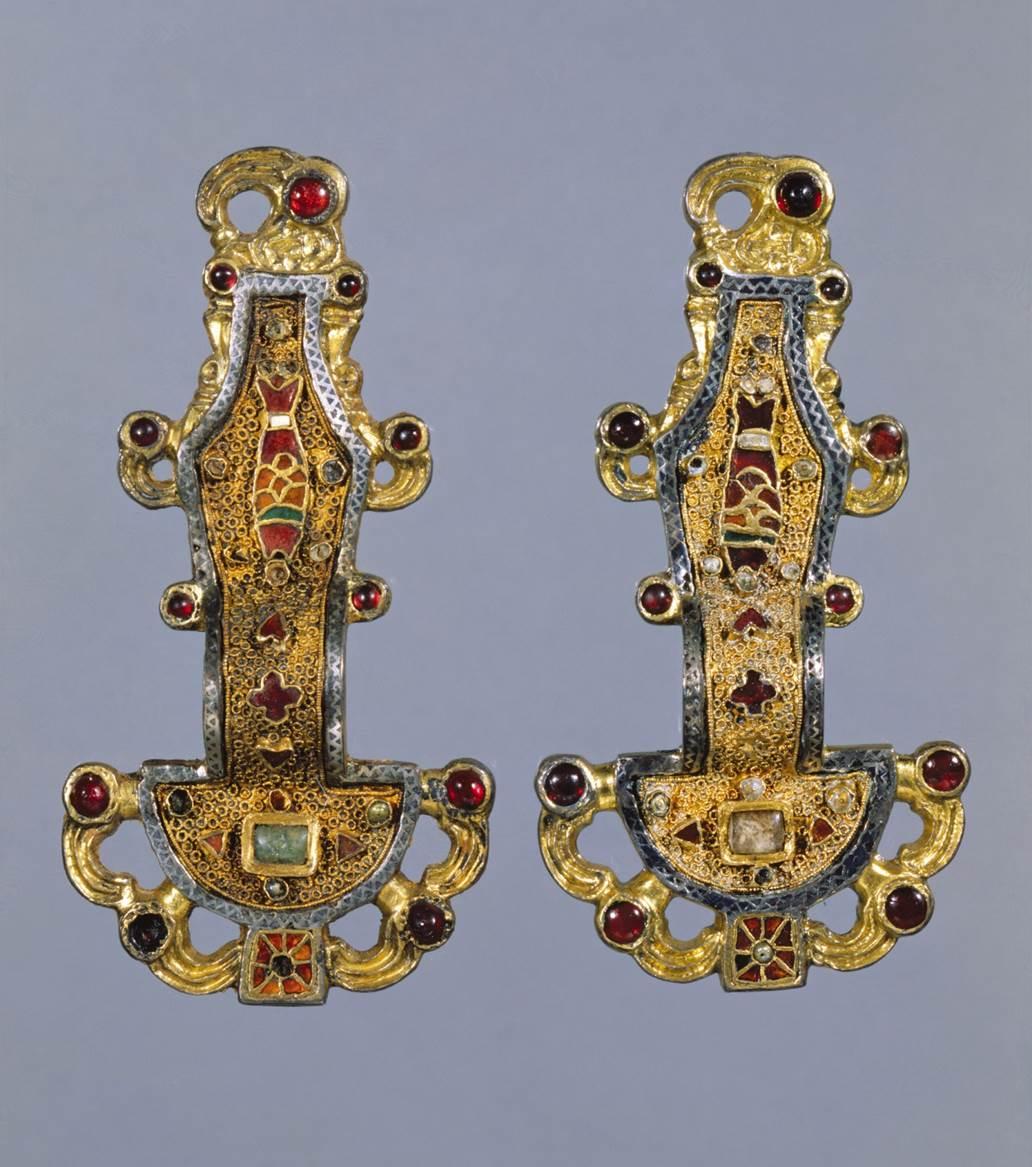

Merogingian Looped Fibulae

Merogingian Looped Fibulae (culture)
Medieval European (Byzantine/Romanesque)

Merogingian Looped Fibulae (date & material)
mid-6th century CE; silver gilt in filigree iwth inlays of garnets & other semiprecious stones

Merogingian Looped Fibulae (use & facts)
Fibulae = brooch used as a cloak fastener; for burials
French dynasty power solidified under Clovis
portable, zoomorphic (animals, fish & eagle)
interlocking animals
displayed wealth & status of owners
Cloisonné = soldering of gold & silver wires (see fish on main brooch body)

Lindisfarne Gospels

Lindisfarne Gospels (culture & creator)
Medieval European - Hiberno-Saxon (Irish); Eadfrith (pages), Ethelwald, & Billfrith (binding & cover)

Lindisfarne Gospels (date & material)
700 CE; ink, pigments, & gold on vellum

Lindisfarne Gospels (use & facts)
illuminated manuscript for display
St. Matthew (cross-carpet page), St. Luke portrait page, & St. Luke incipit page
cross carpet = looks like a carpet with a cross on it
page across from it begins with “novum” = new
Chi Ro (first two letters of Christ’s name in Greek)
St. Luke portrait shows him bearded, writing, haloed, & with a calf

Church of Saninte-Foy

Church of Saninte-Foy (culture & location)
Romanesque; Conques, France

Church of Saninte-Foy (date & material)
1050-1130 CE (reliquary - 9th century); stone, paint, gold, silver, gemstones, & enamel over wood

Church of Saninte-Foy (use & facts)
pilgrim church & reliquary
foy = faith
Romanesque with rounded arches, few windows, stone, & arcaded isles
radiating chapels for pilgrims
reliquary of St. Foy (Faith) contains her skull
Last Judgement Tympanum depicts hell bc role of Church is to save people’s souls (by Gislebertus)
head of reliquary from Roman statue of child (spolia)
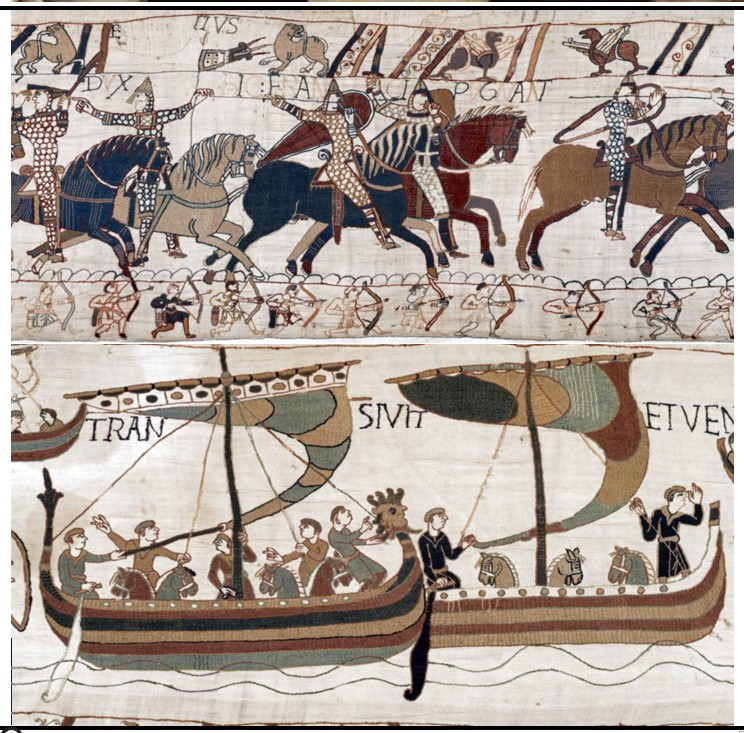

Bayeux Tapestry
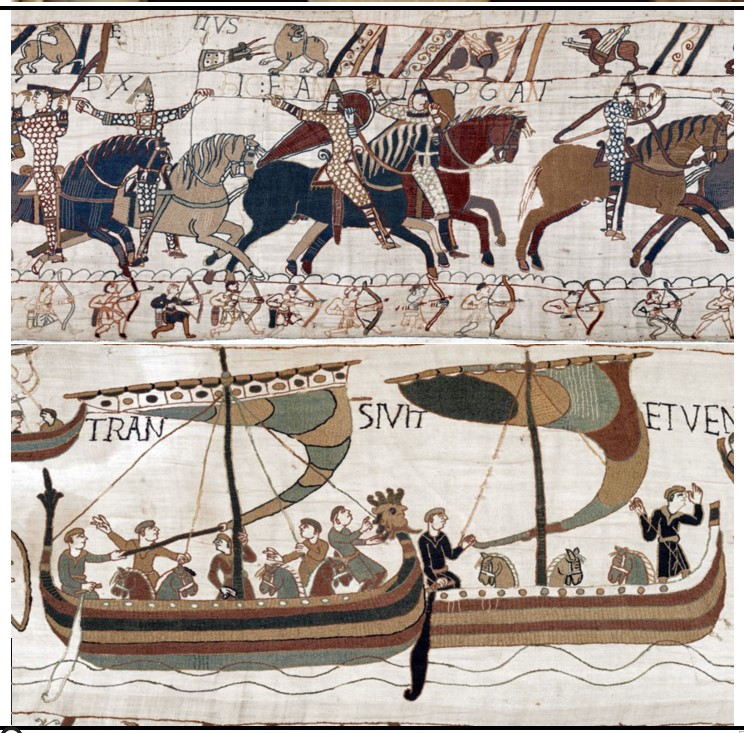

Bayeux Tapestry (culture & location)
Romanesque; Bayeux, France
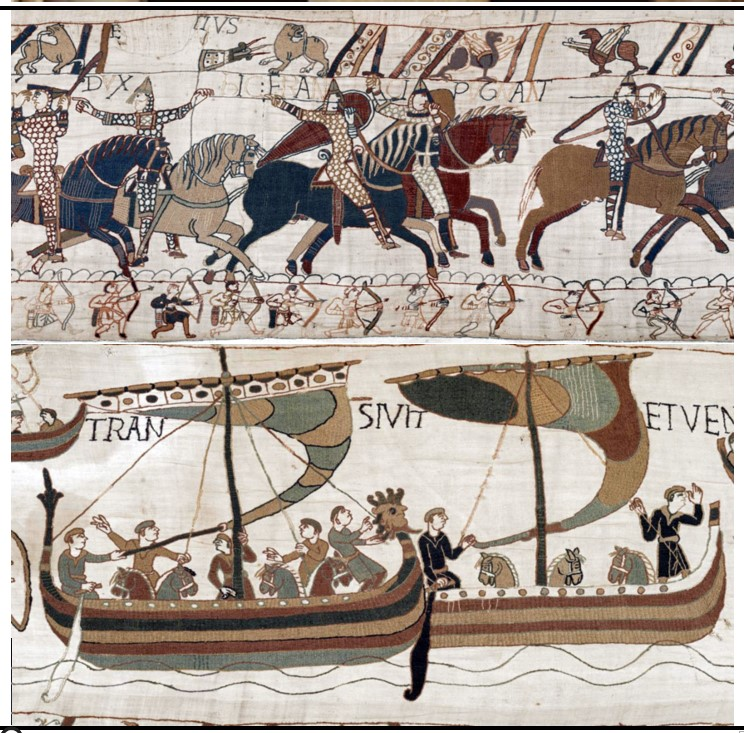

Bayeux Tapestry (date & material)
1066-1080 CE; embriodery on linen
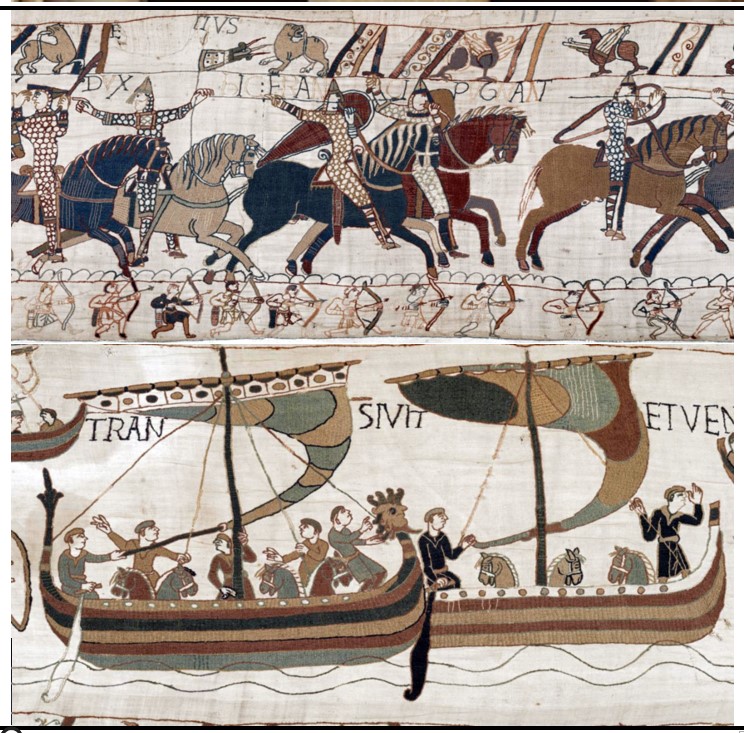

Bayeux Tapestry (use & facts)
Depict William the Conqueror’s great victory over the Anglo-Saxons
depicts the Battle of Hastings (1066)
William, Duke of Normandy defeats Anglo-Saxons (Norman conquest of England)
actually an embroidery

Chartres Cathedral

Chartres Cathedral (culture & location)
Gothic; Chartres, France

Chartres Cathedral (date & material)
1145-1155 CE; limestone & stained glass

Chartres Cathedral (use & facts)
Church
stained glass window: Notre Dame de la Belle Verriere
rose window = colored light shows God/Christ & used to teach, depicting important Church figures & leaders
towers are different
to be a cathedral you need 3 portals
has flying buttresses
Latin cross shape, has wide nave & 7 radiating chapels
said to have garment worn by Virgin Mary when she gave birth to Jesus
tracery = divides windows into sections & supports stained glass rose window
floor has prayer labyrinth (pray while on a path)
has zodiac symbols & jamb statues (outside)

Blue Virgin Window

Blue Virgin Window (culture & location)
Gothic; Chartres, France

Blue Virgin Window (date & material)
1170 CE; stained glass

Blue Virgin Window (use & facts)
Church decoration, helped illiterate learn about Christianity?
Our Lady of the Beautiful Window (Notre Dame de la Belle Verriere)
colored light = divine
part of the lancet window
depicts Mary & Jesus
jewel toned