UCF Principles of Plant Science Exam 1
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
Two systems of plant organs
Shoot system and Root system
What does the shoot system consist of?
vegetative organs like stems and leaves/ reproductive organs like flowers and fruits
What does the root system consist of?
Only roots
What are the characteristics of determinate growth?
-Growth is genetically determined
-Usually cannot regrow or heal
-Maximum size is rarely reached in the wild
-Flowers, fruits, and leaves
What are the characteristics of indeterminate growth?
-Growth only limited by environmental factors
-Usually can regrow and heal
-Can grow all throughout life
-Stems and roots
The cell theory states that
1. All plants and animals are made of cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. All cells come from previous cells by reproduction
What are the four components shared by all cells?
- DNA
- Plasma Membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Ribosomes
What is the plasma membrane?
a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
Serves as a barrier between the cell and its environment. It also conducts the passage of organic molecules, water, oxygen, ions, and waste (CO2 and ammonia)
What is the cytoplasm?
The region between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. It consists of organelles suspended in cytosol and the cytoskeleton
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Provides structure to the cell
What is the function of DNA/ the nucleus?
- Directly synthesizes the production of ribosomes and proteins
- Stores chromatin (DNA + protein) and the nucleolus (where ribosomes are made)
When is DNA visible as chromosomes?
During cellular replication
When is DNA visible as chromatin?
During cellular growth and maintenance, when proteins attach to chromosomes
What are ribosomes?
- Structures responsible for protein synthesis
- They are NOT organelles
- They can be free or embedded in the endoplasmic reticulum
What are the unique characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
- Endomembrane system
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
A series of interconnected sacs and tubules that modify proteins and synthesize lipids
What is the golgi apparatus?
Flattened membranes that receive proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them and transports them
What is the mitochondria?
- Site of cellular respiration
- contains its own DNA and ribosomes
What are the unique structures of plant cells?
- Cell wall
- Central vacuole
- Plastids such as chloroplast
What is the central vacuole?
- Stores and regulates water through osmosis
- Contains water, ions, nutrients, and waste
- Is surrounded by the tonoplast
What is a chloroplast?
- Site of photosynthesis
- Contains chlorophyll and other pigments
- Contains its own DNA and ribosomes
- Pigments are stored in thylakoids which stack to make grana
What are the other plastids?
- Chromoplast (yellow/ orange)
- Amyloplast (stores starch)
What is the middle lamella?
Thin pectin layer that binds adjacent cell walls
What is the primary cell wall?
- Occurs on all plant cells
- Made of cellulose microfibrils
- Thin and flexible
- Some plants contain only this wall
What is the secondary cell wall?
- Made up of layers deposited inner to primary cell wall
- Made of lignin and cellulose for sturdiness
- Occurs as cells reach maturity
- Its growth pushes cell membrane further in, possibly leading to cell death
What determines the direction of cell growth?
Orientation of cellulose microfibrils
What are plasmodesmata?
Pores which allow communication between cells
All plant tissue originate from what?
Meristematic tissue
What does it mean for plant tissue to be totipotent?
The tissue can regenerate the entire plant
What are meristems?
Regions of continuous cell division and growth
What are the three types of meristems?
Apical, lateral, and intercalary (grasses only)
What are apical meristems?
- Regions of cell division at the end of stems (shoot apical meristems) and roots (root apical meristem)
- Produce three types of primary meristematic tissues
What are the three types of primary meristematic tissue produced by the apical meristem?
Protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium
What is the protoderm?
Gives rise to epidermis
Function of ground meristem?
Gives rise to ground tissue (photosynthetic, storage, support)
Function of the procambium?
gives rise to vascular tissue (transport)
What are lateral meristems?
- Also called secondary meristems
- Responsible for secondary growth (girth)
- Located in two regions
What are the two regions of lateral meristems?
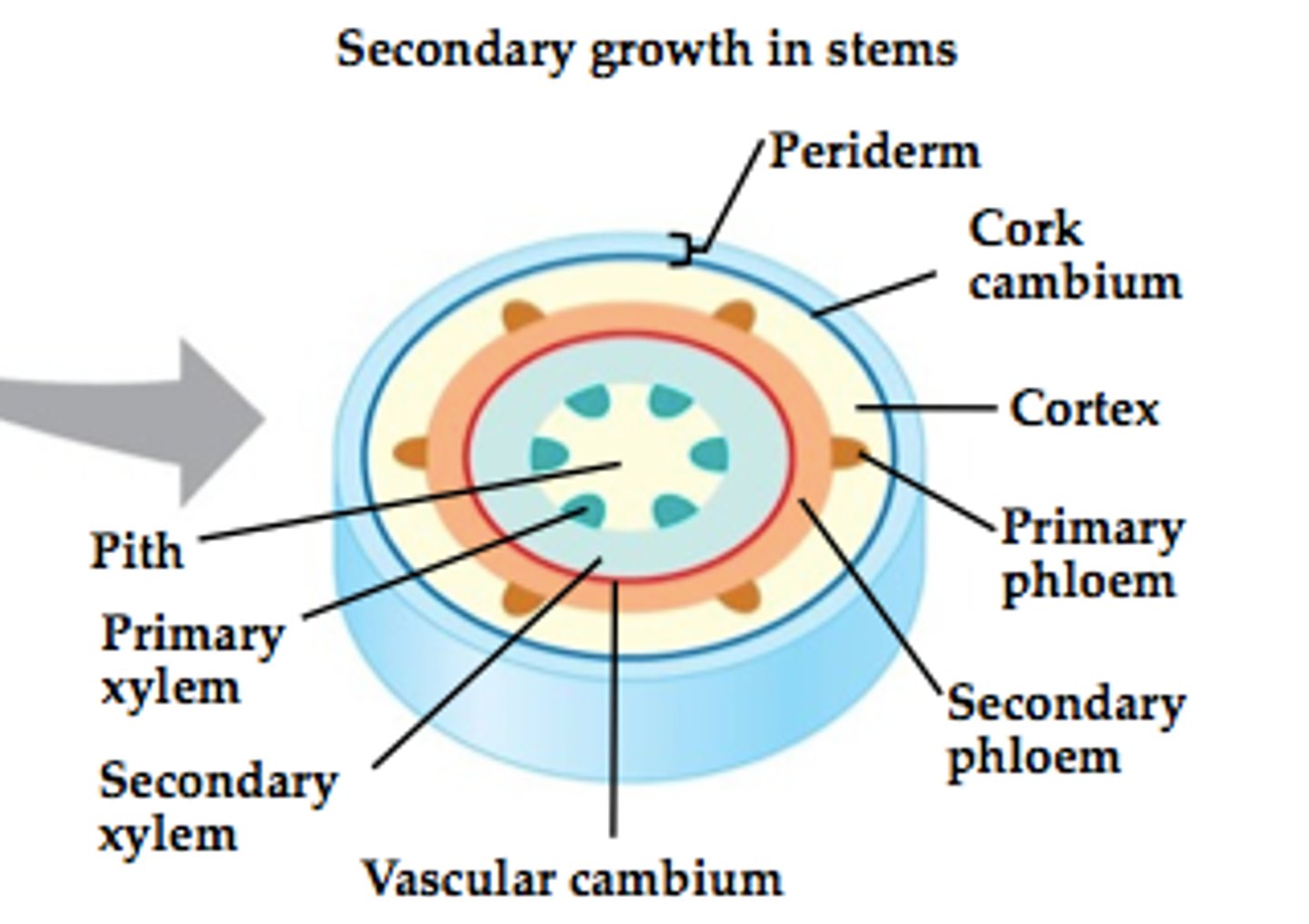
Vascular cambium and cork cambium
What is the vascular cambium and what does it do?
- Arises from the procambium
- Gives rise to vascular tissue
What is the cork cambium and what does it do?
- Arises from pericycle and the cortex
- Produces periderm (secondary dermal tissue)
What are the typical components of a seed?
- Seed coat
- Embryo (new plant)
- Endosperm or cotyledon (nutrients)
First phase of eudicot embryogenesis?
The seed contains the endosperm (triploid) and the zygote (diploid)
Second phase of eudicot embryogenesis?
The zygote divides to form the proembryo which is attached tp the micropyle by the suspensor. The endosperm begins to divide
Third phase of eudicot embryogenesis
The embryo proper is in globular stage, a spherical mass of cells
Fourth phase of eudicot embryogenesis
Embryo proper is in the heart stage. The heart stage gives rise to the cotyledons
Fifth phase of eudicot embryogenesis
Embryo proper is in torpedo stage- the shoot apical meristem is between the cotyledon and the root apical meristem is anchored to the suspensor
Sixth phase of eudicot embryogenesis
The mature embryo includes the radicle, the hypocotyl, the epicotyl, and the ovule has developed into the seed coat
What stage is missing in monocot embryogenesis?
The heart stage
What are the two parts of the seed coat?
Testa (outside) and tegmen (inside)
Hilum
Where the seed attaches to the endocarp (inner layer of fruit)
Microphyle
Where pollen tubes entered (seed coat)
Embryo axis from top to bottom
- The plume
- The radicle
What is the plume?
Young shoot containing the shoot apical meristem and the leaf primordia (developing leaves)
What is the radicle?
embryonic root
What is the hypocotyl?
the region between the cotyledon attachment point and the radicle
What is the epicotyl?
the region between the cotyledon attachment point and the shoot tip
Unique characteristics of monocot seeds?
- Test and tegmen are fused
- Fruits have only one seed and the pericarp
- Root tip is protected by the coleorhiza (sheath like structure)
- Plume is protected by the coleoptile
Scutellum
the name of the single cotyledon. Has a vascular connections with the rest of the embryo
Aleurone
outer layer of endosperm which secretes enzymes during germination
Methods of seed dispersal
wind, animal, water, self-dispersal
Physical dormancy
type of seed coat barrier that uses impermeability to water and oxygen
Chemical dormancy
type of seed coat barrier that uses compounds to inhibit germination
Physiological dormancy
type of embryonic barrier that requires environmental conditions to complete maturation
Endodormancy
type of embryonic barrier in which internal biochemical processes must be met before germination can begin
Ecodormancy
type of embryonic barrier in which external factors are not optimal for germination
Common germination requirements
- sufficient light
- proper temperature
- oxygen
- water
epigeous germination
hypocotyl elongates, cotyledon extends above ground
Hypogenous Germination
epicotyl elongates and the cotyledon remain underground
Only type of germination that does not form a hook
Hypogeous monocots
What occurs when the coleoptile is exposed to sun light?
It stops growing and is pierced by the plume
Two types of roots
Tap root system
Fibrous root system
Root functions
Anchorage, support, absorption, nutrient storage
Root cap
protects apical meristem
What is behind/ above the apical meristem?
the area of elongation
What is above the area of elongation?
The area of maturation where epidermal cells form extensions called root hairs, improving absorption
From what does the shoot system originate?
The plume of the embryo
Functions of a stem
Support
Conduction- moves water up from roots and photosynthesis products down from leaves
Photosynthesis- in green stems
Food storage- mainly starches
What are stem nodes?
Points of attachment for leaves
Internode region of the stem
Area between nodes that elongates to ensure separation of leaves
Axillary bud
Found between the stem and the leaf
Can give rise to a new shoot with its own apical meristem
Secondary meristem consists of...
the vascular cambium and the cork cambium
The vascular cambium divides into the...
secondary xylem(inside) and the secondary phloem (outside)
The cork cambium produces
Periderm tissue
The protoderm produces...
epidermis
The shoot apical meristem produces...
Procambium
Ground Meristem
Protoderm
The procambium produces the...
Primary xylem
Primary phloem
Fascicular cambium
The ground meristem produces
pith and cortex
When does the periderm replace the epidermis
In shoots at the end of the first year of growth
lenticels
elevated regions with large intercellular space that allows gas exchange in shoots
rhytidome
old layers of periderm that die and are pushed out, producing the texture of bark
Inner bark includes the...
secondary phloem
cortex
phelloderm
outer bark includes the...
cork cambium
periderm
cork
wood consists of the...
original pith
primary xylem
secondary xylem
What is heartwood?
oldest and innermost layer of secondary xylem. It is darker in color
Tylosevessel elements prevent water flow
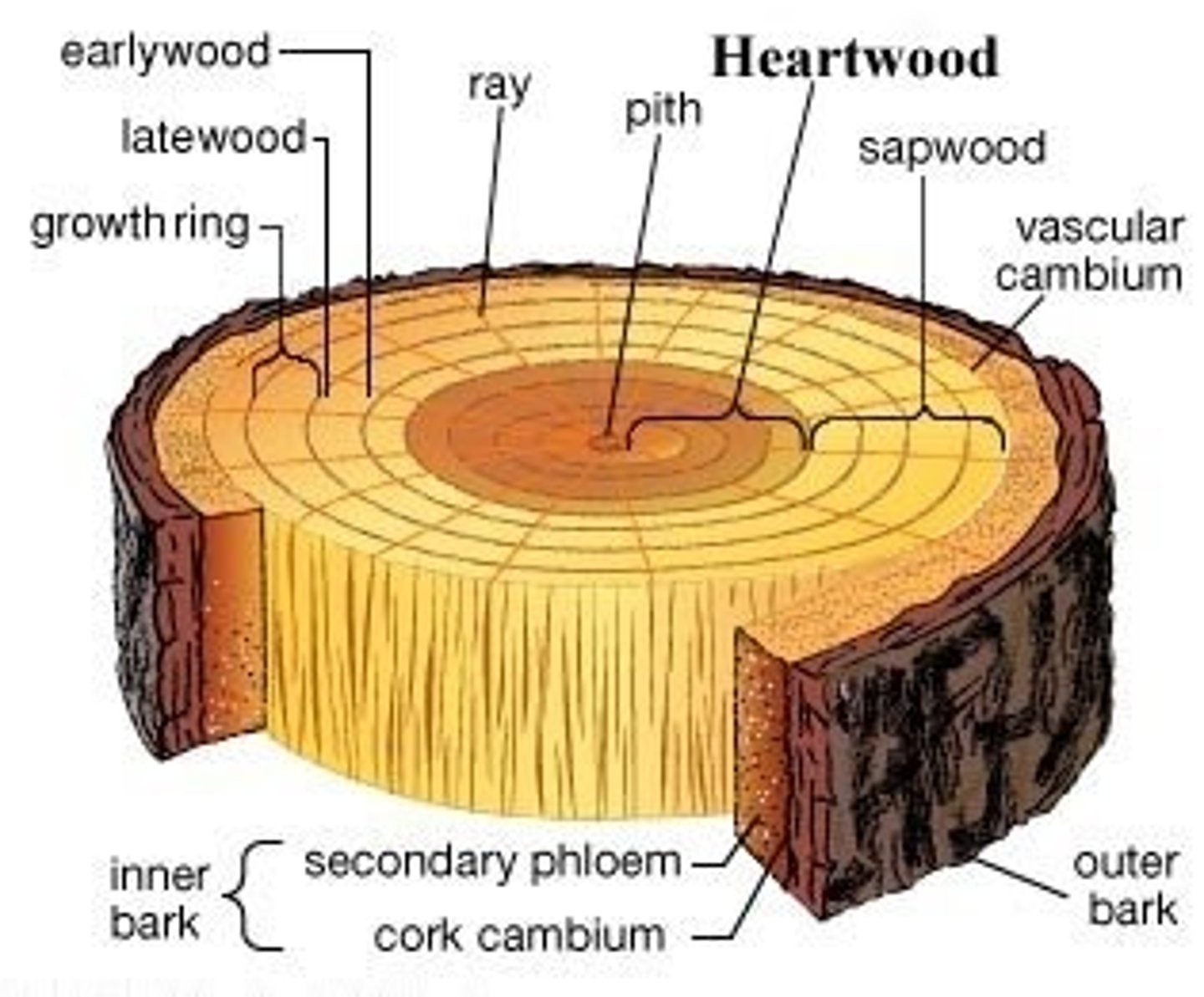
What is sapwood?
Water conducting xylem in the periphery of heartwood and is lighter in color
Lateral (axial) buds types
Monopodial and sympodial
Monopodial type of branching
buds do not degrade and all shoots continue to grow
Sympodial type of branching
terminal buds degrade and lateral buds closest to the apex become the new terminal shoot
Blade (lamina) of leaf
flat, usually widest part