Marine Ecology Exam 2
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Define Salt Marsh
Transition zone from ocean to land, where saltwater and freshwater mix
Distribution of salt marshes (2)
Middle to high latitudes
Low energy coasts
Biogenic communities
Ecological communities that are created, modified, or maintained by living organisms
Examples of animals living in salt marshes (6)
Ribbed mussels
Silversides
Coffee bean snail
Fiddler crabs
Periwinkles
Sesarma spp
Succession of salt marshes
Mudflat → grasses → rushes → shrubs
Bottom-up hypothesis
Physical forces (nutrients, physical factors, tides) mediated the energy flow at the bottom of the web
Major vegetation zones highlighting the relative roles of __________ and ___________ ________ in determining the zonation of marsh plants
competition
physiological stress
Foundation species
Those that create habitats and modify the environment with positive effects on the diversity, distribution, and abundance of associated organisms
Examples of foundation species (8)
Reef-building corals
Kelp
Seagrasses
Saltmarsh cordgrass
Mangroves
Oysters
Hydrothermal vent tubeworms
Sponges
Services that foundation species provide (3)
Substrate
Reduced biotic & abiotic stress
Increased food supply
Facilitation
Interactions between 2 or more species in which at least 1 species benefits, and non are negatively affected
Ecosystem engineers
Organisms that directly or indirectly modulate the availability of resources to other species by causing physical state changes in biotic or abiotic materials
Facilitation dominates under _______ stress
High
Competition dominates under ______ stress
Low
4 Fundamental Models of Ecology
Fundamental vs Realized Niche
Competition
Invasion success
IDH and species diversity
Facilitation can…..
Mitigate effects of niche-shrinking factors
Expand the space/area of the fundamental niche
Phase shift
Large, abrupt, and persistent changes in the structure and function of an ecosystem, where it suddenly shifts from one community type to another
Phase shifts are caused by (3)
Disturbances
Human impacts
Loss of key species
Threats to salt marshes (5)
Trophic cascades & runaway grazing
Invasive species
Eutrophication
Toxic pollutants
Climate change - sea-level rise
Services Salt Marshes provide (4)
Key nursery grounds for commercially/recreationally fished shellfish & finfish
Buffer shorelines from storm damage & wave-driven erosion
Sequester & store carbon
Process nutrients that enter estuaries w/ terrestrial runoff
What order is kelp bed/forest in?
Laminariales
Define kelp forest
Large brown algae that form a floating surface canopies
Define kelp bed
Large brown algae that do not form a surface canopy
Examples of subtidal ecosystems? (3)
Coral reefs
Seagrass meadows
Sand/mud seafloors
What do kelp blades do?
“Leaves” light capture, gas exchange, nutrient uptake, waste removal

What are pneumatocysts?
Gas-filled floats
What are stipes?
Long “stem” support, connecting structures

What are holdfasts?
Rootlike attachment to substrate
How many species of kelp are there?
30 species
What is the range of subtidal/sublittoral zone?
Low tide to continental shelf break

What type of kelp is this?
Giant Kelp

What type of kelp is this?
Bull Kelp
Why is kelp brown?
Fucoxanthin
What is the function of Fucoxanthin?
Pigment that assists in light absorption for supporting photosynthesis
Distribution of kelp?
Temperate & subpolar regions
Resources needed for kelp (5)
Hard substrate
Temperature
High Nutrients (N, P)
Light
Wave motion
High temperature = _______ nutrients
low
What is a key limiting nutrient?
Nitrate
Most kelp forests are associated with ______ areas that deliver _______ to the surface.
upwelling
nutrients
Warm water impacts kelp __________ (3)
Growth
Tissue integrity
Reproduction
What is consisted in the canopy layer of kelp forests?
Long stipes, often to surface
What is consisted in the understory layer of kelp forests?
Shorter stipes, often close to bottom
What is consisted in the substrate layer of kelp forests?
Encrusting, clumping ot filamentous algae
When is the lowest bottom temperature?
Spring
When is the warmest temperature on the surface?
Summer
Highest abundance & recruitment occurs during the season of __________
Spring
Lowest abundance occurs during the __________
late summer/fall
Kelp forests in SoCal have decline due to marine ____________
Heatwaves
Significance of Kelp Forests in Ecosystem (3)
Foundation species/ecosystem engineers
High productivity
Support high diversity
Differences between kelp forests & terrestrial forests
Kelp lasts fewer than 25 years
Kelps are faster growing
Kelp forests are _____ diverse in terms of animal phyla, _______ diverse in terms of animal species
more
less
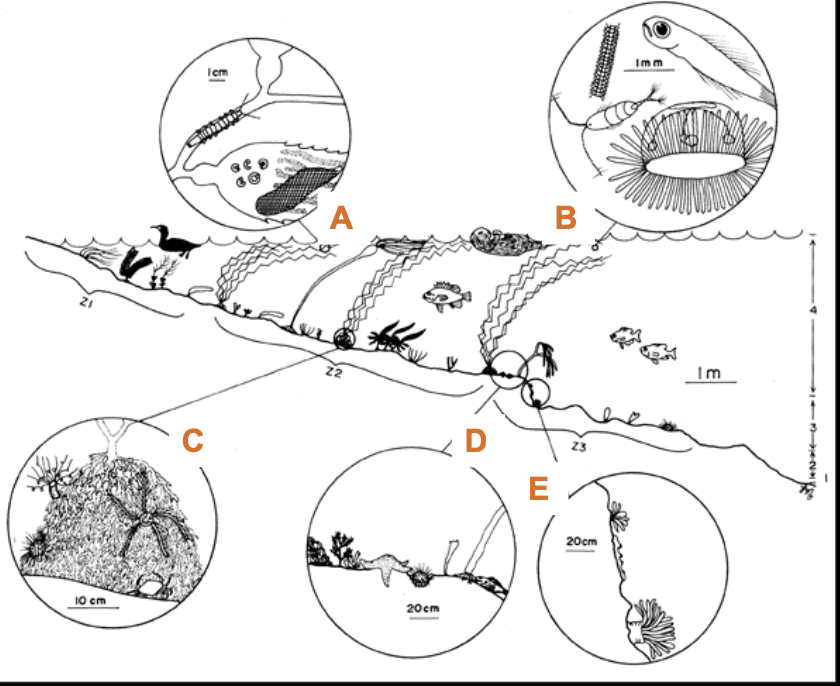
What is “A”?
Canopy & frond assemblage
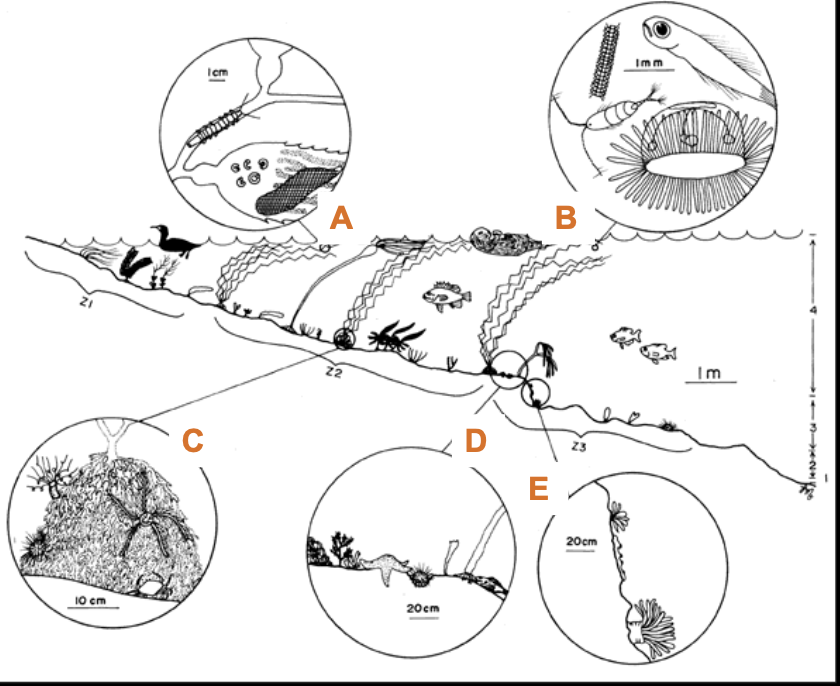
What is “B”?
Planktonic Assemblage
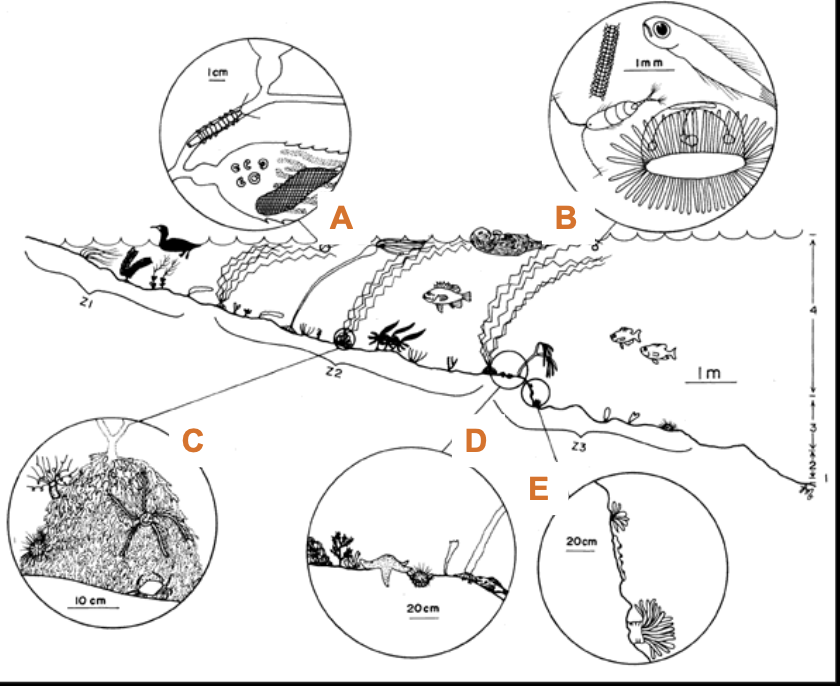
What is “C”?
Holdfast Assemblage
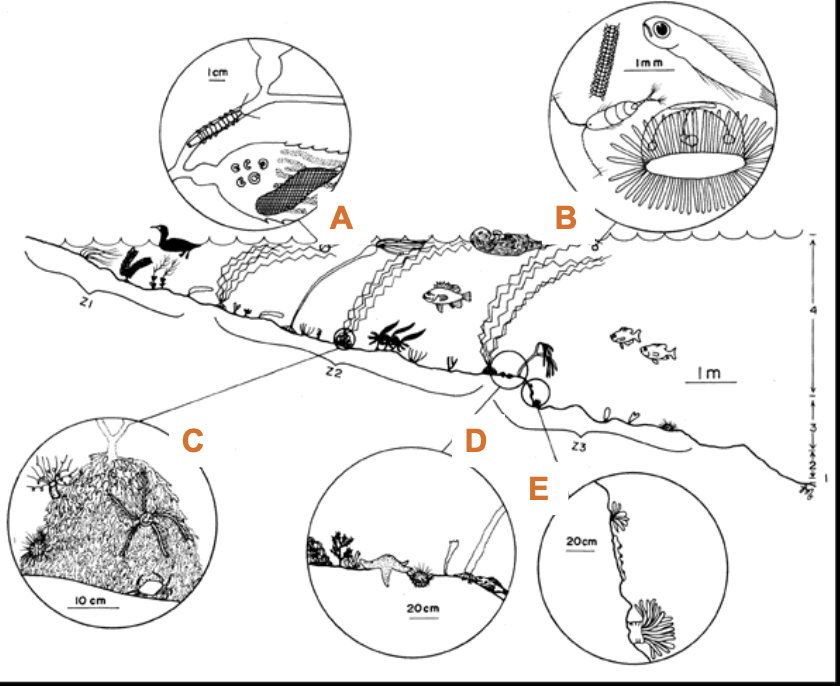
What is “D”?
Horizontal Substrate Assemblage
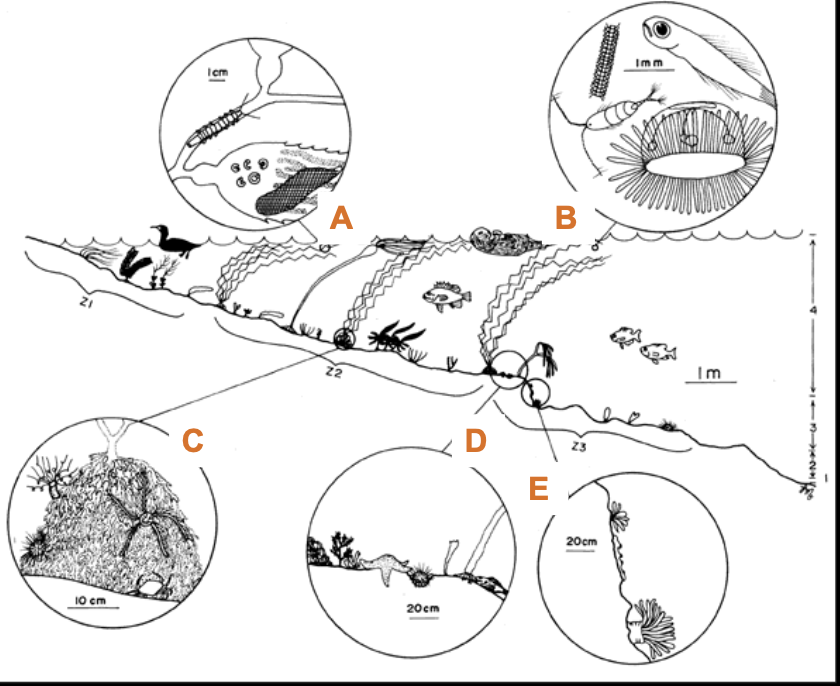
What is “E”?
Vertical wall assemblage
A large proportion of kelp forest productivity is _________
allochthonous = exported to other habitats
Define Functional Diversity
A diversity of species that form similar functions in an ecosystem
Define functional redundancy
When more than one species performs a similar task or function in the ecosystem
Biotic factors that influence kelp forests (3)
competition
grazing
predation
Kelp forest competition types (2)
Light
Space
Kelp forest predators (2)
Urchins
Seastars
Range of the _______ zone is 200-1000m
Twilight
Range of the ______ zone is 0-200m
Photic
Range of the ______ zone is 200 to 8000m
Aphotic
Only ___% of epipelagic food sinks to meopelagic
20%
Characteristics of mesopelagic fish (6)
Small
Big mouth
Unspecialized diet
No swim bladder
Soft, weak bones
Tubular eyes
Do deep-sea habitats have seasons?
No
Bioluminescence is used for (4)
Prey attraction
Communication
Courtship
Defense
Characteristics of deep-sea habitat (5)
No sunlight
Cold temperatures
Slow currents
High oxygen
Low-food
High pressure
Only about ____% of the food produced in the photic zone makes it past the mesopelagic
5%
Deep sea fish are ____ and _____
Sluggish and sedentary
Much of the sinking organic matter is ______ before it reaches the seafloor
consumed
There is ____ organic content within sediment
low
Benthic fauna is dependent on organic matter from the __________
Euphotic zone
Given equivalent annual primary productivity, high-latitude regions have higher standing stocks than tropical regions. It’s more ________ with greater _______
higher
variable
export
Some habitats within the deep-sea are (3):
Hydrothermal vents
Whale fall
Cold seeps
What are the stages of whale fall? (4)
Mobile scavenger
Enrichment opportunists
Sulfophilic
Reef
Common reactions of chemosynthesis (2)
Aerobic sulfide oxidation
Anaerobic methanogenesis
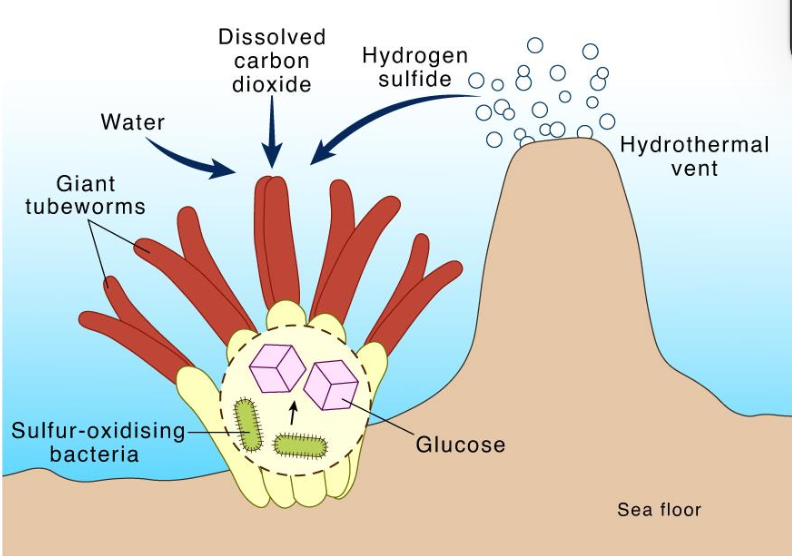
Primary production done by chemosynthetic bacteria such as (3):
Free-living bacteria
Endosymbionts
Ectosymbionts
Regions where cold, hydrocarbon rich water escapes from ocean floor
Cold seeps
Cold seeps are found in what regions of the earth?
Subduction zones
The gas in cold seeps comes from ______ ______ where organic matter has been buried for millions of years
Deep sediments
The anaerobic oxidation of methane by sulfate-reducing bacteria produces ___________
Bicarbonate
The bicarbonate reacts with calcium in seawater to form ________ ____________, creating biogenic carbonate rock around the seep.
Calcium carbonate
Examples of pattern of ecological succession (4)
Bacterial mats
Mussel colonies
Tube worm assemblages
Stony coral assemblages
What kind of gas is methane?
Greenhouse gas
Microbes consume most ______ before it reaches the ocean/atmosphere
Methane
Chemosynthetic communities incorporate methane into _______ and some _______ buried in sediments
Biomass
Carbon
Are cold seeps vulnerable to climate change?
Yes
Where do hydrothermal vents form?
Active seafloor spreading centers/mid-ocean ridges
Hydrothermal fluids between ____ °C and ____ °Cexit along the ridge axis of the spreading center
100-400°C
Hydrothermal vents are rich in (5):
Hydrogen sulfide
Manganeses
Iron
Methane
Hydrogen
The division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition for an ecological niche is called
Resource partitioning
Environmental Gradients (4)
Temperature
Oxygen
Toxic metals
H2S
The division of limited resources by
species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche
Resource partitioning
The sibogliniid tubeworms house symbiotic sulfide-oxidizing bacteria. in specialized structures called ___________
Trophosome
Mobile predators in hydrothermal vent communities (3)
Vent eelpout
Vent octopus
Pacific White Skate