Biology Y11 mock
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The types of pathogens
Bacteria
Fungi
Viruses
Protists
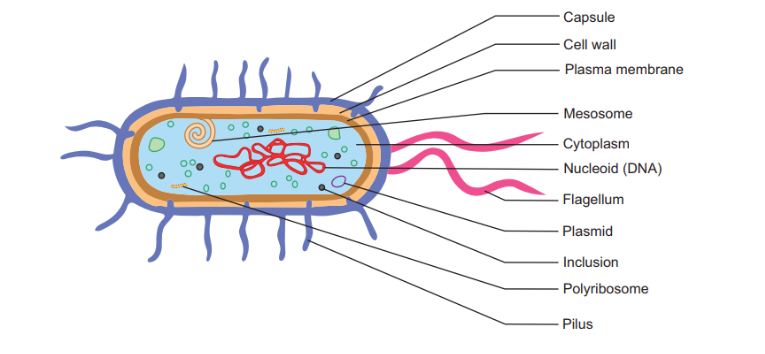
Bacteria
single celled prokaryotic organisms
reproduce rapidly in the body
may produce toxins
can be treated with antibiotics
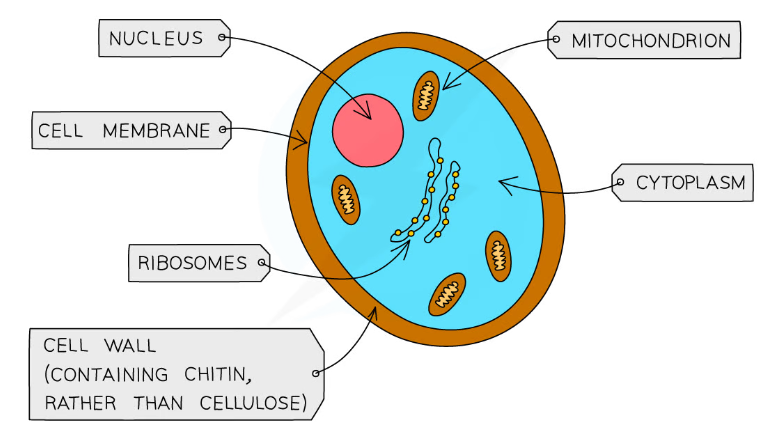
Fungi
single or multi-celled eukaryotic organisms
grow on moist surfaces
can be treated with anti-fungals
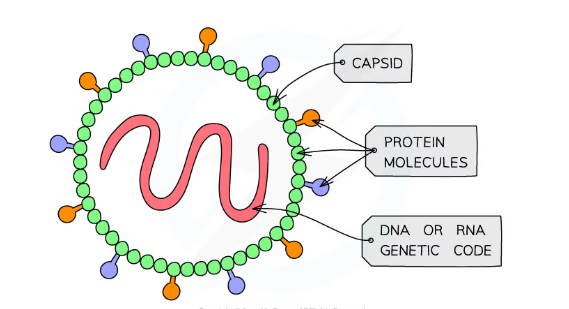
Viruses
Tiny particles
damage cells by reproducing inside them
can be treated with anti-virals
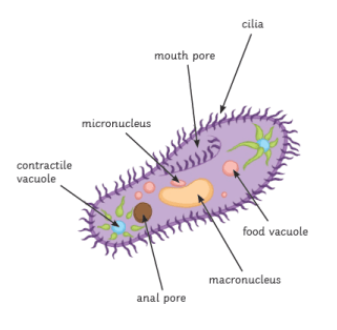
Protists
single celled eukaryotic organisms
cannot usually be treated with antibiotics
Ways of transmission
animals
water
food
contact
bodily fluids
air droplet infection
Vector
an organism that transmits a pathogen from one organism to another.
Barriers to infection
The eyes:tear glands make antiseptic liquid,blink reflex,eyelashes
The nose:Hairs trap particles
The skin:physical barrier,produces antimicrobial secretions
Trachea and bronchi mucus:mucus traps pathogens,swallowed to stomach
The stomach:produces acid
Cuts:Blood clots
Hair follicles:glands make antiseptic oil
Phagocytosis
ENGULF the pathogen
DIGEST the pathogen
DIFFUSE out the waste
Lymphocytes
ANTIBODIES binds to ANTIGENS with complementary receptors
When many pathogens are bonded with antibodies it is called AGGLUTINATION
Produce ANTITOXINS which neutralise toxins
Salmonella
pathogen- bacteria
symptoms- vomiting,diarrhoea,abdominal cramps
transmission- unhygienic kitchens,under cooked foods
treatment- antibiotics
prevention- vaccinated poultry,cooking foods properly
Gonorrhoea
pathogen- Bacteria
symptoms- burning pain when urinating,thick yellow/green discharge,infertility
transmission- sex (contact,bodily fluids)
treatment- antibiotics
prevention- contraception
Malaria
pathogen- protist
symptoms- fever,sweats,headaches,vomiting,diarrhoea
transmission- Vectors
treatment- antimalarial drugs
prevention- don’t get bit by mosquitoes
How do vaccines work?
Vaccines contain dead or inactive pathogens
Lymphocytes clone and produce antibodies
Some lymphocytes develop into memory cells
If a pathogen infects the body in the future,the response is FASTER,LARGER and LONGER LASTING
Herd immunity
If a large proportion of the population is immune to a pathogen,the spread of the pathogen is very much reduced.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Identical copies of one type of antibody
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
A mouse is injected with chosen antigen
The mouse then produces specific lymphocytes
The lymphocytes are removed from the mouse
These lymphocytes are fused with tumour cells
The hybridoma cell clones quickly
These clones release many identical antibodies
Discovery of drugs
Traditionally drugs were extracted from plants and micro-organisms
Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming and came from a type of mould called penicillium.
Why do new drugs have to be trialled and tested before they can be used in medicine?
So they can be seen if they are stable,safe and effective.
Pre-clinical testing
Pre-clinical testing is where we test the drug in a lab on cells,tissues and live animals.Scientists try to see if it damages the cells.
Clinical trials
Using low doses- this is used to check for side effects
Finding the optimum dosage-they try it on a bigger group increasing dosage
Peer review-many experts examine the trail to check quality,importance etc
Blind trials and double blind trials
A double blind trial is where neither patient or doctor knows if the patient is receiving a placebo or the actual drug.However a blind trail is where the patient does not know whether they are receiving the placebo or not but the doctor does
Health
The state of physical and mental wellbeing
Factors affecting health
diet,stress,life situations,substance abuse,trauma,PAL level
Interactions of diseases
A virus living in cells can trigger some cancers.
Immune reactions initially caused by a pathogen can trigger allergies such as skin rashes and asthma.
Severe physical ill health can lead to depression and mental illnesses.
Defects in the immune system mean that an individual is more likely to suffer from infectious diseases.
Ion deficiency in plants
Nitrate deficiency causes stunted growth as nitrate ions are needed for protein synthesis and therefore growth.
Magnesium deficiency causes chlororsis as magnesium ions are needed to make chlorophyll.
Risk factors for disease
diet
exercise
smoking
obesity
What is the role of the stomata and guard cells?
To control gas exchange and water loss.
How and how often do bacteria multiply?
By simple cell division as often as every 20 minutes if they have enough nutrients and stay at stable temp.
Are monoclonal antibodies specific?
Monoclonal antibodies are specific to one binding site on one protein antigen.
They can therefore target a specific chemical or type of cell within the body.
Uses of Monoclonal antibodies
To treat some diseases
For cancer the monoclonal antibodies can be bound to a radioactive substance,a toxic drug or a chemical which stops cells dividing
In research
To locate or identify specific molecules by binding the antibodies to dye.
In laboratories
Used to measure the levels of hormones and other chemicals in the blood.
Diagnosis
In pregnancy tests they bind to hCG produced.
What is a risk factor?
Risk factors are something that can increase your risk for disease.
These can be
aspect of someones lifestyle
substances in the person’s body or environment
Risk factors for cardiovascular disease
smoking
high fat/cholesterol diet
lack of exercise
Common risk factors
Smoking → lung disease/cancer and can cause tissue damage in unborn babies
Alcohol → liver damage and changed brain function,can cause premature birth and miscarriages
Carcinogens → can cause cancers (ionising radiation)
What are cells?
Cells are the basic building blocks of every living organism
What are sub-cellular structures in both animal and plant cells?
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
What are sub-cellular structures that only PLANT cells contain?
Chloroplasts
Cell wall
Permanent vacuole
Function of the nucleus
Contains genetic material,DNA
Controls the activities of the cell
Function of mitochondria
Where aerobic respiration takes place
(provides energy)
Function of cytoplasm
Where most chemical reactions take place
It contains enzymes for this
Function of cell membrane
Controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
It contains receptor molecules.
Function of ribosomes
Where protein synthesis occurs
Uses RNA
Function of chloroplasts
These absorb light with chlorophyll and use this to complete photosynthesis.
This produces food.
Function of permanent vacuole
Filled with cell sap.
Used for storage and keeps shape of the cell
Function of cell wall
This supports the cell and strengthens it.
What is cellular respiration?
It is an exothermic reaction (transfers energy to the environment)
It is the process of transferring energy from glucose.
This is happening continuously in living cells.
The energy transferred allows all living processes to take place.
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
Mitochondria
Stages of the cell cycle
INTER-PHASE
Sub-cellular structures replicate
DNA duplicates
MITOSIS
Chromosomes line up and are pulled apart to opposite poles.Two nuclei form.
CYTOKINESES
Cell membrane and cytoplasm divides.
What is produced from the cell cycle?
TWO daughter cells.
These are identical.
Why is cell division important?
It allows growth and development of multicellular organisms.
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane.
What can osmosis do to Red blood cells?
In dilute solutions,it can cause animal cells to swell up and burst.
This is called Lysis.
If there is a loss of water from osmosis the red blood cell will shrink.
What happens to a plant cell in pure water?
The cell contents push against the cell wall and the cell becomes turgid.
What happens to a plant cell in a salty solution?
The cell contents lose water by osmosis.They shrink and pull away from the cell wall.
The cell becomes flaccid.
What happens to a plant cell in a very salty solution?
The cell undergoes full plasmolysis as the cells lose more water.
What happens to a plant cell when the sugar content increases in a solution?
As the concentration of sugar increases so does the percentage change in mass.
How would you find the concentration of cell cytoplasm in the investigation of Osmosis?
It can be estimated by reading off the concentration of sucrose at the point where the line of best fit crosses.
What happens in CHD?
Layers of fatty material build up inside the coronary arteries,narrowing them,reducing the blood flow and resulting in a lack of oxygen to heart cells.
What are statins?
They are drugs used to reduce the blood cholesterol level.This reduces the rate of build in arteries.
What are the pros and cons of Statins?
Pros
reduce rate of build up
decrease risk of heart attack
Cons
Have side effects
Have to be kept up with
What are stents?
They are metal mesh paced in an artery and then opened up by inflation of tiny balloon to hold a narrowed blood vessel open.
What are the pros and cons of Stents?
Pros
No anaesthetic required
Relatively cheap
Cons
Ineffective against severely blocked or narrowed arteries
What are pathogens?
Microorganisms that cause infectious disease
What happens in Phagocytosis?
Phagocyte engulfs the pathogen
The pathogen is digested
These broken down materials diffuse out
What do antibodies do? (the proccess)
Lymphocyte detects non-self antigen and releases antibodies
The antibody binds to the antigen with the complementary shape
Many pathogens and antibodies are bonded.This is agglutination.
What do antitoxins do?
Lymphocyte detects toxins and releases antitoxins
These neutralise the toxins
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
6CO2+6H2O→C2H12O2+6O2
What might the glucose produced in photosynthesis be used for?
respiration
storage by being converted to starch
to produce lipids for storage
to produce cellulose and strengthen cell wall
used to produce amino acids for protein synthesis
What effect does light intensity have on the rate of photosynthesis?
As the light intensity increases so does the rate of photosynthesis.
What effect does temperature have on the rate of photosynthesis?
As temperature increases so does the rate of photosynthesis.
However after a certain temp enzymes denature and therefore the rate decreases.
What effect does carbon dioxide concentration have on the rate of photosynthesis?
An increase in concentration causes an increase in the rate of photosynthesis.
What effect does the amount of chlorophyll have on the rate of photosynthesis?
Large amounts of chlorophyll means an increased rate of photosynthesis.
What is translocation?
Transport of dissolved sugars from leaves to all other plant cells.
What happens in Mitosis?
DNA is copied
Chromosomes begin to align at the equator of the parent cell
The chromatids are separated to different poles by spindles
Chromosomes recoil up and form nuclei
How to calculate the length of stages in cell cycle:
Number of cells in particular stage
Total number of cells x length of cell cycle
What is meristem tissue?
It is a tissue in plants that is able to differentiate into any type of plant cell and is able to do this throughout the entire life of the plant.
What are the uses of meristems in plants?
Produce clones of plants quickly and economically.
Rare species can be cloned to protect from extinction.
Crop plants with special features such as disease resistance can be cloned to produce large numbers of identical plants for farmers.
What is a tissue?
A group of cells with a similar structure and function.
What are plant cells,prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic.
They have a cell membrane,cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
What are bacteria cells,prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic.
They are much smaller in comparison and they have cytoplasm and a cell membrane surrounded by a cell wall.Also,their genetic material is not enclosed by a nucleus. It is a single DNA loop.
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + …………………………………………………………..Energy release
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration?
Glucose → Lactic acid + small energy release
Why is there much less energy transferred with anaerobic respiration?
Because the oxidation of glucose is incomplete.
How does the body react to the increased demand for energy during exercise?
The heart rate,breathing rate and breath volume increase to supply the muscles with more oxygenated blood.
This enables increased cellular respiration so more energy transferred to meet the demands of the muscle cells.
What happens when, during exercise, not enough oxygen is supplied to the muscle cells?
Anaerobic respiration takes place in muscles.
This causes a build-up of lactic acid and creates an oxygen debt.
During long periods of vigorous activity muscles become fatigued and stop contracting efficiently.
What is oxygen debt?
It is the amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to react with the accumulated lactic acid and remove it from cells.
What happens to the lactic acid after exercise?
Blood flowing through the muscles transports the lactic acid to the liver where it is converted back into glucose.
what is the heart?
An organ which pumps blood around the body in a double circulatory system.
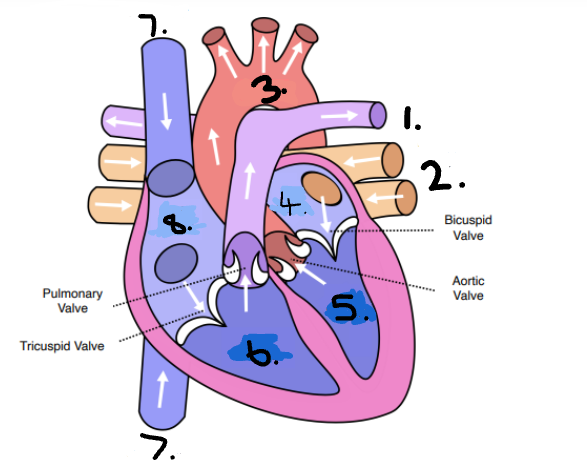
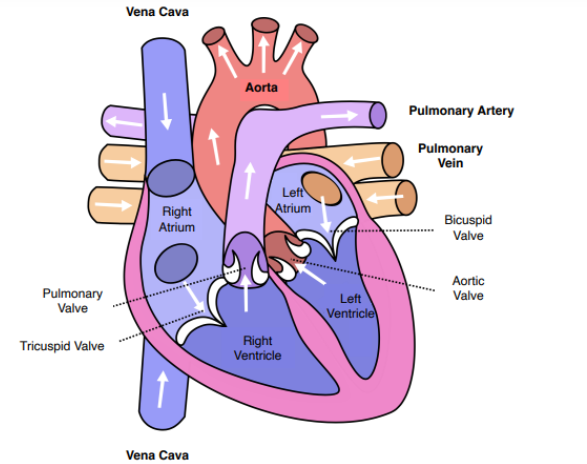
Identify the numbers on the heart.
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
left atrium
left ventricle
right ventricle
Vena cava
right atrium
What do the group of cells called ‘pacemakers’ do?
they control the natural resting heart.
They are located in the right atrium.
Describe how blood flows through the heart.
Blood flows into the two atria from the vena cava and pulmonary vein.
The atria contract,pushing the blood into the ventricles.
The ventricles contract, forcing the blood into the pulmonary artery and the aorta,and out of the heart.
The blood then flows to the organs through arteries, and returns through veins.
The atria fill again and the whole cycle starts over.
Why is the left side of the heart thicker?
As there is more muscle to generate a higher pressure to pump blood a longer distance.
What is the function of arteries?
To transport blood away from the heart.
What is the function of veins?
To transport blood towards the heart.
What is the function of capillaries?
They allow exchange of materials between blood and tissues.
What is the structure of arteries?
Thick outer wall
Thick layer of muscles and elastic fibres to maintain and withstand the high pressure and stretch and recoil as each pulse passes
smooth lining
small lumen
What is the structure of veins?
smooth lining
large lumen (to prevent friction)
fairly thin outer wall
thin layer of muscles and elastic fibres
contain valves to stop the back-flow of blood
What is the structure of capillaries?
very small lumen
wall made of a single layer of cells
permeable walls to allow easier diffusion
Why do red blood cells contain haemoglobin?
Because it binds to oxygen so they can transport it.
What are the advantages of a heart transplant?
lasts long
effective