X-ray Production
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
xrays
discovered x-rays in 11/8/1895 by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen
prodcued by e- interacting with matter
properties of xray
no mass
unaffected by electromagnetic fields
travel in straight lines
exponentially attenuated by matter
cannot be focused
electron shells
max. #: 7
names: K, L, M, N, O, P, Q
e- per shell formula: 2n^2
ionization
removal of an orbital e- from an atom
resulting ion pair
electron binding energy
strength of attachment an e- has to the nucleus
excitation
electron is moved to a higher electron shell
types of radiation
characteristic
bremmstrahlung
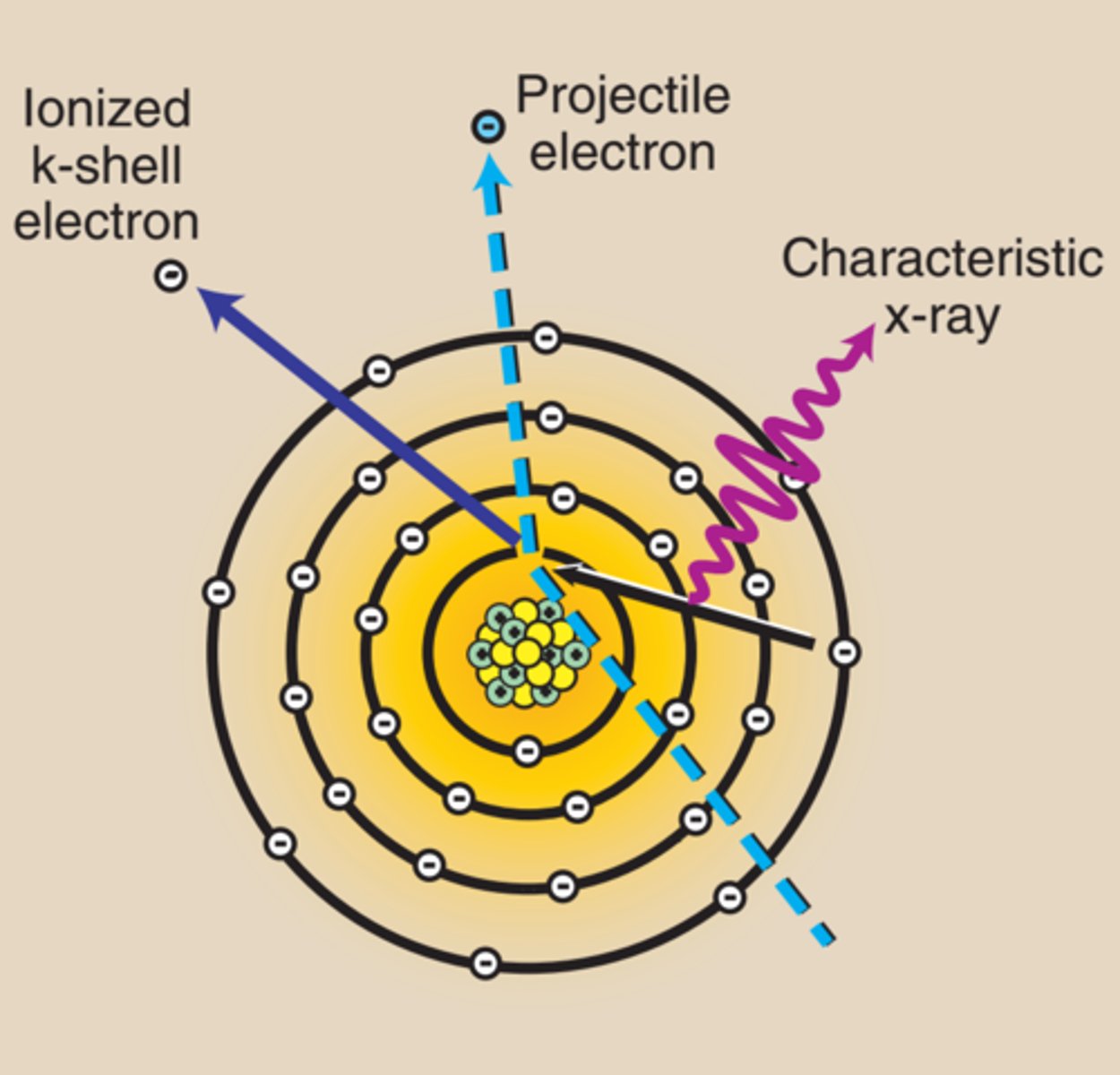
characteristic radiation
produced when a high-speed e- dislodges an inner-shell e- from the target and causes ionization of that atom
x-ray is emitted when an outer shell e- fills an inner shell void
x-rays emitted from shells termed from their origin
only K characteristic xrays of Tungsten useful in making diagnostic radiograph
bremsstrahlung radiation
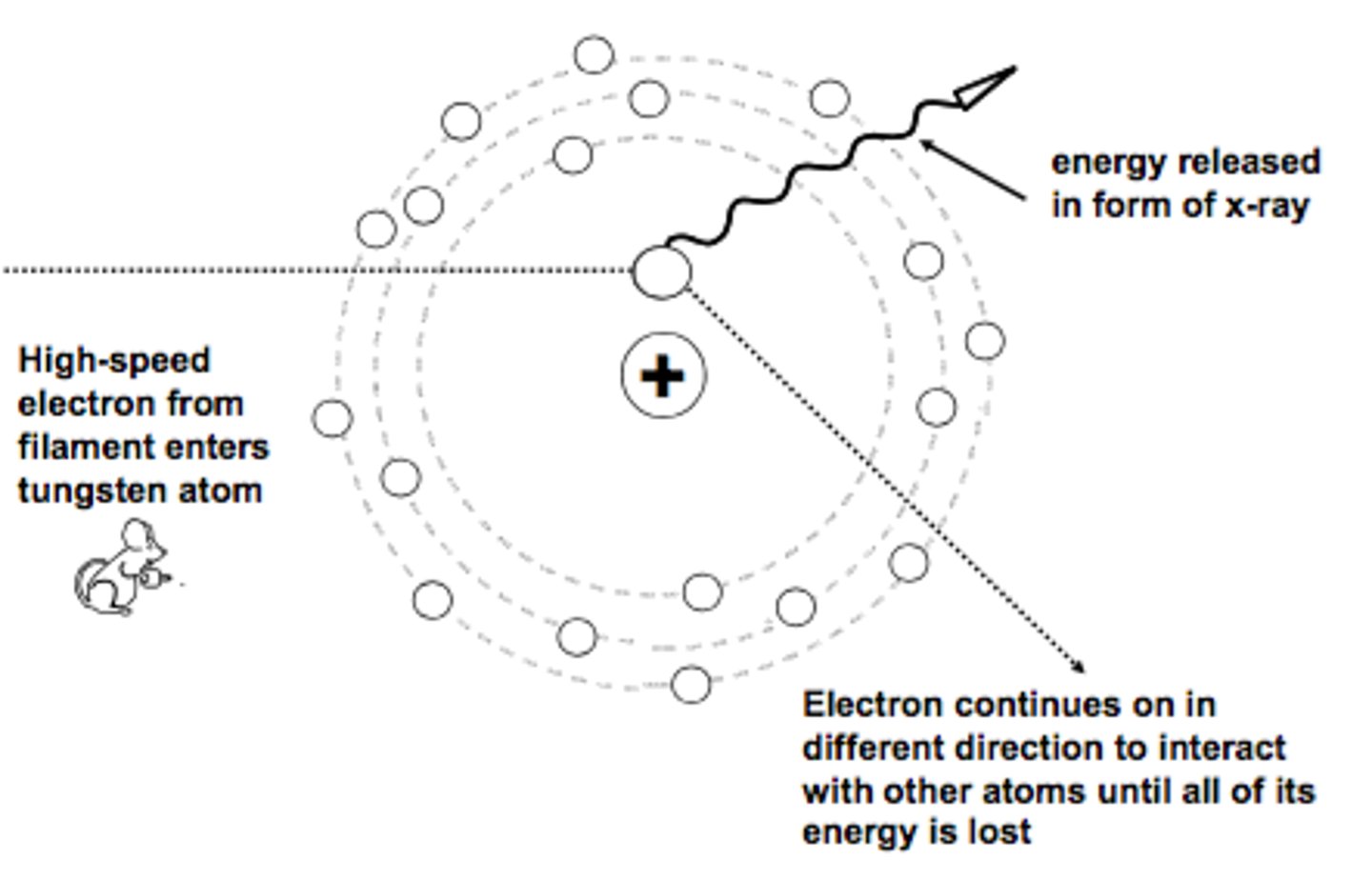
braking radiation
projectile e- slowed by the electric field of target atom nucleus resulting in loss of kinetic energy
electrostatic force increases with increasing Z#, closer to nucleus
no threshold of 70 kVp
most common in diagnostic range
ways of losing kinetic energy
heat
characteristic
bremsstrahlung
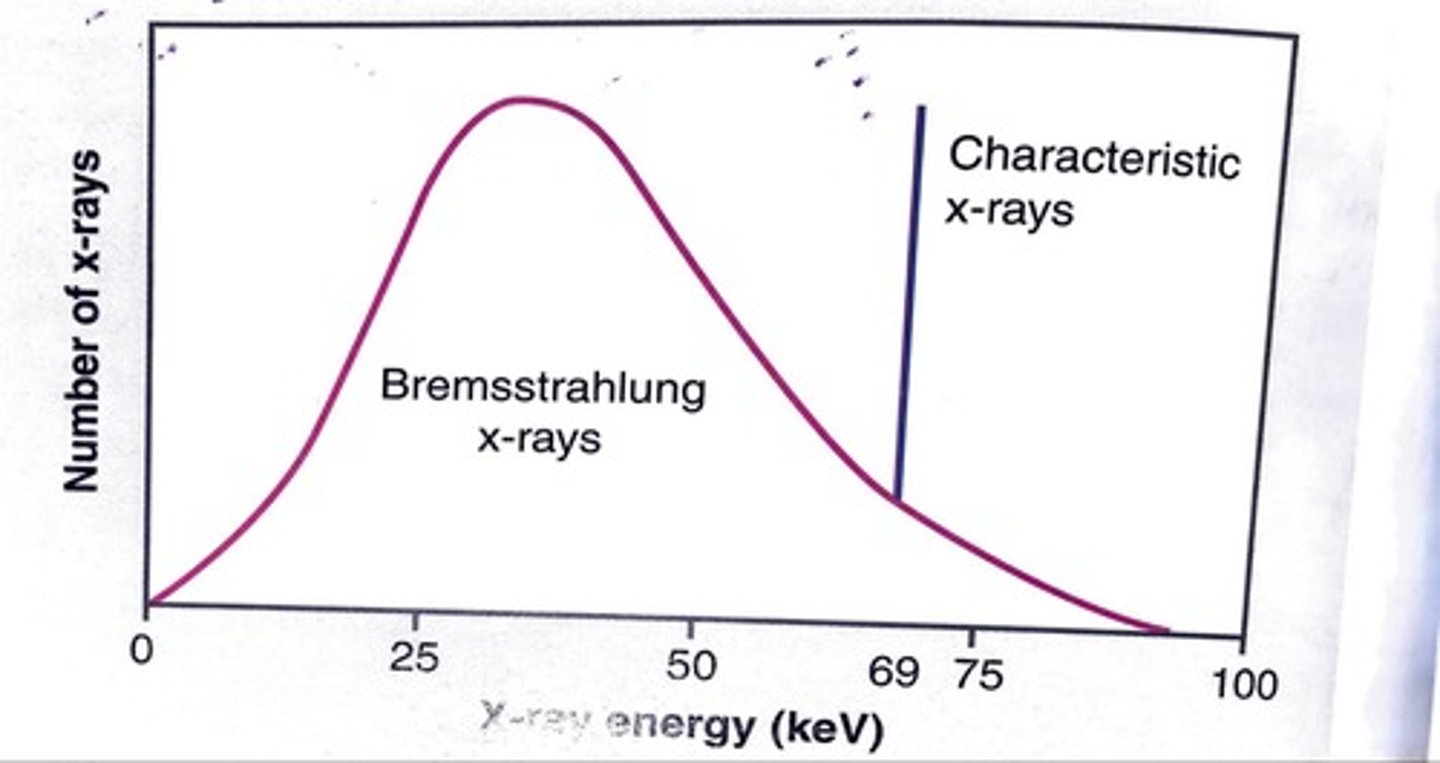
xray emission spectrum
characteristic: discrete, specific values, based on target material
bremsstrahlung: continuous, 0 max energy possible, peak = 1/3E
filters
absorb undesirable low energy xrays
harden the beam
Genz rays
5-15 keV
filter: plastic
superficial
50-150 kVp
filter: Al, Cu
orthovoltage
150-400 kVp
filter: Thoraceus (Sn, Cu, Al from beam to pt)
megavoltage
filter: transmission target, beam flattening
beam direction
high energy: more forward, narrower, more intense in the forward direction
KE coming in, EM coming out
beam direction dependency
target design affects xray direction
high atomic Z#
diagnostic, superficial, and orthovoltage: no bending magnet
therapeutic: transmission target
megavoltage xrays
4 MV: 10% xrays produced
25 MV: 65% xrays produced
water used to dissipate heat