[BOTAONE-LE2] photosynthesis
1/54
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
an anabolic, endergonic, carbon dioxide (CO2) requiring process that uses light energy (photons) and water (H2O) to produce organic macromolecules (glucose).
How water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide are used to form oxygen and glucose.
Is a redox process → Water is oxidized, carbon dioxide is reduced
6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy > C6H12O6 + 6O2
Complete equation for photosynthesis
In all photoautotrophic organisms.
Where does photosynthesis take place?
Heterotrophic
Humans, animals, fungi, most protozoa
Ingests food for energy
Requires complex organic compounds of nitrogen and carbon (such as that obtained from plant or animal matter) for metabolic synthesis
Autotrophic
Plants, lichens, and algae
Produces its own food
A living thing that can make its own food from simple chemical substances such as carbon dioxide
Anabolic
build
Small molecules are assembled into large ones and energy is needed. Build complex molecules from simple ones.
Example: amino acid to proteins and Photosynthesis (builds sugar from smaller molecules)
Catabolic
break
Large molecules into simpler molecules, release energy.
Example; Breaking down of glucose molecules and Cellular respiration (breaking down of glucose)
Endergonic Reaction (ENDO - "In")
Absorbs energy
Non-spontaneous reaction
Absorbs energy, meaning it requires energy
Examples: Photosynthesis and when energy is absorbed in the ATP-ADP cycle
Exergonic Reaction (EXO - "Out")
Releases energy
• Spontaneous reaction
Can happen even with little or no energy
Example: Cellular respiration and when energy is released in the ATP-ADP cycle
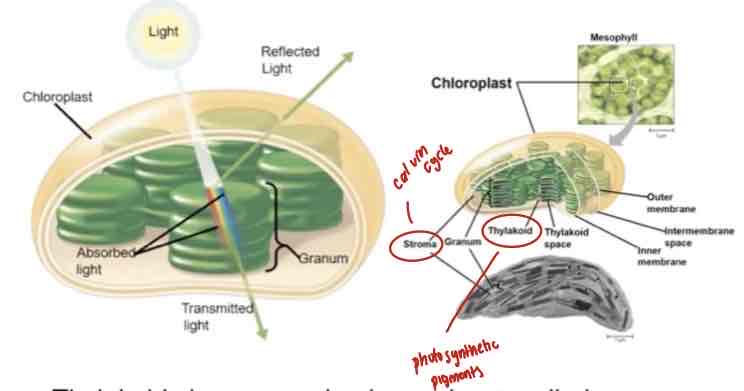
the leaves, specifically in mesophyll (chloroplasts)
Where are the major site of photosynthesis in true leaves
Light dependent reactions
Light independent/ calvin cycle/ dark reactions
The two processes of photosynthesis
The light dependent reactions
Conversion of light (solar) energy to chemical energy (ATP and NADPH)
photochemical procesS
Need sunlight
Inside the thylakoids.
Oxidizes water into oxygen.
Some energy is used to make ATP.
Reactants:
Water
LightNADP+
ADP+P
Products:
ATPNADPH
LIGHT
Consists of certain particles called photons;
each photon has a fixed quantity of energy.
Is a form of electromagnetic energy, which travels in waves
Wavelength
What is the distance between crest waves that determines the electromagnetic energy
Electromagnetic spectrum
entire range of electromagnetic energy or radiation
Visible light spectrum
Includes the colors of light we can see (reflected radiation)
Includes the wavelengths that drive photosynthesis.
Photosynthetic pigments absorb the visible spectrum.
Chlorophyll a
(blue-green-color pigment) absorbs red-orange and blue-violet regions
main light capturing or photosynthetic pigment
Found in all autotrophic organisms.
Chlorophyll B
accessory pigment that broadens the spectrum used for photosynthesis.
(yellow-green-colored pigment) absorbs light from the red-blue region
In all true plants
a slight structural difference between the pigment molecules.
What is The difference in the absorption spectrum between chlorophyll a and b
Carotenoids
accessory pigments that absorb excessive light that would damage chlorophyll.
(orange-colored pigment) absorbs blue-green and violet region
THE ACTION SPECTRUM FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Description: A graph plotting a pigment's light absorption versus wavelength
Profiles the relative effectiveness of different wavelengths of radiation in driving a process.
• Absorption spectrum of Chlorophyll A - suggests that violet-blue and red light work best for photosynthesis.
Thylakoids
in cell membrane in cyanobacteria
In chloroplasts in algae
WHERE ARE THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS FOUND? (1. Generally, 2. In Cyanobacteria, and 3.Algae)
Photosystems
Thylakoids have organized complexes Called..
PS1, PS2, ATP synthase
What is a photosystem composed of
Photosystem I (PS I) : P700
Photosystem II (PS II): 680
The thylakoid membrane is populated by two types of photosystems which are
Their large nitrogen requirement for Rubisco and other photosynthetic enzymes (need rubisco)
Rubisco accounts for about 25% of the nitrogen in photosynthetic cells
Their dependence on products of the light-harvesting reactions (ATP and NADPH), which in turn depend on irradance, i.e. the light received by the photosynthetic cell (no light no reaction)
majority of g3p will regenrate RuBP to turn half a glucose thats why its so inefficient
What are the 3 most notable features of carbon-fixation reactions
Calvin Cycle or C3 pathway
is the main biosynthetic pathway of carbon fixation.
Rubisco
both a carboxylase and an oxygenase.
As a carboxylase, it initiates carbon fixation reactions.
As oxygenase, it catalyzes a reaction between Rubisco and oxygen under conditions of CO2
photorespiration
Initiates breakdown of sugars to CO2
It occurs in the light (photo);consumes 02 while producing CO2 (respiration); and uses up ATP but produces no sugar molecules.
Photorespiration reduces photosynthetic efficiency of the Calvin cycle by as much as 50%.
Carbon fixation
occurs in the dark reaction or light-independent reaction of the photosynthesis process.
The Calvin Cycle or dark reactions
takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. Unlike in the Krebs cycle wherein the products are used for ATP synthesis, the product of the this cycle is used for the production of glucose.
carbon fixation, carbon activation & reduction, and RuBP regeneration
The 3 parts of calvin cycle
C4 plants
Live in hot, moist environments
15% of plants
Grasses, corn, sugarcane
Divides photosynthetic spatially
Light rn - mesophyll cells
Calvin cycle - bundle sheath cells
CAM plants
cactus
5% of plants
Live in hot, dry environments
Cactus, ice plants
Stomates closed during the day and open during the night.
Light rxn- occurs during the day.
Calvin cycle - occurs when CO2 is present.
Hatch and Slack Pathway
To fix carbon dioxide, this pathway is the alternate to the C3 cycle.
C3 plants
C3 vs C4
Uses calvin cycle for the dark reaction of photosynthesis
C3 Plants
C3 vs C4
These plants are cool-season plants commonly found in cool and wet areas
C3 plants
80% of total green plants are..
Its product is also a 3 carbon compound (phosphoglyceric acid)
C3
C3 vs C4
these plants are abundant in temperate conditions
C4
C3 vs C4
These plants use hatch-slack pathway for the dark reaction in photosynthesis
warm-season plants, commonly found in dry areas
C4
C3 vs C4
the product is a 4 carbon compound (oxaloacetic acid)
About 15% of plants are…
C4
C3 vs C4
These plants are abundant in tropical conditions
C3 plants
C3 vs C4
In this, the bundle sheath cells do not contain chloroplasts.
___plants possess only one CO2 acceptor. __ plants do not consist of secondary CO2 acceptor.
It performs photosynthesis only when stomata are open.
C4 plants
In this, the bundle sheath cells contain chloroplasts.
__ plants possess two CO2 acceptors. ___ plants consist of secondary CO2 acceptor.
It performs photosynthesis even when stomata are close.
Calvin cycle > glucose
Glycolysis > atp,nad, pyruvate
Acetyl Coa> fadh, acetyl coa
Citric acid cycle > nadh, fadh, atp
Electron transport chain or Oxidative phosphorylation > conversion of nadh and fadh to ATP
Overall process of atp production
C3 plants
The optimum temperature for photosynthesis is very low.
less efficient in photosynthesis.
The photorespiration rate is very high.
CO2 fixation is slow
In this, the dark reaction takes place only in the mesophyll cells.
C4 plants
The optimum temperature for photosynthesis is high.
C4 plants are more efficient in photosynthesis.
Photorespiration is absent.
CO2 fixation It is comparatively faster .
In this, mesophyll cells will only perform the initial steps of the cycle. main steps are carried out in bundle sheath cells.
Rice, Wheat, Soybean, Oats
Example of C3 plants
Corn, Sugarcane, Sorghum
Examples of c4 plants
Light reactions (summary)
Are carried out by molecules in the thylakoid membranes
Convert light energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH
Split H20 and release O, to the atmosphere
Calvin cycle reactions (summary)
Take place in the stroma
Use ATP and NADPH to convert
CO, to the sugar G3PReturn ADP, inorganic phosphate, and NADP+ to the light reactions
“photo”
Light reaction (thylakoid)
“synthesis”
Calvin cycle (stroma)
Light dependent reaction process summary
Photo-excitation (PS2)
Pushes to ETC (PS2)
Photolysis (split of H2O) (in thylakoids)
Chemiosmosis (H+ goes down ATP synthase)
ADP > ATP reduction
NADP+ > NADPH reduction