deez nuts
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Strategy
The set of goal-directed and integrated acitons a firm takes to gain and sustain competitive advantage
Strategic Management
Combines analysis, strategy formulation, and implementation in the quest for competitive advantage
Mastery of strategic management enables you to:
View a firm in its entirety (i.e., at the “30,000-foot level”)
Think like a general manager (i.e., see the “Big Picture”)
Position your organization for superior performance
A good strategy is based on three elements
An accurate diagnosis of the competitive challenge
Analysis of the firm’s external and internal environments
A guiding policy to address the competitive challenge
Formulation of corporate, business, and functional strategies
A set of coherent actions that reflect the firm’s guiding policy
Implementation of the strategy
Competitive Advantage
Superior performance compared to other competitors in the same industry or the industry average
Sustainable competitive advantage
Achieved by firms that outperform their competitiors or the industry average over a prolonged period
“Holy Grail” of successful strategy
Competitive Disadvantage
When a firm underperforms its rivals or the industry average
As with competitive advantage, it is relative
Competitive Parity
Two or more firms that performa at the same level
Generic business strategies
Differentation Strategy: Provide goods or services that consumers value more higly than those of its competitors (Nordstrom)
Cost Leadership Strategy: Provide goods or services that are similar to those of competitors, but at the lower prices (Walmart)
Blue Ocean: A strategy that combines both differentiation and cost-leadership activities (Trader Joe’s)
A firm offers a differentiated product/service at low cost
Uses value innovation to reconcile trade-offs
Blue Oceans represent:
• Untapped market space
• Creation of additional demand
• Opportunities for highly profitable growth
Strategic Positioning
A unique position within an industry that allows the firm to provide value to customers while controlling costs
Stakeholder
Organizations, groups, and individuals that:
Can affect or be affected by a firm’s actions
ahve a vested claim or interest in the performance or survival of the firm
Internal Stakeholders
Stockholders, employees (including executives, managers, and workers), and board members
External Stakeholder
Customer, supplier, alliance partners, creditors, unions, communities, media, and governments
Shareholders v. stakeholders
Stakeholder strategy
Integrative approach to managing a diverse set of stakeholders
goal is to gain and sustain competitive advantage
Stakeholder strategy
Gain and sustain competitive advantage
Benefits performance
Reveal important
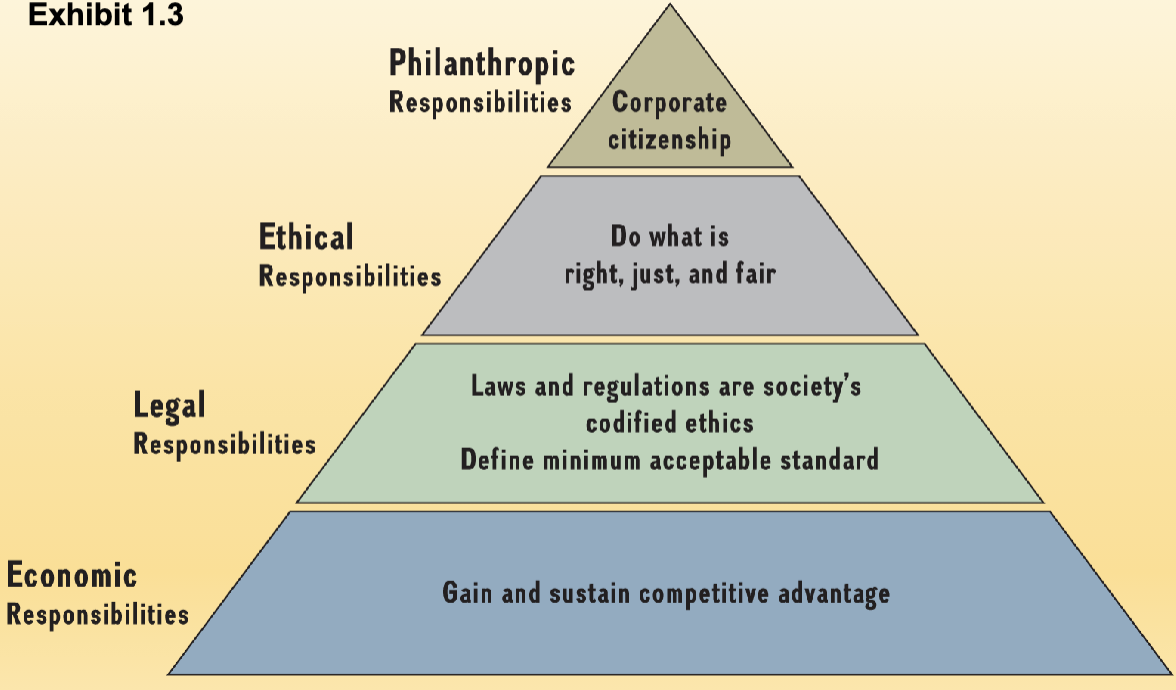
Pyramid of Corporate Social responsibility
AFI Stands for…
Analysis, Formulation, Implementation
Strategic leadership
Use power and influence to implement strategy and reach goals
Formal authority
ceo (position)
Informal authority
Get people to do things (persuasion)
Function of innate abilities and learning
Strategic leaders Mainly do
Face-to-face meetings
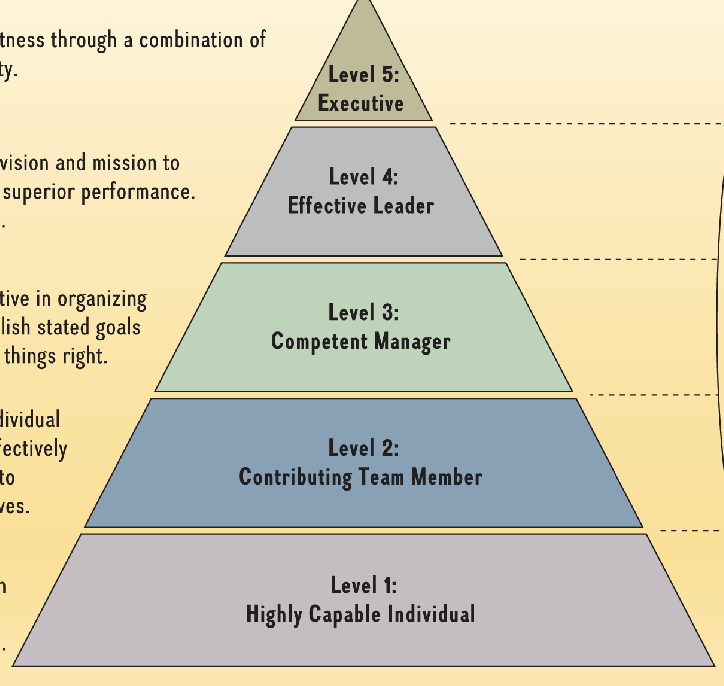
Level-5 Leadership pyramid
Strategy Process
Where and how to compete
1. Corporate (where)
industry, markets, and geography
2. Business (how)
cost leadership, differentiation, or value innovation
3. Functional (how to implement)
different strategies require different activities
Vision, mission, values
Vision: What do we want to accomplish
Expressed as a statement
uses the infinitive form of a verb (to be, to create)
forward thinking and inspiring
Mission: How do we accomplish our goal
how the vision is accomplished
Values: What commitments do we make?
What safeguards do we put in place?
how do we act both legally and ethically as we pursue our vision and mission?
Vision and competitive advantage
strongest when customer oriented
internal stakeholders help define
org. structure align
Product oriented vision statements
Define a business in terms of a good or service provided
Focus on improving exisitng products and services
Force managers to take a more myopic view
Customer oriented vision statements
solutions to customer needs
allow companies to adapt to changing enviroments
Problem solving for the customer
Mission: Strategic commitments
Credible actions that back up the vision and mission statements
costly
long term
difficult to reverse
Three approaches to strategic management
Top down
formal, data, top down, military
Scenario planning
Formal top down, probability of things happening, develop strategic responses
asks what if questions
Planned emergence
Beings with strategic plan, but less formal
Black Swan event
High impact and highly improbable
Strategic initiatives
Activity that firm pursues
Two decision making modes
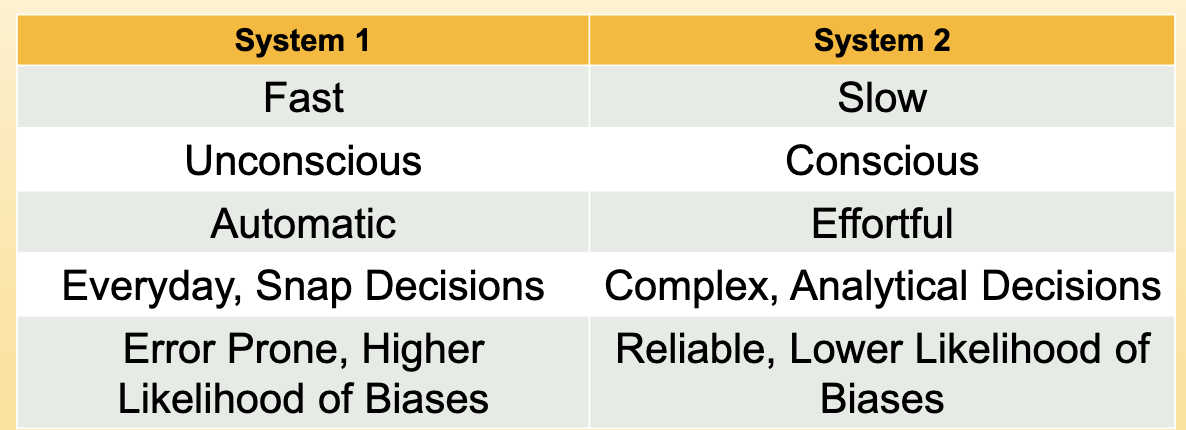
Cognitive biases
Group think
Confirmation bais
Illusion of control
Devil’s Advocacy
Challenge with alternative viewpoints
General Enviroment
Hard to predict and difficult to control
Industry enviroment
Strategic leaders have some control over
Scanning and Monitoring
Scanning:
predicts environmental changes to come
detects changes already under way
Monitoring:
tracks evolution of environmental trends
Competitive Intelligence
Identifies rivals’ strengths and weaknesses
PESTLE Framework
Political
Government bodies, social movements can exert to influence firm
Economic
money, exchange rates, interest rates, relatively stabel economies with strong growth potential
Sociocultural
Society cultures, norms, and values
Technological
new knowledge
Legal
Laws enacted
Environmental
Industry and Industry analysis
Industry:
Group of incumbents
same set of suppliers and buyers
Analysis:
Identify and industry’s profit potential
Derive implications
5 Forces model
Strengths and weaknesses
Competitive advantage
Threat of new entrants:
Entry barriers
bargaining power of suppliers:
powerful if only a few firms dominate the industry
suppliers sell to several industries
bargain power of buyers
force price down
bargain for higher quality
play competitors against each other
threat of substitute
same needs in different way
competition
balanced competitors
slow growth
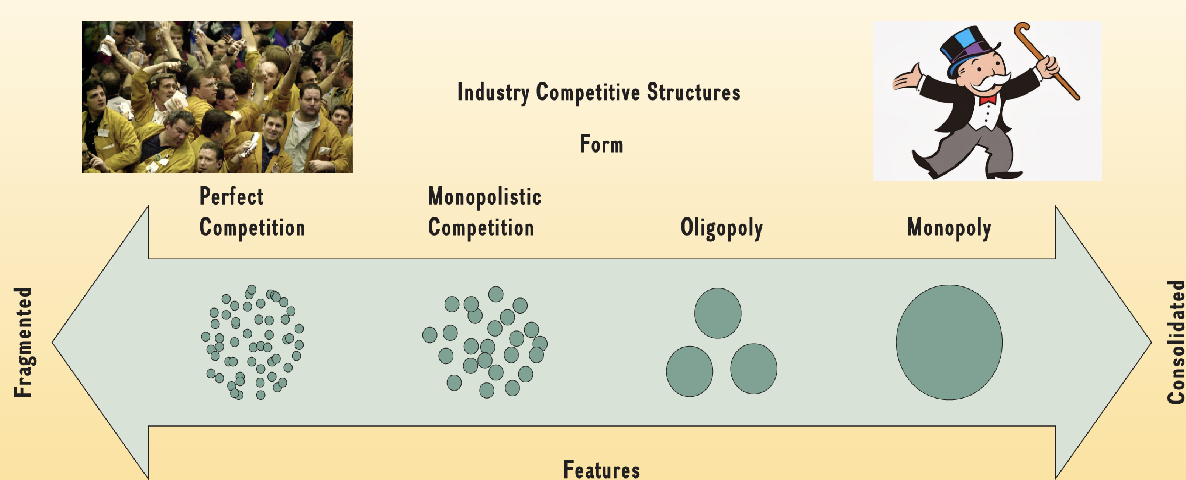
Competitive industry structrue
Number and size of competitors
Core competencies
Unique strengths embedded deep within a firm
allow the firm to differentiate from rivals
expressed through structures, processes, and routines
Resources: Tangible and Intangible
bundled to create organizational capabilities
Capabilities are the source of a firm’s core competencies
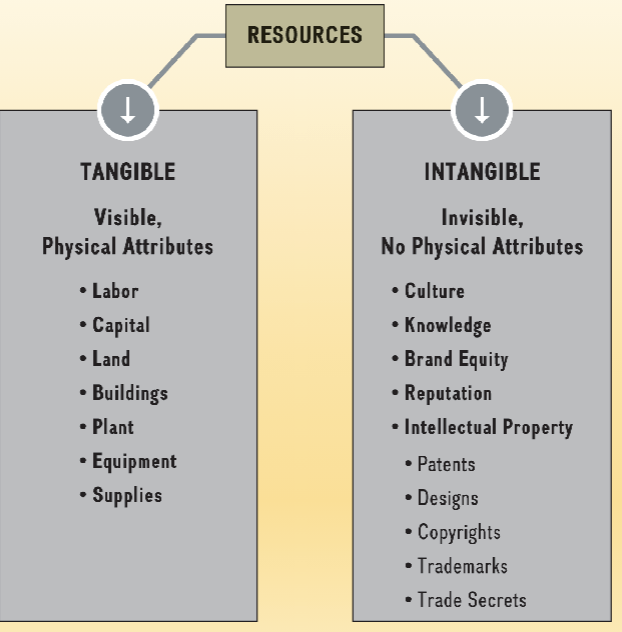
Resource-based view of the firm
An internal analysis of a company
an external analysis of the industry and its competitive environment
Can leave to competitive advantage if they are valuable, rare, and hard to duplicate
Critical assumptions of the RBV
Resource Heterogeneity
Resource Immobility
VRIO
Valuable - in formulating and implementing strategies
Rare - or uncommon; difficult to exploit
Inimitable - or diffiuclt/expensive to copy
Organized - to capture the value of the resource
Preventing Imitation
Physical uniqueness: impossible to duplicate
Path dependency: hard to duplicate bc of all that has happened along the path
Causal ambiguity: impossible to explain
Social complexity: result from social engineering
Core Rigidity
former core competency that has turned into a liability
turns a resource from an asset to a liability
Value Chain
Transforming inputs into outputs
Through primary and support activities
each activity adds incremental value
each activity also adds incremental costs
Value-chain analysis
looks at the sequential process of value-creating activities within a firm
Value is the amount buyers are willing to pay
The value received (by the firm) must exceed the costs of production
Primary activities
Firm activities add value directly
inbound logistics: receiving, storing and distributing inputs
Operations: transforming inputs
Outbound logistics: collecting storing and distribuing product to the buyer
Marketing and sales: purchases of products adn services by buyers and how to get buyers to make those purchases
Service: to enchance or maintain the value
support activities
add value indirectly
Procurement: purchase inputs
Tech devlopemtn
HR
General Adminsitraiton
Outsourcing
cannot create value in either a value chain activitiy or a support function
fe organizations possess the resources and capablitites required to achieve competitive superiority
Accounting Profitability
Assesses firm performance
compares and benchmarks firm performace to competitors and industry average
Limitations of accounting data
backward-looking
focuses mainly on tangible assets
Shareholder value creation: definitions
shareholders
own shares of stock, are legal owners of public companies
Risk capital
money provided for an equity share
cannot be recovered if firm goes bankrupt
Total return to shareholders
Stock price appreciation + dividends
Market Capitalization:
Dollar value of total shares outstanding
number of outstanding shares x share price
Limitations of shareholder value creation
Volatile stock prices
Macroeconomic factors affect stock prices
Stock prices can reflect the mood of investors
Economic value creation
What we pay and what customers will pay for
Opportunity costs
Best forgone alternative
Balanced Scorecard
helps managers achieve strategic objectives
uses internal and external performance metrics
Balances both financial and strategic goals
Pros and cons
Triple Bottom Line
Profits: economic dimension
People: social Dimension
Planet: Ecological Dimension

Business-level Strategy
Goal directed actions to achieve competitive advantage in a single product market
How should we compete?
Who: which customer segments?
What: custoemrs needs will we satisfy
Why: do we want to satisfy them?
How: will we satisfy our customers’ needs?
Strategic position
Strategic profile based on value creationa nd cost in a specific product market
Valuable and unique position, which:
meets customer needs
maximizes product value
lowest possible product cost
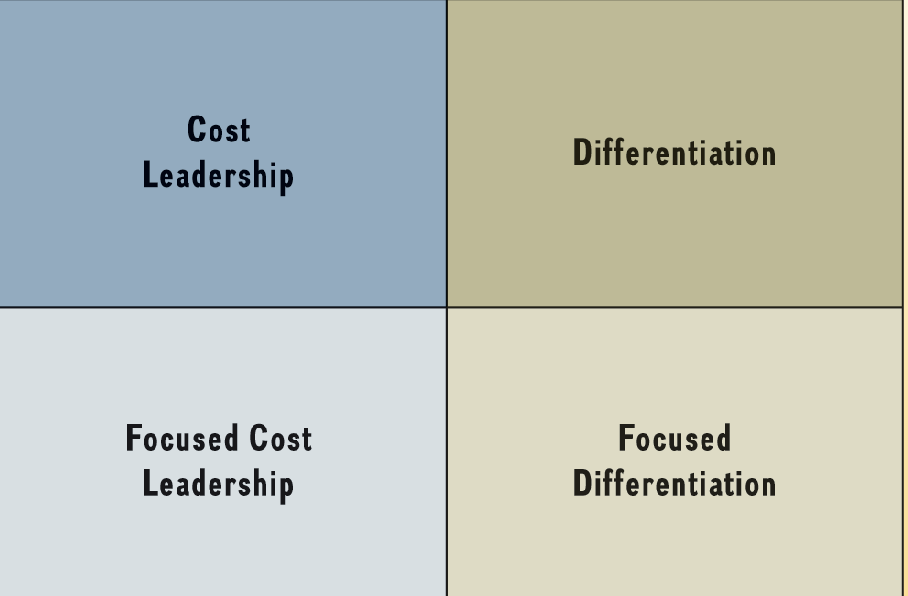
Focused business strategies
narrower competitive scope
Focused differentiation: mont blanc pens
Focused cost leadership: BIC pens
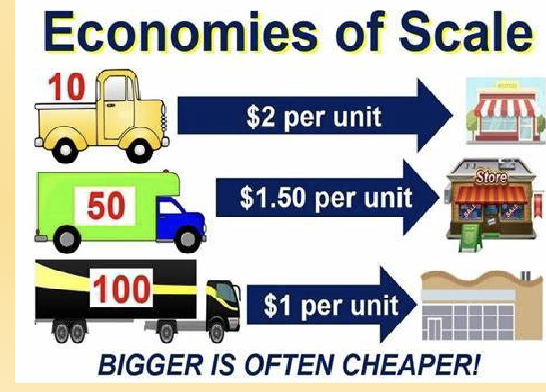
Economies of Scale (size)
Decreases in cost per unit
Achieved as output increases
spreads fixed costs over a larger output
Economies of Scope (range)
savings that come form producitng two or more outputs at less cost
Shares the same resources or technology

Perceived value
three drivers
Product Features
Customer Service
Complements
Drivers that keep costs low
Cost of input factors
raw materials, capital, labor, and it services
Economies of scale:
decreases in cost per unti as output increases
learning-curve effects
less time ot product output with experience
Diseconomies of scale
firm is too big
complexitites of too much coordination
Learning curve
Less time to produce output with experience