Rates of Reactions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
rate
A measure of change over time.
2
New cards
particle theory
All matter is in constant motion with the speed represented by the average kinetic energy (temperature) of the system.
3
New cards
kinetic energy
Energy associated with the __motion__ of molecules.
4
New cards
collision theory
All particles in motion will randomly collide with one another. For a collision to result in a **reaction**, the collision must be **effective**. An effective collision (one that results in the **formation of products**) must satisfy **two** conditions.
5
New cards
effective collision
1. Reactant **orientations** must be favourable.
2. Collision must occur with sufficient **energy**.
6
New cards
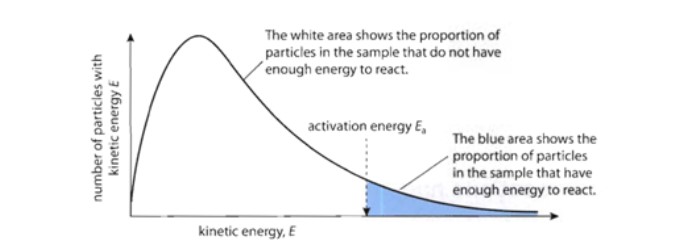
Maxwell-Boltzmann Curve
### *A.K.A. Kinetic Energy Distribution:*
In most reactions, only a **small fraction** of the total collisions have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. The collision energy depends on the **kinetic energy** of the colliding particles.
Plotting the number of particles versus the kinetic energy of the particles gives a curve like the one below:
**NOTE:** The curve represents the distribution of the kinetic energy of collisions __at a given temperature__. The activation energy is __**independent**__ of temperature (it does not change when temperature changes!).
In most reactions, only a **small fraction** of the total collisions have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. The collision energy depends on the **kinetic energy** of the colliding particles.
Plotting the number of particles versus the kinetic energy of the particles gives a curve like the one below:
**NOTE:** The curve represents the distribution of the kinetic energy of collisions __at a given temperature__. The activation energy is __**independent**__ of temperature (it does not change when temperature changes!).
7
New cards
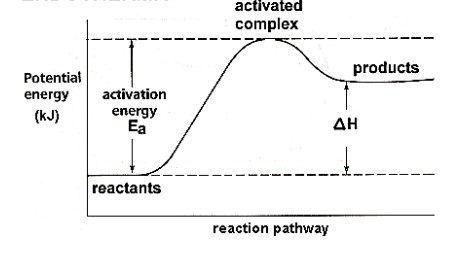
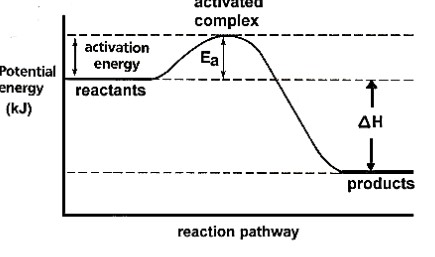
potential energy diagram
Shows the relative **potential energies** of reactants, transition states and products as a reaction progresses.
8
New cards
potential energy
Energy __within__ molecules (i.e. the bonding energy).
9
New cards
activation energy
The __minimum__ amount of __kinetic energy__ that the reactants must collide with to make the reaction proceed (energy __barrier__ the reactants must overcome to form products).
* E*a*
* E*a*
10
New cards
activated complex/transition state
A __temporary__ arrangement of atoms that form as bonds are breaking and new bonds are forming (highly __unstable__).
11
New cards
endothermic
12
New cards
exothermic
13
New cards
surface area
When increasing this (**grinding, slicing, dissolving**) of __**solid**__ reactants, it exposes more molecules to each other than before, hence increasing the frequency/probability of effective collisions, increasing the rate (opposite occurs when this is *small*).

14
New cards
concentration
With an increase in the number of **reactant molecules present**, there is an increase in the frequency/probability of effective collisions occurring, hence increasing the rate (the reverse is true when this is *low*).

15
New cards
temperature
By increasing this, the molecules have more **kinetic energy** which increases the frequency/probability of effective collisions. With more energy, the **activation barrier** can be more easily overcome more often, increasing the rate (the *opposite* occurs when this is *low*).

16
New cards
volume/pressure
### ***** ONLY FOR A GAS SYSTEM!!! *****
By decreasing this factor of a container and and increasing the other, the molecules have less space to move and are in closer proximity to one another, hence increasing the frequency/probability of effective collisions, increasing the rate (*increasing* the former and *decreasing* the latter decreases the rate).
By decreasing this factor of a container and and increasing the other, the molecules have less space to move and are in closer proximity to one another, hence increasing the frequency/probability of effective collisions, increasing the rate (*increasing* the former and *decreasing* the latter decreases the rate).
17
New cards
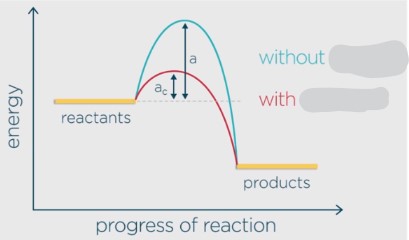
catalyst
Allows for an alternate pathway of **lower activation energy** so that more collisions can overcome the barrier more often, increasing the rate. They are **not consumed** in reactions and can be **reused**.
18
New cards
mol/Ls
Overall order: 0
(write units of the rate constant k)
(write units of the rate constant k)
19
New cards
/s
Overall order: 1
(write units of the rate constant k)
(write units of the rate constant k)
20
New cards
L/mols
Overall order: 2
(write units of the rate constant k)
(write units of the rate constant k)
21
New cards
L^2/mol^2s
Overall order: 3
(write units of the rate constant k)
(write units of the rate constant k)
22
New cards
rate law equation
Relates the **rate of a reaction** to the **concentrations of the reactants**, each concentration is expressed with an **order (exponent)**.
* **m** and **n** are the **reactant orders** determined from __experimental data__
* The **rate constant** is **k**, which makes the two sides of the equation equal to each other (units of k will change depending upon the __overall order__ of the reaction)
* **m** and **n** are the **reactant orders** determined from __experimental data__
* The **rate constant** is **k**, which makes the two sides of the equation equal to each other (units of k will change depending upon the __overall order__ of the reaction)
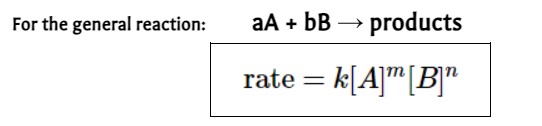
23
New cards
reaction mechanism
The overall sequence of **elementary steps** by which a chemical reaction occurs.
* A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is called a multistep or complex reaction.
* A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is called a multistep or complex reaction.
24
New cards
rate-determining step
When a reaction takes place in a series of steps, the overall rate of the chemical reaction is only as fast as the rate of its **slowest step** (the step with the **largest activation energy**).
* **The coefficient of each reactant in this is the order of each reactant in the rate law equation!**
* **The coefficient of each reactant in this is the order of each reactant in the rate law equation!**
25
New cards
reverse endothermic
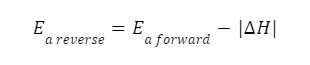
26
New cards
reverse exothermic
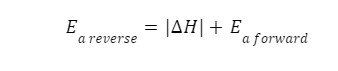
27
New cards
reaction intermediates
Stable chemical compounds that do NOT appear in the overall reaction.
28
New cards
rate-determining step
The overall rate of the chemical reaction is only as fast as the rate of its slowest step (the step with the **largest activation energy**). The rate law equation is dependent on this step; **the coefficient of each reactant in the this step is the order of each reactant in the rate law equation!**