Chapter 9 - Games & strategic behavior
Using Game theory to analyze strategic decisions
Basic elements of a game:
- Players
- Strategies available to each player
- Payoffs each player receives for each possible combination of strategies
Payoff matrix: table that describes the payoffs in a game for each possible combination of strategies.

Dominant strategy: one that a yields a higher payoff no matter what the other players in a game choose.
Dominated strategy: any other strategy available to a player who has a dominant a strategy.
Nash equilibrium: any combination of strategy choices in which each player's choice is his/her best choice, given the other players' choices.
Prisoner’s dilemma
Prisoner's dilemma: game in which each player has a dominant strategy, and when each plays it, the resulting payoffs are smaller than if each had played a dominated strategy.
Cartel: coalition of firms that agree to restrict output for the purpose of earning an economic profit.
Repeated prisoner's dilemma: standard prisoner's dilemma that confronts the same players repeatedly.
Tit-for-tat: strategy for the repeated prisoner's dilemma in which players cooperate on the first move, then mimic their partner's last move on each successive move.
Games in which timing matters
Decision tree = game tree: diagram that describes the possible moves in a game in sequence and lists the payoffs that correspond to each possible combination of moves.
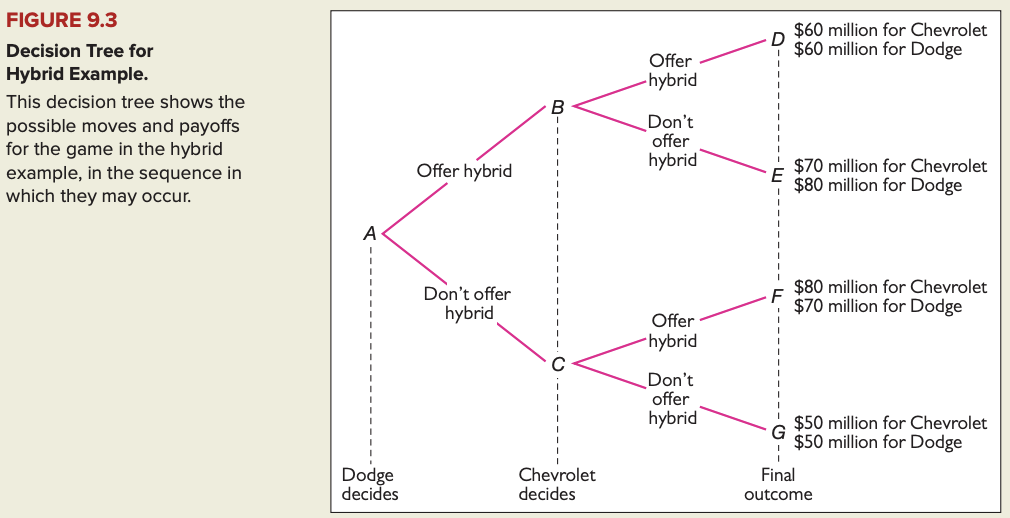
Credible threat: threat to take an action that is in the threatener's interest to carry out.
Credible promise: promise to take an action that is in the promiser's interest to keep.
Commitment problems
Commitment problem: situation in which people cannot achieve their goals because of an inability to make credible threats or promises.
Commitment device: way of changing incentives so as to make otherwise empty threats or promises credible.