Lecture 11 (Viral Diseases of Cats II)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
b) from exotic cats
FIV spread to cats more than 1,000 years ago and is thought to have evolved
a) from dogs
b) from exotic cats
c) from ferrets and weasels
d) from HIV
false
t/f: the FIV vaccine is DIVA compatible
a) FeLV
transmission:
-vertically from infected queens to kittens
-horizontally among cats that live together or fight
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) FIV
transmission:
-via bite wounds
-horizontally among cats that live together is uncommon
a) FeLV
b) FIV
a) FeLV
viremia:
virus shed in saliva, nasal secretions, feces, milk and urine
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) FIV
viremia:
high concentration in saliva
a) FeLV
b) FIV
a) FeLV
viral propagation to other tissues:
-targets lymphoid organs (thymus, spleen, lymph nodes)
-immune response unable to clear infection
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) FIV
viral propagation:
-drop in lymphocyte count
-inversion of T-lymphocyte ration (CD4:CD8)
-immune response unable to clear infection
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) fever, malaise, diarrhea
*malaise = a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or uneasiness
the clinical signs for FIV are best summarized as:
a) fever, Lymphadenopathy, and Leukopenia
b) fever, malaise, diarrhea
a) fever, Lymphadenopathy, and Leukopenia
*Lymphadenopathy = swelling of the lymph nodes
*Leukopenia = reduction in the # of white cells in the blood
the clinical signs for FeLV are best summarized as:
a) fever, Lymphadenopathy, and Leukopenia
b) fever, malaise, diarrhea
b) FeLV
in __________ infection, after an asymptomatic phase, we see a progressive infection or a regressive infection (cat remains infected but reverts to an viremic state and is unlikely to shed the virus) months to years later
a) FIV
b) FeLV
a) FIV
in __________ infection, after an asymptomatic phase, we see cats remaining asymptomatic or having progressive dysfunction of the immune system
a) FIV
b) FeLV
d) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
a primary clinical syndrome associated with this virus can cause lymphoid hyperplasia for several months in the primary stages of infection and then continued hyperplasia or even lymph node atrophy in late stages of disease
a) Feline Calicivirus
b) Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis
c) Feline Panleukopenia
d) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
e) Feline Coronavirus
d) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
this virus is associated with primary clinical signs of anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, and thrombocytopenia with multiple abnormalities in 40% of cases and this is associated with a poor prognosis // non-regenerative anemia is common in advanced cases
a) Feline Calicivirus
b) Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis
c) Feline Panleukopenia
d) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
e) Feline Coronavirus
d) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
in addition to primary clinical signs this virus is associated with secondary gingivitis/stomatitis, conjunctivitis, meningitis, and other opportunistic infections
a) Feline Calicivirus
b) Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis
c) Feline Panleukopenia
d) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
e) Feline Coronavirus
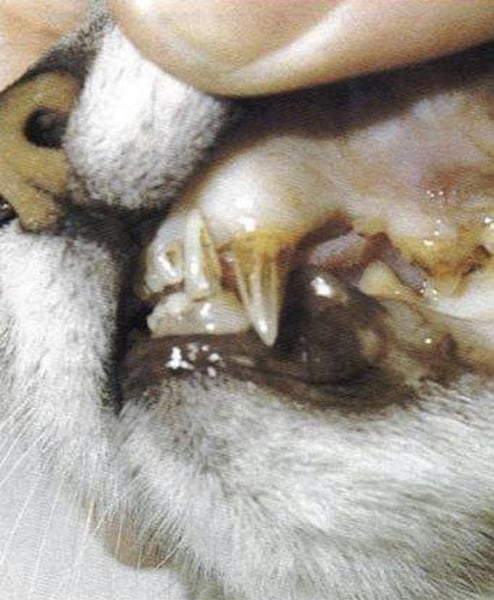
b) Stomatitis
the most common clinical disease in FIV (although it also occurs with FeLV) is....
a) Glomerulonephritis
b) Stomatitis
c) Otitis Externa
d) Anemia
a) Feline Calicivirus
Stomatitis is a common late-stage event in FIV infection when this opportunistic agent gets involved:
a) Feline Calicivirus
b) Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis
c) Feline Panleukopenia
d) Feline Leukemia Virus
e) Feline Coronavirus
a) adult males
FIV transmission is closely tied to bite wounds. This explains why approximately 80% of FIV positive cats are:
a) adult males
b) adult females
c) female kittens
d) male kittens
b) rare
We mention lactogenic transmission in FeLV, but what about FIV? With FIV, queen to kitten transmission is...
a) impossible
b) rare
c) common
a) FeLV
*FeLV: 1/3 of household can become infected, in one study 18% of adults were infected within 7years
*FIV: may not spread in a household with no fighting; remember its concentrated in saliva
which one has a greater (but still small) chance of spreading in a household even without fighting:
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) antibody
diagnosis of FIV infection is by detection of ____________ via SNAP
a) antigen
b) antibody
false - unstable
t/f: FeLV and FIV are stable in the environment
true
t/f: virus burden in FIV is generally too low for antigen testing, however antibodies take time to develop so early infections are also missed with antibody SNAP tests
a) FIV
antibodies produced were known to persist for 4+ years in some cats and in all cases the vaccine wasn't DIVA compatible
the vaccination against ____________ was removed from market in 2017
a) FIV
b) FeLV
true - implied that this would prevent a shelter etc from assuming your cat is FIV positive and euthanizing it
t/f: FIV Vaccinated cats should be permanently identified with a microchip indicating this history
false - they'll have positive antibody results
t/f: clients should be informed that vaccinated cats will have negative FIV antibody test results
b) FIV vaccine in a cat with FIV is of no benefit
c) FIV vaccine in a cat with FIV would give unmet false expectations to owners resulting in questions about vaccine efficacy
d) FIV vaccine in a cat with unknown status could result in future true positive FIV tests being assumed to be from the vaccine
testing of cats prior to vaccination is essential to ensure negative status. reason for this include:
[select all that apply]
a) FIV vaccine in a cat with FIV is medically harmful
b) FIV vaccine in a cat with FIV is of no benefit
c) FIV vaccine in a cat with FIV would give unmet false expectations to owners resulting in questions about vaccine efficacy
d) FIV vaccine in a cat with unknown status could result in future true positive FIV tests being assumed to be from the vaccine
false - DIVA principle could not be used
t/f: DIVA principle was used to identify true positive cats from vaccinated cats pertaining to the FIV vaccination
c) that FIV transfer between cat species has occurred in the past, but is quite infrequent today.
Data reveals that in most species endemic for FIV (lions, pumas, domestic cats, etc.) there is genetically distinct species-specific FIV Strains. This suggests:
a) that FIV zoonosis from wild cats to domestic cats is an imminent threat
b) that FIV transfer between cat species has never occurred
c) that FIV transfer between cat species has occurred in the past, but is quite infrequent today.
a) FeLV
although complicated by elective euthanasias, one study found that the survival of __________ infected cats compared to controls was 47% at 3 years and only 29% at 6 years
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) FIV
although complicated by elective euthanasias, one study found that the survival of __________ infected cats compared to controls was still 94% at 3 years and 80% at 6 years
a) FeLV
b) FIV
retroviruses
Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) and feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) are ___________ with global impact on the health of domestic cats
a) FeLV
__________ can cause tumors (mainly lymphoma), bone marrow suppression syndromes (mainly anemia), and lead to secondary infectious diseases due to suppression effects on the bone marrow and immune system
a) FeLV
b) FIV
a) FeLV
_______ is more pathogenic, and was long considered to be responsible for more clinical syndromes than any other agent in cats; however, today it is less commonly diagnosed than in the previous 20 years
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) FIV
________ can cause an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome that increases the risk of opportunistic infections, neurological diseases, and tumors; however, it does not cause sever clinical signs itself
a) FeLV
b) FIV
b) FIV
in most naturally infected cats, _________ itself does not cause severe clinical signs, and _________-infected cats may live many years without any health problems
a) FeLV
b) FIV
-FeLV: likely to spread in homes and shelters
-FIV: very unlikely to spread in homes and shelters
FeLV vs FIV:
one is spread by close contact and body fluids so spread is expected in homes and shelters (age association though), the other is spread by fighting so it is very unlikely to spread in homes or shelters. which is which?
b) FeLV
with __________ an infected cat may develop a regressive infection with a normal lifespan, no longer contagious, and the possibility to test negative
a) FIV
b) FeLV
a) Rabies
Family Rhabdoviruses; Genus Lyssavirus = ____________
a) Rabies
b) FIV
b) FIV
Family Retroviruses; Genus Lentivirus = ______________
a) Rabies
b) FIV
c) Rhabdovirus
Rabies is a:
a) Herpesvirus
b) Retrovirus
c) Rhabdovirus
d) Lentivirus
a) cats
Rabies diagnoses in the USA show that the majority of infections are in:
a) cats
b) dogs
c) both of the above
how do cats become infected with rabies?
a) contact with raccoons
b) contact with bats
c) both of the above
e) Feline Rabies
this virus infects the limbic system resulting in restlessness, wandering, hypersensitivity to stimulus, loss of appetite, ataxia, and anxiety
a) Feline Calicivirus
b) Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis
c) Feline Panleukopenia
d) FeLV
e) Feline Rabies
b) dumb rabies
Rabies in cats most commonly presents as:
a) furious rabies
b) dumb rabies
b) Modified Live
which of the following is not an available version of the Rabies Vaccine for cats?
a) Inactivated
b) Modified Live
c) Recombinant (Canarypox)
a) HPAI H5N1
____________ has been in Asia since 1996 with waves of infections and deaths noted in tigers, panthers, and domestic cats of Asia and Europe.
a) HPAI H5N1
b) LPAI H7N2
b) LPAI H7N2
in 2016-2017 the CDC investigated an outbreak of __________ among about 500 cats in a NYC animal shelter
a) HPAI H5N1
b) LPAI H7N2
true
t/f: Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus (FIPV) and Feline Enteric Coronavirus (FCoV) are considered one virus, but some literature still refers to an FIP virus, and this is likely to continue
b) Feline Enteric Coronavirus
this virus is characterized by oronasal transmission, it replicates in enterocytes, it is highly infectious, and causes inapparent or mild signs of enteritis and/or respiratory disease
a) Feline Herpes Virus
b) Feline Enteric Coronavirus
c) Feline Leukemia Virus
b) Feline Panleukemia Virus
b) FIP
___________ is a disease with extremely diverse clinical manifestations
-"wet" form: the most characteristic sign is a considerable amount of effusion in the thorax and abdomen felt as a "fluid wave"
-"dry" form: lesions commonly occur in eyes and CNS but granulomas may also be found in the peritoneal cavity
a) FIV
b) FIP
c) FeLV
d) FVR
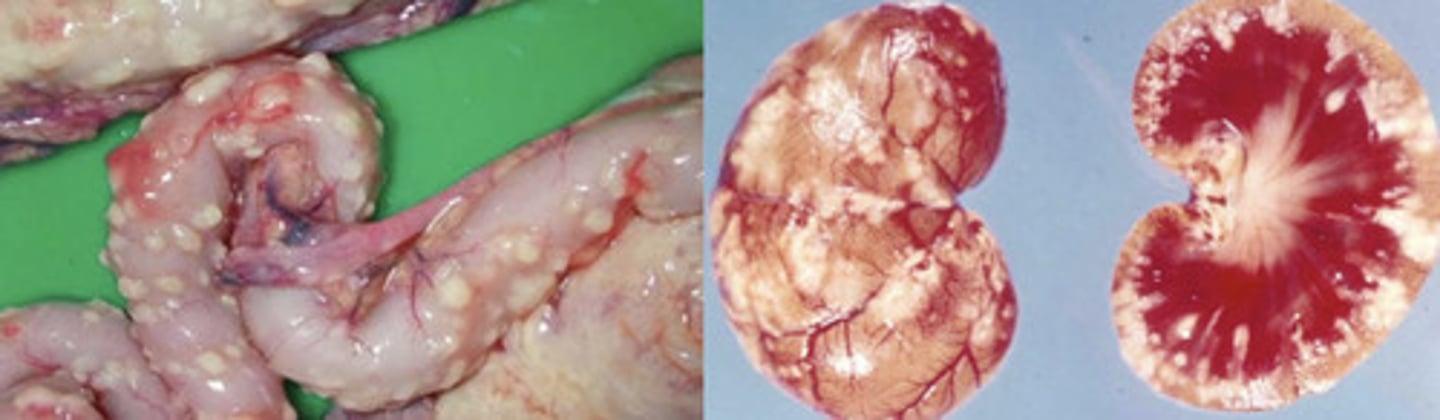
b) FIP
the typical lesions of effusive _______ are pyogranuloma and fibrinous plaques on the serosal surfaces of abdominal organs
a) FIV
b) FIP
c) FeLV
d) FVR
b) FIP
associated with dyspnea, mild pyrexia, and muffled heart sounds. when involving the eyes, we see uveitis, keratic precipitations, and changes in the coloration of the iris
a) FIV
b) FIP
c) FeLV
d) FVR
b) non-effusive
in the _______________ form of FIP, lesions commonly occur in the eyes and CNS, but granulomas may also be found in the peritoneal cavity leading to more diverse/vague clinical signs
a) effusive
b) non-effusive
a) high
overall, case fatality for FIP is:
a) high
b) low
e) the immune response (complexes, compliment, etc) causes disease
in Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) what is the pathogenesis (cause of disease)?
a) immunosuppression leading to eventual, lethal secondary infections
b) the virus targets lymphoid organs leading to blood and immune disorders
c) viral propagation causing drop in lymphocyte count and inversion of the CD4:CD8 T cell ratio
d) virus targets rapidly dividing cells
e) the immune response (complexes, compliment, etc) causes disease
1. wet
2. dry
the immune response to Feline Coronavirus, when causing FIP, can result in serum exudation (aka the _____1______ form) or in granulomas (aka the _____2_______ form)
b) FIP
on necropsy, you find pyogranulomatous foci in the form of punctate fibrinous plaques on the serosal surface of the intestines...this is characteristic of effusive ___________
a) FIV
b) FIP
c) FeLV
d) FVR
b) uveitis - inflammation of the uvea
detecting ___________ as the first clinical sign of FIP in kittens is helpful
a) diarrhea
b) uveitis
c) ascites
d) nasal discharge
90% (Cattery)
50% (Single-Cat household)
Coronavirus-specific antibodies are present in up to _________% of cats in catteries and in up to ________% of cats in single-cat house holds
b) 3 to 5 %
only about ____ of FCoV-infected cats will develop FIP in multiple-cat households
a) 1%
b) 3 to 5 %
c) 5 to 10%
d) 10%
c) Mutated FCoV
FIP is suspected to be derived from a:
a) HPAI
b) LPAI
c) Mutated FCoV
d) Mutated FeLV
does not
FIP as a disease generally [does/does not] spread from cat to cat
epithelial and lymphoid cells
while FCoV normally replicates in enterocytes, with FIP we see low levels of viral replication in ____________ & _________________ cells
b) tropism
current theory for FIP pathogenesis is that the FCoV that normally would cause mild diarrhea or respiratory illness results in a persistent infection in which it mutates to replicate in the immune system through a change in:
a) infectivity
b) tropism
c) stability
a) FCoV has mutated into the FIPV biotype. In the face of clinical signs this = FIPV. No clinical signs = high risk of developing FIPV
when interpreting RT-PCR FIPV results, if the FCoV biotype comes back as FIPV then the interpretation should be:
a) FCoV has mutated into the FIPV biotype. In the face of clinical signs this = FIPV. No clinical signs = high risk of developing FIPV
b) FCoV has not mutated; unlikely to have FIP
c) FCoV cannot be typed. Unknown strain. Cannot rule out FIPV
b) FCoV has not mutated; unlikely to have FIP
when interpreting RT-PCR FIPV results, if the FCoV biotype comes back as FECV then the interpretation should be:
a) FCoV has mutated into the FIPV biotype. In the face of clinical signs this = FIPV. No clinical signs = high risk of developing FIPV
b) FCoV has not mutated; unlikely to have FIP
c) FCoV cannot be typed. Unknown strain. Cannot rule out FIPV
c) FCoV cannot be typed. Unknown strain. Cannot rule out FIPV
when interpreting RT-PCR FIPV results, if the FCoV biotype comes back as Indeterminate then the interpretation should be:
a) FCoV has mutated into the FIPV biotype. In the face of clinical signs this = FIPV. No clinical signs = high risk of developing FIPV
b) FCoV has not mutated; unlikely to have FIP
c) FCoV cannot be typed. Unknown strain. Cannot rule out FIPV
a) RT-PCR on effusions in cats with wet/effusive disease
b) RT-PCR on tissue biopsies or aspirates in cats with dry form
which of the following are useful FIP Diagnostics?
[select all that apply]
a) RT-PCR on effusions in cats with wet/effusive disease
b) RT-PCR on tissue biopsies or aspirates in cats with dry form
c) Molecular Testing of Blood Serology
d) Molecular Testing of Feces
-there is no treatment for healthy seropositive cats
-supportive treatment for coronaviral enteritis
talk about treatment of FCoV infection
FIP
the _________ vaccine is an example of a temperature-sensitive vaccine that cannot replicate at core body temp // it is given intranasal and results in mucosal immunity at the sight of infection
c) not generally recommended (have little to no indication)
the FIP vaccine falls into which of the 3 categories according to the American Association of Feline Practitioners?
a) core (all cats should receive the vaccine)
b) non-core (recommendation is based on risk for exposure)
c) not generally recommended (have little to no indication)