Building and Managing Complex Systems: Concepts, Challenges, and Strategies in Software Development
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What is the difference between writing a program and building a system?
Building a system involves more parts, tasks, people, tools, and encompasses greater complexity and size.
What are the two dimensions of complexity in system building?
Breadth of complexity and depth of complexity.
What does complexity in breadth refer to?
It includes more functionalities, features within each functionality, varieties of interfaces, users, and data.
What happens if the input data increases to 1 trillion in Assignment 1?
The complexity increases significantly due to the size and scale of data.
What does complexity in depth refer to?
It involves more linkages and connections, data sharing, control passing, nested loops, and multiple hierarchical levels.
What is one method to handle complexities in system building?
Simplification through decomposition of the problem and solution, modularization, and separation of concerns.
What is a technique sometimes used to handle complexities that is not often advertised?
Reducing the problem.
How can technology and tools improve handling complexities?
By using databases, programming platforms, computing networks, multi-developer configuration management, modeling techniques, and automated testing.
What is a note regarding the first use of new technologies or processes?
The first time you use them, they may actually increase complexity.
What is one way to improve processes and methodologies in handling complexities?
Coordinating multiple people performing different tasks and providing guidance for overlapping incremental tasks.
What are the key questions in task breakdown for handling complexity?
1. Who performs what task? 2. How is the task completed with what technique or tool? 3. When should which task start and end? 4. Who should coordinate the people and tasks?
What is an example of a modified assignment to illustrate complexity increase?
Showing the largest and smallest of the read-in numbers.
What is another example of a modified assignment that increases complexity?
Sorting the read-in numbers in ascending order.
What is the impact of increased size and complexity on system building?
It leads to an increase in effort required to manage the system.
What is the significance of control passing among functionalities?
It adds to the complexity by requiring careful management of how data and control flow between different parts of the system.
What does modularization of a solution entail?
Breaking down a solution into smaller, manageable modules that can be developed and tested independently.
Why is it important to separate concerns in problem-solving?
It helps to simplify the problem and solution by focusing on one aspect at a time.
What role does automated testing play in managing complexity?
It helps ensure that different parts of the system work correctly as complexity increases.
What is the relationship between task coordination and complexity?
Effective coordination is essential to manage the complexities arising from multiple tasks and people.
What is the challenge of measuring separate artifacts and outcomes in complex systems?
It requires clear guidance to ensure that each aspect is evaluated effectively.
What are the key considerations when handling problems in system development?
Considerations include whether to have a separate test group, how to report problems, the information required for reports, who prioritizes problems, how fixes are returned, whether all problems should be fixed, and how fixes are integrated back into the system.
What are some non-technical considerations for developing and supporting a system?
Non-technical considerations include effort and schedule expansion, assignment and communication expansion, and the need for processes and tools to manage increased complexity and communication paths.
How does the number of people affect communication paths in a system?
For n people, the number of potential communication paths is calculated as ∑ (n-1) = [n x (n-1)] / 2.
![<p>For n people, the number of potential communication paths is calculated as ∑ (n-1) = [n x (n-1)] / 2.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b08e4d3c-99c9-4eaa-b193-f97ad66adc45.jpg)
What are the main activities involved in building a large, complex system?
Main activities include requirements gathering, design (abstraction, decomposition, cohesion, interaction, coupling analysis), implementation (coding and unit testing), integration and tracking, separate testing (functional, component, system, performance), and packaging/releasing the system.
What preparations are needed for supporting a system like payroll before release?
Preparations include estimating the number of expected users, identifying known problems and expected quality, training for users and support personnel, and planning for fix and maintenance cycles.
What post-release support is necessary for a system?
Post-release support includes establishing a call center for problem resolution, addressing major problem fixes and code changes, and implementing functional modifications and enhancements.
What are the three P's that require coordination in systems development and support?
The three P's are Processes (methodologies), Product (final and intermediate artifacts), and People (developers, support personnel, and users).
Why is coordination important in large systems development?
Coordination is important due to the increased number of parts, developers, and users, which complicates communication and requires structured processes.
What is the relationship between effort and software product quality?
The relationship between effort and software product quality is complex and varies based on the specific context of the development process.
How does complexity affect software development effort and quality?
Complexity can increase both the effort required for software development and the potential quality of the software product, but the exact relationship can vary.
What is the initial step in learning to code according to the notes?
Starting by learning how to code in some programming language with a small, hypothetical, and well-defined problem.
What common experience do programmers face when writing code?
The program usually does not work on the first try, and may require several attempts to get it right.
What are some key activities involved in the programming process?
Testing the program, re-reading and re-thinking problem requirements, tracing, and debugging.
What is the problem statement for the example program discussed?
Given a collection of lines of text stored in a file, sort them in alphabetical order, and write them to another file.
What are some considerations when defining program requirements?
Input formats, sorting, special cases, boundaries, error conditions, performance, real-time requirements, and security.
What are design constraints mentioned in the notes?
User interface, typical and maximum input sizes, platforms, and schedule.
When should testing occur during the programming process?
Testing should occur while the program is defined, developed, and after it is completed.
What are the different kinds of tests mentioned?
Acceptance (validation), verification, unit testing, black-box, and white-box testing.
What is the focus of Version 1 in the estimation process?
Estimating the total minutes to write a program that reads lines from one file and writes sorted lines to another file.
What does Version 2 of the estimation process consider?
Whether the assumption of working straight through on the task without interruptions is realistic, and estimating the calendar time for completion.
What is the purpose of Version 3 in the estimation process?
To divide the entire program into separate developmental tasks and subtasks.
What class is suggested to be created for the program, and what methods should it include?
A class called StringSorter with three public methods: Read, Write, and Sort.
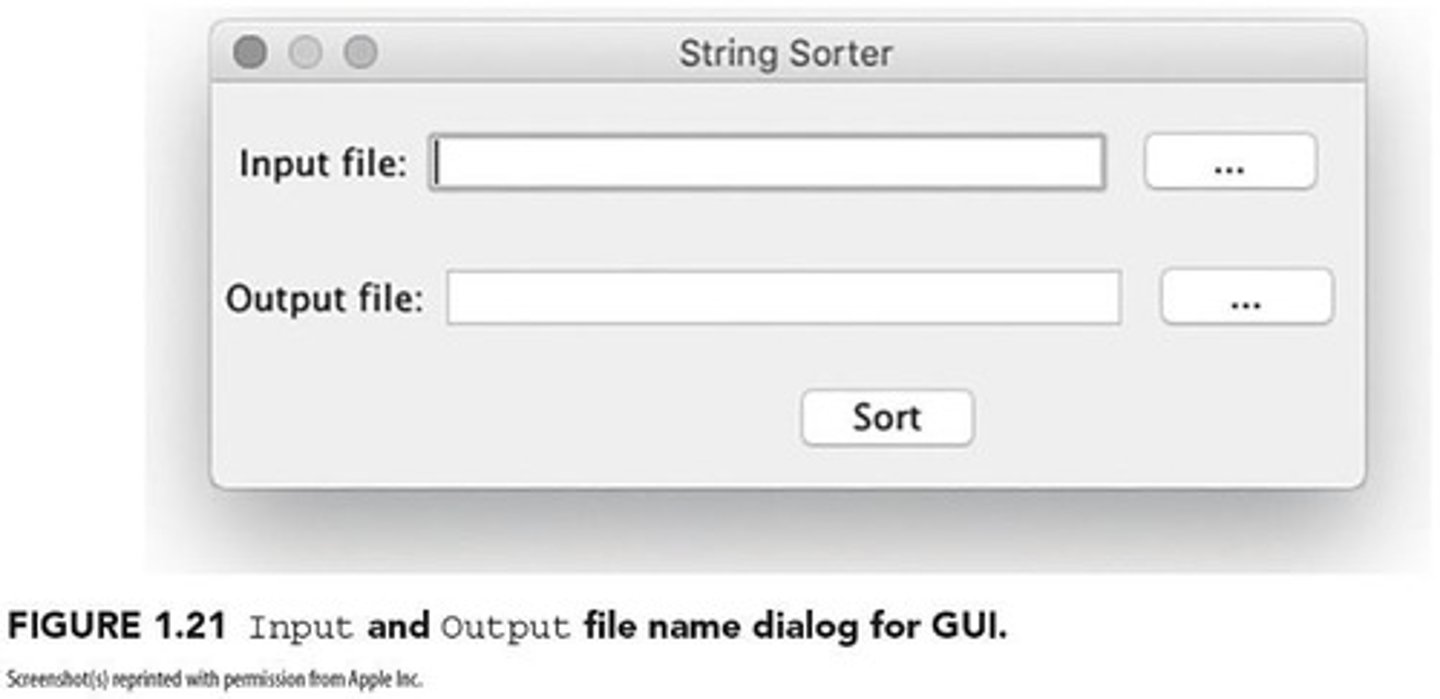
What sorting algorithm is suggested for the StringSorter class?
Finding the largest element, placing it at the end of the array, and then sorting the rest of the array using the same mechanism.
What should be estimated in Step 1 of Version 1?
The ideal total time to complete the task.
What should be estimated in Step 2 of Version 2?
The estimated calendar time started, ended, and breaks.
What is a common assumption made when estimating time for programming tasks?
That the programmer can work without interruptions.
What is an example of a task that might interrupt programming work?
Going to the restroom or drinking water.
What is the significance of acceptance testing?
It validates that the program meets the requirements and is acceptable to the client.
What does verification testing ensure?
It ensures that the program is built correctly according to specifications.
What is the difference between black-box and white-box testing?
Black-box testing focuses on input/output without knowledge of internal workings, while white-box testing involves testing internal structures or workings of the program.
What is the importance of re-reading and re-thinking problem requirements?
To ensure that all aspects of the problem are understood and addressed, as initial assumptions may be incomplete.
What is the purpose of the IndexOfBiggest method?
To return the index of the biggest element in an array.
What are the first two steps in the development process of the IndexOfBiggest method?
1) Understand the problem — requirements; 2) Perform some design based on requirements.
What types of requirements should be considered when understanding the problem?
Functionalities and non-functionalities such as performance, security, modifiability, and marketability.
What should be included in the design phase of the IndexOfBiggest method?
Organizing functionalities, focusing on input/output, and considering constraints like speed and programming language.
What are the key activities in the coding/implementation phase?
A) Converting input/output to specific UI; B) Sequencing processing; C) Ensuring correct algorithm conversion; D) Using language libraries properly.
What is the purpose of the verification/testing phase?
To check program results against predetermined expected inputs and debug if necessary.
What should be done if the program results do not match expected outcomes during testing?
Debug the program, fix the issues, and retest until all test cases produce expected results.
What are some questions to consider after completing the coding work?
1) How long did it take to complete? 2) How much effort was expended? 3) Does the solution solve the complete problem? 4) How good is the work?
What was the class's average estimated time to implement a simple program that computes the average of numbers?
Estimates ranged from 10 minutes to 1 hour.
What was the range of elapsed time reported by the class for assignment completion?
The range was from 5 days to 46 minutes, mostly between 1 and 3 hours.
What was the range of effort reported by the class in person hours?
The range was from 8 person hours to 40 person minutes, mostly between 1 and 3 person hours.
What is a simple problem that students were asked to solve in class?
To write a program that accepts numerical inputs, computes the average, and outputs the answer.
What should be included in the design phase regarding input/output?
Consider the specific UI interface or I/O format for the program.
What is the significance of test cases in the verification phase?
Test cases are predetermined inputs used to validate that the program produces expected results.
What is a possible outcome if the solution does not match the problem requirements?
The solution may need to be revised or improved to better align with the requirements.
What does the term 'debug' refer to in the context of programming?
The process of identifying and fixing errors in the code.
What should be done after fixing issues during the testing phase?
Retest the program to ensure that it now produces the expected results.
How can one measure the quality of the work done on the program?
By evaluating the code, design, documentation, and testing.
What are some non-functional requirements to consider during the design phase?
Performance, security, modifiability, and marketability.
What is the importance of sequencing processing in the implementation phase?
It ensures that the program processes data in the correct order to achieve the desired outcome.
What is the expected outcome of the IndexOfBiggest method?
To accurately identify and return the index of the largest element in the provided array.