Positive Psychology: Biological Basis of Happiness
Biological Basis of Happiness
Neuroscientists and psychologists have started to investigate the brain states associated with ^^happiness components^^ and to consider the relation to ^^well-being^^
As well as the ^^neuroanatomy of pleasure^^ which elicits ^^positive feelings^^
Brain’s hedonic networks, and speculated on the potential interaction of ^^hedonics with eudaimonic^^ networks
Understand how brain works underlying ^^fundamental pleasure relate to higher pleasures^^, such as music, dance, play, and flow to contribute to happiness
Genetic Factors
- In a comprehensive investigation, happiness (subjective well-being) was measured in a birth-record based sample of several thousand middle-aged twins using the well-being scale of Multidimensional Personality Questionnaire
- Twin studies suggested that ^^genetic factors count for 35-50% of happiness^^
- ^^44-52% of the variance^^ in well-being were ^^associated with genetic variation^^
- When twins have been retested after few years, authors fund that the ^^heritability^^ of the stable component of ^^subjective well-being approaches 80%^^
Genes
- Molecular genes open a new way to neurobiology markers of happiness
- 5-HTTLPR (Serotonin Transporter Polymorphism)
- This gene is coding serotonin distribution in brain cells and therefore leads to ^^mood regulation^^
- MAO-A (Monoamine Oxidase)
- gene that involved in ^^regulating happiness^^
- located on chromosome X involved in mood regulation and it is a catabolic enzyme for ^^serotonin, dopamine, and nonadrenalin^^
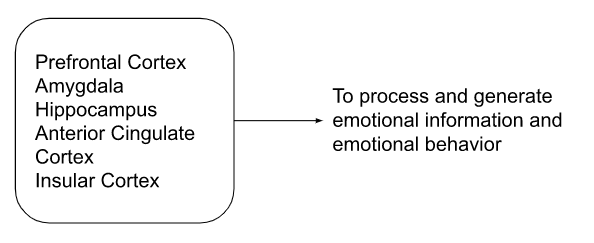
The Brain and its Emotional Circuitry
Brain and Neurotransmitters
- Thoughts, feelings, activities, learning and love, all conducted by brain including mood and emotions
- The brain weighs over a kilogram (2.2 lbs) and has a estimated 86 billion neurons
- Signals are transmitted along each nerve electrically, by gradients of charged ions, and ^^each neuron makes hundreds of connections to those around it.^^
Parts of the Brain
- Limbic System
- has the most influence on ^^identifying the form of emotions^^
- memory processing, decision-making, motivation, processing of information
- ^^increasing metabolism^^ of limbic system leads to ^^depression in individuals^^
- Prefrontal Cortex
- involved in ^^emotion processing^^, shows asymmetric activation in relation to positive and negative emotions
- Basal Ganglia
- planning and coordination of movement
- reward and reinforcement
- responsive to positive emotional stimuli
- damage to part of the basal ganglia, known as the ventral pallidum, causes anhedonia -- the inability to ^^experience pleasure^^
Emotional Circuitry of the Brain
Hedonic Hotspots
- Nucleus accumbens, ventral pallidum, orbitofrontal, cingulate, medial prefrontal and insular cortices
- Brain Stem
- pleasure-activated brain networks that are widespread
Neurotransmitters
- A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that carries, boosts, and balances signal between neurons and target cells throughout the body
- Neurotransmitter molecules work constantly to keep our brains functioning, managing everything from our breathing to our heartbeat to our learning and concentration levels.
- They can also affect a variety of psychological functions such as ^^fear, mood, pleasure, and joy.^^
Chemicals that make you Happy
Serotonin
- ^^mood stabilizer^^
- more sensitive to diet than any other neurotransmitter
- correlated with ^^satisfaction, happiness, and optimism^^
- serotonin levels are reduced in depression, and most modern antidepressant drugs (serotonin uptake inhibitors/SSRIs)
- research indicated that ^^increase of serotonin level was related to positive mood^^
Dopamine
- ^^the “reward” chemical^^
- released during pleasurable situations
- ^^positive mood^^ is associated with (but not necessarily caused by) increased levels of dopamine in the brain
- ^^changes in cognition^^ observed in positive mood are due to the ^^increased dopamine^^ levels associated with positive mood
Norepinephrine
- Antidepressants such as the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (Reboxetine) also reduce positive emotional perceptual bias in healthy subjects
- Norepinephrine positively colors the ^^emotional perception of facial expressions^^ in humans
Endorphins
- works as a ^^painkiller^^
- released after exercise
- natural rewards circuits
- Endorphins also surge during pregnancy
- they ^^minimize discomfort and pain and maximize pleasure^^
- this helps us to continue functioning despite injury or stress
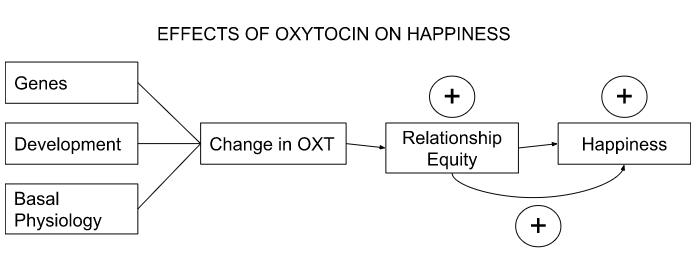
Oxytocin
the ^^“love” hormone^^
released during sex, childbirth, and lactation
oxytocin creates ^^intimacy, trust, and builds healthy relationships^^
the cultivation of oxytocin is essential for creating strong bonds and improved social interactions
released during intercourse, childbirth, breastfeeding
Genes and Neurotransmitters
- Since each neurotransmitter coded by a special gene, genetic factors have a clear and significant effect on happiness
DRD2 → dopamine, serotonin
VMAT2 → norepinephrine
HTRIA → endorphins
C578BL67 → melatonin
Endocrine Glands
- release hormones control various processes like ^^growth, metabolism, and emotional regulation^^ and so on
- most related glands with mood states are ^^pituitary and adrenal glands^^
Cortisol
- this hormone release from the ^^adrenal glands^^ is in response of ^^inflammation or decrease the level of Glucocorticoid^^
- the role of this hormone in psychological process is ^^managing stress^^
- Cortisol has been shown to be a consistent marker for depression. High levels of morning cortisol have been linked to ^^depression and neuroticism^^
Adrenaline/Epinephrine
- both ^^a hormone and a neurotransmitter^^
- Adrenaline has many functions in the body, regulating heart rate, blood vessel, and air passage diameters, and metabolic shifts
- Adrenaline release is a crucial component of the ^^fight-or-flight^^ response of the sympathetic nervous system
- Individuals with higher levels of ^^“personal growth” and “purpose in life”^^ registered lower and mroe stable levels of salivary cortisol and urinary adrenaline
Physical Health and Happiness
- Several studies concluded that ^^positive mood in individuals is a strong predictor of physical health^^ and there is a significant correlation between positive mood and physical health
- People with happiness ^^behave healthier^^ (weight loss and practice) than others
- People with happiness ^^inhibited the risky behaviors^^
- Researchers stated that people ^^with happiness experience a long life^^
Neuroplasticity
- ^^Physiological changes in the brain^^ that happen as the result of our interactions with our environment
- The connections among the cells in our ^^brains reorganize^^ in response to our changing needs
- This process allows us to ^^learn from and adapt^^ to different experiences
Positive Emotional States and Processes
Affect
- a person’s ^^immediate physiological response^^ to stimulus
- based on an underlying ^^sense of arousal^^
Emotion
- involves ^^judgment^^ on important things
- ^^need for appraisal^^ important for our own well-being
- emotional responses occur as we become ^^aware of our experiences and evaluate the situation^^
Mood
- general ^^free-floating feelings^^ that last longer than an emotion
- mood is a ^^thought^^ tied to ^^expectations of future positive or negative affect^^
Happiness
- positive emotional state that is ^^subjectively defined^^ by each person
Subjective Well-Being
- ^^individual’s appraisal^^ of their own lives capture the ^^essence of well-being^^
Positive Affect + Life Satisfaction = Subjective Well-Being
Positive Affect
- a person’s immediate physiological response to a stimulus
- Examples: joviality, self-assurance, attentiveness, warmth, gladness, calmness, excitement, and confidence
Life Satisfaction
- a sense of ^^contentment and peace^^ stemming from small gaps between ^^wants and needs^^