DPT 745 Week 4 Lecture Notes Pt. 4
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parotid Region and Ear
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
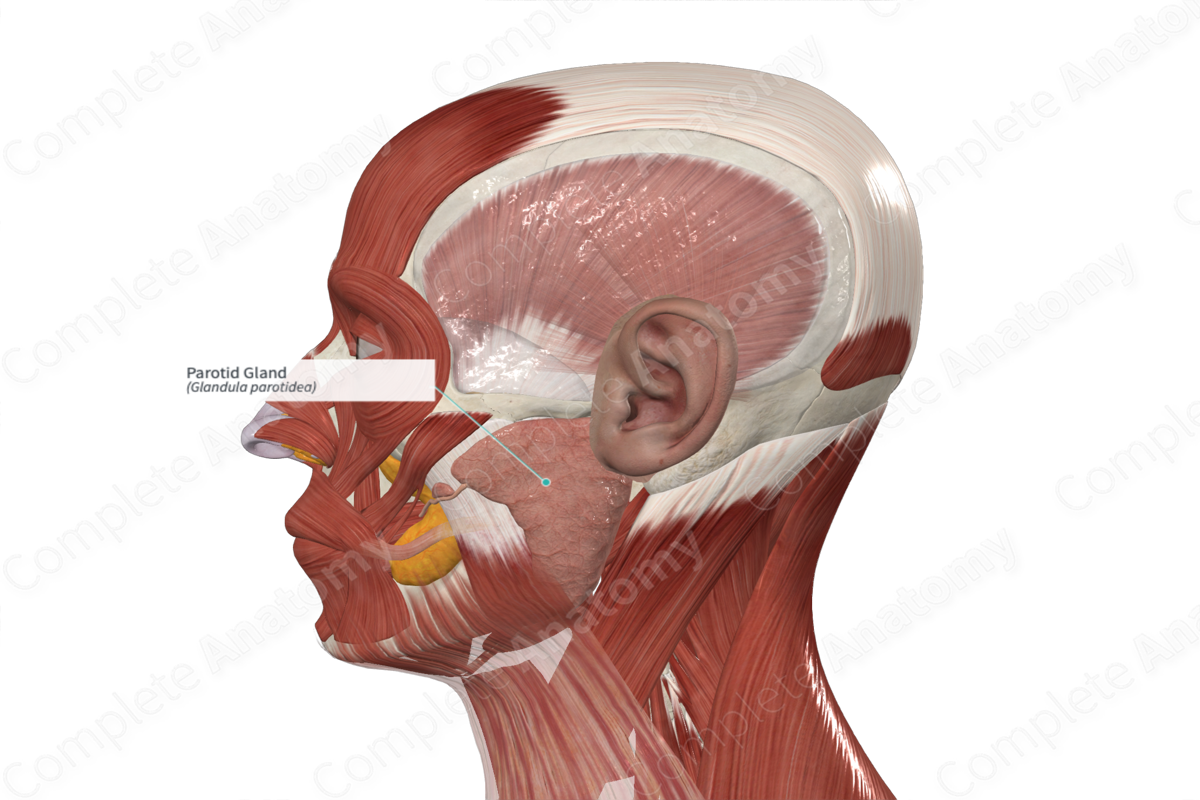
Parotid
duct
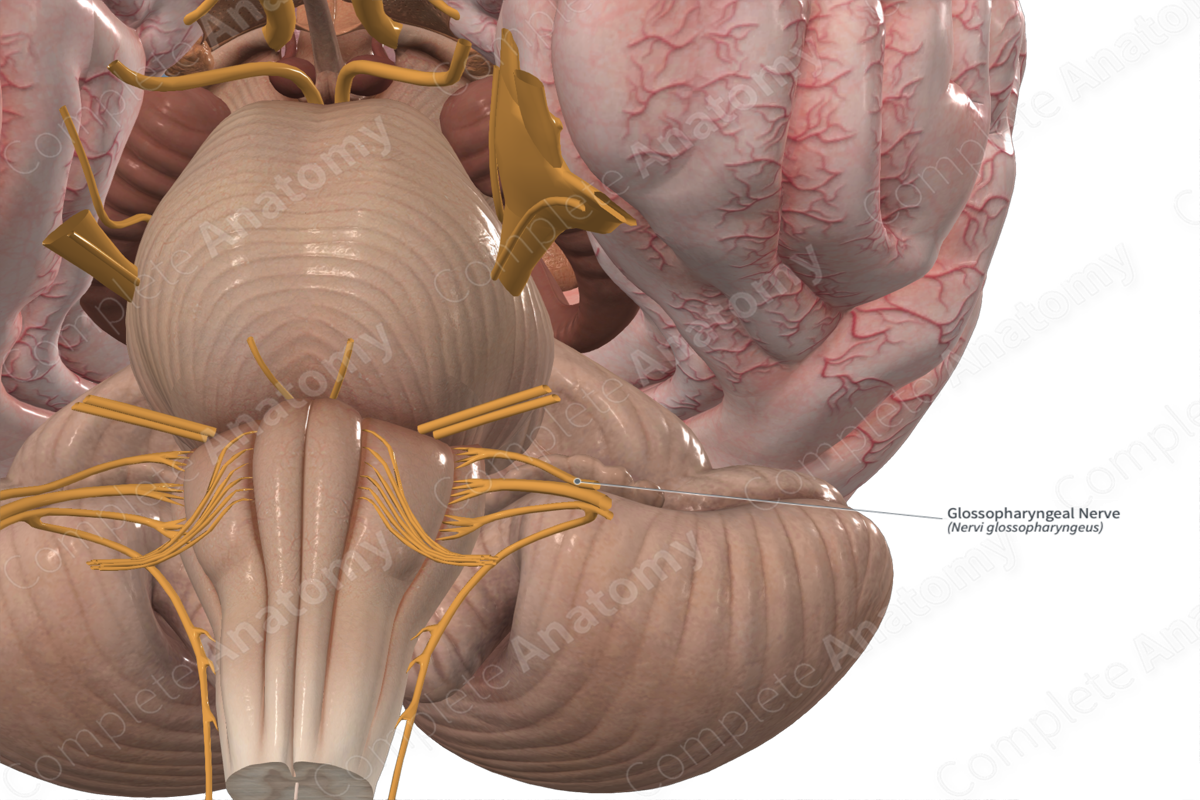
glossopharyngeal
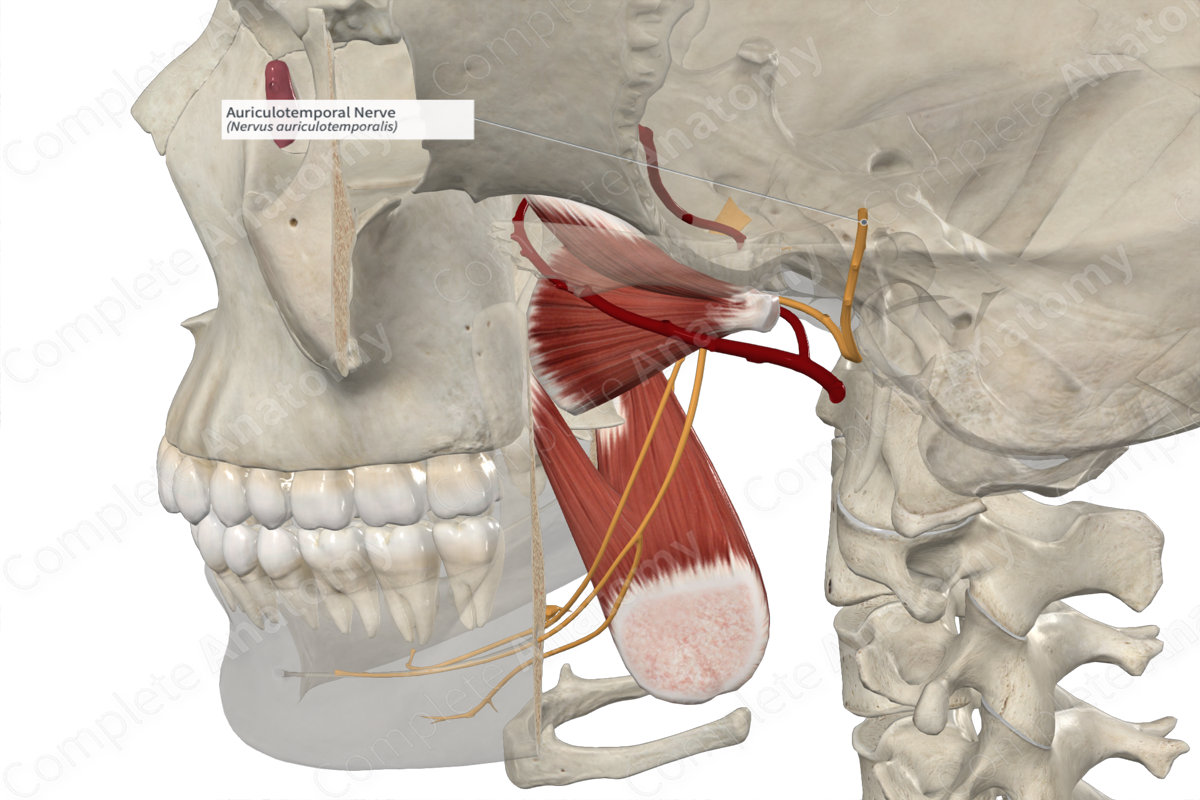
Auriculotemporal
_____ Gland
• Largest of the paired salivary glands.
• Located anterior and inferior to the ear
• Parotid _____ - extends from the gland to the oral cavity penetrating the buccinator muscle to allow saliva to enter the mouth
• Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers are carried by the _____ nerve
– Synapse of the preganglionic to postganglionic nerve fibers occurs in the otic ganglion.
– _____ nerve carries postganglionic nerve fibers to the parotid gland
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Auriculotemporal nerve
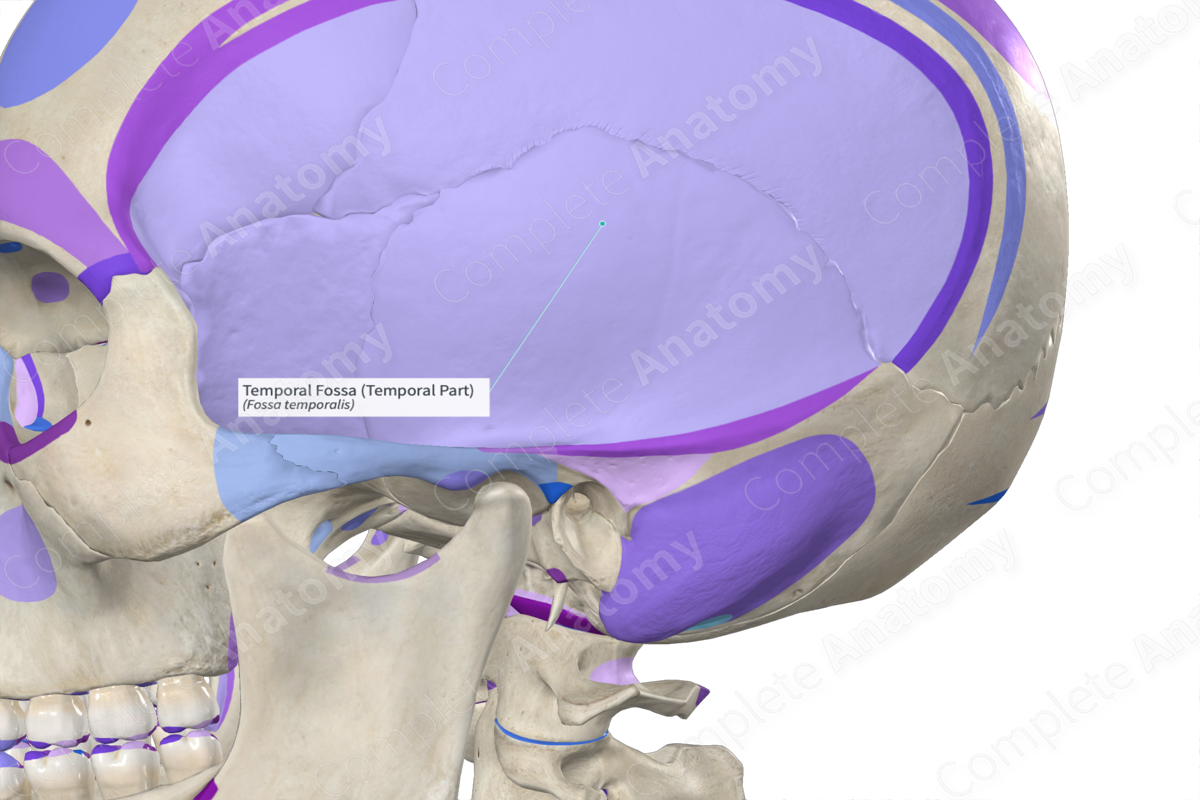
Temporal
_____ Fossa
It is located on the lateral side of the skull. It is bounded by the temporal lines and zygomatic arch
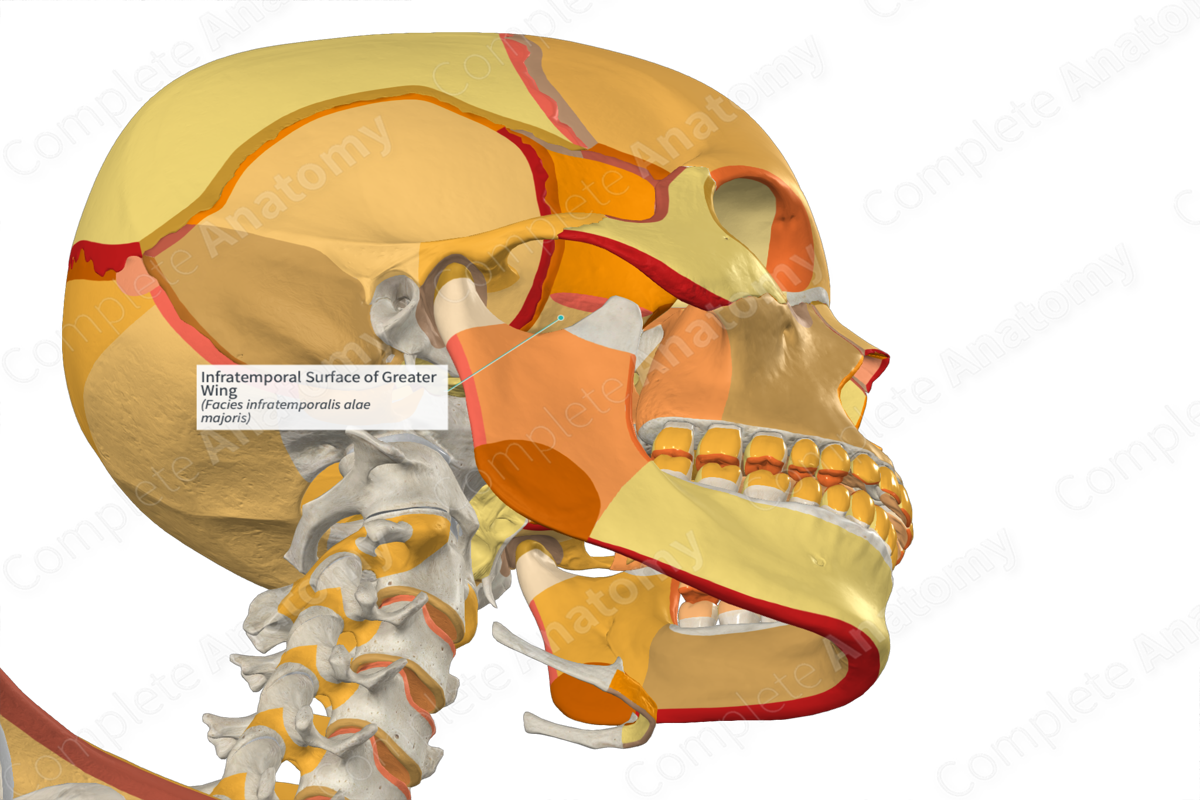
Infratemporal
_____ Fossa
• Inferior to the temporal fossa and partially covered by the masseter
• It is bounded anteriorly by the maxilla, posteriorly by the condylar process of the mandible, medially by the lateral pterygoid plate and laterally by the ramus of the mandible
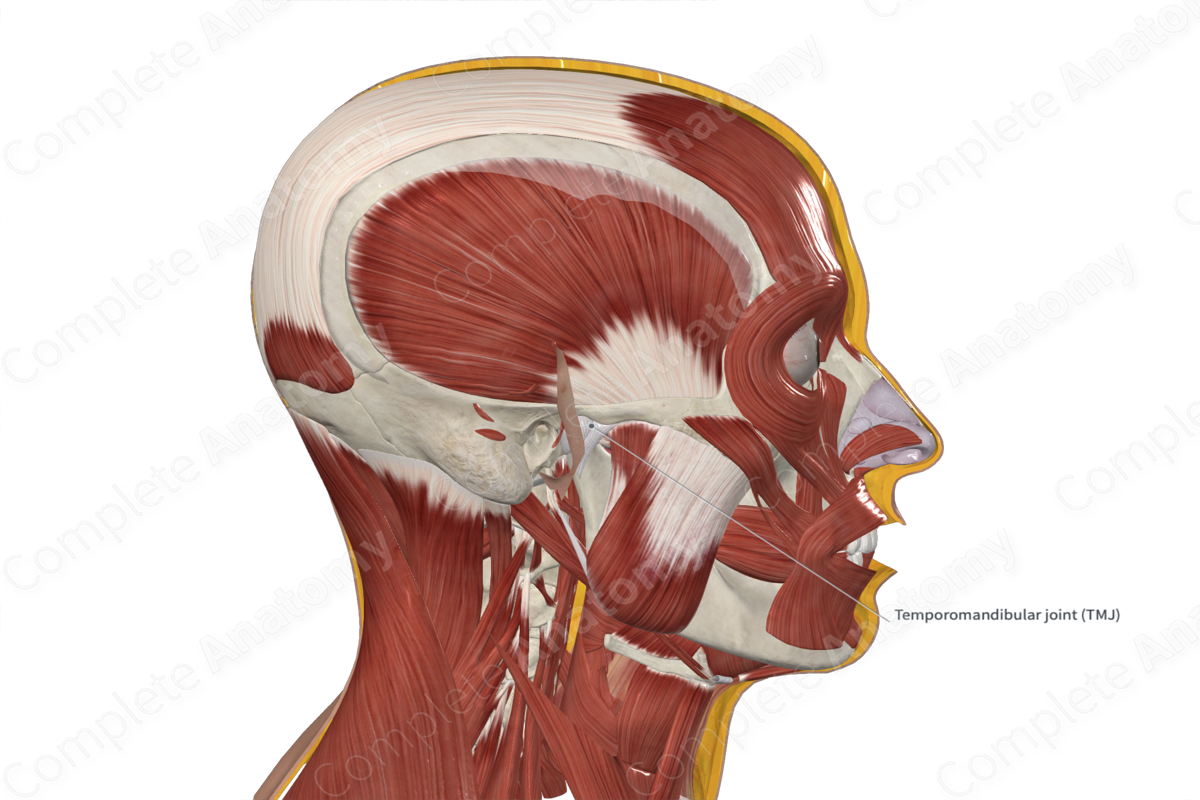
TMJ
Hinge
Sliding
___
• Articular disc is found between the head of the mandible and the mandibular fossa. The disc is more intimately associated with the head of the mandible and therefore moves with the head of the mandible as it slides anteriorly during opening and closing of the mouth.
• _____ movements - between head of mandible and disc
• _____ movements - between disc and mandibular fossa
• Synovial joint with loose fibrous capsule. It is the articulation of the head of the mandible with the mandibular fossa and articular tubercle of the temporal bone
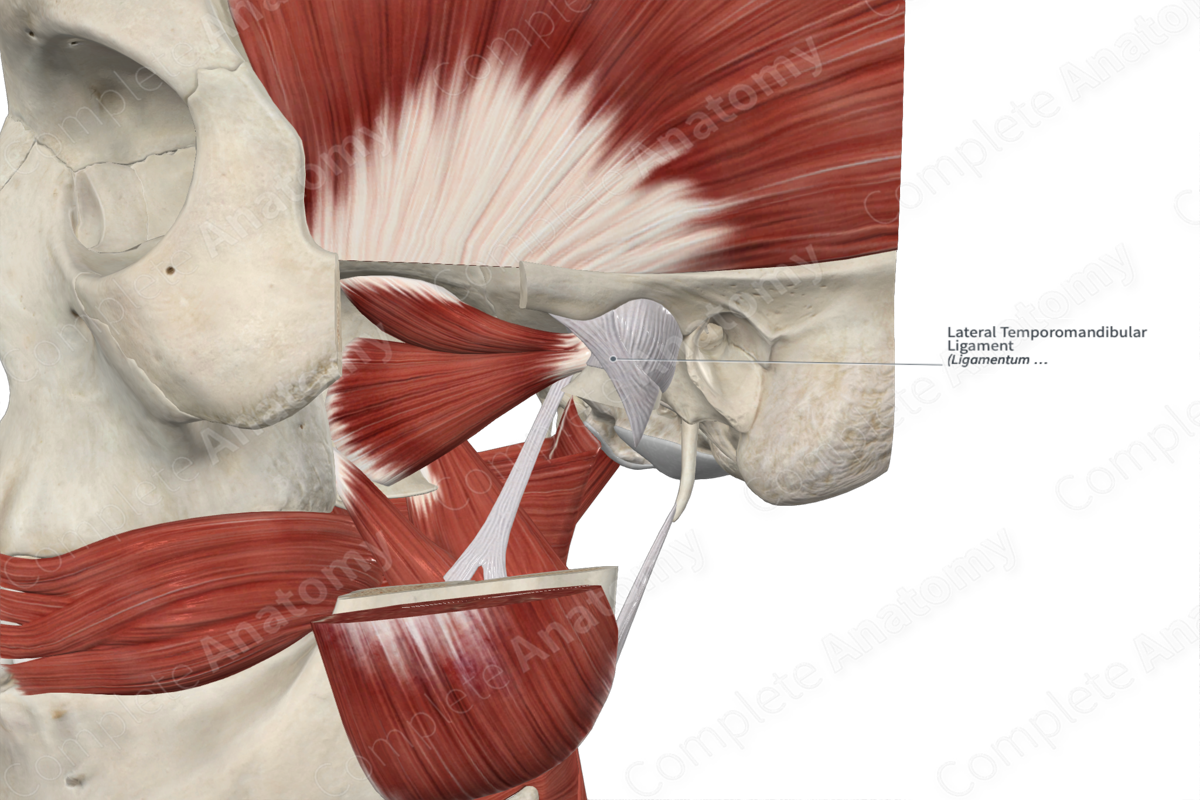
• Temporomandibular ligament - thickening of the lateral capsule
Temporomandibular ligament
temporal
maxillary
Vessels to TMJ
• External carotid a.
• Superficial _____ a.
• _____ a.
External
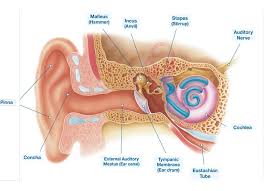
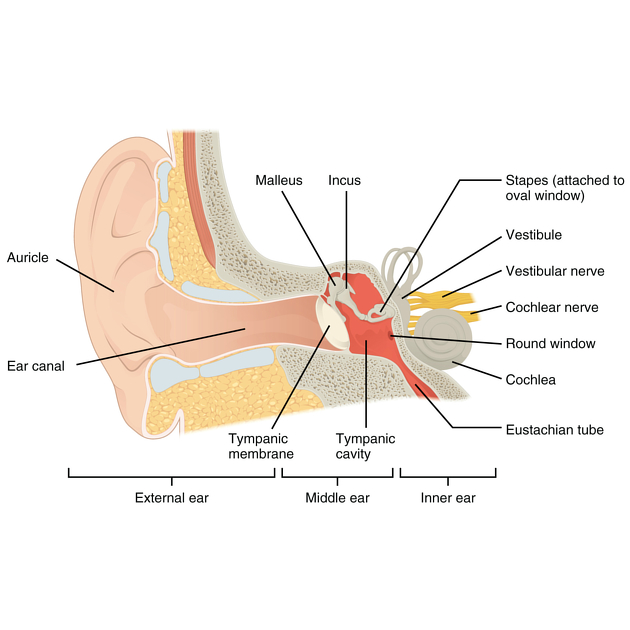
Ear
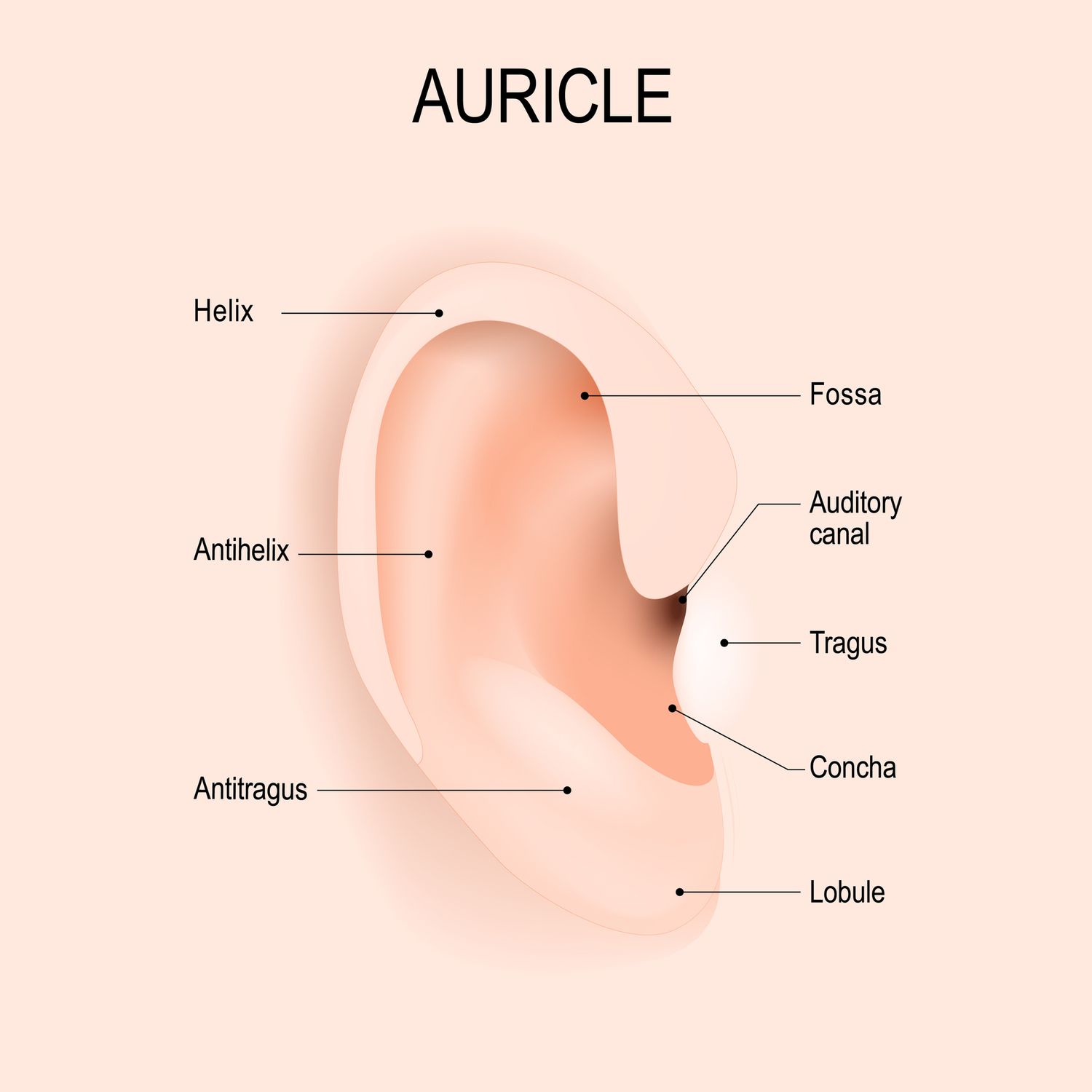
• _____ ear – simple apparatus for collection of sound waves
– Auricle (pinna)
– External auditory canal
– Tympanic membrane
Auricle
External auditory canal
Tympanic membrane
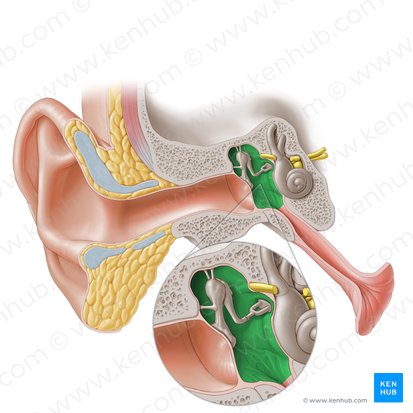
Middle
_____ Ear
• located in the temporal bone and houses the auditory ossicles
– “Six sided box”
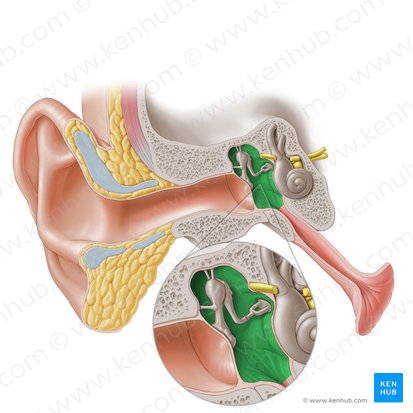
Tympanic cavity
Ossicles
Malleus, incus, stapes
Malleus
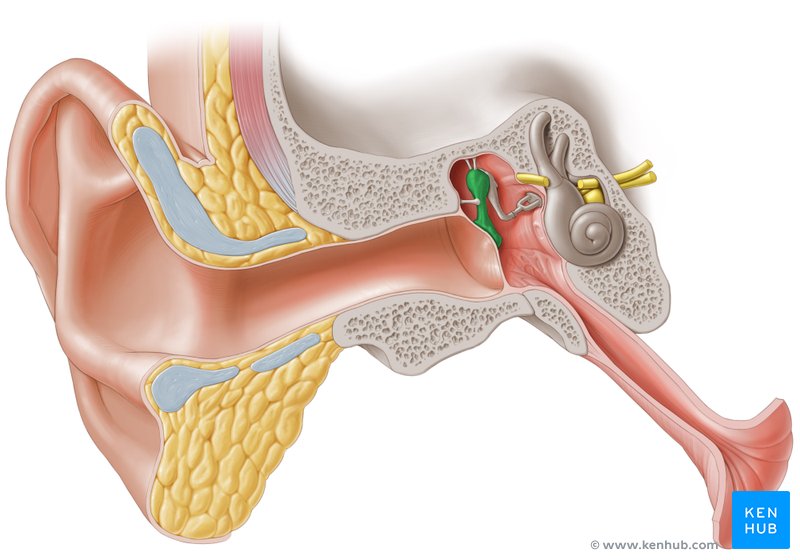
Incus
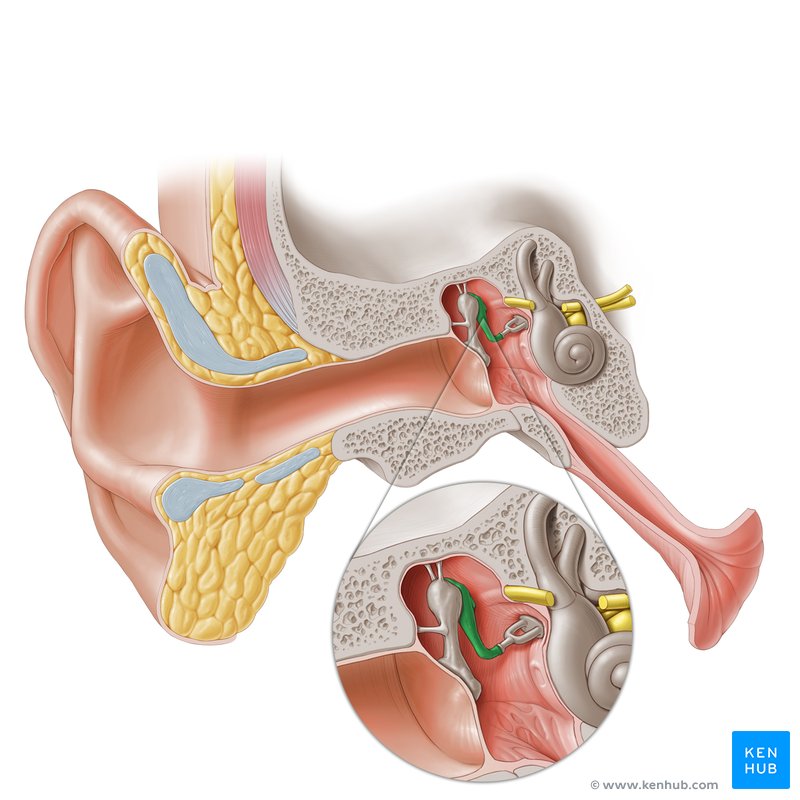
Stapes
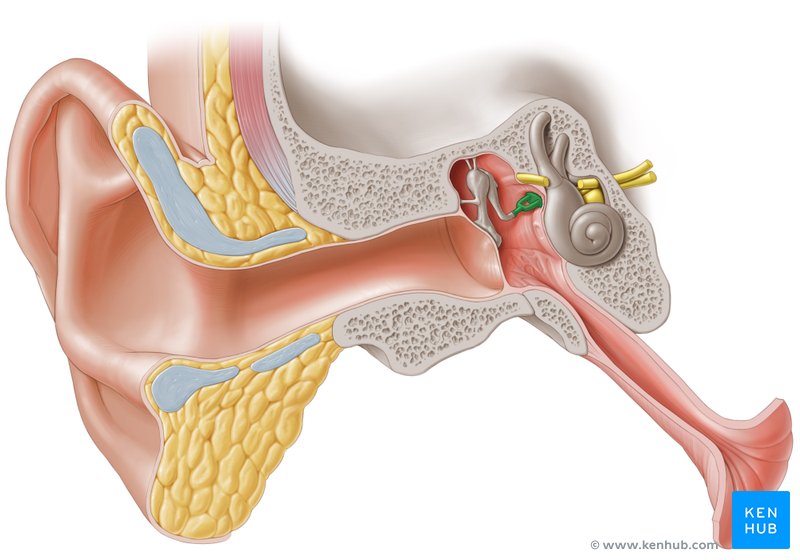
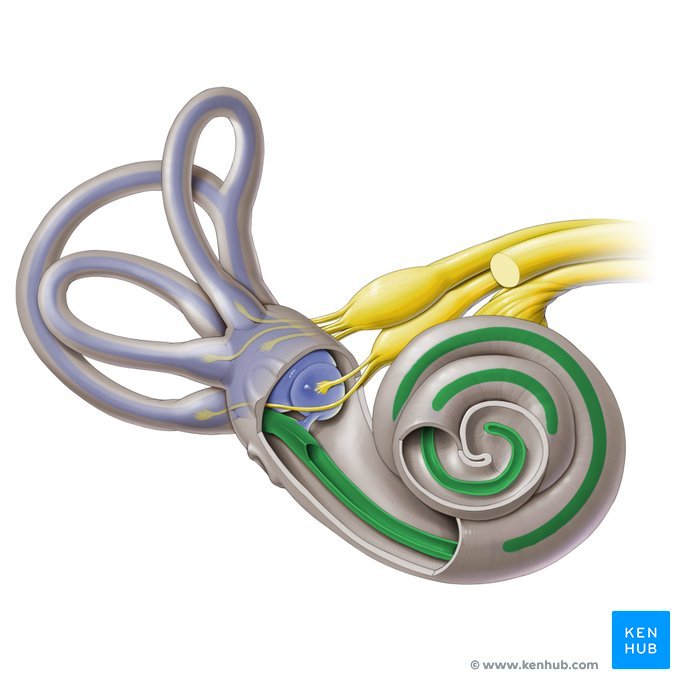
Inner
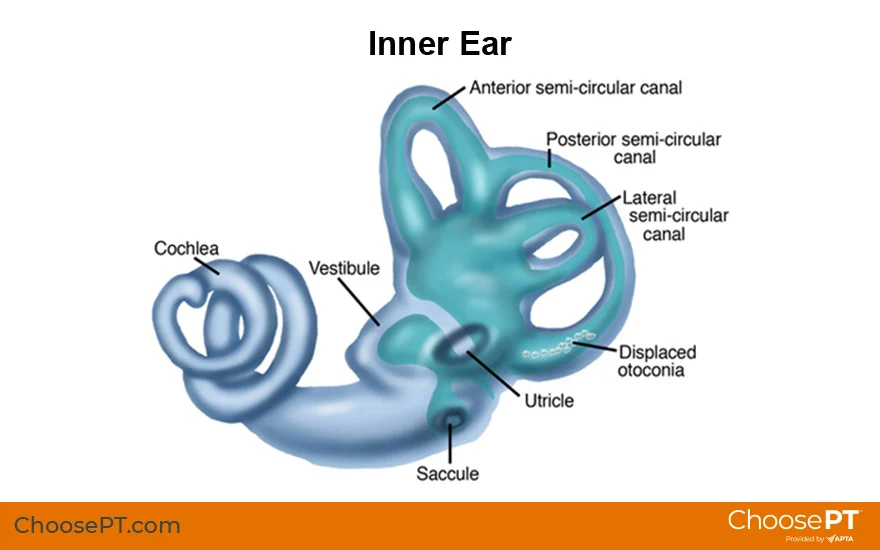
_____ Ear
• Bony labyrinth
– Semicircular canals
– Vestibule
– Cochlea
• Membranous labyrinth
– Semicircular duct
• Cristae ampullaris
– Utricle and saccule
• Maculae
– Cochlear duct
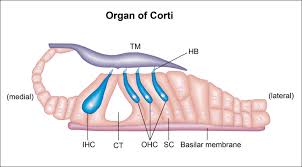
• Organ of Corti
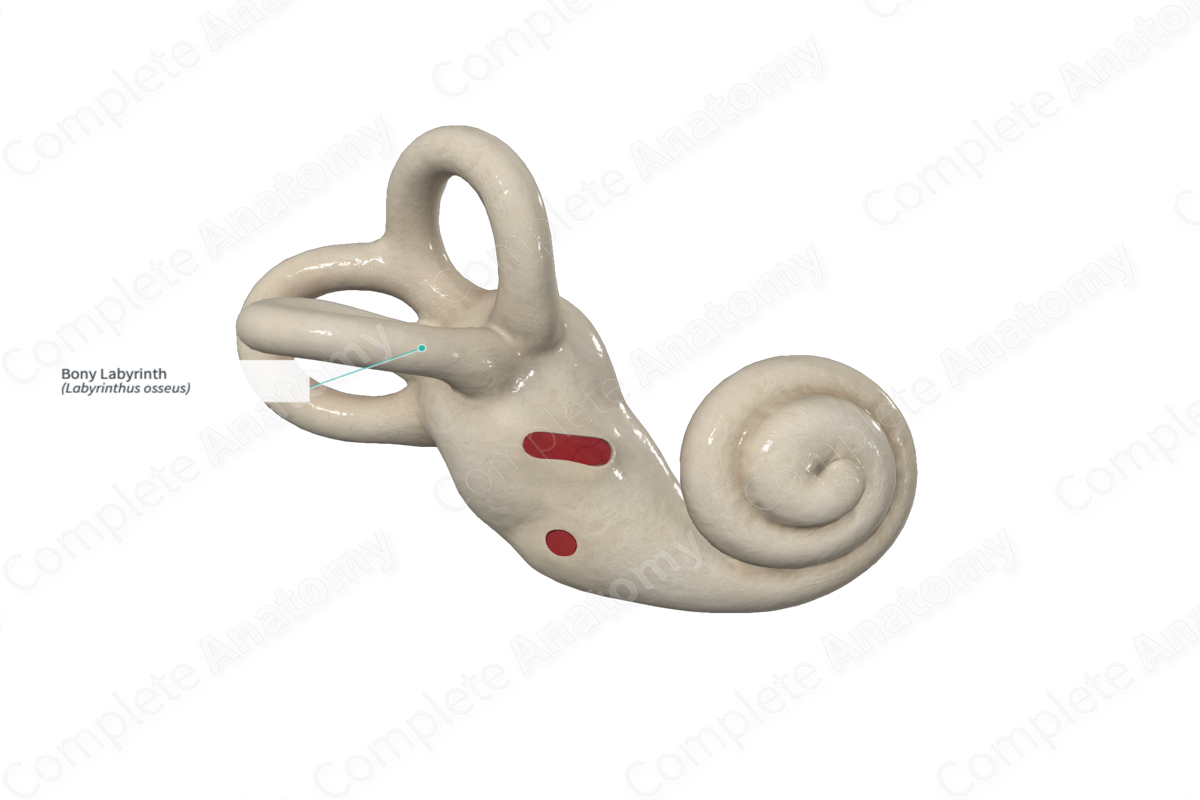
Bony labyrinth
– Semicircular canals
– Vestibule
– Cochlea
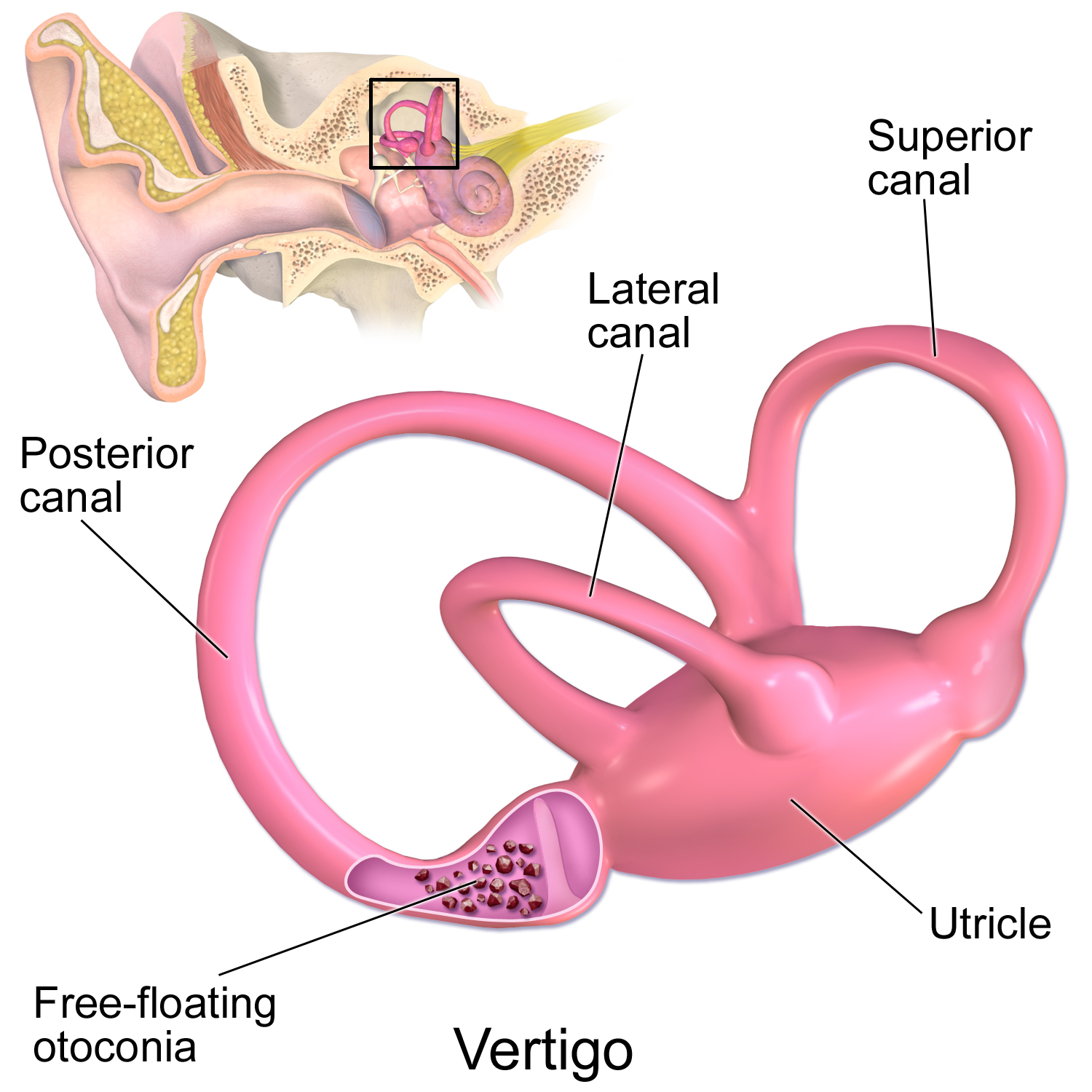
Semicircular canals
three fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that play a crucial role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation
Vestibule
A central cavity within the inner ear's bony labyrinth. It's a key component of the vestibular system, which is crucial for maintaining balance and spatial orientation
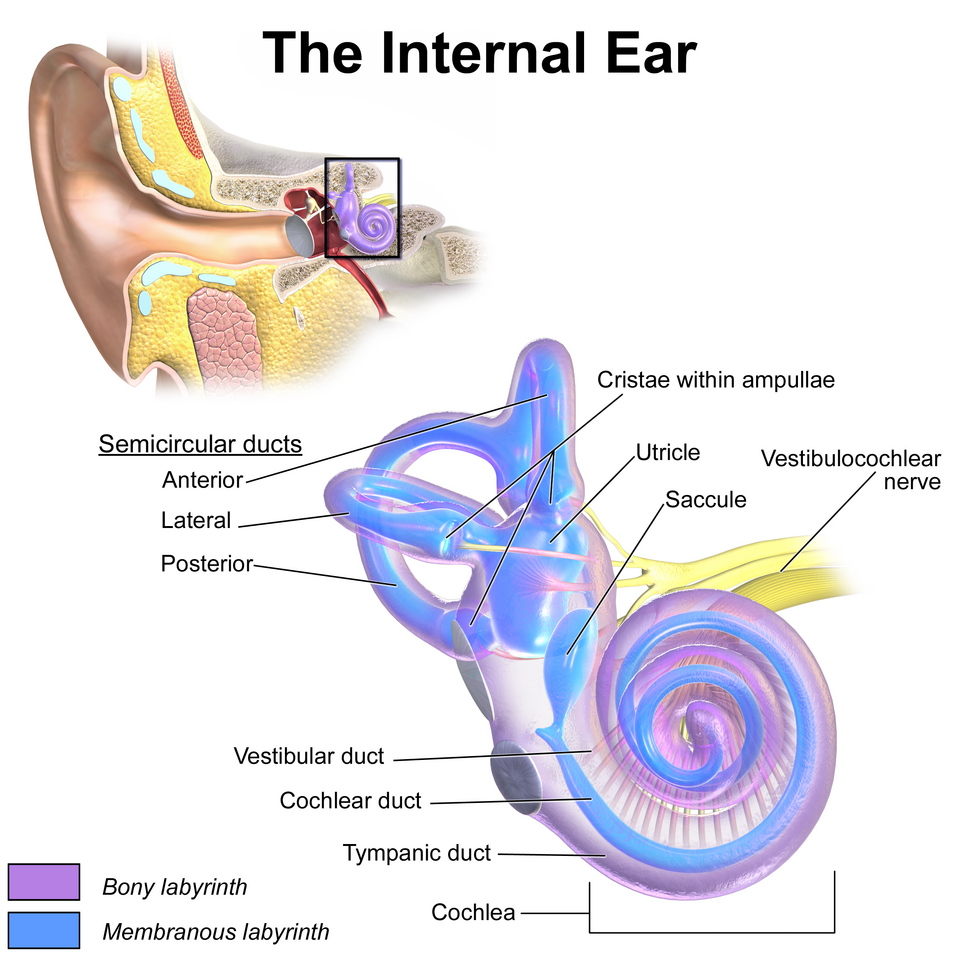
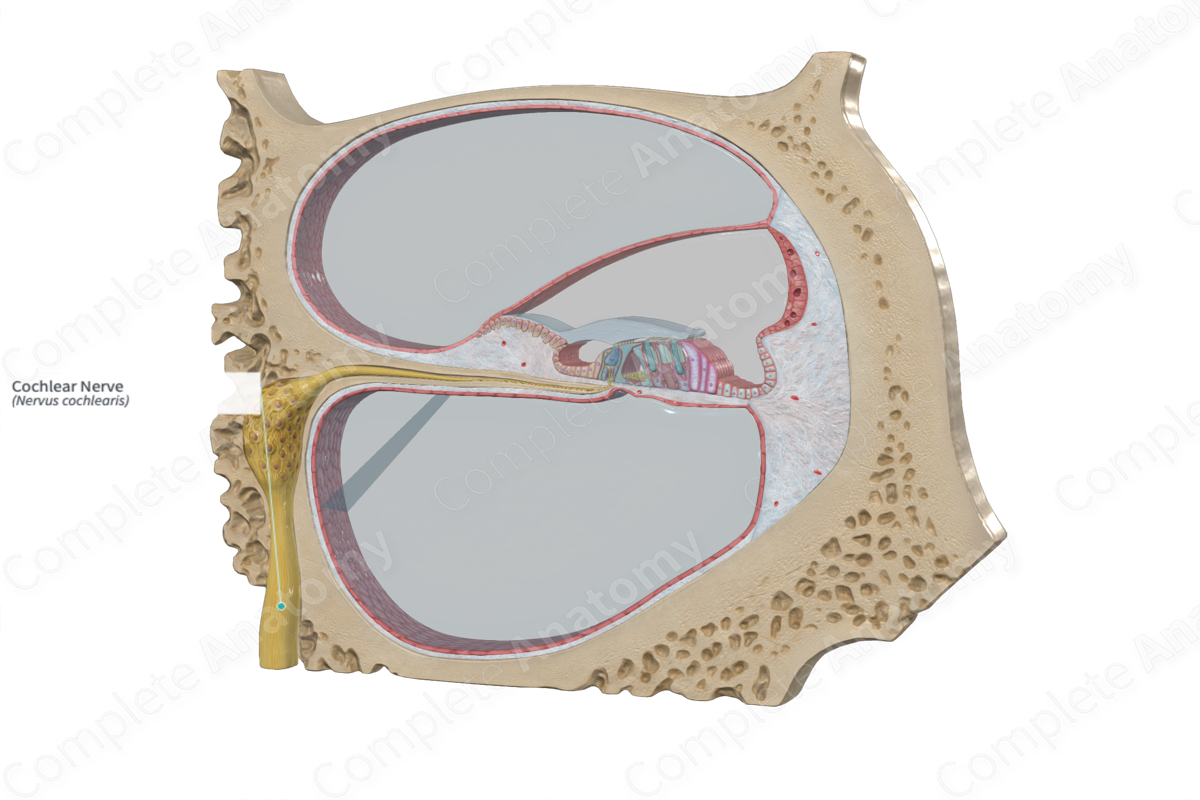
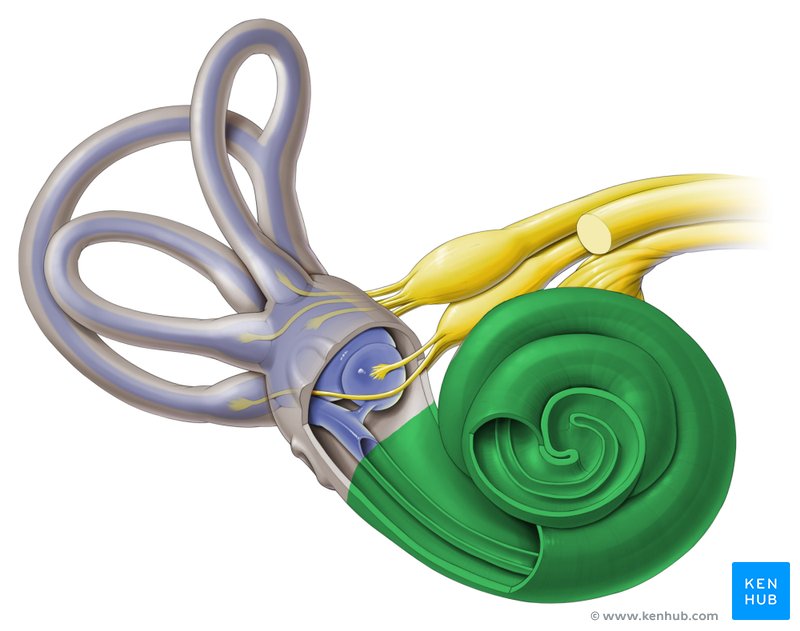
Cochlea
The spiral cavity of the inner ear containing the organ of Corti, which produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations.
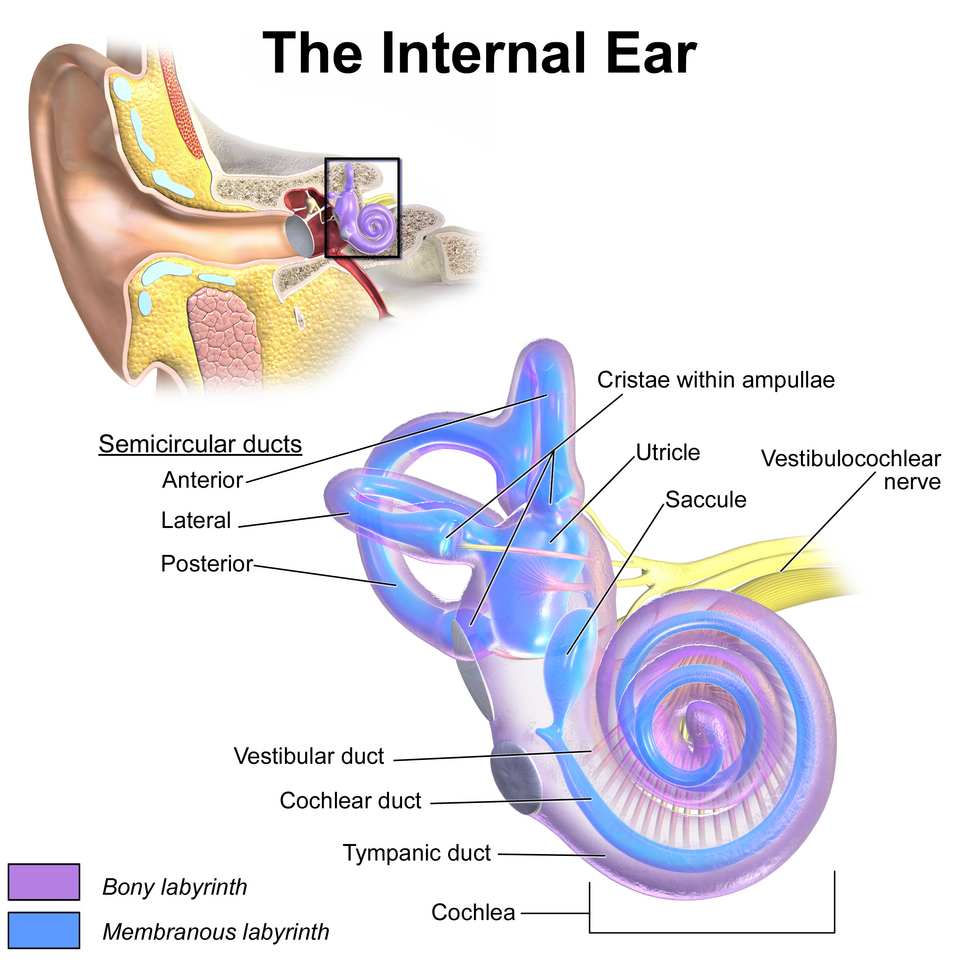
Membranous labyrinth
– Semicircular duct
• Cristae ampullaris
– Utricle and saccule
• Maculae
– Cochlear duct
• Organ of Corti
A system of interconnected sacs and ducts within the inner ear, filled with a fluid called endolymph. It's embedded within the bony labyrinth and plays a crucial role in both hearing and balance.
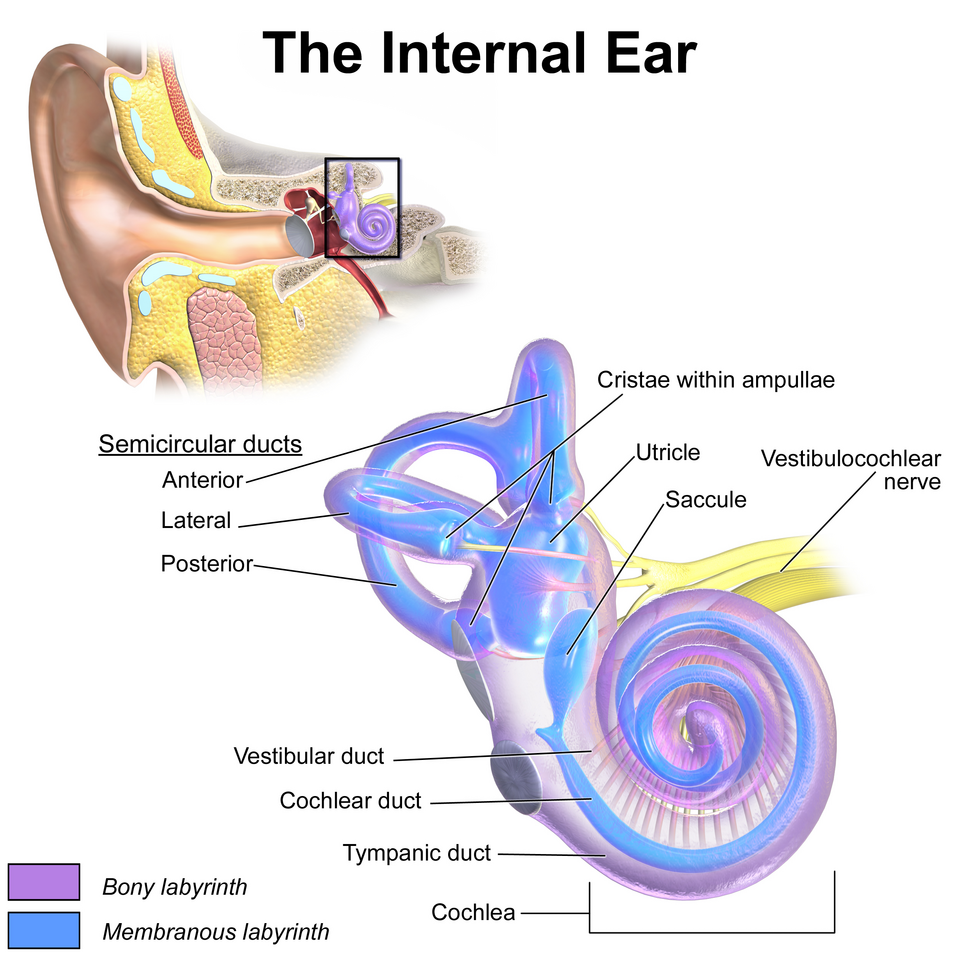
Semicircular duct
Contains cristae ampullaris
Cristae ampullaris
A sensory organ in the inner ear, specifically located within the ampullae of the semicircular canals
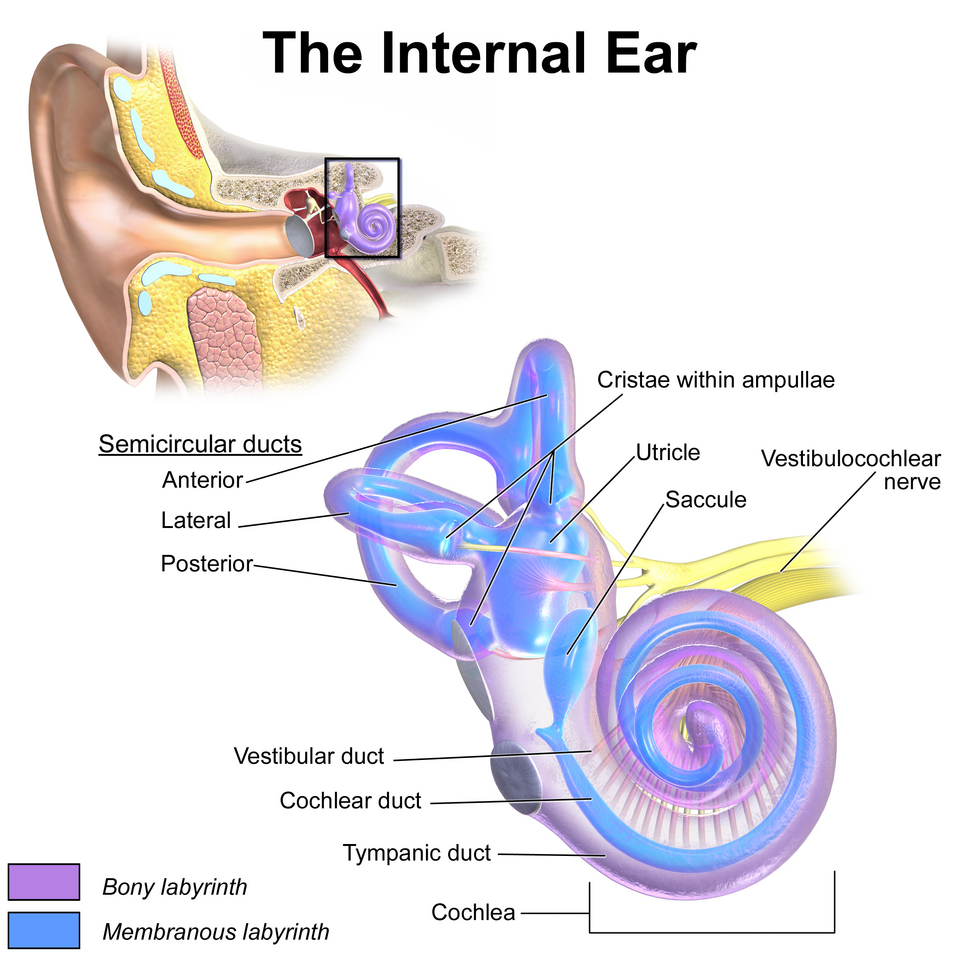
Utricle and saccule
Contains maculae
Two small, fluid-filled sacs within the inner ear's vestibular system, responsible for helping with balance and spatial orientation
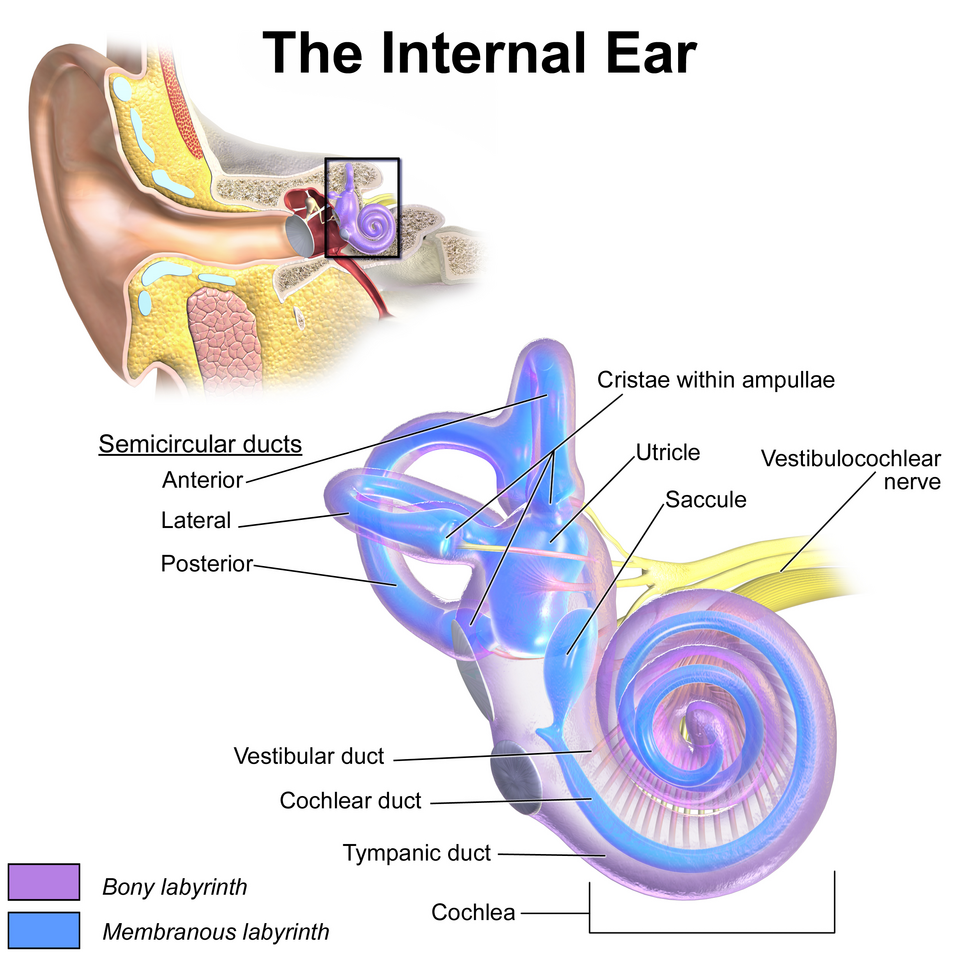
Maculae
A sensory structure in the inner ear, specifically found within the utricle and saccule, that detects linear acceleration and head position
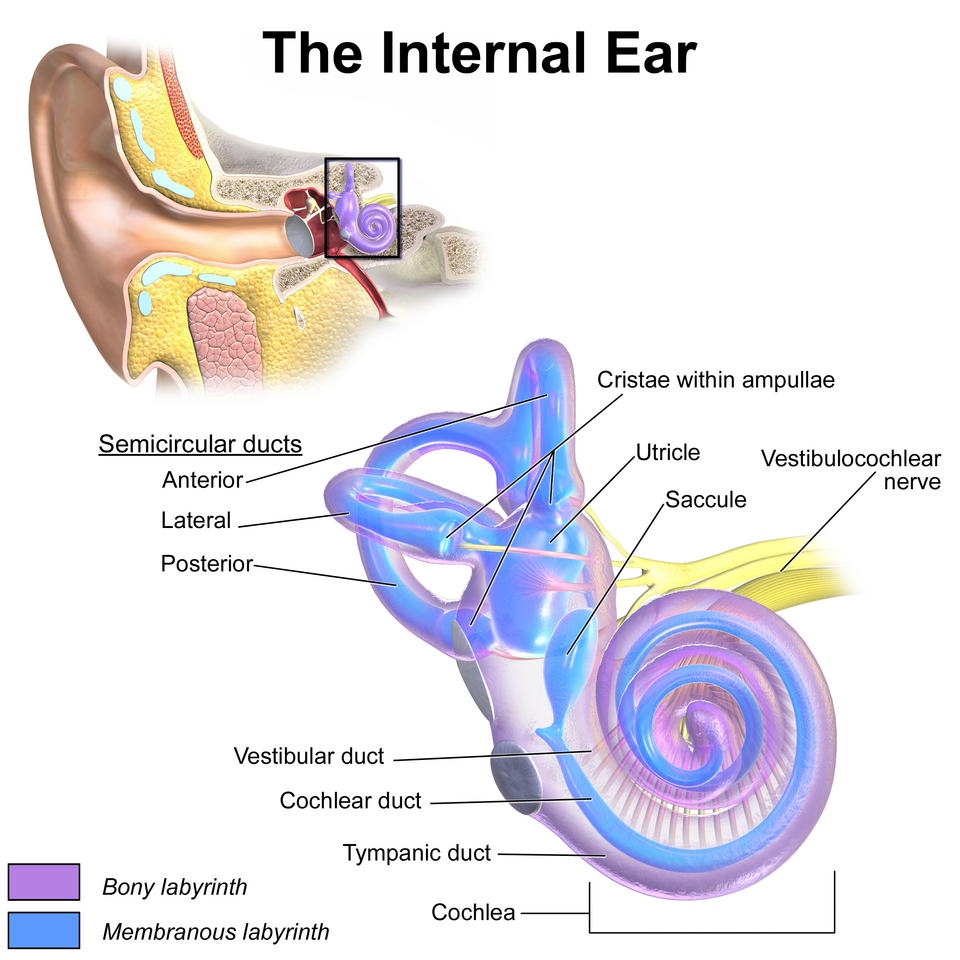
Cochlear duct
Contain organ of Corti
a fluid-filled tube located within the bony cochlea of the inner ear. It plays a crucial role in hearing by converting mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain can interpret.
Organ of Corti
An inner ear organ located within the cochlea that contributes to audition
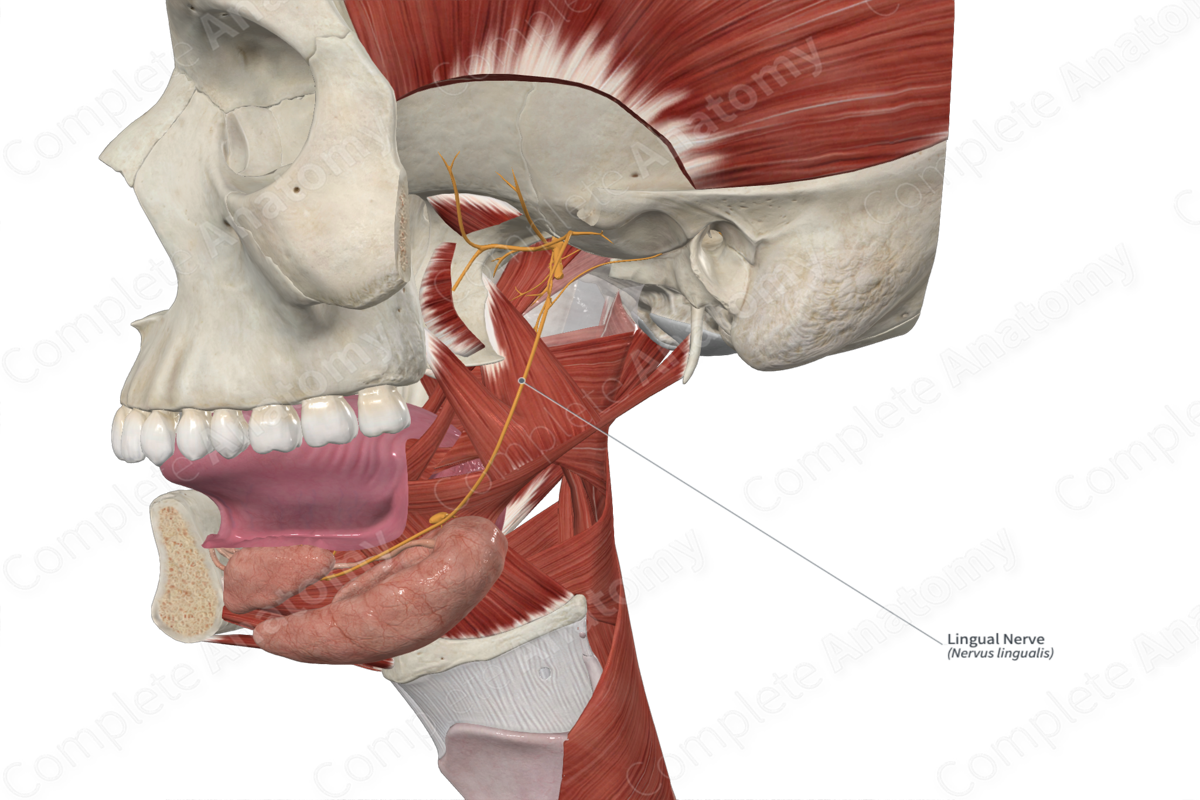
Lingual nerve
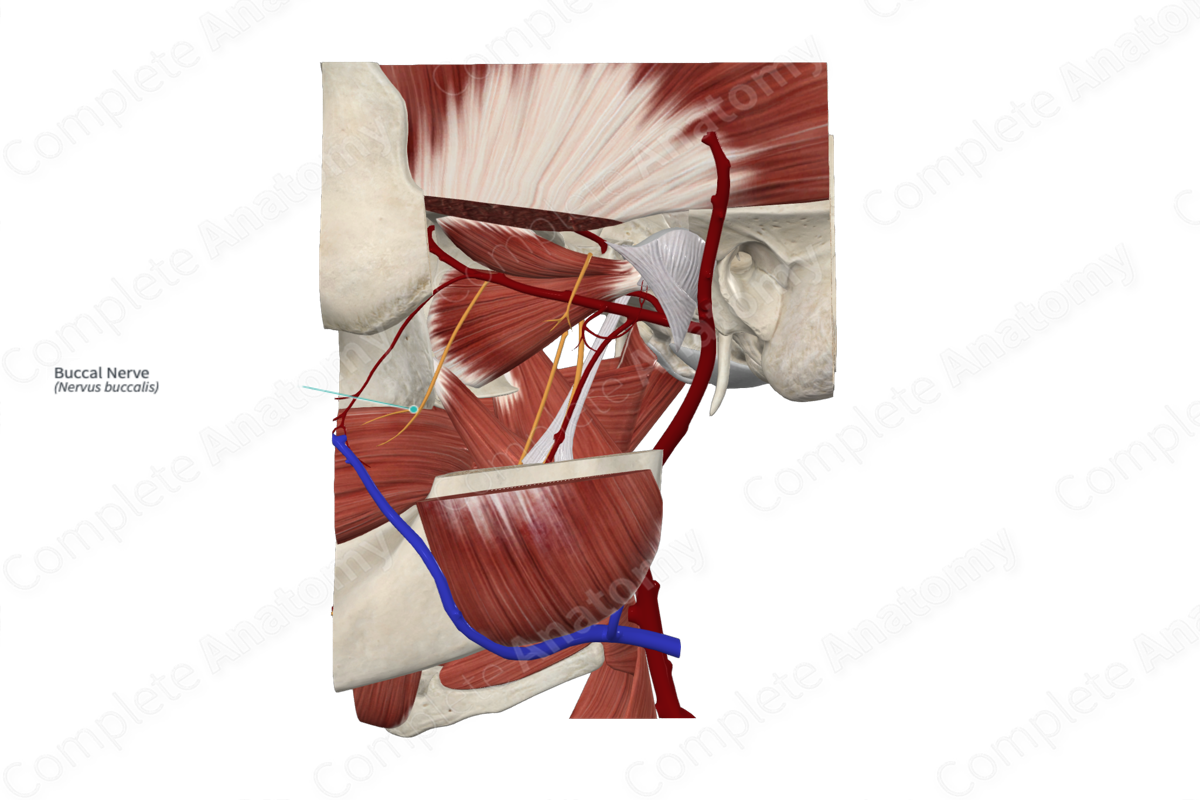
Buccal nerve
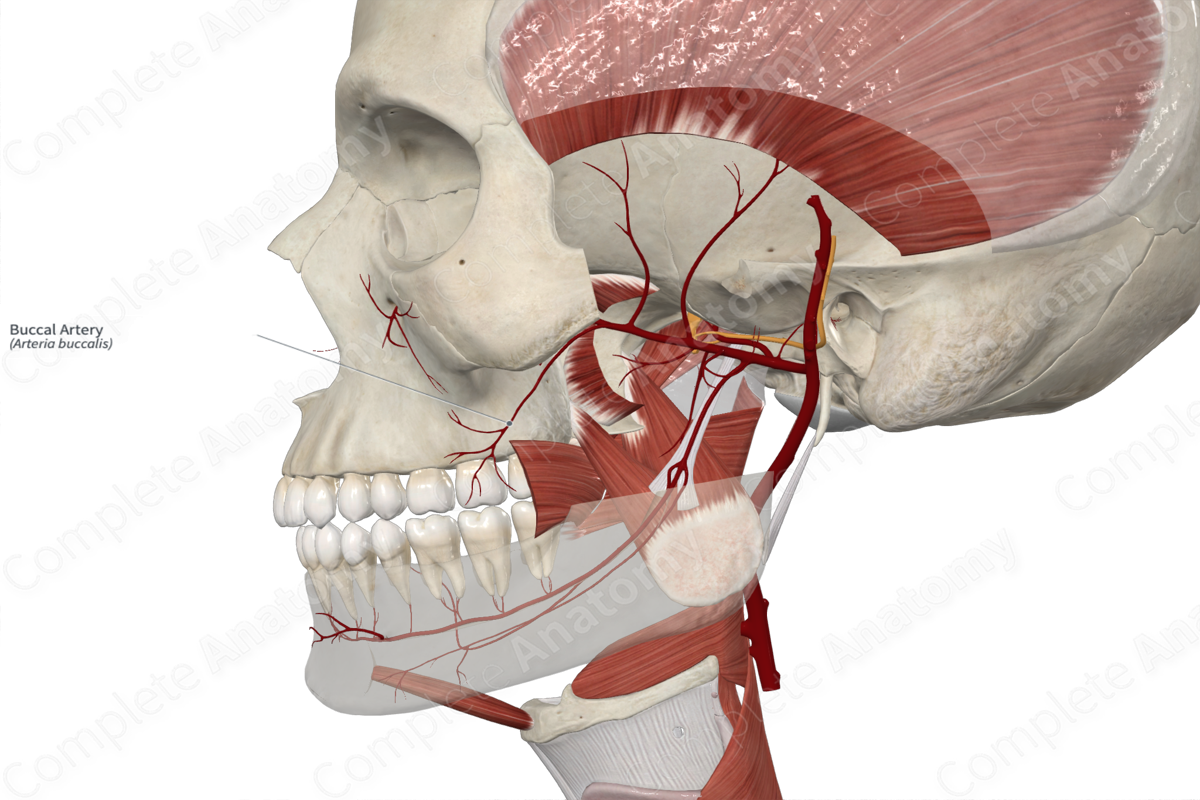
Buccal artery
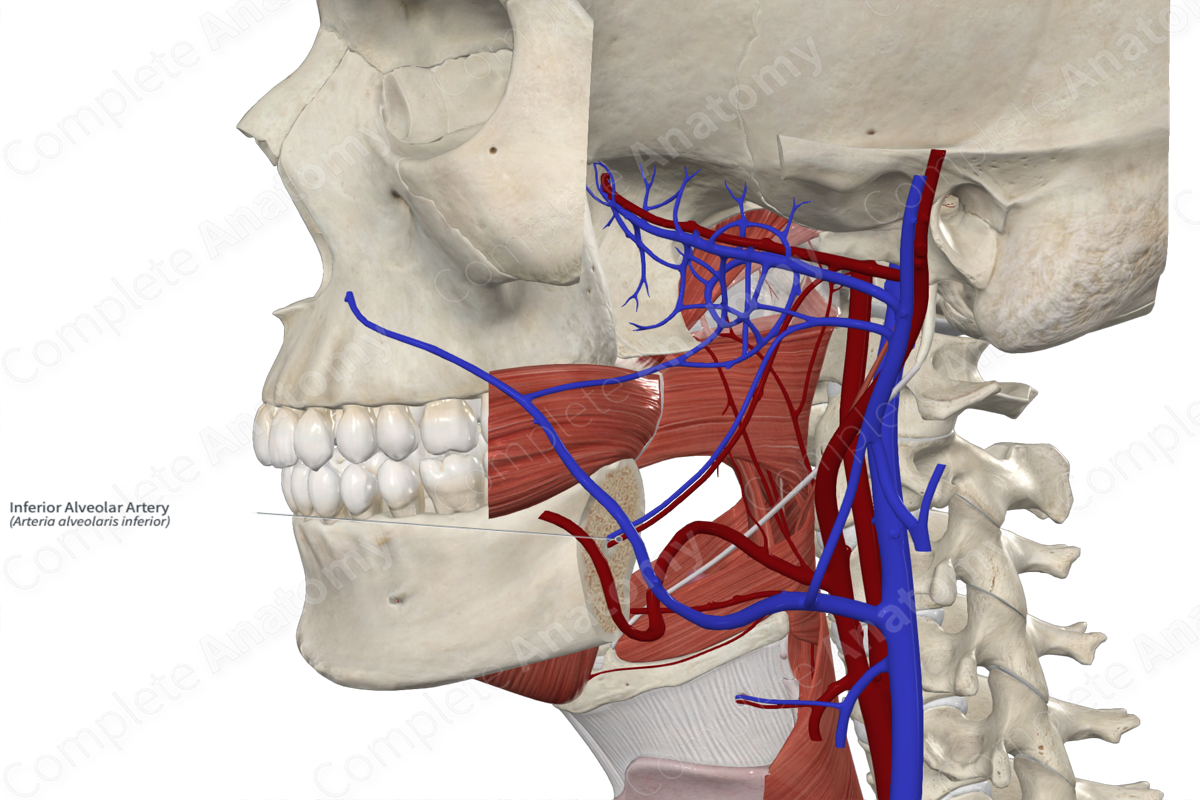
Inferior alveolar artery
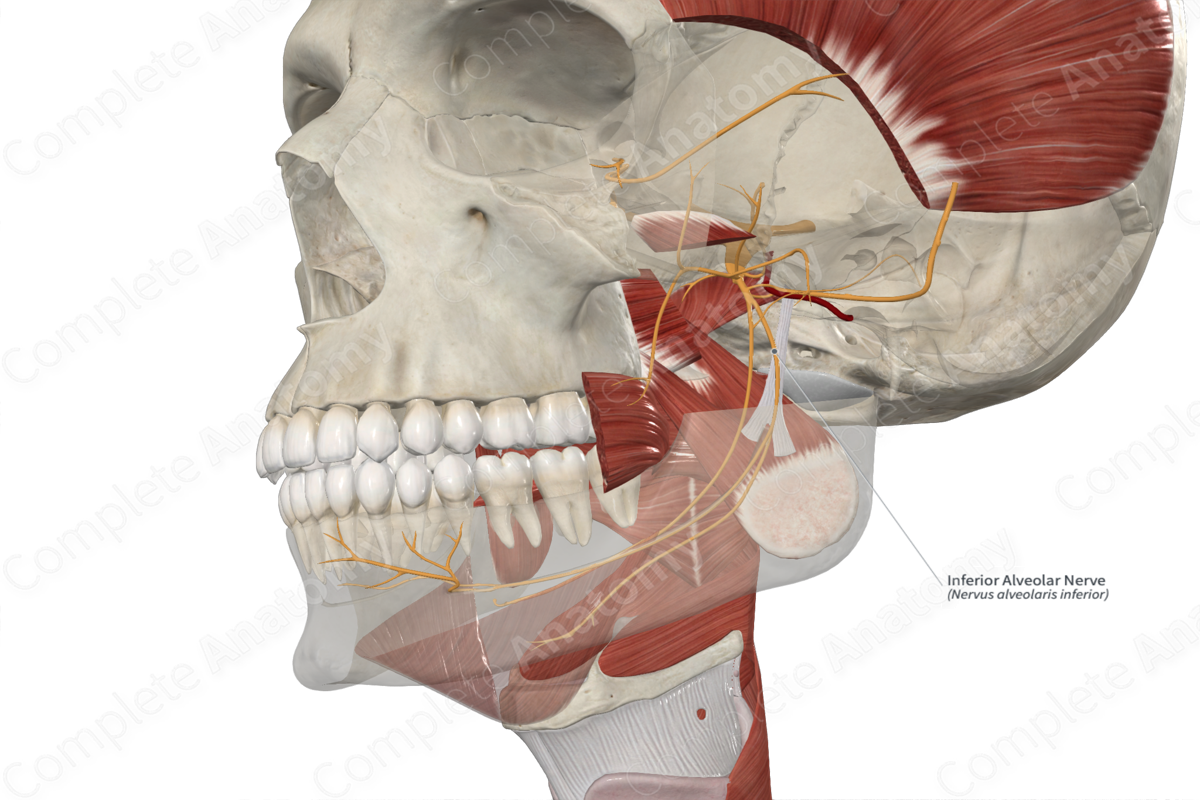
Inferior alveolar nerve
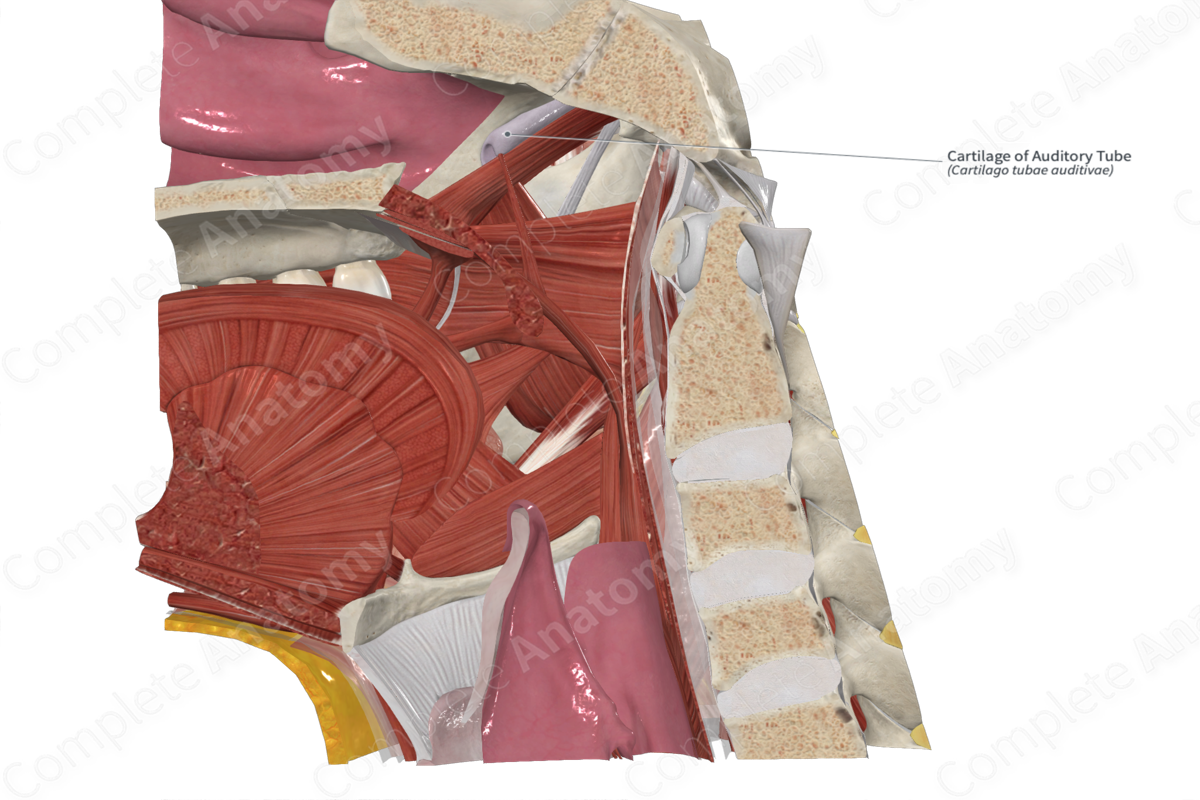
Pharyngotympanic tube
Oval window
An opening in the bony wall between the middle ear and the vestibule of the inner ear
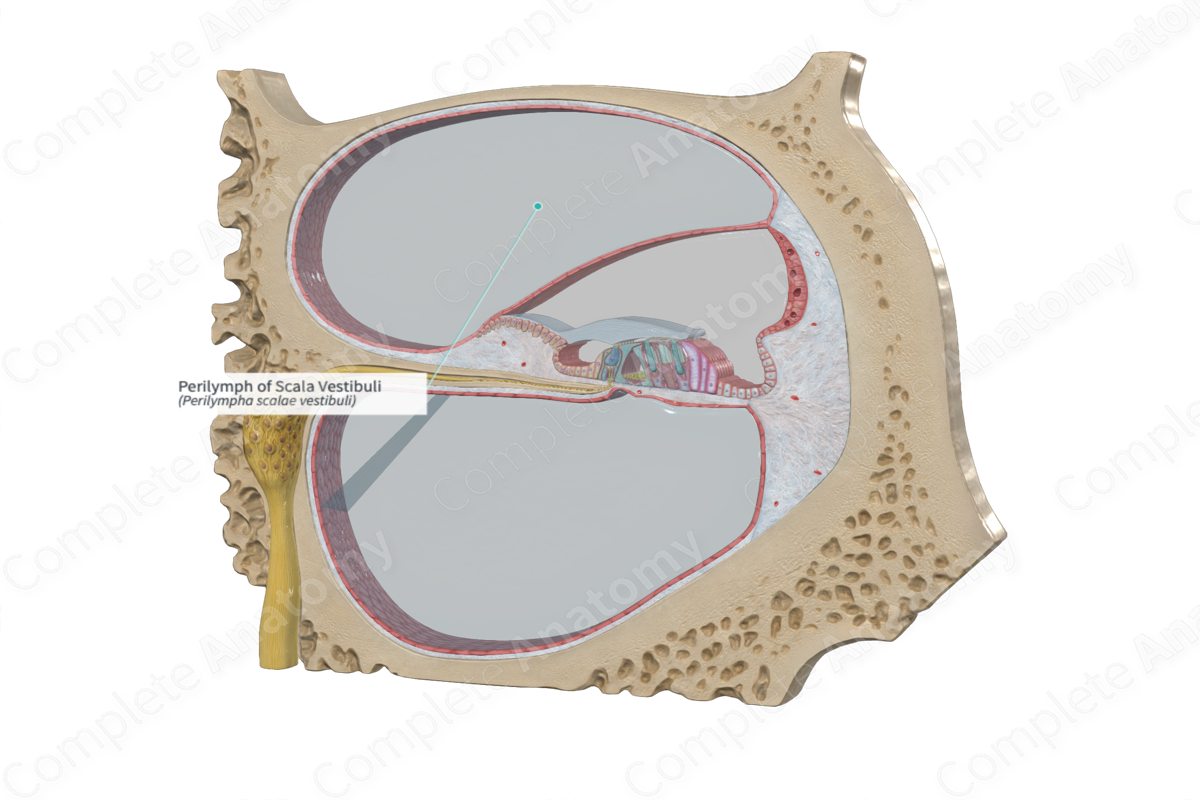
Scala vestibuli
A fluid-filled chamber within the cochlea of the inner ear.
Transmits sound vibrations from the oval window to the cochlear duct, ultimately leading to the perception of sound.
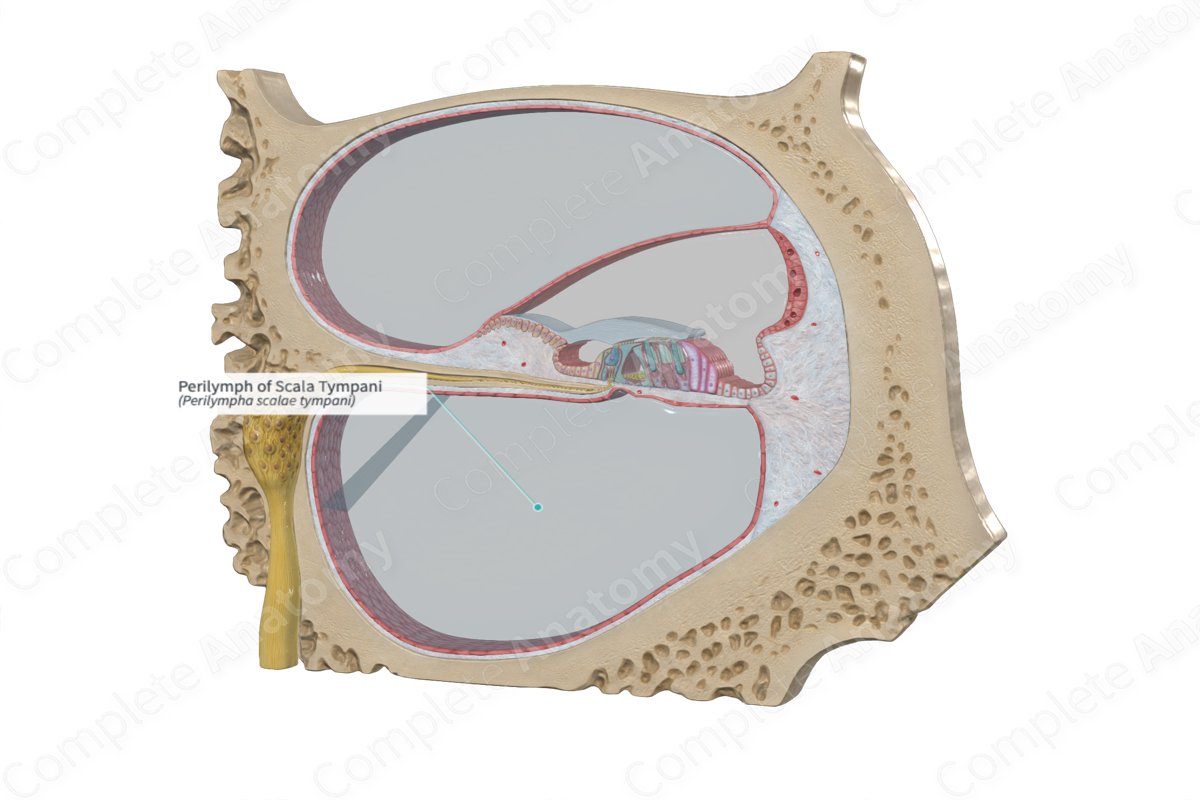
Scala tympani
A fluid-filled chamber within the cochlea of the inner ear.
Plays a crucial role in hearing by transmitting sound vibrations
Scala media
A fluid-filled chamber within the cochlea of the inner ear.
The middle section of the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear responsible for hearing.
Responsible for sound processing and transmission
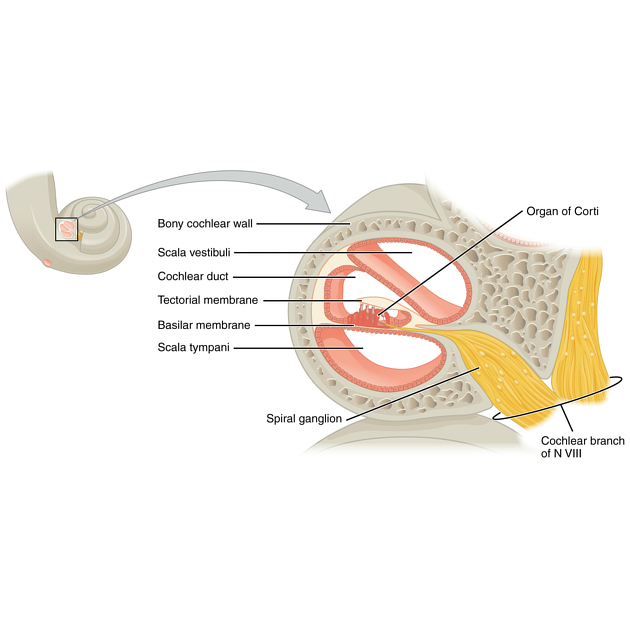
Cochlear nerve