LZHS Bio II Animal Kingdom Part 3 (Vertebrates)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
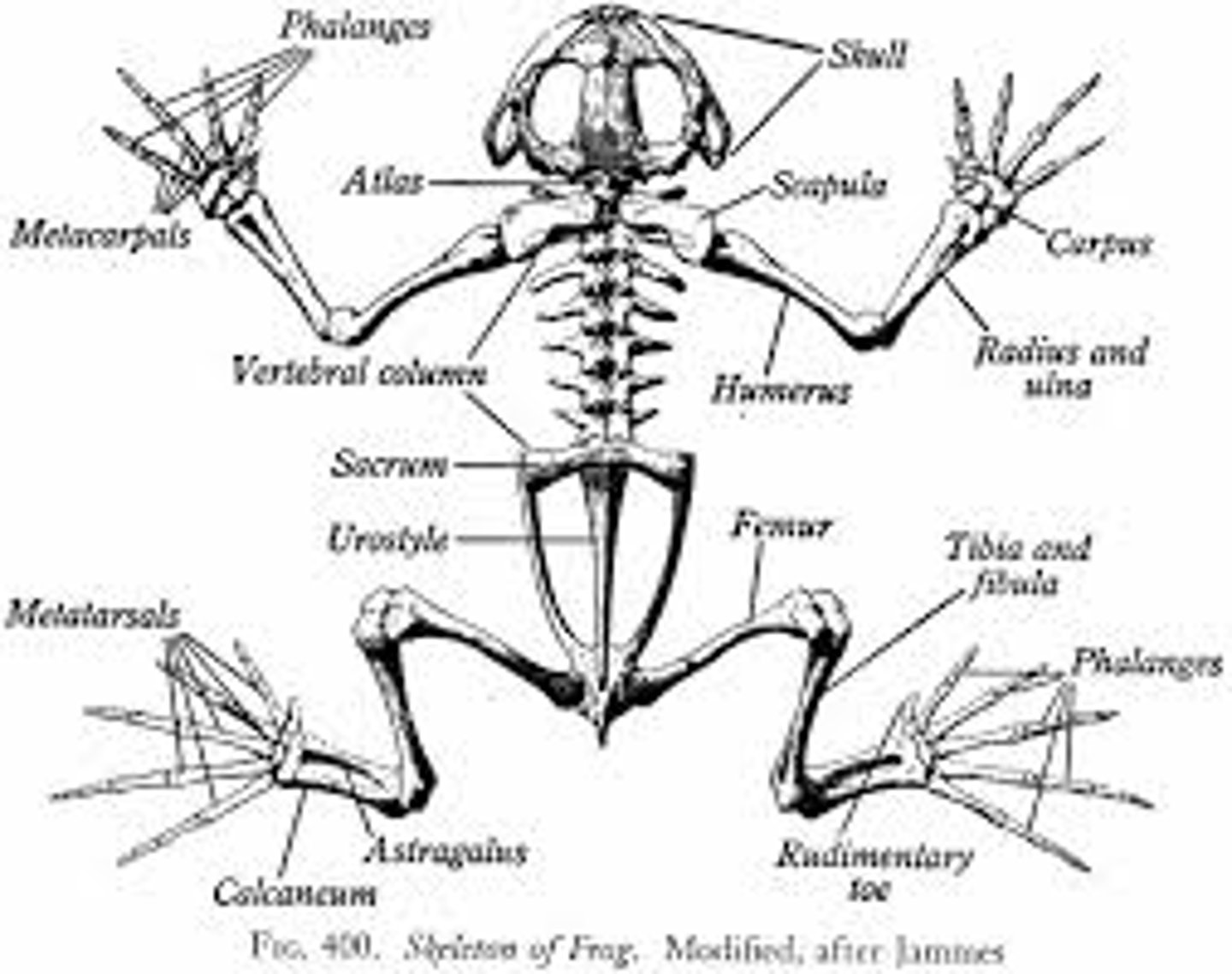
Vertebrae
bones or cartilage that surround the dorsal nerve cord and form the spine
Cranium
skull that protects the brain
Chemoreception
the ability to detect chemicals in the environment

Lateral line
organ which allows fish to sense vibration in the water.

External fertilization
process in which fertilization occurs outside of the body.

Cartilage
a flexible, lightweight material made of cells surrounded by tough fibers of protein.

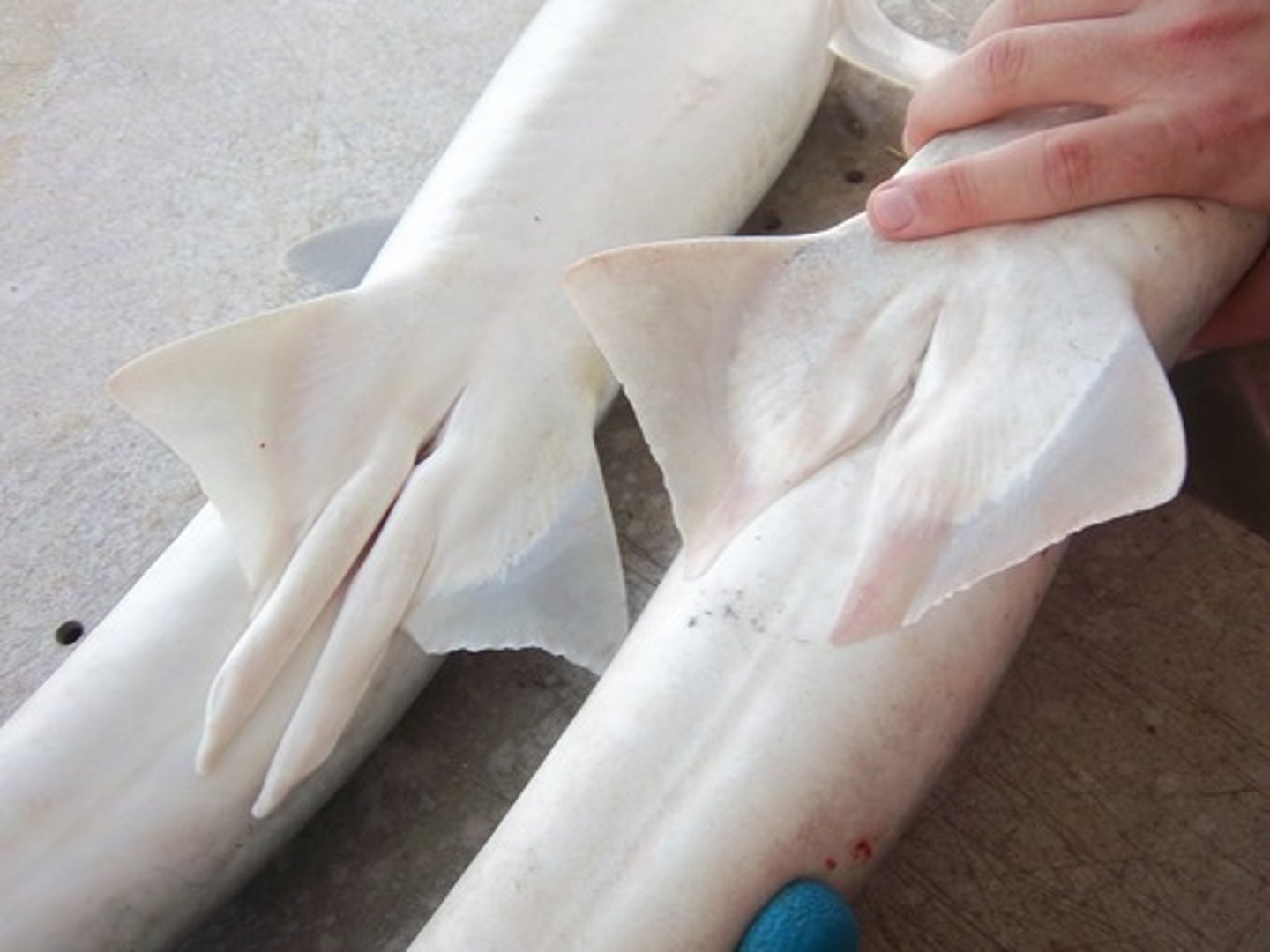
Placoid scales
small, tooth-like spines that feel like sandpaper.
Internal fertilization
fertilization which occurs inside the body of the female
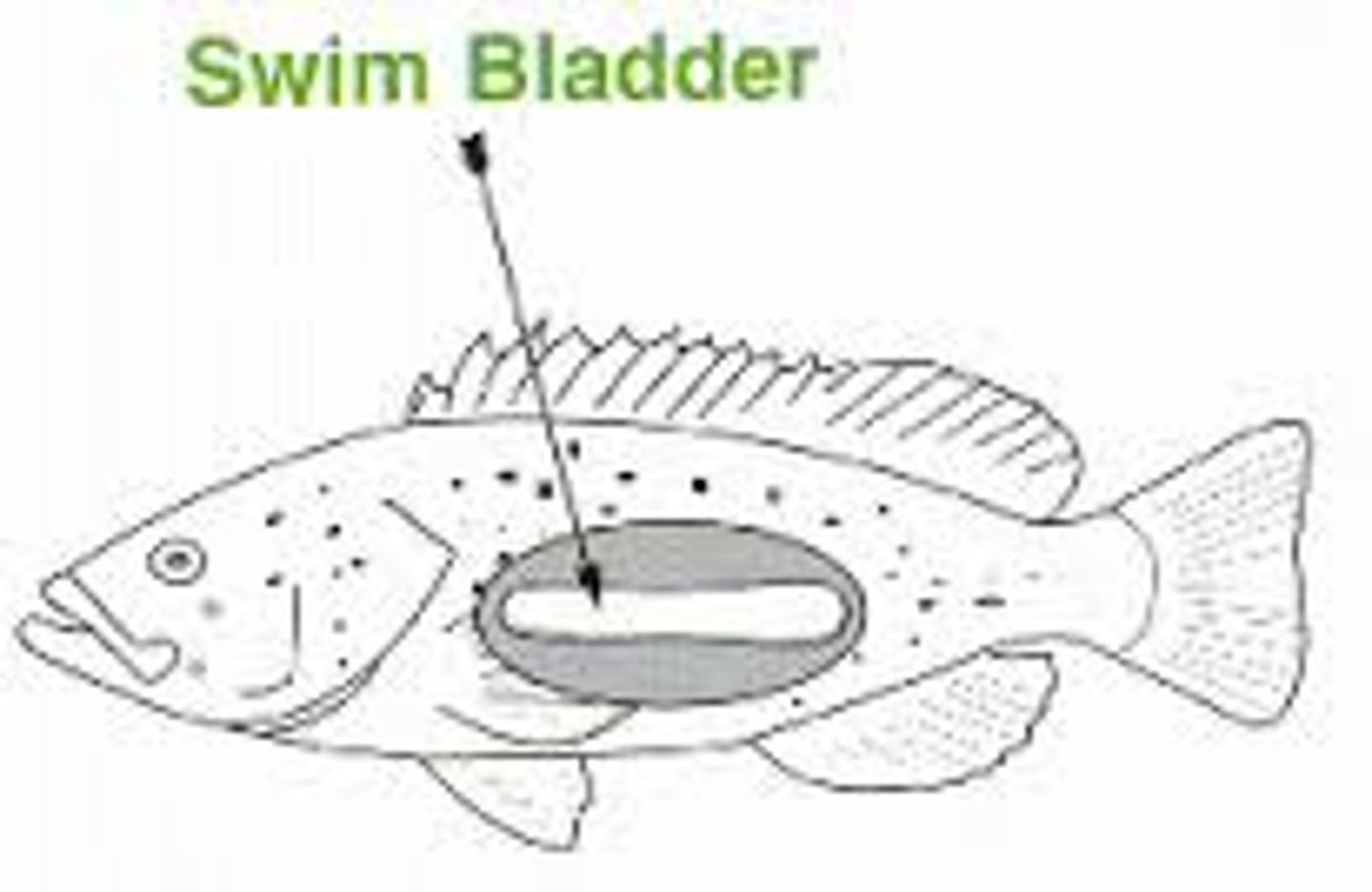
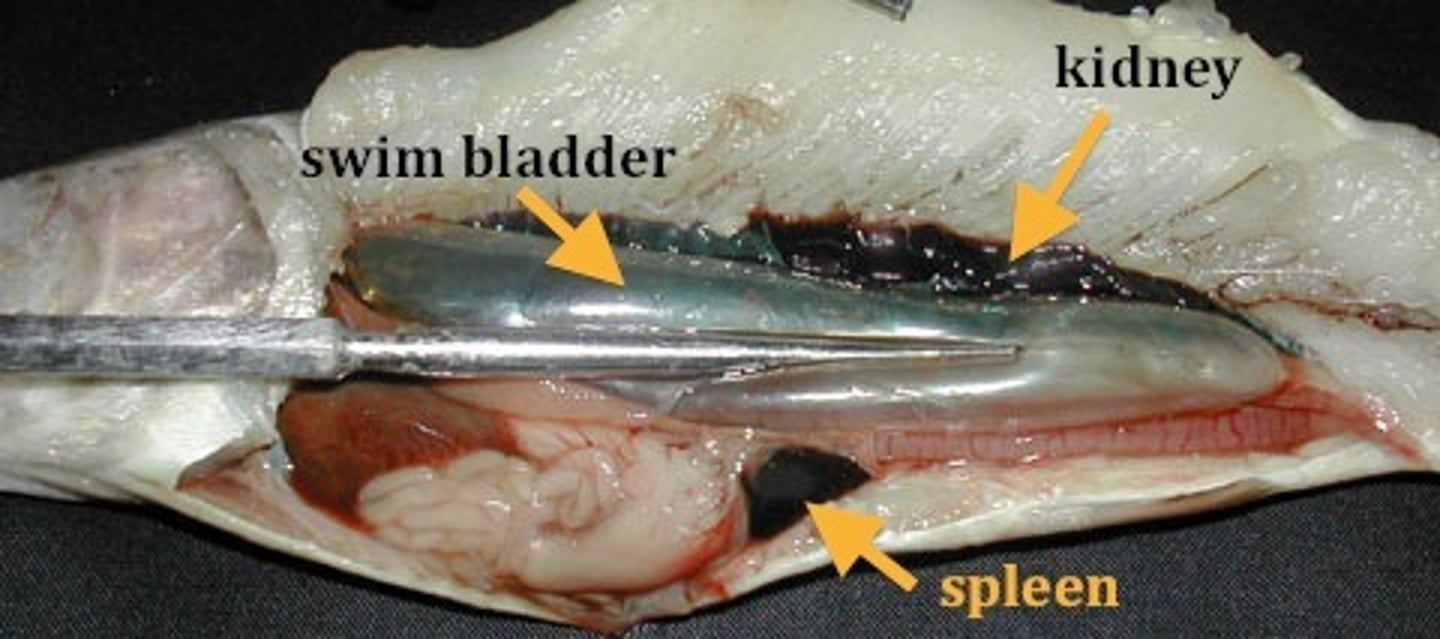
Swim bladder
a gas-filled sac that is used to control buoyancy.
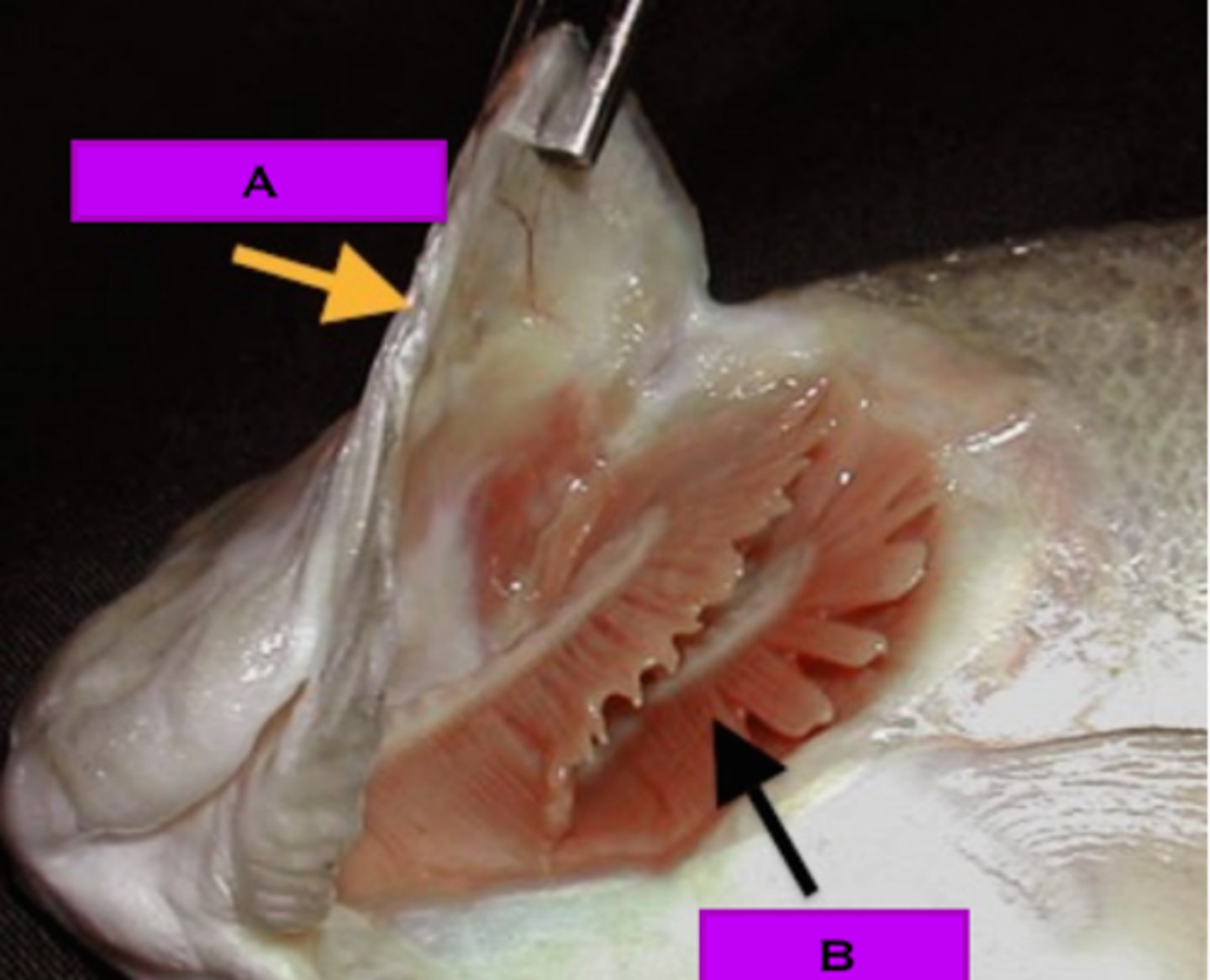
Operculum
a hard plate that opens at the rear and covers and protects the gills of bony fish
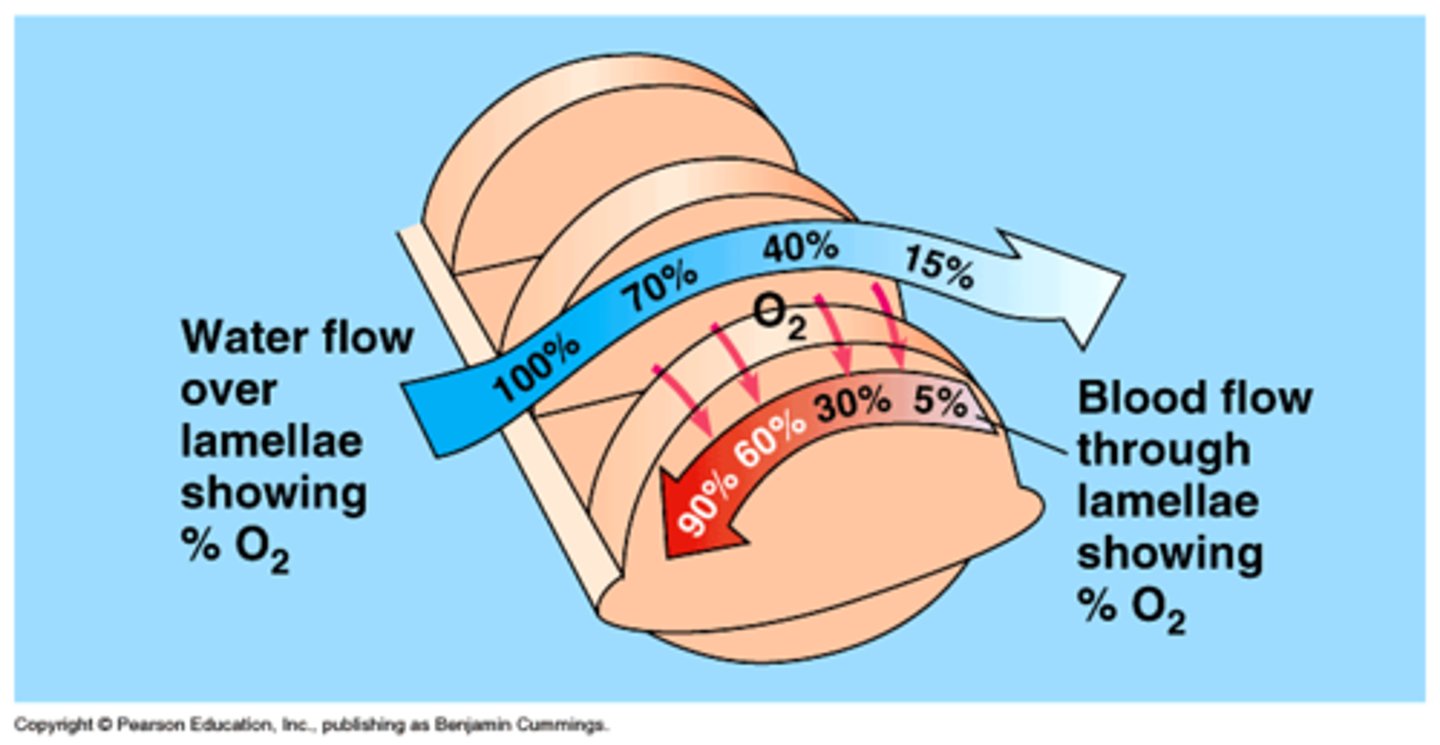
Countercurrent flow
an arrangement whereby water flows away from the head and blood flows toward the head.
Claspers
modified pelvic fins that the male uses to transfer sperm into the female's body.

Classes Myxini & Cephalospidomorphi
Used to be "Agnatha" which means "without jaws"
Jawless fish: Hagfish (marine) and Lamprey (freshwater) that are parasitic
*Keep their notochord throughout their life!

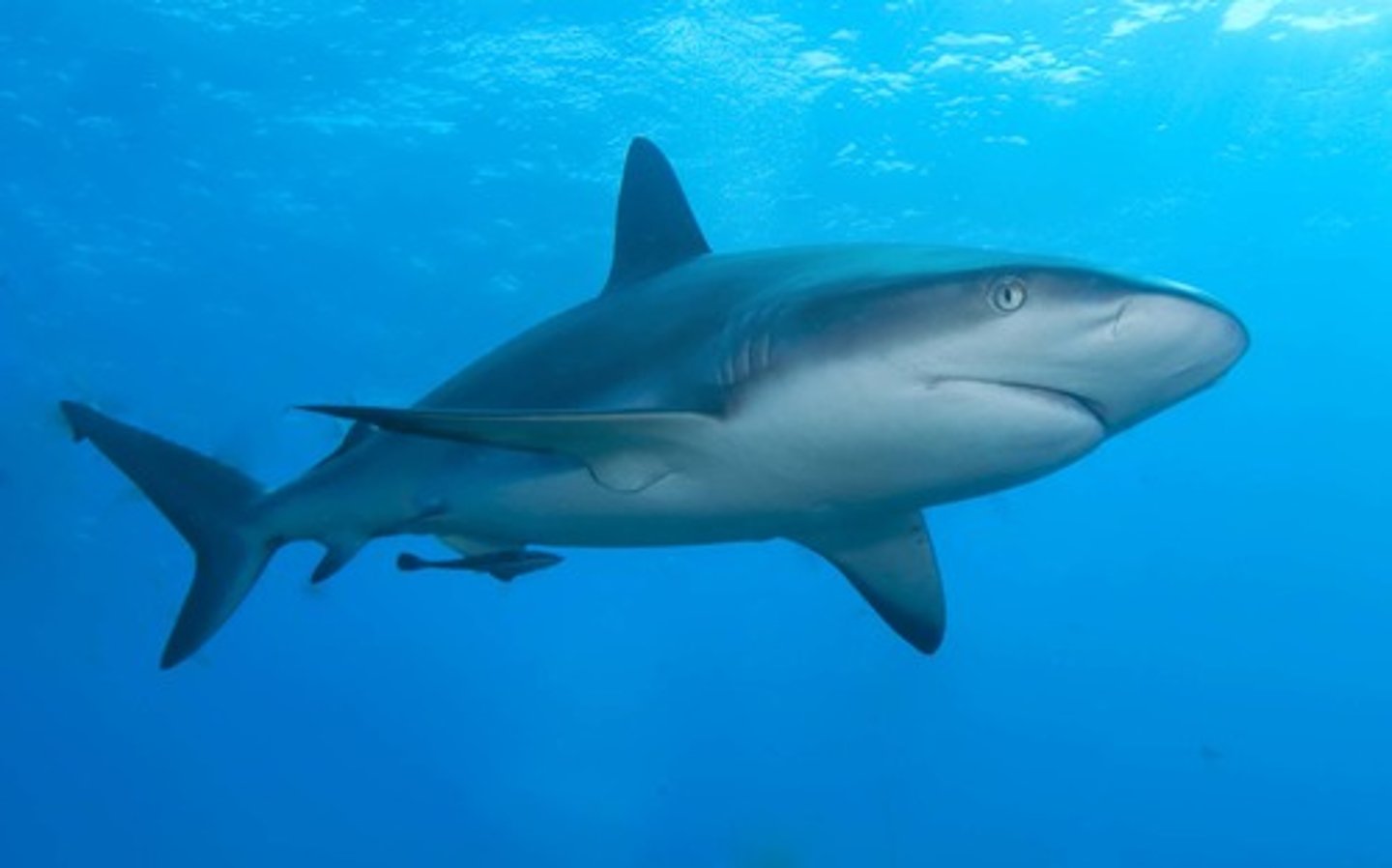
Class Chondrichthyes
Cartilaginous fish: sharks, skates, and rays; known for internal fertilization

Classes Actinopterygii (ray finned) & Sarcopterygii (lobe finned)
Bony fish; known for their bony skeleton, presence of a swim bladder and operculum; lobe finned fish are known for lung development
Acanthodians
The first known fish to have paired fins and jaws

Excretory System of fish
contain a urinary bladder and kidneys
Olfactory bulbs
The part of the brain that connects to specialized nerve cells found in shark nostrils; allow for keen chemoreption
Jacobson's organ
in the roof of the mouth of reptiles and is sensitive to odors
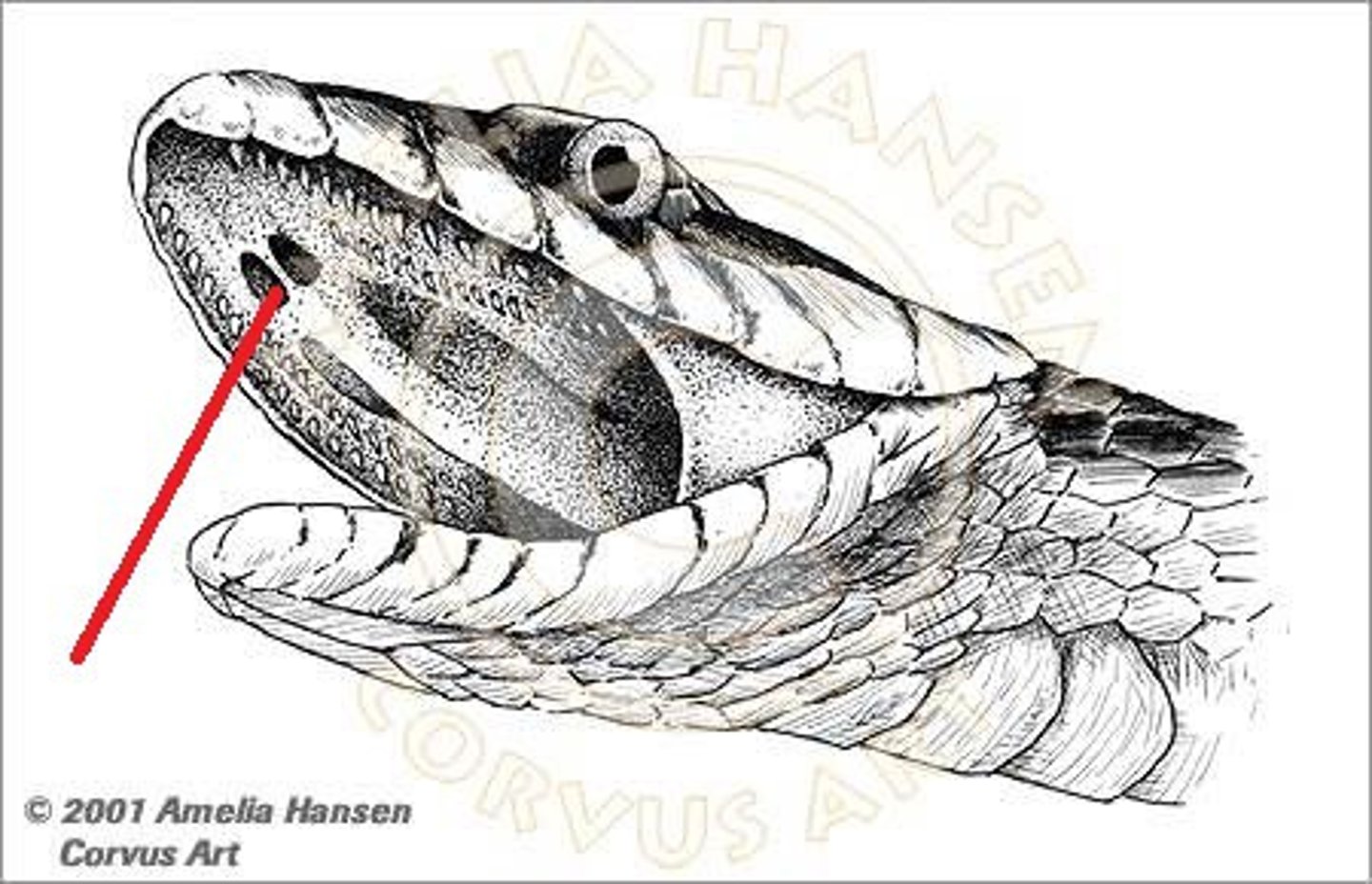
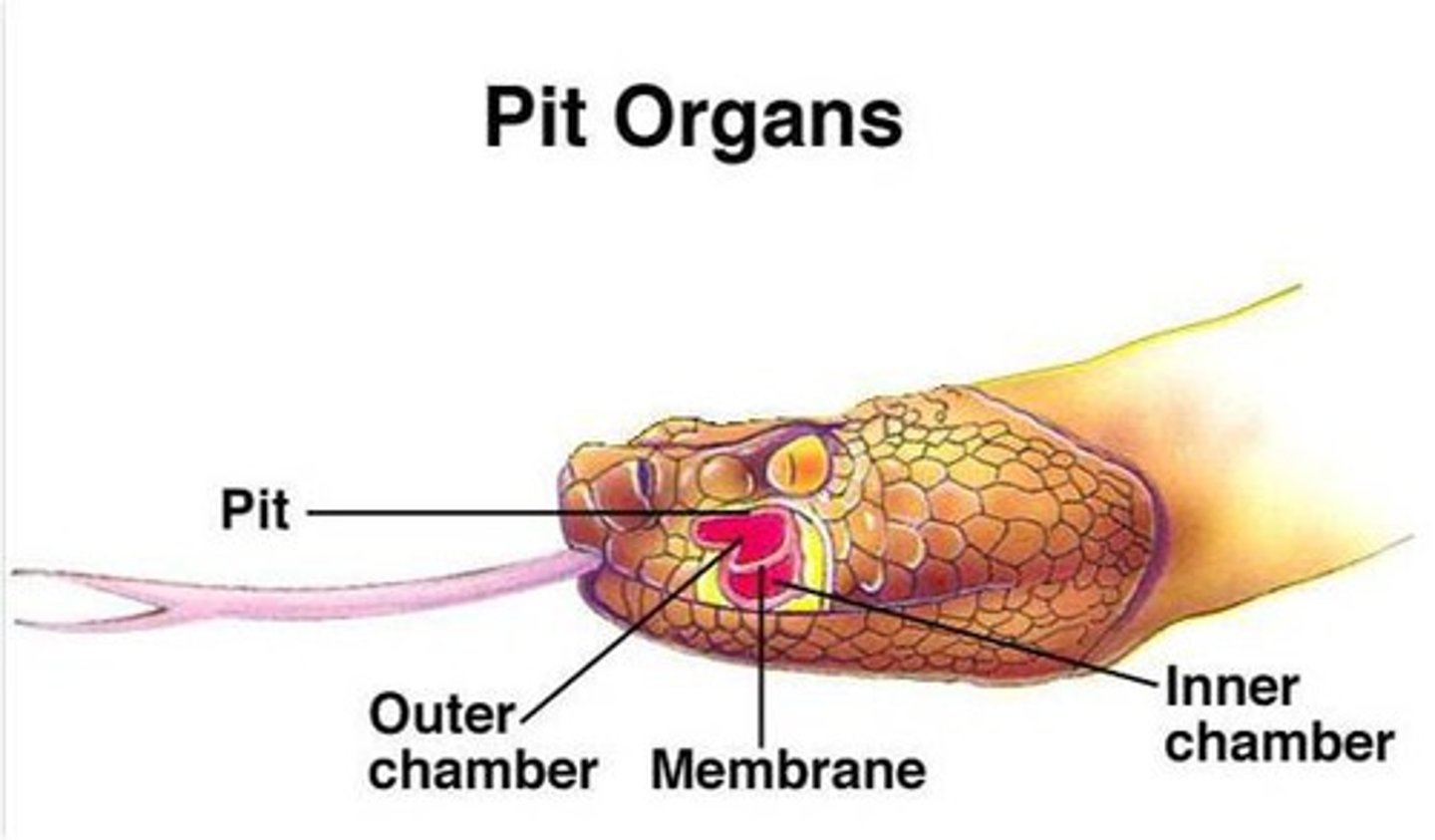
Pit organs
heat sensitive pits in snakes found below each eye
Ectotherm
animal that warms its body by absorbing heat from its surroundings (use behavior to move around in response to what the animal needs to maintain the narrow range required to survive)

Endotherm
metabolism creates internal body heat; most have fur or feathers to retain heat (mammals & birds)

Viviparity
(mainly mammals, some lizards & snakes)
NO SHELL; Young stay inside mother until mature enough to be born; Nutrition comes from placenta

Ovoviviparity
(only some reptiles)
Eggs may be laid shortly before hatching; Eggs hatch inside mother; Nutrition from yolk

Oviparity
(most reptiles, all birds, 3 species of mammals)
Each egg in enclosed in a tough protective shell; Eggs are deposited in a safe place;
Nutrition from yolk

Placenta
structure which nutrients & oxygen are transferred from mother to embryo (mainly mammals, some lizards & snakes)
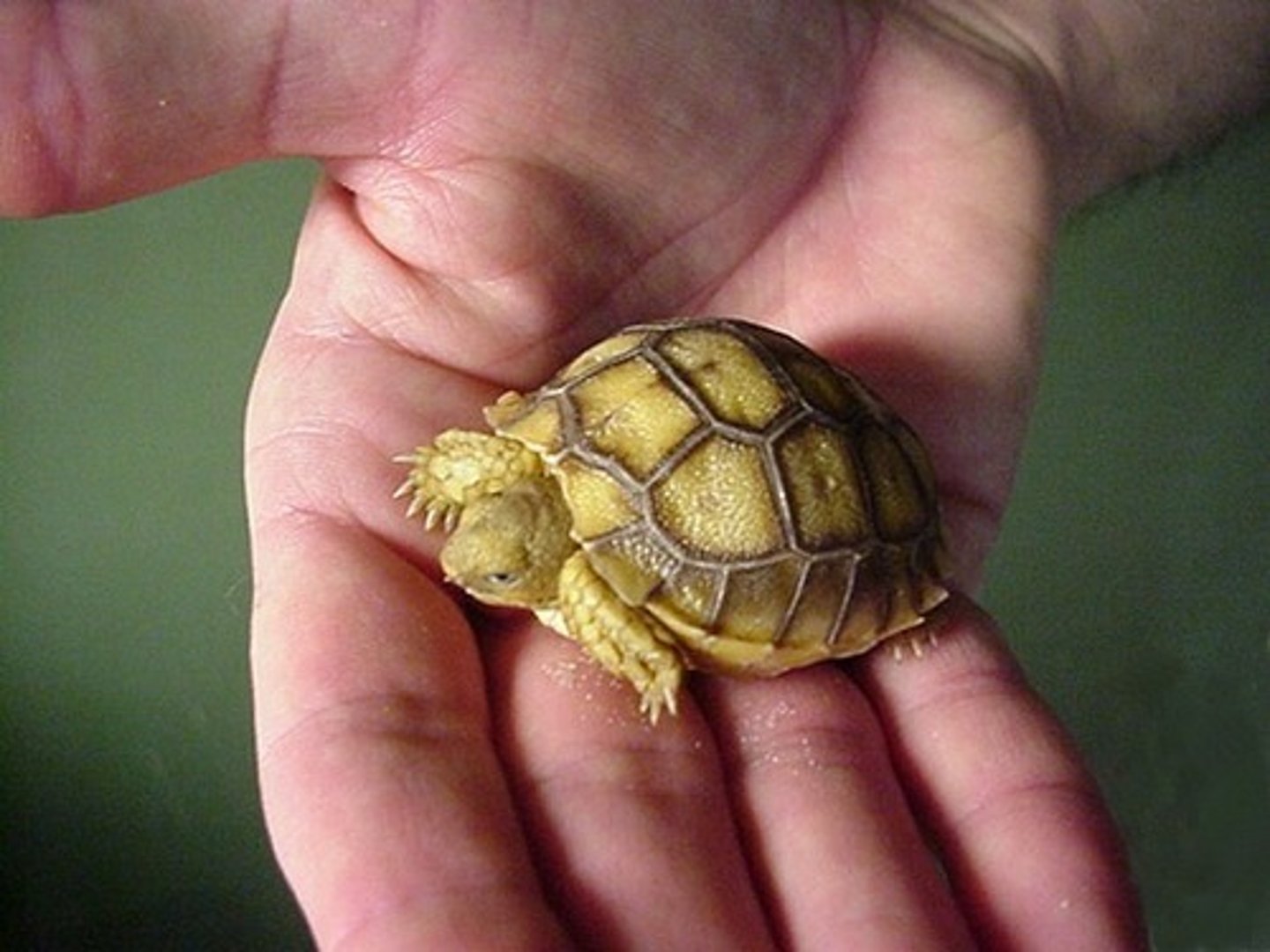
Carapace
the dorsal part of the shell of a turtle or tortoise

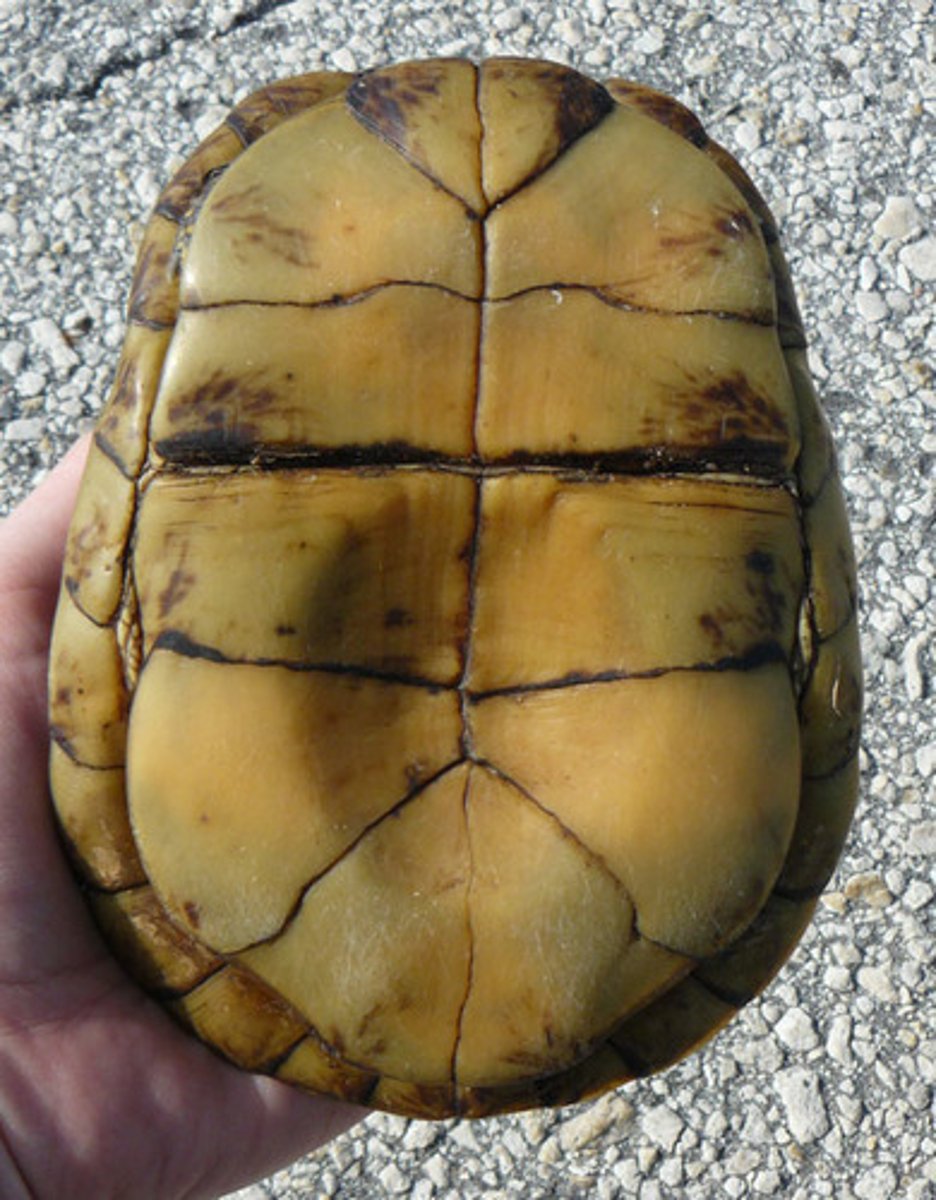
Plastron
the ventral part of the shell of a turtle or tortoise

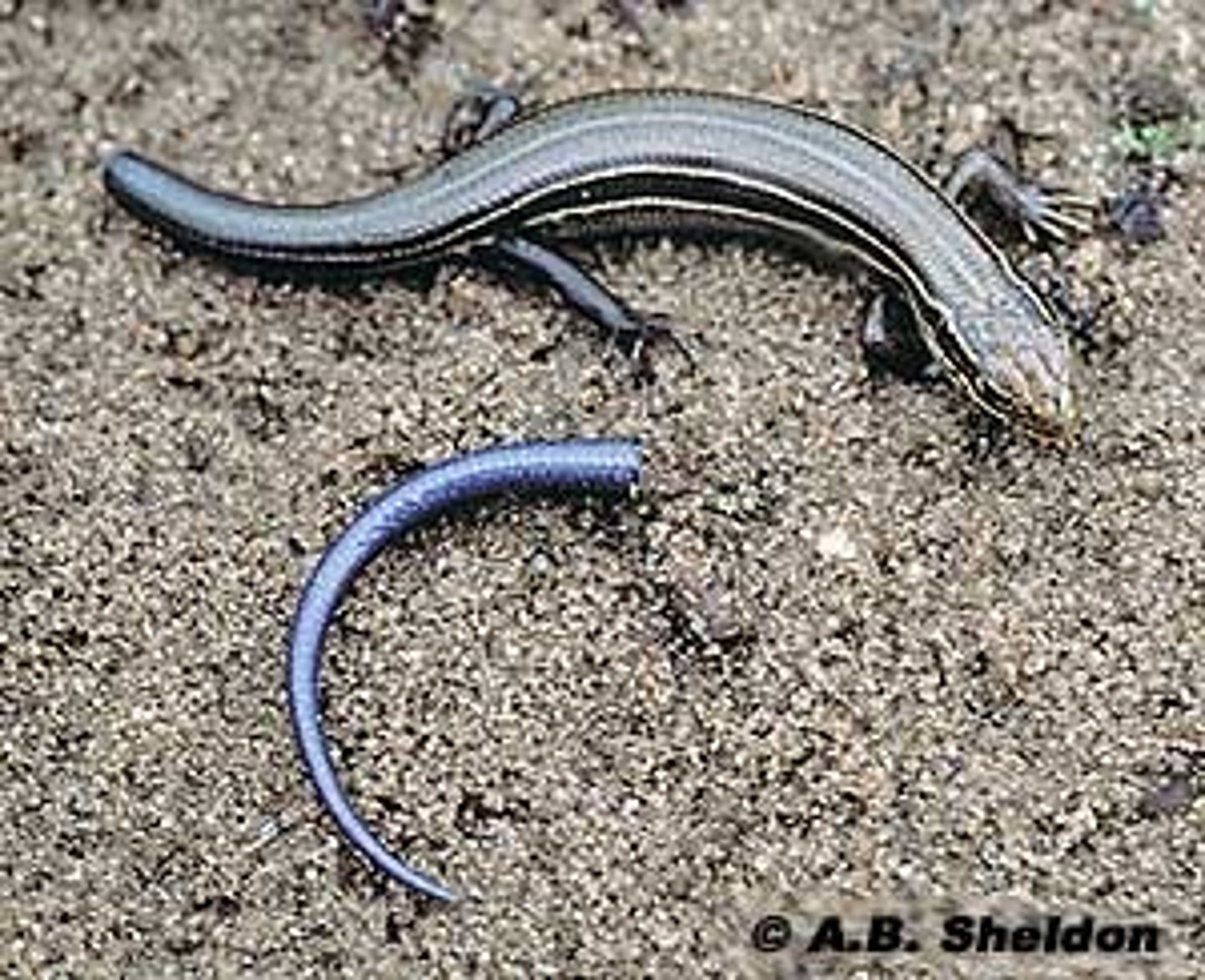
Autotomy
the ability of an animal to detach its tail or other body part and survive

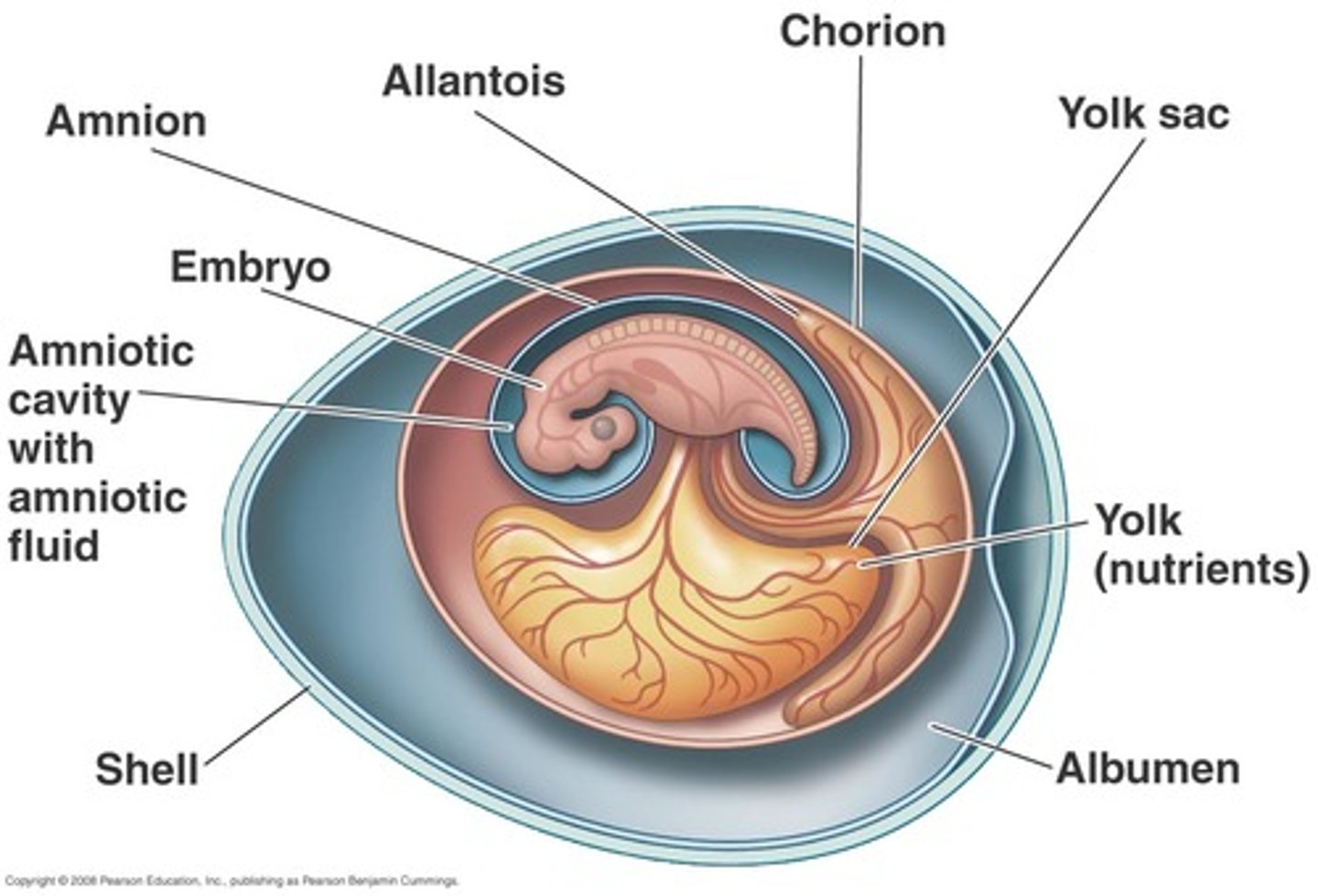
Amnion
thin membrane enclosing the fluid that the embryo floats in
(1 of 4 watertight membranes that makes the amniotic egg)
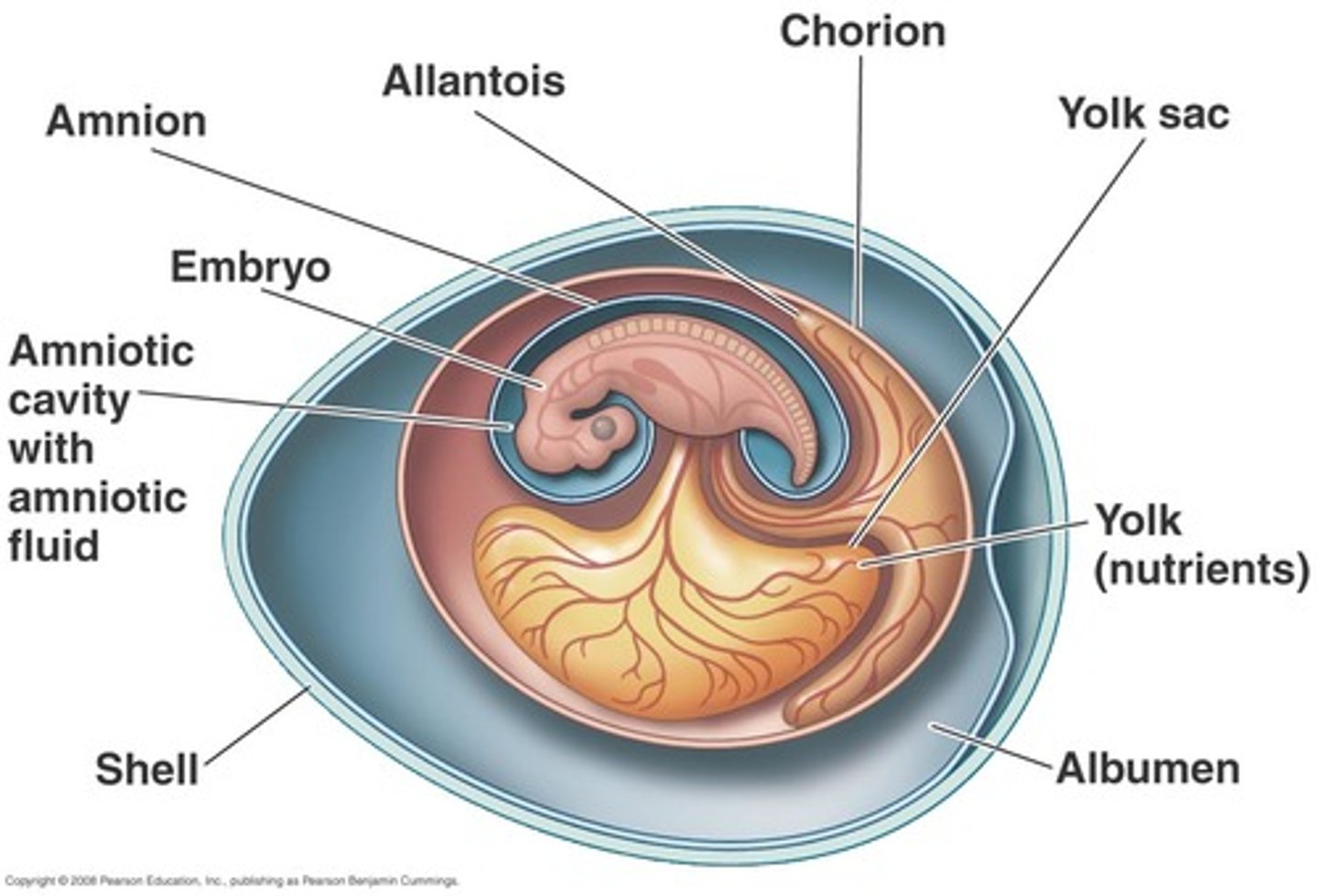
Yolk sac
encloses the yolk; which is the food for the developing embryo
(1 of 4 watertight membranes that makes the amniotic egg)
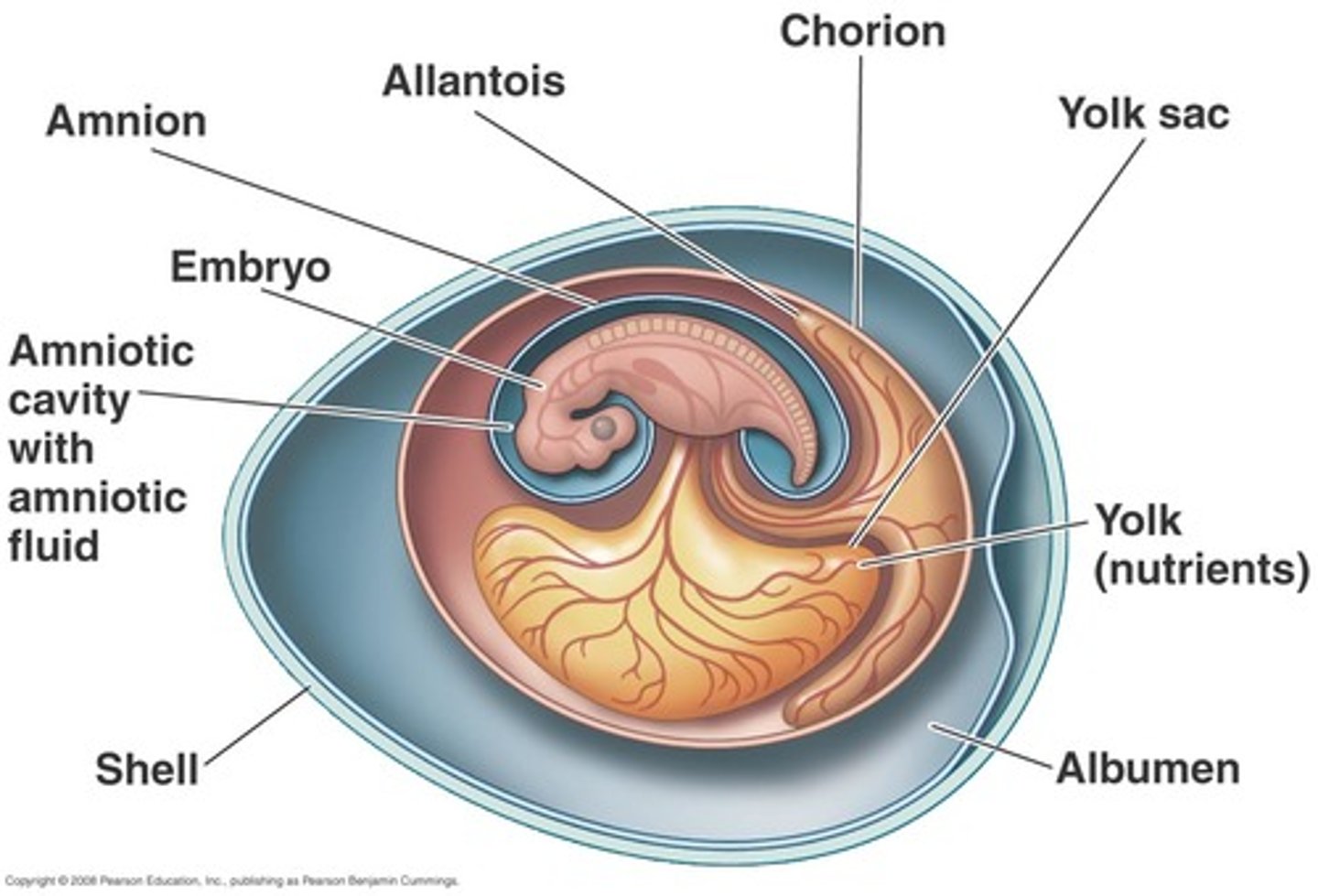
Allantois
stores waste produced by the embryo; vessels exchange gases
(1 of 4 watertight membranes that makes the amniotic egg)
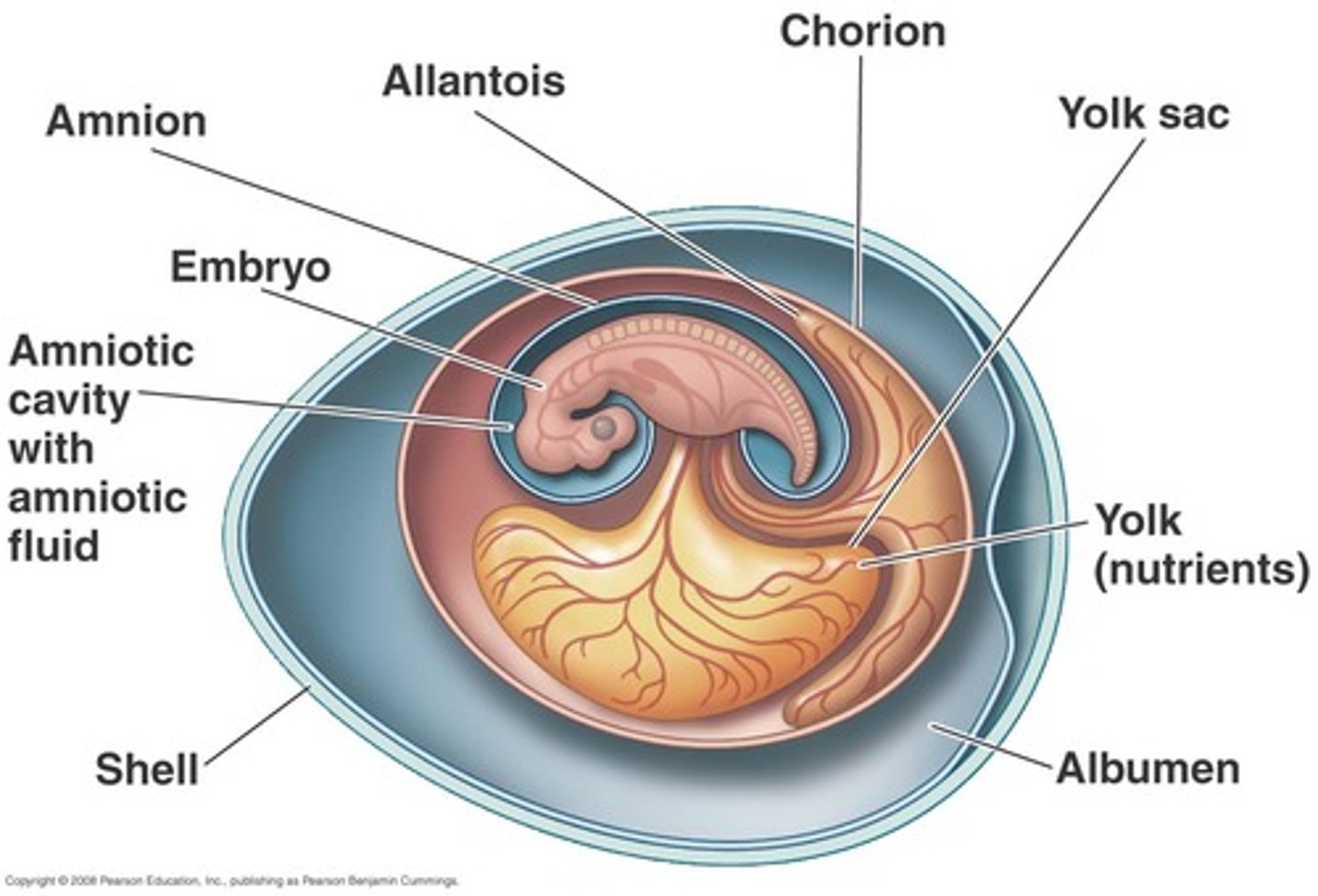
Chorion
provides protection; surrounds other membranes (outermost membrane)
(1 of 4 watertight membranes that makes the amniotic egg)
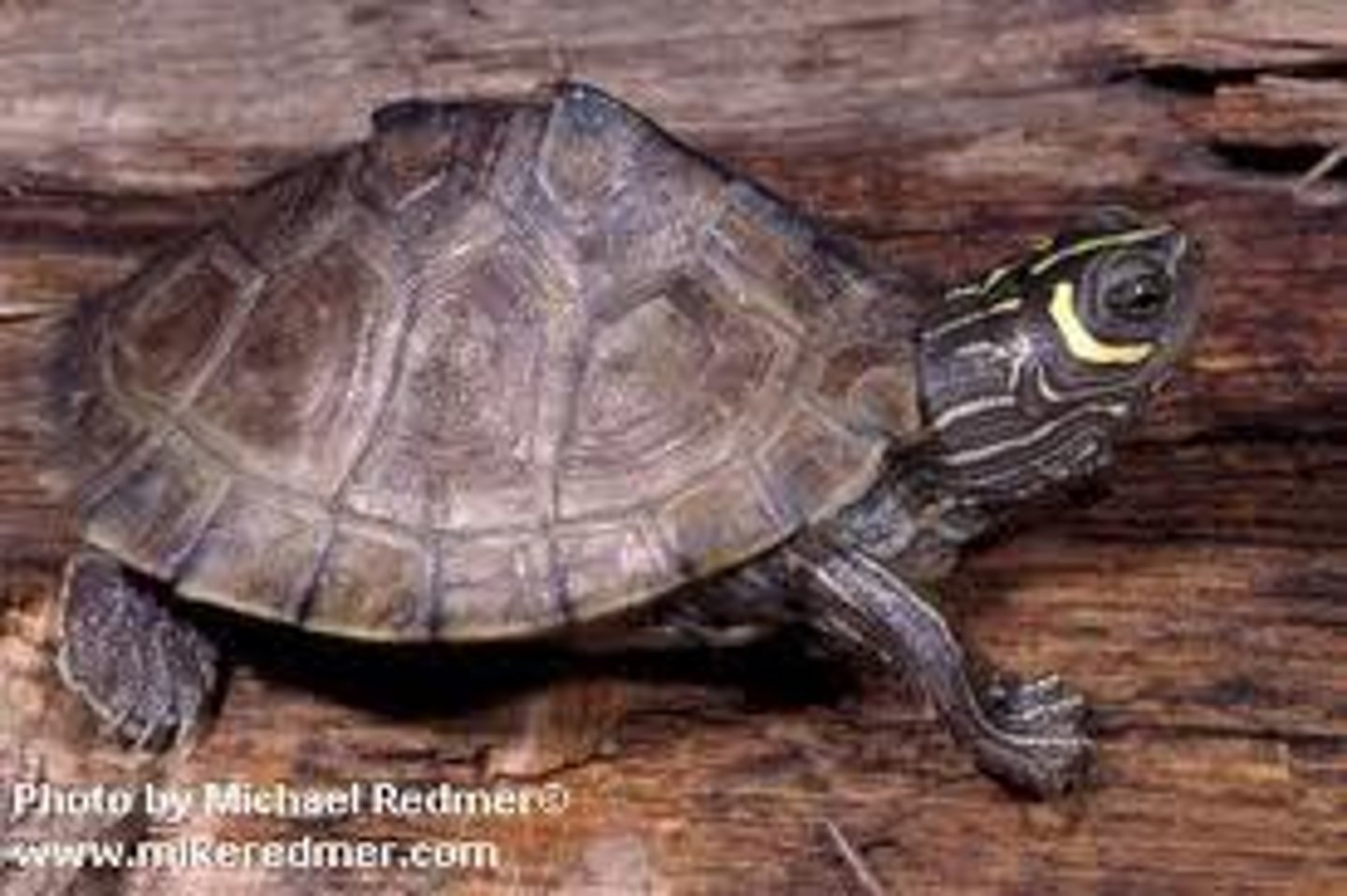
Order Chelonia
Earliest fossil ("oldest reptiles"), body covered by a shell, beak instead of teeth
Ex: turtles (aquatic) & tortoise (terrestrial)

Order Crocodilia
Reptiles that are the most closely related to dinosaurs; known for having a 4 chambered heart, caring for their young; and having a valve to cover the opening to the lungs
Ex: Alligators & Crocodiles
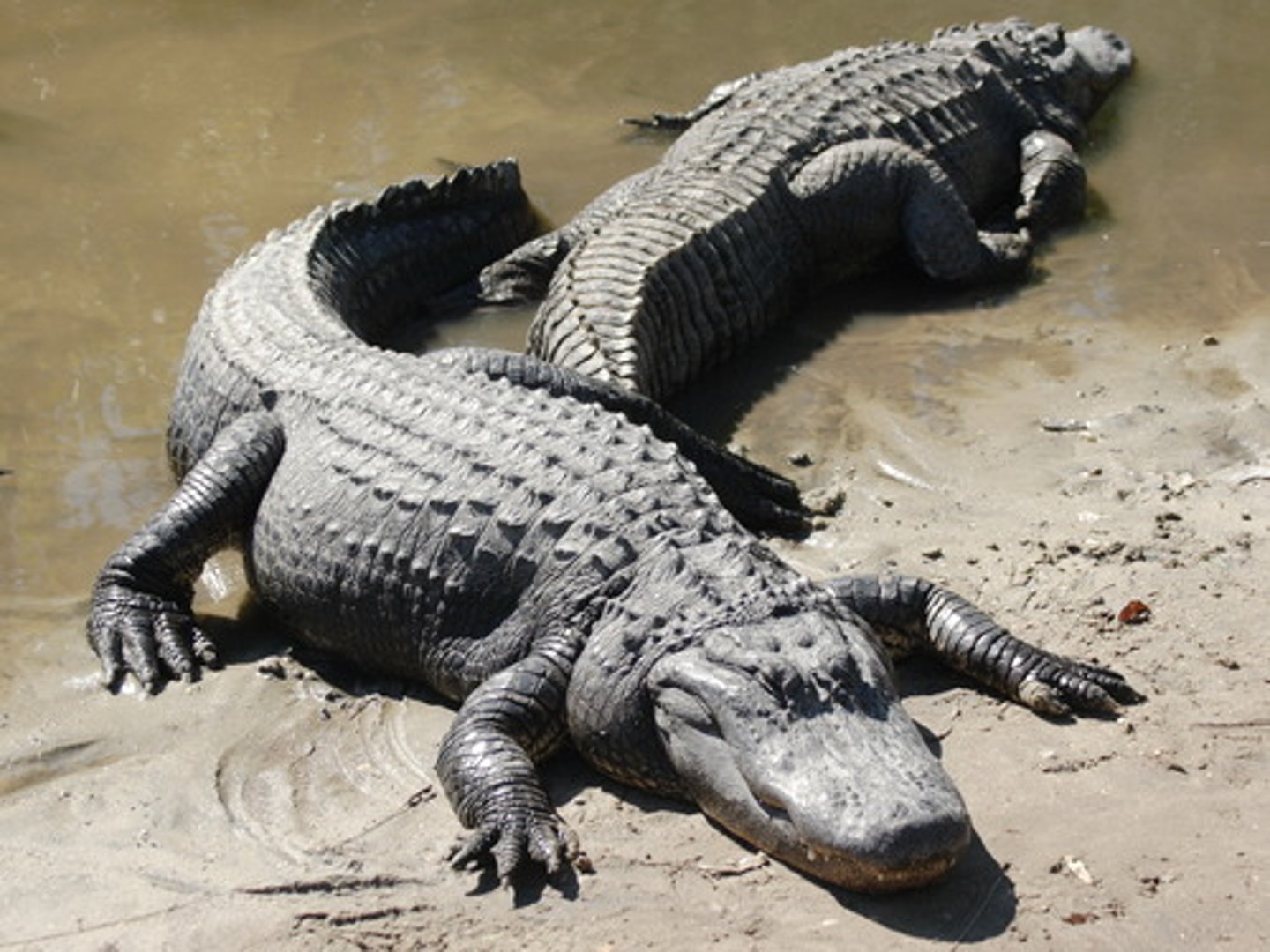

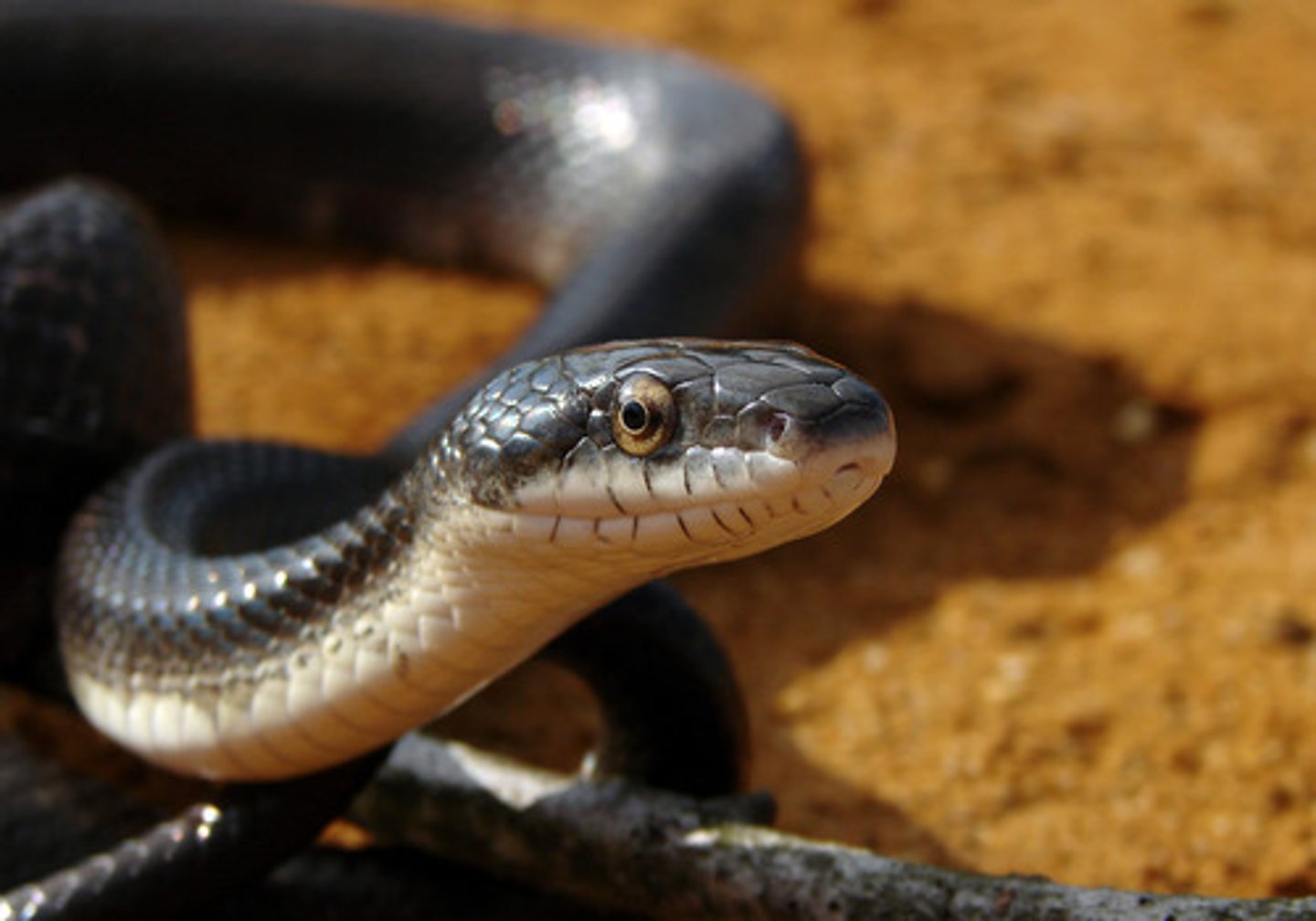
Order Squamata
Largest living reptilian order; known for many specialized adaptations
Ex: lizards and snakes

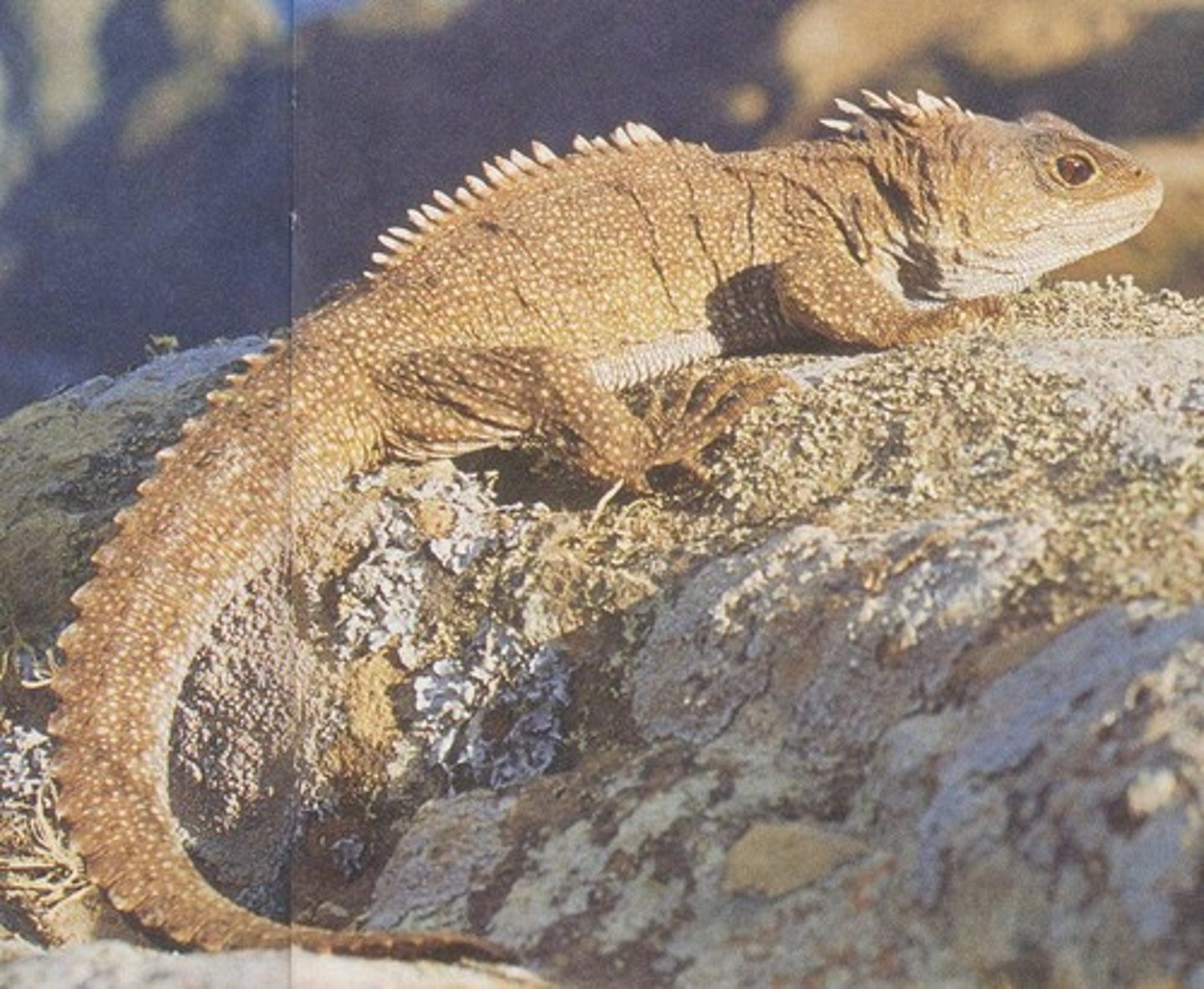
Order Rhynchocephalia
Nicknamed the Ancient Reptiles (though not the oldest); known for being active at low temperatures; named for the spiny crest that runs down their back
Ex: Tuatara

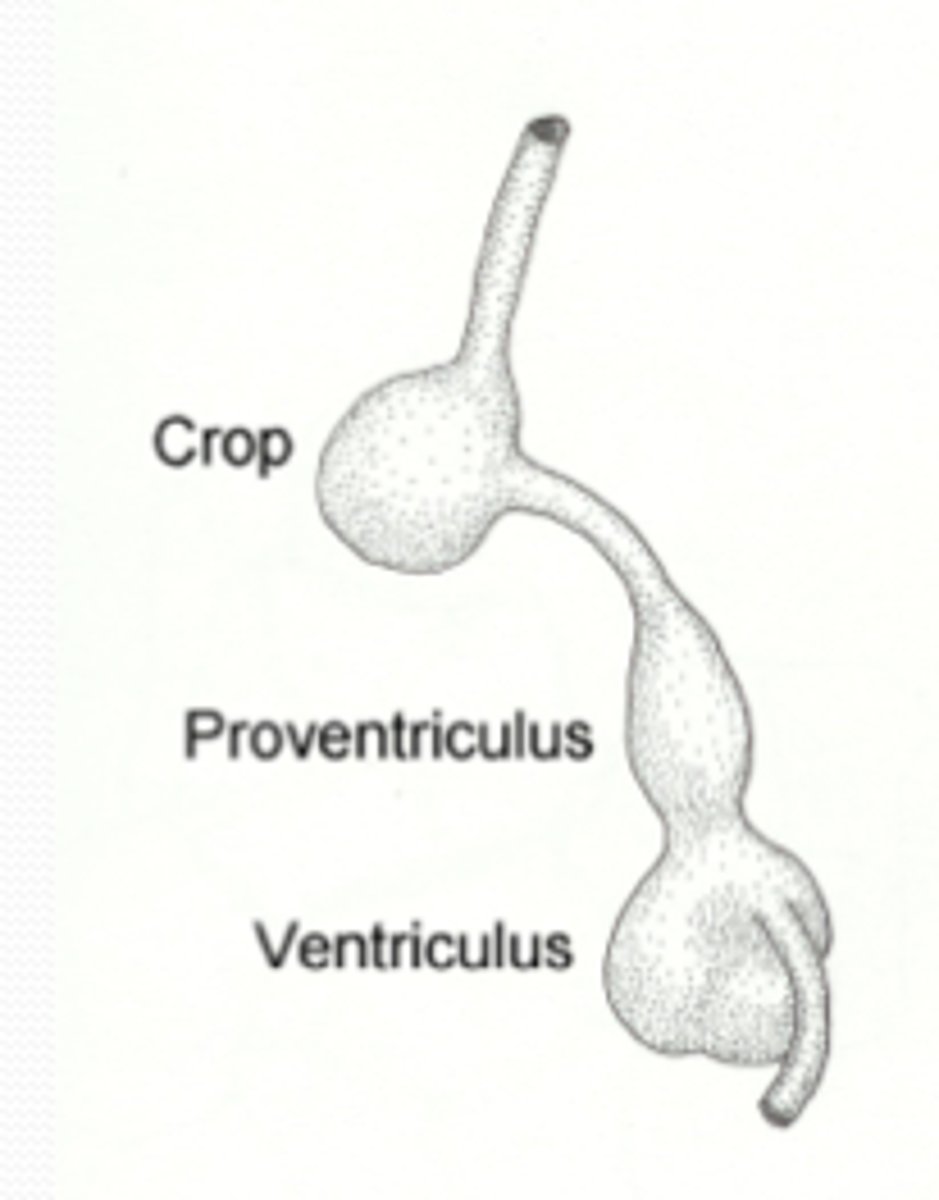
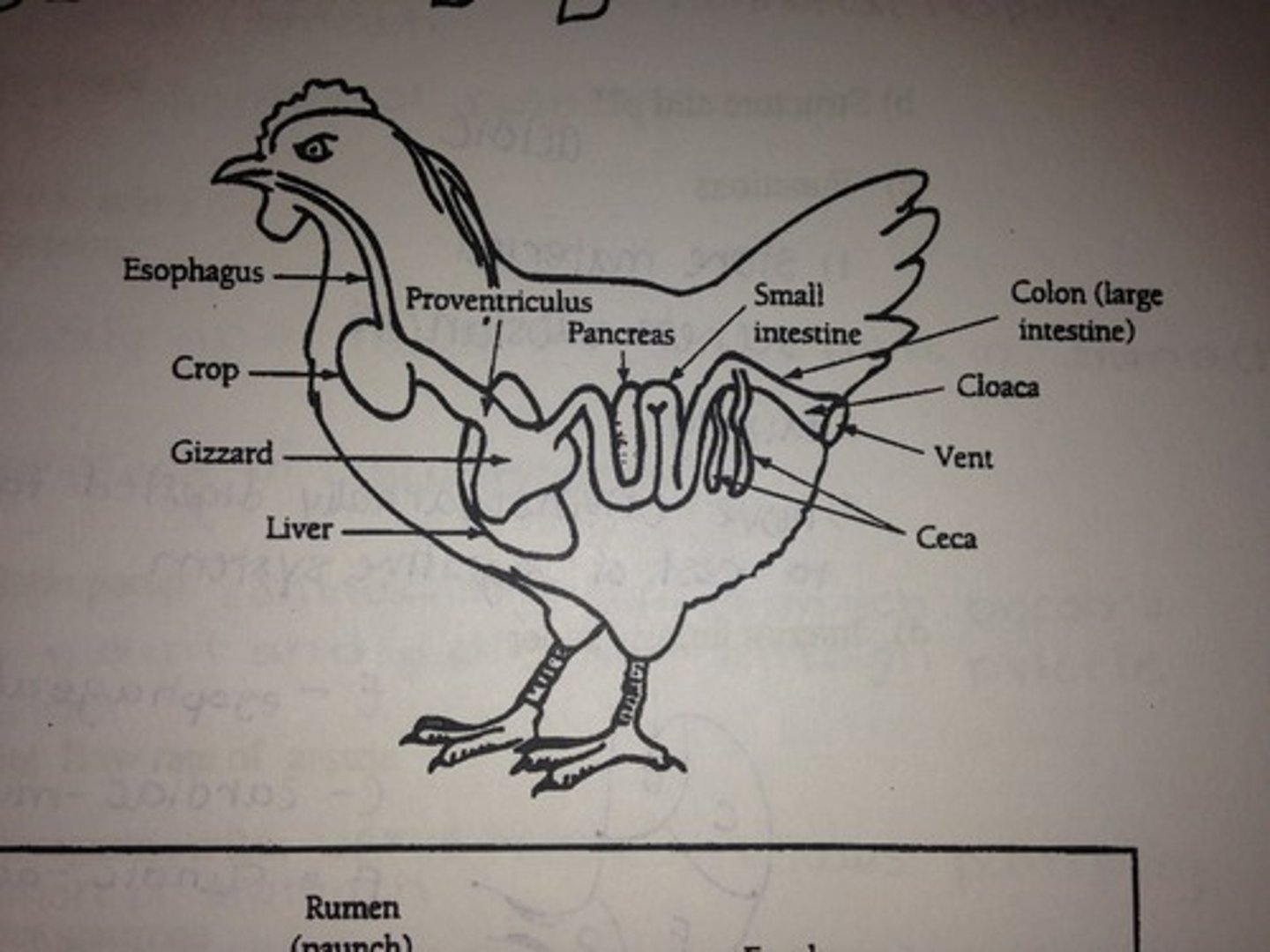
crop
follows the esophagus passageway in a bird's digestive tract; used to store and moisten food
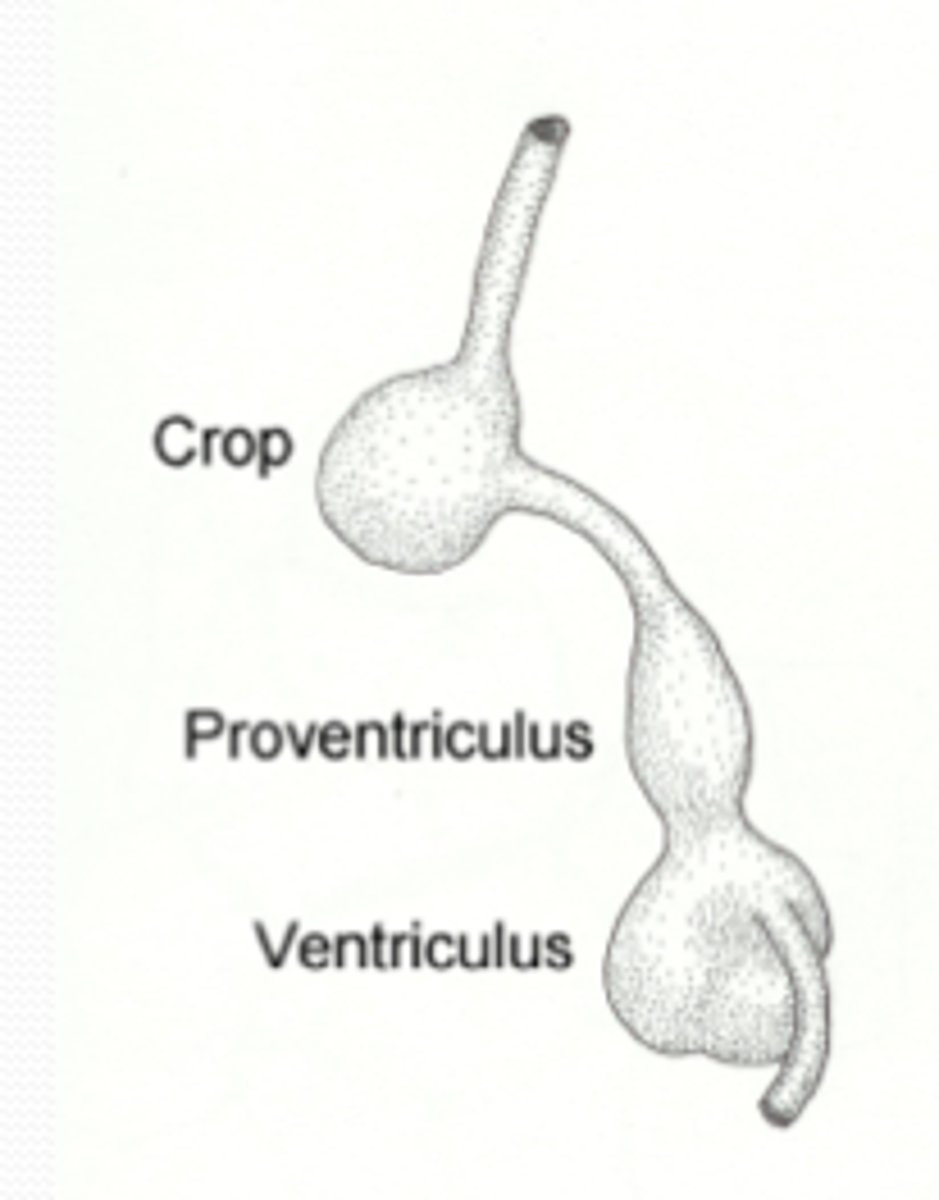
proventriculus
1st chamber of a bird stomach; where food breakdown begins using digestive enzymes (chemical)
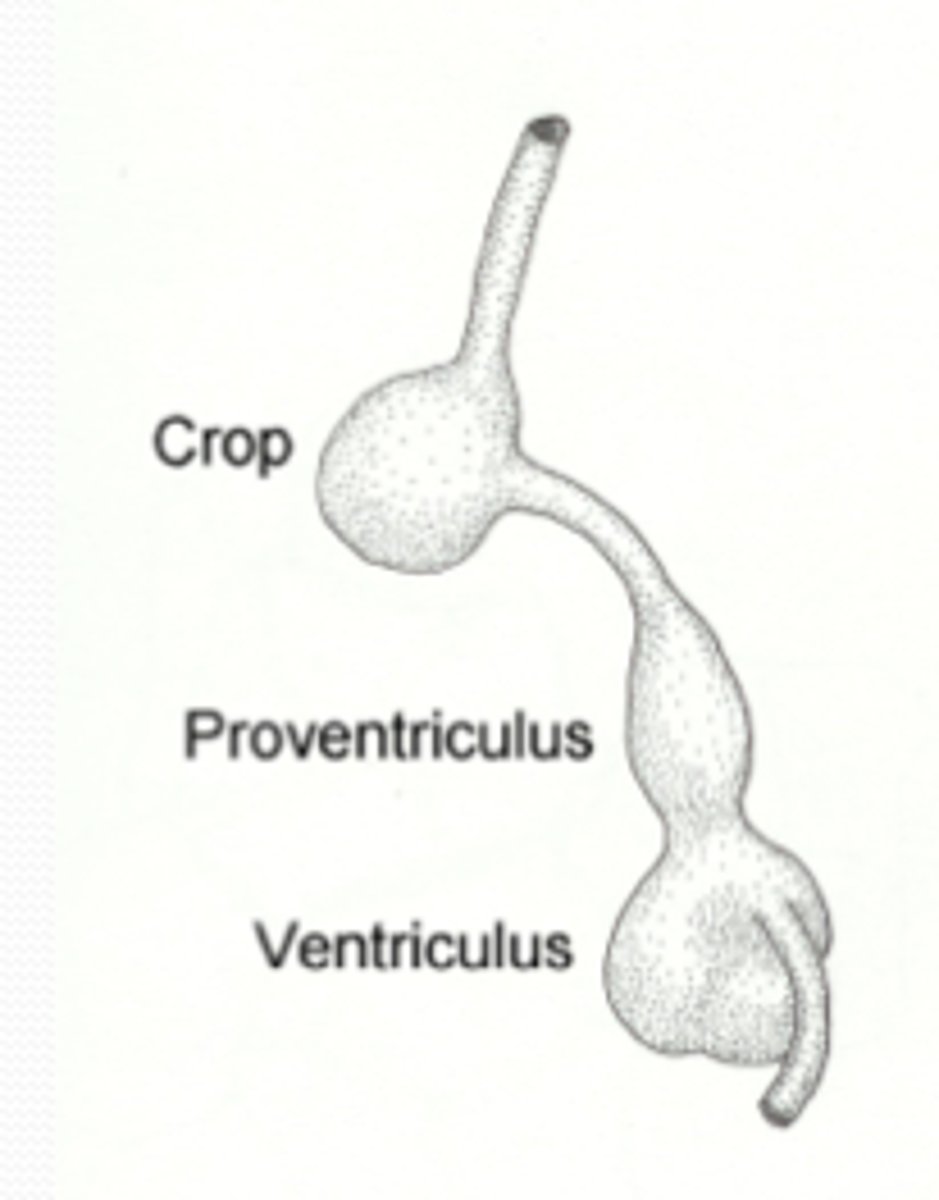
gizzard (ventriculus)
2nd chamber of a bird's stomach; muscular part (mechanical); may contain stones they swallow
precocial young
many eggs produced; long incubation; young can move about and feed themselves as soon as they hatch; Ex: Ducks and chickens

altricial young
few eggs produced; shorter incubation; hatch blind, naked, and helpless; Ex: hawks, pigeons

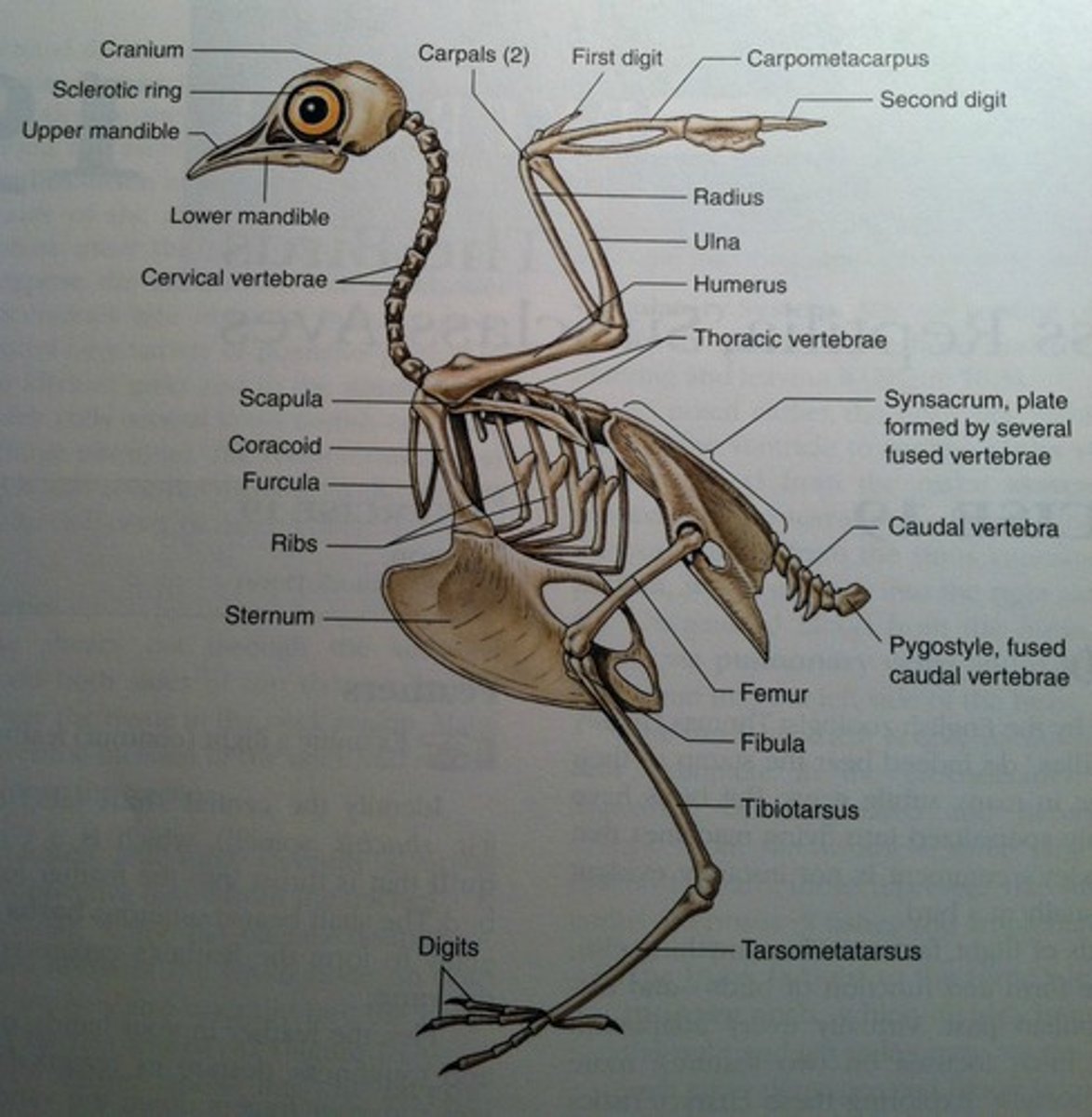
bones in the wing of a bird
humerus, radius, and ulna (just like in a human arm)
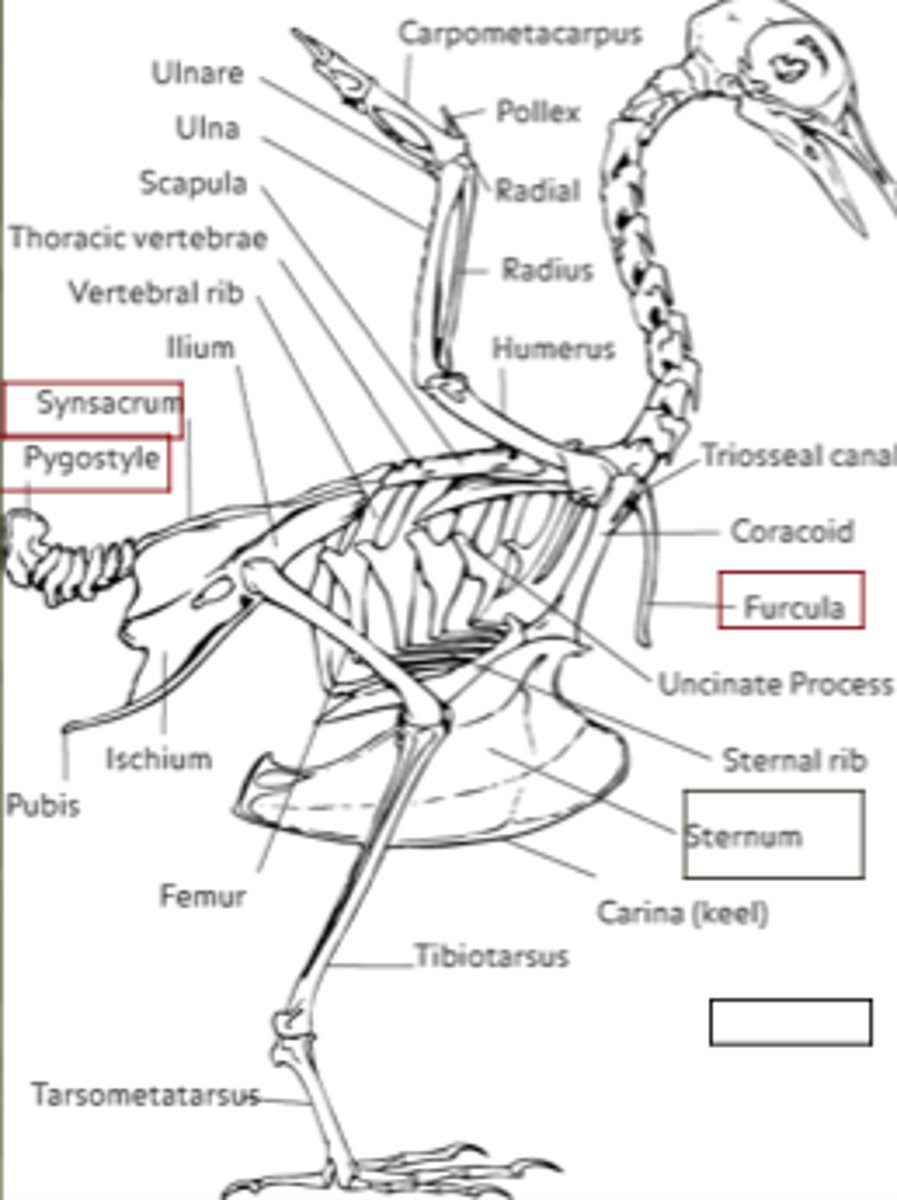
Skeleton modifications for flight
lightweight hollow bones, fusion of bones (i.e. pelvic girdle), and the pygostyle (tail)
Order Apodiformes
Hummingbird

Order Galliformes
Turkey

Order Psittachiformes
Parrot, parakeet, cockatiel
Colorful hooked beak; 2 toes forward, 2 toes backward; many threatened with extinction

Order Struthioniformes
Ostrich

Order Passeriformes
Robin, Blue Jay, Cardinal
Largest order; song birds; 3 toes forward, 1 toe backward

Order Strigiformes
Owls
Nocturnal, Sharp beak & talons

Order Anseriformes
Swans, geese, ducks
Waterfowl; webbed feet, flat bill; precocial young

Bird Respiratory System
Highly divided with air sacs in addition to the lungs; most efficient respiratory system of ALL terrestrial vertebrates
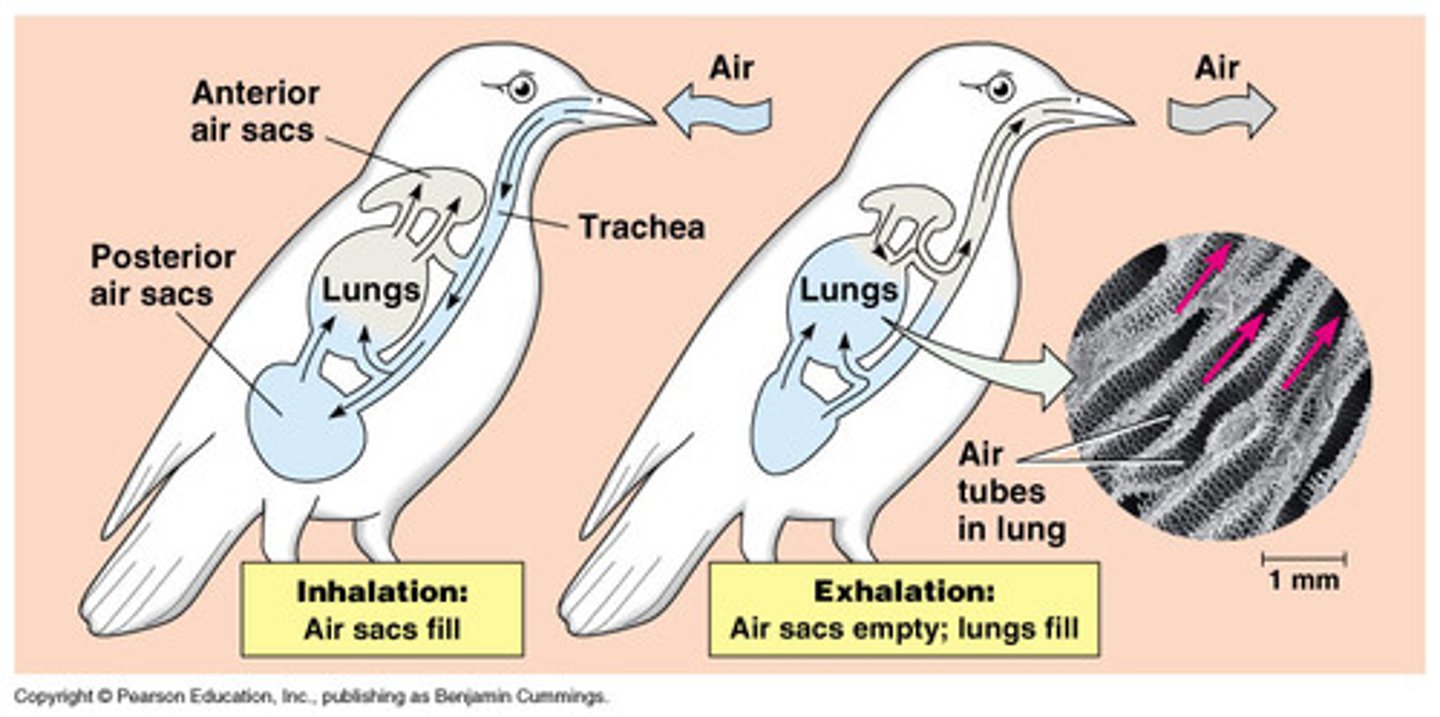
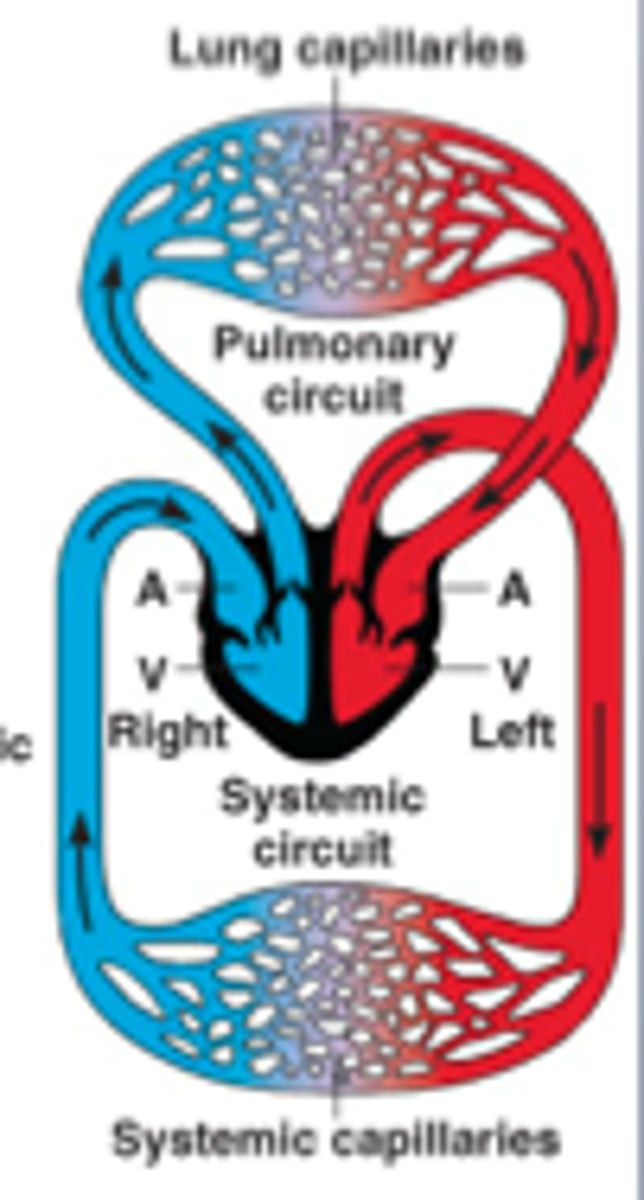
Bird Circulatory System
4 chambered heart; 2 atria & 2 ventricles; oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood do NOT mix
Bird Digestive System
No teeth (beak), food follows a pathway: esophagus, crop, proventriculus, gizzard, small intestine, large intestine, cloaca (rapid digestion)
Bird Skeletal System
Bones are thin and hollow (lightweight), many are fused
Bird Reproductive System
Internal fertilization; lay amniotic eggs (oviparous)

Feathers
modified reptilian scales; made of keratin; 3 types: down, contour, & flight
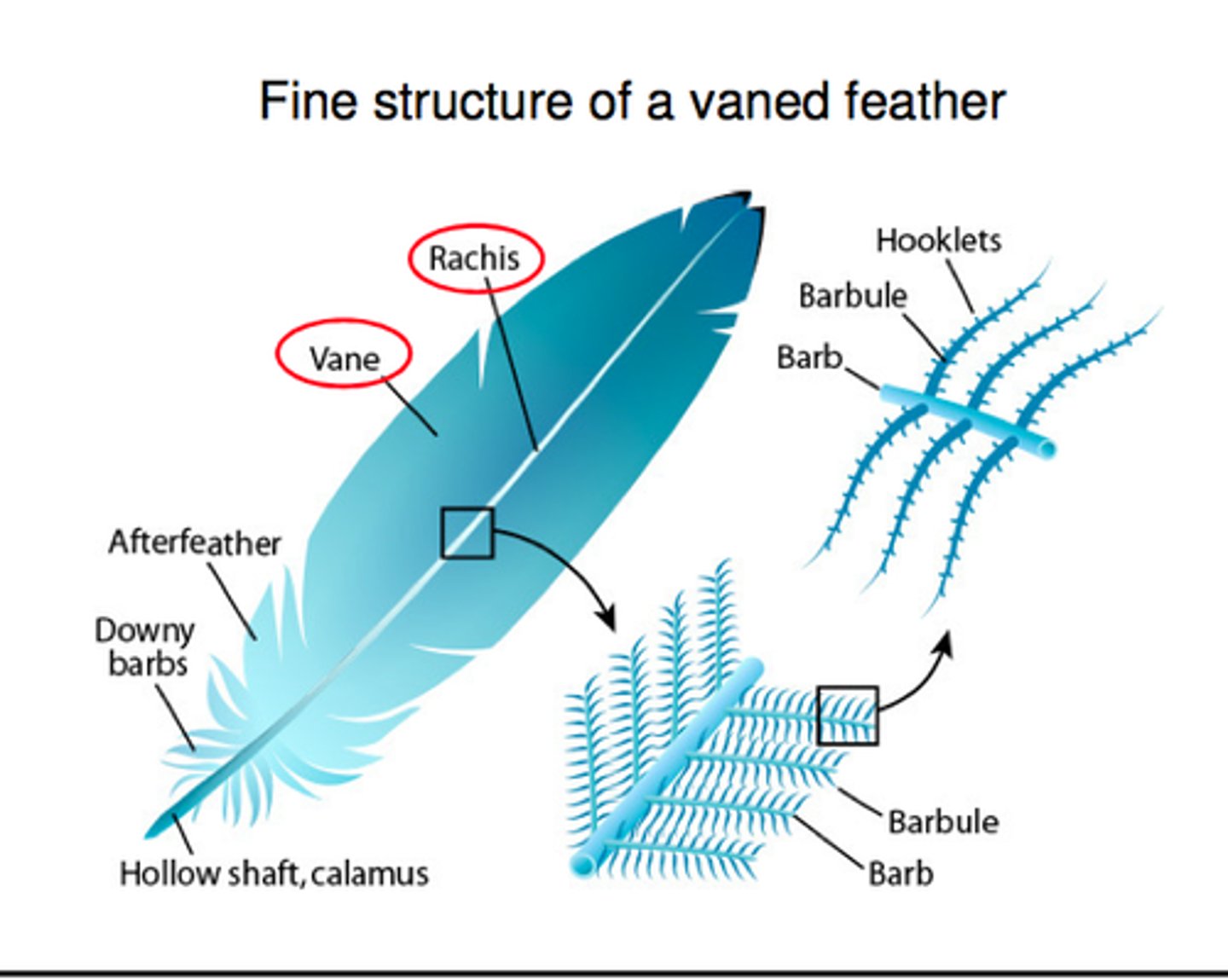
Preening
Process by which birds care for their feathers; use beaks to rub oil from the preen gland located at the base of the tail

Molting
Process by which birds shed their feathers

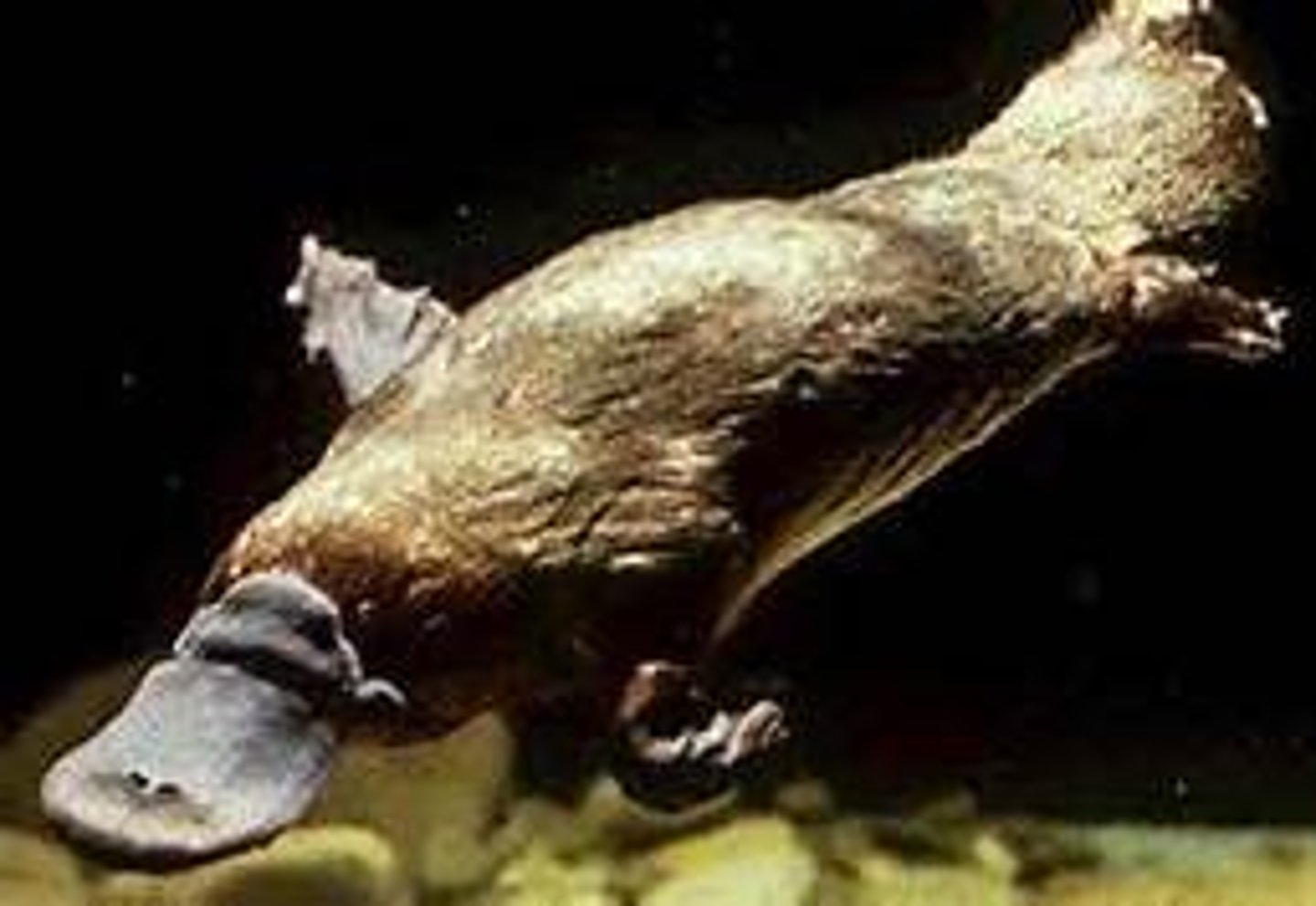
Order Monotremata
the group of oviparous (egg laying) mammals; ; Platypus in/near water & Echidna are terrestrial

Super Order Marsupialia
viviparous mammal; young's development within the mother is short then continues in a pouch
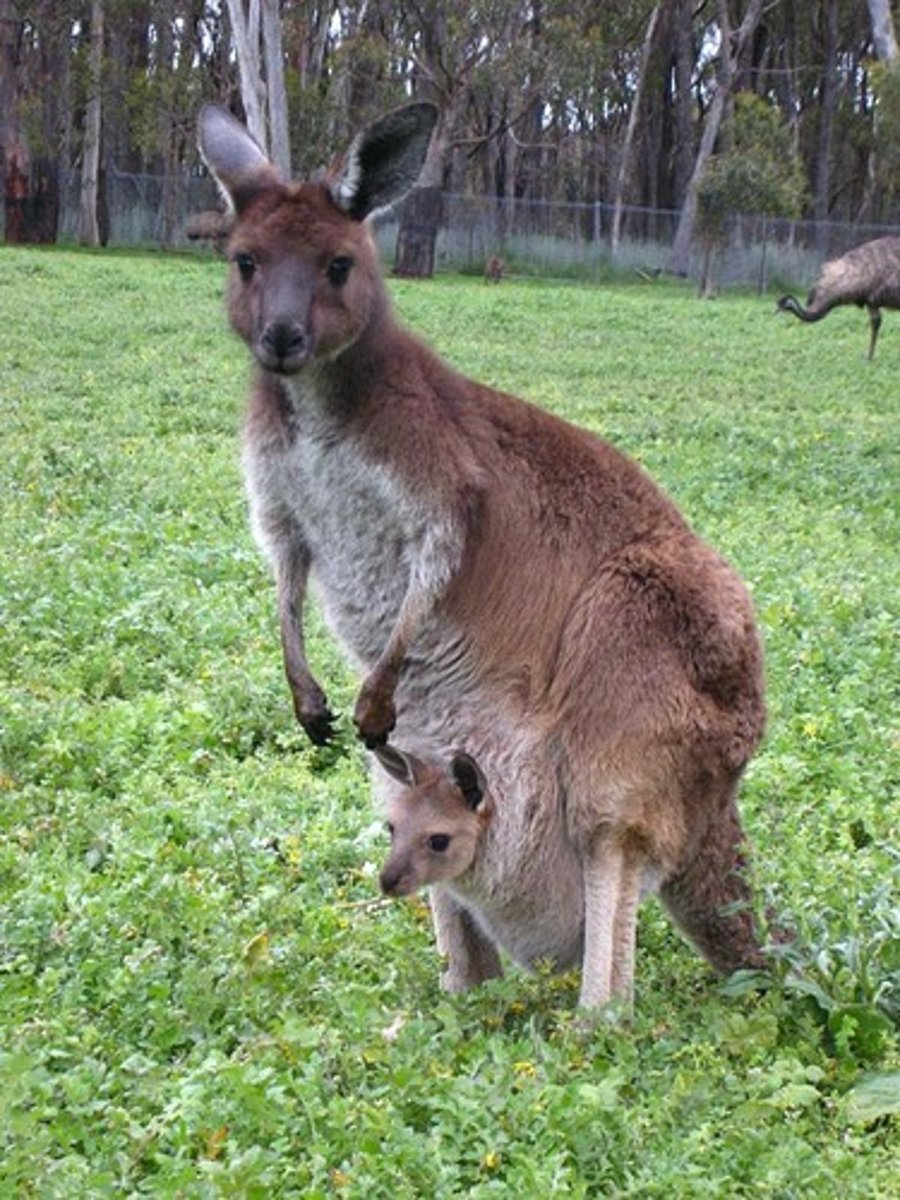

pinniped
an aquatic carnivore, such as a seal; uses modified limbs (flippers) to navigate through the water
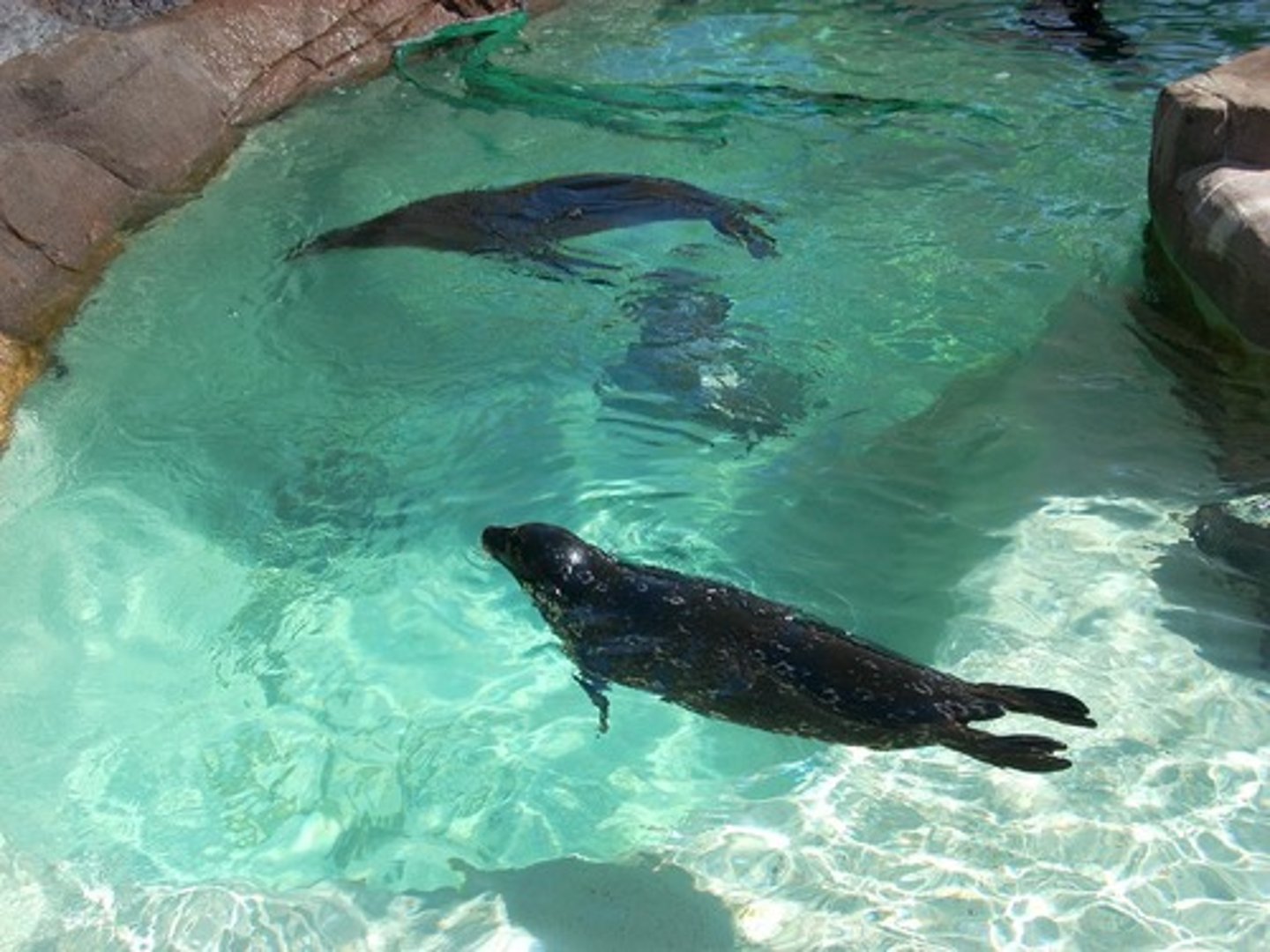

ungulate
mammal with hooves

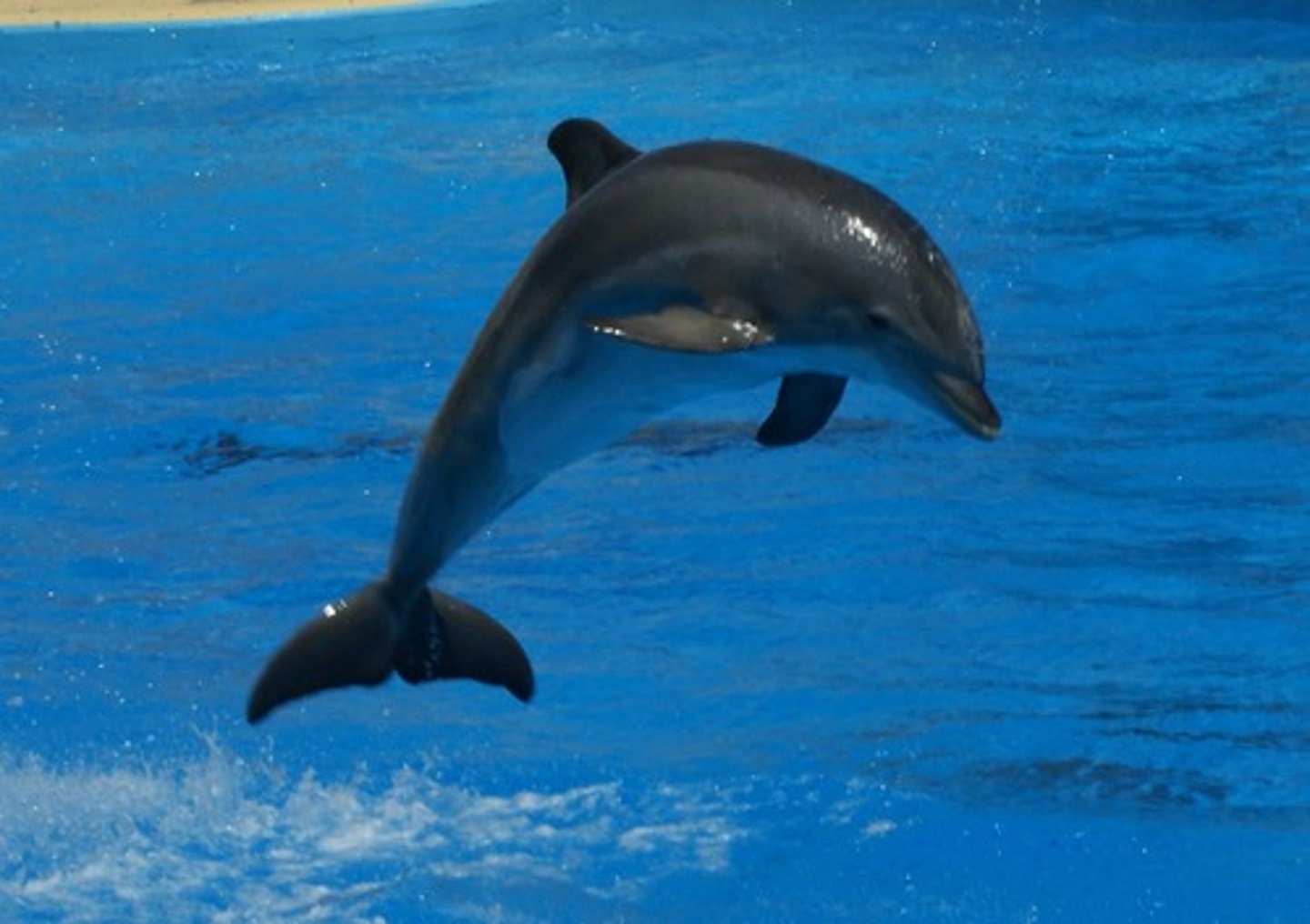
Order Cetacea
2 groups: Toothed & Baleen; they are the only mammals that spend their entire life in the water; Ex: a whale, dolphin or porpoise

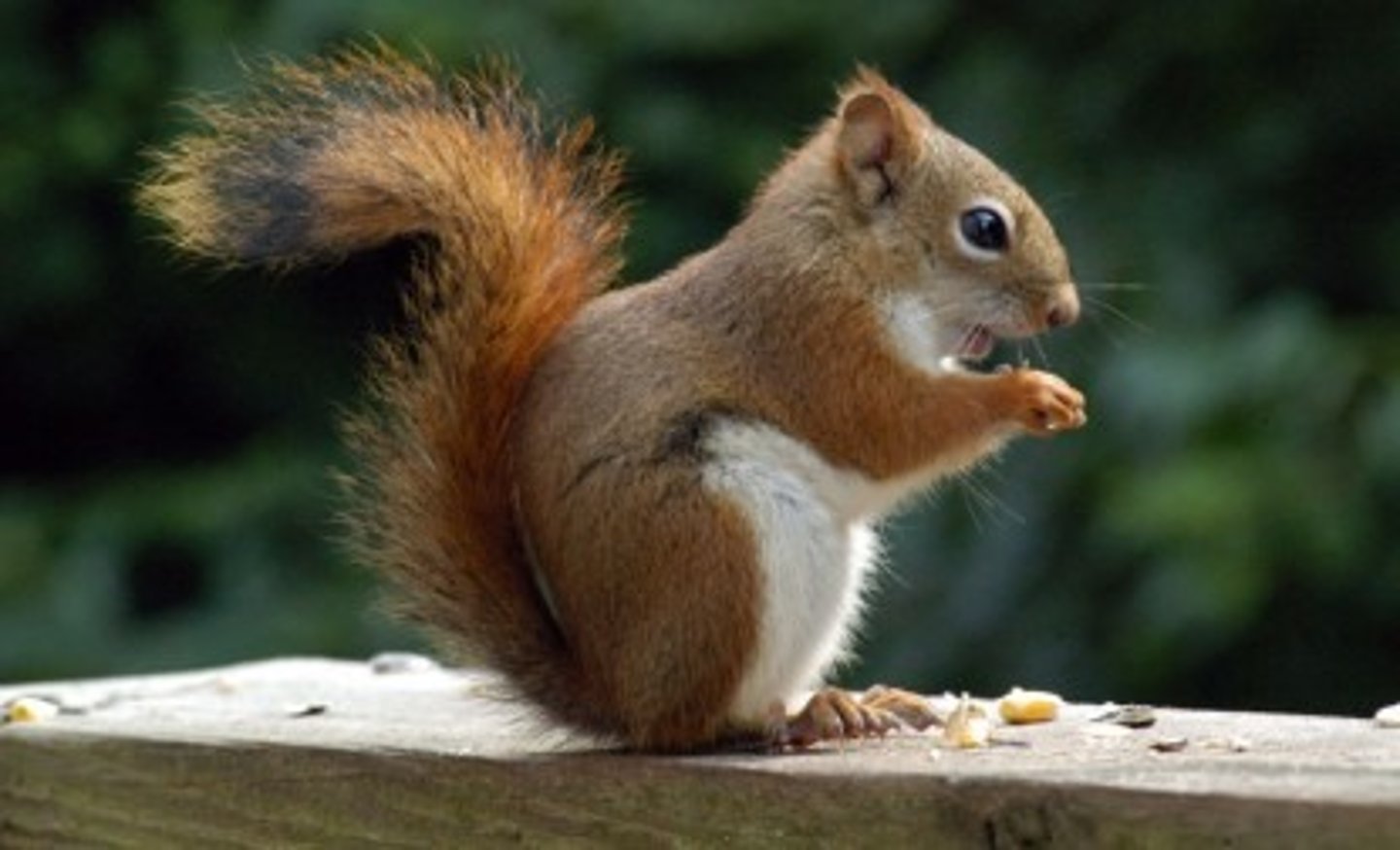
Order Rodentia
Largest Mammalian order; 2 sets of incisors that continuously grow; Ex: squirrel, chipmunk, rat, gopher, porcupine

Order Primates
Prosimians (lemur) & Arthropoids (monkey, ape, humans); have large brains, teeth for being omnivores; & forward facing eyes (depth perception)

Order Chiroptera
Modified front limb is a wing (leathery membrane-like skin stretched between finger bones to hind limb); Only mammals that fly; use ecolocation

Order Carnivora
Found everywhere; eat meat; several adaptations to be a successful hunter
Terrestrial: run well (dogs, cats, bears)
Aquatic: called pinnipeds, streamlined, return to land to sleep & give birth (seals, sea lions, otters)

Order Artiodactyla
Even number of toes; ungulates (have hooves); herbivores with a rumen full of bacteria to digest the plants they eat; Ex: Deer, Cattle, Pigs, Camels & Giraffes

Order Perissodactyla
Odd number of toes; ungulates (have hooves); herbivores with a cecum full of bacteria to digest the plants they eat; Ex: Horses, Rhinos, & Tapirs

Order Proboscidea
Elephants! Trunked nose; largest land mammal; feed 18 hours a day; modified incisors (tusks); 20 month gestation

Gestation
Period of time between fertilization & birth

Amphibian
"double life"; amphibians live on land and in the water; carnivorous
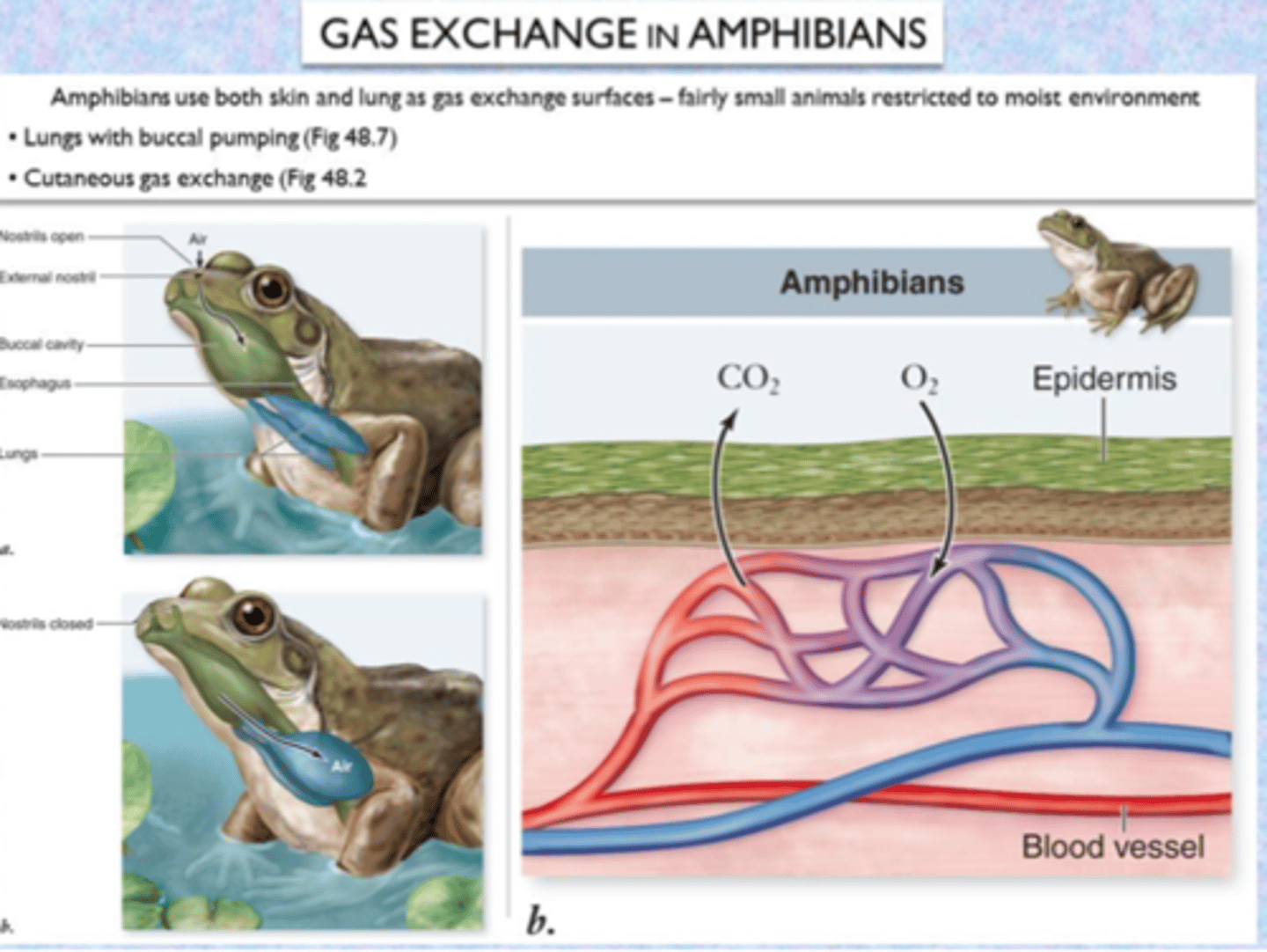
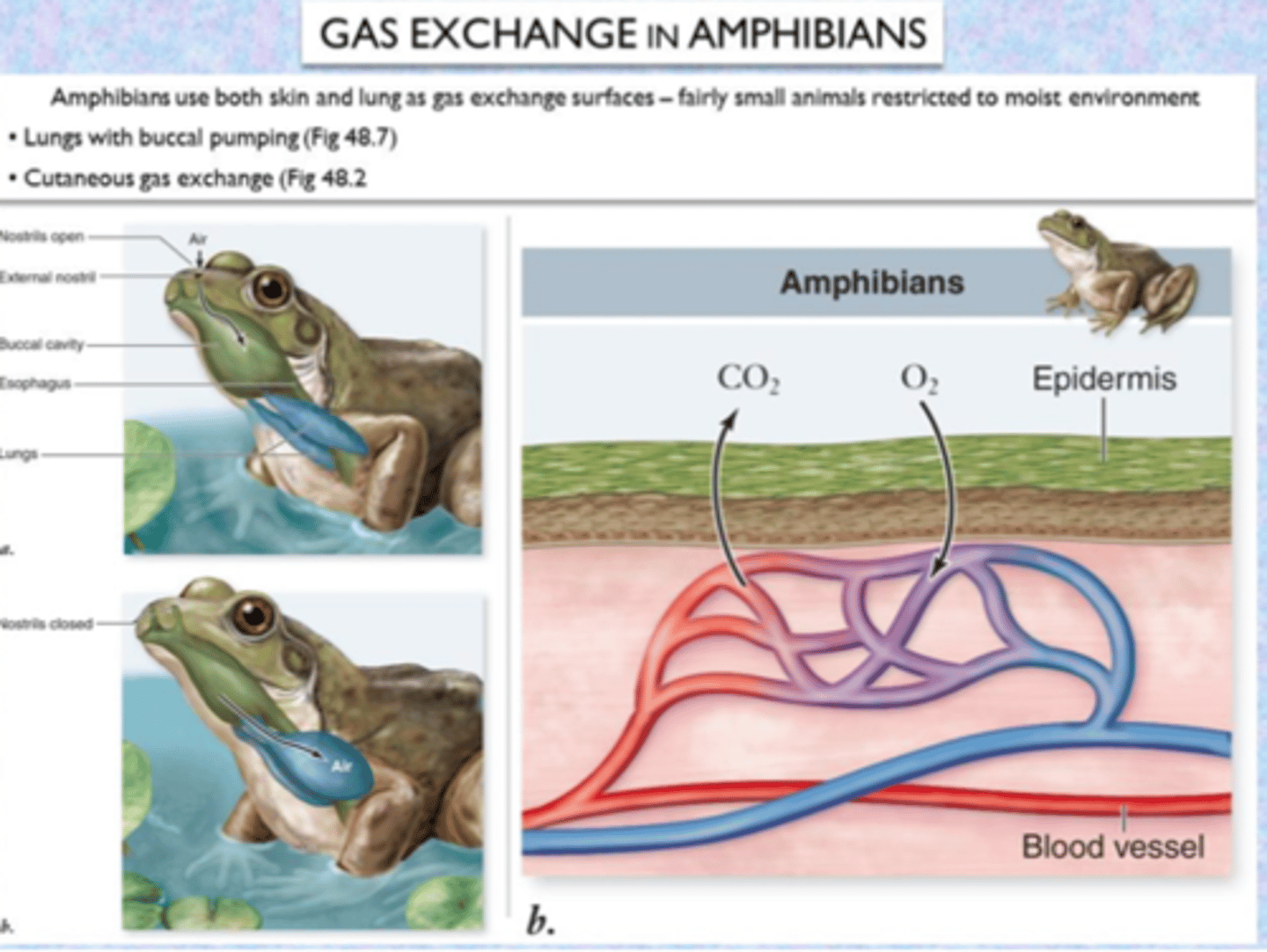
Amphibian Breathing
(Adult vs. Young)
Adult: through skin (cutaneous) & lungs
Young: through gills
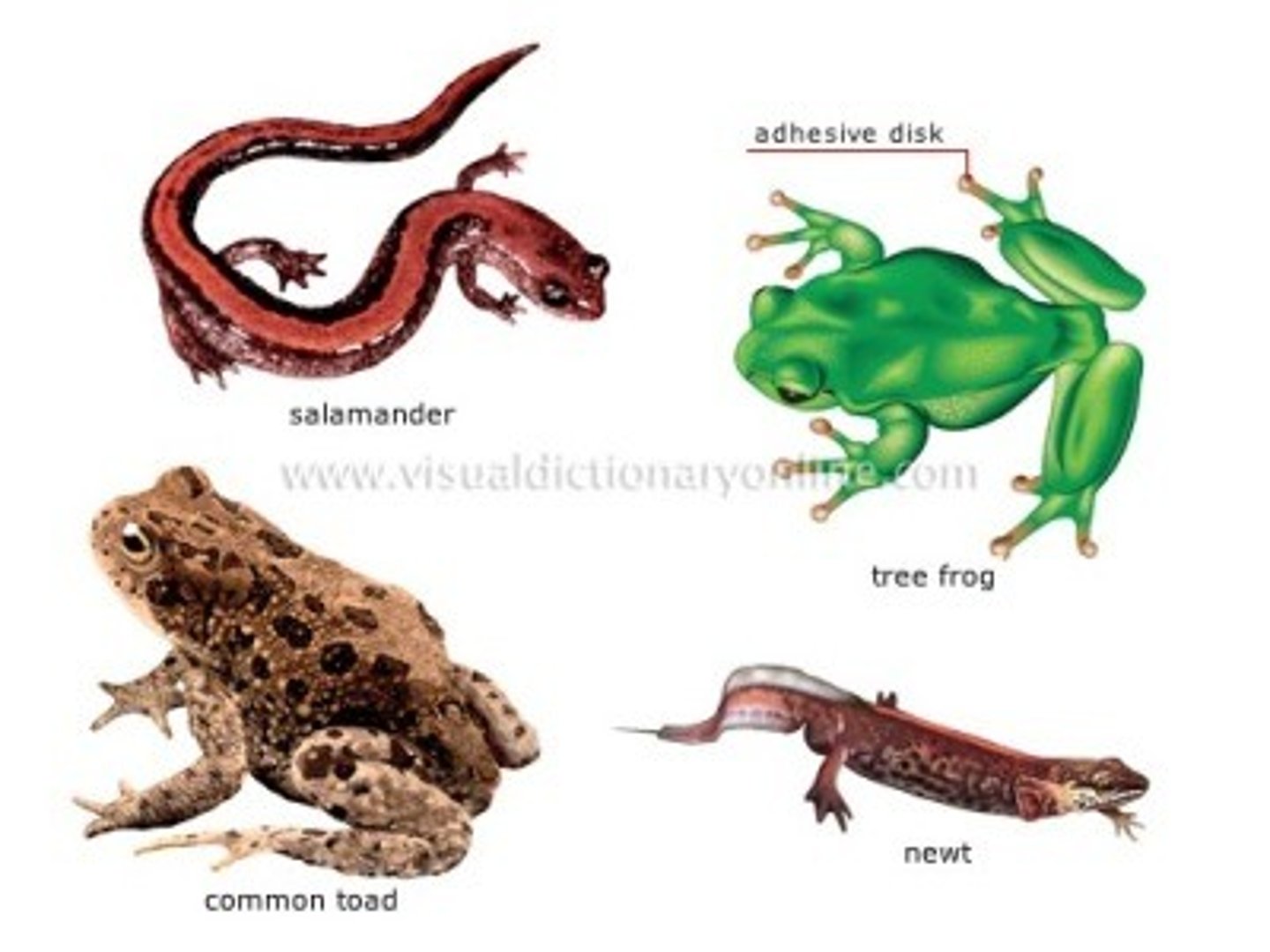
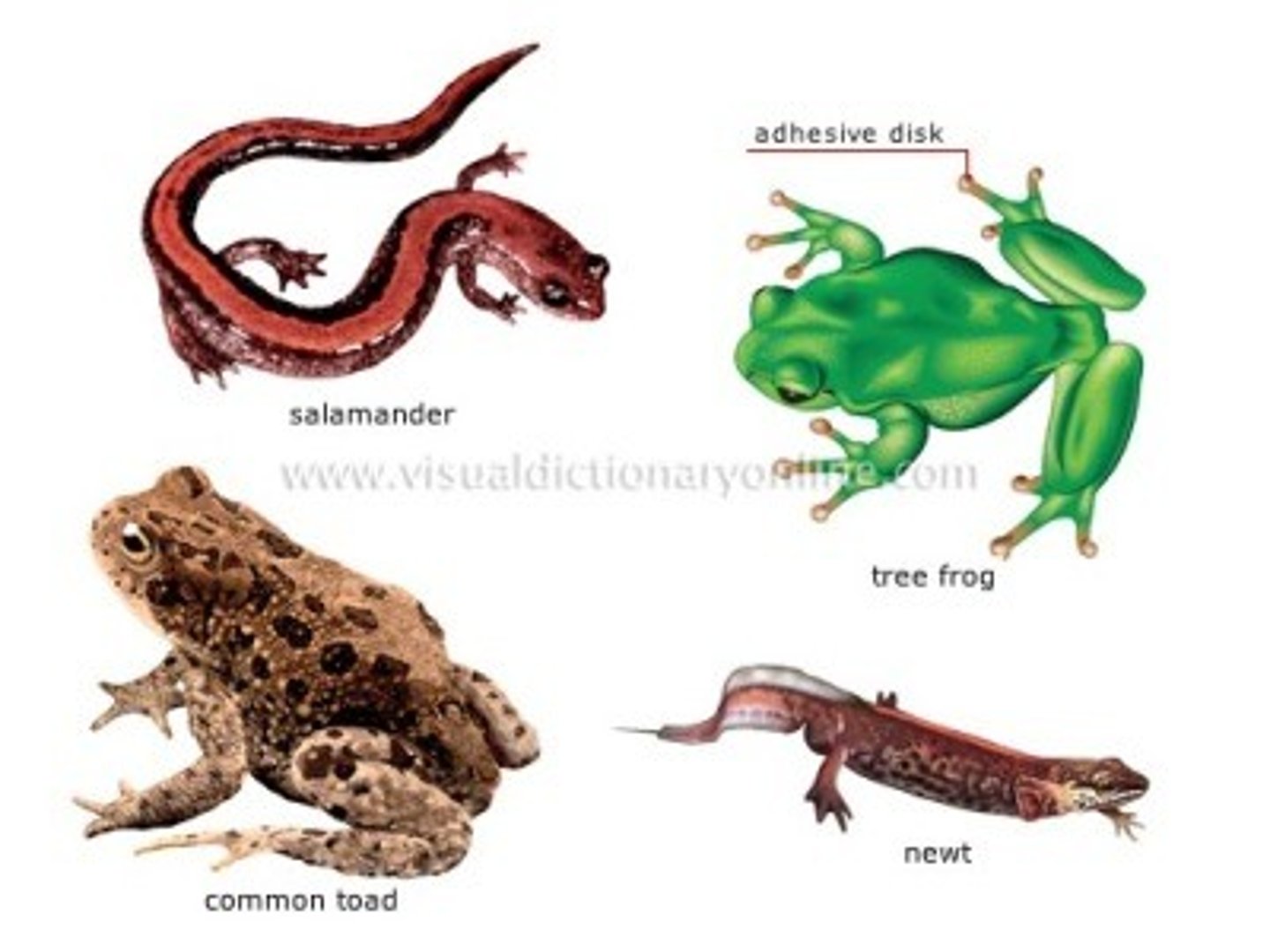
Order Anura
amphibians without tails (tailed larvae = tadpoles); large hind legs
Ex: frogs & toads

Order Gymnophiona
legless amphibians; slender bodies; only amphibian with scales; tropical
Ex: caecilian

Order Caudata
tailed amphibians; distinct head, tail, and limbs
Ex: Newts & Salamandars

Amphibian circulatory system
3 chambered; pumps both oxygenated and deoxygenated

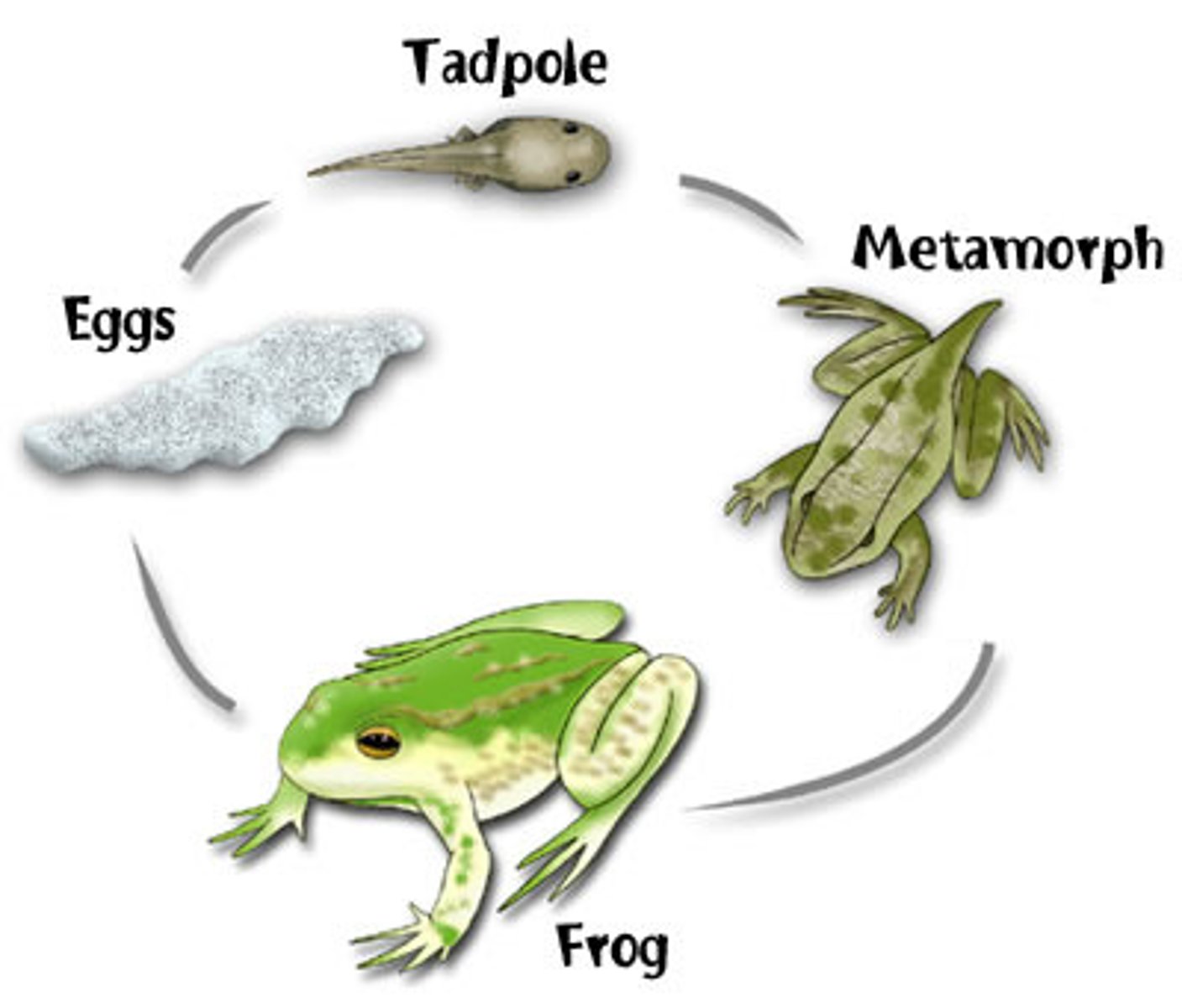
Metamorphosis
series of changes in the life cycle of a frog (limbs develop, lungs replace gills, the tail disappears); can occur in water or in a mother's stomach
The Orders of Class Amphibia
Order Anura, Gymnophiona, Caudata
External fertilization
The type of fertilization most amphibians have; fertilized eggs must be laid in a wet environment
Cutaneous respiration
Skin breathing; skin must be moist to allow for easier gas exchange
Amphibian skeletal system
limbs are attached to fused bone sections called "girdles"; an adaptation for jumping