Biology Summative (Structures and Organelles)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Organelles carry out..
essential cell processes, such as protein synthesis
energy transformation
digestion of food
transport and storage of materials
excretion of wastes
cell division
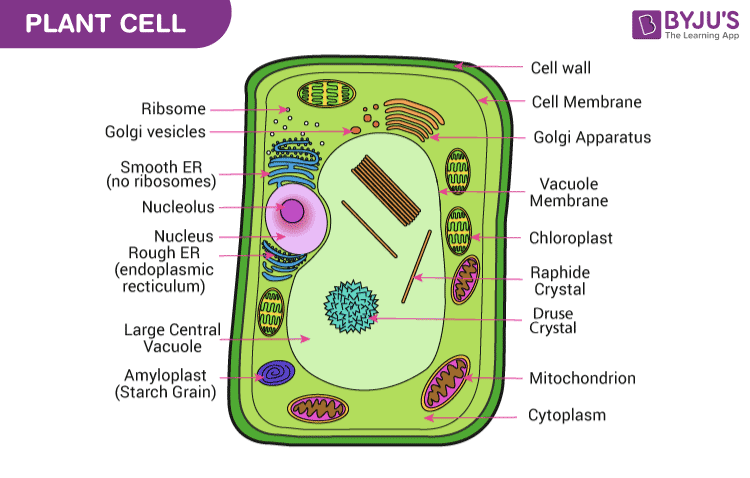
Parts of a plant cell
(14)
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Central vacuole
Mitochondrion
Ribosomes
Vesicle
Golgi apparatus
Endoplasmic Reticulum(Smooth & Rough)
Cell wall(cellulose)
Cell membrane
Chloroplast
Cytoplasm
Microtubule & Microfilaments (Cytoskeleton)
Nuclear pore
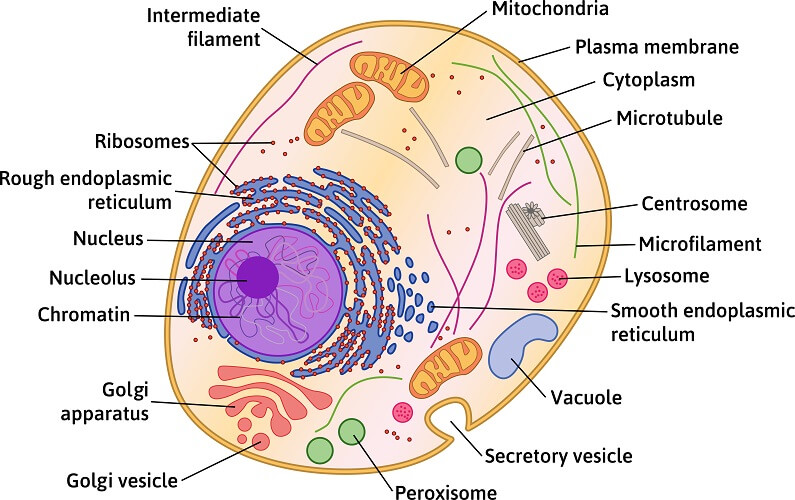
Parts of an Animal Cell
(14)
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Cell membrane
Mitochondrion
Ribosomes
Lysosome
Vesicle
Golgi apparatus
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth & Rough)
Cytoplasm
Centriole (In the centrosome)
Nuclear pore
Cytoskeleton (Microfilament, Microtubules)
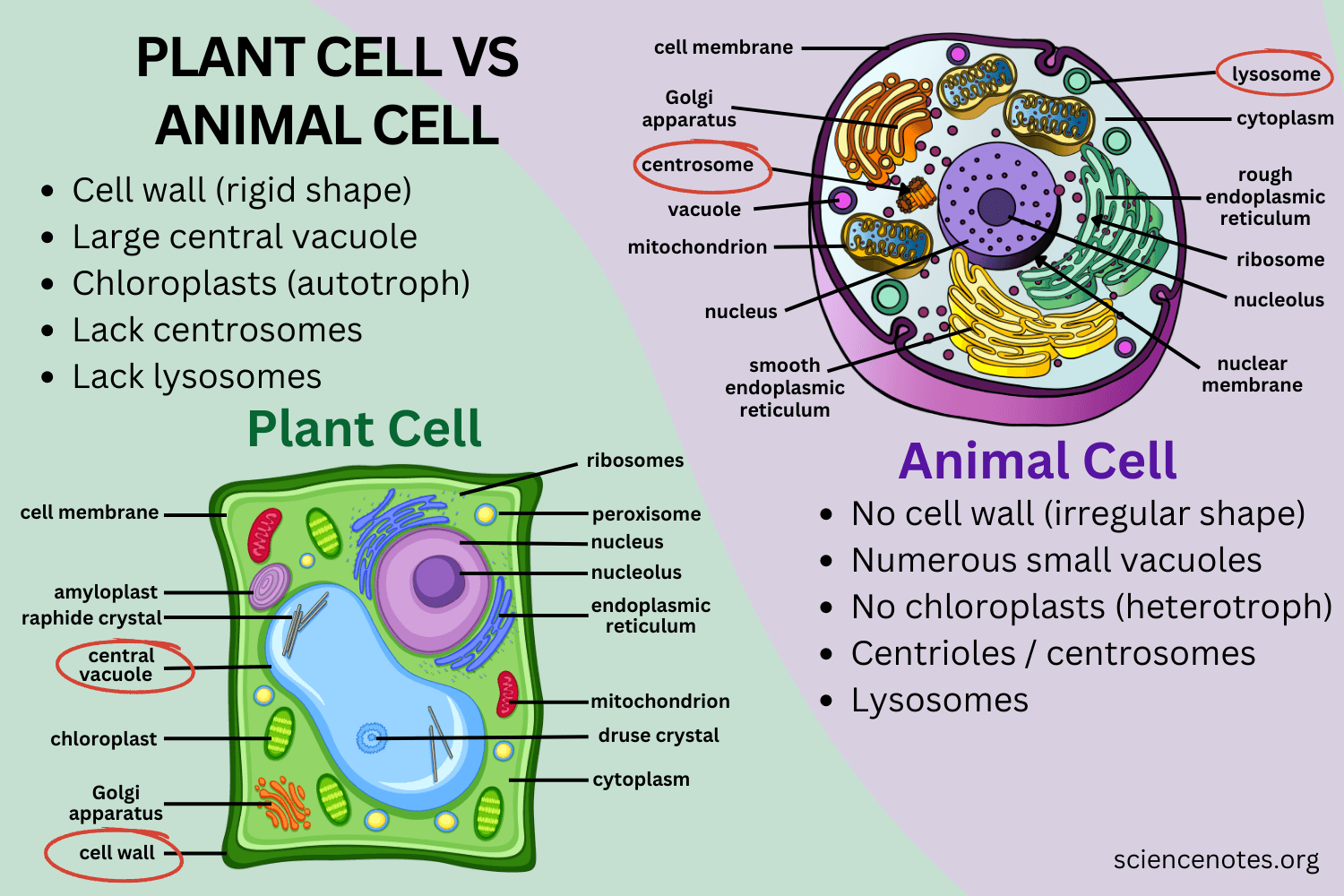
Organelles absent in a plant cell are
centrosomes, lysosomes, centrioles
Organelles absent in a animal cell are
Cell Wall, Chloroplast
Organelles are supported by a structure within the cytoplasm called,,
Cytoskeleton
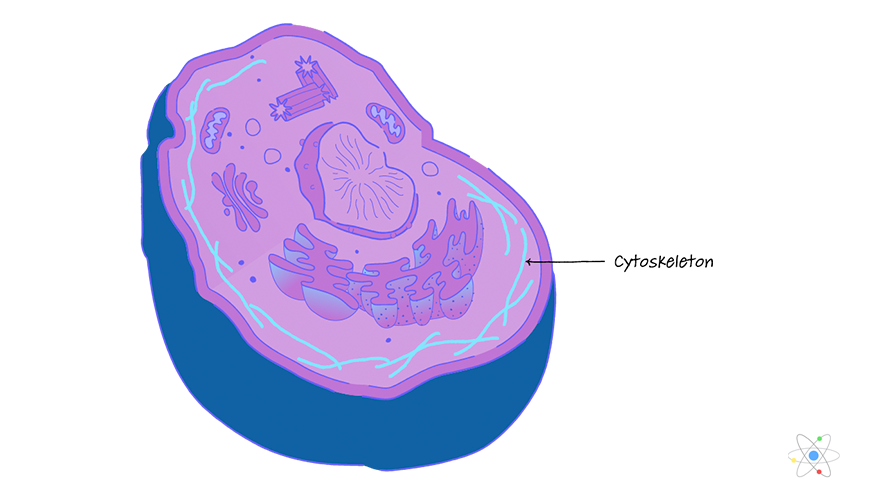
Cytoskeleton is
a supporting network of
long
thin protein fibers
that form a framework for the cell and provide anchor for the organelles
Cytoskeleton is made up of..
thread like filaments made of proteins
Two substructures part of the cytoskeleton
Microtubules, microfilaments
They rapidly assemble and dissemble slide past one another.

Microtubules are …
long
hollow protein cylinders
that form a rigid skeleton for the cell and assist in moving substances
Microfilaments are
thin proteins threads
that helps give the cell shape and enable the parts of the cells to move
Nucleus is..
“the brain of the cell”
Stores genetic information
Control center of the cell that contains directions for the production of proteins and cell divsions
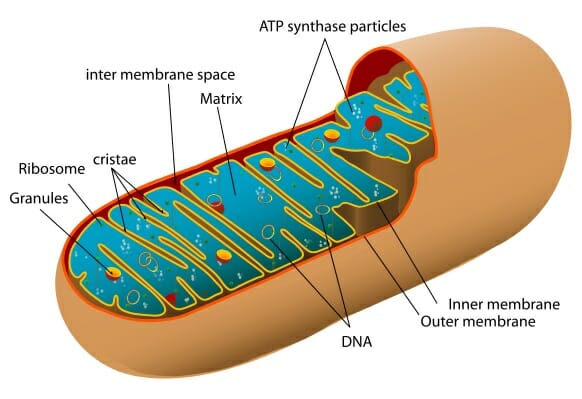
Mitochondria is the..
“Power house of the cell”
It makes ATP molecules during cellular respiration
Converts fuel into usable energy
It has an outer membrane and a highly folded inner membrane that provides a large surface area for breaking bonds in sugar molecules
The membrane of the mitochondrion is made up of..
phospholipid layers
What does the inner layer of the mitochondria hold?
Increases the surface area and holds proteins
(Intermembrane Space)
It has many folds called cristae.
What are plant cell walls made of?
Carbohydrate called cellulose which gives the cell walls their inflexible characteristic (Cellulose)
Functions of cell wall include..
Protects the cell from physical injury.
Gives the cell a sense of organization.
It maintains the shape of the cell.
Regulates the flow of information between cells.
It regulates the expansion of cells.
Provides protection against pathogens.
Cytoplasm is a..
jelly-like fluid that contains the components of the cells.
Cytoplasm is composed of..
water
salt
protein
The cytoplasm is…
enclosed by the cell membrane
The function of nucleolus is to..
produce and assemble the cell’s ribosomes
transcript RNA
made up of proteins and RNA
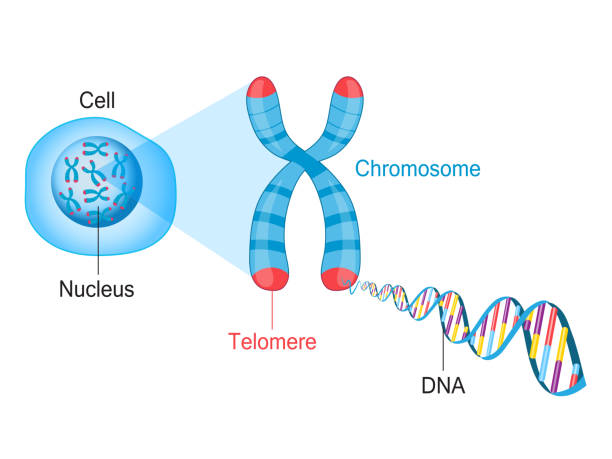
The item inside the nuclear membrane is called..
chromatin, a tangled spread out form of DNA
The function of a prokaryotic cell wall is to..
protect the cell
helps to maintain the cell’s shape
gives the cell support
What are prokaryotic cell walls made out of?
They’re made of a material called peptidoglycan, which is a combination of disaccharides and peptide fragments
What is the ER?
A network of membranes of folded sacs and interconnected channels for protein and lipid synthesis.
The two subunits of the endoplasmic reticulum are..
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
The difference between the rough ER and smooth Er is..
Ribosomes are attached to the rough ER
it has bumps on it and it is the site for transporting material such as protein synthesized
The smooth ER does not have ribosomes attached
the function is to provide a membrane surface where complex carbohydrates are synthesized.
How is the protein synthesized in the Rough ER transported?
They are pack in small vesicles and transported into the Golgi apparatus and the Golgi body adds other substances such as lipid and carbs to customize the cells.
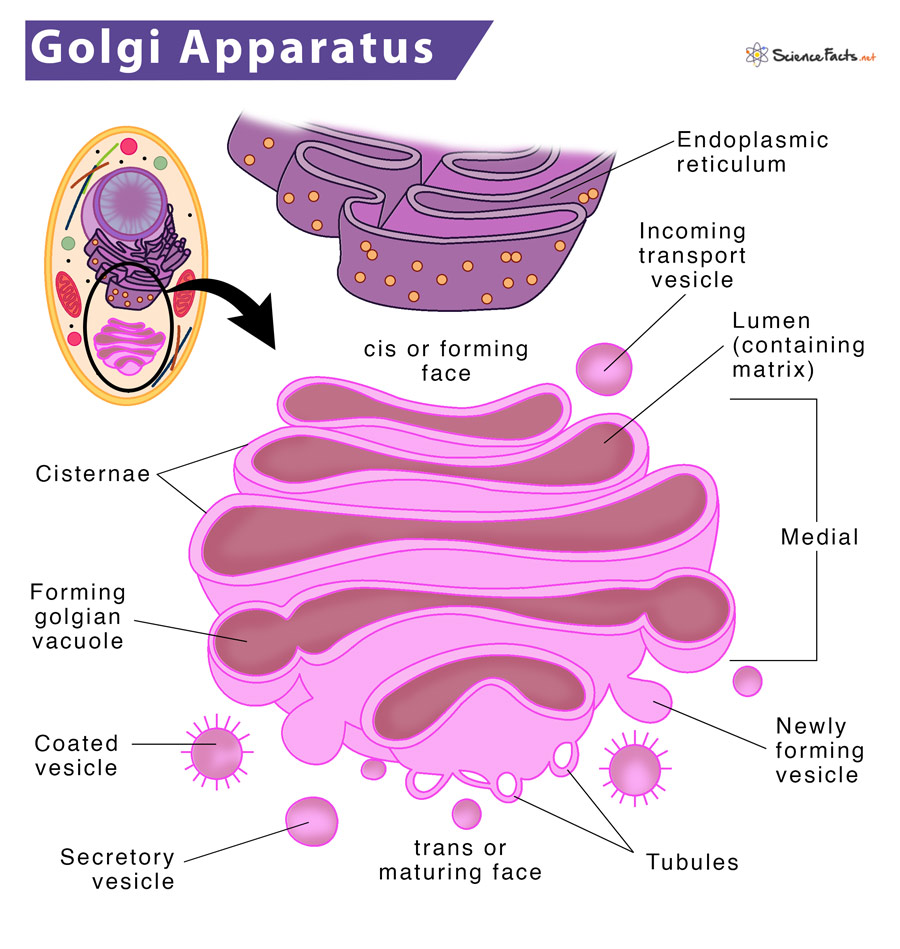
The Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Body/Golgi Complex
Modifies, sorts and ships proteins
Shape of Golgi Apparatus
Flattened stack of membrane
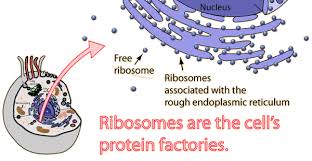
Ribosomes are…
organelles that help manufacture proteins in accordance to their chain of amino acid
How are ribosomes placed in a cell?
Some float freely in the cytoplasm while others are bound to another organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum.
Difference between free ribosomes and Bound ribosomes
Free floating ribosomes produce proteins for use for the cell.
Bound ribosomes produce proteins that will be bound within membranes or used by another cell.
Shape of ribosome
Flattened and spherical
What are ribosomes made of?
RNA
Protein

Vacuole is a …
Membrane bound vesicle used to store food, water, enzymes and other materials
Some store waste product
What does the central vacuole of the plant cell store?
Stores water
Centrioles are organelles..
that occurs in pairs
important for cell division
Where is the centriole located?
It’s located in the cytoplasm next to the nucleus
inside the centrosome
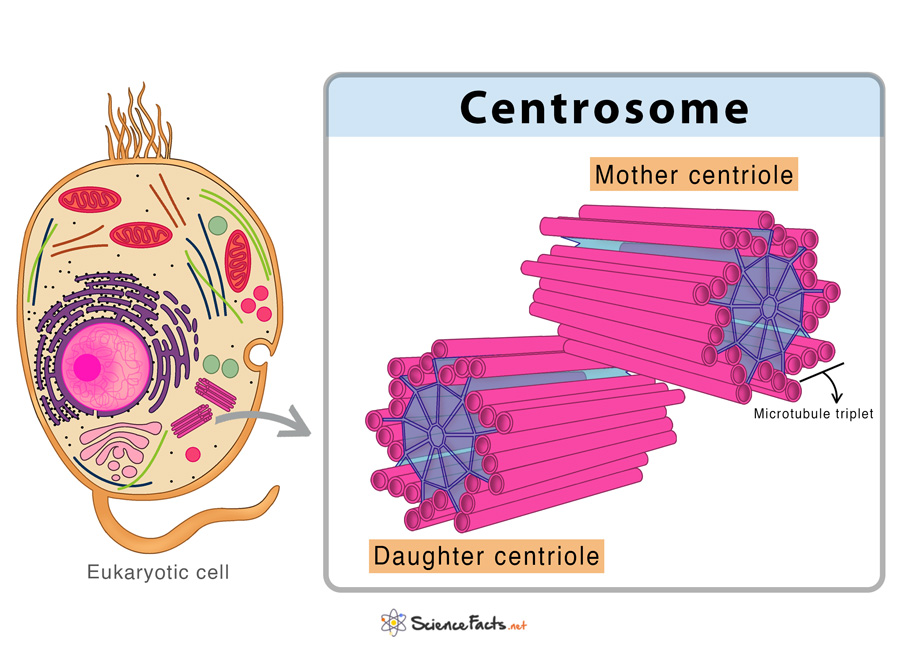
Shape of centriole
Barrel-Shaped, cylindrical structure
The main function of centriole is to..
organize microtubules in the cytoplasm that function during cell division.
Vacuoles are..
larger than vesicles
Difference between vacuole and vesicle
The membrane of vacuole does not fuse with the other organelles while vesicle does
Vacuoles are found in both types of cells(pro & eu)
Vacuoles contain water while vesicles..
are composed of waste, enzymes, nutrients, harmful compounds and ions
Vesicles are..
tiny sacs that transport material outside or within the cell
Where are vesicles made from?
The Golgi Network
A type of vesicle
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are..
a vesicle that contains digestive enzymes, found in animal cells only
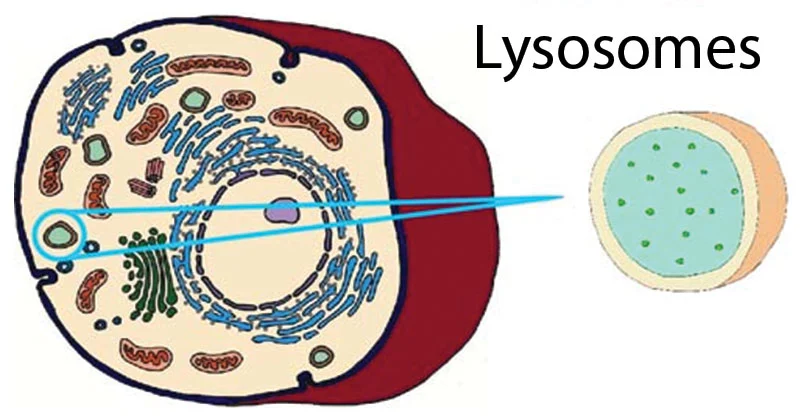
Shape of lysosome
Dense spherical vacuoles
Function of lysosomes
To breakdown worn out cellular substances
Cell’s recycling system
Digest bacteria and viruses that entered the cell
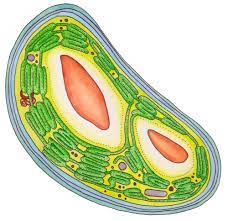
Function of Chloroplast
Capture light energy and convert it to chemical energy
Shape of thakakyloids in chloroplast
Small, disk shaped compartments
Trap energy from sunlight in a pigment called chlorophyll
Cell appendages are..and are located..
cilia and flagella located outside the cell membrane
Shape of cilia
Short, small hairlike structures
Function of cilia
Projection in cell surfaces that aid in locomotion and feeding
Used to sweep substances along surfaces
Cilia is found in
some animal cells, protists cells and prokaryotes
Shape of flagella
Longer and less numerous than cilia
Has tail
Flagella can be found in…
Some animal cells, prokaryotes and some plant cells