BIOL 3370: Exam #2
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
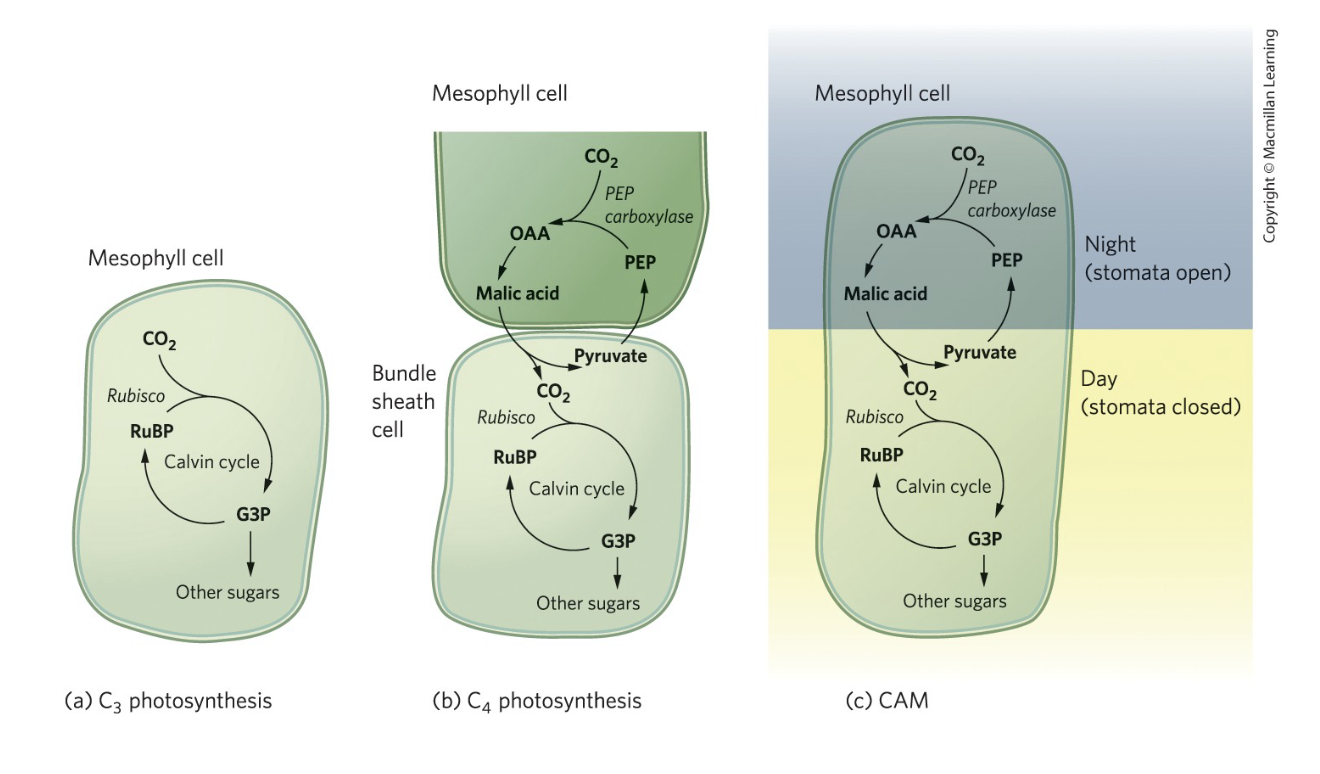
What conditions favored the repeated evolution of C4 and CAM photosynthesis?
Hot, dry environments where photorespiration is costly. These pathways minimize water loss and increase efficiency under stress.
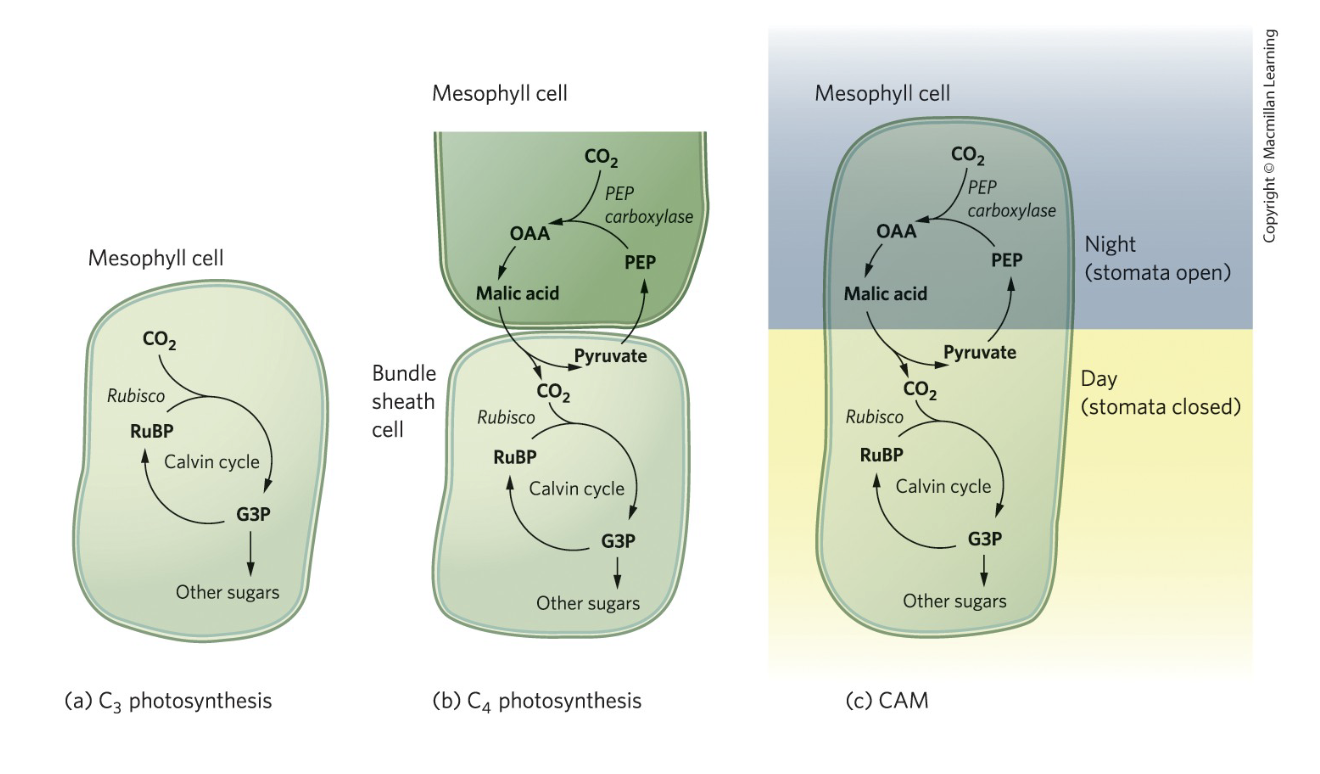
Why don’t all plants evolve C4 or CAM pathways?
They come with energetic and structural trade-offs, making them unnecessary in cooler, wetter environments where C3 photosynthesis works efficiently.
Birds and insects spend energy to assemble nitrogen waste into what form, and why?
Uric acid, because it is less toxic and conserves water.
Conduction, convection, and evaporation can…
Help or hinder thermoregulation by influencing heat gain or loss to the environment.
What is phenotypic plasticity?
The ability of a single genotype to produce different phenotypes depending on environmental conditions.
What conditions favor plasticity?
Highly variable environments where flexibility increases survival.
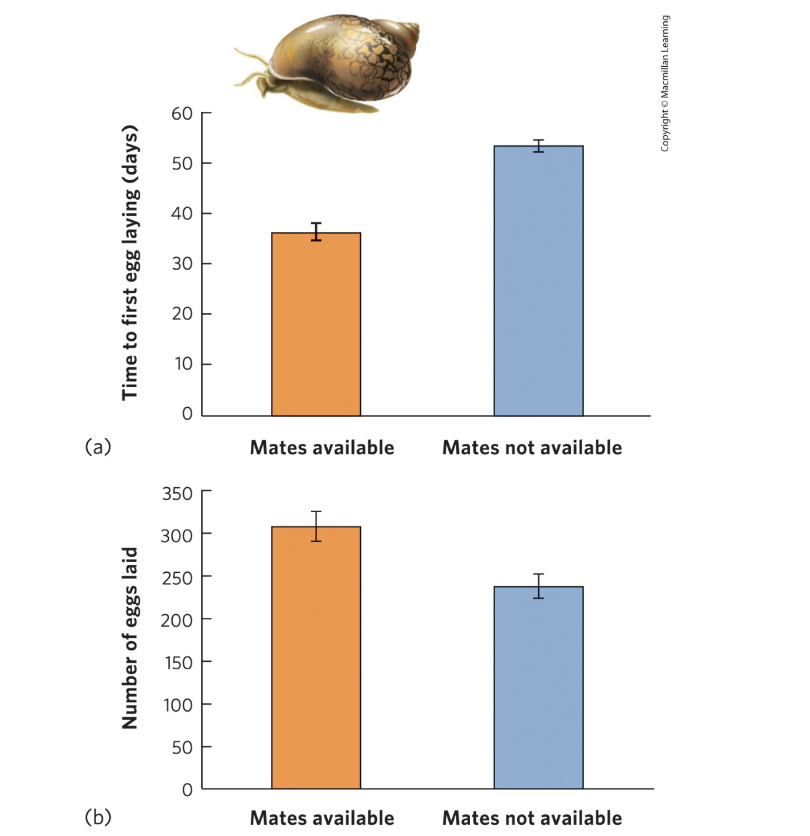
Example of adaptation to predation?
Snails reproducing earlier and producing more eggs when predators are present.
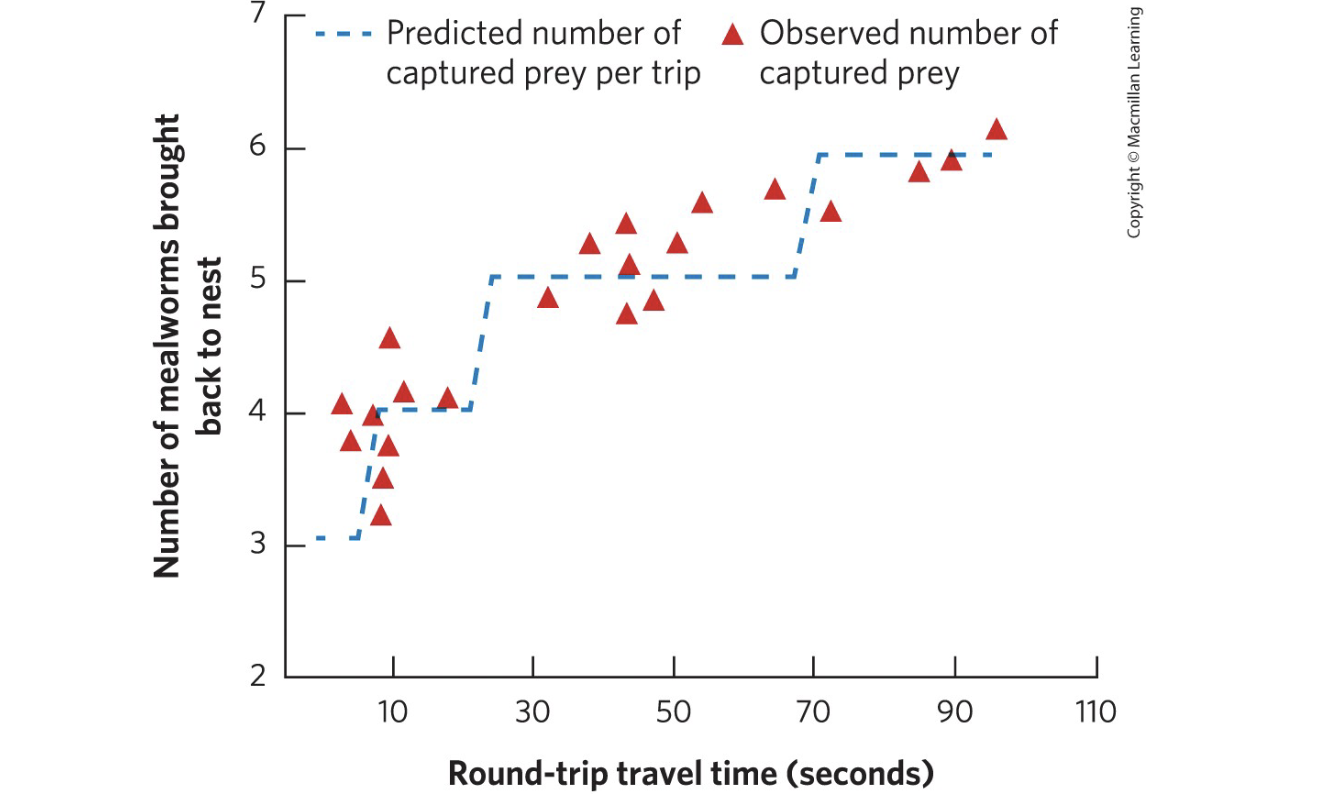
What does optimal foraging theory predict?
The farther an organism is from its nest, the more food it will gather per trip.
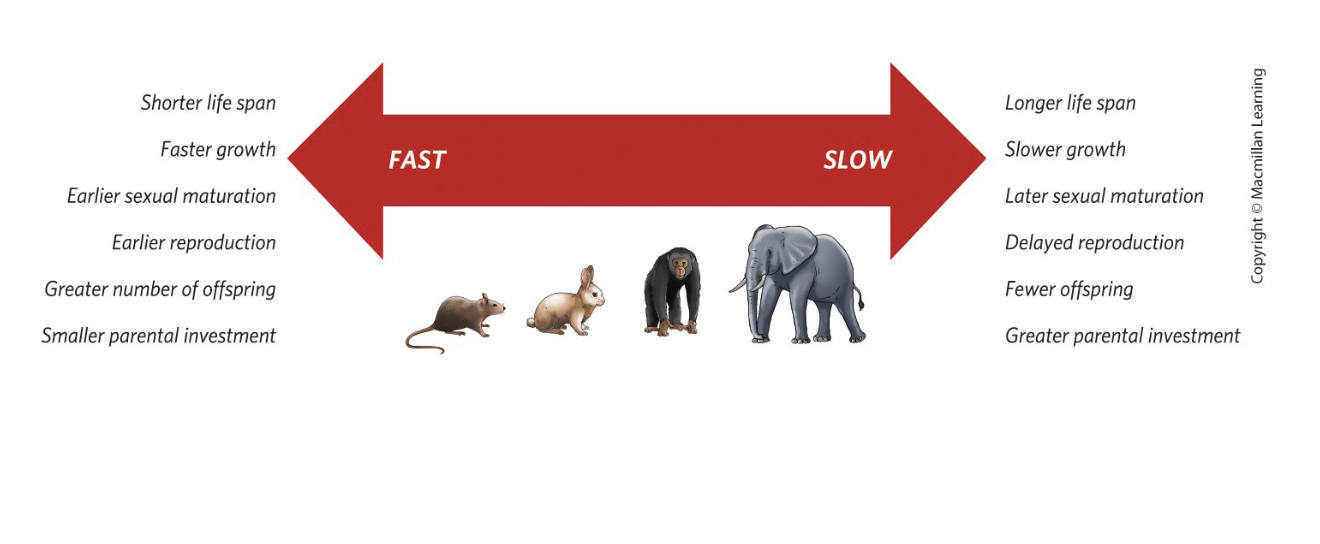
Fast vs. slow life histories?
Fast = early maturity, many small offspring, short lifespan. Slow = late maturity, fewer larger offspring, long lifespan.
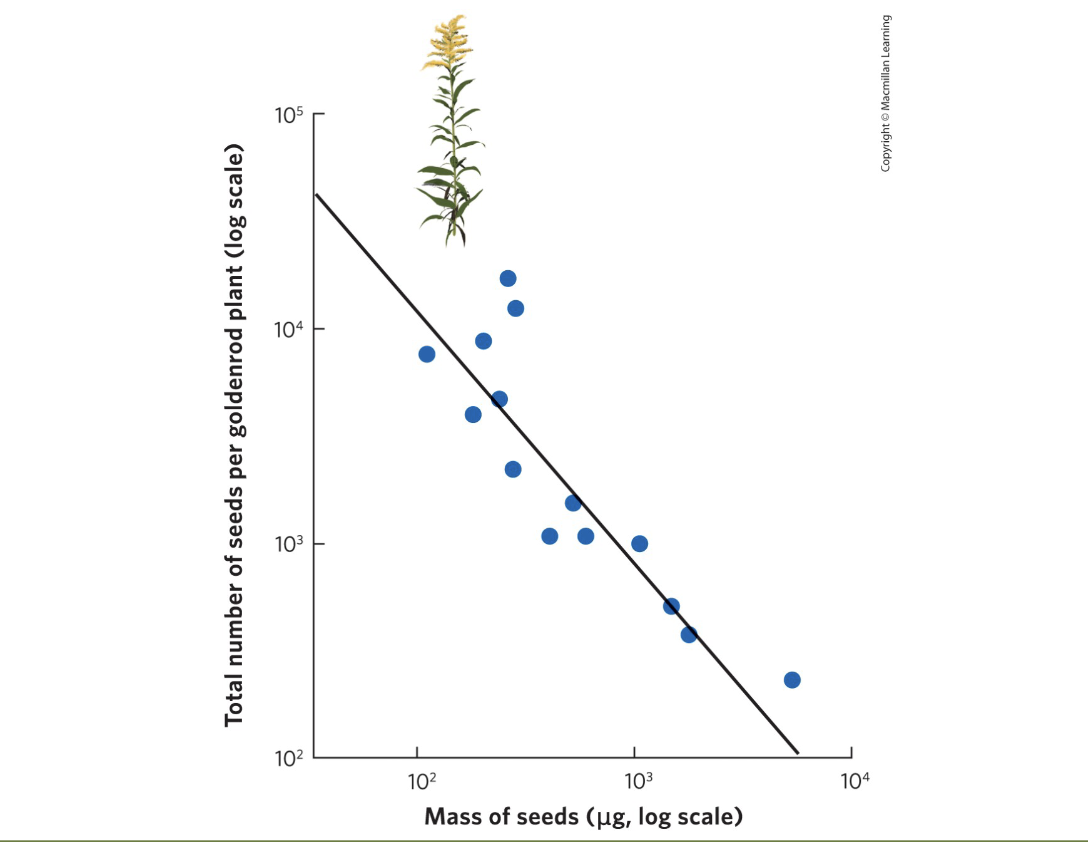
What is the trade-off between offspring size and number?
More offspring means each is smaller with less parental investment; fewer offspring means larger size and higher investment.
Difference between fecundity and parity?
Fecundity = # of offspring per event. Parity = # of reproductive events.
Semelparity vs. Iteroparity?
Semelparity = reproduce once (salmon). Iteroparity = reproduce multiple times (humans).
Benefits of sexual vs. asexual reproduction?
Sexual = genetic variation (Red Queen Hypothesis).
Asexual = fast, efficient, but less variation.
When is hermaphroditism favored?
When mates are scarce, allowing self-fertilization or flexible reproduction.
Define mating systems.
Promiscuity = no bonds, Polygyny = one male, many females, Polyandry = one female, many males, Monogamy = one pair bond.
Why is monogamy more common in birds than mammals?
Male birds can equally help raise offspring, while male mammals usually cannot.
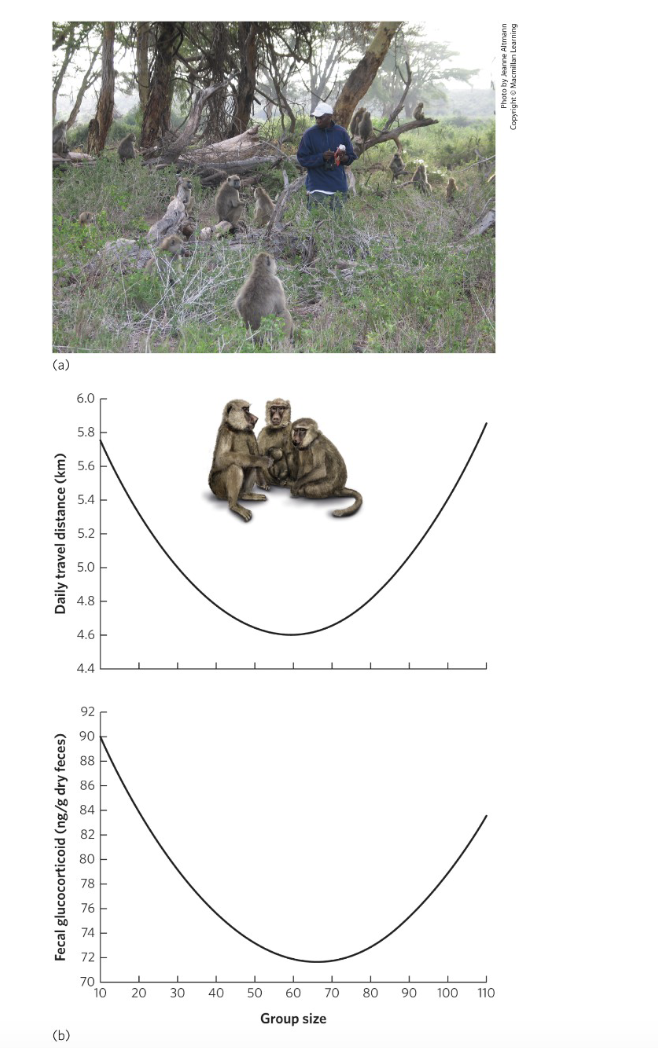
How can living in groups increase fitness?
Protection, cooperative defense, and better foraging.
How can living in groups decrease fitness?
Competition for resources, mates, and increased disease risk.
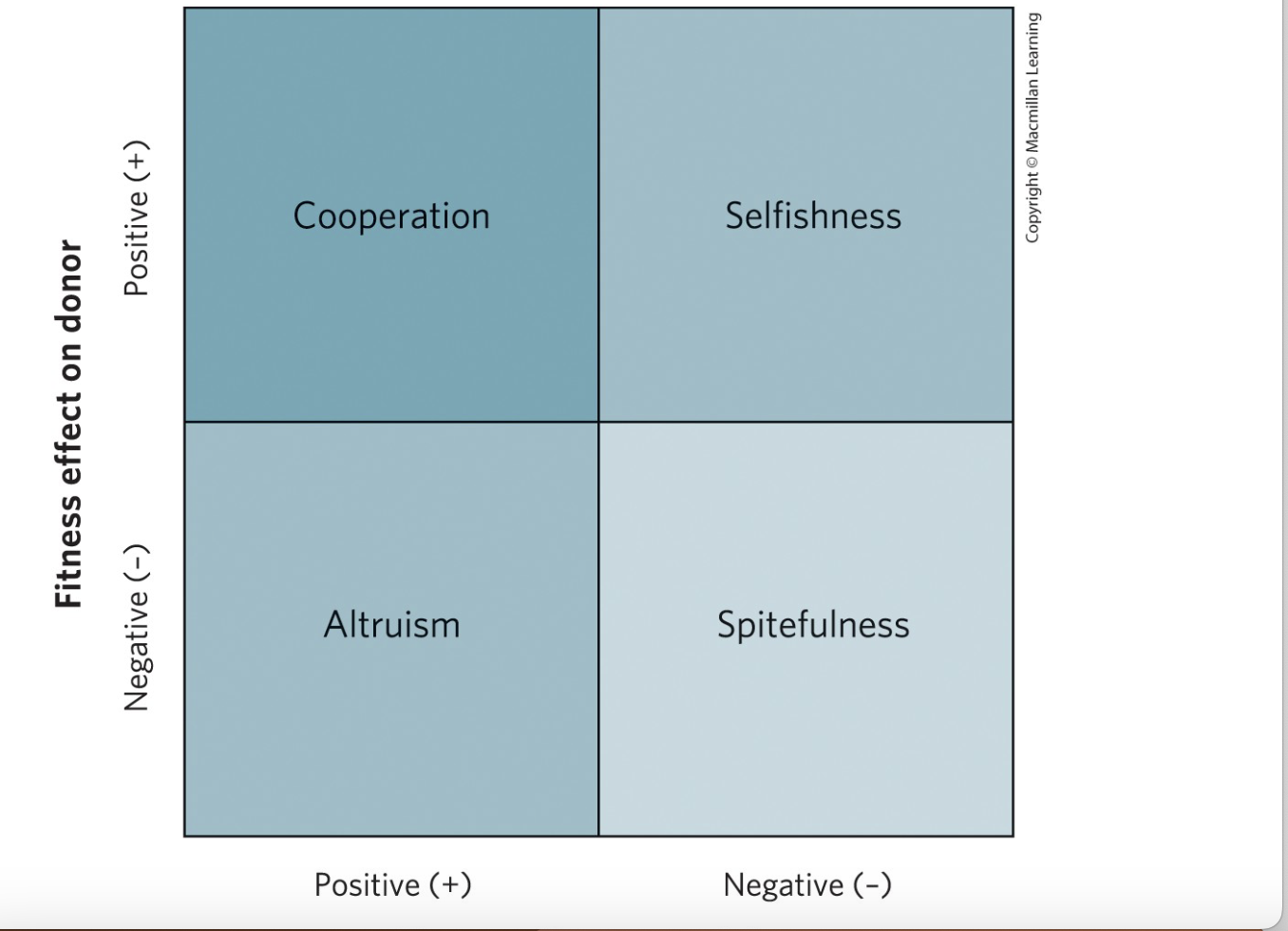
Four types of social interactions?
Cooperation (+/+), Altruism (–/+), Selfishness (+/–), Spite (–/–).
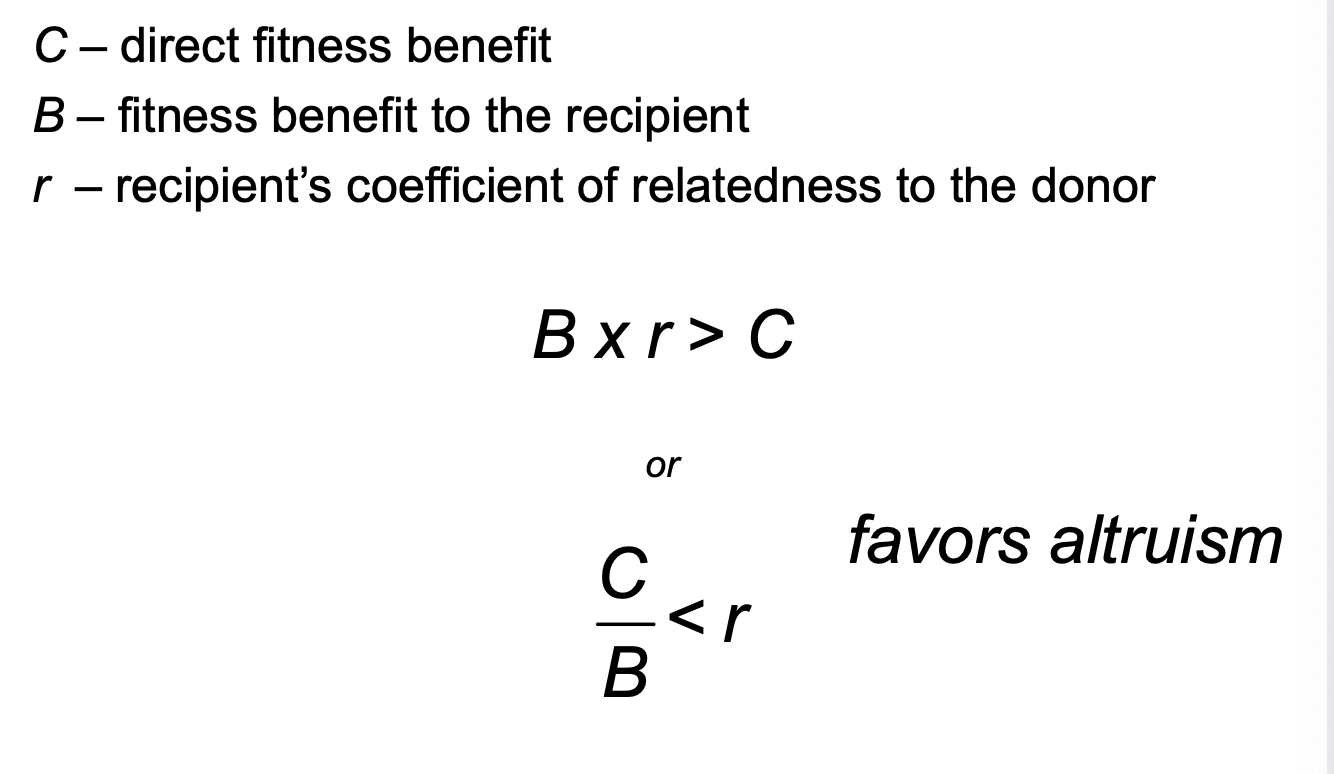
What makes altruism evolve?
Inclusive fitness—Hamilton’s Rule (r × B > C).
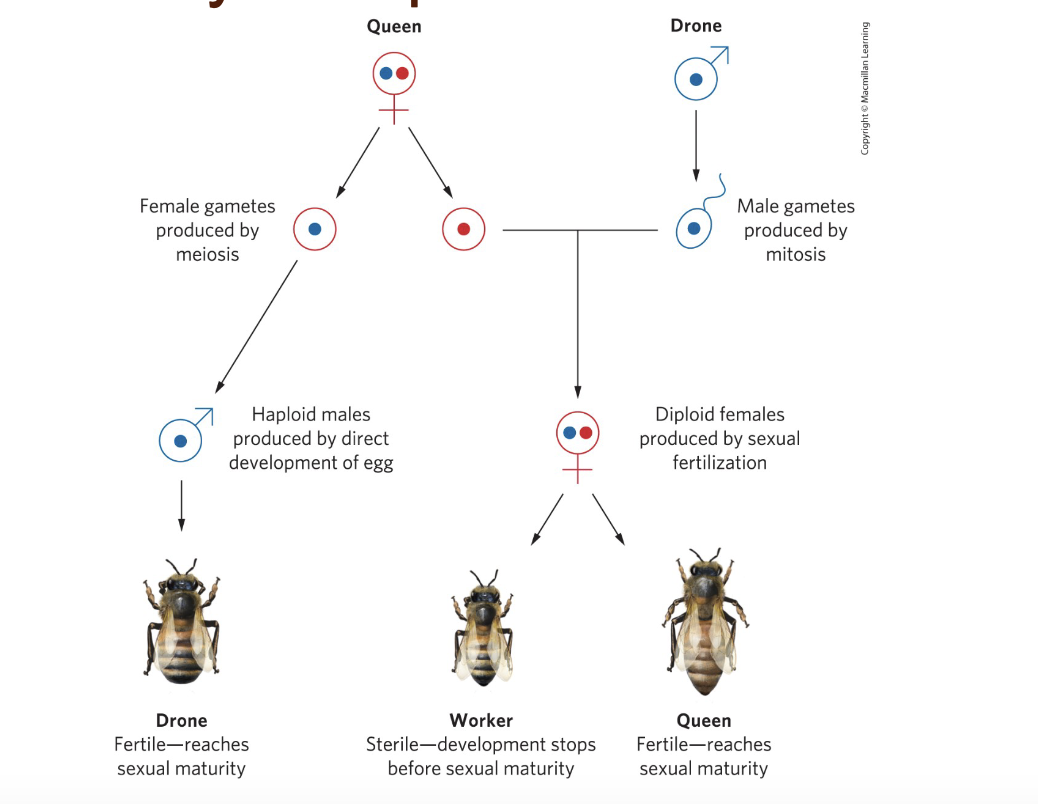
Where has eusociality evolved?
Insects (ants, bees, wasps) and mammals (naked mole rats), often linked to haplodiploidy or high relatedness.
Population Dynamics of Exploited Fish Stocks at Low Population Levels
This study tested whether declining fish stocks fail to recover because of depensatory dynamics (like Allee effects). Out of 128 populations, very few showed evidence of depensation, meaning most fish can recover if overfishing stops.
T/F: Ecosystems with multiple stable states show highly nonlinear feeding, leading to predator saturation.
True
T/F: The Allee Effect and predator saturation have little to no effect on depensation.
False
T/F: Depensation can eventually lead to extinction of a population.
True
T/F: According to the study, fish populations do not have the opportunity to recover from depensation.
False
Costs and Consequences of Variation in the Size of Ruff Leks
Larger leks attract more females, boosting resident male success but increasing fights. Lek size shapes both male competition and female choice.
T/F: Female visitation rates increased with lek size.
True
T/F: Satellite males fought more frequently on larger leks.
False
T/F: Resident male mating success increased with lek size.
True
T/F: The study supported "no preference" models of lek evolution.
False
T/F: Fighting rates among independent males increased with lek size.
True
Adaptive Significance of Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination (TSD) in a Reptile
In Jacky dragons, males at intermediate temps and females at extreme temps had the highest reproductive success, supporting the Charnov–Bull model.
T/F: Genotypic sex determination is the most common form of sex determination in animals.
True
T/F: Female Jacky dragons have highest success at intermediate temps.
False
T/F: Male reproductive success peaks at extreme incubation temps.
False
T/F: Females developing at cooler/warmer temps tend to have higher reproductive success.
True
T/F: Larger body size in males was correlated with higher reproductive success.
True
Global Warming and Flowering Times in Thoreau’s Concord
Over 150 years of data show Concord plants bloom ~1 week earlier. Climate change disrupts pollination, especially for early-flowering species.
T/F: Early flowering species are less sensitive to temperature changes than late flowering species.
False
T/F: Highbush blueberry flowers 21–32 days earlier than in the past.
True
T/F: Changes in flowering can disrupt pollinator interactions.
True
T/F: Species within the same genus respond the same way to climate change.
False
What makes altruistic behavior more difficult to explain?
a. Altruistic behavior increases donor fitness without indirect benefit. b. Altruistic behavior directly harms both individuals. c. Altruistic behavior doesn’t increase recipient fitness. d. Altruistic behavior doesn’t increase donor’s direct fitness. Correct answer: d
On average it would cost an individual 2 offspring to help a brother raise 5 offspring (r = 0.5). Should he help?
Yes, this increases inclusive fitness (Hamilton’s Rule).
Which of the following is true regarding haplodiploidy in Hymenoptera?
a. Haplodiploidy favors selfishness. b. Females are haploid, limiting queens. c. Sisters are more related than mother-daughter, favoring eusociality. d. Males are diploid. Correct answer: c
What does the “cost of meiosis” describe?
The 50% reduction in the number of genes passed to the next generation by sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction.
What is one advantage of being a hermaphrodite?
Less likely to fail to reproduce if mates are limited.
Why is monogamy more common among birds than mammals?
Male birds can help raise young as effectively as females.
In most species, the sex ratio of male to female offspring is…
Nearly even.
What does central place foraging theory predict?
Organisms traveling further should forage longer and make fewer trips to maximize efficiency.
Organisms with slow life histories commonly have…
Later sexual maturity.
According to Lack’s hypothesis, birds should lay the number of eggs that…
Maximizes the number of chicks successfully raised.
Seasonal mismatches between species are becoming…
More common due to climate change, often causing population declines.
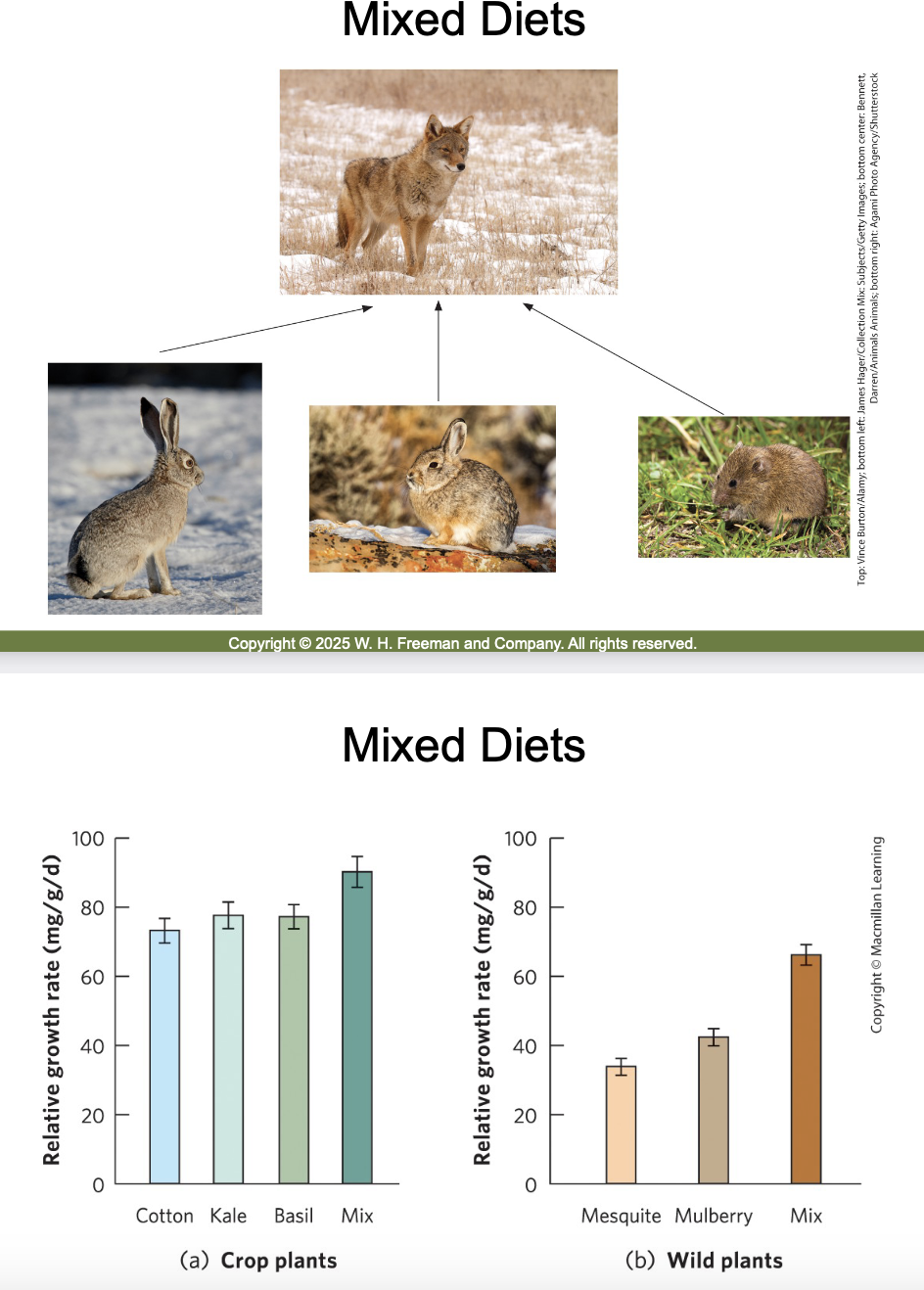
In populations that have a high survival rate, selection tends to favor individuals that reproduce ___ in life and allocate ___ energy to delaying senescence.
Later; more.
Red Queen hypothesis
The hypothesis that sexual selection allows hosts to evolve at a rate that can counter the rapid evolution of parasites
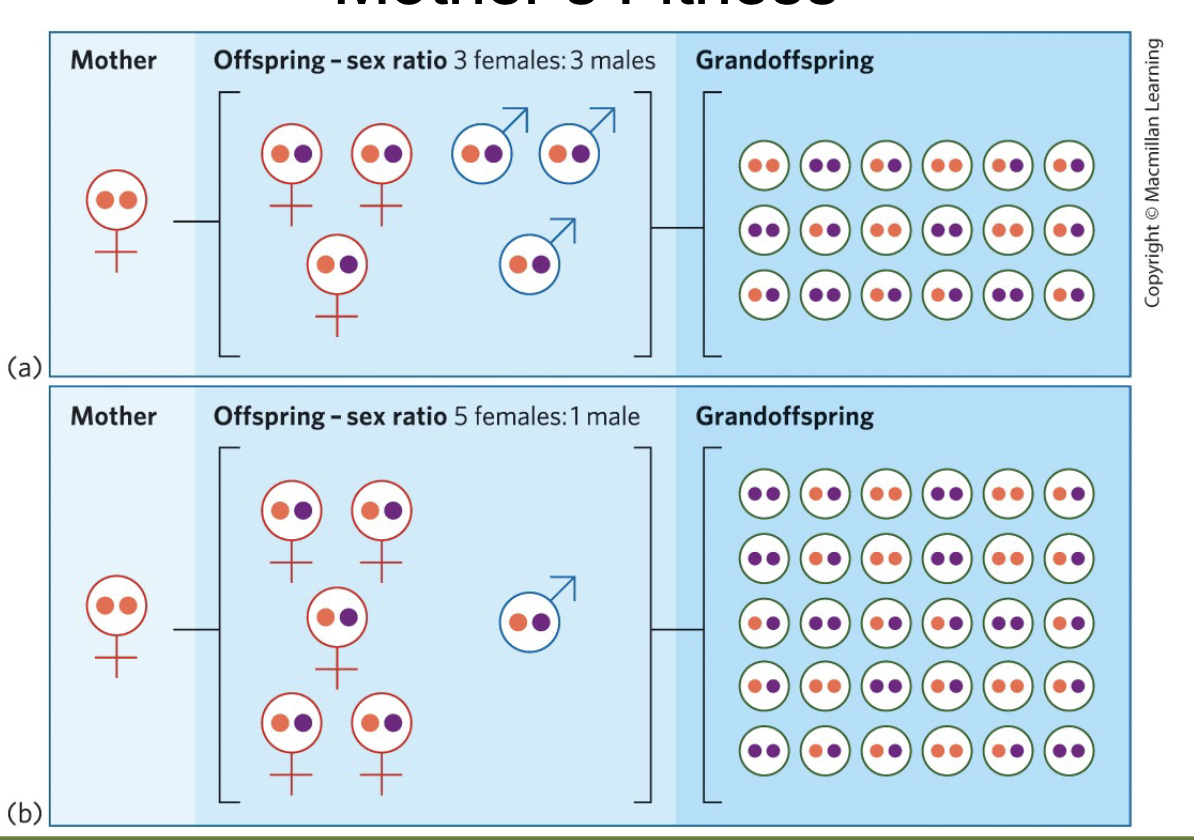
If a female fig wasp enters a fig that already has eggs laid, which of the following offspring choices would maximize her fitness potential?
Producing more sons, because they can mate with the daughters of the first female; producing daughters would lower her fitness since mates are limited.
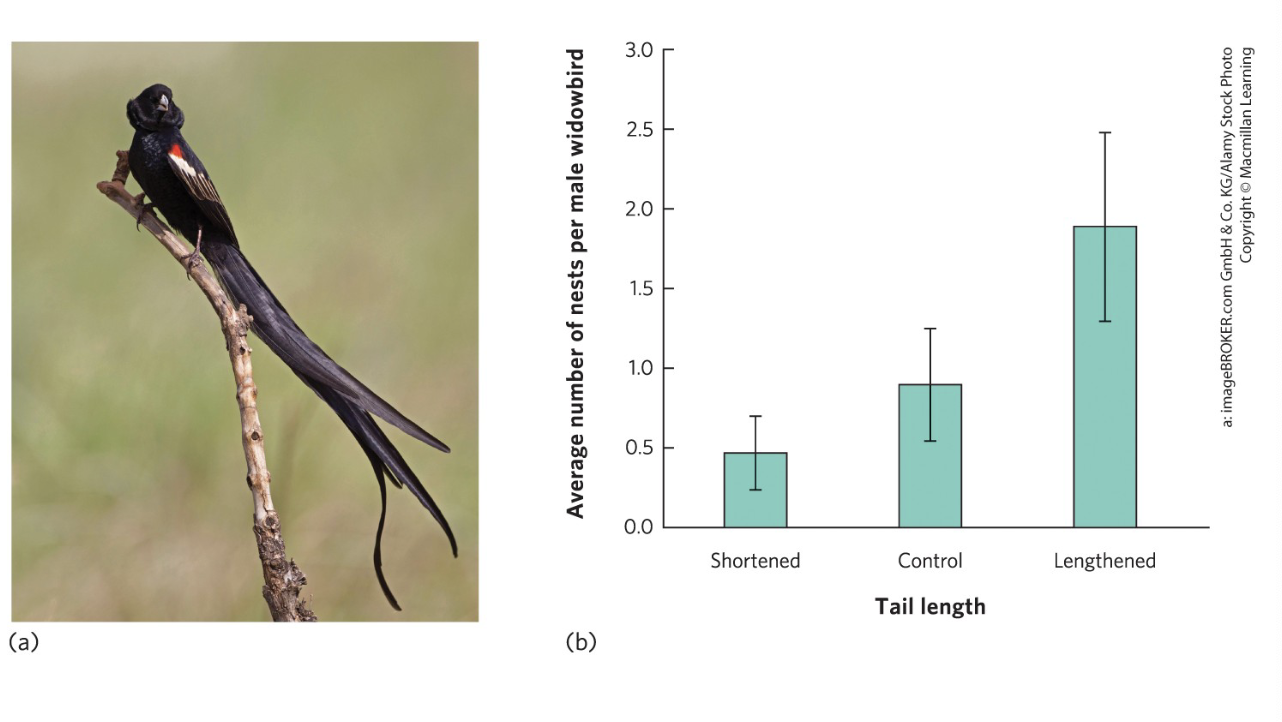
If a male bird with a long tail is much more likely to fall victim to a predator, which of the following would explain why females might choose him?
Because his survival despite a costly trait signals high genetic quality (good genes hypothesis). Females gain indirect fitness benefits by producing offspring with better survival/reproductive potential.
Why has eusociality evolved so many times in bees, ants, and wasps?
Because haplodiploidy increases relatedness among sisters (r = 0.75), making altruism more likely to evolve since helping sisters can pass on more shared genes.