L32 Innate Immunity 2
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Inflammatory Response (student steps on nail)
Mast cells degranulate, send signals attracting more cells to site of injury or infection. Neutrophils enter blood from bone marrow, cling to capillary wall. Mast cells dilate blood vessels so capillaries are leakier. Neutrophils change shape and ‘leak’ through, follow chemical trail to injury site.
Phagocytosis
The process by which cells in the blood ingest and destroy microbes.
Step 1 phagocytosis
Phagocyte adheres to pathogen or disease.
Step 2 phagocytosis
Phagocytes form pseudopods that eventually engulf the particles, forming a phagosome (phagocycitic vesicle).
Step 3 phagocytosis
Lysosome fuses with phagosome forming phagolysosome.
Step 4 phagocytosis
Toxic compounds and lysosomal enzymes destroy pathogens.
Step 5 phagocytosis
Exocytosis of the vesicle removes indigestible and residual material (sometimes).
Phagosome
A phagocytic vesicle formed when a phagocyte engulfs particles.
Phagolysosome
The structure formed when a lysosome fuses with a phagocytic vesicle.
Lysosome importance
Low pH (acidic), reactive oxygen (hydrogen peroxide) and reactive nitrogen intermediates (niitric oxide). Contains enzymes (proteases, lipases, and nucleases) tha digest proteins, fats, and nucleic acids. Hostile environment.
Complement
A system of 9 major proteins/protein complexes (C1-9) that act in sequence to clear pathogens from blood and tissues. (innactive proteins that float around blood)
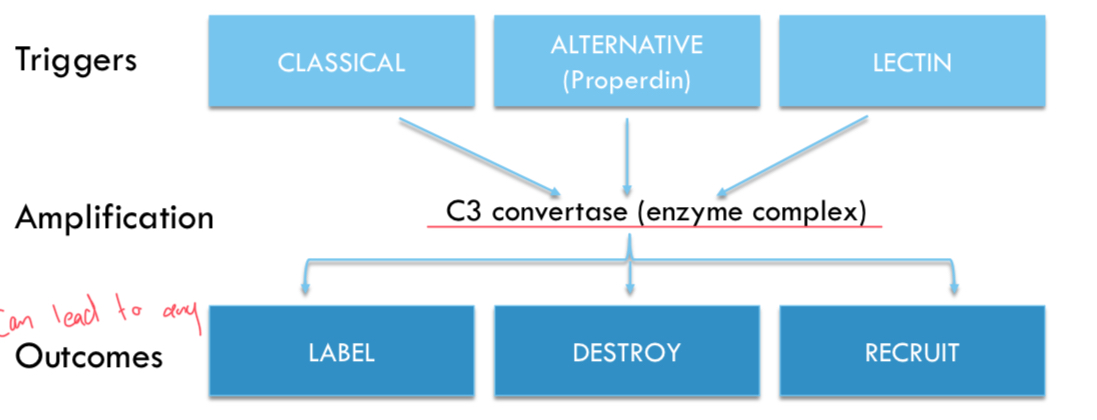
Complement pathways (triggers)
Classical, alternative and lectin. Triggers activity in component of complement pathway.
classical pathway
antibody bound to pathogen binds complement
alternative pathway
pathogen binds complement to surface/pathogen component.
lectin pathway
carbohydrate components of microbes bind complement.
Complement pathway outcomes
Label, destroy, recruit. Triggers could lead to any of these outcomes.
Label (Opsonisation)
Coating of a microbe with antibody and/or complement fragment C3b to label pathogens which bind to complement receptors on phagocytes (Eat me on its back)
C3 Convertase
Enzyme complex in complement pathways that triggers amplification. (middle of pathway)
Destroy- Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
Pores in bacterial cells, formed from activated complement components (C5b and C6-C9) that insert into target cell membrane and allow water and ions to rush in (lysis/death).
Recruit
Phagocytes attracted into site, mast cells degranulate by C3a and C5a, inflammatory mediators released (including proteins that attract phagocytes).