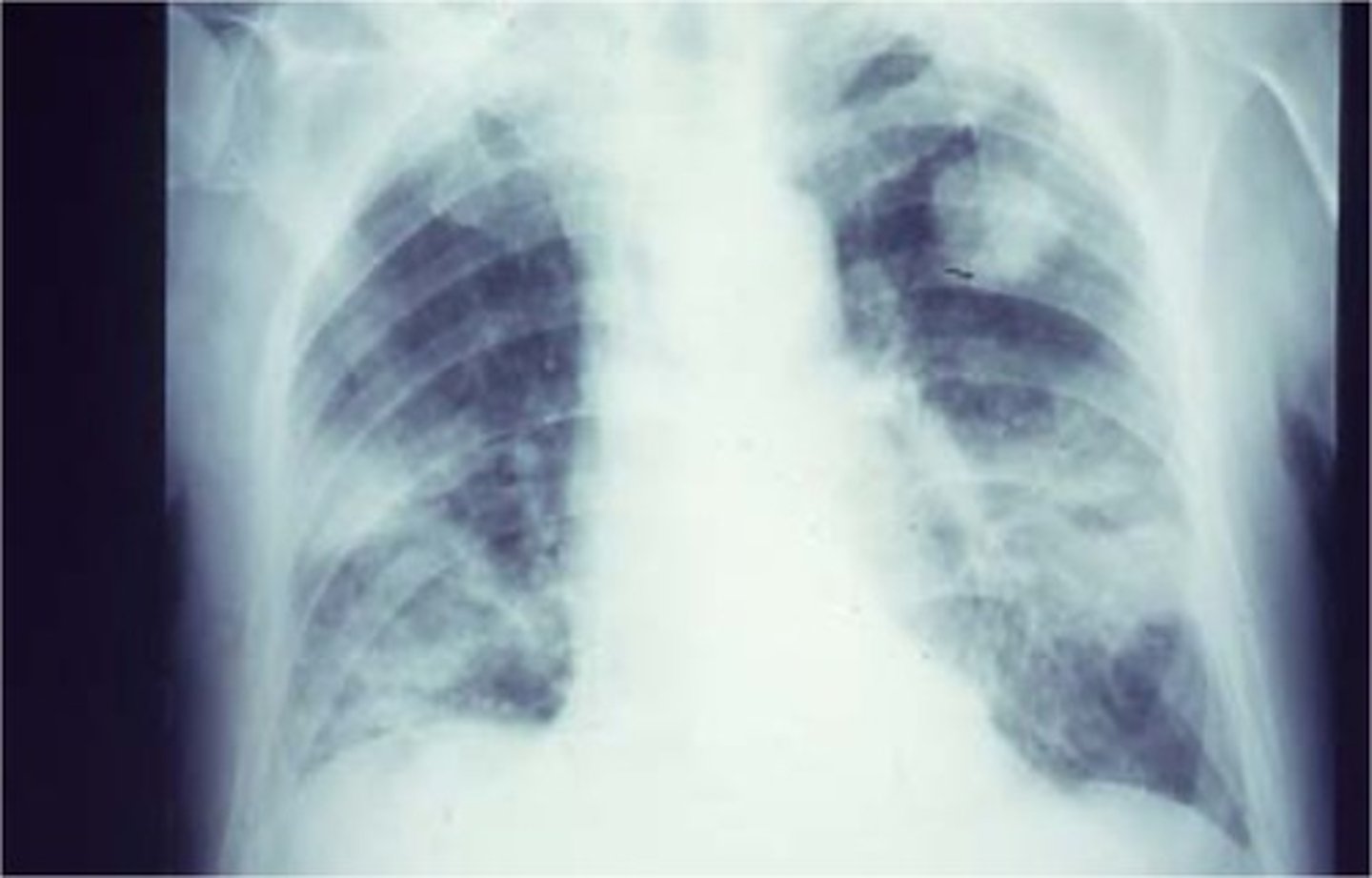
Bacterial Pneumonia
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What does the diagnosis of CAP (community-acquired pneumonia) require?
Symptoms of lower RTI i.e. cough (productive), sputum, breathlessness, chest pain and CXR of pneumonia - where there is pacification of a lobe in the lung (which could be inflammatory exudate or blood).
Who is CAP more common in?
1. Males
2. Elderly- immunocompromised
3. Alcoholics- functional deficit in innate immunity
4. Chronic disease
What is the aetiology of CAP?
1. Conventional bacteria causes 60-80% of all CAP cases.
2. 'Atypical' bacteria causes 10-20% of CAP. (mycoplasma- these can't be killed by penicillins)
3. Viruses cause 10-20% of CAP cases.
What are the 4 aetiological agents that cause CAP?
1. S. pneumoniae.
2. H. influenzae.
3. M. pneumoniae.
4. L. pneumophila.
What is S. pneumoniae? (3)
Streptococcus pneumoniae.
1. Most common cause of CAP in those not having COPD.
2. Its major virulence factor is the capsular polysaccharide.
3. Relative resistance to penicillin is becoming common.
What is H. influenzae? (2)
Haemophilus influenzae.
1. Capsulated version is the primary cause of CAP in children who haven't received HIB (flu vax).
2. Non-capsulated version is an important cause of disease in COPD.
still has a cell wall
What is M. pneumoniae? (3)
Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
1. Mycoplasma is the 2nd most common cause of CAP.
2. Can cause epidemic CAP.
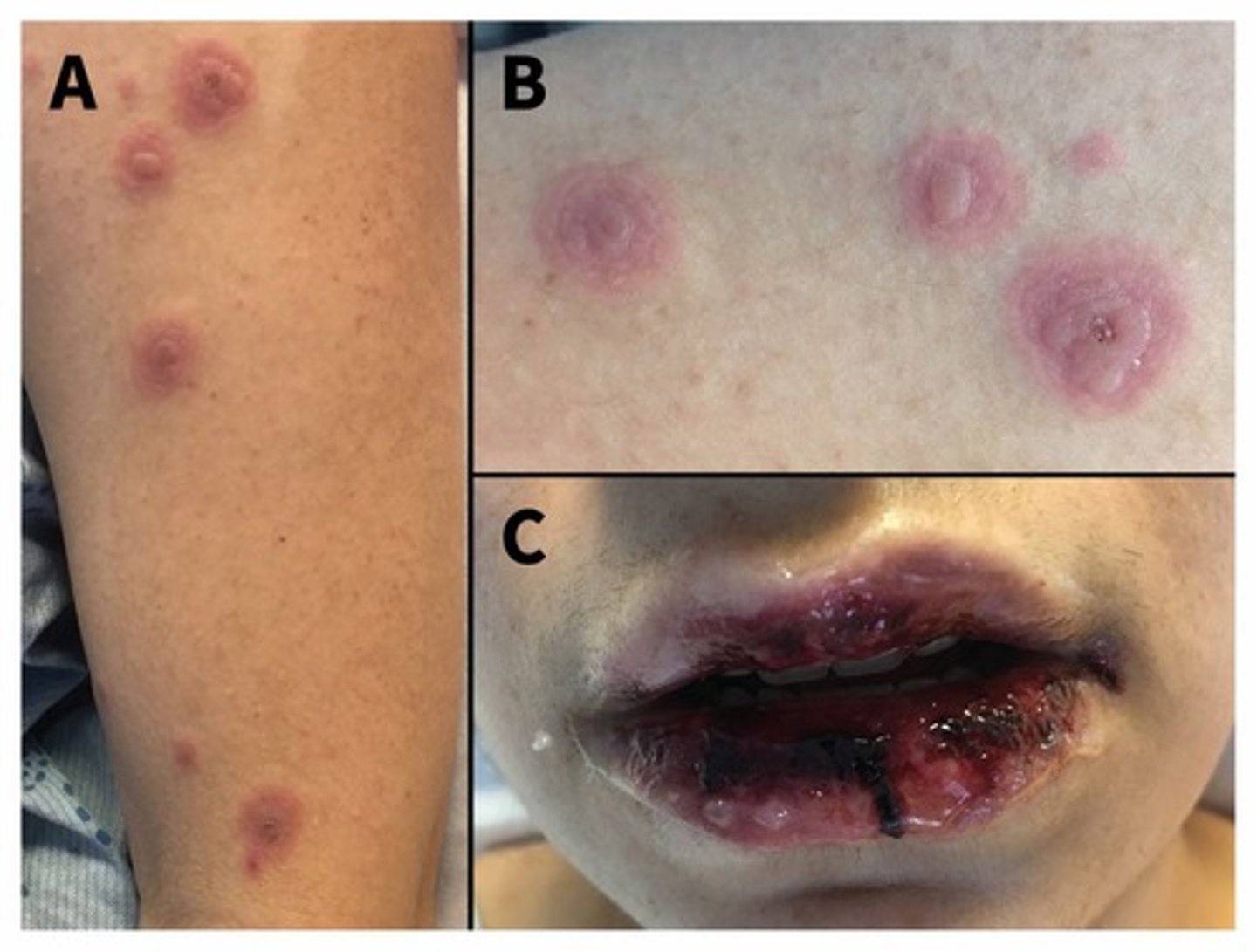
3. Mycoplasma infection has characteristic skin features - target lesions. This can give you inflammation of mucous membranes. There tends to be a long pre illness that doesn't show respiratory symptoms.
These don't have a cell wall and so do not respond to penicillins
What is l. pneumophila? (4)
Legionella pneumophila.
1. Cause of both sporadic and outbreak CAP.
2. Can cause severe disease - specifically in immunocompromised + smokers. Comes with respiratory disease and GI upset.
3. Serogroup 1 causes almost ALL human infection.
4. Needs specific treatment w/ high-dose fluoroquinolone or microlide antibiotics.
can be found in amoeba in water supply, therefore can result in outbreaks in certain areas.
How can you investigate CAP? (4)
1. Confirm diagnosis.- looking at chest X-ray
2. Assess severity.
3. Define aetiological agent- using sputum for example, blood culturing.
4. Identify complications- sepsis, cardiac failure, renal failure. Are other organs involved?
What microbiological investigations can be done with CAP? (4)
1. Sputum analysis + culture.
2. Immunofluorescence on sputum samples.
3. Blood cultures.
4. Urinary pneumococcal + legionella antigen etc.
What is antimicrobial chemotherapy for CAP based on?
1. Assessment of likely pathogen.
2. Severity of illness.
3. Likelihood of drug resistance.
What is the risk stratification of CAP?
CURB 65 score
Confusion (MMT score of 8 or less). new confusion
Urea >7 mmol/L.
Respiratory rate >30/min.
Blood pressure <60 mmHg.
65+ years.
the highest level you can reach on this is 4.
How do you treat someone diagnosed with low-severity CAP? (score of 0-1).
1. Oral antibiotics - Amoxicillin or doxycycline.
2. Only IV if unable to take oral therapy.
3. Should take ciprofloxacin or vancomycin if penicillin-allergic.
4. Can be managed in community unless frail.
How do you treat someone diagnosed with moderate-severity CAP (score 2)?
1. Amoxicillin and clarithromycin -this covers mycoplasma and cladmydia for 7 days or doxycyline.
2. IV if unable to take orally.
3. Normally managed in hospital environ.
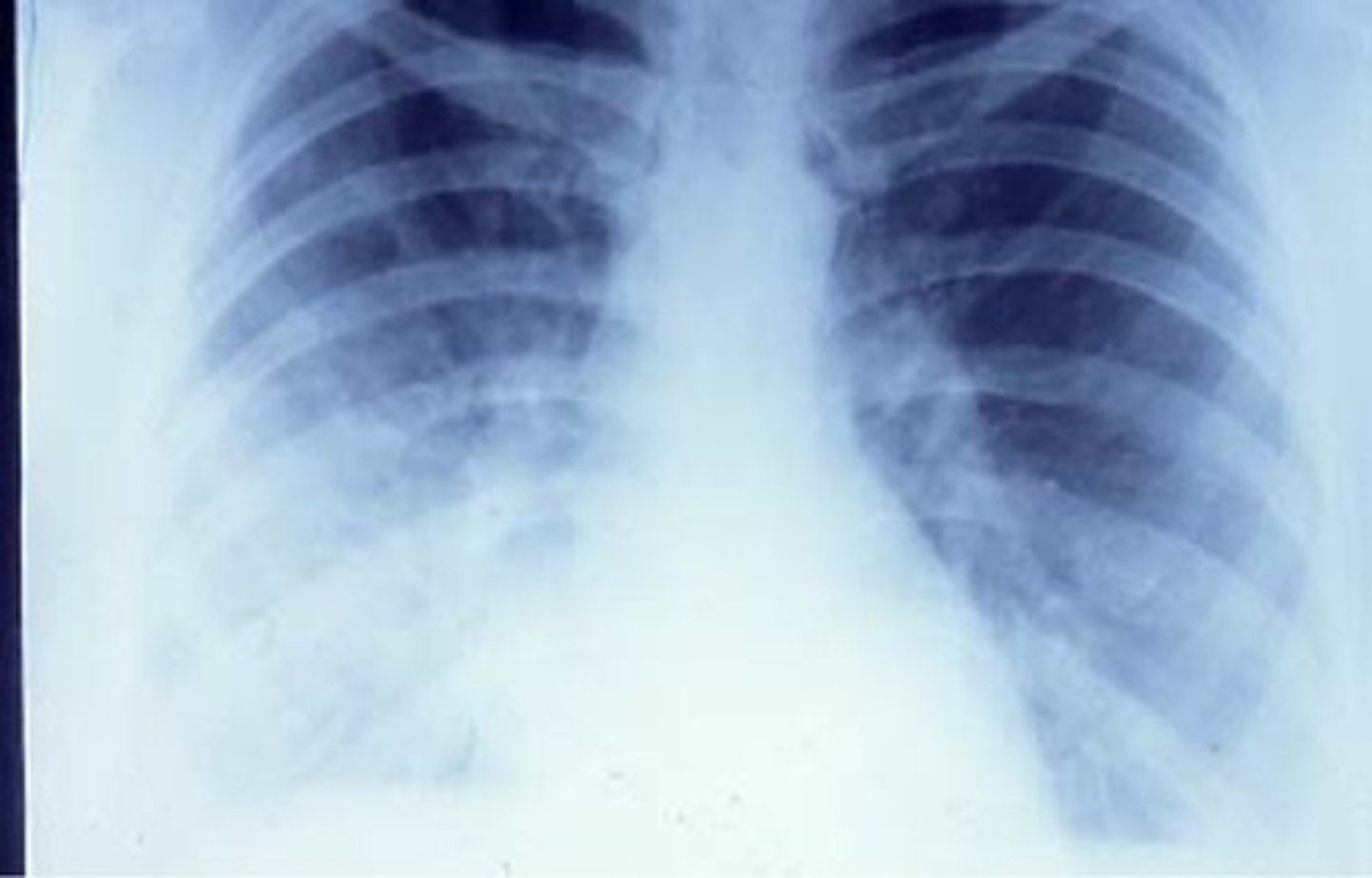
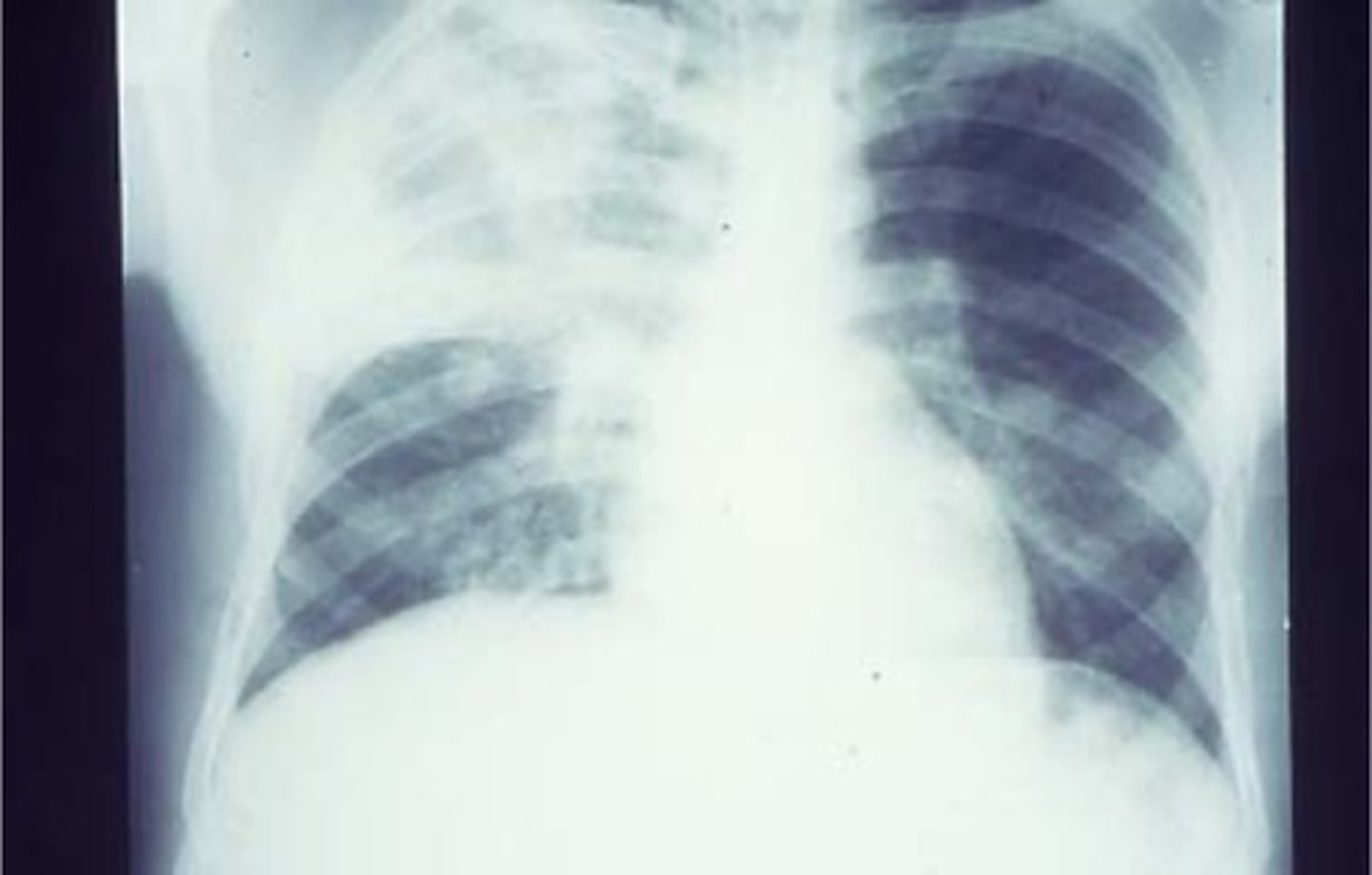
Give a CXR showing right upper lobe pneumonia.
CAP score 2. pneumococcas usually affects one lobe
How do you treat someone diagnosed with severe CAP (score 3)?
1. Co-amoxiclav + amoxicillin- this targets streptococcus + clarithromycin.- this is given for 10 days .This combination is the standard imperical therapy
2. If penicillin allergic, given levofloxacin and vancomycin- these treat legionella pneumoniae very well
3. Very hypoxic + diarrhoea.
CXR - Left and right lower lobe involvement.
Suggests legionella pneumoniae.
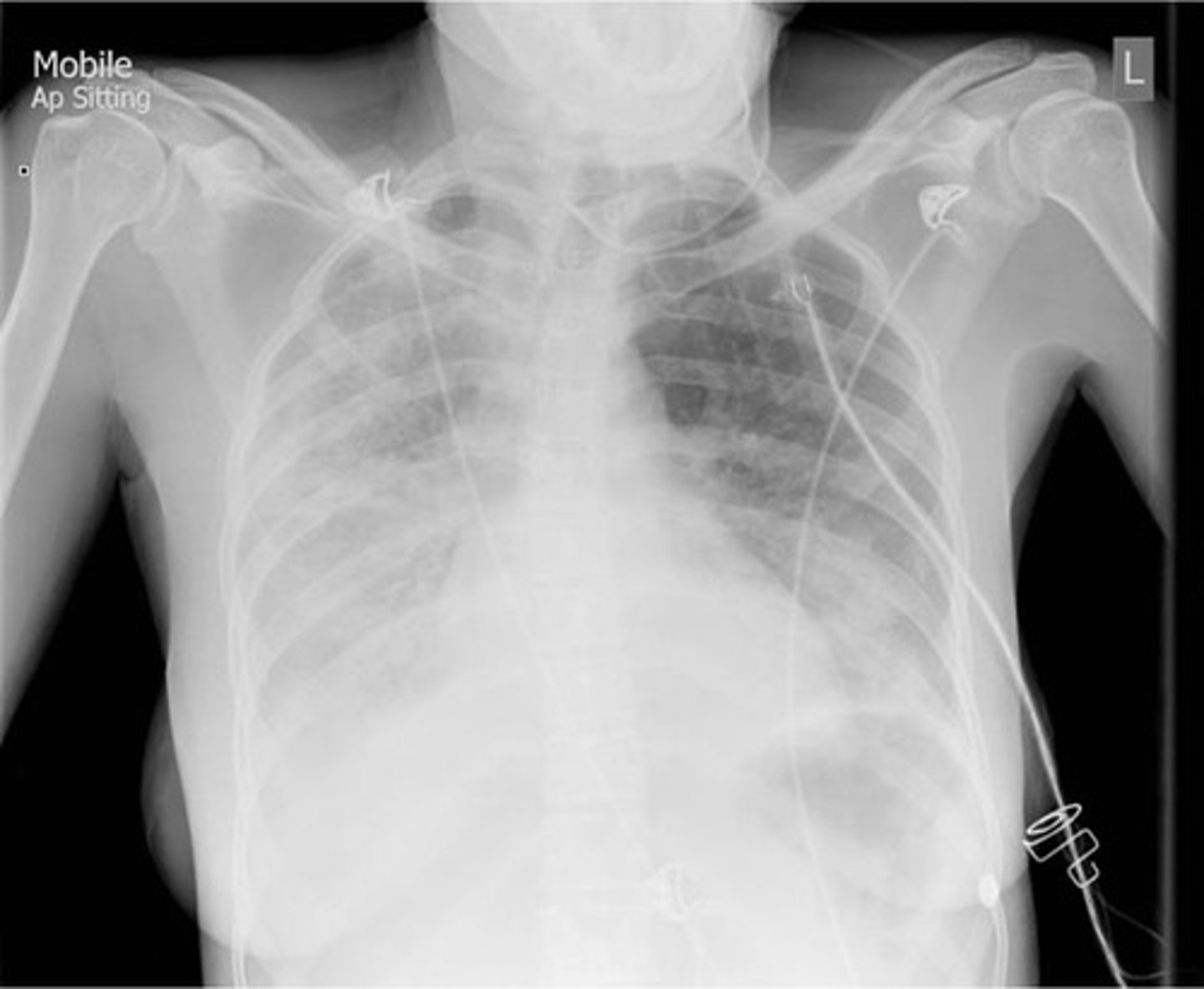
How do you treat someone diagnosed with severe CAP (above 3?)?
1. Continue co-amoxiclav, amoxicillin and clarithromycin.
2. Add levofloxacin.
3. Ensure legionalla antigen in urine requested + culture sputum.
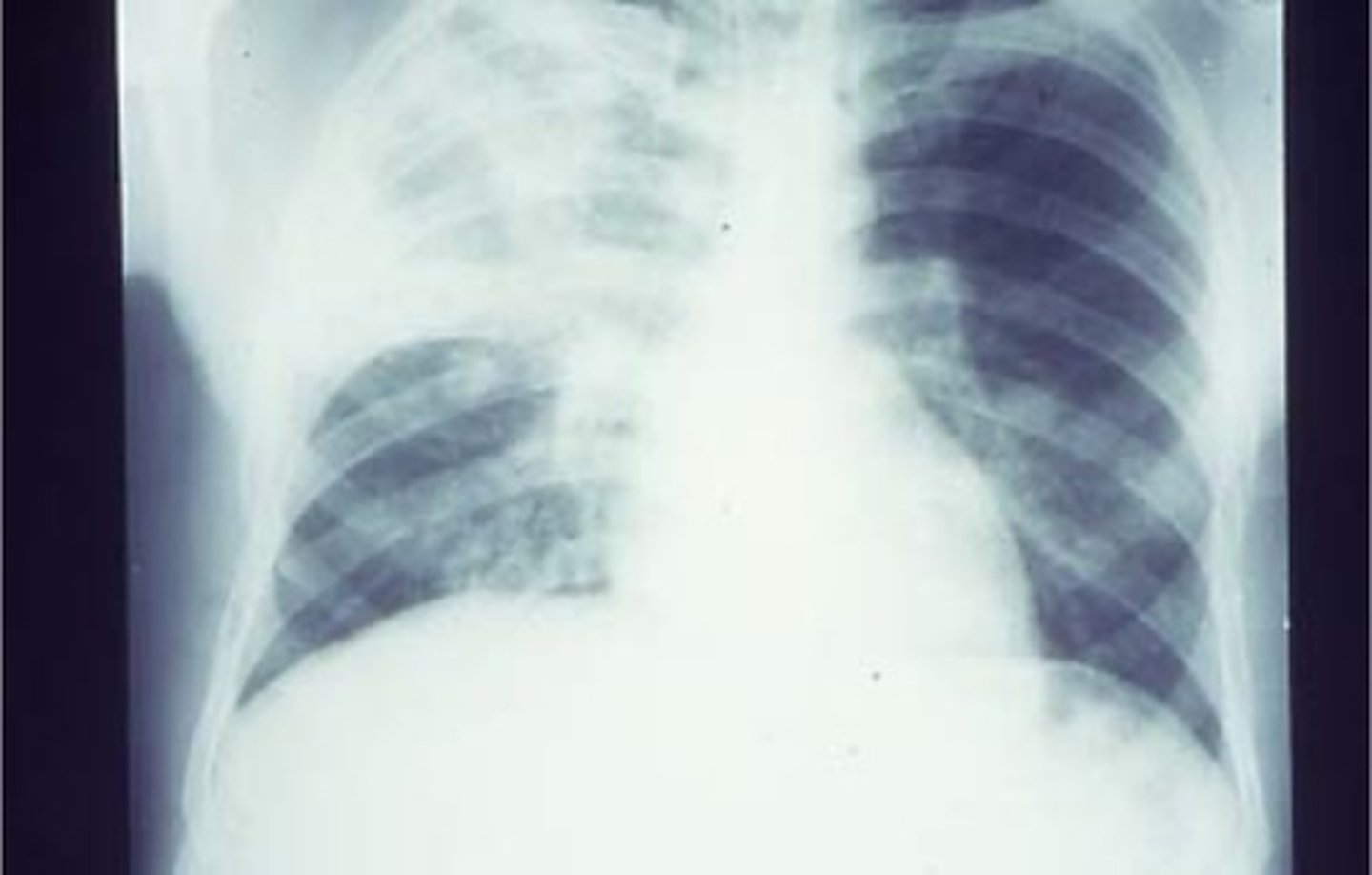
S. pneumoniae - CXR - Lung abscesses with pus.