IB Biology - Cell Structure
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Explain why cells with different functions have different structures
Different organisms have developed unique structures that perform their functions, and do so in a way that is suitable for their specific environments
Cell theory:
all living organism composed of cells
cells are the smallest unit of life
cells come only from other cells
All cells have…
Cell membrane, DNA and cytoplasm
Eye piece graticule:
does not change and is dimension less
Stage micrometer:
mini ruler for microscope (usually used to calculate graticule divisions0
Optical Light microscope:
small and easy to carry
no vaccum needed
simple smaple prep
Mag = x2000
res = 200nm
specimen can be living or dead
Eukaryotic nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts
Electron microscope (general)
large and cant be moved
vaccum needed
complicated prep
mag = x500000
res = 0.5nm
specimens need to be dead
organelles, viruses, DNA
Transmission vs Scanning EMs
TEM:
+ves:
high resolution
internal structures can be seen
-ves:
only thin AND dead specimen
long prep
NO COLOUR
SEM:
+ves:
3d/ thick specimen okay
external structure
-ves:
low resolution
Dead specimen
NO COLOUR
Electron microscope developments:
Cryogenic electron microscopy:
flash freezing solutions w proteins
frozen sol. is then exposed to electrons to produce images of molecules
Freeze fracture (EM):
rapidly frozen sample using liquid nitrogen and physically broken apart in a vaccum
cross section
Optical microscope discoveries:
Condenser: lenses that help direct light from the source
Fluorescent dyes: used to combine w specific cell strcutures when exposed to UV
Immunofluorescence: when antibodies r prepped with dyes and bind w traget molecules complimentary to the antibody
Draw the ultra structure of E. Coli as seen in an electron micrograph
.
Draw and label a diagram of the ultra structure of a generic plant cell
.
Draw and label a diagram of the ultra structure of a generic animal cell
.
Draw a labeled diagram of a palisade cell from the leaf mesophyll
.
State structural differences between plant and animal cells.
Chloroplasts: Plants may have them, animals do not
Cell walls: Plants have them, animals don't
Vacuoles: Plant cells have large and central vacuoles, animal cells have small and temporary ones (if they have any)
Cholesterol: Plant cells don't have them, animal cells have them in plasma membranes
Excess Glucose: Plant cells store as starch, animals store as glycogen
What are the similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
both have a cell memebrane,
cytoplasm and
genetic material
What is the structure of lysosomes?
Membranous sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes, which catalyzes the breakdown or proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates.
Lipid layer
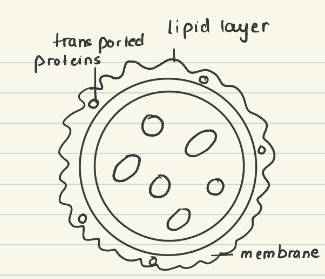
What is the function of lysosomes?
Breakdown of food or unwanted/ damaged substances or hydrolysis of macromolecules occurs in lysosomes
What is the structure of a cell wall?
made of cellulose (plants), peptidoglycan (prokaryotes) and chitin (fungi)
permeable
strong
What is the function of the cell wall in plants?
Provides support and mechanical strength. Prevents excess water uptake
What is the function of the vacuole?
It maintains hydrostatic pressure
What is the structure of a vacuole
It's the fluid-filled internal cavity surrounded by a membrane. It's usually formed from the Golgi apparatus
What is the function of chloroplast?
Site of photosynthesis, as the first step of photosynthesis is the absorption of light- produced glucose
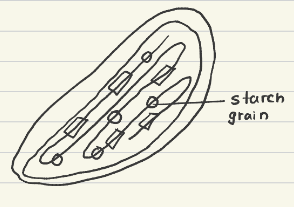
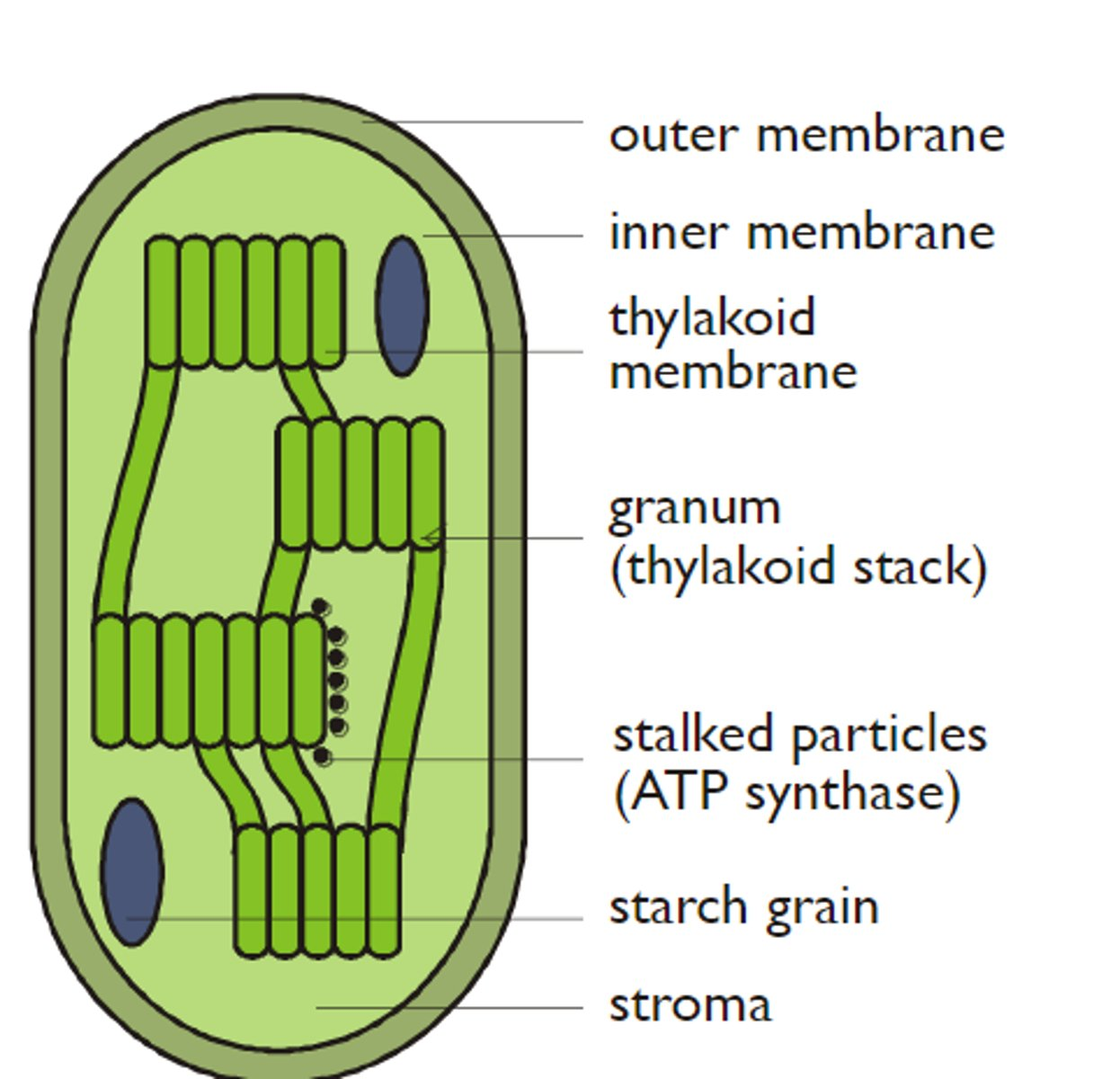
What is the structure of chloroplast in plants?
Double membrane
Thykloid stacks (Granum)- where chlorophyll photosynthesises
DNA strand
70S ribosomes
Stroma (cytoplasm)
starch grain
What is the function of mitochondria?
It's the site of aerobic respiration (ATP production)
What is the structure of the mitochondria?
Double membrane structure, where the outer membrane is smooth and the inner membrane is folded into cristae (singular christa)
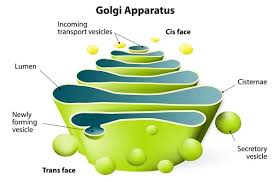
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
It's involved in sorting, storing, modification, and export of materials synthesized in the cell
What is the structure of a golgi apparatus?
Assembly of vesicles and folded membranes located near the cell membrane
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
It transports materials between organelles. For smooth ER, that's lipids. For a rough ER, that's proteins
What is the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Membrane network that may be bare (smooth ER) or studded with ribosomes on its exteriors (rough ER)
What is the function of a nucleus?
It stores genetic material (DNA) as chromatin, and is the site of ribosome assembly
What is the structure of a nucleus?
It's a double membrane structure with pores. The membrane allows compartmentalization of eukaryotic DNA, providing an area where DNA can carry out its functions without being affected by processes happening in other areas of the cells.
What is the function of a plasma membrane?
Semi-permeable and selective barrier surrounding the cell
What is the structure of a plasma membrane?
It's a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins.&
What is the function of a cytoskeleton?
Provides internal structure and mediates intercellular transport
What is the structure of a cytoskeleton?
Filamentous scaffolding within the cytoplasm
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribsosomes are the site of protein synthesis
What is the structure of Ribosomes?
Complexes of RNA and protein. They may be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum
What is the difference in structure between ribosomes in eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Larger in eukaryotes (80S) than prokaryotes (70S)
What are organelles?
Specialized sub-structures within a cell that serves a specific function.
Which 4 kingdoms can eukaryotic cells be divided into?
Protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia
What are eukaryotic cells compartmentalized by?
Membrane-bound structures (organelles)
What is believed to have evolved from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells, via endosymbiosis
What is the summary of distinguishing characteristics of prokaryotic cells in comparison to eukaryotic cells?
DNA is not enclosed within a membrane, and forms one circular chromosome
Lacks membrane-bound organelles
Cell wall is made up of a compound called peptidoglycan
Undergoes binary fission
Characteristically small, usually 1 to 5 micrometers
What is the process of binary fission?
DNA is copied, and 2 daughter chromosomes become attached to different regions on the plasma membrane. The cell then divides into 2 genetically identical daughter cells
What is binary fission?
Asexual reproduction, when prokaryotic cells divide
What is a prokaryotic flagella and what is its function?
Flagella are long, slender projections that contain a motor protein that enables movement
What is a cytoplasm in prokaryotic cells?
Internal fluid component
What is a prokaryotic capsule and what is its function?
A capsule is a thick polysaccharide layer that is used for protection against desiccation and phagocytosis
What is a prokaryotic Plasmid?
Plasmid is an autonomous circular DNA molecules that may be transferred between bacteria (horizontal gene transfer)
What is the function of a prokaryotic Nucleoid region?
Region of cytoplasm where DNA is located. It's non-compartmentalized, and is involved with cell control and reproduction
What is the function of a prokaryotic Ribosomes?
Prokaryotic ribosomes are complexes of RNA and protein that are responsible for polypeptide synthesis
What does the prokaryotic pili do?
Pili's main function is joining the bacterial cells in preparation for transfer of DNA from one cell to another (sexual reproduction)
Also enables adherence to surfaces (attachment pili)
Where is the prokaryotic cell membrane found in?
Just inside the cell wall
What is the function of a prokaryotic cell membrane?
Prokaryotic cell membrane controls movement of materials into and out of cells, plays a role in binary fission of prokaryotic cells.
Semi-permeable and selective barrier surrounding the cell
What is the function of a prokaryotic cell wall?
Prokaryotic cell wall protects and maintains the shape of the cell. Prevents bursting (lysis)
What are the features of prokaryotic cells?
Cytoplasm, nucleoid, plasmid, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, capsule, flagella, pili
What are the distinguishing characteristics of prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
DNA forms one circular chromosome
DNA isn't attached to any proteins
No nucleus
70S ribosomes
Reproduces via binary fission
Size is from around 1-5 micrometers
How does the process of binary fission work?
DNA is copied in response to a replication signal. Two daughter chromosomes become attached to different regions on the plasma membrane, and the cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cell
How do prokaryotes divide?
By binary fission
What components do prokaryotic cells contain?
Cytoplasm, nucleoid, plasmids, 70S ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, capsule, flagellum, pili
Which two distinct domains are prokaryotes classified in?
Archaebacteria and eubacteria
Which kingdom do prokaryotes belong in?
Monera
What are prokaryotes?
Organisms whose cells lack a nucleus
What is Endosymbiotic theory?
claims that chloroplasts and bacteria evolved from prokaryotes
when a larger prokaryote engulfed a aerobically respiring smaller prokaryote and a photosynthesisng smaller prokaryote
Mitchondria and Chloroplast have Prokaryotic features such as:
Circular DNA
70s ribosomes
double membrane