bio unit 3 test review
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
asexual reproduction
-one parent, quickly provides large numbers of offspring
- no variations so all organisms are genetically identical (clones)
-cells preform mitosis and then divide into two cells. cells contain a full set of chromosomes (2n)
sexual reproduction
-two parents allow variation in offspring
-need to find mate, happens more slowly
-must use gametes
-gametes fertilization results in zygote
gametes
special reproductive cells (sex cells)
contain half the normal number of chromosomes
combines during fertilization to restore normal number of chromosomes
-results in a zygote
sperm and egg in animal
pollen and ovules in plants
mitosis (cell division)
used in all forms of asexual reproduction
unicellular use to reproduce
multicellular use to grow/repair damaged tissue
one division of a cell makes two identical diploid(2n) cells with sets of chromosomes in homologous pairs
part of the cell cycle
the cell cycle
interphase - when the cell grows, functions, and copies its dna
G1 phase, S phase, then G2 phasecell division - includes mitosis (equally divides the chromosomes) and cytokinesis (equally divides the cytoplasm)
includes prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
cancer
uncontrolled cell division
caused by mutations in genes that control cell cycle
malignant tumor - cancer cell scan exit tumor, enter blood, and spreader to other parts of body (metastasis)
benign tumor is not cancerous
mutations happen do to chance or exposure to cancer causing substances
meiosis (reduction division)
makes gametes
one cell divides twice producing 4 different haploid (n) cells
separates chromosome pairs so offspring get one chromosome of each pair from each parent
result: 4 daughter cells instead of 2 daughter cells like mitosis
binary fission
bacteria’s way of reproduction
copying the single chromosome and then simply diving into two cells
chromosomes
humans have 46 (22 homologous pairs + 1 pair sex chromosomes)
homologous chromosome pair
chromosomes with the same size and shape and types of genes
carry genes for the same traits
alles
the option for the gene/trait
EX: trait of color in cats is the genes, the alleles are options so black or gray
organisms have two alleles for each gene - one from each parent
if both alles for the gene are the same = homozygous (pure bred)
if different = heterozygous (hybrid)
traits
determined by how the alleles interact with each other in the cell
EX:
dominant/recessive - dominant allele shown over recessive allele
incomplete dominance - neither allele is dominant or appears
codominance - both alleles are dominant and appear
multiple alleles - three or more choices for the allele are found in a population
sex-linked - the allele is located on the x chromosome
polygenic
two or more genes each with its own allele options controls one specific trait
sex chromosomes
females are XX
males are XY
Y chromosome is smaller than X so does not have the same genes
many genes on X chromosome do not have a partner gene
karyotype
visual representation that shows all 23 pairs of humans chromomsomes
genes
determines our traits
the environment can affect expression of genes (ex: temperature)
each gene codes for a making particular protein (ex:proteins)
punnett squares
can be used to predict the probability of inheriting a specific trait
chromosomes defects
caused when a person inherits too many or too few chromosomes
most are lethal
nondisjunction
chromosomes do not separate properly during meiosis when gametes are made
trisomy
one extra chromosome
monosomy
one missing chromosome
down syndrome
not lethal
caused by inheriting an extra chromosome 21
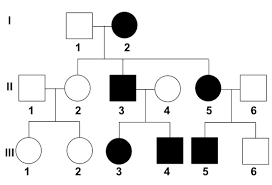
pedigree chart
diagram that traces the occurrence of a trait in a family
sex-linked + recessive
males only need one allele on the X
females must inherit recessive allele on both X chromosomes to show trait
carrier
an individual with one recessive allele and one dominant allele
does not show trait
may pass the recessive allele to the next generation
DNA
the molecule that makes up genes and chromosomes
structure: double helix, two strands of nucleotides, one strand on each side
made of nucleotides containing sugar
made of phosphate group and one of 4 nitrogen bases
4 nitrogen base
adenine
thymine
cytosine
guanine
base pair rule
a - t
c - g
a - u
dna replication
the structure of DNA allows it to replicate itself almost perfectly
uses the base rule to replicate
happens during interphase, BEFORE mitosis
protein synthesis
same thing as translation
making proteins, how genes control your body
codon
a sequence of three bases in DNA
each represents on specific amino acid
ribosomes assemble amino acids in the order as they are listed in DNA codons
how your body functions depends on the order of bases in your genes
RNA
made of nucleotides
types of RNA:
mRNA - messenger RNA, copy DNA code for one gene
tRNA - transfer RNA, carry amino acids to ribosomes
rRNA - ribosomal RNA, form structure of ribosomes
transcription
mRNA copies the DNA code from the gene in the nucleus
translation
tRNA brings the correct amino acids to the ribosomes by matching bases with mRNA codons
mutagenic agents
any environmental factor that causes mutations
EX:
radiations
toxic chemicals
carcinogens
viruses
gene mutations
causes a change in DNA bases of a gene, which can change the shape of a proteins, which can change how a protein functions
happens when DNA bases are altered (substitution, insertion, deletion)
changes the codon which makes the wrong protein
can only be passed to offspring if the mutation happens in reproductive cells (sperm or eggs)
damaged chromosomes
chromosomes that break
duplication - section of chromosomes repeated
deletion - section of chromosome missing
inversion - section of chromosome is backwards
translocation - section of chromosomes Is moved to different chromosomes
cystic fibrosis
produced thick sticky mucus
clogs lungs, difficultly breathing, more infections
common in white europeans
tay sachs
liquid build-up destroys nerve cells in brain and spinal cord
result is death within 1-5 years usually
common in eastern european jewish, french canadian
sickle cell anemia
defective hemoglobin in red blood cells cause sickle cell shape
can’t carry oxygen + cells clump together
common in african americans/western mediterranian
cancer genes
oncogenes - mutations in genes that control cell cycle (mitosis)
cells divide out of control
happens in body cells, not gametes
less than 5% cancers are inherited
polymerase
enzyme proofreads so base pairs are correct