Medical Semiology - PA
ANAMNESIS
don’t write anything that is normal/unrelated
Name
Age
Sex
CHIEF COMPLAINT
Admission date, Emergency/ Programmed.
Main cause of admission, main signs and symptoms.
where, onset, severity, type of pain
FAMILY HISTORY
Father : age, alive/death, any pathology, under treatment/ no treatment
Mother:
Brother/ Sister :
Son/ Daughter:
PERSONAL HISTORY
Allergies , Vaccines (# COVID doses,) , Surgery (if any, date and treatments, if no papers it's “undocumented”), Recent or past (childhood) pathology (age of diagnosis, treatments), bleeding tendencies, blood group
Digestive - ask for UC, ulcers, neoplasms, hepatic diseases (Wilson's, hemochromatosis), anemia, transfusions, tattoos, DM
(if female patient)
First menstruation, Last menstruation, Regular/Irregular bleeding, Pregnancies (if any, numbers and description of any problem related to it) , Abortion, hormonal medications
SOCIAL HISTORY
City, Country side/ Center, Garden/Apartment/House, Animals, Alone/Roommates, Job environment, Lifestyle (exercise, diet), Sexual orientation.
Who does the cleaning, shopping, cooking ?
Digestive - hepatotoxins, hepatitis, diet (fiber, intolerances), smoking (→ pancreatic cancer, peptic ulcers), alcohol (→ gastritis, GERD, peptic ulcers, ASH)
RISK FACTORS/ CHRONIC INTOXICATION
Smoking (how long, packs/day, start and end)/ Alcohol (quantity, type, start and end)/ Coffee
(frequency)/ Drugs (start, end)
Smoking index = years smoking/packs per day
66
20-22 is risk for cardiovasc disease
DRUG HISTORY
Mediations (frequency), Treatments
#-#-#, F=tablets
Digestive - amiodarine → hep, contraceptives → cholestasis, paracetamol → acute liver necrosis
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS / EPICRISIS
Patient, age, sex, presents to hospital emergency/on appointment.
Current + past pathologies
Onset, Setting of development, Manifestations, Treatment.
Each symptoms: Location, Type, Quantity/Severity, Timing.
What exacerbates it ? What relieves it ?
Intoxications that correlate
Meds if related
Ex :The patie wasnt Andrei Ioan has been admitted at the clinic on appointment the 26/04/21 afternoon presenting with nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain and fatigue. The onset was on the 23/04/21 around lunch time when he started to feel a burning sensation of the stomach and chest discomfort. After a while he started to feel nauseated so he decides to lie on the bed where the symptoms relieve after 30 minutes. In the evening same situation appears after dinner and after he vomited later on he decides to take an appointment with the GP. Manifestation seems to be linked to food ingestion. Epigastric pain, nausea and chest discomfort after meals so 2/3 times x day, very sharp and burning pain which the patient describes as 8 on a scale up to 10. Bed rest help the patient relieve the symptoms.
GENERAL PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
write everything, if normal put “according to age and gender”
General state : well, relatively well, influenced, severe, critical
Constitution, nutritional state : ( Hypersthenic/ Normosthenic/ Hyposthenic/)
Height
Weight
BMI = weight/(height)^2
hyposthenic <20
normosthenic 20-24.9
overweight 25-30
obesity I 30-34.9
obesity II 35-39.9
morbid/III >40
Consciousness state : conscious, alert, cooperative
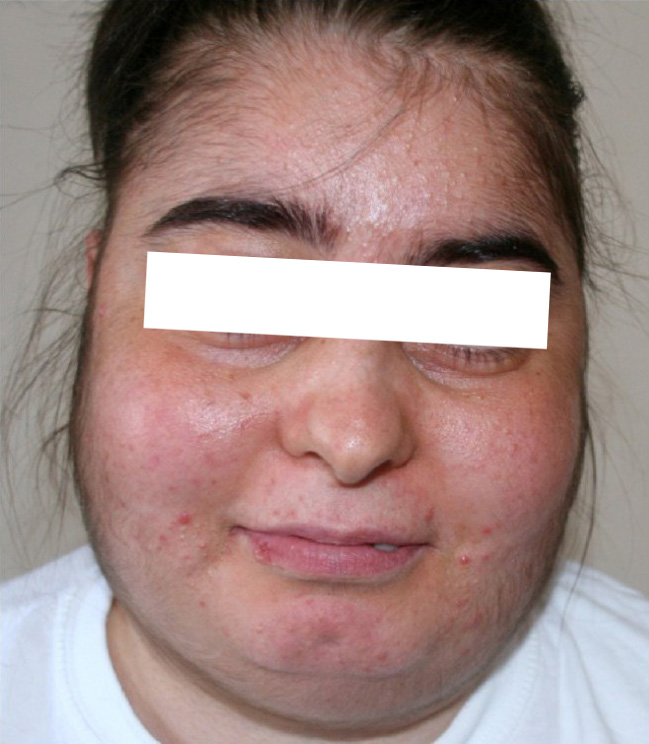
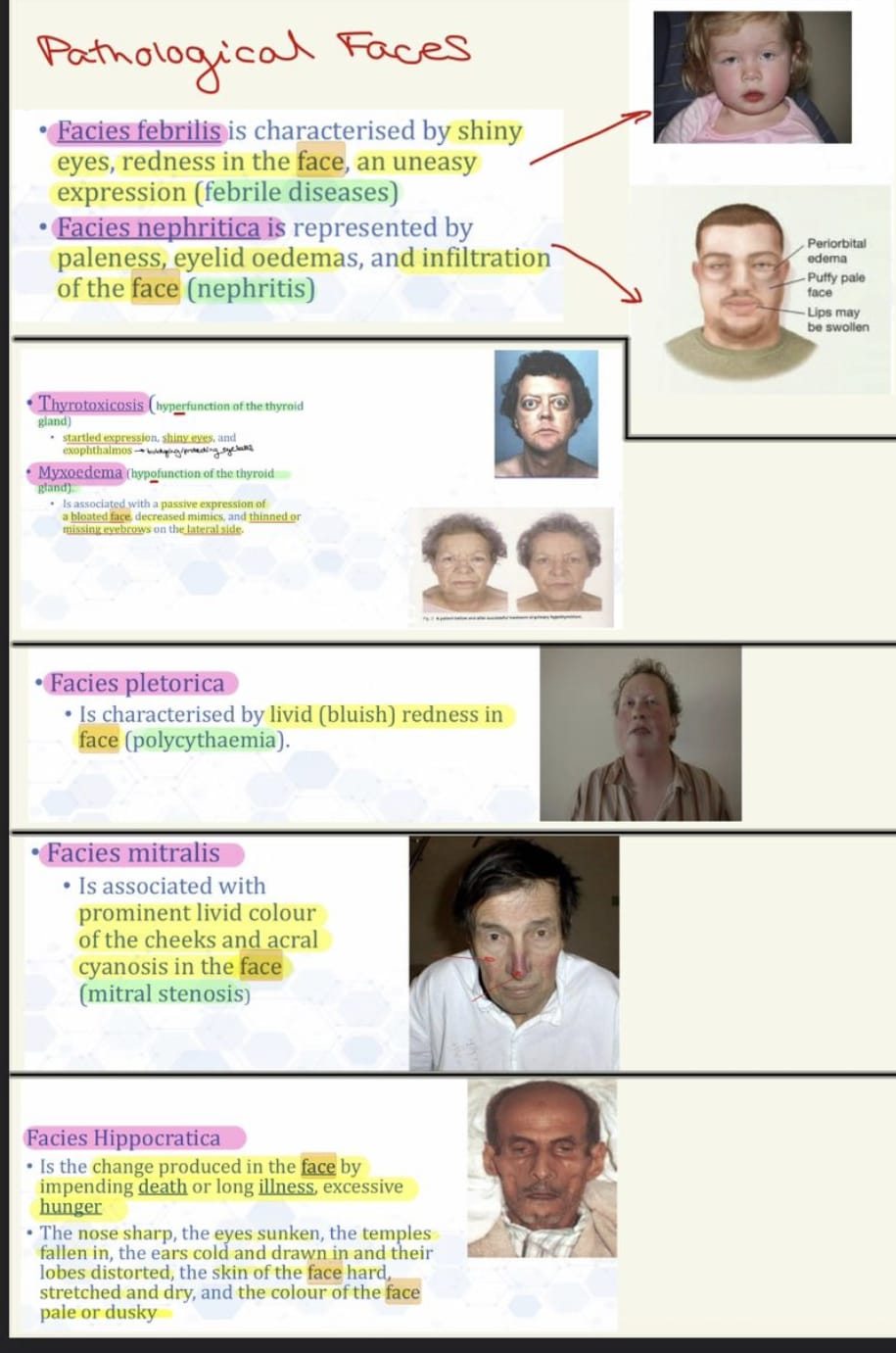
Faces : Normal/Hippocratic/Nephritic/ Febrilis/Mitralis/Plethoric (HTN or polycythemia)/Sclerodermic (mummy face, tiny ulcerations, dry, parrot peak nose, wolf teeth)/Basedow or Graves (bulging eyes, retroocular m hypertrophy, exophthalmos)
Endocrine face : Acromegaly (massive supraorbital arcs, big nose + tongue)/ Cushing (moon face, erythematous) / Thyrotoxic/ Myxedema (dry skin)
Symmetry / Paresis
Lymph nodes: Palpable/Not palpable
if palpable → inflammatory (rubbery, painful, not adherent) or tumoral (not painful, tough, attached)
Preauricular, posterior auricular, occipital, tonsillar, submandibular, submental, superficial cervical, posterior cervical, deep cervical chain, supraclavicular
Skin : “normally coloured skin", Color, Hydration (“well hydrated"), “normal skin turgor”, Temperature, Lesions, Mobility, Turgor, Scars
Translucent + thin → chronic hypoperfusion
Mucosa : Color, Patches/Ulcer, Nodules
Eyes - conjunctiva pale → anemia, sclera yellow → icterus, watery/dry
Oral
Connective - Adipose tissue : pear-shaped, apple-shaped, pyknic (short + fat)
Musculo-Skeletal : Hyper/Normo/Hypo Tonic, Hyper/Normo/Hypo Kinetic, Hypo/Normo/Hypertrophic, Gait
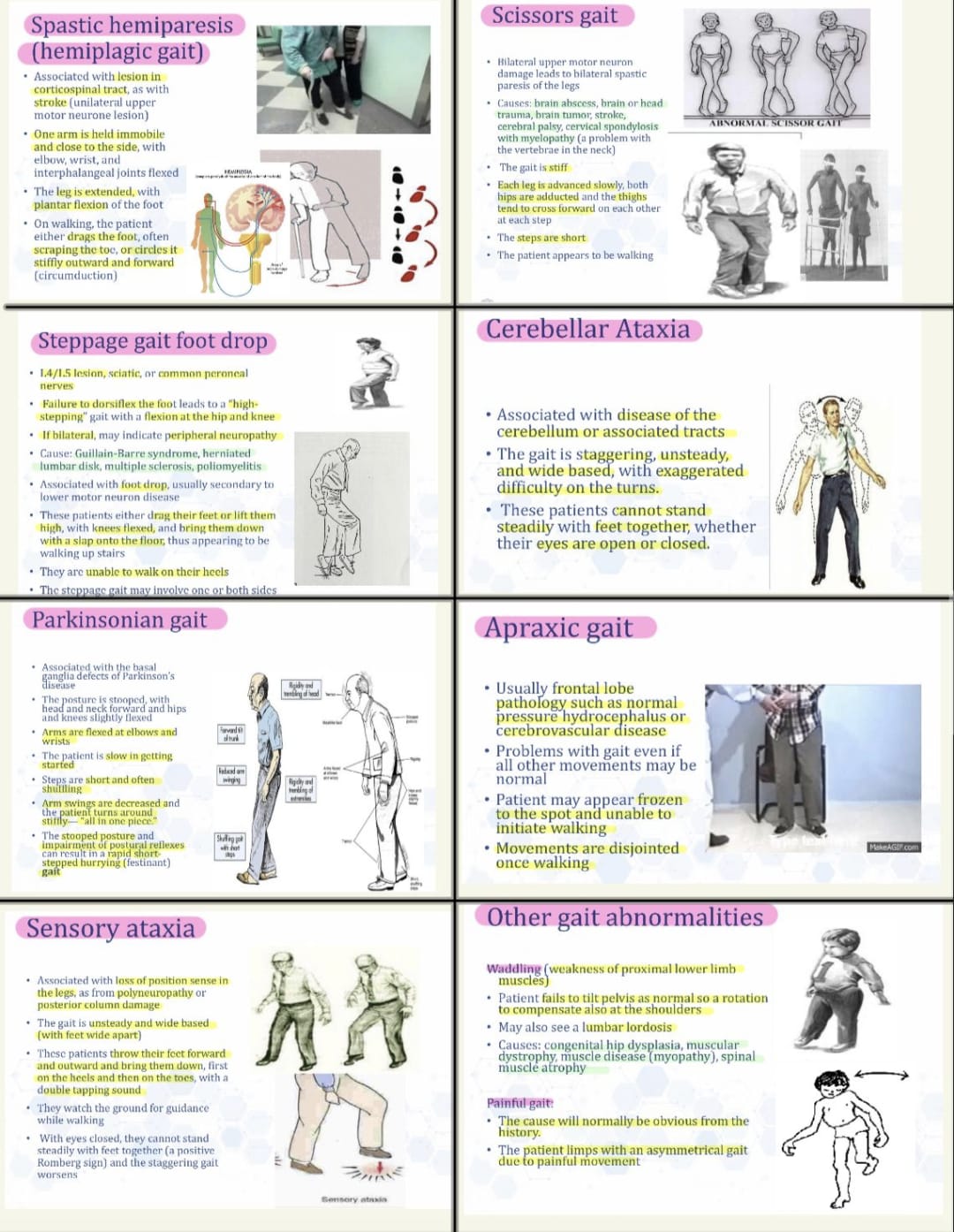
Osteo-Articular : “full integrity of bone system”, “no pain in movement”
“good range of motion in all joints. no evidence of swelling or deformity”
spine percussion → “no pain at spine tap”
Appendages :
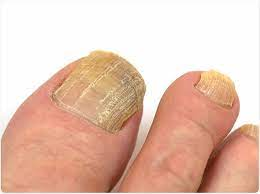
Nails
Hair
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Inspection : Respiratory rate → >20 = tachypnea
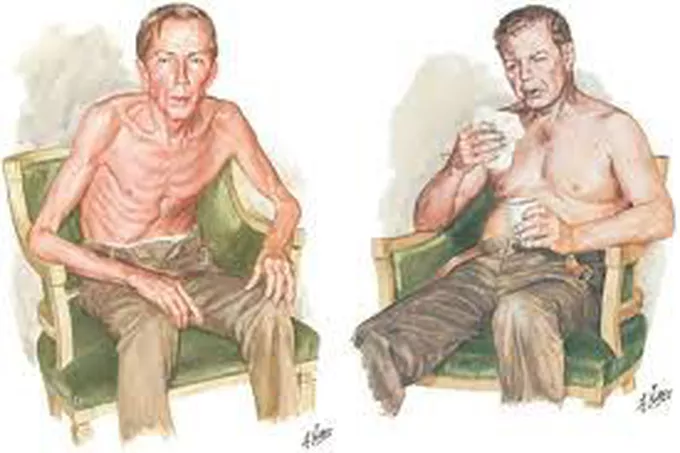
COPD
Blue boater → cyanotic lips, clubbing, congestive conjunctiva, hypercapnia, hypoxia
Pink puffer → emphysematous thorax, deflated diaphragm, pul HTN, skinny

Cyanosis → tachypneic, blue lips, voluminous breathing, orthopneic position, expressed accessory m, lower limb edema
Lateral decubitus → laying on one side
Symmetrical/Asymmetrical thorax
barrel thorax → ant post diameter is wider, less diaphragmatic mobility, increased intercostal spaces → marker of COPD
funnel chest (pectus excavatum) → depression in the lower portion of the sternum
pigeon chest (pectus carinatum) → sternum is displaced anteriorly, increasing the anteroposterior diameter → hypoventilation
kyphoscoliosis
Movement - “Well maintained diaphragmatic mobility “ (no if using accessory m)
posterior thorax → thumbs @ 10th rib
anterior thorax → thumbs @ costal margins
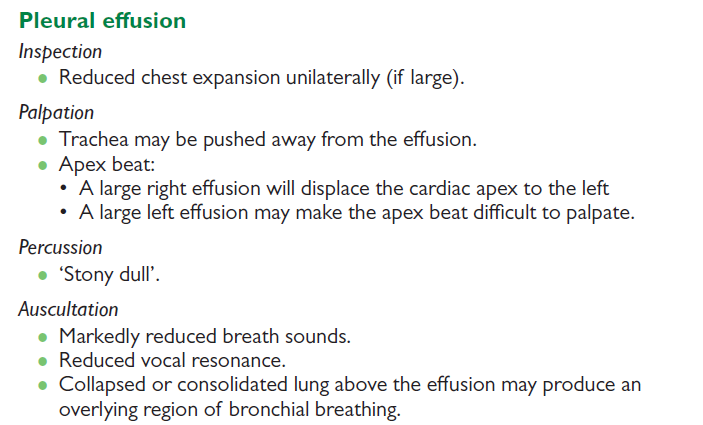
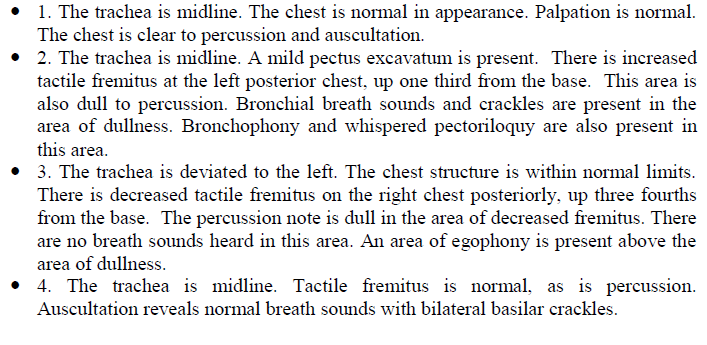
Palpation : Tactile fremitus Hyper/Normo/Hypo resonant (normal, increased, decreased, or absent)
Tactile fremitus - physiologically decereases
Absent → pleural effusion
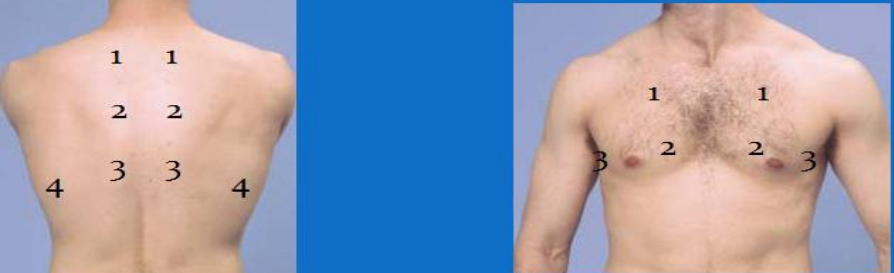
Percussion: Hyper/Normo/Hypo resonant with Mobile/Stuck diaphragm.
(locate pathological resonance), ant thorax not necessary
start at supraclavicular
seated patient, hugging arms
not to be done in emphysema
to count intercostals → 7th intercostal space is lower edge of scapula
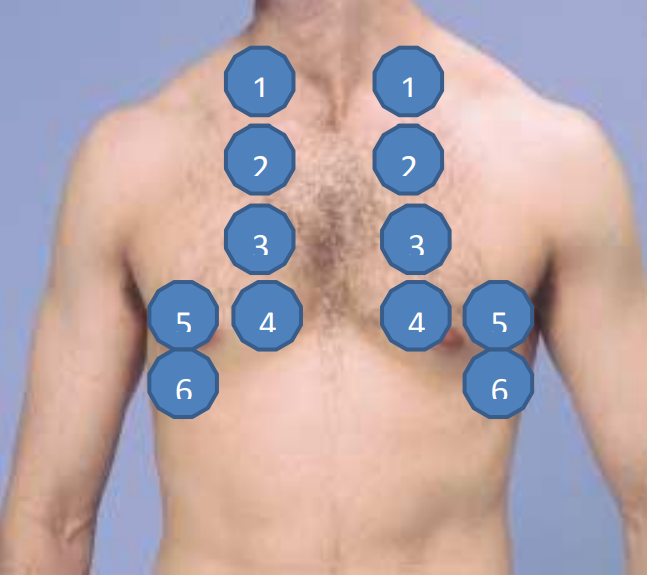
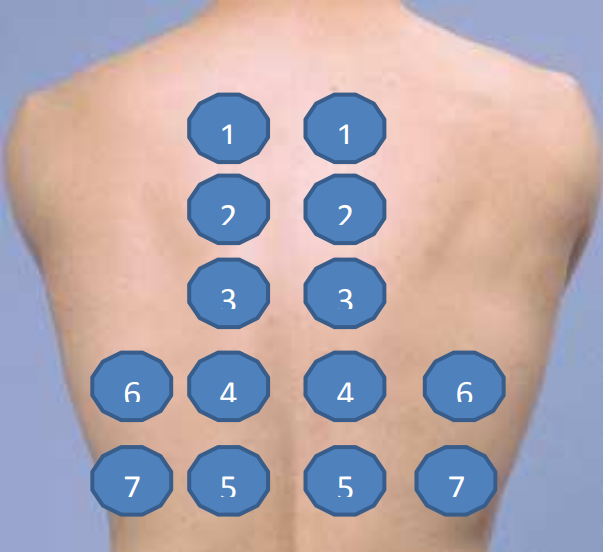
Hyperresonance → COPD
Hyporesonant → atelectasis
Auscultation : “normally detectable/present bronchial breathing and vesicular sounds”
FIRST - bronchial breathing → lower neck + subclavicular spaces
ask patient to breathe thru mouth
at what point in resp cycle does the sound occur?
left vs right side
Transmitted voice sounds → patient says “ee” → “a” sound = pneumonia
reduced sound → local is pneumothorax, effusion, pneumonia (@ base)
global is COPD, asthma
Wheeze → continuous musical whistling in ant thorax, narrowed airways → asthma + COPD
stridor → inspiratory
Crackles (rales) → discontinuous, from fluid, coarse is infection, fine is fibrosis, physio @ base, LHF
Ronchi → low-pitched, “snoring”
Rub → “step in snow”, in both phases, in dry pleuritis (not wet)
Atelectasis → increased tactile fremitus, percussion dullness, abnormal breath sounds
if unsure if physio sound → ask patient to cough, if increased sound it’s patho (pneumonia)




CARDIOVASCULAR EXAMINATION
Patient supine w/ upper body raised 30 degrees, or turned to left or leaning forward - examiner on right side
Inspection of precordium - scars, v collaterals, chest shape (left asymmetry from congenital RVH, precordium bulge from effusion, barrel from cor pulmonale, parasternal bulge from aortic aneurysm), pulsations (→ SVC/subclavian v obstruction, parasternal is a. dilation), abnormal movements (inward apex excavation in systole from adhesive pericarditis)
Harzer sign - epigastric pulsation from RVH or in thin patients, visible pulsation of apical beat in DCM
Palpation - apex beat (normal/strong/diffuse/impalpable), Palpable/ Not palpable cardiac thrills, 5th intercostal space on midclavicular line (lay patient on left if can’t feel it), normal diameter is 1 intercostal space
LVH + dilated cardiomyopathies change 6th intercostal space
Percussion - Cardiac dullness in Normal/Abnormal range showing a Normal/Abnormal sized heart
Auscultation - Rythmic/Arythmic cardiac sounds with/without superimposed pathological sounds or bruits (locate and describe pathological sounds)
diaphragm - 1 + 2nd heart sounds, systolic murmurs
bell - 3rd + 4th heart sounds, diastolic murmurs
l lat decubitus - for mitral stenosis, S3, S4
sitting + forward - for aortic regurgitation
standing up - mitral valve prolapse
Mitral - 5th interspace, at apex (best for hearing S1)
Tricuspid - 4th interspace, l sternal edge
Pulmonary - 2nd interspace, l sternal edge
Aortic - 2nd interspace, r sternal edge
Erb-Botkin - 3rd interspace, l sternal edge (for aortic insufficiency, pericarditis)
patent ductus arteriosus - 1+2nd interspaces below l midclavicular area
Feel carotid pulse (occurs w/ S1)
Murmurs: must describe timing, intensity, location of max intensity, radiation, pattern, character, variation w/ position
“medium pitched, grade 3/6, blowing holosystolic murmur, best heard at apex, radiating to left axilla” (mitral reg.)
S3 - “ken-tuck-y”, gallop
S4 - “da-lub dub”, before S1 (late diastole)
Extra hearts sounds:
Pericardial friction rub - scratching, high-pitched, use diaphragm on Erb point, patient forward
Systolic - midsystolic click (av valve prolapse), high pitched, heard medial to apex, patient sitting + forward
ejection click (semilunar stenosis), high-pitched early in systole, w/ diaphragm at a or p areas
Diastolic - opening snap (mitral stenosis), early in diastole, @ apex at l lat decubitus position
pericardial knock (constrictive pericarditis), in early diastole
Peripheral pulse -
JVP (assesses right heart) - OF IJV, supine, 15° trunk elevation, press on liver if you can’t see it (hepatojugular reflux)
radial (medial to styloid process), temporal (in front of ear), carotid (for pulse character + waveform, supine, 15° trunk elevation, medial to scm), brachial (medial side of fossa), femoral, popliteal (deep), post tibial (post+inf to medial malleolus), dorsalis pedis (lat to exterior hallucis longus, b2 1+2nd metatarsals)
Rate, Rhythm, Symmetry, Quality (pulsus bisferiens in aortic reg, collapsing, celer + altus, parvus + tardus, filiformis)
Radio-radial pulse + radio-femoral pulse if abd/arcus aortae stenosis
Vital signs - BP, HR, RR, temp
ECG
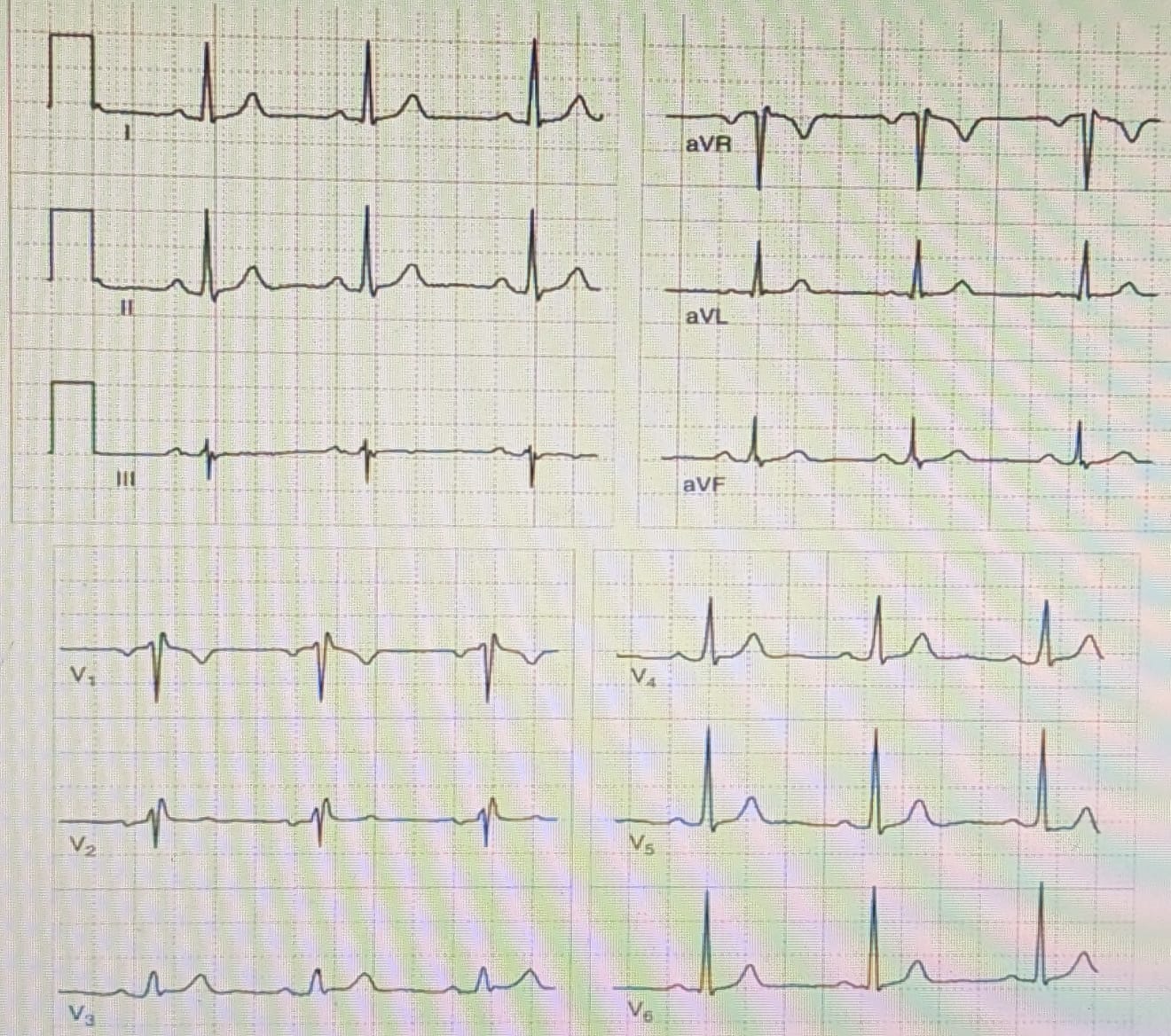
Cardiac rhythm - origin, rhythmicity (sinus rhythm)
P waves + in leads II and aVF, normal is DII + V1
1 big square - 0.2s
ventricular rhythm - R-R intervals
atrial rhythm - P-R intervals
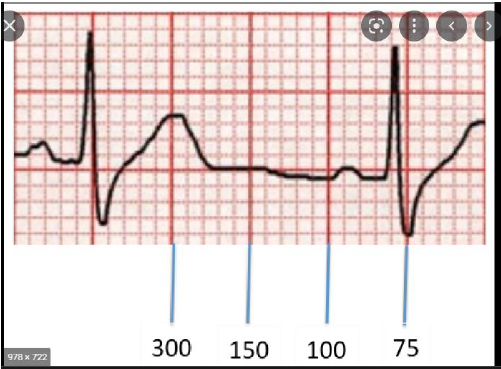
HR: 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50
Axis - are heights of QRS from leads I and aVF + or - ? (physio +) Where do the quadrants overlap?
normal is 0-90°
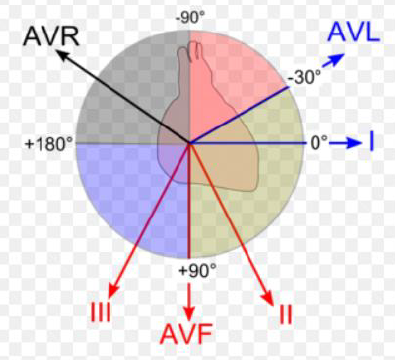
QRS
ST segments + T waves
PQ + QT intervals
Aortic regurgitation - by asc aortic dissection, RF, IE
LV v overload → increased LV end-diastolic → increased pul p → dyspnea + pul edema
Manifestations - widened pulse p (bw systolic + diastolic), water-hammer pulse, apical beat hyperdynamic, Quincke sign, S3, early diastolic murmur, Austin Flint murmur (mid-diastolic)
Investigations - ecg shows LVH + left axis deviation, pbc and cultures +
Aortic stenosis - by calcification (DM) or RF
increased LV afterload → LVH → decrease systemic flow → MI
Manifestations - angina, syncope, HF, powerful apex beat, ejection click, S3+S4, crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur, radiates to carotids
Investigations - BNP, ecg shows LVH, AF
Tricuspid stenosis - by RF, IE, lupus
less flow to RV → RAE, obstructed v return (hepatomegaly, less pul flow, edema)
Manifestations - edema, fatigue, increased JVP, RVH, ascites, tricuspid opening snap, diastolic murmur
Investigations - CBC, tall P waves (RAE), AF and atrial flutter (for albin)
Tricuspid regurgitation - by RF, IE, prolapse, diseases causing pul HTN
RV v overload → RHF
Manifestations - of RHF (edema, ascites, hepatomegaly), JVD, S3+S4 (increases w/ ins),
Investigations - no ECG abnormalities, cardiomegaly, dilated RV on echo
Pulmonary stenosis - by congenital diseases
Pulmonary regurgitation
either by pulmonary valve dilation (pul HTN), by infection or congenital
Manifestations - dyspnea, angina, edema, palpitations, abd distention, JVD, palpaple S2, S split, Graham steel murmur (early diastolic decrescendo), holosystolic tricuspid regurgitation murmur
Investigations - ECG shows RVH + E
Mitral stenosis - by RF
Calcified valve → left atrial p increased → pul v HTN → AF
Manifestations - LFH (dyspnea, orthopnea), mitral face, apical impulse lat displaced, opening snap
Investigations - LAE, RVH on ECG
Mitral regurgitation - by RF, myxomatous degeneration
increased preload → increased stroke v → increased left atrial pressure
Manifestations → LHF (dyspnea, orthopnea, pul edema), S2 split, holosytolic murmur towards axilla
Investigations - BNP, LVH + LAE in ECG, AF

ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION
Inspection : In supine position the abdomen Is/Is not in xypho-pubian plane
Participating/Not participating in respiratory movements.
Teguments, collateral circulations, stretch marks
Normal hernia free points With/Without protruding masses.
Auscultation : Normal/Abnormal , Present/Absent peristaltic movement.
Palpation : feet lying or bent
Superficial palpation : on each quadrant
Abdomen is Elastic/Tender in…(which one)… quadrants With/Without specific tenderness or pain.
Deep palpation : along each quadrant, Elastic/Tender abdomen, Murphy sign Positive/Negative, use 2 hands
Palpate liver - patient takes deep breath, upwards movements w/ fingers, feel surface of liver then edges, Inferior margin of the liver Is/Is not palpable
croash/Murphy maneuver → sticking fingers under ribs after patient takes deep breath
Spleen is/Is not palpable. - palpate from right iliac fossa to other side, patient taking deep breaths
palpable when enlarged, portal htn, you can feel inf pole
Kidneys - one hand pressing on top, the other under to touch kidneys
palpable in liver enlargement, PKD
Percussion : supraumbilical then to lateral borders, liver in interspaces, splenic border, suprapubic
Hyper/Normo/Hypo resonant percussion Alternating/ Not alternating tympanic and dullness sounds.
Fluid wave test for ascites is Negatve/Positive
Shifting dullness - turn on one side and wait, percuss from lat to medial, transmitted on palm thru impulse of movement by liquid → ‘wave sign’ of ascites
Liver - percuss for prehepatic diameter is 12cm, (lowest part you hear dullness) → inf margin, work up
from right iliac fossa → thoracic cage
Spleen - from right iliac fossa to axillary line, bw 7-9th interspaces
Kidney - in acute urinary retention, tympanic sounds physiological
Giordano maneuver bilaterally Positive/Negative
Duodenal ulcer - pain occurs after eating (after an hour)
Dysphagia : difficulty swallowing, check for tumours, achalasia, peptic ulcers, if oropharyngeal it's infections or Zenker's, if esophageal it's tumors or peptic strictures
Odynophagia : swallowing feels painful, caused by chemical irritants
Heartburn : caused by peptic ulcers, GERD
Dyspepsia : indigestion, gastric is nausea and vomiting, intestinal is defecation disorders
Tenesmus : urge to go toilet but can't go, check for rectal cancer if with blood
Nausea and vomiting: in acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastroenteritis, gastroparesis
If morning - alcoholics and pregnant
If after eating - peptic ulcers, psychiatric
If 4h after meal - gastroparesis
Continuous - depression
Irregular - major depression
Green vomit - bile (small bowel obstruction)
Undigested food - achalasia
Partially digested - gastroparesis, gastric outlet obstruction
Hematemesis - upper GI bleed (above angle treitz)
Pruritis - pregnant, cancer, cirrhosis
Gastroparesis : early satiety, post prandial bloating, abd discomfort
Diverticuli - dilations, cause extreme bleeding
Peptic ulcers - episodic pain after meals
Biliary pain - severe, right upper/epigastric, after fatty foods
Pancreatic pain - epigastric radiating to back, relieved by sitting up/leaning
Small bowel obstruction - periumbilical
Colonic pain - like small bowel but relieved by defecation/flatus
Bowel ischemia - right upper/central, exacerbated by eating
Renal colic - lumbar (costovertebral angles), tender to touch
Bladder pain - suprapubic, diffuse, severe
Prostatic pain - dull, in lower abdomen or rectum
Ureteral pain - variable, exacerbated after urination
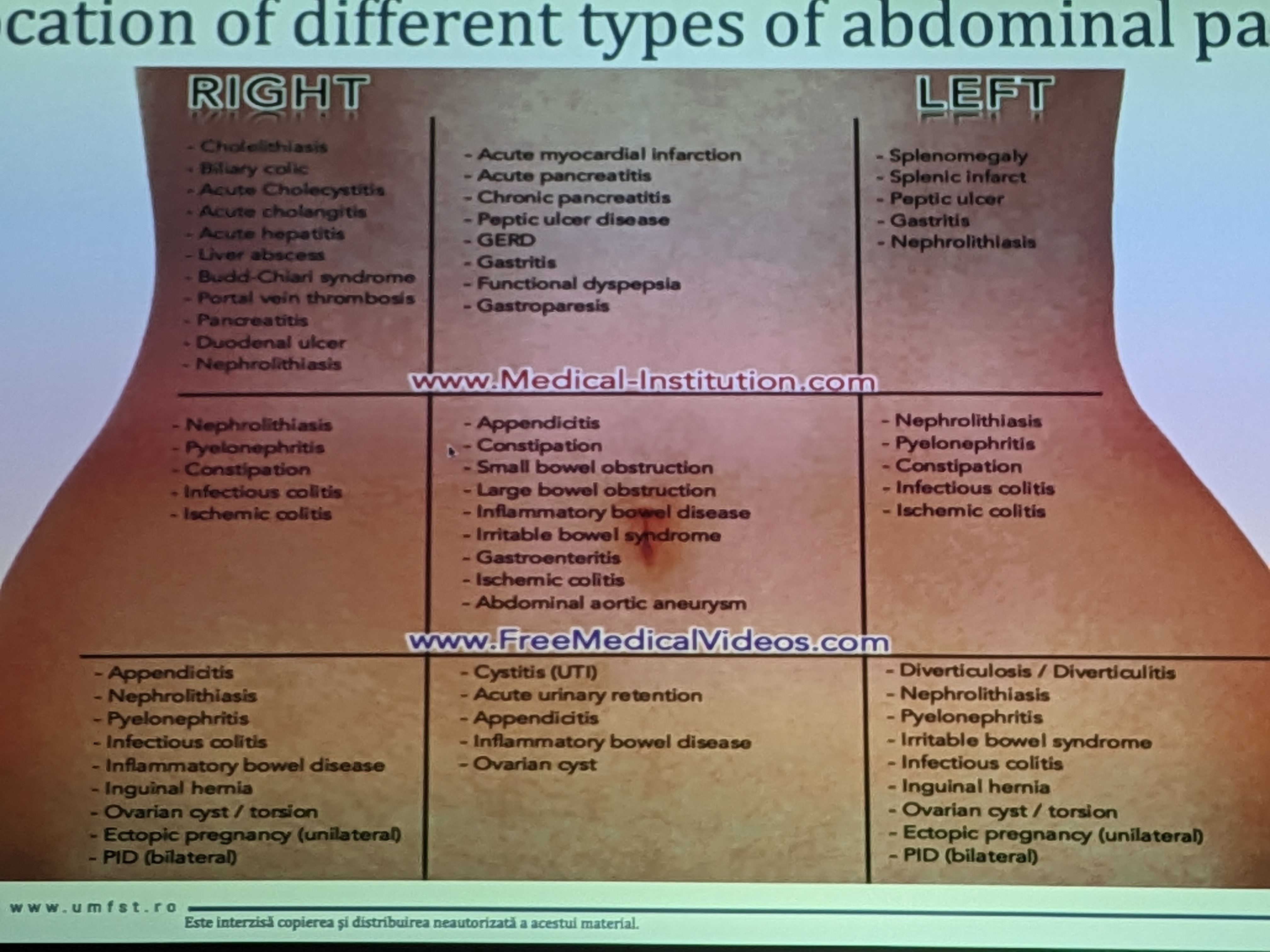
Topographical divisions
Murphy sign - acute cholecystitis, 9th interspace
Bar from left to right - acute pancreatitis
Appendicitis - McBurney point → 1/3 iliac spine - umbilicus
- Lanz point → 1/3 of the way between the two anterosuperior iliac spines
- Gerota clock - position appendix
- Iacobovici triangle - linea alba, Lanz, McBurney
- Iupsoas manoeuver - raise legs and press on appendix
Courvesier sign - pancreatic head tumour
Virchow/Troisier node - gastric tumour
Acute pancreatitis - Turner sign - flank bruises, Cullen sign - periumbilic bruises
Immobile patient - peritonitis
Patient on all 4s - pancreatitis
Obesity - w/ cholelithiasis (female, fatty, 40)
Peripheral edema - nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, malabsorption
Limbs :
Leukonychia, koilonychia - hypoalbuminemia
Clubbing- cirrhosis, IBD, celiac
Blue lunale nails, Keyser Fleischer rings - Wilson's
Palmar erythema - liver
Dupuytrens contracture
Axilla - adenopathies from gastric cancer (Virchows nodes)
Circumoral pigmentation - peutz jager
Tongue - iron/B12 deficiency swollen, leukoplakia in alcohol, candidiasis in iron deficiency
Acanthosis nigricans in axilla - DM
Findings:
Abdomen is firm, smooth, elastic, painless, palpation was not tender, no pathological resistances