CMS II: Ortho - Lower Extremity
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What does a POSITIVE Ober test indicate?
tight TFL or ITB
- will be unable to keep their leg lowered

What does a POSITIVE Homan's test indicate?
positive if patient experiences pain
- indicates possible DVT
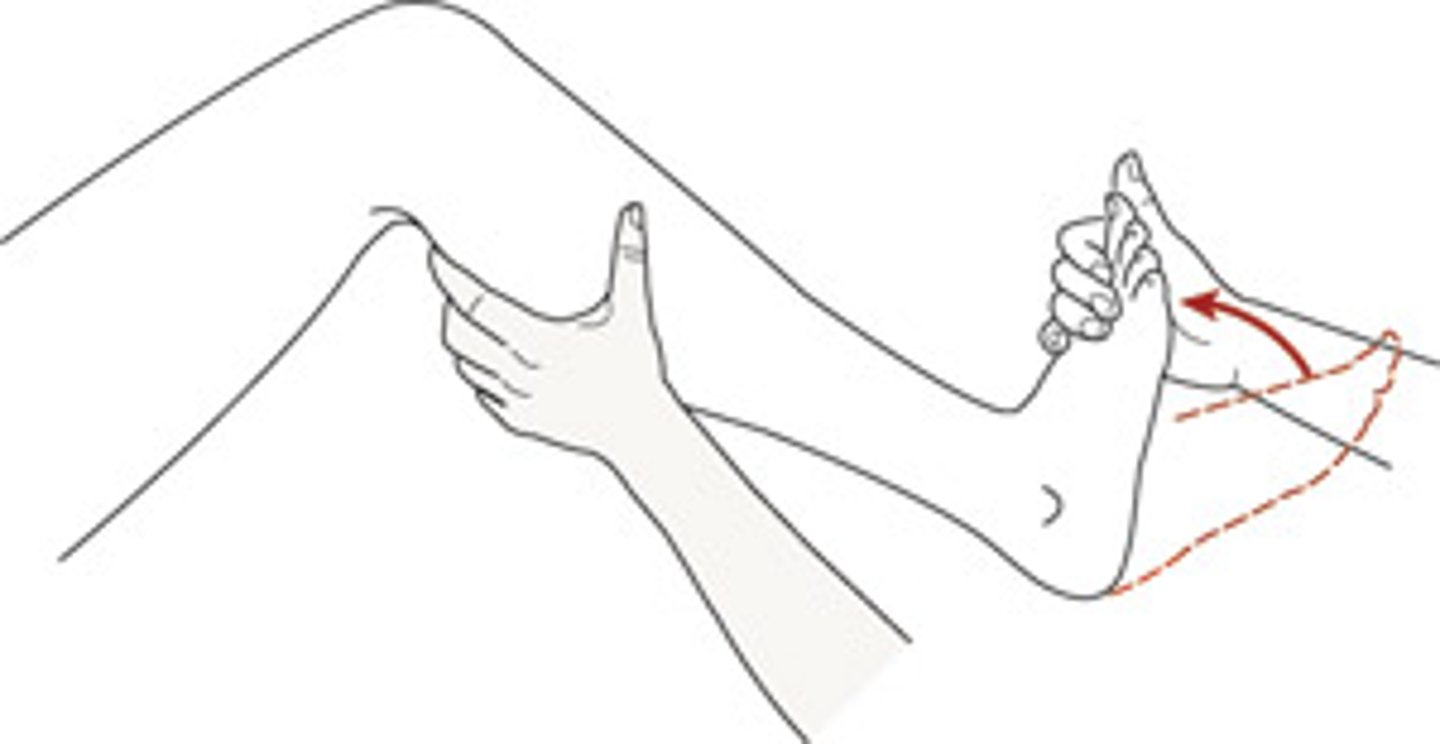
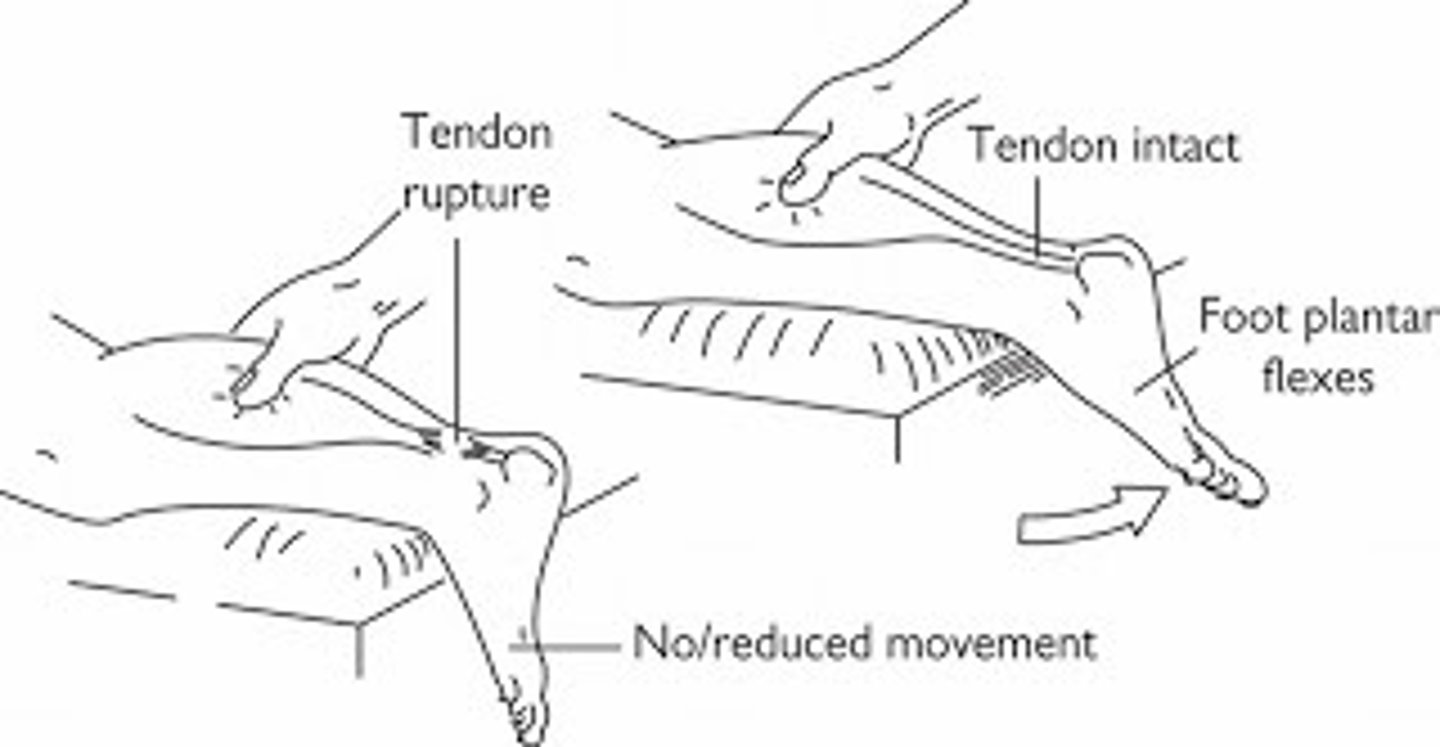
What is a POSITIVE Thompson test?
positive if the ankle does NOT plantarflex
- indicates a torn Achille's tendon
What causes ITB syndrome?
occurs when the iliotibial band becomes irritated and rubs on the lateral femoral epicondyle
- results from repetitive flexion/extension
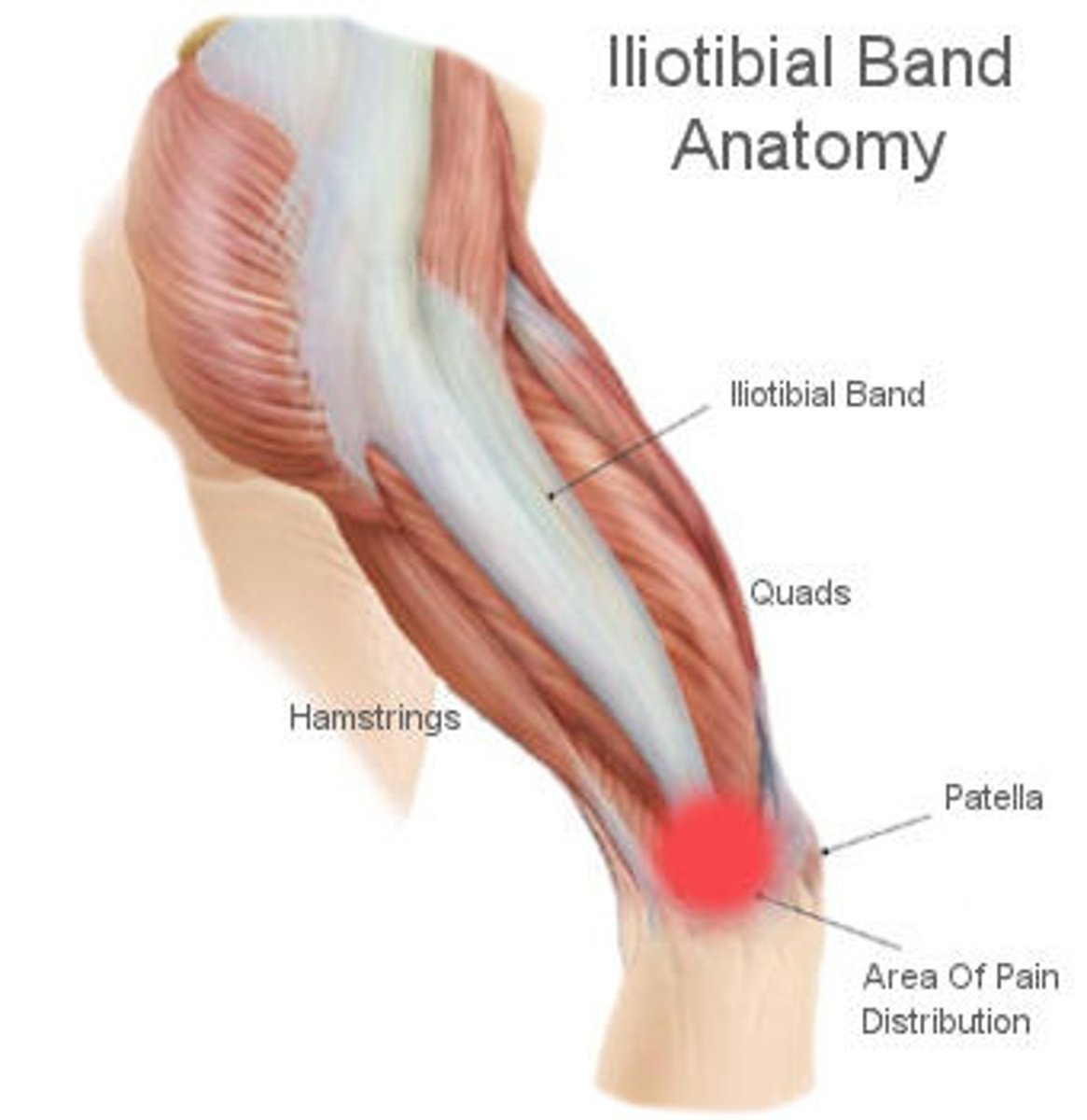
What type of pain will a patient with ITB syndrome present with?
pain in the ANTEROLATERAL aspect of the knee
- most painful when the heel strikes the floor while walking
- can be asymptomatic with rest
What non-surgical options are recommended for treatment of ITB syndrome?
PT
NSAIDs
RICE
Activity modification
If not responsive → corticosteroid injection
What is compartment syndrome? What is the most common cause and compartment involved?
occurs when there is an increase in intracompartmental pressures that could compromise blood flow
- m/c after a tibial fracture
- m/c in the anterior compartment
What is considered a NORMAL intracompartmental pressure?
<10 mmHg
What is considered a DANGEROUS intracompartmental pressure?
>40mmHg
*significant when >30mmHg
What are the 6 P's associated with compartment syndrome?
SEVERE leg Pain
Paresthesia
Pallor
Paralysis
Pulselessness
Poikilothermia
If a patient presents with compartment syndrome with paresthesias in the foot/dorsal region, what compartment is most likely involved?
anterior/lateral
If a patient presents with compartment syndrome with paresthesias in the plantar region, what compartment is most likely involved?
posterior
If a patient presents with compartment syndrome with pain with passive EHL stretching, what compartment is most likely involved?
anterior
If a patient presents with compartment syndrome with pain with passive FHL stretching, what compartment is most likely involved?
posterior
If a patient presents with compartment syndrome with pain with passive dorsiflexion of the ankle, what compartment is most likely involved?
superior
If a patient presents with compartment syndrome with pain with passive inversion of foot, what compartment is most likely involved?
lateral
What type of compartment syndrome is considered an EMERGENCY? What is the 1st line treatment?
ACUTE - will require a fasciotomy
What type of compartment syndrome occurs persistently due to intense exercise and subsides with d/c of activity?
chronic/exertional compartment syndrome
What type of tendonitis will present with pain at the insertion point on the SUPERIOR pole of the patella?
quadriceps tendonitis
What type of tendonitis will present with pain at the insertion point on the INFERIOR pole of the patella?
patellar tendonitis
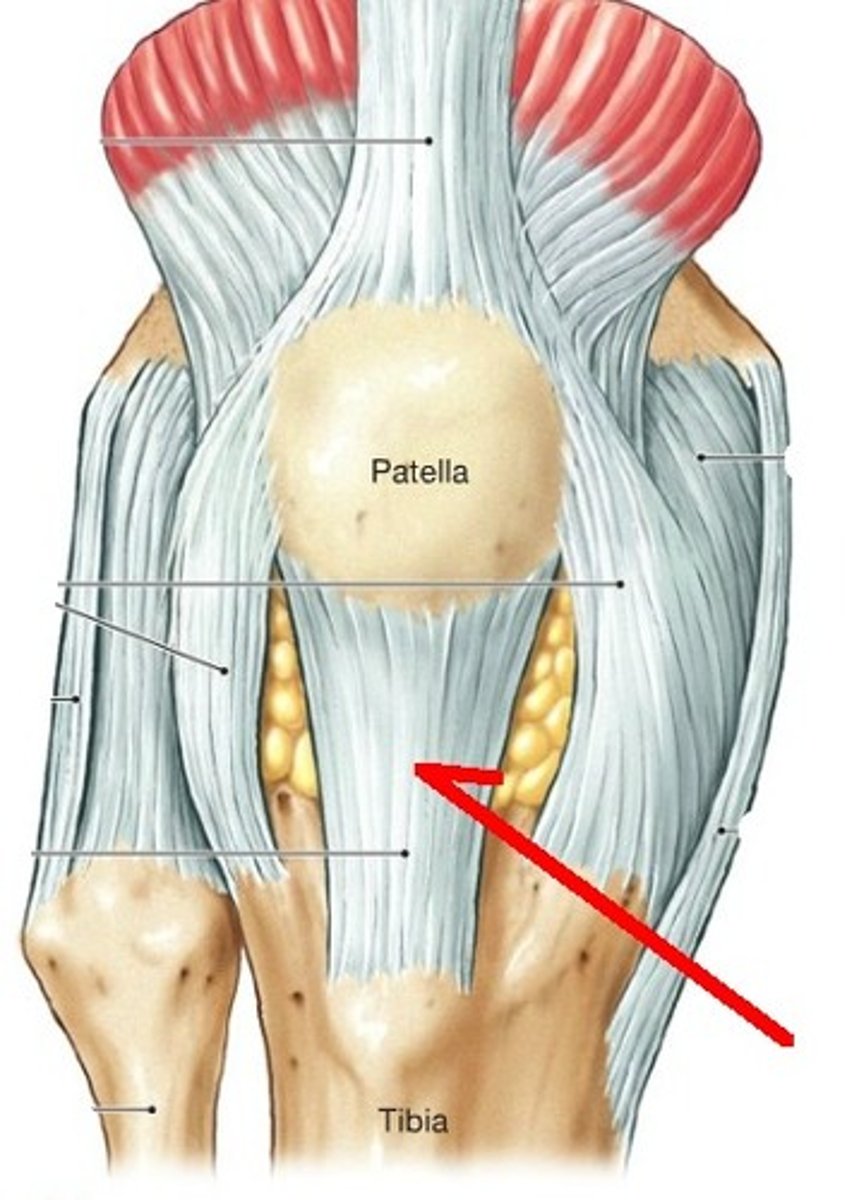
In YOUNGER patients with patellar/quadriceps tendinitis, what is the m/c cause?
jumping/kicking (overuse/overload)
"jumper's knee"
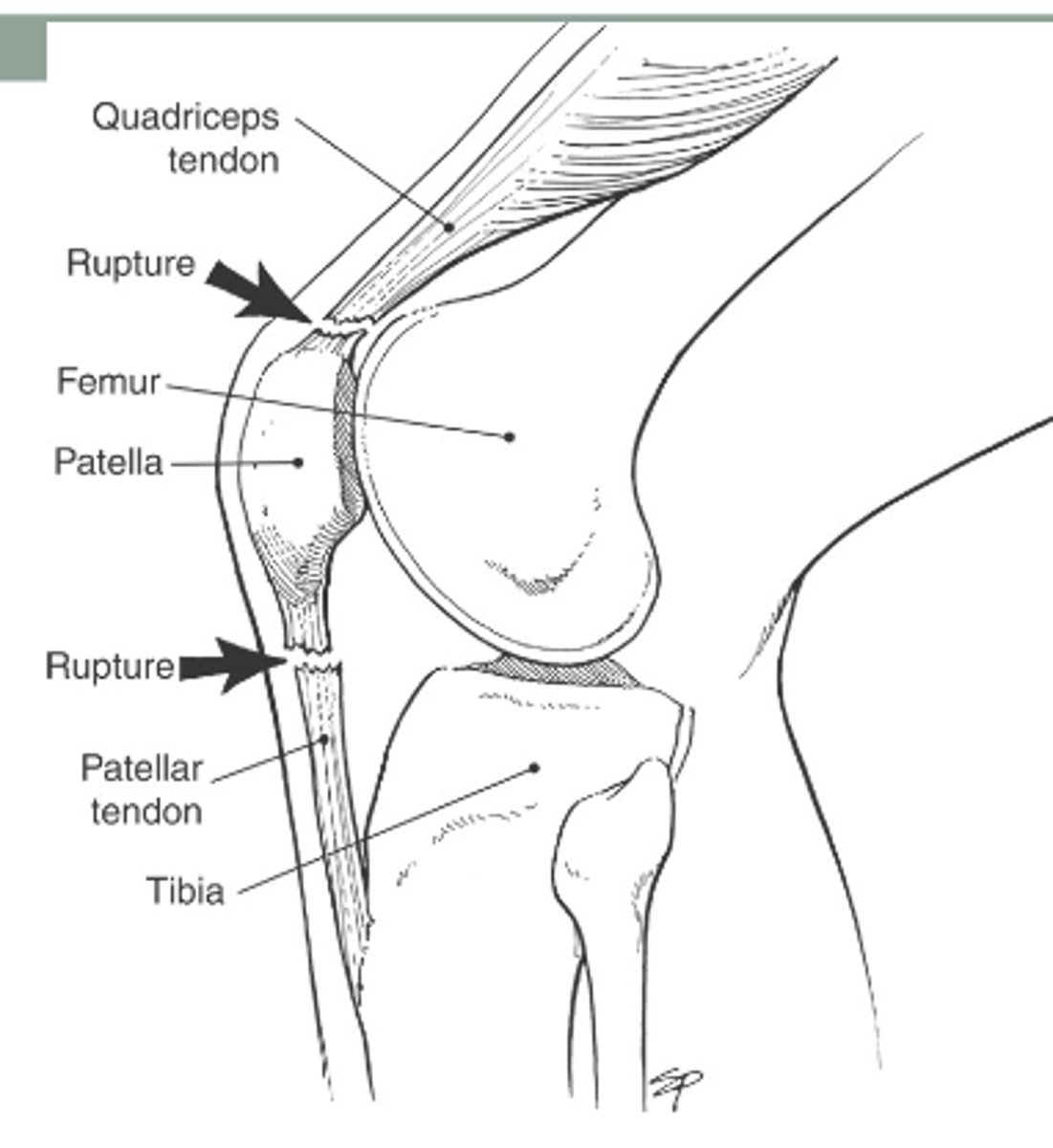
What is a hallmark symptom of patellar/quadriceps tendinitis?
anterior knee pain
- noted after exercise, prolonged sitting, squatting and sitting
What is involved in the non-surgical treatment of patellar/quadriceps tendinitis?
Rest
Knee immobilizer
NSAIDs
Analgesic creams
Heat/ice
Steroid injections
PT
What is the most common gastrocnemius tear?
acute strain or rupture of the medial head of the muscle
Who most commonly suffers from a gastrocnemius tear?
athletes >30 y/o
What type of pain is common with a gastrocnemius tear?
Pulling/tearing sensation in the calf
Pain is proximal + medial
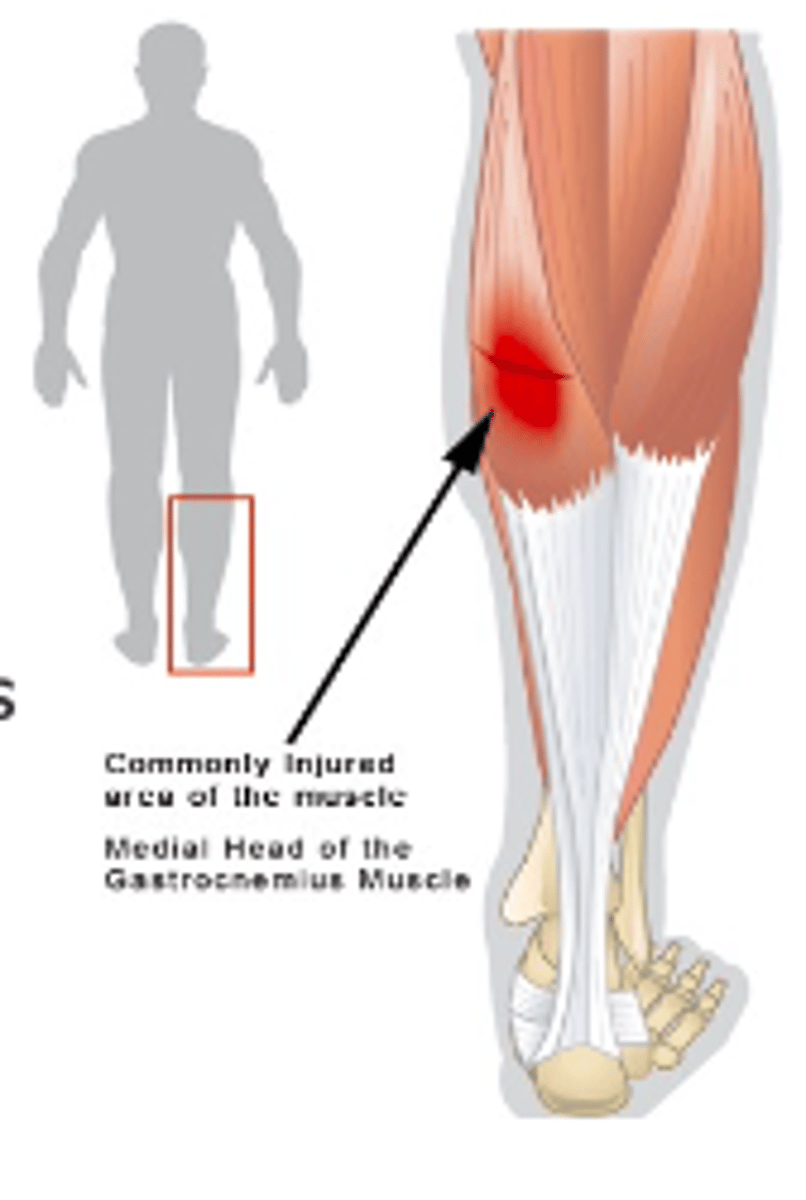
What treatment options are recommended for a gastrocnemius tear?
NSAIDs
RICE
Calf sleeve or compression hose
CAM boot/tall pneumatic walker
Gentle PT
**surgery is rare and reserved for very severe cases
What are TWO terms used to describe a BENIGN synovial cyst on the knee?
Baker cyst
Popliteal cyst
Can a popliteal cyst produce pain?
Yes - pain can be mistaken for DVT
- if it ruptures, it can result in severe calf pain (m/c in elderly)
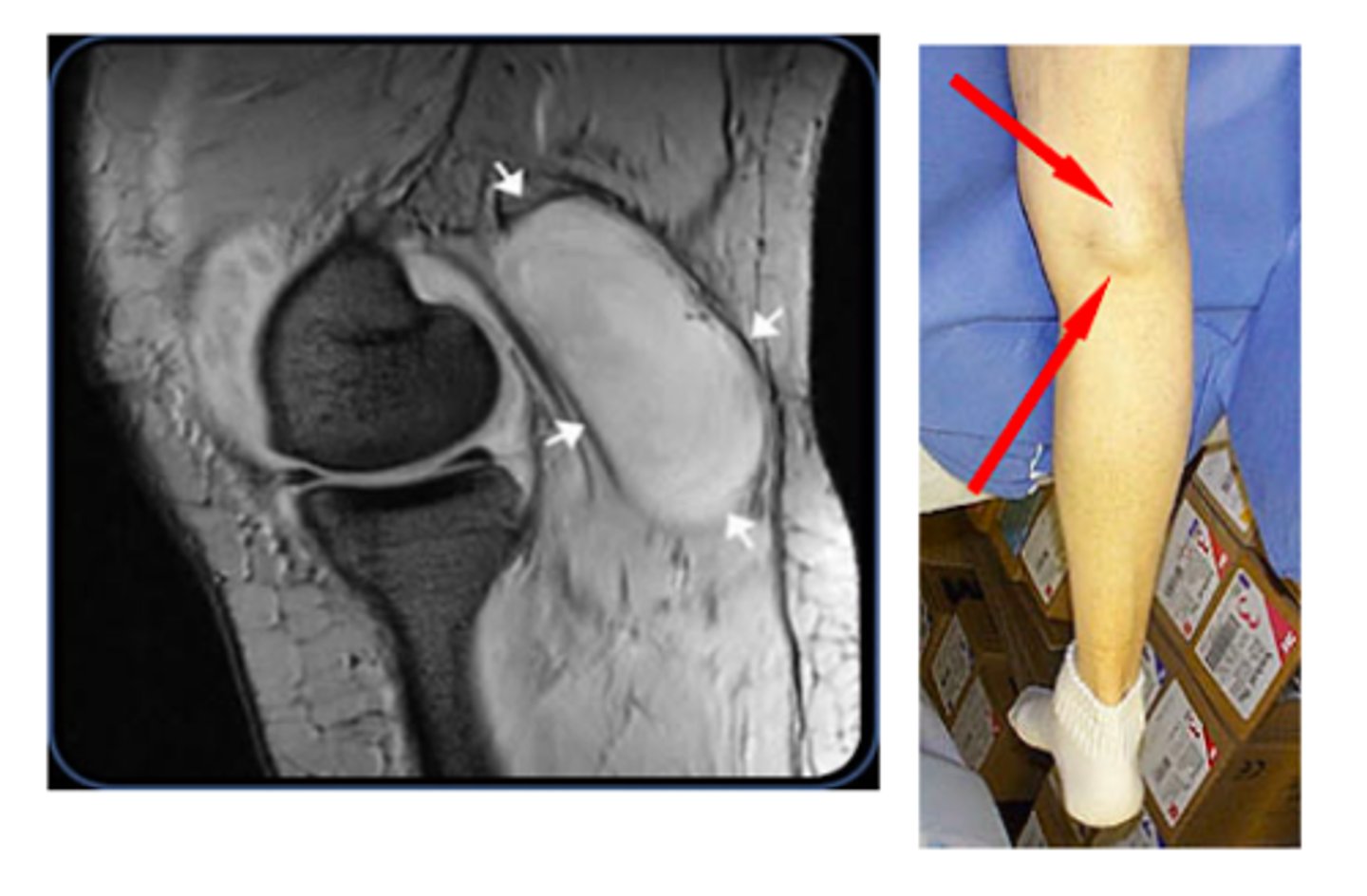
Is aspiration of a popliteal cyst recommended?
NO - only provides transient relief (not worth it)
What is a contusion?
an injury to bone or soft tissue due to DIRECT blunt trauma
- presents as a PAINFUL "bruise" due to rupture of capillaries
T/F. Disability from a contusion is MINOR, but it can be very painful.
TRUE - if there is excessive swelling, it could lead to compartment syndrome
What is the m/c site for a contusion?
thigh
What can occur as a complication of contusions?
myositis ossificans traumatica
- leads to formation of bone in soft tissue/muscle
What is recommended in the treatment of contusions?
Minor analgesics
RICE
PT
Surgical excision - if ossification is present
What is medial tibia stress syndrome? How will it present?
shin splints - inflammation of the tibial periosteum due to repetitive muscle contractions
- will present with gradual onset of pain in the ANTEROMEDIAL aspect of the distal leg
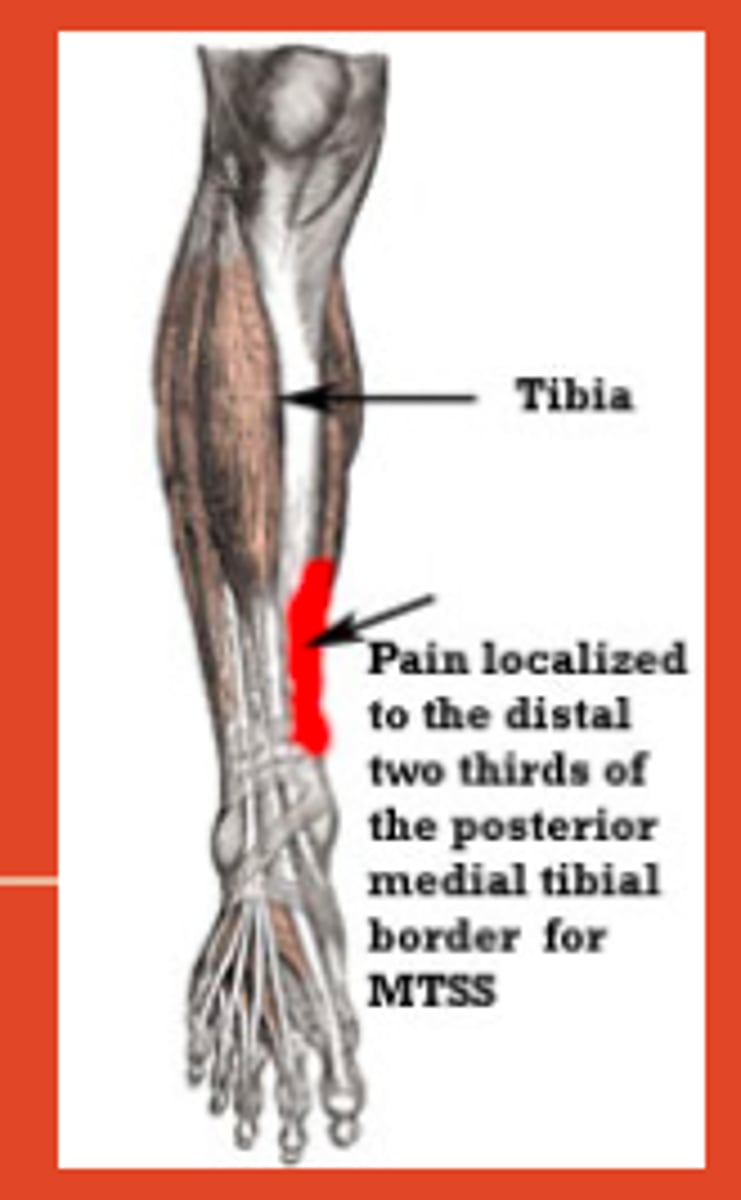
Shin splints is associated with what?
running on a hard + uneven surface and FLAT feet (planus)
Treatment for shin splints is _______.
conservative
- rest/ice/massage/NSAIDs/PT
What type of fracture results from a hairline or microscopic break in the bone?
stress fracture
Which type of LE stress fracture has the worst prognosis?
anterior tibial stress fracture
What diagnostic test can CONFIRM presence of a stress fracture?
MRI (exception to soft tissue rule)
*XR might not show injury for up to 3 weeks
When should surgery for a stress fracture be considered?
no response to conservative treatment (rest, splints, cast, etc)
What are 70% of amputations as a result of (3)?
DM
Severe infection
PVD
What is the BEST type of amputation to have if needed?
BKA - below the knee amputation (transtibial)
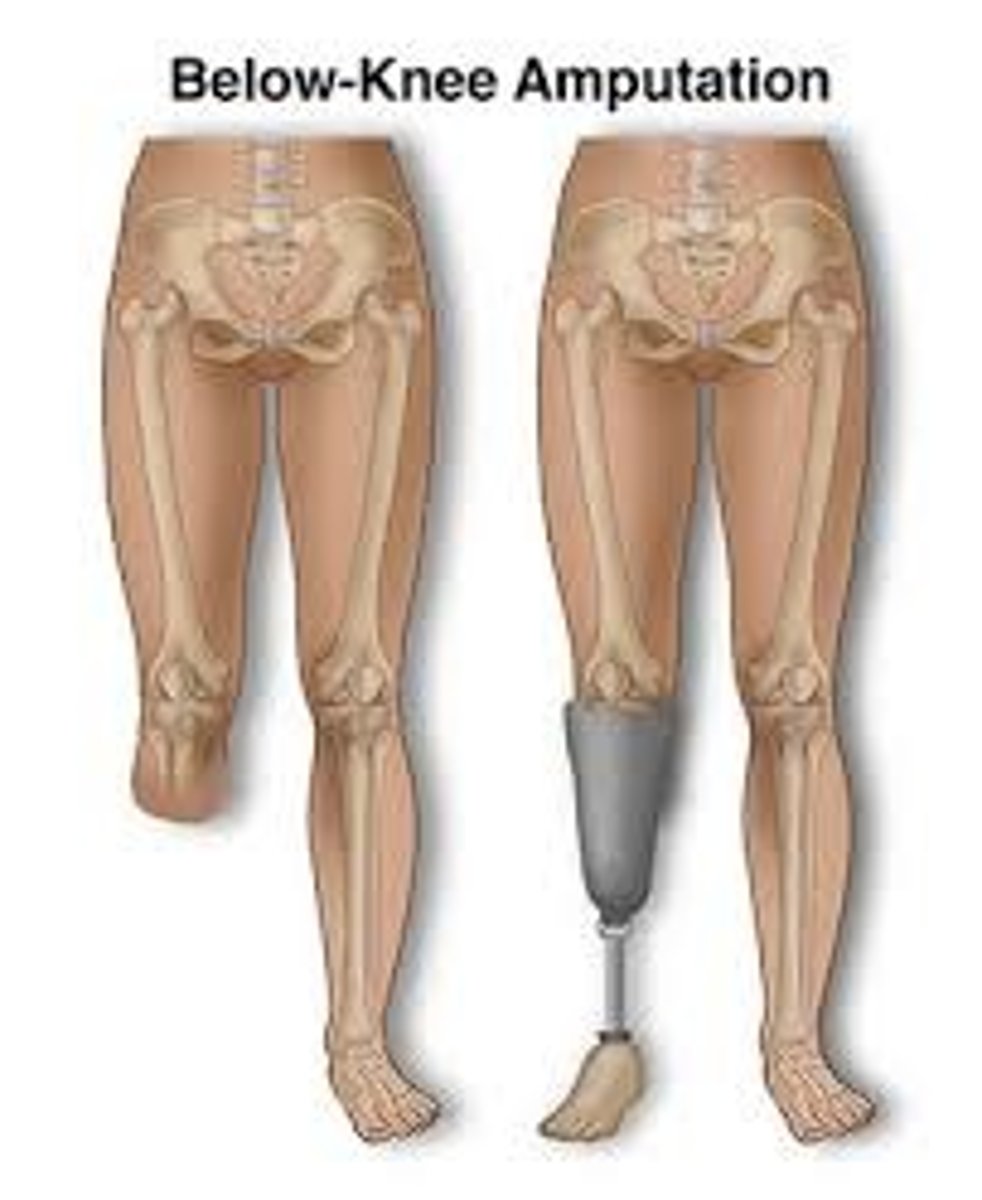
What complication occurs in 55-85% of amputees? How can it be treated?
phantom limb sensation on the missing limb
- treatment includes: nerve medications, TENS unit and pain management
What is Virchow's triad?
SHE
- venous Stasis
- Hyper-coagulability
- Endothelial injury
*presence of triad increases risk for DVT
DVT can most commonly cause what pulmonary condition?
pulmonary embolism
- will present with dyspnea, chest pain and hemoptysis
What is a hallmark symptom of a DVT?
unilateral swelling of the calf or thigh
*can occur +/- pain
What is the GOLD STANDARD to confirm a DVT?
venography
T/F. A duplex U/S can be useful for diagnosing proximal clot formation.
TRUE
What is the GOLD STANDARD to confirm a PE?
pulmonary angiography
A patient with a score of >2 on the Wells probability score is at an increased for what?
a DVT
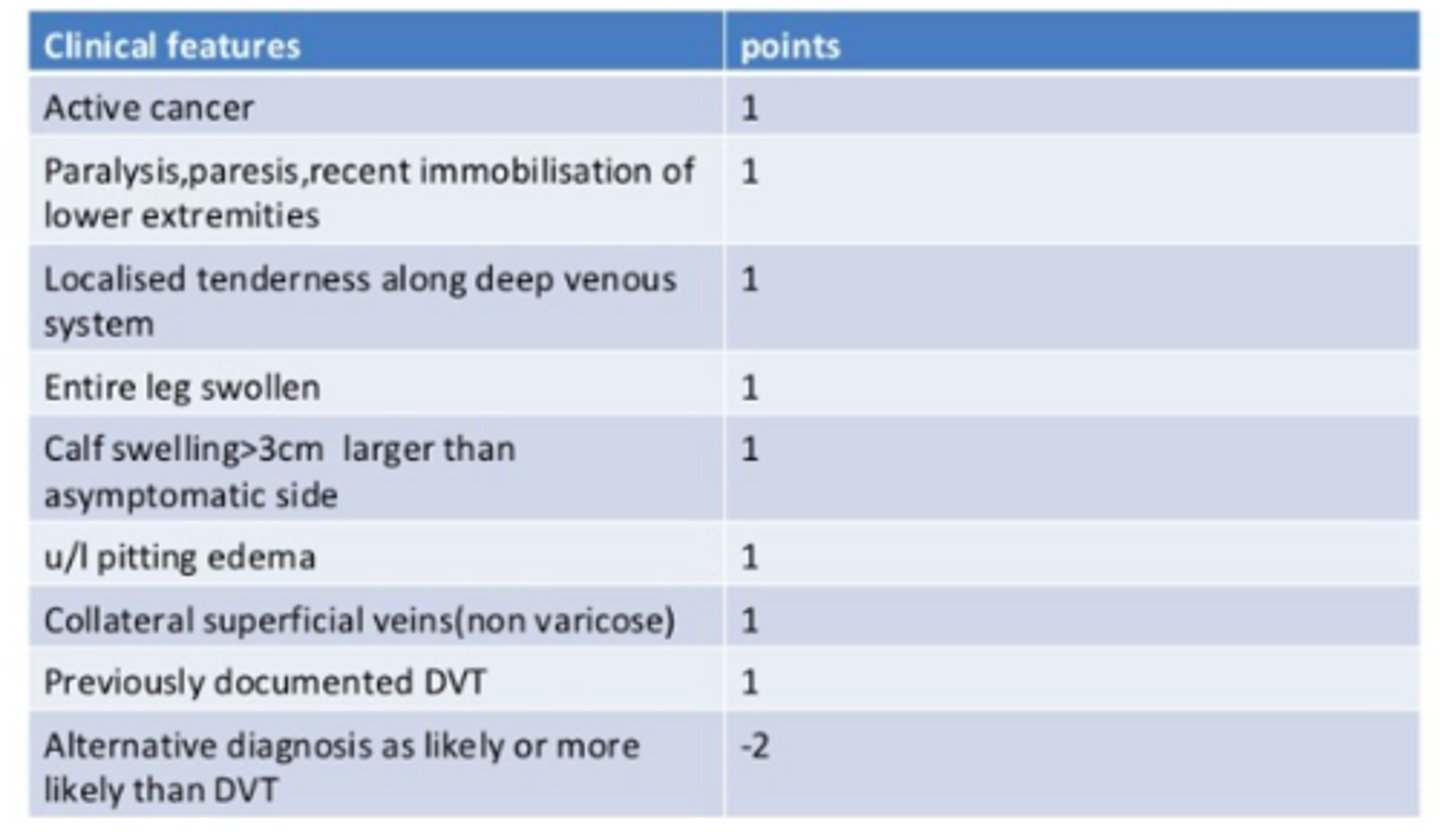
T/F. A patient with risk factors for a DVT/PE should receive prophylactic treatment.
TRUE
- can prescribed enoxaparin, warfarin, xarelto
_________ is discomfort in the legs with either a neurogenic or vascular cause.
claudication
Neurogenic claudication is associated with what? How will it present?
spinal stenosis
Will present with pain that begins in the buttocks and radiates to the legs while walking (proximal to distal)
- does NOT immediately stop with rest from walking
Vascular claudication is associated with what? How will it present?
peripheral vascular disease which causes compromise blood flow with walking
Will present with pain w/ activity that is relieved with rest
- progresses from distal to proximal
For vascular claudication, what PE findings can also present with symptoms of pain? (3)
diminished/absent pulses
Pallor
ABI <0.9