1509 Final
1509 Lecture Notes
Normal pH- 7.35-7.45
Nursing process- ADPIE
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
Subjective- said by the subject or patient
Objective- comes from your observation, you can see it
What’s up?
W- Where is it?
H- How does it feel?
A- Aggravating and alleviating factors
T- Timing
S- Severity (pain scale)
U- Useful other data
P- Patient perception of the problem
Planning Care- What is most threatening to my patient?
Outcome Statements-
Measurable
Realistic
Appropriate time frame
Say “No” to vague words
Evaluate and Reevaluate every time you walk in the room and have an interaction with a patient
Chapter 14: Causes of Infection
Understand infection, causes, and protection
Pathogens (causes a disease)
Microorganism- (only seen with microscope)
Bacteria (give antibiotic)- (take probiotic to help with antibiotic 30 minutes after taking the antibiotic)
Viruses (anti- virtual)
Fungi
Primary- caused by one pathogen
Secondary- caused by a different second pathogen
Localized- found in one area of the body
Systemic- spreads to other organs through the bloodstream
Health-care associated infection (HAI)- an infection acquired while the patient is receiving care in a healthcare setting
Defenses-
Primary: block or trap invading pathogens,
Skin, mucous membranes, GI system
Secondary: cellular level in reaction to toxins secreted by pathogens
Inflammatory process, elevated temperature complement cascade
Tertiary: specialized white blood cells lymphocytes fight infection
B cells or T cells
Contact Precautions- (gloves and gown)
Droplet Precautions- (gloves, gown, mask, shield)
Airborne Precautions- (N95 mask, negative pressure room)
Chapter 17- Vitals
BP
Temp
Pulse
Respirations
Pain
Oxygen Saturation
Blood pressure
Cardiac Output- the amount of output of blood from the heart in one pump
Systolic (top) and Diastolic (bottom- relax of blood coming back)
Pulse Pressure (<30 or >50 Adbornaml)
Korotkoff’s sounds- thumbing
DO NOT use if amputation, mastectomy, dialysis shunt, dressing/cast/brace, vascular surgery, or trauma, IV
Hypertension
>140 on 2 consecutive reading
Primary- results from an unknown cause
Secondary- results from, another problem, fix the problem, fixes the BP
Risk Fix- family history, smoking, stress, alcohol use, obesity
Permanent Damage- CVA, MI, congestive heart failure, kidney failure retinal damage
Hypotension
20-30 mmHG of a “normal”
Orthostatic hypotension/postural (standing up to fast)- Hypotension- position changes result in a systolic drop 15-25 mmHg or diastolic 10 mmHg
Transition to Trendelenburg
Temperature- the amount of heat produced by the body
Core temperature- temperature of deeper structures and tissues
The liver produces 15-20% of body heat
Factors affecting body temperature
Environment
Time of day
Gender
Stress
Illness
Stress
Medication
Oral 98.6
Tympanic 98.6
Rectal 99.6
Axillary 97.6
Hyperthermia- elevations over 105
Hypothermia- below 95 degrees
Pulse- a wave of blood through arteries
Point of maximal impulse (PMI)- Midclavicular line down 4 or 5 ribs- need a full minute
Pulse deficit- the difference between heart pulse and radial pulse
Pulse Beat- 60-100
Rate, rhythm, strength
bradycardia, tachycardia
+1- weak
+2- strong
+3- bounding
Respiration
Ventilation- air in and out of the lugs
Inhalation or inspiration/exhalation or expiration
Rate/minure
Depth
Rhythm
Pattern
Respiratory effort
Tachypnea- >20 bpm
Bradypnea- <12bpm
Eupnea- normal breathing 12-20
Dyspnea- labored/ difficult breathing
Orthopnea- difficulty breathing unless upright
Tidal Volume- the amount of air inhaled in one breath 300-500
Adventitious Sounds- abnormal sounds
Stertorous- noisy, snoring, labored respirations audible without a stethoscope
Stridor- high-pitched crowing sound, partial obstruction, MED EMERGENCY
Rhonchi- continuous, low-pitched rattling, partial obstruction of larger airways d/t secretions
Rales/crackles- air moving over secretion in the lungs, short, choppy
Acute- sudden onset, serve symptoms, shorter course- opioids
Chronic- longer duration, ongoing, little change- ancients, therapy
Assessment Components:
Comprehensive health assessment: in-depth, whole person (i.e admission)
Inspection: Visual inspection
Penlight: Perrla (Pupils equal, round reactive to light, accommodating)
Otoscope- Inspect the lining of the nose, tympanic membrane, ear canals,
Ophthalmoscope- internal structure of eyes
Palpation: application of hands= touching patient
Abnormalities on the skin or tissue below
Skin turgor, growths, edema, size & location of body parts
Distention of bladder & strength of pulses, temp, texture, moisture, pain
Dorsal- more sensitive assessment of temperature
Classified according to depth of compression
Light 1-2 cm
Moderate 2-3cm
4-5 cm
Percussion: striking body parts with tips of fingers
Blunt percussion use fist rather than fingertips to tap
Elicit sounds to help locate/determine size of structure below the surface
Solid? Hollow? Fluid?
Auscultation: listening to sounds produced by the body
Belching (eructation) Flatus (rectal gas)
Bell side for lower-pitched sounds
Heart Valves, murmur
Diaphragm side for higher-pitched sounds
Heart sounds, breath sounds, bowel sounds
Olfaction- detect odor characteristics of health problems
Halitosis (bad breath)- poor hygiene, sinus infection, strep throat, gastric upset
Stress- sour smelling breath
Kidney failure & uremia- ammonia or urine smell on the breath
Liver disease- musty or sweet breath
Diabetic (non-compliant)- acetone or fruity aronma
Infectious drainage- foul odor
GI Bleed- rusty/iron stool or vomit
Head to Toe shift Assessment
Neurological- Vital signs, LOC & Orientation (AOX4), Facial symmetry, Pupillary size & reaction (Perrla), Speech, Hand grip, Feet Flexion
Cardiovascular- Blood pressure & pulse, skin color, temp, moisture, mucous membranes, Jugular vein distinction (JVD), Heart sounds, peripheral pulses, capillary refill, edema, extremities (color, temp, clubbing), activity tolerance
End of the Unit
Chapter 8- Infection
Body Defense Mechanisms- Skin & Mucous Membrane, Cilia, Gastric Acid (pH 1-5), Immunoglobulins, Leukocytes & Macrophages, Lysozymes, Interferon, Inflammatory Response
Inflammatory Response
Vascular Response- Increase blood flow to the area
Inflammatory Exudate- inflammation, warm feeling, red looking
Phagocytosis (the forming of scabs) and purulent exudate- kick out whatever is trying to enter the body, plasma left over (drainage)
Risk Factors for Infection- aging, environment, chronic disease, immunocompromised, dysphagia, immobility, incontinence, instrumentation
Dysh- dysfunction
A- absent of it
Dysphagia- difficulty swallowing
Aphagia- absent of swallowing
Dysphasia- difficulty speaking
Aphasia- absent of speak
Localized Infection- microbes in one area, pain, redness, swelling, site warmth
Laboratory Assessment- Culture, Sensitivity, Serum Antibody, CBC with diff, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
Asepsis- Free from organisms
Medical- “clean technique”- reduce pathogen/prevent, PPE
Surgical- “sterile technique”- an item or area that is free of all microorganisms and spores
Respiratory tract infections-
High mortality rates
Highest-risk= endotracheal, nasotracheal, and tracheostomy tubes
Bypass normal defense of URT
Genitourinary tract infections-
Most common
Urinary tract= sterile
Catheter insertion allows organisms to enter
Cauti (catheter-associated urinary tract infection)
Secure device, avoid back flow, closed systems
Remove as soon as possible
Bacteremia= bacteria in the blood- can turn sepsis respone
Excellent sterile technique is required
Surgical Wound Infection-
Original dressing applied in OR= sterile
Monitor for change instructions
Dressing observation
Wound assessment
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)-
Difficult to treat
Spread easily
High mortality rate
Can become a superbug
Contact isolation required
Vancomycin HCL IV antibiotic used to treat
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE)-
Enterococci are normal flora in GI/Urinary tract
Transmitted direct or indirect contact
Indwelling catheters, central venous catheters, immunocompromised, critically ill, multiple antibiotic use, surgical patients, extended hospital stays,
Requires isolation
Extremely contagious
Requires combination therapy to treat
Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)-
Gram + bacterium
Over grow & release toxins= cause diarrhea
20+ stools/day, fever, bloating, abdominal pain
Fecal-oral transmission
HAND-WASHING
Antibiotics stopped
Metronidazole (Flagyll) Vancomycin given
High recurrence
Therapeutic Measures-
Antibiotics treat bacterial infections
Antiviral medications treat viral infections (aimed at symptom
control not cure)Antifungal drugs for fungal infections but long-term use required
Bactericidal=kill bacteria
Bacteriostatic=inhibit growth, immune system required for final
destruction. Not for immunocompromised patientsAntibiotics metabolized by the liver, excreted by kidneys.
Disorders of organs may delay metabolism and require dose
adjustments
Nursing Considerations-
Probiotics=restore normal GI flora (30 Minutes)
Specimen for culture BEFORE antibiotic therapy
Monitor anaphylactic reactions (antibiotic reaction)
Blood work monitoring (peak & trough)
Superinfection= oral thrush, yeast
Chapter 9- Shock
Hypovolemic Shock- circulatory collapse resulting in organ damage and death without immediate treatment
Tissue Perfusion- adequate blood volume, effective cardiac pump, effective blood vessels
Compensation- change in one or both of nonfailing tissue perfusion mechanisms
Shock- failure in compensation
Metabolic and Hemodynamic Changes in Shock
Sympathetic Nervous System
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Oliguria
Cool, clammy skin with pallor
Urination drops
Decreased blood pressure
Effect on Organ and Organ Systems
Tissue ischemia (lack of blood flow- oxygen to an area) and organ injury
Brain death if anoxic over 4 minutes
Hypovolemic Shock- low volume, blood loss
Apply pressure if bleeding
Initial symptom: Tachycardia
Administer isotonic fluid therapy as ordered
(Diaphoresis- excess sweating)
Anaphylactic Shock- (allergic reaction to something)
Extreme hypersensitivity reaction to antigen
Teach allergy avoidance methods
Most Common: food allergies
Carry epinephrine autoinjector
Carry medical alert information
Therapeutic Measures for Shock
Maintain airway/respiratory support
Provide cardiovascular support
Maintain circulatory volume
Control bleeding
Treat cause/ identify source of infection
Nursing Care
Maintain airway, oxygenation
Monitor vital signs
Monitor intake and output
Provide fluids as ordered
Provide warmth- more blood can flow through body
Relieve pain
Monitor for pressure injury (vasopressor use)
Urticaria- hives
Laryngeal Edema- swelling of the airway
O-: Can give blood to anyone
Chapter 10- Nursing Care of Patients in Pain
Acute-
Lasts less than 3 months
Prompts an inflammatory response
Signs and symptoms are short-term, objective, and physical (for example, increased heart rate)
Chronic-
Last more than 3 months
Signs and symptoms persistent
Risks of Uncontrolled Pain
Body produces a stress response that causes harmful substances to be released from injured tissue
Reactions
Breakdown of tissue
Increased metabolic rate
Impaired immune function
Negative emotions
Prevents patient from participating in self-care activities
Opioid Addiction
Tolerance
Physical dependence
Addiction/psychological dependence
Pseudo addiction
Pain Treatment
Analgesics
Opioid
Nonopioid
Adjuvant- originally prescribed for one thing but found it can help with something else
Opioid Antagonists
Other treatments
Analgesic Routes
Oral
Rectal
Inhalation
Transdermal
Intramuscular
Subcutaneous
Intraspinal
IV
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA)- they can control the pain med themselves
Endorphins: the body's natural reaction to pain
Chapter 11: Nursing Care of Patients With Cancer
Cancer Concepts-
Neoplasm- any new growth or including abnormal cell growth of tissue
Benign- abnormal cells present, not cancer yet but may be growing, can do treatment
Malignant- cancerous
Cancer Pathophysiology
Mutation of cellular genes
Abnormal cell growth
No cell division limit
Risk Factors For Cancer
Viruses- biggest viruses HPV
Radiation
Chemicals
Irritants
Genetics
Diet
Hormones
Immune factors
Cancer Types
Carcinoma- tissue of the skin, gland, and digestive, urinary, and respiratory tract linings
Sarcoma- connective tissue, including bone and muscle
Leukemia- blood, plasma cells, and bone marrow
Lymphoma- lymph tissue
Melanoma- skin cells
Metastasis- (most common, lung, brain, bones)
Invade blood or lymph vessels
Lodge and grow in a new location
Most Common Cancers
Men- prostate, lung, colon
Women- breast, lung, colon
Therapeutic Interventions
Surgery
Radiation Therapy- radiation kills bad cancer cells but also kills the good cells
Chemotherapy- chemicals to kill cancer
Side Effects of Radiation
Fatigue
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia
Mucositis
Xerostomia- dry mouth
Skin reactions
Bone marrow depression
Chemotherapy
Action
Routes of administration- usually IV
Combination chemotherapy
Side effects of chemotherapy
Bone marrow depression at nadir
Leukopenia- low white blood cells
Thrombocytopenia- low platelet count
Anemia- low red blood cells
Nadir- the lowest count
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Stomatitis
Alopecia- hair loss
Neurotoxicity
Hospice Care
Less than 6 months prognosis
Inpatient
Outpatient
Interdisciplinary team
Family/caregivers
Chapter 19 Med/Surg- Patients with immune disorders
Allergic Rhinitis
Common allergy
Seasonally= hay fever
Throughout the year= perennial
Environmental & airborne
Responses with- Sneezing, nasal itching, runny nose, itchy red eyes
Dark eye circles= allergic shiners (venous congestions in maxillary sinuses)
TX: Antihistamines, nasal decongestants, corticosteroids, saline nasal spray
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)- Chronic inflammatory skin response
Familial
Itching, edema, dry skin, eruptions of blisters
Decreased sweating, skin thickening
Symptom management
No diagnostic tests
Anaphylaxis- severe reaction
Can fall into- respiratory (happens first) & cardiac arrest
Immediate treatment required
Smooth muscle spasms (bronchial narrowing, wheezing, dyspnea, edema)
Cramping, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, hypotension
Neurological changes
IV epinephrine, vasopressor drugs, F&E support, respiratory support
Urticaria (Hives)
Red, raised, itchy patches
Typically trunk & proximal extremities
Treatment depends on the severity
Corticosteroids, topical steroid creams, antihistamines, histamine blockers
Contact Dermatitis- (looks rash)
Skin becomes red, itchy, fragile vesicles
Poison ivy, poison oak most common, latex
Symptom control-antihistamines (drug that blocks the histamine), topical agents
Chapter 20 Med/Surg- HIV & AIDS
HIV- Human immunodeficiency virus- (Causes destruction of immune cells)
T lymphocytes malfunction
B lymphocytes dysfunctional
Initial infection🡪 symptomatic stage= 8-12 yrs
Person-to-person transmission
Infected blood, vaginal secretions, semen, breast milk, body fluids containing blood
Casual contact does not spread the virus (hugging, shaking hands, sharing eating utensils, closed-mouth kissing, sharing towels, bathroom fixtures)
AIDS- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Late phase caused by HIV
Not all cases develop AIDS
T lymphocytes drop below 200!
Transmission
Sexual contact (oral & anal higher rates)
Females at higher risk
Needles
Mother 🡪 infant
Signs & Symptoms FOR BOTH HIV/AIDS
Extreme fatigue
Headache
Fever
Lymphadenopathy- swelling of lymph nodes
Diarrhea
Sore throat
SOB
Weight loss
Night Sweats
Shingles- Chickenpox
Peripheral Neuropathies- numbness of the nerves
Treatment
Pre-exposure with ARV
Daily pill
Transmission precautions
Complications
AIDS Wasting Syndrome- loss of more than 10% of body weight for more than 30 days, diarrhea, weakness, fever
HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder- targets neurological system, memory loss, loss of motivation, irritability
Cancer- immunocompromised, abnormal cells are not being destroyed
Opportunistic Infections- infections that occur more often with weakened immune systems
Candida Albicans, cytomegalovirus, mycobacterium avium complex, pneumocystis pneumonia, tuberculosis
Diagnosis
HIV Antibody tests
CBC/Lymphocyte count
T-Lymphocyte count
Viral load testing
General tests
Hepatitis A, B, C, liver panels, syphilis screen
Therapeutic Measures
Goal= prevent or delay development of opportunistic diseases
ARV
Reduce viral loads
6 drug classes available
Affects viruses at different stages
3 medications in 2 different classes used in combination
Adherence is important!!
Nursing Considerations
Ineffective protection
Pain
Fatigue
Imbalanced nutrition
Diarrhea
Impaired skin integrity
Risk for low self-esteem
Resources
Counseling
END OF UNIT
Chapter 53- Integumentary Function, Assessment, and Therapeutic Measures
Subjective Assessment
History of Skin Disorders
Risk Factors
Hair
Nails
Medications
Exposures
WHAT’S UP?
Physical Assessment
Inspection and Palpation
Color- Pallor (pale), Erythema (redness)
Lesions
Moisture
Edema- usually legs from the feet always hanging down
Vascular Markings- bruising, aging spots, dots on skin
Integrity
Cleanliness
Turgor
Hair Distribution- (Alopecia)
Color
Quantity
Thickness
Texture
Nails
Color
Shape
Texture
Thickness
Abnormalities
Diagnostic Tests
Culture
Biopsy- aspiration
Wood’s Light Examination- turn the lights off, blue light to show different fungus
Skin Testing- check for bacterial, fungus, wound cultures
Allergy testing can cause anaphylactic shock because they don’t know what they are allergic to
Therapeutic Measures
Open Wet Dressings- (advantage)= promote healing from the inside
Balneotherapy
Topical Medications- (Ointment)= specific to an area
Dressings
Tegaderm- transparent dressing -see-through it
![]()
Chapter 26- Wound Care
Terminology Related to Wound Healing
Dehiscence: Partial or complete separation of outer wound layers
Evisceration: The rupturing of a wound
Eschar: Hard, dry, leathery dead tissue (not helpful tissue, don’t want it)
Granulation tissue: New tissue that grows and fills in a wound (you need to have)
Sinus tract: Tunnel that develops between two cavities or between an infected cavity and the skin’s surface (underground tunnel, can’t see it)
Wound Conditions
Edema- Swelling
Erythema- Redness
Necrotic- Dead tissue
Ischemia- Reduced blood flow
Purulent- Containing pus
Classification of Wounds
Contusions- bruise, everything stays intact
Abrasions- a superficial wound, that rough up the top layer
Puncture wounds- punctured the skin
Penetrating wounds- puncture wound with something still in the wound
Lacerations- usually accidentally wound, wound won’t come together
Categories of Wound Contamination
Clean: Not infected- (usually the most common)
Clean-contaminated: Has direct contact with normal flora and potential for infection
Contaminated: Grossly contaminated by breaking asepsis
Infected: Infectious process established
Colonized: High number of microorganisms present without signs of infection (ex. MRSA)
Risk Factors for Pressure Ulcer Development
Being elderly
Being emaciated or malnourished
Being incontinent of bowel or bladder
Being immobile
Having impaired circulation or chronic metabolic conditions (ex. Diabetes, obesity, heart disease)
Assessment Parameters: Pressure Ulcers
Pallor: Related to impaired circulation (pale)
Erythema: Increased capillary blood flow due to inflammation (redness, feel very warm)
Jaundice: High serum level of bilirubin; skin is more susceptible to loss of integrity (yellow)
Bruising: Note any discolored areas that are found to determine if new breakdown occurs
Three Phases of Wound Healing
Inflammatory
Occurs when the wound is fresh; includes both hemostasis and (phagocytosis= eating all the pus) -(open fresh wound)
Reconstruction (proliferation)
Occurs when the wound begins to heal, about 21 days after injury (rebuild tissue, healthy tissue, most vulnerable time for the wound to heal)
Maturation (remodeling)
Occurs when the wound contracts and the scar strengthens (give the scar strength)
Types of Wound Closures for Healing
First intention
Wound is clean with little tissue loss, edges are approximated, and wound is sutured closed (closes on its own)
Second intention
There is greater tissue loss, wound edges are irregular, and wound is left open (leave the wound open, maybe close tissue underneath)
Third intention
Wound is left open for some time to form granulation tissue and then sutured closed (just leave the wound open)
Signs of Wound Infection
Redness or increased warmth
Swelling
Wound drainage
Unpleasant smell
Pain around wound
Fever above 100°F
Wound Drainage
Sanguineous- bloody drainage
Serous- yellowish (not infection)- looks like oil- serum
Purulent- containing pus, thick yellow green
Bilious- green (not infection green)
Serosanguineous- both blood and liquid
Seropurulent- mixture of serum and pus
Protein and Wound Healing
Protein intake is required for wounds to heal.
Patients who are tube fed may not get enough protein and calories which slows wound healing.
Wound Documentation
Amount and color of drainage on old dressing
Length, width, diameter, and depth of wound
Sinus tracts and their length
Color of wound
Appearance of surrounding skin
Type of dressing applied
Chapter 54- Nursing Care of Patients with Skin Disorders
Pressure Ulcers
Pathophysiology
Pressure Against Skin
Tissue Anoxia
Etiology
Risk Factors for Pressure Ulcers
Immobility
Impaired Circulation
Impaired Sensory Perception
Elderly
Very Thin or Obese
Prevention for Pressure Ulcers
Assess Daily
Cleanse and Dry Daily and PRN
Lubricate Daily
Clean Incontinence Promptly
Use Moisture Barrier PRN
Do Not Massage Reddened Areas
Shift every Weight every 15 min
Turn/Reposition at Least every 2 hr
Keep Heels Off Bed
Pad/Protect Bony Prominences
Use Pressure-Reducing Mattress
Use Lift Sheet to Move
Provide Nutrition and Hydration
Braden Scale
Sensory Perception
Moisture
Activity
Mobility
Nutrition
Friction and Shear
Signs/Symptoms Pressure Ulcers
Pain
Redness
Blanching?
Open Ulcerated Area
Color Tip
Black
Necroses
Yellow
Infection or Slough
Red
Healing
Therapeutic Interventions for Pressure Ulcers
Remove All Pressure
Debride- removal of the dead skin or tissue (removal of something)
Mechanical- scissors and forceps can be used to remove nonviable tissue
Enzymatic- involves application of topical enzyme debriding agent
Autolytic- debridement of synthetic dressing or moisture retentive dressing over the injury
Surgical- involves removal of devitalized tissue, slough (lose yellow tissue), with a sharp instrumental tool
Cleanse
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Maggots
Leeches
Dressings Pressure Ulcers
Types
Hydrogel
Polyurethane Film
Hydrocolloid Wafer
Biological
Alginate
Gauze
Moist Environment
Caution with Tape
Stages Pressure Ulcers
Deep Tissue Injury (pg. 1115)
Stage I
Skin Intact, Red, Does Not Blanch
Stage II- blister
Partial Thickness Skin Loss
Stage III
Full Thickness Skin Loss, May Have Eschar
Stage IV
Damage to Muscle, Bone, or Support Structures
Unstageable
Dermatitis
Pathophysiology
Inflammation of the Skin
Etiology
Allergens
Irritants
Heredity
Stress
Types of Dermatitis
Contact
Irritant
Allergic
Atopic
Seborrheic
Dermatitis Signs/Symptoms
Rash, Itching
Lesions
Scales
Crusts
Fissures
Macules
Papules
Pustules
Complications Dermatitis
Infection
Sepsis
Therapeutic Interventions Dermatitis
Antihistamines
Analgesics
Antipruritics
Steroids
Colloidal Oatmeal Baths
Wet Dressings
Psoriasis
Pathophysiology
Inflammatory Disorder
Proliferation of Epidermal Cells
Scaling
Aggravating Factors
Stress
Strep Pharyngitis
Hormone Changes
Cold Weather
Skin Trauma
Some Drugs
Signs/Symptoms Psoriasis
Papules, Plaques
Silvery Scales
Itching
Complications Psoriasis
Infection, Fever, Chills
Arthritis
Nail Changes
Lymphadenopathy
Psoriasis Therapeutic Interventions
Therapeutic Interventions
Tub Baths
Corticosteroids
Salicylic Acid
Keratolytics
Vitamin D Creams
Retinoids
Coal Tar, Anthralin
UV Light
Chemotherapy
Occlusive Dressings
Fish Oil Supplements
Herpes Simplex
Pathophysiology
Viral Infection
HSV1 – Above Waist
HSV2 – Below Waist
Primary Infection
Direct Contact
Respiratory Droplet
Fluid Exposure
Lies Dormant
Recurs with Stress
Herpes Simplex Signs/Symptoms
Prodromal Phase
Burning, Tingling
Vesicles and Pustules
Burning, Itching, Pain
Contagious Until Scabs Form
Therapeutic Interventions Herpes
Antiviral Agents (Acyclovir/Zovirax)
Topical
Oral
Antibiotics for Secondary Infection
Avoid Triggers of Recurrence
Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
Pathophysiology
Acute Inflammation/ Infection
Painful Vesicules
Follows Nerve Distribution
Usually One-sided
Etiology Shingles
Reactivation of Varicella Zoster Virus (Chickenpox Virus)
Occurs with Reduced Immune Function
Elderly
AIDS
Immunosuppressed
Signs and Symptoms Shingles
Vesicles, Plaques
Irritation
Itching
Fever
Malaise
Pain
Prevention Shingles
Avoidance of Infected Persons
Varicella Vaccine (Varivax)
Zostavax
Complications Shingles
Postherpetic Neuralgia
Persistent Dermatomal Pain
Hyperesthesia
Ophthalmic Herpes Zoster
Sepsis
Therapeutic Interventions Shingles
Acyclovir
IV, Oral, Topical
Analgesics
Anticonvulsants/Antidepressants
Antihistamines- for itching
Corticosteroids
Antibiotics for Secondary Bacterial Infection
Fungal Infections
Pathophysiology/Etiology
Direct Contact with Fungus
Overgrowth with Antibiotic Therapy
Grows in Warm Moist Environment
Types
Tinea Pedis- athletes feet
Tinea Capitas- Ring worm of Scalp
Tinea Corporis- Ringworm of Body
Tinia Cruris- Ringworm of Groin- jock itch
Candidiasis- oral trush
Cellulitis
Pathophysiology
Inflammation of Skin/Connective Tissue
Infection
Staphylococcus/MRSA
Streptococcus
Etiology
Open Wound/Trauma
May be Unknown
Cellulitis Signs/Symptoms
Warmth
Redness
Edema
Pain, Tenderness
Fever
Lymphadenopathy
Therapeutic Interventions
Antibiotics
Topical
Systemic
Debridement
Pediculosis (Parasitic Disorders)
Pathophysiology/Etiology
Infestation by Lice
Transmission by Direct Contact
Types
Pediculosis Capitis
Pediculosis Corporis
Pediculosis Pubis
Pediculosis
Signs and Symptoms
Itching
Papular Rash
Presence of Lice, Nits, and Excreta
Therapeutic Interventions
Pediculosides
Permethrin, Pyrethrin, Lindane
Mechanical Removal
Antipruritics
Topical Corticosteroids
Patient Education
Self Medication
Removal of Nits
Cleaning of Clothing and Objects
Inspection of Family and Friends
Scabies
Pathophysiology
Sarcoptes Scabiei Mites
Burrow into Skin
Etiology
Contact with Infected Clothing or Animals
Scabies
Signs and Symptoms
Itching
Rash
Burrows
Diagnosis
Shaving of Lesion
Microscopic Evaluation
Scabies
Therapeutic Interventions
Topical Scabicides
Permethrin
Crotamiton
Antipruritics
Patient Education
Self Medication
Treat Family Members
Wash Clothing and Linens
Itching May Continue 2 Weeks Following Treatment
Malignant Skin Lesions
Cancer Arising From
Basal Cell Layer
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Epidermis
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Menalocytes
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant Skin Lesions
Risk Factors
Ultraviolet Rays
Fair Skin
Genetic Tendency
X-Ray Therapy
Chemicals
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Prevention
Limit Exposure to UV Rays
Use Sunscreen
Wear Protective Clothing
Report Changes in Moles
Malignant Skin Lesions- Therapeutic Interventions
Surgical Excision
Chemotherapy
Radiation Therapy
Dermatological Surgery
Rhinoplasty
Blepharoplasty
Rhytidoplasty
Otoplasty
Cyst
Saclike growth
Liquid, semifluid, solid material
Epidermoid cyst most common
Treatment
Intralesional steroid
Antibiotic
Excision
END OF UNIT
Chapter 32- Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Pancreatic Systems Function, Assessment, and Therapeutic Measures
GI Anatomy and Physiology
Oral Cavity and Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas
Accessory Organs of Digestion
Produce or Store Digestive Secretions
Liver
Hepatic Portal Circulation
Bile
Liver Functions
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Amino Acid Metabolism
Lipid Metabolism
Synthesis of Plasma Proteins
Formation of Bilirubin
Storage
Detoxification
Activation of Vitamin D
Gallbladder- Stores Bile
Pancreas
Amylase
Starch to Maltose
Lipase
Emulsified Fats to Fatty Acids/Monoglycerides
Trypsin
Polypeptides to Peptides
Bicarbonate Juice
Aging and the GI System
Fat Absorption Slower
Atrophy of Large/Small Intestine
Decreased Mucous Secretions
Decreased Elasticity of Rectal Wall
Weakness of Intestinal Wall
Faulty Absorption of Vitamins B1 and B12, Calcium, Iron
Assessment
Health History
Travel
Elimination
Medications
Clostridium Difficile
Nutritional Assessment
Family History
Cultural Influences
Physical Assessment
Inspection
Jaundice
Auscultation
Percussion
Palpation
Abdominal Girth
Height and Weight
Body Mass Index
Oral Cavity
Abdomen
Diagnostic Tests
Laboratory Tests
CBC
Electrolytes
Bilirubin
Liver Enzymes
Stool Tests
Radiographic Tests
Flat Plate of the Abdomen
Upper GI Series (Barium Swallow)
Lower GI Series (Barium Enema)
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
Endoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Lower Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Proctosigmoidoscopy
Colonoscopy
Enteral Nutrition
When oral intake not possible
Gravity
Pump
Intermittent
Continuous
Feeding Tube Nursing Care
Placement Check
Residual
Complications
Irritation
Obstruction
Aspiration/regurgitation
Displacement
Cramping/bloating
Therapeutic Measures
Gastrointestinal Intubation
Decompression
Diagnosis
Treat/relieve obstructions
Gavage feedings
Medications
Promote healing
Lavage
Chapter 33- Nursing Care of Patients with Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders
Nausea- urge to vomit
Vomiting- Expelling stomach contents through esophagus and mouth
Therapeutic Interventions N/V
Protect Airway
Medications
IV Fluids
Nasogastric Tube
Dietary modifications
Obesity
Weight 20% or greater than ideal body weight
BMI (height-to-weight ratio)
Caloric intake exceeds energy expenditure
Comorbidities- diseases caused by obesity
Diseases Associated with Obesity
Heart disease, diabetes, atherosclerosis, gallbladder disease, hypertension, depression, sleep apnea
Morbid Obesity
BMI >40
Supportive Nursing Care- Obesity
PATIENT EDUCATION!!
Support groups
Surgery
Behavior modification
Medication
Bariatric Surgery- Weight Loss surgery
Limits stomach size
Steatorrhea means there's too much fat in your stool (poop). It's a symptom of fat malabsorption. That means your digestive system is having trouble breaking down and absorbing fats.
Complications
Vomiting
Protein deficiency
Vitamin deficiency
Mineral deficiency
Dumping syndrome
Acute gastric distention
Steatorrhea
Intestinal leakage
Infection
Erosion
Postoperative Care for Bariatric Surgery
Clear liquid diet
Pureed foods
Solids at 6 weeks post-op
Post-op assessment
Oral Health- Inflammatory Disorder
Important to Overall Health
Stomatitis
Aphthous Stomatitis- (canker sores)
HSV1
Halitosis
Oral Hygiene
Prevents Pneumonia
Reduces Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
Prophylactic Antibiotics
Xerostomia (Dry Mouth)
Artificial Saliva Substitute
GERD
Gastric secretions reflux into esophagus
Damage esophagus
The inability of sphincter to close
GERD Signs/Symptoms
Heartburn
Regurgitation
Dysphagia
Bleeding
GERD Complications
Aspiration
Bronchospasm
Pneumonia
Asthma
Scar Tissue
GERD Diagnosis
Barium Swallow
Esophagoscopy
GERD Therapeutic Interventions
Lifestyle Changes
Medications
Antacids
H2 Receptor Antagonists
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Prokinetic Agents
GERD Nursing Care
Education
Lose Weight
Low-fat, High-protein Diet
Avoid Caffeine, Milk Products, Spicy Foods
Gastritis- Inflammation of the stomach mucosa
Remove Irritating Substance
Bland Diet of Liquids/Soft Foods
Inflammation of Stomach Mucosa
Acute
Chronic
hemat/o (blood) hem/o (blood)
Therapeutic Interventions Gastritis
Treat Cause
Bland Diet
Antacids
Anti-emetics
Ulcers (Peptic Ulcer Disease)
Stomach
Pylorus
Duodenum
Named by location
esophageal, gastric- worse with food, duodenal- improves with food until digestion takes place then gets worse
Complications
Supportive Care- Ulcers
Control bleeding
Reduce pain
Replace fluids
Education
Medications
Chapter 34- Nursing Care of Patients with Lower GI Disorder
Lower GI System
Small Intestines
Large Intestines
Rectum
Anus
Constipation- Feces held in the rectal cavity
Water absorbed
Hard, dry, painful defecation
Many causes
Obstipation
Complication
Fecal impaction
Ulcers
Oozing
Megacolon
Abdominal distension
Bowel loops
Supportive Care- Constipation
Increase fiber
Exercise
Behavior modification
Increase fluid intake
Medications
Education!
Diarrhea- rapid passing of fecal matter
Decreased water absorption
Bacterial or viral
Supportive Care- Diarrhea
Identify Cause
Replace Fluids/Electrolytes!
Increase Fiber/Bulk
Medications
Lactinex Restores Normal Flora
Antimicrobial Agents
Abdominal Hernias- Protrusion through abdominal wall
Etiology
Weakness in Abdominal Wall with Increased Intra-abdominal Pressure
Abdominal Hernias Signs/ Symptoms
None
Bulging
Complications Abdominal hernias
Strangulated Incarcerated Hernia
Supportive Care Abdominal Hernias
None
Observation
Support Devices
Surgery
Decrease intra-abdominal pressure
Signs of strangulation/incarceration
Support brief
Skin integrity
Anorectal Problems
Hemorrhoids- enlarged veins within the anal tissue caused by increased pressure in veins
Internal- above the internal sphincter- usually not painful unless they prolapse
External- below the external sphincter- cause itching snd pain when inflamed and filled with blood
Fissures- cracks or ulcers in lining of the anal
Supportive Care Anorectal Problems
Postoperative
Pain Control
Prevention
Comfort Measures
Dressing Changes
Stool Softeners
Sitz baths
Lower GI Bleeding
Hematochezia- bleeding from the colon or rectum usually bright red active bleeding
Melena- black and tarry stools- bleeding above or in small bowel- older blood
Signs & Symptoms Lower GI Bleeding
Hypotension
Lightheadedness
Nausea
Diaphoresis- sweating
Pallor
Clammy skin
Tachycardia
Ostomy- Surgically created
Stoma- portion of bowl that is sutured onto the abdomen
3 types
Ileostomy- end stoma formed by bringing the terminal ileum out to the abdominal wall
Colostomy- where in the bowel it is formed
Urostomy- opening in belly made during surgery- more for urine and liquid
Supportive Nursing Care- Ostomy
Pain
Anxiety & fear
Home care
EDUCATION!!!
WOCN- Wound, ostomy, continence nurse
Chapter 35- Liver, Pancreatic, Gallbladder Disorder
Hepatitis- inflammation of the liver from viral or bacterial infection
No symptoms 🡪 life-threatening
A (fecal-oral, vac)-B (blood and bodily fluids, vac)-C(needle shares, unprotected sex, no vac)-D (blood and bodily fluids)- E (contaminated water, uncooked meat)
Hepatitis Complications
Chronic liver failure
Acute liver failure
Chronic infections
Hepatitis Therapeutic Measurs
Monitor liver status
Symptoms relief
Supportive Care
Promote healing
Nutritional support
Antivirals
Laboratory Tests
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)- liver pictures
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)- liver pictures
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Bilirubin
Prothrombin Time (PT)- look at first
Cirrhosis- progressive replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue
Drinking is #1 cause of Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease
Signs & Symptoms
Anorexia
Nausea
Vomiting
Weight loss
Fatigue
Jaundice- yellow
Pruritus- itching
Cirrhosis/Chronic Liver Disease Complications (CHEAP)
Clotting defects
Hepatorenal syndrome- acute kidney injury with advanced liver disease
Encephalopathy- bleeding and abdominal distension
Ascites- serous fluid in the abdominal cavity from hypertension
Portal Hypertension- persistent elevated blood pressure in portal vein
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome- brain disorder caused by thiamine (B) deficiency, behavior thing
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis- inflammation of the gallbladder
Cholelithiasis- formation of gallstones in the gallbladder
Signs & Symptoms
Epigastric pain
RUQ tenderness
Right shoulder pain
Murphy’s sign- inability to take a deep breath when an examiner's fingers are pressed below the liver margin
Gas/belching
Nausea/Vomiting
Supportive Nursing Care Cholecystitis
Pain control
Infection prevention
Fluid & electrolyte support
Post-surgical care
END OF UNIT
Chapter 45 Musculoskeletal Function and Assessment
Anatomy & Physiology
Muscles- soft tissue that functions to produce force in motion. When muscles contract, it changes the length and shape of that muscle.
Joints- between bones and allow for movement on either end of the bone
Bones
Tendons- connect bone to muscle
Ligaments- connect bone to bone
Fasciae- membranous tissue enclosing muscles
Skeleton
Skeleton plays several roles-it’s biggest is in movement. It also protects organs and tissues. For example, it protects the brain within the skull and the lungs within the thoracic cage.
Bones within the skeleton contain and produce bone marrow, they also store excess calcium which is necessary for blood clotting and proper functioning of nerves and muscles.
Skeleton is stabilized by the muscular system, which contributes to heat production to maintain normal body temperature
Muscular system aids in the return of blood from the legs by compression on veins.
Calcium and phosphate are being removed and replaced (remodeled) all the time to maintain normal blood levels.
Parathyroid hormone increases the removal of calcium and phosphate from the bones.
Calcitonin (hormone from thyroid) promotes retention of calcium.
206 bones make up the skeleton
-Axial: flat, irregular bones
-Appendicular: limbs consist of long bones. Same structure: diaphysis (shaft) and two ends epiphyses
Structure of the Skeleton
Skull
-8 cranial bones
-14 facial bones
-3 small auditory bones in the middle ear
-Immovable joints, sutures (synarthrosis)
-When babies are born, the skull is not fused, which allows for passage through the birth canal.
Vertebral Column
Spinal column-named by location and number
-33 bones vertebrae
-Atlas- 1st seven cervical vertebrae. Articulates with occipital bone of skull to form a pivot joint with axis, 2nd vertebrae.
-12 thoracic vertebrae articulate with posterior ends of the ribs.
-5 lumbar largest & strongest
-Sacrum- 5 fused vertebrae, articulates with the os coxae at the sacroiliac joints
-Coccyx- 4 fused vertebrae serves as an attachment point for muscles of the perineum
Thoracic Cage
-12 pairs of ribs and sternum
-Protects heart & lungs, upper abdominal organs from injury
-Flexible, expands upward and outward during breathing
Synovial Joints- moveable joints (diarthroses)
Bursae- small sacs of fluid between the joint and structures that cross over the joint. Lessen wear in areas of friction
Joints
Symphysis- between vertebrae, pubic bone
Ball & socket- movement in all planes, shoulder, hip
Hinge- movement in one plane, elbow, knee, between fingers and toes
Combined hinge- temporal bone, mandible
Pivot- rotation, neck, radius, and ulna (distal to elbow)
Gliding- side to side, wrist
Saddle- movement in several planes, thumbs
Muscle Structure
Fibers
Fibers are specialized for contraction
With contraction, muscles shortens and exerts force on a bone
Each fiber has its own motor nerve ending
Anchored by tendons
Muscles are anchored by tendons (connective tissue)
2 tendons per muscle
At least 2 tendons, each to a different bone
Stationary muscle attachment is origin, movable muscle attachment is the insertion
With contraction, muscle moves the bone in a certain direction
700
700 skeletal muscles (figure 45.4 page 889)
Without synergism, we would be unable to maintain balance or have fine motor control (walking, talking)
Role of Nervous System
Voluntary movement
-Skeletal muscles are voluntary: conscious control initiates nerve impulses to cause contraction
Involuntary regulation
-Involuntary regulation (CNS) keeps slight contraction on muscles-which keeps our posture
Posture
Coordination
Aging and the Musculoskeletal System
Figure 45.6 (page 890)
One function of estrogen (females) and testosterone (men) is strong bone maintenance.
After menopause, bone loses more calcium than is replaced.
Can offset bone loss with weight-bearing exercise, which will increase bone density
Damage to weight-bearing joints-leading to pain and stiffness
Muscle strength declines: leading to more falls accidents
Assessment of the Musculoskeletal System
Subjective Data
History- age, gender, allergies, pre-existing conditions, risk factors (smoking, sedentary lifestyle)
Injury- pain scale, when did it occur, tx Family: some conditions can be hereditary
Occupation
Family History
Diet History- calcium, vit D intake can affect musculoskeletal disorders
Physical Assessment
Inspection, Palpation, Range of Motion
Inspect- asymmetry, swelling, ecchymosis, color Palpate- pulses below involved area, warmth, weakness ROM- contracture, deformities, altered gait The nurse should expect muscle spasms following a hip fracture.
Psychosocial Assessment
Deformities Affect Body Image
changes in body image, lifestyle alterations to consider, coping with this and the stress
Diagnostic Tests
Laboratory Tests
Calcium 8.5-10.5 mg/dL
Phosphorus 2.6-4.5 mg/dL
Calcium & Phosphorus: when calcium increases, phosphorus decreases and vice versa. Bone disorders cause an imbalance
Alkaline Phosphatase m: 45-115/f: 30-100 units/L
increases when bone is damaged. Increases reflect osteoblast activity (bone forming cell)
Myoglobin 50-120 mcg/mL
Protein in striated muscle. Causes red color. Myoglobin rises in the blood with damage.
Muscle Enzymes
When muscle tissue is damaged, enzymes are released into the blood.
Uric Acid m: 4.4-7.6 f: 2.3-6.6 mg/dL
indicated gout (painful inflammatory arthritis- next chapter). Usually found in the urine.
Rhabdomyolysis- muscle destruction relating to an injury- serious and potentially fatal- crush syndrome- Creatinine Kinase 5x greater than normal. Dark urine, muscle weakness, myalgia. Tx goal- restore fluid/ electrolyte balance
Xray
look at bone and soft tissue damage (alterations in bone alignment and spacing
CT
joints or spine
Myelogram
can’t have a CT or MRI. Head down so contrast flows up to the neck
MRI
diagnosing soft-tissue injuries. More accurate for the vertebral column. Can use contrast. NO METAL! Noisy tube- make sure pt know what to expect
Arthroscopy
scope, saline injected into the joint, joint visualized from different angles. Local or light general anesthesia. They can do the repair then as well.
GT scan/ Thallium Scan
Visualization of entire skeleton. G/T radioactive isotopes. Gallium concentrates in areas of tumors, inflammation and infections. Thallium identifies bone cancer. “Hot spots” increased circulation in abnormal bone areas that concentrates the radioactive substance. Indicates bone disease
Biopsy
Microscopic exam to confirm cancer, infection, inflammation.
Ultrasonography
sound waves detect osteomyelitis, soft tissue disorders, traumatic injuries
EMG
nerve conduction study. Measures muscle’s electrical impulses. Diagnoses muscle disease or nerve damage
Chapter 46 Nursing Care of Patients with Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Musculoskeletal Medications
Treat muscular disorders
Dystonia- movement disorder (muscle relaxants help)
Antispasmodics- anti spasm medication
Treat bone disorders
CNS involvement
Bone and Soft Tissue Disorder
Strain- stretched, muscle or tendon
Sprain- stretched and then rotated, ligament
Dislocation- joints are moved out of their normal position
Bursitis- overuse, causes inflammation
Rotator Cuff Injury- shoulder, part of nerve gets pinched under your shoulder
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome- compression of the median nerve
Tunnel swelling
Numbness
Relieve Inflammation
Splint
Anti-inflammatory
Surgery
Teach Prevention- for ex. Typing on a keybord
Fractures- break in the bone
Cause
Trauma
Pathological (From Disease )
Open- broke through the skin (watch for infection)
Closed- stays under the skin
Complete- bone has totally snapped
Incomplete- the bone has not totally snapped
Displaced- bones are out of alignment
Fractures S/S
Pain
Decreased ROM
Limb Rotation
Deformity, Shortening of Limb
Swelling
Bruising
Fractures Diagnostic Tests
X-Ray- show if there is a break, hard structure
CT scan- further testing to see tissue
Emergency Treatment
Splint It As It Lies!
Seek Medical Treatment
Treatment
Manual Realignment /closed reduction
Bandages/Splints
Casts
Open reduction internal fixation
External fixation
Complications of Fractures
Nonunion- delaying or no healing
Neurovascular compromise- to detect abnormalities
Hemorrhage- bone is highly vascular
Infection
Thromboembolic Complications
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Fat Embolism Syndrome- fat blood clot going out to system
Pain
Paresthesia- painful tingling or burning
Pallor
Paralysis- late symptom
Pulselessness- a late and ominous sign
Poikilothermia- extremity is cool to the touch
Supportive Nursing-Care Fractures
Cast Care
Traction Care
Pain Control
Neurovascular Checks
Skin Care
Nutrition
Self Care Deficits
Psychosocial
Osteomyelitis- infection of Bone
Prevention is Key!
Long-term Antibiotic Therapy
Incision and Drainage
Amputation
Supportive Nursing-Care Osteomyelitis
Iv antibiotics
Education
Osteoporosis- (Porous Bone)- Low Bone Mass
Take Calcium and Vitamin D together to help
Deterioration
Fragile bones
Prone to Fractures
Imbalanced Remodeling Process
Osteoporosis S/S
Dowager’s Hump
Height Decreases
Back Pain
Fracture
Osteoporosis Diagnostic Tests
Dual-energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)- screening tool to measure bone density
Serum Calcium- levels are low
Vitamin D- levels are low
Serum Phosphorus- levels are high
Serum Alkaline Phosphatase- levels are high
Supportive Nursing Care- Osteoporosis
No cure
Treat symptoms
Education
Gout- build-up of uric acid
Systemic connective tissue disorder
Urate deposits- tophi
Men > Women
Attacks: intra-articular
S/S: edema, erythema, tophi, tight skin
Supportive Nursing Care- Gout
Medication
NSAIDS
Allopurinol- drink plenty of water
Diet
Alcohol in moderation
Avoid high-purine foods
Increase water intake: 3 quarts
Osteoarthritis- Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
Most common
Wear & Tear
Normal aging
Idiopathic
Supportive Nursing Care- Osteoarthritis
No cure-supportive treatments
Pain control
Medications
Exercise
Diet
Surgery
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Chronic
Progressive
Systemic
Body systems
Supportive Nursing Care- RA
Medications- DMARDS- mexitrexstae
Heat/Cold
Surgery
Chapter 29: Oxygenation and the Respiratory System
Respiratory System
Upper Tract
Thoracic Cavity
Lower Tract
Thoracic Cavity
Alveoli = gas exchange
Where gas is exchanged from air to blood of pulmonary circulation. Resp system supplies oxygen to the body and expels carbon dioxide.
Hair in nose blocks particles.
Nasal mucosa warms and moistens the air.
Cilia moves particles toward pharynx to be coughed out or swallowed.
Irritant receptors – triggers sneeze/cough.
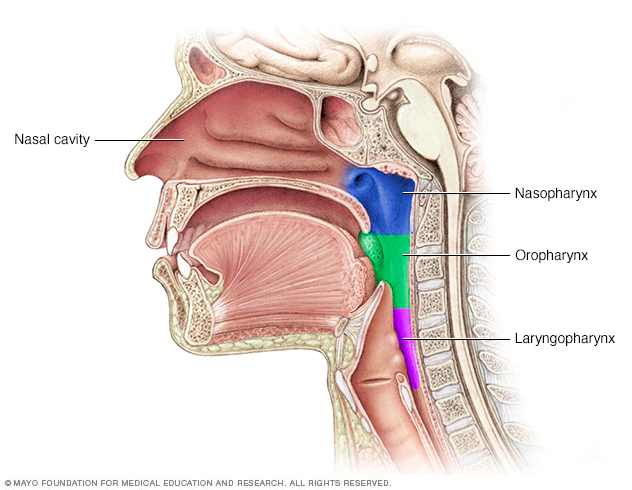
Pharynx – posterior to nasal and oral cavities. Soft palate and uvula rise to block nasopharynx during swallowing.
Oropharynx – soft palate to base of tongue – tonsils here.
Laryngopharynx – dorsal to pharynx and connects to esophagus.
Trachea: larynx to primary bronchi.
Mucosa traps dust and microorganisms in the cilia and sweep it up to pharynx where it can be swallowed.
In bronchial tree, cartilage is replaced with smooth muscle.
Bronchioles – all smooth muscle to maintain patency.
Gas exchanges occurs in alveoli (air sacs).
Ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the alveoli.
Primary resp muscles, and secondary. Resp center in brain. N 12-20 breaths/minute. Impulses come from brain down nerves to contract resp muscles to make your muscle move, diaphragm contract and flatten in inhale. Ease of thoracic and lung expansion is called compliance.
Exhalation is passive – lungs compress as lung tissue recoils and compresses alveoli. At rest- no energy used. Forced exhalation is active- contracting thoracic muscles.
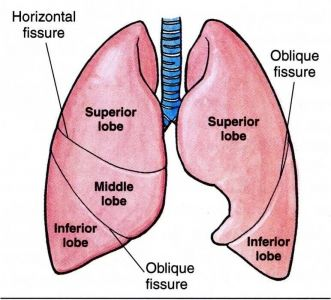
R lung – shorter, broader, larger. 3 lobes, 55% of gas exchange. 2 fissures.
L – 2 lobes (heart in the way).
Blood Gases
In simple form:
PAO2 (75-100 MM HG)
Arterial blood – bright red. Heparinized needle to prevent clotting.
Veinous blood – dark red.
PACO2 (35-45 MM HG)
PH (7.35-7.45)
HCO3 (22-26 MEQ/L)
O2 saturation (95-100%)
Oxygen is carried in the blood to hemoglobin.
Blood carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ions. CO2 is converted in the rbc into hydrogen and bicarbonate. The bicarbonate leaves the rbc to go to the plasma. The hydrogen in the rbc turns into Hgb. 98% of oxygen is carried in the blood bound to iron of hemoglobin in rbc. Oxygen carried in the blood bound to rbc attached to hemoglobin.
Breath in gases, they travel down resp track to alveoli. Pulmonary artery travel to alveoli carrying deoxygenated blood. Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart and then the body. Gas will travel from area of higher concentration to lower concentration. The partial pressure of CO2 is higher in the pulmonary artery than in the alveoli, so it goes into the alveoli. Partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli, so it goes into the pulmonary vein.
Higher pressure of oxygen in blood than carbon dioxide. Tissues have lower partial pressure of oxygen, so oxygen will move from blood to the tissue. CO2 formed as by produce and will go into the blood.
Take blood from artery to check arterial blood gas- your acid base balance. That’s your pH. Decrease in RR, excess carbon dioxide in the blood- lowers the pH- resp acidosis. Increased RR- exhaling more CO2, less in the blood- higher pH- resp alkalosis. Hyperventilation, anxiety, high altitude.
Resp system compensates from metabolic pH changes. Metabolic acidosis: kidney dz, uncontrolled diabetes, severe diarrhea. Acidosis- too much CO2- RR increase. Metabolic alkalosis: too many antacids, vomiting. Body wants more CO2 in blood, so it will decrease RR. Resp compensation happens quickly.
Drawing blood gas-take from radial artery- painful- hold pressure for 3-5 minutes or until bleeding stops.
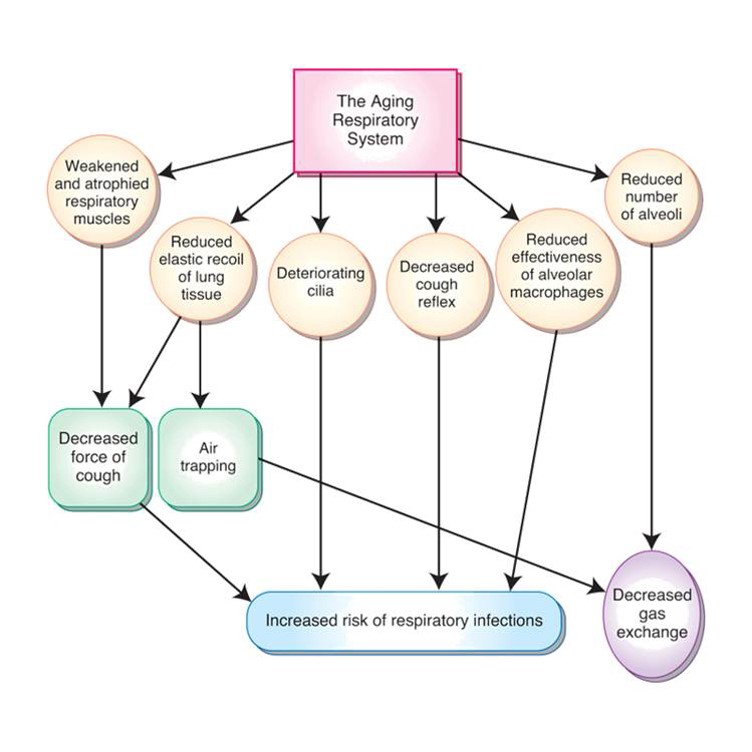
Weak, atrophied muscles- decreased cough.
Pneumonia
Reduced recoil of tissue- reduced cough and air trapping.
Cilia deteriorate, decreased cough reflex, reduced alveolar macrophage effectiveness—increased risk of resp infections and aspiration.
Reduced number of alveoli—decreased gas exchange.
Respiratory Assessment
Inspection – nose, rr, accessory muscle usage, retraction, cyanosis, periods of apnea, chest shape (barrel chest- COPD).
Palpation – resp excursion- rough measurement of chest expansion on inspiration; Crepitus (rice krispies) air leak with pneumothorax or leaky chest tube.
Percussion – tap and compare sounds- N same bilaterally except over heart.
Auscultation – abnormal sound- adventitious. N RR 12-20.
If someone is hypoxic, what will you see? Cyanosis! Central- blue lips, oral mucosa, nails.
Cyanosis is a late sign of o2 depravation.
Notice it in: Nose, ears, mucous membrane
What if your pt has edema, thickened hands/ toes, nail polish, hypothermia and you can't get nO2 sat? O2 probe on ear and toes.
Rhonchi: low pitched wheezes continuous on inspiration and expiration, snoring, gurgling or rattle like quality, occurs in bronchi, pneumonia, CF- cough can temporarily clear the sound.
Deeper in the lungs.
Wheezes: narrowed airway- fine high-pitched violin sound on expiration- asthma, chronic bronchitis, COPD, smoking, pneumonia.
Stridor- airway obstruction-loud crowing noise- heard w/out stethoscope- obstruction foreign body/ tumor, kids with croup.
Louder in the throat. Something blocking the trachea.
Medical emergency!!
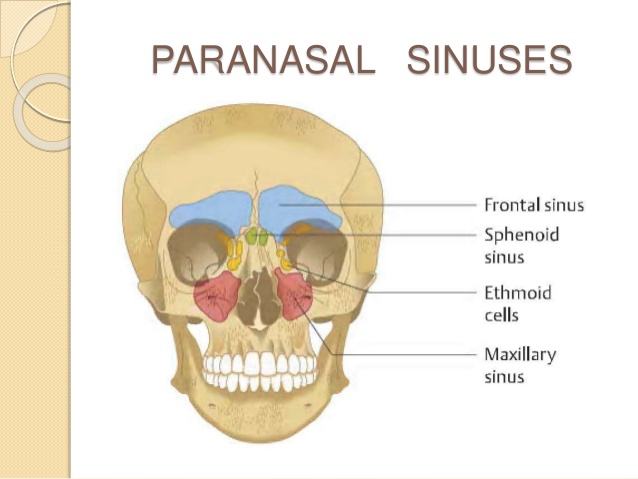
Inspection starts at sinuses.
Respiratory Patterns

Eupnea – normal

Hyperpnea – increased rate and depth – fear/anxiety.
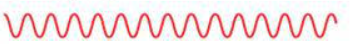
Tachypnea – rapid shallow breathing.

Bradypnea – slow, apnea (absence).

Apnea – 20 sec or more with no breath.
Less than 20 secs with symptoms.

Kussmaul’s – fast and deep no pauses – emergency response to acidosis, fast, deep, labored, hyperventilation. Seen with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Breathe may smell fruity

Cheyne-stokes – fast and deep, then slow with periods of apnea – will see near death.

Shallow – minimal using accessory muscles.

Agonal – irregular, periods of apnea. After cardiac arrest breathing.
Oxygen Therapy
O2 saturation >90% on room air.
Low-flow nasal cannula – flexible catheter with 2 short nasal prongs.
Most effective. More comfortable. Delivers lowest concentration (24-45%). Low flow, 2-3 L.
COPD 2-3 L max.
Simple face mask – 5-10 L/min 40-60% concentrations.
If need for higher concentration.
Claustrophobic
Partial rebreather – reservoir. Allows mixing of room air and O2.
50% and greater concentrations
Reservoir. Mask with open ports.
Nonrebreather – closed ports, limits mixing of room air & o2. The reservoir holds o2 but not exhaled air.
Closed ports, limits mixing. For 70-100% oxygen concentration—highest concentration.
Can breathe out air but can’t breathe back in their own air
Venturi mask – precise % of o2.
For precise percentages of oxygen needed
For chronic lung disease with CO2 retention.
Respiratory Medication
Nebulized Mist Treatment
Directly into lungs
Reduces systemic side effects.
Use of supplemental O2
Mixed with oxygen and saline.
Inhaler uses propellants to deliver the medication.
Spacer helps, dry powder inhaler doesn’t use propellant. Make sure you know how to use different kinds.
Bronchodilators, steroids- GIVE FIRST 1
Relax bronchial muscles. Used with asthma & COPD. Help you breath better. Give these first to open up the airways!
Short acting: albuterol last 2-4 hours
Long acting: 2x daily, help keep the airways open. Usually paired with inhaled steroid- Advair, Dulera, Symbicort
s/e: increased HR, nervous/ shaky, but should increase O2 sats.
Mucolytics: thins secretions, use after bronchodilators. 2
Carbocisteine, pulmozyme, mucomyst, acetylcysteine.
Can be given nebulized to trach.
Use with excessive mucous, productive cough.
Metered dose inhalers
Directly into lungs
Bronchodilators, steroids
Expectorants: stimulate cough & promote drainage 3
Mucinex, guafenesin.
Promotes drainage & lubricates the respiratory tract- stimulates cough.
Symptomatic relief of dry, non-productive cough
Increase fluids with this medication!
Nursing Treatments
Incentive spirometry – if having trouble, start slow and increase volume. Slow, deep breathing between. INHALED EVENT, AT LEAST 2-3 EVERY HOUR
Encourages deep breathing.
Reduces risk of atelectasis (collapsed lung)
Post-operative
Chest physiotherapy (CPT) – weak or ineffective cough and at risk for secretions. Use percussion to produce sound waves into the chest to loosen secretions. May use cup, hand, or vest.
Moves secretions.
Weak or ineffective cough
COPD, CF, bronchiectasis
BEFORE A MEALTIME
LISTEN TO THEIR LUNG SOUNDS
Let’s go back to CPR basics with choking pt. conscious – Heimlich, unconscious – start CPR.
Alternative Airway
Tracheotomy
Surgical opening into the trachea, temporary or permanent
Tracheostomy
Tube to maintain patency- insert piece into the placement
Cancer, trauma, tumor, prolonged ventilation, excessive secretions
Outer cannula, inner cannula, obturator
Obturator is guide that is used during insertion- keep one at bedside for emergency. If tube gets removed.
Outer cannula is always in place secured by ties or velcro strap (ex: behind the neck)
Inner cannula- removed every 8 hours and as needed to clean. Some may have balloon cuff.
Communication is hard- air comes out tube and not past vocal cords. The fenestrated tube has holes that if they plug trach, they can talk. Some have valve to allow them to speak. If cuffed- cuff needs to be deflated in order to talk.
Alternative Airway
Intubation- nasal or oral
Tube into trachea to maintain oxygenation
Short-term, going to be less than 7 days
Used with mechanical ventilation.
Control (they can set it) or assist (always you to breath in between) ventilation
Intubation can damage vocal cords and surrounding tissues, so usually short term. Long term– trach
If intubated: lung sounds bilaterally, tube placement, protect skin, move tube. They will have cuff inflated.
Need to suction-
sterile- visible secretions, crackles/wheezes, drop in O2.
Anxious if alert, oral cares. VAP (ventilator associated pneumonia- good hand hygiene, oral cares, elevated HOB 30-45%.
Unable to speak. Monitor ABG, Oxygen saturation. When removed tube—high fowlers, watch for resp distress, laryngeal edema
Positive pressure ventilation (ppv)
Independent breathing-cannot maintain blood gases.
Severe respiratory distress, sleep apnea, als
Cpap
bipap
PPV
Unable to breath on their own. Pushes air into lungs at preset intervals. Can control or assist with breathing.
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation
able to breath on own but unable to maintain normal ABGs. Severe resp distress, sleep apnea, ALS (weakens resp muscles)
Mask fits over nose or mouth and nose. Good if alert, cooperative, not a lot of secretions, able to breath on own for periods of time.
CPAP
continuous pressure- same amt of positive pressure maintained throughout inspiration and expiration to prevent airway collapse.
BiPAP
higher positive pressure for inspiration, lower level of expiration.
Monitor for skin irritation, semi-fowlers to prevent gastric distension, humidifier on machine can reduce dryness to nose/ mouth,
Air leak- irritating can blow to eyes- reposition.
Chapter 30: Upper Respiratory Tract Disorders
Epistaxis
Nosebleed
Anterior or posterior
Etiology:
Dry, cracked mucous membranes.
Trauma
Nose picking, blowing.
Disease process
Supportive Nursing Care – Epistaxis
Lean forward.
Pressure (without trauma)
Ice packs
Vasoconstriction
Packing
Airway obstruction
Avoid bending over.
Sinusitis
Inflammation of sinus mucosa
If you don’t take care of it, can turn into sinus infection.
Acute or chronic
Bacterial infection
Viral illness
3-5 days
Allergies
Nasotracheal intubation/ng tube
Signs & Symptoms
Local pain
Purulent nasal drainage
Fever
Foul breath
Complications
Osteomyelitis – infection of bone
Orbital cellulitis
Abscess
Meningitis
Supportive Nursing Care – Sinusitis
Relieve pain.
Nasal irrigation (chronic)
Medication
Increase fluid.
Warm, moist packs
Corticosteroids
NO antihistamines!!
Pharyngitis
Sore throat
Inflammation of pharynx
Bacterial or viral
Strep throat #1 (streptococci)
Signs & Symptoms
Sore throat
Dysphagia
Exudate
Fever
Headache
Stomachache/vomiting (children)
Supportive Care – Pharyngitis
Throat culture
Medications
Increase fluids.
Rest
Laryngitis
Inflammation of larynx lining
Irritation
Viral, environmental, bacterial, fungal
Signs & Symptoms
Hoarse
Cough
Dysphagia
Fever
Supportive Care – Laryngitis
Rest (including vocal rest)
Increase fluids.
Humidified Air
Medications
Tonsillitis
Strep throat
Infection of tonsil tissue
Viral (most common) or bacterial
Signs & Symptoms
Sore throat
Fever
Chills
Dysphagia
Pain
Myalgia
Red, swollen.
Exudate
Supportive Care – Tonsillitis
Throat culture
Medications
Increase fluids.
Rest
Saline gargles
Tonsillectomy
Influenza
Viral infection of respiratory tract
New strains yearly
Droplet transmission
Contact transmission
Yearly flu shot (> 6 months)
Look for egg allergies
HAND HYGIENE!!!
Signs & Symptoms
Abrupt onset
Fever
Chills
Myalgia
Sore throat
Cough
Malaise
Headache
2-5 days intense symptoms
Supportive Care – Influenza
Nasal swab
Symptom treatment
No curative treatment
Medication
Increase fluids.
Rest
Respiratory Assessment
Respiratory X-rays
Bronchitis- inflammation of the bronchial tree.
Excessive mucous, congested airway
Bronchiectasis- dilation of bronchial airways, become flabby and scarred. Secretions pool and are difficult to cough up. BROCHODIALTOR- SIDE EFFECT- SHAKE, TEMURS
Infection is common
Occurs secondary to chronic respiratory disorder
Vitamin D deficiency may play role
Can produce as much as 200mL of thick sputum
Wheezes/Crackles
CT scan provides view of dilated airway
Pneumonia- acute inflammation from infectious agents entering the lungs. Categorized by how it’s acquired.
Fever, chills, chest pain, dyspnea, fatigue, productive cough. Crackles & wheezes, blood-tinged sputum.
Different types: Bacterial, Fungal (most common), Viral (AIDS), Aspiration (GERD), Ventilator-Associated, Chemical (inhalation of chemical toxins)
Can be confined to one lobe or throughout the lungs
X-Ray
Hear less airflow on the spot of pneumonia
RAISE THE HEAD OF THE BED FIRST
Tuberculosis- Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chronic productive cough, blood-tinged sputum, chest pain, fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss, low-grade fever
Affects the lungs, but kidney, liver, brain, and bone may be affected
Meds can turn urine orange
3-month testing while on medication- tough on liver, hypertoxicity
N95 MASK
Pleural effusion- excess fluid in the pleural space. *SYMPTOM*
SOB, cough, tachypnea, decreased lung sounds, often pain
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)- Group of pulmonary disorders (umbrella). Difficulty exhaling d/t narrowing airway, blocked with inflammation,
exacerbations- (symptoms get out of control)
(Obstructive- air moving out)
Cough, chronic sputum production, dyspnea, crackles, wheezes, barrel-chested, accessory muscles.
Deliver oxygen Nasal Cannula 2 L
Per lip breathing- increase the duration of the excoriation, get more air out
INCREASE PROTEIN
Atelectasis- collapse of lung
Asthma- chronic inflammation and edema of mucosal lining. Narrowed airways and air trapping.
Chest tightness, dyspnea, coughing, difficulty moving air out.
Wheezing on expiration- hear them up high
Cystic Fibrosis- exocrine glands disorder that affects the lungs, GI tract, sweat glands. Thick, tenacious secretions, cause airway obstruction.
Coughing, purulent sputum, finger clubbing, hemoptysis. Foul-smelling stools, bowel obstruction, cirrhosis, cholelithiasis.
Sweat test for Diagnostic testing
Pneumothorax- air in the chest
Hemothorax- blood in the pleural space
Empyema- a collection of pus in the pleural space
Retraction- pulls in while breathing
Pulmonary embolism- traveling blood clot, blockage in pulmonary arteries, ADMINISTER OXYGEN, First sign could be stabbing chest pain
Hypoxemia- not getting enough oxygen, Hunger for air
USE OF INHALER:
SHAKE
PLACE ON LIPS
INHALATION
HOLD
EXHAUL
Chapter 47- Neurologic System
Neurologic System
Two Divisions
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Includes nerves of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Electrical Impulses
Neurons
Afferent
A=Affect or senseEfferent
E= Effect or action
Synapses
Circuit
Synapse: small gap between neurons
Impulse becomes chemical
One way
Medication work here
Spinal Cord
Transmit impulses 🡪🡨 brain
Nerves attach by roots
Meninges
Offer protection
Circulating CSF
Offer protection
Spinal Nerves
8 cervical pairs
12 thoracic pairs
5 lumbar pairs
5 sacral pairs
1 coccygeal pair
Referred by letter & number
Reflexes
Fast, involuntary response to stimulus
Stretch
Flexor
Brain
4 areas
Cerebrum
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal
Diencephalon
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
Brainstem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Cerebellum
Cranial Nerves
Carry out motor impulses to muscles
12 pairs
Autonomic Nervous System
2 divisions
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Integrated by hypothalamus
Sympathetic
Dominant in stressful situations
Fear, anger, anxiety, excitement
“S” is for STRESS
Parasympathetic
Dominates during relaxation
“P” is for PEACEFUL
Nerulogical Assessment
Assessment:
Establish present function
Detect changes/alternations
Diagnosis determines frequency
Rapid detection & intervention!!
Paresis- weakness or partial paralysis.
Dysphagia- difficulty swallowing.
Health history
Physical Examination
Glascow Coma Scale
Level of Consciousness
Abnormal posture
Mental Status
Aphasia- unable to speak
Examination of the eyes
Examination of muscle function
Upper/Lower
Left/Right
Hand grasp, arm drift, plantar strength
Anisocoria- unequal pupils
Nystagmus- involuntary movement of the eyes
Diagnostic Testing
Lumbar Puncture
X-ray
Computed Tomography (CT)
Magnetic Resonance Imagine
Angiogram
Myelogram
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Supportive Nursing Care
Assistance with position change & ambulation
Monitor for sensory loss
PT referral
Proper body alignment
Splints, footboards, foot support
Paresthesia- abnormal sensation (burning or tingling).
Contractures- Permanent muscle contractions occurring from lack of use.
ADL assessment & assistance
Communication assessment
Nutrition assessment
Family assessment
Dysarthria- difficulty speaking.
Expressive aphasia-difficulty or inability to verbally communicate with others.
Receptive aphasia-inability to understand spoken language.
Chapter 48- Care of Patients with CNS Disorder
Dementia- not a diagnosis
Progressive loss of mental functioning
Can progress to Alzheimer’s
Reduced blood flow
Short-term memory affected first
Disorientated to time
Aphasia- absent of speech
Behavioral problems
Delirium- mental disturbance that is temporary. MEDICAL EMERGENCY. Treatable
Disorganized thinking
Safety #1 priority
Supportive Nursing Care- Dementia
Medications-
Slow progression
Reduce symptoms
Improve cognition
Donepezil (Aricept)
Memantine (Namenda)
LTC facility placement
Parkinson’s Disease- decrease of dopamine
Chronic, degenerative movement disorder
Destruction of cells 🡪 decreased dopamine production🡪 impairment of semiautomatic movements
Tremors, changes in posture & gait, rigidity, slowness of movements
Akinesia- loss of muscle movement
Acetylcholine- excitatory neurotransmitters
Parkinson’s Disease S/S
Gradual onset
Muscular rigidity
Bradykinesia- slow movement
Akinesia
Postural changes
Tremors- ipsilateral (same side) then contralateral (opposite side)
Alterations in mobility, ADL function
Increased symptoms with fatigue
Supportive Nursing Care- Parkinson’s
Fall risk!
Support impaired swallowing
Symptom control (no cure)
Medications
Entacapone (Comtan)- prolongs levodopa action
Levodopa/Carbidopa (Sinemet)- convert into dopamine in the brain
Not with food or after (food after medication)
Discolors urine
15 minute range, every 4 hours
“Drug Holiday”- off medication and restarted on lower doses
PT/OT- maintain the function that they have for awhile
ROM/PROM
Dietary support (thickened liquids)
Bed/chair alarm (facility dependent)
Alzheimer’s Disease
Women > Men
Most common dementia type
Deficiency of acetylcholine
Alzheimer’s Disease 5 A’s
![]()
Stage 1
2-4 years
Increasing forgetfulness
Stage 2
Longest in duration
2-12 years
Progressive cognitive deterioration
Irritability
Depression
Aphasia
Disrupted sleep
Hallucinations
Seizures
Stage 3
Progression to complete dependency
Inability to converse
Incontinence of B & B
Loss of emotional control
Inability to move independently
Inability to swallow
Tube feedings
Duration depends on health status
Supportive Nursing Care- Alzheimer’s
No cure
Focus on minimizing effects & maintaining independence
Medications
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors (donepezil (Aricept) ) Inhibit acetylcholine breakdown
NMDA antagonists (memantine (Namenda) ) prevents overexcitation
Antidepressants
Antipsychotics
Antianxiety
Safety assessment
ADL assistance
Chapter 49- Nursing Care of Patients with Cerebrovascular Disorder
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Temporary impairment blood to the brain
Deprives brain of glucose and oxygen
Symptoms resolve
15% of all Strokes are preceded by TIA
Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) CVA
Inadequate Blood Flow to Brain
Infarction of Brain Tissue
Permanent Damage if Not Reversed
Neurological Deficits
Etiology
Ischemic- deficient blood supply
Thrombotic- stroke occurs when occlusion builds up in an artery
Embolic- caused by a blood clot
Hemorrhagic- rupture of a cerebral blood vessel that allows blood to escape the blood vessel
Subarachnoid- surface of the brain
Intracerebral- occurs in the deeper tissue of the brain, caused by uncontrolled hypertension
Risk Factors Modifiable
Hypertension
Smoking
Diabetes Mellitus
Cardiovascular Disease
Atrial Fibrillation
Carotid Stenosis
TIA
Sickle Cell Anemia
Dyslipidemia
Obesity
Excessive ETOH intake
Poor Diet
Physical Inactivity
Oral Contraceptives
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Age
Gender
Heredity
Prior Stroke or Heart Attack
Warning Signs
Sudden Numbness or Weakness- typically one-sided
Sudden Confusion
Sudden Change in Vision
Sudden Trouble Walking/Dizziness
Sudden Severe Headache
CALL 911!
S/S
Depend on Area of Brain Affected
One-Sided Weakness/Paralysis
Dysphagia
Sensory Loss
Mental Status Changes
Visual Disturbance
Speech Disturbance
Diagnostic Testing
CT Scan- give TPA
EKG
CBC, Electrolytes, Glucose
Metabolic Panel
PT, INR
NIH Stroke Scale
Carotid Doppler
Carotid Angiography
Supportive Nursing Care- Stroke
Thrombolytic Therapy
Airway Management
Control
Hypertension- the bottom number is the more important one
Fever- less than 99.6
Glucose
Thrombolytic Therapy
TPA Dissolves Clot- don’t give TPA if you do not see the clot
4.5 Hour Time Window
May Reverse Symptoms
Or prevent progression
TIME LOST IS BRAIN LOST!
Prophylactic Management
Treat Cause of Stroke
Physical, Occupational, Speech Therapy
Antiplatelet Agent- aspirin, Plavix
Anticoagulant Agent- Warfin, Heparin
Antihyperlipidemic Agent
Antidysrhythmic Agent
Maintain Patent Airway
Surgery
Carotid endarterectomy- is surgery to treat carotid artery disease. The carotid arteries are the main blood vessels that carry oxygen and blood to the brain. In carotid artery disease, these arteries become narrowed. This reduces blood flow to the brain and could cause a stroke.
Prevention
Control
Weight
Hypertension
Cholesterol
Smoking Cessation
Aspirin or Warfarin
Early Recognition and Treatment
Long-Term Affects
Impaired Motor Function
Impaired Sensation
Dysphagia/Aphagia
Dysphasia/Aphasia
Emotional Lability
Impaired Judgment
Unilateral Neglect
Nursing Process: Assessment
LOC
Restlessness
Dizziness
Vision Changes
Pupil Changes
Vital Signs
Pain
SpO2
Paresthesias
Weakness
Paralysis
Seizures
Respiratory Status
Swallowing
Chapter 51- Vision and Hearing
Eyeball Structures
Sclera- outer, white
Cornea- clear part
Retina- light sensitive
Optic nerve- back part that sends signals
Iris- color of the eye
Lens
Aging Sensory System
EYES:
Color vision fades
Glare adaption difficulties- more so at night
Peripheral vision decreases
Depth perception decreases
Farsightedness
Lens opacity
EARS:
Unable to filter background noises
Impaired verbal communication
Inner ear cell damage
High pitch loss
Assessment
Patient history
Nutrition history
Family history and genetic risk
Current health problems
Visual acuity
Visual field
Extraocular muscle function
Pupillary reflexes
Color vision
Inspect & palpate
Supportive Nursing Care- Eyes
Regular eye examinations
Eye hygiene
Nutrition
Eye safety & injury prevention
Eye irrigation
Medication administration
Ear
3 areas
Outer ear
Auricle
Auditory canal
Middle ear
Air-filled
Vibrations transmitted through auditory bones
Inner ear- bony labyrinth- HEARING
Hearing
Equilibrium
Assessment
Health History
Physical Examination
Inspection & palpation
Auditory acuity testing
Whisper test- hearing function in each ear
Rinne test- conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
Weber test- third test to determine hearing acuity
Balance testing- ROMBERG TEST
Diagnostic Testing
Audiometric testing- screening tool to determine type and degree of hearing loss
Tympanometry- tympanic membrane and evaluate middle ear function
Caloric test- function of 8th cranial never and asses vestibular reflexes of inner ear that control balance
Electronystagmogram- unilateral hearing loss of unknown origin, vertigo, or ringing in the ears
CT/MRI
Laboratory tests
Ear cultures- drainage from ear canal
Pathology examination- tissue obtained during surgery ruled out
Supportive Nursing Care
Medications
Maintenance
Assistive Hearing Devices
Chapter 52- Sensory Disorders- Vision & Hearing
Eye Infections & Inflammation
Types of Conjunctivitis- inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by either virus or bacterial- PINK EYE
Allergic Conjunctivitis- itching and redness of the eye, swelling of the conjunctiva and the eyelid
Viral Conjunctivitis- redness of the eyes and periodic itching, increased lacrimation
Bacterial Conjunctivitis- redness, dryness of eye and skin around them mucopurulent discharge
Diabetic Retinopathy- retinal blood vessels affected
Diabetic complication- more so from uncontrolled
Total blindness can result
Retinal Detachment S/S
Sudden vision change
Flashing lights
Floaters
“Looking through a veil”
Curtain
No pain
Retinal Detachment Therapeutic Interventions
Laser Reattachment
Cryosurgery
Scleral Buckling
Glaucoma- Group of Diseases that damage optic nerve- pressure within the eye
Elevated pressure
Silent, progressive, irreversible
Lifelong treatment
Glaucoma Acute Angle-Closure- Pain- No Benadryol
Narrow angle blocks aqueous fluid
MEDICAL EMERGENCY
Signs & Symptoms
Severe eye pain
Blurred vision
Rainbows around lights
Redness
Photophobia
Tearing
Steamy-appearing cornea
Glaucoma Primary Open-Angle- NO PAIN
Degeneration of drainage system
Gradual
Painless
Signs & Symptoms
Headache
Halos around lights
Visual changes
Glaucoma Treatments
Medications- decreased the pressure in eye and try to drain the fuild
Miotics
Carbachol (Isopto Carbachol)
Pilocarpine (Pilocar)
Agents to decrease production of aqueous fluid
Dipivefrin (Propine)
Timolol (Timoptic)
Mydriatics: DO NOT GIVE TO AACG
Atropine, diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine
Cataracts
Opacity in lens
Signs & Symptoms
Loss of visual acuity
Halos
Difficulty reading
Glare sensitivity
Double vision
Decreased color vision
Macular Degeneration
Slow, progressive loss of central/near vision
Daily screening
Amsler Grid- the only time you use it is with Macular Degeneration
Eye Medications
Diagnostic- stain the eye (yellow), wear gloves, tissues
Anesthetics- topical
Antiangiogenic- growth factor, inhibits the growth
Allergy relief
Antibiotics
Antivirals
Antifungals
Anti-inflammatories- bring down inflammation
Lubricants- artificial tears
Miotics- cause the pupil to constrict
Osmotic- decreases pressure
Beta-Adrenergic Blockers
Hearing Loss
Congenital or Acquired- Congenital- disorder that present at birth, Acquired- aquired during the lifetime
Effects communication, social life, work
Conductive- stops sounds from getting through the outer or middle ear (Hearing Aids)
Sensorineural- caused by lesion/disease of the inner ear, Ex: Lyme Disease, Viral/Bacterial Infection or tramua
Therapeutic Measures
Optic Medications
Diagnostic
Cerumenolytics- liquid solutions that help thin, softer, etc ear wax
Anti-inflammatory
Analgesics
Antibiotics
Presbycusis- gradual hearing loss in both ear
Chapter 21- Cardiovascular System Function, Assessment, and Therapeutic Measueres
The Heart
In mediastinum
Pericardial sac: Three layers- tissue that surrounds the heart
Fibrous pericardium- outer most layer
Parietal pericardium- middle layer
Visceral pericardium (epicardium)- inner most layer
Serous fluid between inner layers
Cardiac Structure and Vessels
Four chambers
Right/left atrium, right/left ventricle
Cardiac layers
Epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
Coronary arteries
Valves
Tricuspid, pulmonic, mitral, aortic
Blood Flow
Vena cava » right atrium » tricuspid valve »
right ventricle » pulmonic valve » pulmonary
artery » lungs » pulmonary veins » left
atrium » mitral valve » left ventricle (thicker wall, pumps out with 5x the force)» aortic
valve » aorta
Cardiac Conduction
Sinoatrial (S A) node- pacemaker, beat of heart
Atrioventricular (A V) node
Bundle of HIS
Right and left bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Cardiac Output (CO)
Amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle in 1 minute
Stroke volume multiplied by heart rate = C O
Hormones and The Heart
Epinephrine increases
Aldosteraone
Blood Vessels
Arteries- carry blood away from the heart, thicker, more muscle
Veins- carry blood towards the heart
Capillaries- tiny, take waste out to the tissue
Blood Pressure
Blood force against blood vessel walls
When blood flow to the kidneys is decreased, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Mechanism, protects the organs
Aging
Atherosclerosis- deposition of lipids in the arterial walls
At risk for developing orthostatic hypotension🡪 falls.
Cardiovascular Disease
Number 1 cause of death
Healthy lifestyle
Smoking cessation
Exercise
Dietary fat reduction
Normal B P, glucose, cholesterol levels
Normal weight
Cardiovascular Assessment
Health history
Physical assessment
General appearance
Vital signs
Orthostatic BP
Height/weight
Diagnostic studies
Physical Examination
Inspection
Oxygenation, skin color
Extremities: Hair, skin, nails, edema, color
Jugular vein distention- right sided heart failure from liver
Capillary refill
Clubbing
Put index fingers at the nailbeds/first joint together.
If there is a diamond shape in the space at the nailbeds, this is normal.
Physical Examination
Palpation
Point of maximum impulse- apical pulse (by the heart pulse)
Extremity temperature
Poikilothermy- when your body temp is same as environment time
Edema
Thrill- vibration caused by blood flowing through the fistula (feel it)
Bruit- listen to the incision cite- whooshing sound, (hear)
Physical Examination
Auscultation
Heart sounds
Murmurs
Pericardial friction rub
Cardiovascular Testing
X-ray: size, position, contour, structures (enlargement, fluid, calcification, heart failure)
Computed Tomography (CT): evaluates heart structures (plaque w/ atherosclerosis)
Angiography: view blood vessels and coronary arteries * check kidney function* because they use *iodine*, allergic to shellfish
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: identifies ischemia and abnormalities
Electrocardiogram: records electrical activity, enlarged chamber size, electrolyte imbalances, dysrhythmias
Echocardiogram: ultrasound, heart enlargement, CAD, pericardia effusion
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE): transducer into esophagus
Stress test: dysrhythmias and ischemia, effects of exercise on the heart
Cardiac Catheterization: catheter into heart, detects chamber pressures, cardiac disease- risk for: bleeding first, check everything distal from the point of entry
Blood Studies
Cardiac biomarkers
Creatine kinase, troponin (sign of heart attack, chest pain), myoglobin
C-reactive protein
Homocysteine
Lipids- deals with cholesterol, fats
Triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids
Magnesium
Potassium- can become toxic fast in pt. (3.5-5 number range)
Therapeutic Interventions
Exercise
Smoking cessation
Diet
Oxygen
Medication-vasodilators, antihypertensives, antidysrhythmias, antianginals, anticoagulants, thrombolytics
Anti-embolism devices-TEDS, SCDs
Cardiac surgery
Chapter 22 Hypertension
Hypertension
High blood pressure
Average of at least 2 or more BP readings on 2 different occasions
Change in vessels, increase in blood thickness, increased fluid volume contribute to elevated BP
Hypertension Primary (Essential)
Chronic elevation from unknown cause
Hypertension Primary (Secondary)
Known cause
Sign of another problem
Kidney abnormality
Adrenal glad tumor
Congenital defects
Once treated, bp returns to norm.
S/S Hypertension
Often no signs or symptoms
Headache, bloody nose, severe anxiety, SOB
“Silent Killer”- don’t know they have it
Often found when seeking care for unrelated issues
Risk Factors Modifiable
Lifestyle modifications
Diet
Exercise
Antihypertensive drugs
Cholesterol
Risk Factors Non-Modifiable
Family HX
Age
Race & ethnicity
Diabetes mellitus- Type 1
Hypertension Meds
Combined Alpha & Beta blockers
Alpha2 Agonists
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor
Angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARB)
Calcium channel blockers
Direct vasodilators
Diuretics- start with, get rids of the fluid
Thiazide diuretics
Loop diuretics
Potassium-Sparing diuretics
(Sympatholytics) Beta Blockers
Diuretics
Take with food to avoid GI upset
Assess edema
Assess BP for hypotension
Electrolyte imbalances- Potassium
Nocturia- excessive urination at night
Diuretics Meds- monitor potassium levels
Potassium-Sparring- high potassium can be caused
spironolactone (Aldactone)
Loop- low potassium can be caused
bumetanide (Bumex)
furosemide (Lasix)
Thiazide (& like)- low potassium can be caused
hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
metolazone (Zaroxolyn)
Beta Blockers (OLOL)- monitor bradycardia, check pulse first, can’t stop abruptly
atenolol (Tenormin)
metoprolol (Lopressor)
metoprolol XR (Toprol XL)
propranolol (Inderal)
Combined Alpha & Beta Blockers- cause vasodilation, BP could drop
carvedilol (Coreg)
labetalol (Normodyne)
Alpha2 Agonists
clonidine (Catapres)
guanfacine HCL (Tenex)
ACE Inhibitors (PRIL)- reduce BP, LISTEN TO LUNG SOUNDS AND NEW ONSET COUGH
fosinopril (Monopril)
lisinopril (Zestril, Prinvil)
quinapril (Accupril)
enalapril (Vasotec)
captopril (Capoten)
benzepril (Lotensin)
ARB (TAN)
losartan (Cozaar)
olmesartan (Benicar)
valsartan (Diovan)
Calcium Channel Blockers- prevent movement, extra calcium
amlodipine (Norvasc)
diltiazem (Cardizem)
nifedipine (Procardia)- change vessel lining of the heart, smooths muscle contractions
verapamil
Direct Vasodilators
hydralazine (Apresoline)
minoxidil (Loniten)
Hypertension Complications
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Atherosclerosis
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Heart failure
Cerebral-vascular accident (CVA/Stroke)
Pulmonary edema
Kidney disease
Renal damage
Eye damage- so much pressure and tiny vesssels
Hypertrophy- increased size caused from hypertension and overwork muscle
Hypertensive Emergency
Severe hypertension
Systolic > 180
Diastolic > 120
Target-organ dysfunction (MI, HF, dissecting aortic aneurysm)
CVA
Gradual reduction is desired to prevent decreased blood flow to kidneys, heart, brain
Patient Education
Lifelong BP control
Self-care lifestyle measures
Prescribed medical regimen
Dizziness may increase the risk of falling.
Rise slowly to prevent orthostatic hypotension.
Chapter 23- Valve, Inflammatory, Venous Disorders
Cardiovascular Meds
Nitrates
Anticoagulants
Antiplatelet agents
Thrombolytics
Potassium channel blockers
Vasopressors
Inotropic agents
ACE inhibitors
Beta-adrenergic blockers
Diuretics
Calcium channel blockers
Cardiac glycosides
Angiotensin receptor blockers
Vasodilators
Cardiac Valve Disorders
Mitral, tricuspid, pulmonic, aortic
Forward blood flow compromised with stenosis
Blood back up = regurgitation (hear murmurs)
Stagement blood is clotting blood
Increases workload of heart
Increases pressures in chambers
Cardiomyopathy
Enlargement of heart muscle
Complications: heart failure, myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction (MI)
No cure
Types:
Dilated
Hypertrophic
Restrictive
Heart failure s & s: dyspnea, fatigue, orthopnea, atypical chest pain, syncope, crackles
Cardiomegaly on x-ray
Anticoagulants
Heart failure treatment as needed
Palliative care
Left ventricle goes to lungs, so back up will spill over into the lungs, s/s everything pulmonary, wet lung sounds, pulmonary edema/hemorrhage
Right sided heart failure = rest of the body, backs up to liver, JVD, perfilary edema, spleen swelling
Thrombophlebitis
Clot 🡪inflammation within a vein
Most common vein disorder
Legs most common
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) most serious d/t PE risk
Platelets attach to vein wall
Cells and fibrin collect
Stasis of blood flow, damage to wall lining, increased coagulation=Virchow’s triangle
Thrombophlebitis S/S
None
Superficial veins
Redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness
Palpation reveals vein feels like a cord (induration)
DVT- most several form, most worried about PE (large clot into a smaller vessel), O2
Located in leg usually
Swelling, edema, venous distension, pain in deep calf (usually), warmth, tenderness
DEHYRDRATION
TED STOCKING
AMBULTIATION IS IMPORTANT
Thrombophlebitis Complications
Pulmonary embolism
Life-threatening emergency
Chronic venous insufficiency
Varicose veins
Recurrent DVT
Thrombophlebitis Prevention
ID risk factors
Prevent dehydration
Antiembolism devices (teds/scds/IPCDs)
Mobility
Medication
Heparin
Coumadin
International normalized ratio (INR)-measures effectiveness
Chapter 24- Occlusive Cardiovascular Disorders
Cardiovascular Disease
Leading cause of death in US
Education important!
Every 25 secs a coronary event happens
Every minute someone dies from coronary event
1 in 3 women affected
Decreases with higher education
<high school education higher incidence than college degree
Arteriosclerosis- normal part of aging
Thickening
Loss of elasticity
Calcification of arterial walls
Atherosclerosis- plaque inside arteries, not normal part of aging
A Type of arteriosclerosis
Can start in childhood
Causes coronary artery disease (CAD)
Partial or total occlusion of the artery=reduced blood flow
Distal ischemia
Atherosclerosis
Pathophysiology
Injury, inflammation
Smooth muscle cells grow
Collagen and fibrous proteins are secreted.
Lipids, platelets, clotting factors accumulate.
Scar tissue replacement
Fatty streak
Plaque build-up—reduced blood flow
Reduced blood flow from narrowing artery
Calcium fibrous cap—rupture/ tear
Blood clot forms.
Atherosclerosis Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Age
Gender
Ethnicity
Genetic predisposition for hyperlipidemia
Atherosclerosis Modifiable Risk Factors
Alcohol
Obesity
Sedentary lifestyle
Stress
Tobacco
Diabetes
Hypertension
Elevated Cholesterol
Elevated LDL apolipoprotein B
Elevated homocysteine
Atherosclerosis Diagnostic Tests
Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL)- under 200
High-Density Lipoproteins (HDL)- lose some weight, quit smoking
Radiological studies
Atherosclerosis Therapeutic Measures
Diet
Smoking
Exercise
Medications
Angina Pectoris- chest pain from ischemia
Narrowed vessels can’t dilate
Less oxygen/blood to heart
Angina Pectoris Types
STABLE ANGINA
Exertion, familiar pattern
Pain is predictable.
More so during a physical activity
UNSTABLE ANGINA
Pain is unpredictable.
Rest/ sleep occurance
Meds don’t help
MI risk
DO NOT need to be doing anything
VARIANT ANGINA (PRINZMETAL)
Coronary artery spasm
Cyclic pain
Longer duration
IF NOT FOUND: can be serious and lead to other things, not as painful as other two
Angina Pectoris S/S
Men- more common S/S
Heaviness, tightness, viselike, crushing pain in chest center
Radiate to arms, shoulder, neck, jaw, or back
Pale, diaphoretic, dyspneic
Women
Chest or jaw pain
Heartburn
Atypical
N/V
Angina Pectoris: Medication
Vasodilators #1- improve blood flow going to the heart, nitro (under the touge)
Calcium channel blockers
Beta Blockers- watch for bradycardia
ACE Inhibitors- pril
Statins- high cholesterol, watch liver function studies (AST, ALT)
Antiplatelets- aspirin, Plavics (anticoagulant)
Acute Coronary Syndrome- MI
Encompass CAD continuum
Silent ischemia
Sudden cardiac death
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Non-ST-segment elevation MI (NSTEMI) ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI)
TIME IS MUSCLE
MI S/S
Crushing, viselike pain
Radiates: Arm/shoulder/neck/jaw
Diaphoresis (sweating)
Dizziness, fainting
Dyspnea
Nausea
Restlessness
EMERGENCY!
Women and MI
Leading cause of death
African American women at higher risk
Higher mortality rate
Prodromal (not common) symptoms the month before
More tired
SOB
S/S don’t show to having a heart attack
Atypical symptoms
Older Adults and MI
Report to health care provider
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Fast/slow heartbeats
Chest discomfort
May have silent MI
Collateral circulation may offer protection
MI Diagnosis
Consider patient history
Diagnostic tests
Serial E C G
Serum cardiac troponin I or T (not going to show elevation right away, check again 4-6 hours)
Myoglobin
Creatine kinase (C K)-M B
C R P
Magnesium
Potassium (3.5-5)
MI Therapeutic Interventions- MONA (Morphine, oxygen, nitro, aspirin)
Antiarrhythmics
Weight loss
Smoking cessation
Statins
ACE inhibitors
Oxygen
Aspirin
Morphine sulfate
Thrombolytics
Vasodilators
Beta blockers
Arterial Thrombosis (hanging out) & Embolism (gets away and goes on adventure)
Occlusions most common in lower extremities
Thrombus
Embolism
“6 Ps”
Arterial Thrombosis/Embolism- Therapeutic interventions
Anticoagulants
Thrombolytics
Thrombectomy
Embolectomy
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Chronic narrowing of arterial vessels
Lower extremities
Atherosclerosis (plaque) leading cause
Organic disease
Functional disease
Intermittent claudication- pain in calf during exercise, blood supply to muscle decreases
DO NOT use heating pads
SHOULD NOT have TEDS on
Raynaud’s Disease
Vasoconstrictive response
Fingers, ears, lips, toes, nose
Primary or secondary
Skin turns white, then blue
Re-warm slowly- prevent injury to area
Wear gloves
Avoid vasoconstrictors
Varicose Veins
Primary:
Structural defect in vessel wall
Incompetent valves
Blood pooling
Superficial veins
Secondary:
Deep veins
Blood stasis/ increased pressure
Dilation of collateral and superficial veins
Varicose Veins- S/S
Telangiectasias (spider veins)
Dull pain
Cramping
Edema
Heavy feeling in lower extremities
Ulceration (from blood just sitting there)
Disfigurement of lower extremity
Goals: improve circulation. Relieve pain
Compression socks
Laser ablation procedures
Chapter 25- Cardiac Dysrhythmias
Cardiac Conduction System
Sinoatrial (SA) node: 60 to 100 beats per minute, your pacemaker (SINUS)- working as it should
Atrioventricular (AV) node: 40 to 60 beats per minute
Bundle of His
Right and left bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Cardiac Cycle
One heartbeat
Electrical representation of contraction and relaxation of atria/ventricles
![]()
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Shows cardiac electrical activity
12-lead ECG = 12 different cardiac views
Waveforms change appearance in different leads
Waveforms upright in lead Two
Continuous monitoring often in lead Two
Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG)
Shows electrical activity of the heart
Dysrhythmias- abnormal rhythm
Process for Arrhythmia Interpretation
Is it regular?
What’s the rate?
P waves?
PR interval?
QRS interval?
QT interval?
Normal sinus rhythm:
Rhythm-regular
HR: 60-100
P waves- rounded, preceed QRS
Normal Sinus Rhythm- 60
Sinus Brady(slow)cardia- 40
![]()
Sinus Tach(fast)ycardia- 140
![]()
Atrial Flutter- (abnormal), heart contracting fast, AV, shock heart back into normal rhythm
![]()
Atrial Fibrillation- (AV)- no defined P waves- 300-650 bpm
![]()
Ventricular Tachycardia- Ventriculus have taken over, 3 or more contractions in a row, wide bases, S/S: SOB, Sweating, Lightheaded, Pt. is dead, does not have pulse, bp (CPR)
![]()
Ventricular Fibrillation- Ventriculus, can’t determine rate, complete loss of cardiac output, defibulator- vefib, every minute decrease surivial rate
![]()
Asystole- dead, have to have rhythm to shock, CPR
Chapter 26- Heart Failure
Heart Failure
Inability of ventricles
Dyspnea
Fatigue
Fluid volume overload- isn’t pumping effectively
Right/Left (thicker wall, pump 5x force, get blood out) sided
Causes
MI 🡪 cardiac ischemia
CAD
HTN- Hypertension
Left-Sided Heart Failure- backups into lungs
Afterload
Left side🡪 Lungs- everything pulmonary
Reduced gas exchange
SOB
Cyanosis
Pulmonary edema
Acute HF
Pink, frothy sputum
Left-Sided Heart Failure Causes
Aortic Stenosis
Cardiomyopathy
Coarctation of aorta
Hypertension
Heart muscle infection
Myocardial infarction
Mitral regurgitation
Right-sided heart Failure- backup to rest of the body
Preload
Increased work of right ventricle
Cor pulmonale- right ventricles increases in size
Abnormal emptying
Right🡪Systemic build-up
Right-Sided Heart Failure Causes
ASD
Cor pulmonale- right ventricles increases in size
Left-sided HF
Pulmonary HTN
Pulmonary valve stenosis
Chronic Heart Failure S/S
Fatigue
Weakness
Dyspnea
Cough
Crackles & Wheezes
Tachycardia
Chest pain
Edema
Anemia
Nocturia
Cyanosis
Altered mental status
Malnutrition
Chronic Heart Failure Complications
Hepatomegaly
Splenomegaly
Pleural effusion- Left sided heart, fluid in pleural space
Left ventricular thrombus
Cardiogenic shock
Chronic Heart Failure Diagnostic Testing
Laboratory tests
BNP
BUN
Creatinine
Liver enzymes
X-Ray
EKG-Dysrhythmias
Echocardiogram
Stress testing- consent is required
MRI
Cardiac catheterization/angiography- inside vessels, inside view of chambers
Chronic Heart Failure Theraputic Interventions
Improve pumping ability & decrease oxygen demands.
ID & treat underlying cause.
Increase strength of heart’s contraction.
H2O/Na balance
Decrease workload- diuretic
Chronic Heart Failure Drug Therapy
Oxygen
ACE inhibitors, ARBs, ARNis
Beta blockers
Diuretics
Inotropes
Vasodilators
Anticoagulants
Chapter 36- Urinary System Function & Assessment
AP
Urinary System Consists of:
Two Kidneys
Two Ureters
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
Kidneys: Urine Formation
3 part process:
Glomerular Filtration
Tubular reabsorption
Secretion
Glomerular Filtration Rate: measures kidney function
AP- Kidneys
Form urine
Regulation of BP
Regulation of electrolyte balance
Regulation of acid-base balance
Erythropoietin production
Vitamin D activation
AP- Ureters
Eliminate urine
Kidney to bladder
Peristalsis
Compression to avoid backflow
AP- Bladder
Behind pubic symphysis
Temporary urine storage
AP-Urethra
Eliminates urine from bladder
Urine Characteristics
Amount
~1000-2000 mls/24 hrs
Color
Straw/Amber
Diluted=lighter
Concentrated=darker
Freshly voided=clear
Cloudy=infection
Specific Gravity
Kidneys’ concentrating ability
1.005-1.030
Higher= concentrated
Lower= diluted
pH
4.6-8 (avg 6)
Elements of Urine
Urine is 95% water
Nitrogenous waste: Urea, creatinine, uric acid
Nursing Assessment
Health History
Pain/Burning with Voiding
New Onset Edema, Shortness of Breath, Weight Gain
Fluid Intake
Functional Ability
Physical Assessment
Vital signs
Lung sounds
Edema
Daily weights
I & O
Laboratory Testing
Urinalysis (urine analysis)
Diagnostic test
Assesses urinary system, kidney disease, systemic disease
Room temp 1 hours/refrigerate
Urine Culture
Bacteria in urine
Sensitivity to antibiotics
Renal Biopsy
Identify kidney disease
Pyelogram
Xray examination
Nephropathy
U/S, CT, MRI
Laboratory Testing
Renal Function Tests
Serum Creatinine (Male: 0.61-1.21mg/dL, Female: 0.51-1.11mg/dL)
Waste product from muscle metabolism
Very good indicator of kidney function
Blood Urea Nitrogen (8-21mg/dL)
Waste product of protein metabolism excreted by kidneys
Elevated levels=kidney disease, dehydration, high-protein diet, heart failure
Serum Uric Acid (male: 4-8mg/dL, female: 2.5-7mg/dL)
Purine metabolism end product and breakdown of body proteins
Elevated levels=possible renal disease
Bun-creatinine ratio (10:1 to 20:1)
Evaluates hydration status
Urinary Incontinence
Involuntary leakage of urine
Stress incontinence
Involuntary loss of <50 ml urine
Coughing, sneezing, laughing
Urge incontinence
Involuntary loss with strong desire to void
Functional incontinence
Inability to physically get to the toilet
Overflow incontinence
Involuntary loss due to over-distention
Total incontinence
Continuous, unpredictable loss of urine
Often neurologically impaired
Urine Retention- Inability to empty the bladder completely
Acute Retention
Post-surgical
Extreme pain
Risk for bladder rupture
Chronic Retention
Enlarged prostate
Diabetes
Pregnancy
Obstruction
Palpation
Percussion
“fullness”
Bladder scan
Urinary Catheters
Indwelling catheters
Justifiable reasons
Medical emergency
Urinary tract obstruction
Medical procedure
High infection rate!
Intermittent
Unable to void
Every 3 hours
Taught self-cath for home
Suprapubic
Through abdomen into bladder
Long-term situations
Chapter 37- Nursing Care of Patients W/ Disorders of Urinary System
Urinary Tract Infections
E. Coli
Lower: urethritis, prostatitis, cystitis
Upper: pyelonephritis, urethritis
Women > Men
Risk factors
Incomplete emptying
Contamination
Instruments
Reflux
Anatomical
pregnancy
S/S UTI
Dysuria
Urgency
Frequency
Incontinence
Nocturia
Hematuria
Back/Flank pain
Foul-smelling urine
Cloudy
Fever
UTI
LIMIT Caffeine
Urethritis
Chemicals
Bacteria
Trauma
STI (Gonorrhea/Chlamydia)
Cystitis
90 % E. Coli
Perineal ascend
Pelvic pain/ pressure
Pyelonephritis
Hx of UTI
Sexual intercourse
Spermicide- vaginal birth control
Structural problems
Urosepsis- UTI leads to sepsis
Supportive Nursing Care UTI
Education
Medication
Increase fluids
Renal Calculi- Kidney Stones
Crystal masses
Concentrated urine gathers salts
<5 mm, passed in urine
Renal Calculi S/S
Extreme flank pain
Radiating pain
Hematuria- blood in the urine RBC
Costovertebral tenderness!
Anuria (<50 ml daily)
Oliguria (<400 ml daily)
Renal Calculi Prevention
Hydration
Diet
Exercise
Renal Calculi Diagnostic Tests
Blood tests: Calcium, uric acid, blood urea nitrogen (B U N), creatinine
Urinalysis: Hematuria, crystals, urine pH
Two 24-hour urine collections
Helical computed tomography (CT) scan
Renal ultrasound
Abdominal x-ray
IV pyelogram- X-Ray exam injects contrast material into kidneys
Supportive Nursing Care
Pain management
Surgical intervention
Urine straining
Antibiotics
IV fluids
Medications
Allopurinol
Flomax
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia- noncancerous enlargement of prostate gland
Nonmalignant growth
Increased effort
Increased time for urination
Goal=slow enlargement process
S/S BPH
Obstruction
Decrease the size/force of stream
Difficulty starting urination
Dribbling
Retention
Fullness
Midstream stop
Irritation
Nocturia
Dysuria
urgency
Supportive Nursing Care- BPH
Medication
Flomax (Tamsulosin)
Proscar (Finasteride)
Surgical intervention
TURP- surgery to remove inside part of prostate gland
Incontinence education
Chapter 38- Endocrine System, Function, and Assessment
Anatomy & Physiology
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Glands
Adrenal Glands
Pancreas
Nursing Assessment
Health history
Physical examination
Inspection
Palpation
Diagnostic Testing
Hormone tests
Stimulation- inject a certain substance, to see if you kick out the hormone
Suppression- inject substance, to suppress hormone
Urine
Nuclear scanning
Radiographic tests
Ultrasound
Biopsy
Chapter 40- Endocrine Pancreas
Diabetes Mellitus- affects pancreas
Defects in insulin secretion
Result in elevated blood glucose levels
Insulin
Glucagon- raise blood glucose levels
Type 1
(Juvenile diabetes, insulin-dependent, IDDM)
Destruction of beta cells- which produces the insulin
No insulin
Type 2
(Adult-onset, non-insulin-dependent, NIDDM)
Resistance
Inadequate insulin amount
May require insulin
Heredity
Obesity
S/S
Polydipsia- excessive amounts of fluid- thirsty
Polyuria- body makes too much urine
Polyphagia- extreme hunger
Glycosuria- glucose or sugar in your urine
Nocturia- wake up in night and need to pee
Ketoacidosis- high levels of ketones cause the blood to become more acidic
Diagnostic Testing
Fasting Plasma Glucose
<100mg/dL
Pre-diabetic 100-126mg/dL
Diabetic > 126mg/dL
Random Plasma Glucose >200mg/dL
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test >200mg/dL
Glycohemoglobin, aka hemoglobin A1C
Normal 4-6%
A1C:
6= (fasting) 126
7= 154
8= 183
9= 212
10= 240
11= 269
12= 298
Prevention
Type 2 prevention
Weight-loss
Exercise
-7% body weight, 150 minutes/week
Metformin
Goals of Treatment
Preprandial glucose 80 to 130 milligrams per deciliter
Peak postprandial glucose <180 milligrams per deciliter
Blood pressure <140/90 millimeters of mercury
Glycohemoglobin <7%
Therapeutic Interventions
Nutrition therapy
Exercise
Medication
Monitoring
Education
General Principles
Type 1
Avoid wide swings in blood glucose.
Type 2: Control
Blood pressure
Weight
Lipids
Regular eating schedule
Insulin
Daily
Subcutaneous
Site rotation
Pump
Onset/Peak/Duration
Ex: Lantus, Humalog
Sliding scale
Mixing
Oral Medicaiton
Type 2
NOT insulin pills
Pancreas stimulation
Metformin (Glucophage)
decreases glucose production in liver
Glipizide (Glucotrol)
stimulates insulin secretion
Januvia
reduces glucagon secretion/ increases insulin release
Works when BG is high
Byzetta, Victoza, Trulicity- SQ injection
mimics to cause insulin release/ reduce glucagon release
Self-Monitoring
Before meals
HS
May require more
Continuous monitoring
High Blood Sugar Complications
Hyperglycemia- high blood glucose (blood sugar)
Diabetic Ketoacidosis- Type 1
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)- Type 2
Long-term Complications
Circulatory system
Eyes
Kidneys
Nerves
Infection
Supportive Nursing Care-Diabetes
EDUCATION!!!!!
Nutritional management
Lifestyle modifications
Blood glucose monitoring
Medication