Lecture 3: Radiographic Interpretation
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
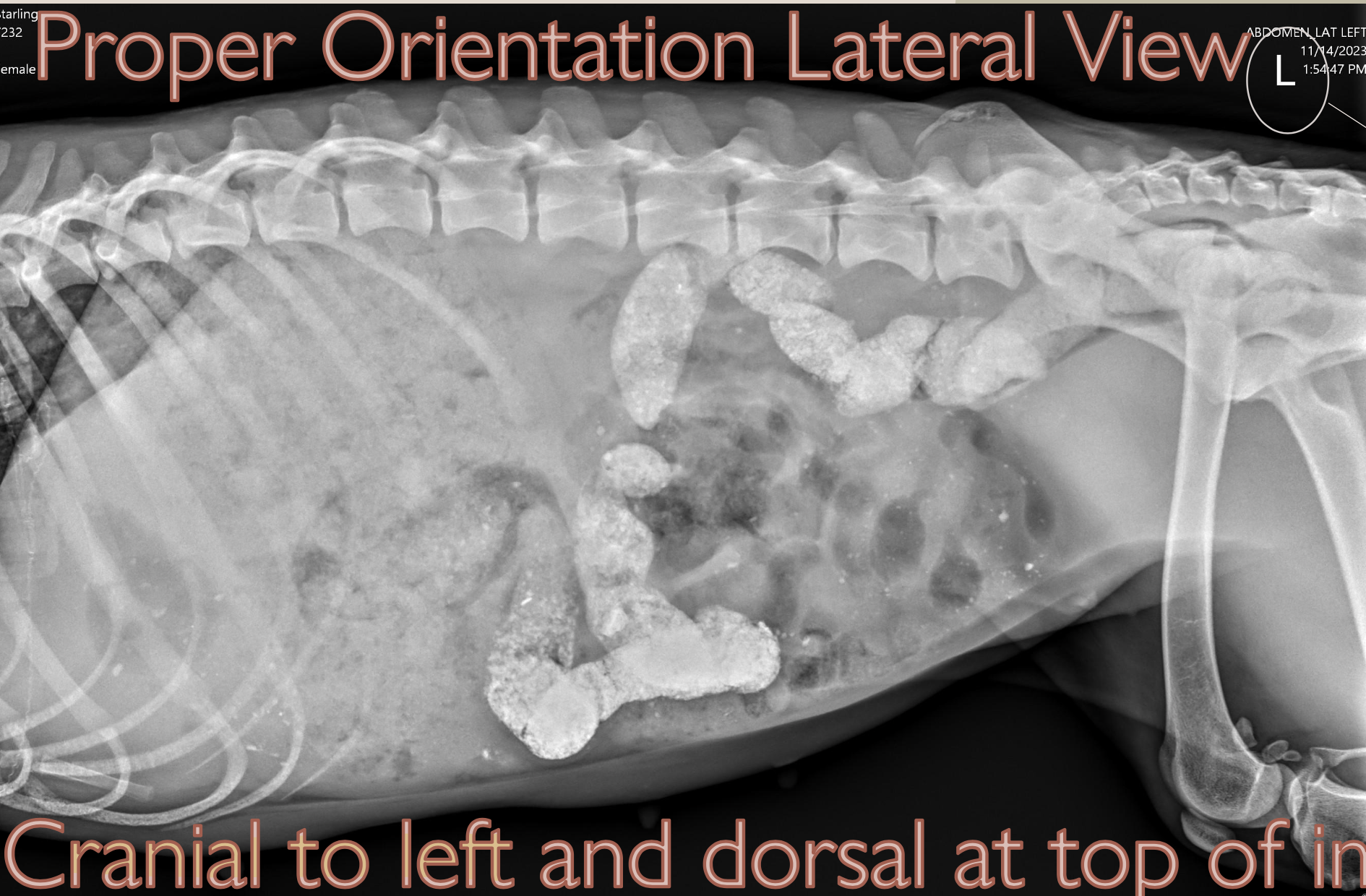
What is the proper orientation for a Lateral View?
Cranial to the Left
Dorsal at the Top
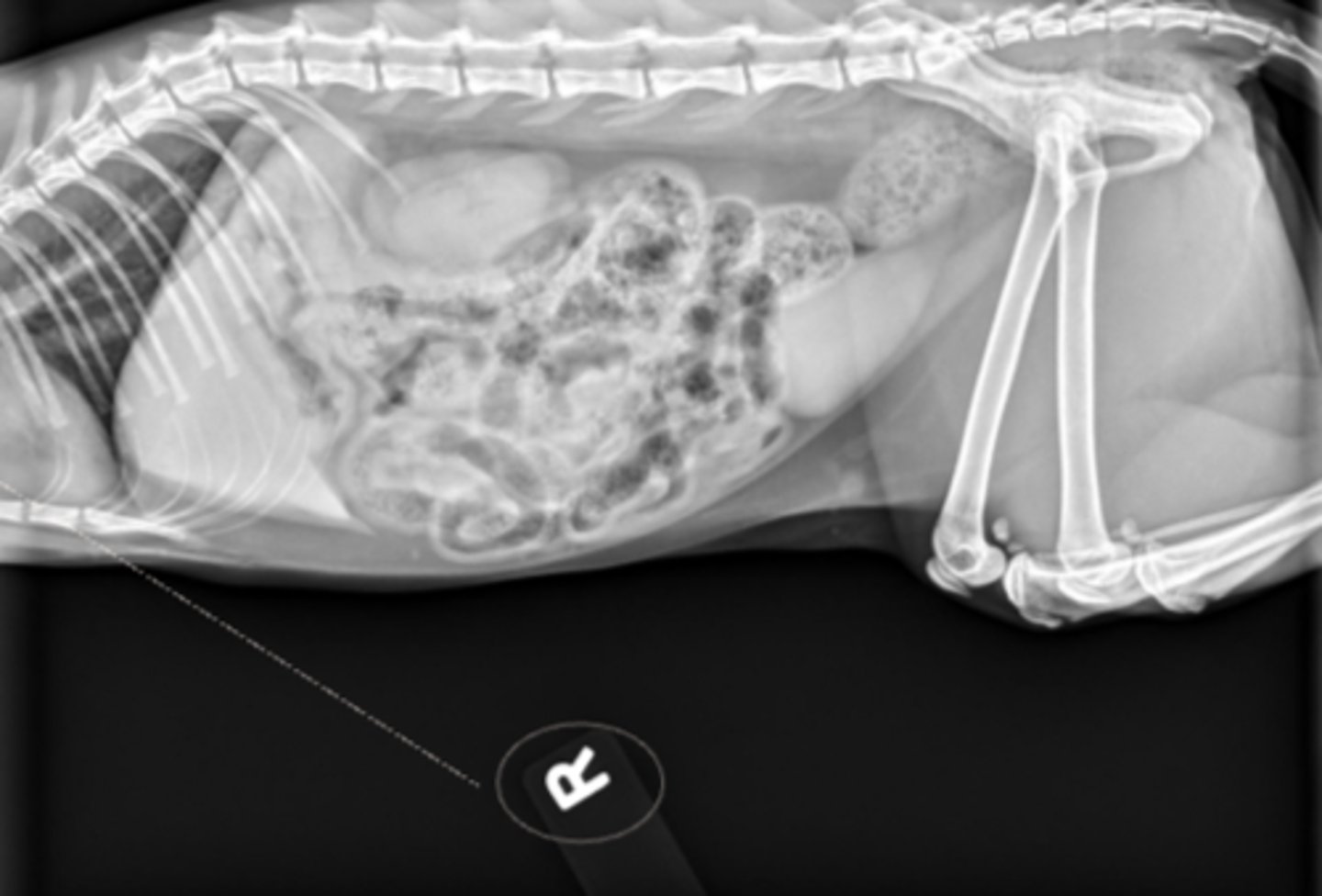
What is unique about the way this indicator was placed?
“R” indicator tells this is a R lateral abdomen with the cranial to the reader’s left
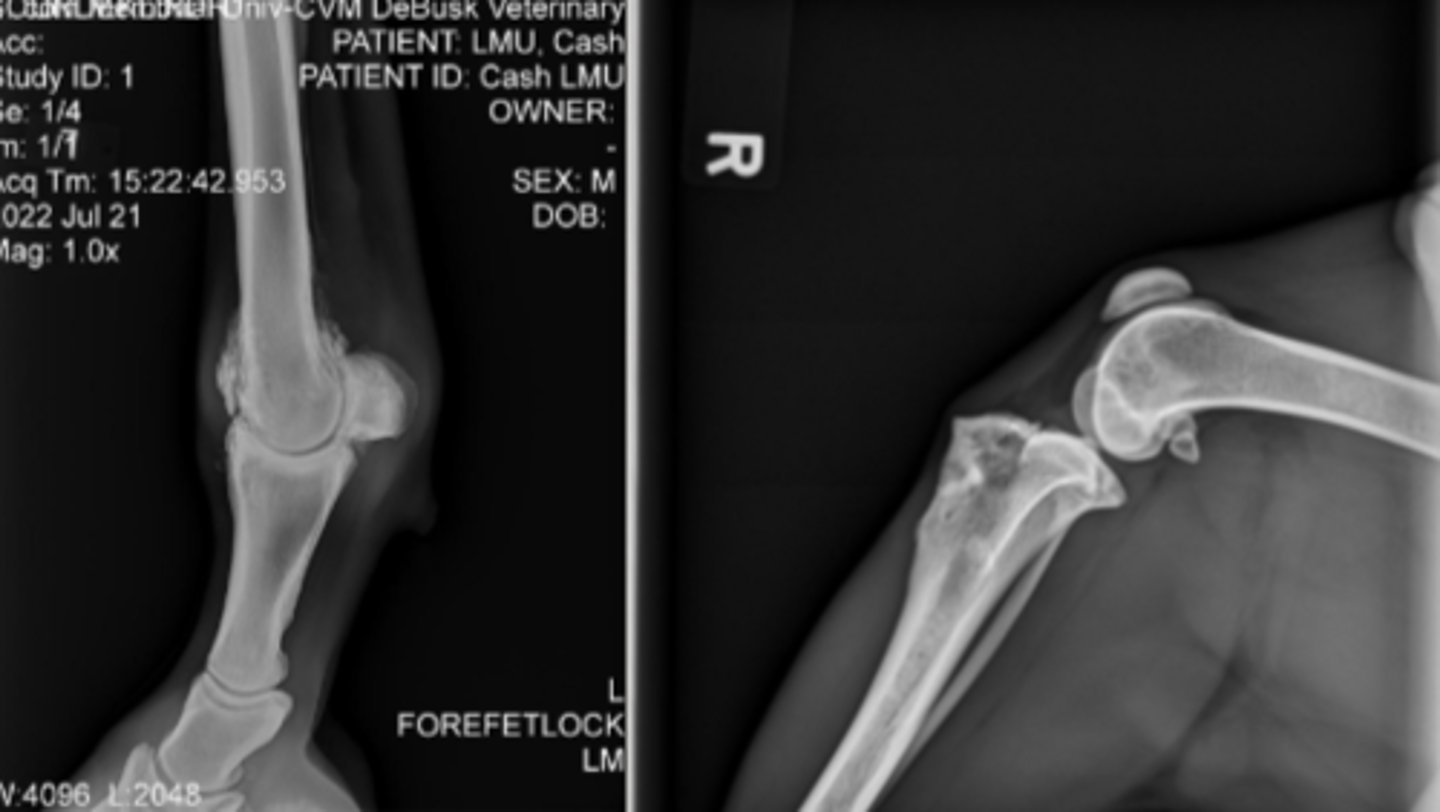
How should extremities be oriented in the medial-lateral projection?
Cranial or Dorsal to the readers left
How should a patient be oriented for ventrodorsal (VD)/dorsoventral (DV) views?
Cranial at the top of the image with the patient’s Right to the readers left
How is Ventrodorsal (VD) and D
What is the appropriate way to read radiographs?
What does that mean? (2)
Systematically & Repetitive
Read radiographs in the same manner every time
Develop your own system so you don't miss anything
T/F - Different materials interact with x-rays differently
True
What are the 2 types of opacities?
1. Radiolucent
2. Radiopaque
Match:
Radiopaque
Radiolucent
Black
White
Radiopaque = white
Radiolucent = black
What is an example of radiopaque and radiolucent?
Radiopaque: Urinary Stones
Radiolucent: Air
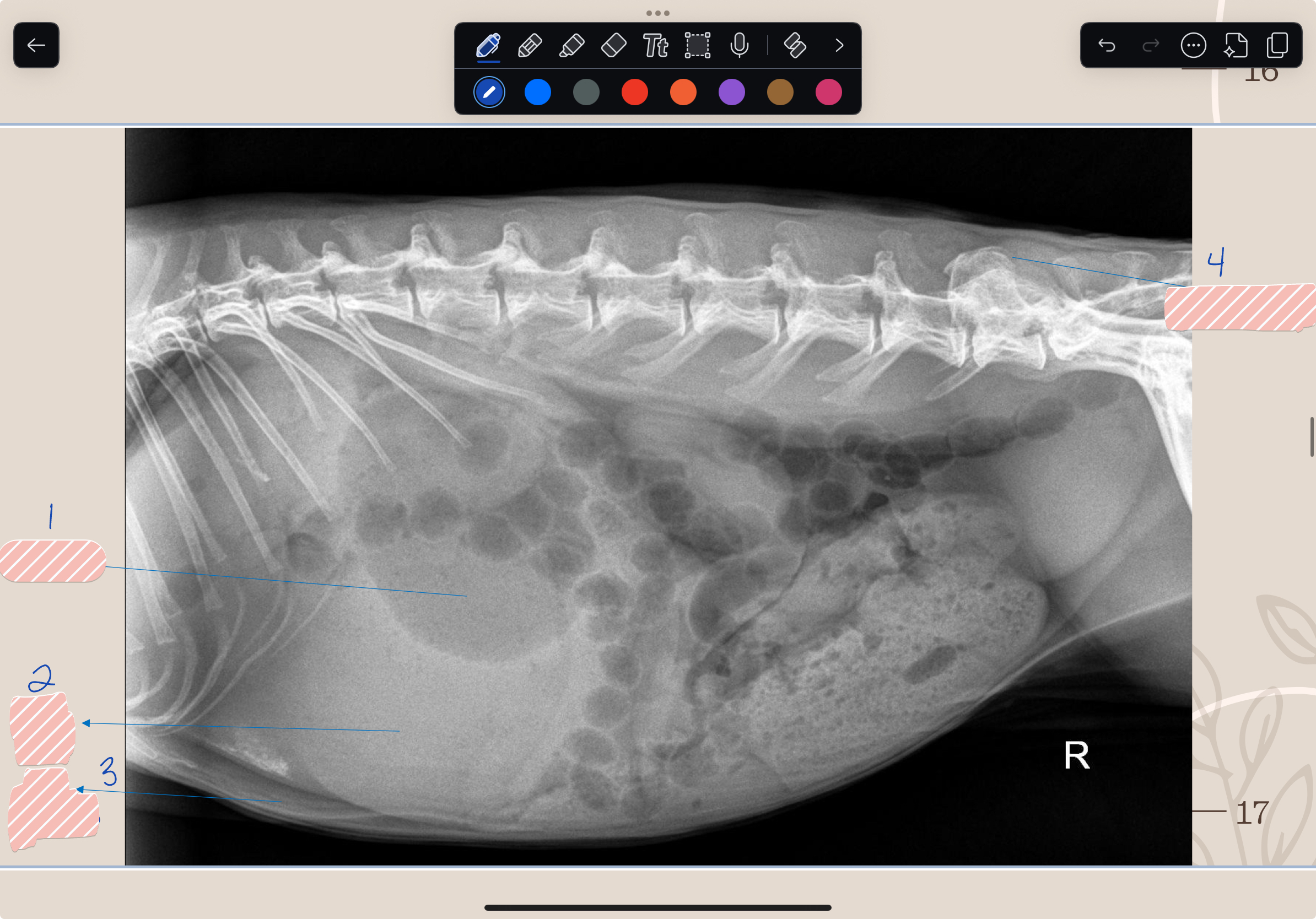
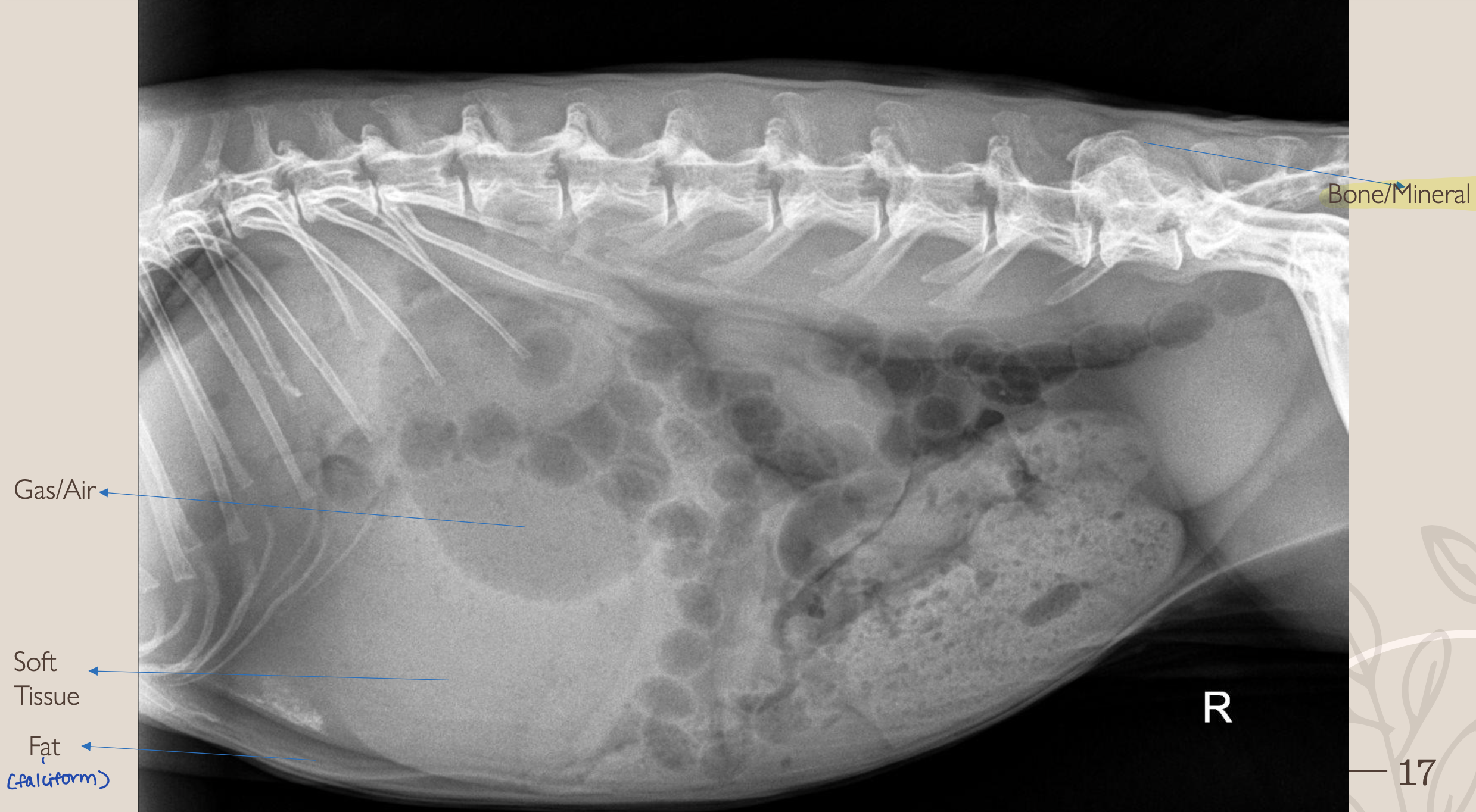
What is #1?
Gas/Air
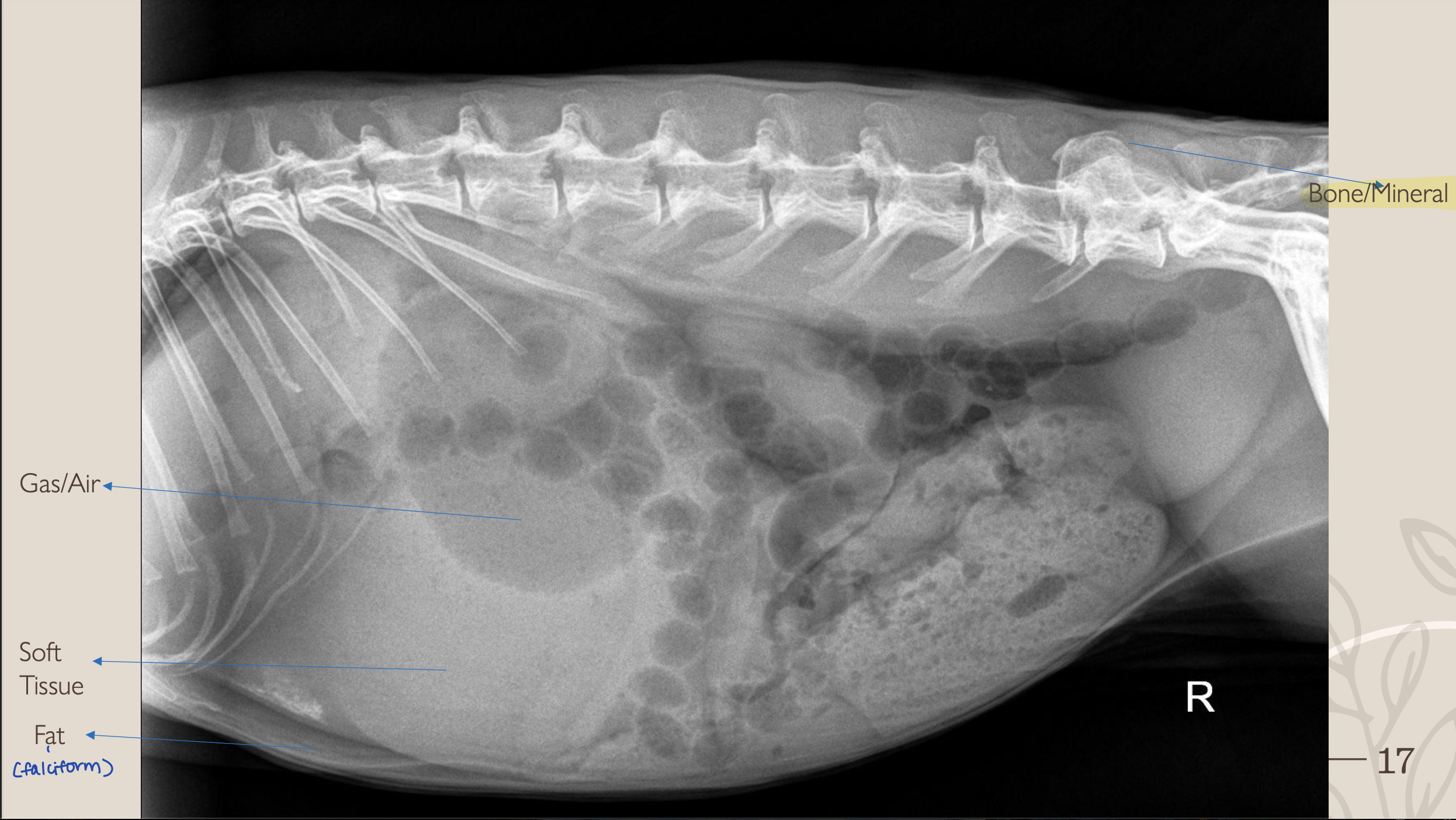
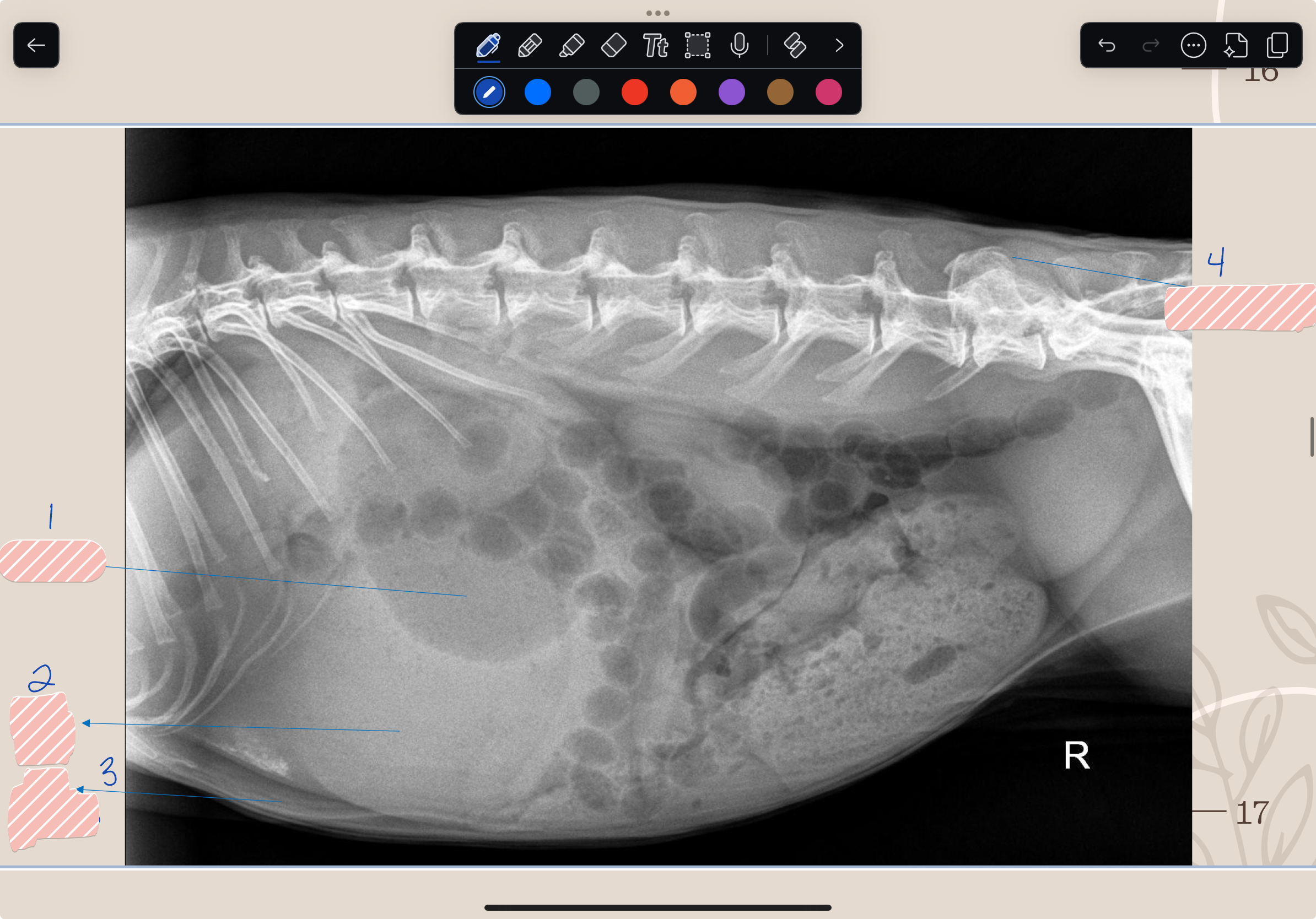
What is #2?
Soft Tissue
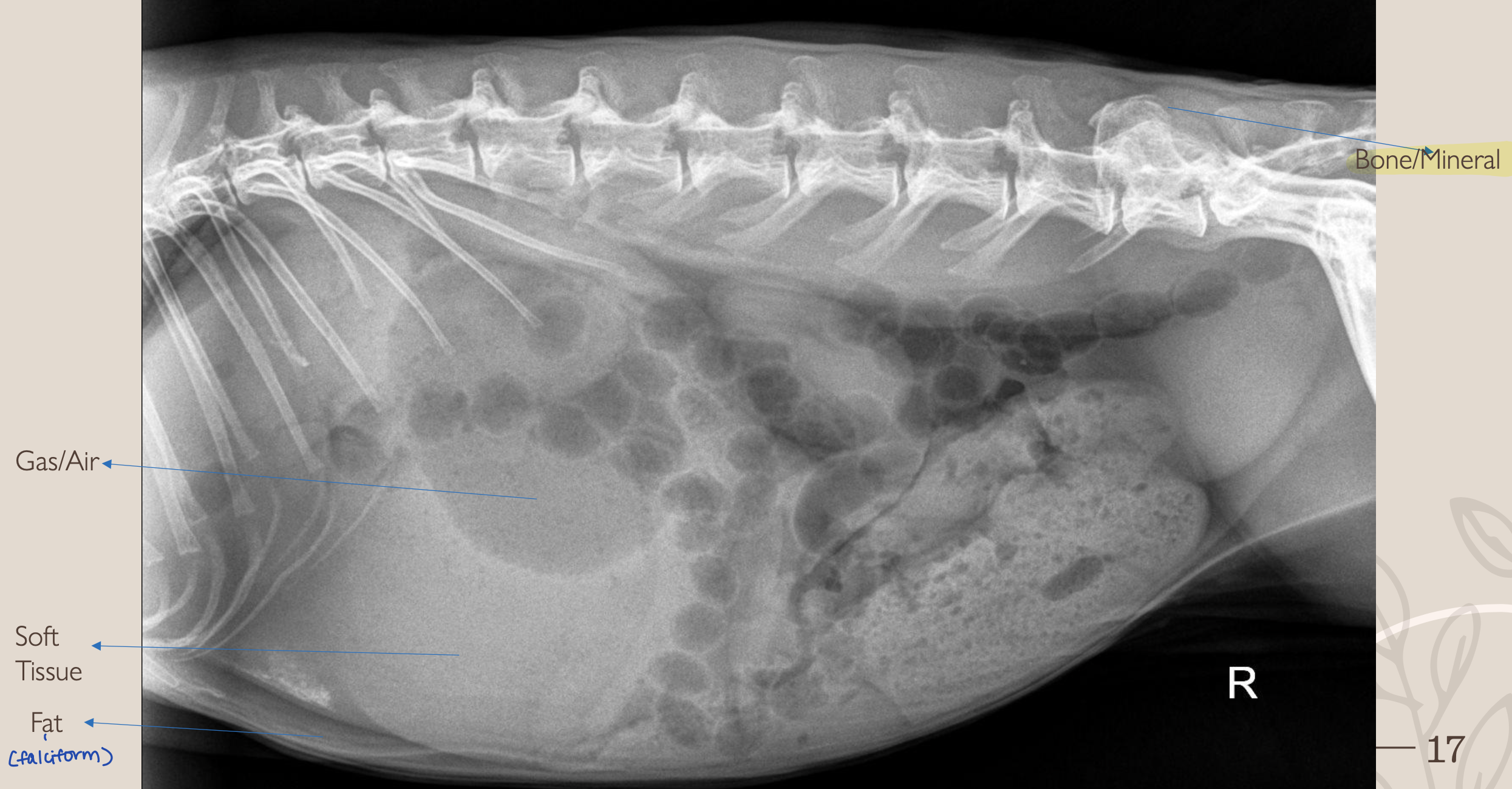
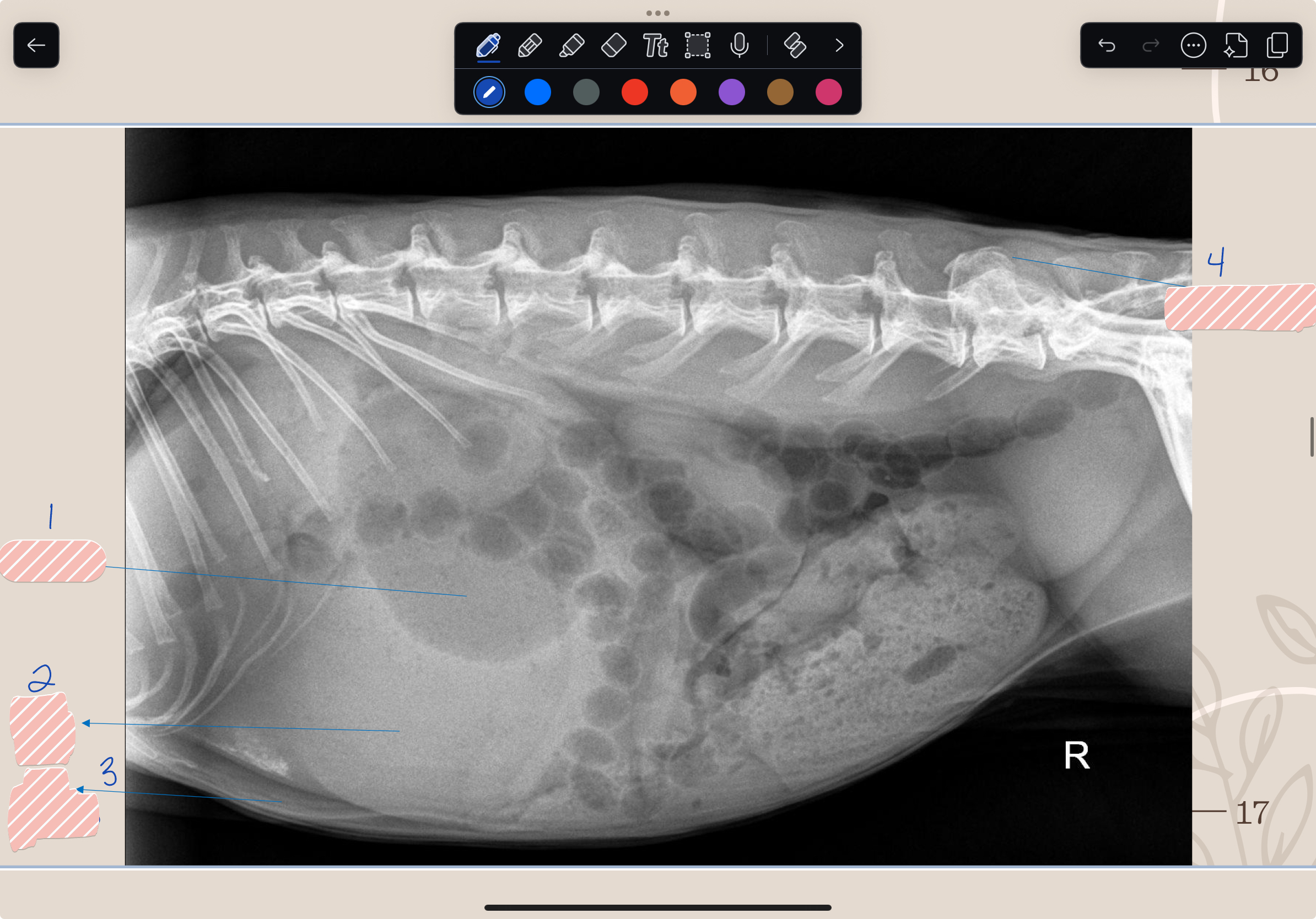
What is #3?
Fat
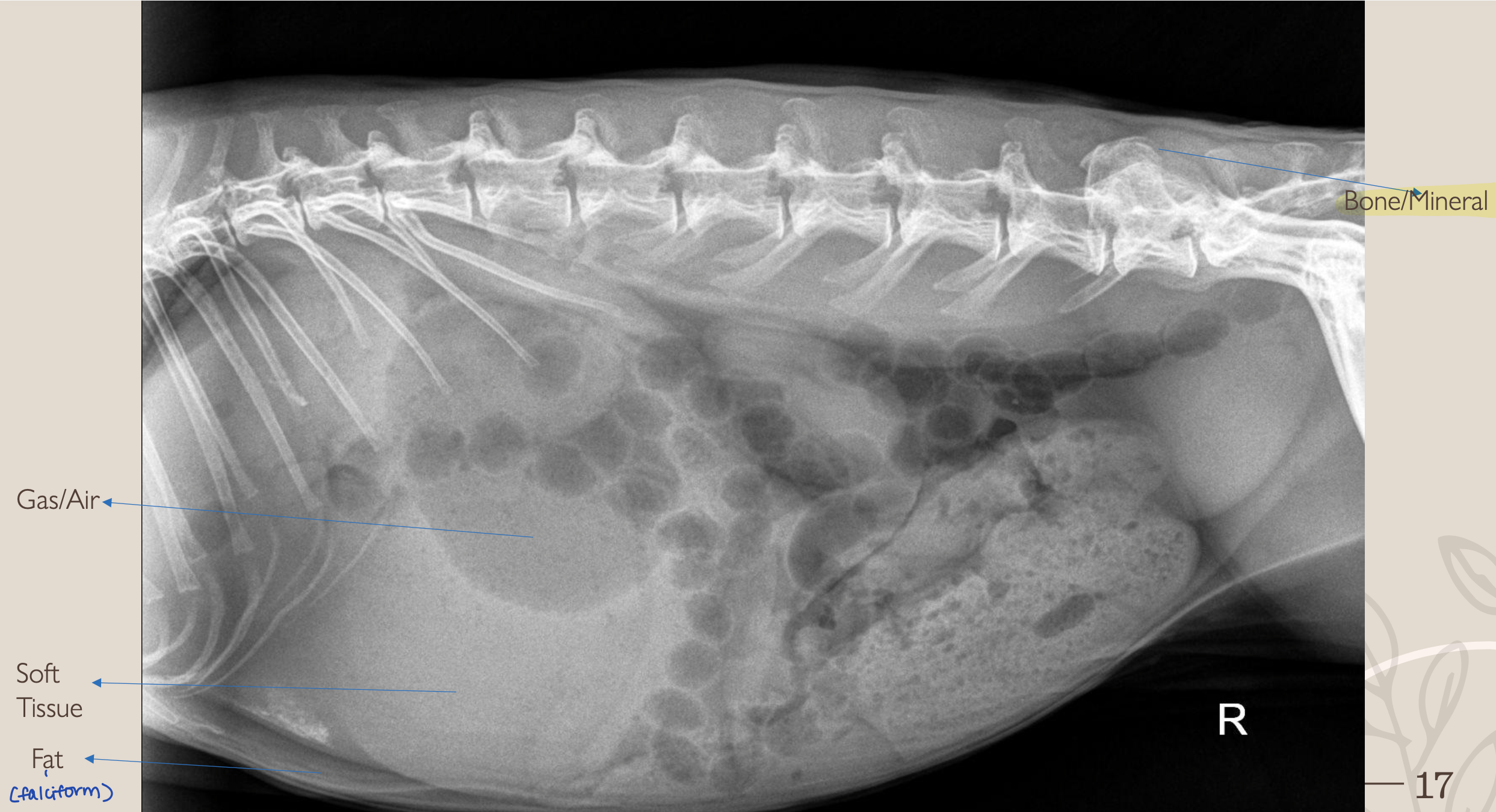
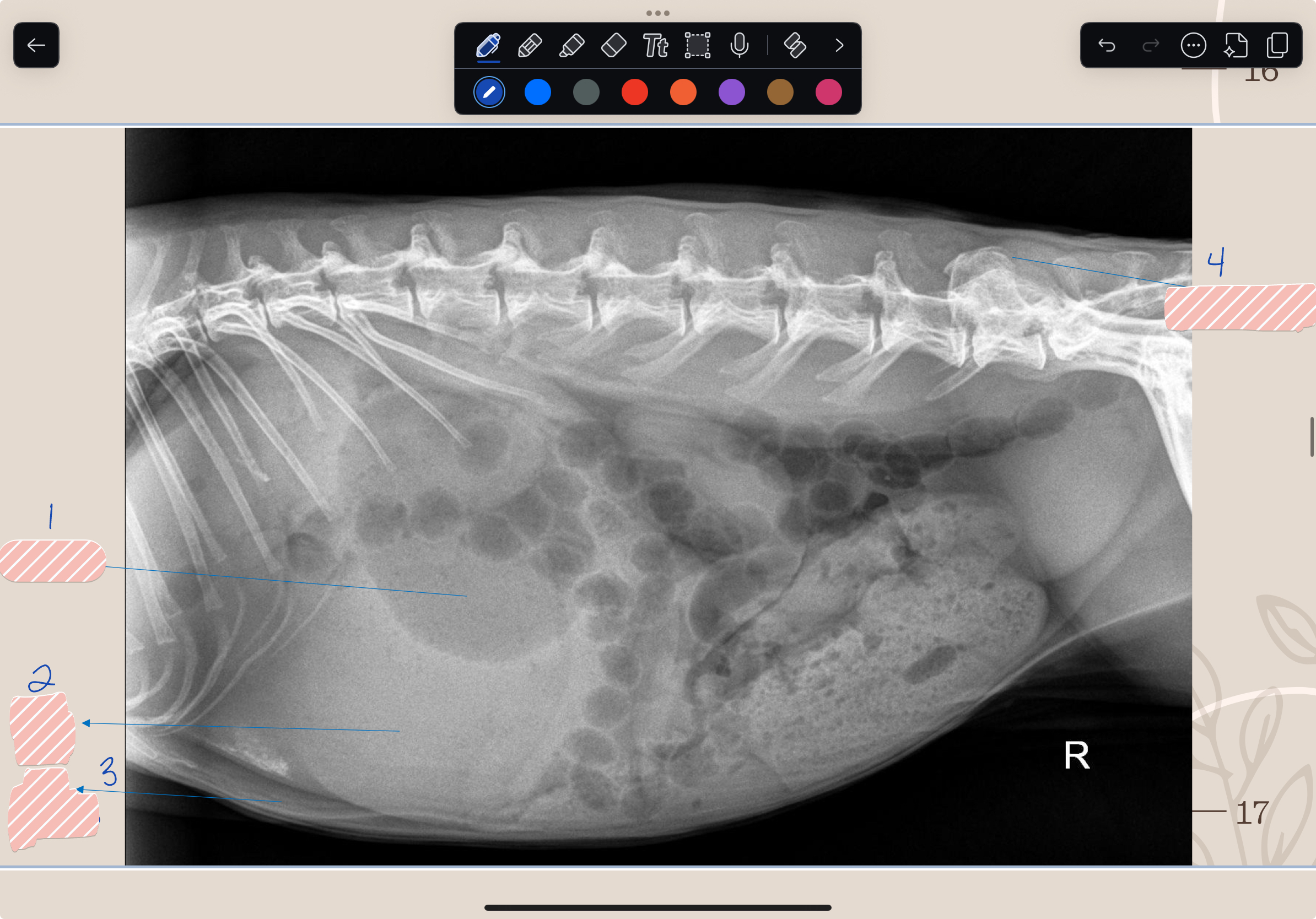
What is #4?
Bone/Mineral
What are the 6 Roentgen signs?
1. Size
2. Shape
3. Number
4. Location
5. Margination (smooth vs. rigid)
6. Opacity
*ALL these should be in a report
With an x-ray, a 3D structure becomes a 2D image. What 4 things can this cause?
1. Magnification and Distortion
2. Motion
3. Summation
4. Border Effacement or Silhouette Sign
_____ occurs due to the distance between the structure and the receiver
Magnification (enlargement of a structure)
What does magnification do to an image since it’s spread over a larger area?
Reduces detail (of the image)
When does Distortion occur?
When the object and the receiver are NOT parallel
Need everything to be aligned together
Radiographs will always have some degree of what? How do you minimize it?
Distortion
Minimize distortion using standard positioning
What is Summation?
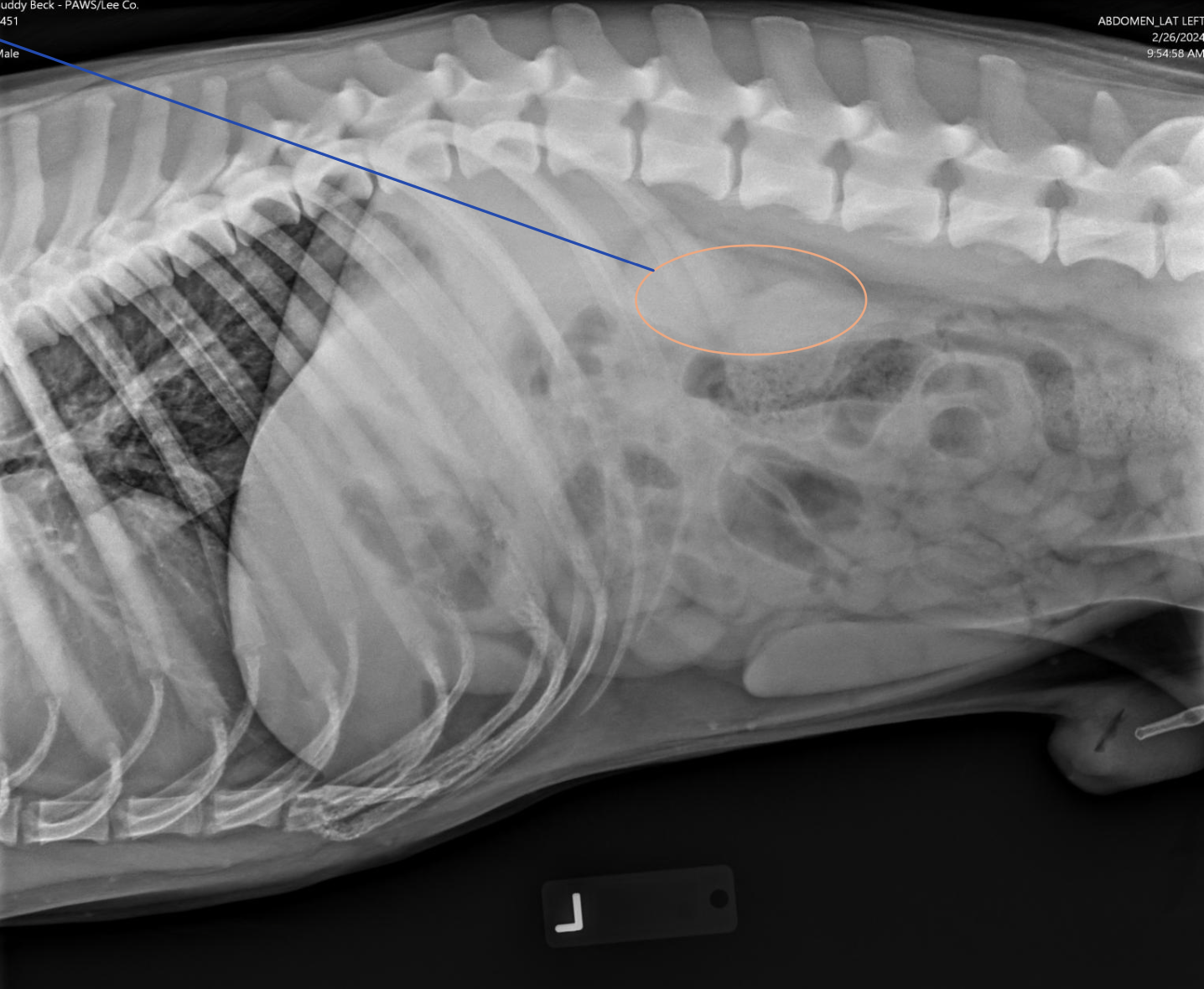
What term defines: “opacity created that does NOT represent a structure that is present within the patient”?
Superimposition
What organ is Summation/Superimposition common in? Where?
Kidneys (on lateral views)
Caudal Pole of R kidney with Cranial Pole of L kidney
What can the summation of the kidneys be misinterpreted as?
A mass
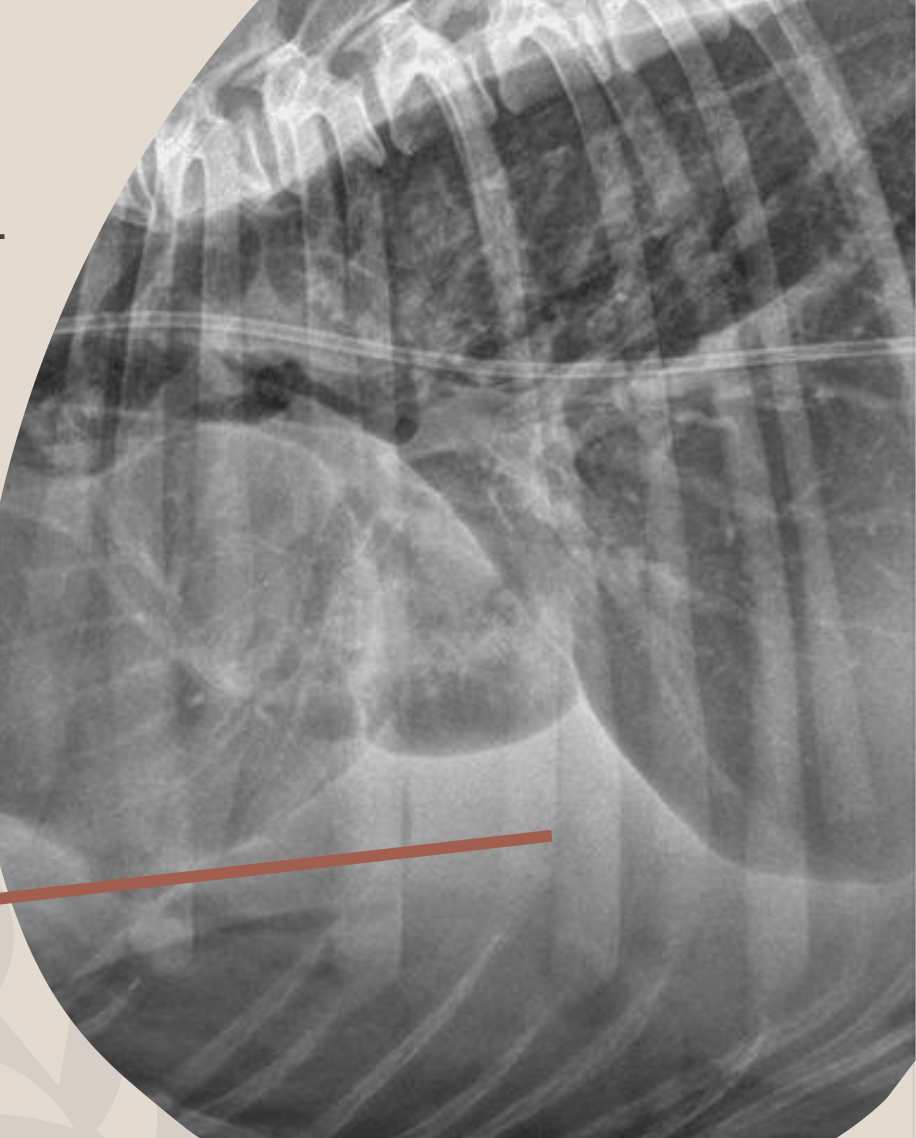
What term defines: “Two structures in contact with each other that has the SAME opacity”?
Causes a loss of margin distinction
Boarder Effacement/Silhouette Sign
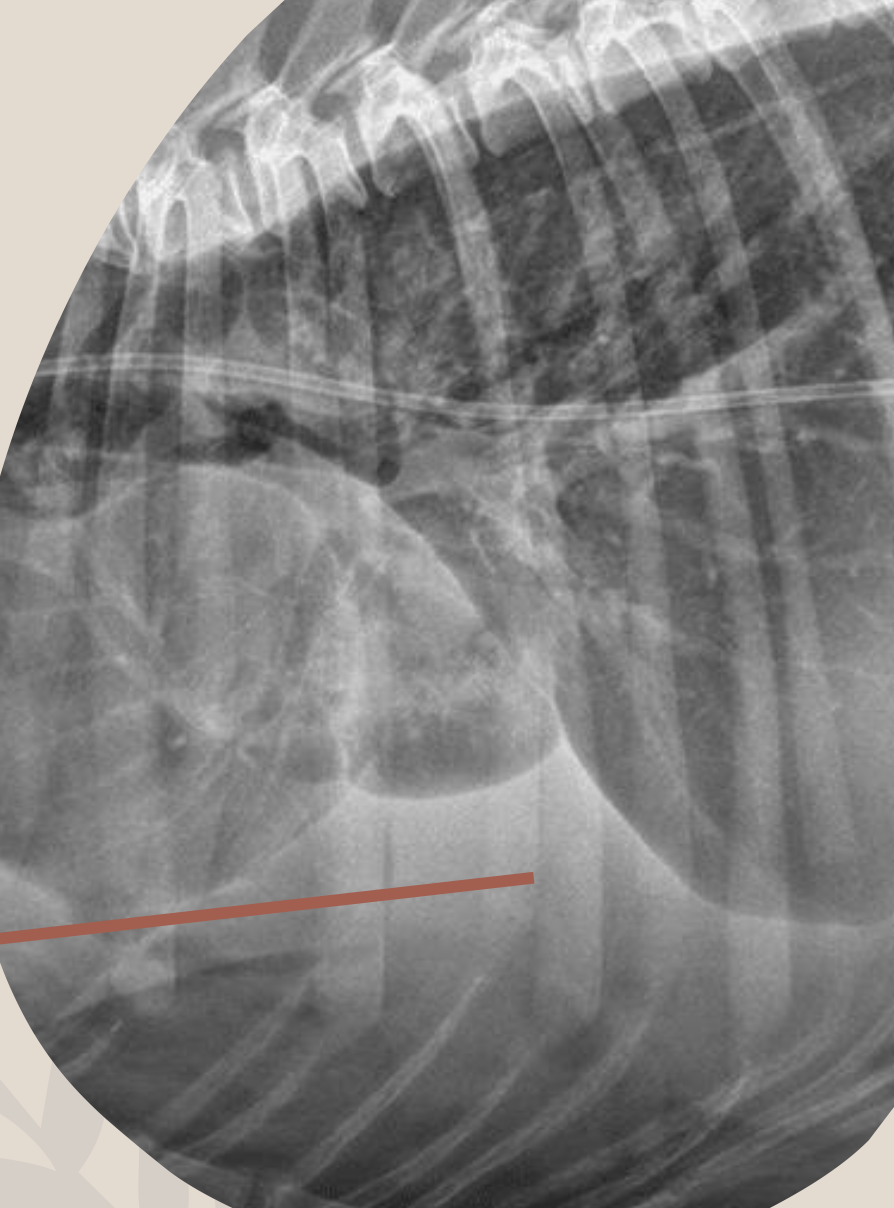
Why can’t the heart be seen in this picture?
(where arrow is pointing)
Boarder Effacement: fluid is sitting on top with the same opacity
What term is used to describe when an image is too bright?
Underexposed
Undercooked cookies are lighter
What term is used to describe when an image is too dark?
Overexposed
Overcooked cookies are darker
What things may cause an image to be underexposed?
kVp or mAs is too LOW
What things may cause an image to be overexposed?
kVp or mAs is too HIGH
If an image is underexposed, do you need more/less x-rays?
What about if the image was overexposed?
Underexposed = need MORE x-rays
Overexposed = need LESS x-rays (too many x-rays)
Underexposure has more “_____”
“Noise”
Contrast or Detail?
Ability of an x-ray beam to penetrate tissue depends on its energy
The x-ray beams energy directly ties to a varying kVp with a stable mAs
Contrast
What term defines: “links directly to the differing of opacities based on varying degrees of x-ray beam absorption”
Degree of x-ray beam absorption = differing of opacities
Contrast
Higher/Lower kVp gives more/less contrast because more/less x-rays are transmitted through the patient to the plate
Higher kVp gives less contrast because more x-rays are transmitted through the patient to the plate
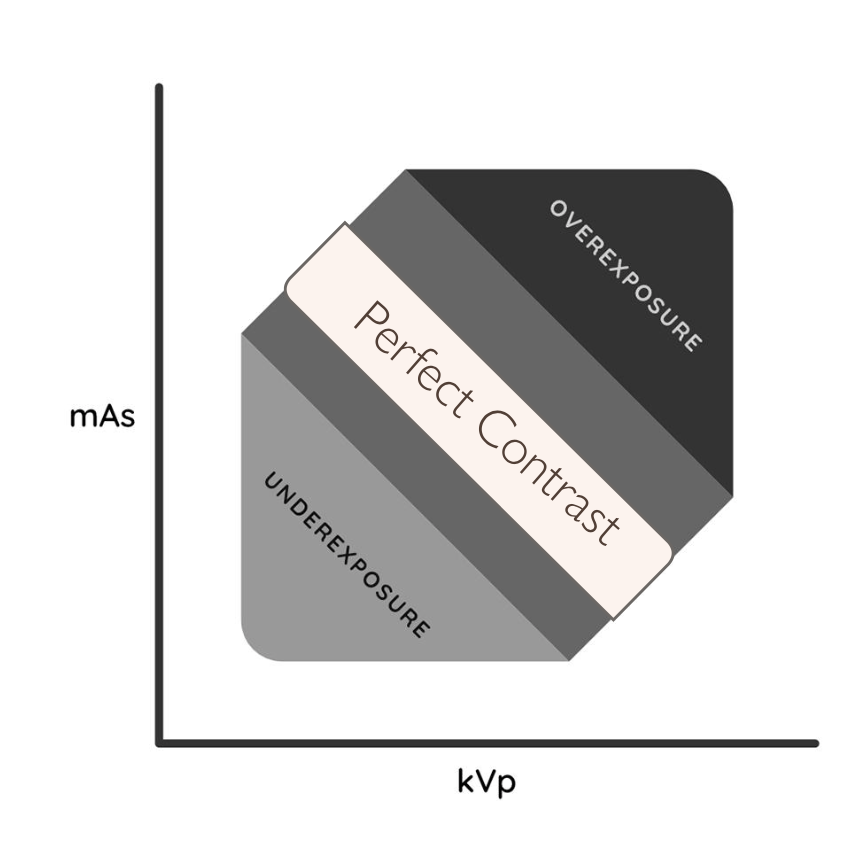
Higher/Lower kVp allows a varying absorption so higher/lower contrast
Lower kVp allows a varying absorption so higher contrast
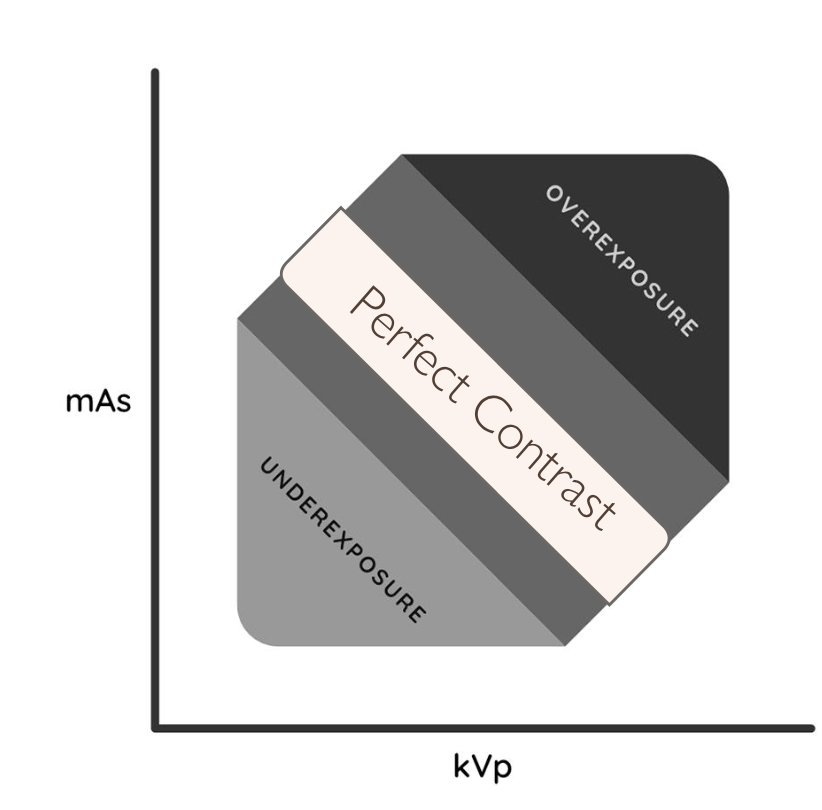
What term defines: “spatial resolution or sharpness”?
Detail
Contrast or Detail?
“How close can lines be together and still be distinguished?”
Detail
What 5 things can influence detail?
1. Exposure factors
2. Matrix of IP (Pixels)
3. Software
4. Monitor
5. Readers visual acuity
What radiograph technology is being described?
1. High number better image but larger file
2. Check out numbers when purchasing machines
Pixel: Picture Element
What radiograph technology is being described?
1. Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
2. Standardized format
DICOM
What does PACS stand for?
Picture Archiving and Communicating System
What 6 things should be labeled on a radiograph (document)?
1. Patient name
2. Patient number
3. Species
4. Date
5. Area radiographed
6. Right or left