PSYCH1X03 - Classical Conditioning
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit/Week 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Classical Conditioning (CC)
Learning of contingent relationship between two stimuli, paired at the same time/space
CC
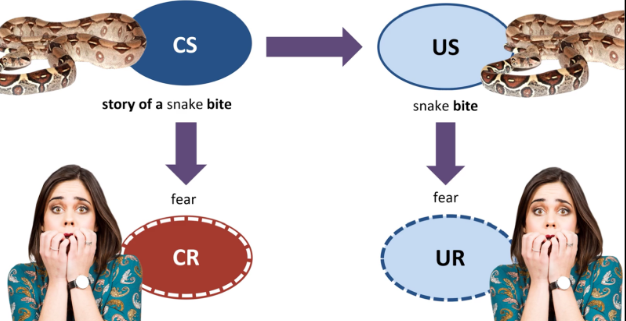
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
Natural, triggers response without needing learning
(i.e. eating a lemon triggers response)
CC
Unconditioned Response (UR)
Natural, response triggered by US (i.e. salivating after eating lemon)
CC
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
Learned, previously neutral stimulus associated with US (i.e. seeing lemon)
CC
Conditioned Response (CR)
Learned, occurs once contingency between US & CS is learned (i.e. salivating after seeing lemon)
CC
Contingency
Stimulus reliably predicts another stimulus
CC
Acquisition
Learning of contingency
CC/Acquisition
Acquisition Rate (multiple)
Learning occurs at a positive & decreasing rate; negatively accelerated increasing graph of learning
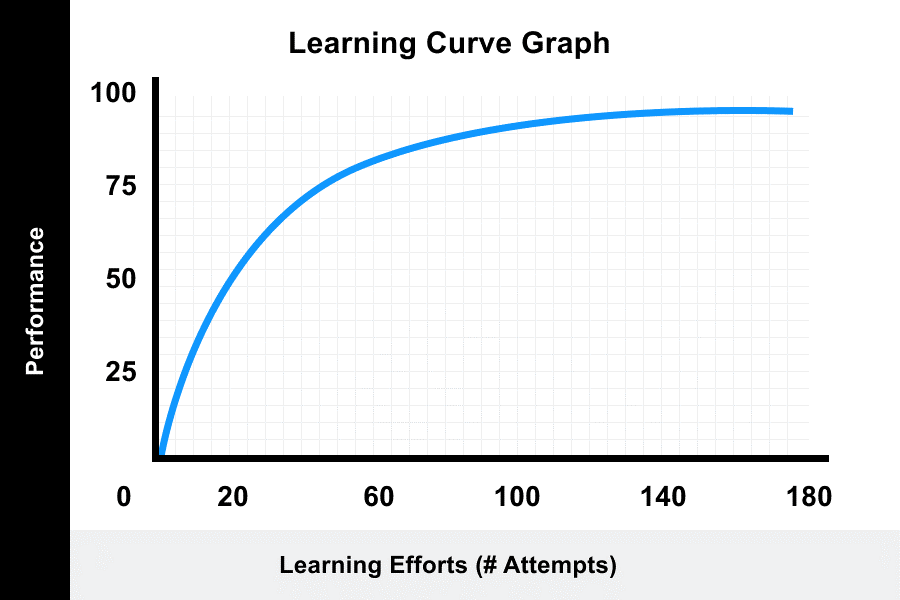
CC/Acquisition
Acquisition Rate (singular)
One trial is sometimes sufficient to acquire contingency (i.e. rats’ neophobia/fear of new food, taste aversion to avoid poison)
CC
Stimulus Contiguity
Contingency forms when neutral stimulus is presented at the same space & time as response causing stimuli
CC
Short-delay conditioning
Presentation of CS before US in a short delay (ineffective if CS & US are presented too closely or far)
CC
Extinction
Gradual decrease and elimination of CS after CS no longer accurately predicts US
CC/Extinction
Unlearned CS Theory
CS would return to naivety prior to learning; expect reacquisition to take same time as original training
(false)
CC/Extinction
Inhibitory Contingency Hypothesis
New inhibitory response is formed, competes against original CS; original CS still exists, expect reacquisition to be very quick
(true)
CC/Extinction
Spontaneous Recovery
Sudden recovery of CR being caused by CS after rest period
CC/Extinction
Rest Period
Period of time without extinct CS presentation
CC/Extinction
Renewal
Appearance of an extinct CR in new environment, shows that inhibition relies on environment
CC/Extinction
Reacquisition
Rapid acquisition of contingency after extinction
CC
Stimulus Generalization
Stimuli similar to CS will also elicit CR; magnitude of similarity with CS will effect intensity of CR. Offers efficiency and flexibility
CC/Stimulus Generalization
How is it tested?
Tested through contingency of 500Hz with electric shocks. Different Hz will cause difference in fear levels, depending on closeness to 500Hz
CC/Stimulus Generalization
Generalization Gradient
A normal distribution graph that describes strength of CR elicitation depending on similarity to CS
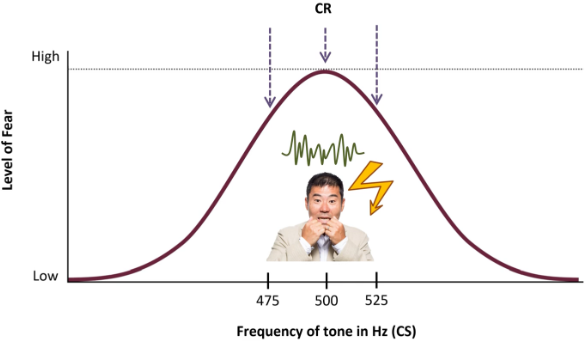
CC/Stimulus Generalization
Effect of Extinction
Flattens generalization gradient
CC
Stimulus Discrimination
Constriction of CS range that can elicit CR. Refines learning
CC/Stimulus Discrimination
Conditioned Stimulus+ (CS+)
Accurate predictor of US presence
CC/Stimulus Discrimination
Conditioned Stimulus (CS-)
Accurate predictor of US absence
CC/Stimulus Discrimination
How is it tested?
Tested through contingency of 500Hz predicts electric shock (CS+) and contingency of 600Hz predicts no electric shock (CS-). CS+ presentation elicits fear, CS- presentation elicits no fear.
CC/Stimulus Discrimination
CS+ & CS- Together
Causes intermediate response
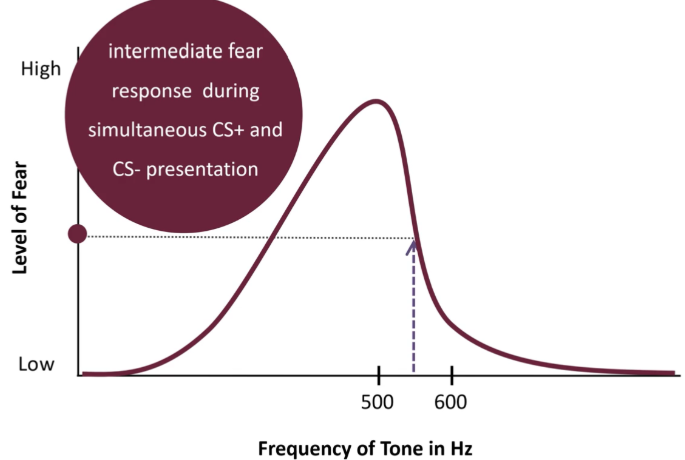
CC
Higher-order conditioning
Association of new CS2 with original CS1 to produce weaker CR
CC
Phobias
Persistent and exaggerated fear of CS
CC/Phobias
Therapy
Treatment to cause extinction of CS
CC/Phobias/Therapy
Implosive Therapy
Confrontation of phobia using imagination; presentation of CS in absence of US. Can be traumatic.
CC/Phobias/Therapy
Systematic Desensitization
Gradual exposure to CS through generalization gradient. More accessible
CC
Homeostasis
Body’s tendency to maintain a stable physiological environment
CC/Homeostasis
Compensatory Response
Body’s preparatory actions to maintain homeostasis based on environmental cues (CS’s)
CC/Homeostasis
Example: Drug Administration
US: Drug administration
UR: Compensatory response
CS: Environmental cues
CR: Compensatory response in preparation
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Unconditioned Stimulus (US) is…
Drug administration, drug enters body
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS) is…
Environmental cues, any stimulus associated with drug administration
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Unconditioned/Conditioned Response (UR/CS) is…
Compensatory response, body activates learned counter-measures to maintain homeostasis
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Addiction/Withdrawal
CS elicits CR, causes craving for US (drugs)
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Example: Vietnam Veterans
Many Vietnam Veterans were addicted to heroin. After de-tox, only 5% of veterans relapsed in comparison to 20% relapse rate of the general population. Due to lack of environment (war) that causes US.
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Enigmatic Drug Overdose
Continued usage of drug builds tolerance. Overdoses sometimes occur even when taking regular dosages because body doesn’t have learned environmental cues for compensatory response.
CC/Homeostasis/Drug Adm.
Example: Siegel Morphine Tolerance Study
Morphine administered to rats in familiar & unfamiliar environments. Rats in unfamiliar environments had stronger physiological responses.
CC/Neurology
Healthy Brain Activity
More activity in orbital frontal cortex; judgement, decision marking, impulse inhibition
CC/Neurology
Unhealthy Brain Activity
More activity in anterior cingulate cortex; reward anticipation
CC/Neurology
Long-term Potentization (LTP)
Strengthening of synaptic connections between neurons. Neurons become better at completing the pathway → become better at doing the action
CC/Textbook
Learning
Behaviour mechanisms undergo relatively permanent change, based on experience
CC/Textbook/Learning
Performance
Demonstration of learning, but learning cannot be defined by performance, as performance can be altered for a variety of reasons
CC/Textbook/Learning
Maturation
Change in mechanisms of behaviour based on aging and not experience; contrasted with learning
CC/Textbook/Learning
Latent Learning
Learning of new information/skill that does not immediately change behaviour
CC/Textbook/Learning/Latent
Example: Tolman’s Mouse Experiment
Group of mice allowed to explore a maze with no food; no performance change; performance changed when food was placed at the exit; only once reward was presented was performance representative of learning
CC/Textbook/Learning
Associative Learning
Learning of connection between two different stimuli with reinforcement (CC & IC)
CC/Textbook/Learning
Non-associative Learning
Modification of response to singular stimulus, without reinforcement
CC/Textbook/Non-associative
Habituation
Decreased response to a repeated stimulus that lead to no consequences (i.e. tuning out white noise)
CC/Textbook/Non-associative
Reflexive Orienting Response
Involuntary and immediate reaction to something new in the environment
CC/Textbook/Non-associative
Dishabituation
After habituation to a stimulus, attention to a new stimulus source will cause original reflexive response to original stimuli (i.e. after habituation to white noise, car honk will cause return of noticing white noise)
CC/Textbook/Non-associative
Sensitization
Increased response to a repeated stimulus that have relevance (i.e. increased attention while watching horror movie)