13. Cell Membrane Structure
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is a phospholipid?
A molecule that contains 2 fatty acid tails, a glycerol and a phosphate head joined by an ester bond
Define hydrophobic:
A property that results in a molecule orientating away from water
Define hydrophillic:
A property that results in a molecule orientating towards from water
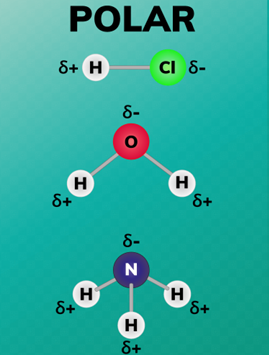
Define polar:
A molecule which is has an uneven distribution of charge
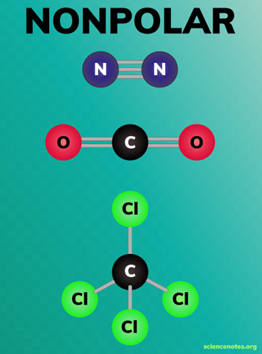
Define non-polar:
A molecule which is has an even distribution of charge
Define bilayer:
Two layers
What is the function of cell membranes?
Cell membrane control the movement of substances in and out of the cell
→ This creates cellular compartments with different conditions
What does the cell surface membrane create?
An enclosed space separating the internal cell environment from the external environment.
Describe the structure of phospholipid:
> A molecule of glycerol
> A phosphate group, which forms the phosphate head
> Two fatty acid tails, making up the lipid tail
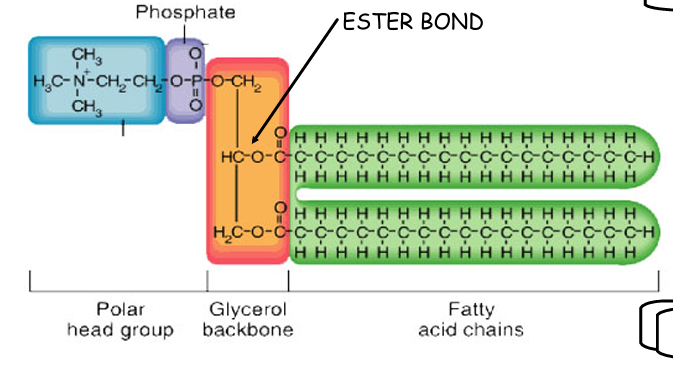
What do phospholipids contain?
2 distinct regions
→ hydrophobic and hydrophilic
Is the phosphate group polar or non- polar?
Polar
What does the phosphate head interact with?
Water molecules
→ as it is hydrophilic
Is the lipid tail polar or non- polar?
Non- polar
What does the lipid tail not interact with?
Polar molecules
→ hydrophobic
What do phospholipids attempt to form?
A stable environment
Describe the phospholipid bilayer:
Phospholipids have a hydrophilic phosphate and two hydrophobic fatty acid tail.
The hydrophilic head will orientate itself towards the aqueous cytoplasm.
The hydrophobic tails will orientate themselves away from the aqueous cytoplasm. ꞏ
As cells are surrounded by aqueous cytoplasm on all sides, the phospholipids will form a bilayer with the hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads groups facing outwards.
What is the function of glycoprotein?
A protein with a carbohydrate group attached.
Use for cell signalling and recognition.
Very important in recognising which cells are foreign and need to be destroyed by immune system.
What is the function of the channel protein?
Used to transport large, charged molecules i.e. ions across the membrane.
What is the function of the carrier protein?
Used to transport large polar molecules across the membrane
What is the function of cholesterol?
Associates with fatty acid chains and affects the fluidity of membrane.
→ More cholesterol=more rigid (less fluid)
→ Lower temperatures - more fluid
What is the function of phospholipids?
Contains hydrophobic fatty acid chains and hydrophilic phosphate heads.
- Forms the bilayer.
Who presented the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane?
Singer and Nicholson
What did the fluid mosaic model display?
Their model displayed the cell membrane as an integration of proteins and other molecules into the phospholipid bilayer.
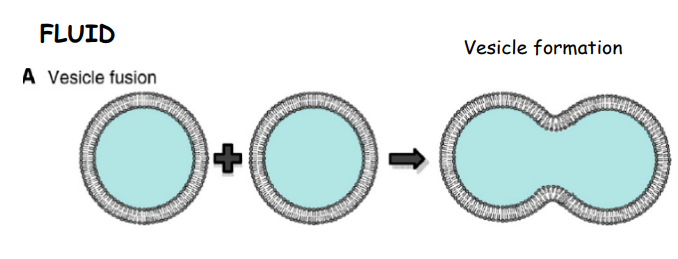
Describe the fusion of cell membranes:
The membranes have fused to form one cell indicating fluidity allows membranes to fuse.
The phospholipids allow fluidity and movements.
Fluidity allows proteins in the phospholipid bilayer to move.
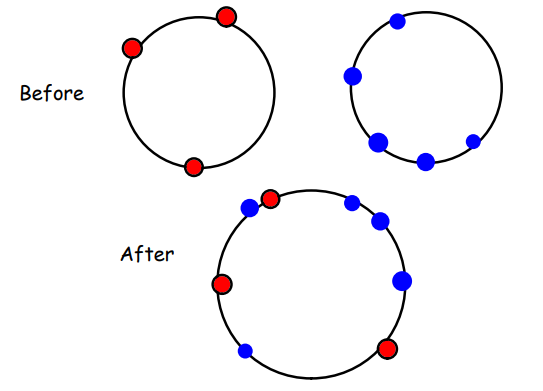
Explain how the results of this experiment provide evidence for the fluid mosaic model?
The cells membranes have fused together showing that the membranes are fluid.
The position of red and blue proteins in the fused cell differs than their original position showing that the membrane is fluid as there has been considerable sideways movement of proteins.
The new cell contains the combined number of proteins as the original cells and they are integrated within the membrane in a mosaic pattern
Where do the movement of charged particles have to take place?
The movement of charged particles through a membrane has to take place through a carrier protein that spans the protein membrane.
→ Fluid mosaic model supports this method of transport as carrier protein is embedded in the bilayer in the fluid mosaic model.
Suggest the thickness of a cell membrane:
7.5 nm -10 nm on average