Chemical Kinetics and Cell Growth in Bioprocessing
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Chemical Kinetics
Study of reaction rates and mechanisms.
Reaction Kinetics
Speed of reactants converting to products.
Rate of Reaction
Change in concentration over time.
Irreversible Reaction
Reaction that proceeds in one direction only.
Mass Balance
Equation accounting for mass changes in reactions.
Volumetric Rate
Rate of reaction per unit volume.
Zero-Order Kinetics
Rate independent of reactant concentration.
First-Order Kinetics
Rate proportional to reactant concentration.
Rate Constant (k)
Specific constant for reaction rate.
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Intermediate formed during enzyme reactions.
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
Model describing enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Vmax
Maximum rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Concentration (C)
Amount of substance per unit volume.
Reaction Rate Equation
Mathematical expression for reaction rate.
Activation Energy
Energy required to initiate a reaction.
Closed System
No mass exchange with surroundings.
Rate of Change
Speed at which concentration varies.
Substrate (S)
Reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Product (P)
Substance formed from a chemical reaction.
Reactants (A, B)
Starting materials in a chemical reaction.
Consumption Rate
Rate at which reactants are used up.
Production Rate
Rate at which products are formed.
Initial Condition
Starting concentration at time t=0.
E
Enzyme in a catalyzed reaction.
S
Substrate that is converted to product.
P
Product formed from substrate reaction.
Vmax
Maximum reaction velocity (mol l-1 min-1).
[S]
Substrate concentration (mol l-1 or mol m-3).
r
Reaction rate (mol l-1 min-1).
Km
Michaelis constant (mol m-3).
kcat
Catalytic constant or turnover number.
e
Enzyme concentration in reaction.
Zero-order reaction
Rate independent of substrate concentration.
First-order reaction
Rate depends on substrate concentration.
Michaelis-Menten equation
V = Vmax[S] / (Km + [S]).
Substrate saturation
Condition when [S] exceeds Km.
Enzyme-substrate complex
Intermediate formed during enzyme catalysis.
Rate constant
k, typically first-order (time-1).
Experimental data
Used to determine Michaelis-Menten parameters.
Trendline fitting
Method to extract parameters from plotted data.
Graph plotting
Visual representation of reaction rates versus substrate.
Reaction velocity
Speed of product formation over time.
Enzyme kinetics
Study of reaction rates involving enzymes.
Catalysis
Process of accelerating a chemical reaction.
Reaction mechanism
Stepwise process of substrate conversion to product.
Monod equation
Describes cell growth rate in bioreactors.
Specific growth rate (𝜇)
Rate of cell growth per time unit (s-1).
Maximum growth rate (𝜇max)
Highest specific growth rate achievable (s-1).
Substrate concentration ([S])
Concentration of substrate in solution (mol m-3).
Michaelis constant (𝐾+)
Substrate concentration at half Vmax (mol m-3).
Rate of reaction (rB)
Speed of enzymatic reaction (mol l-1 min-1).
Maximum velocity (Vmax)
Maximum reaction rate achievable (mol m-3 s-1).
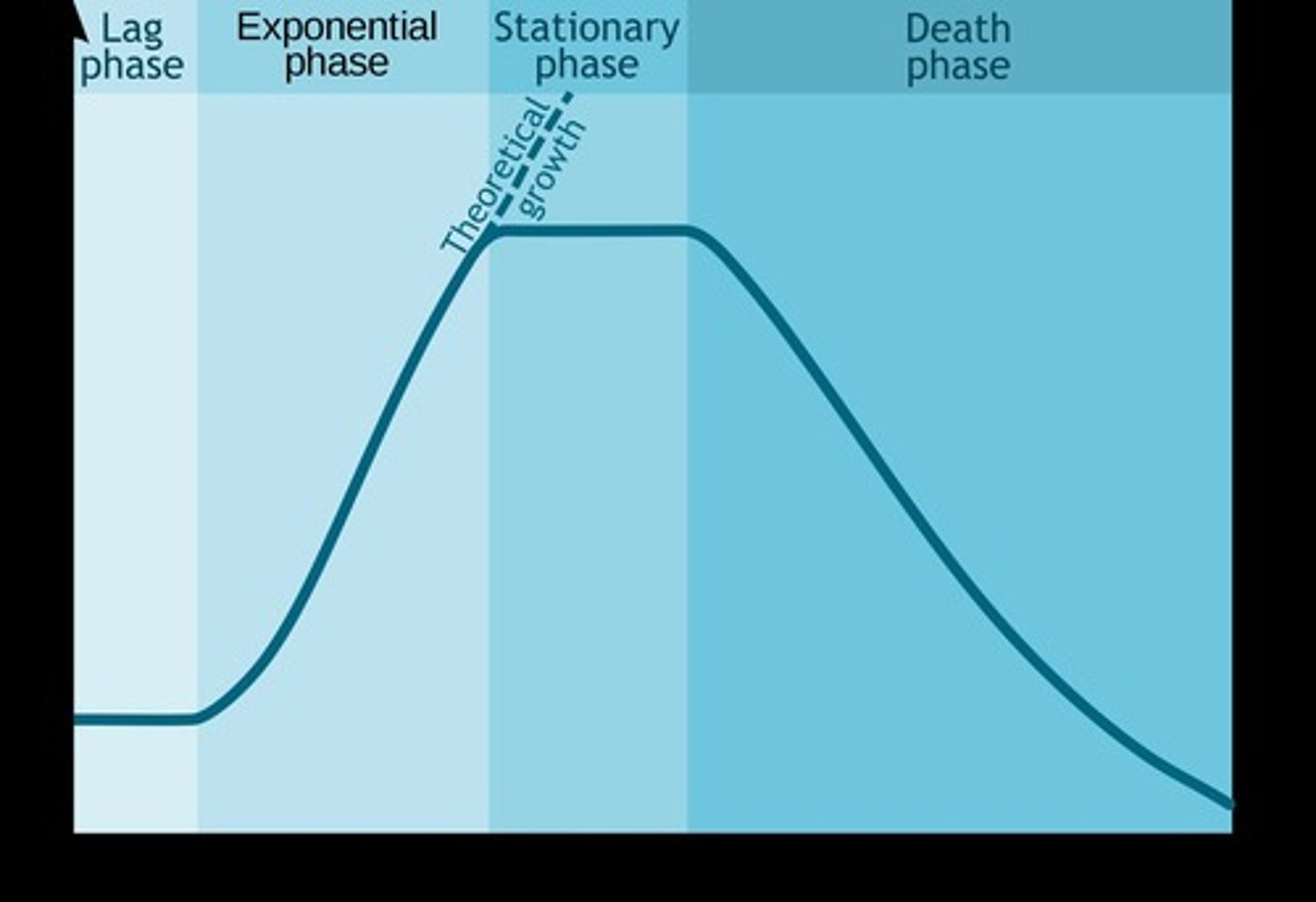
Lag phase
Initial phase where cells acclimatize and grow in size.
Exponential phase
Rapid cell division and biomass increase occurs.
Stationary phase
Growth rate equals death rate; toxins accumulate.
Death phase
Cell numbers decline exponentially due to toxins.
Acceleration phase
Transition from lag to rapid growth phase.
Decline phase
Growth slows before entering stationary phase.
Growth rate (r@)
Rate of biomass increase over time.
Biomass
Total mass of living cells in culture.
Primary metabolites
Compounds produced during exponential growth phase.
Secondary metabolites
Compounds produced during stationary phase, often pharmaceuticals.
Toxin accumulation
Build-up of harmful by-products during growth.
Enzymatic processes
Biochemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes in cells.
Nutrient consumption
Utilization of resources for cell growth.
Bioreactor
Controlled environment for cultivating microorganisms.
Growth curve
Graphical representation of cell growth phases.
Growth rate (𝑟@)
Rate of biomass increase over time.
Biomass production
Amount of biological material generated.
Initial concentration (𝑋)
Starting amount of cells in culture.
Specific growth rate (𝜇)
Rate constant for cell growth per concentration.
Doubling time (𝑡Z)
Time required for cell concentration to double.
First-order kinetics
Reaction rate proportional to concentration.
Cell concentration (𝑥)
Amount of cells per volume unit.
Exponential growth phase
Rapid increase in cell number.
Lag phase
Initial period of adaptation before growth.
Stationary phase
Growth rate equals death rate, no net increase.
Death phase
Decline in cell number due to unfavorable conditions.
Turbidity meter
Device measuring microbial density via light scattering.
Monod equation
Model relating growth rate to substrate concentration.
Substrate concentration ([S])
Amount of nutrient available for cell growth.
Maximum growth rate (𝜇max)
Highest specific growth rate achievable.
Half-saturation constant (𝐾+)
Substrate concentration at half maximum growth rate.
Linear kinetics
Growth model assuming constant rate over time.
Reaction order
Determines how growth rate changes with concentration.
Slope of ln 𝑥 vs. 𝑡
Represents specific growth rate (𝜇).
Separation of variables
Mathematical method for solving differential equations.
Exponential growth equation
Describes growth as a function of time.
Homologue of Lineweaver-Burk equation
Used to calculate Monod parameters from experimental data.