HW 6: Chapter 29:Exchange Rates and International Capital Flows
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are the two functions of purchasing power parity?
Economists often use PPP exchange rates for international comparison of GDP and other economic statistics.
Knowing the purchasing power parity helps track and predict exchange rate relationships.
The purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rate provides information that can help a broad number of individuals, businesses, and governments in making financial decisions. It allows businesses to compare prices of the same product or service in different countries to see which would be the most cost-effective source. For global decision-making, PPP enables the international comparison of GDP and other economic statistics. The market exchange rates tend to align with the PPP exchange rate in the long run, so the PPP exchange rate provides a means of controlling exchange rates in the long run and predicting them, which is useful for investors, businesses, and governments.
Assume a U.S investor is looking to make a profit from the foreign exchange market. This investor believes that the exchange rate for British pounds to dollars will increase in the future. What should the U.S investor do?
exchange dollars for British pounds today and wait for the exchange rate to increase
Say that a British pound is currently worth $1.50 in U.S. currency. However, the investor believes that in a month, the British pound will be worth $1.60 in U.S. currency. This investor could change $24,000 for £16,000. In a month, if the pound is worth $1.60, then the portfolio investor can trade back to U.S. dollars at the new exchange rate, and have $25,600 and a nice profit.
True or false?
A country whose currency is strong against the U.S. dollar is likely to suffer from increased unemployment.
True
Despite its positive effects, a domestic currency that is strong against the U.S. dollar is likely to cause some increase in the level of unemployment. The fall in demand for domestically produced goods and the damage from lack of sales in the export industry are likely to cause contraction that can lead to businesses closing and some level of increased unemployment.
WHY? (Your answer was false)
One common misunderstanding about exchange rates is that a “stronger” or “appreciating” currency must be better than a “weaker” or “depreciating” currency. After all, is it not obvious that “strong” is better than “weak”? Do not let the terminology confuse you. When a currency becomes stronger, so that it purchases more of other currencies, it benefits some in the economy and injures others. Stronger currency is not necessarily better, it is just different.
Which of the following, if any, are results of "depreciating" currency?
A decrease in the exchange rate of the depreciating currency
An increase in the amount of the depreciating currency exchanged for a given amount of another currency
When a currency depreciates, the exchange rate decreases and the currency is weakened. A lower exchange rate means that the amount of currency needed to buy a given amount of another currency is greater. Equivalently, the amount of other currencies that can be bought with a given amount of the given currency is lower.
Of the following, which count as a source of demand for the U.S. dollar?
Foreign investors who make direct investments in the U.S. economy.
Demand for the U.S. dollar can be traced to four sources: U.S. exporting firms that earned foreign currency and are trying to pay U.S.-based expenses, foreign tourists visiting the United States, foreign investors who wish to make direct investments in the U.S. economy, and foreign investors who wish to make portfolio investments in the U.S. economy.
If a currency appreciates or "strengthens", then ___________.
there is an increase in the quantity of other currencies received for a given amount of currency sold
When a currency appreciates, the exchange rate of the currency increases and the currency is strengthened. A higher exchange rate means that the amount of currency needed to buy a given amount of another currency is less. Equivalently, the amount of other currencies that can be bought with a given amount of the given currency is greater.
Which term is used for an exchange-rate policy in which the central bank sets a fixed value for the exchange rate?
Hard peg
A hard peg is an exchange-rate policy in which the central bank sets a fixed value for the exchange rate.
How does the "supply" of U.S. dollars affect the dollar's exchange rate?
A higher supply of U.S. dollars will lower the exchange rate.
A larger supply of U.S. dollars will make for a "lower" exchange rate.
Which type of exchange rate system is one in which governments do not intervene but rather let the market completely determine exchange rates?
Floating exchange rates
Exchange rate systems fall between the two extremes of hard peg fixed exchange systems on one end, and floating exchange rate systems on the other. In a floating exchange-rate system, the market completely determines the exchange rate without intervention from governments.
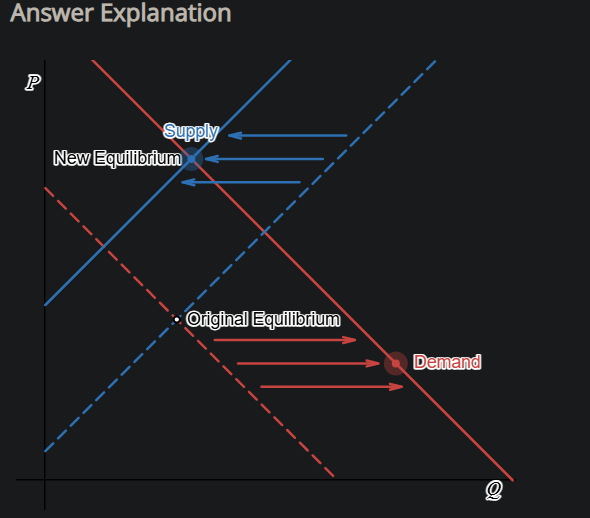
Suppose the Japanese yen is expected to appreciate in the foreign exchange market. Illustrate the impact of this event by shifting the supply and demand curves in the appropriate direction.
Supply of the Japanese yen decreases and demand of the Japanese yen increases. If the Japanese yen is expected to appreciate in value, it means the yen will become more expensive to purchase. As a result, investors are more likely to demand more yen today at the lower price and supply less of the yen today while they wait for the higher price before selling.
A stronger U.S. dollar __________
decrease exports from America
increases imports to America
A stronger U.S dollar will decrease exports from America as foreigners find American goods now relatively more expensive. At the same time, Americans find foreign goods relatively cheaper and will purchase more goods from abroad. This will increase imports to America.
Which of the following terms means using the U.S. dollar as the currency of a country outside the United States?
Dollarizing
Dollarizing means using the U.S. dollar as the currency of a country outside the United States.
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is reached where __________.
The demand curve for currency intersects with its supply curve
In the foreign exchange market, equilibrium exchange rate occurs at the intersection of the demand curve and the supply curve.
True or false?
The exchange rate that equalizes the prices of internationally traded goods across countries is the arbitrage exchange rate.
False
We call the exchange rate that equalizes the prices of internationally traded goods across countries the purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rate. A group of economists at the International Comparison Program, run by the World Bank, have calculated the PPP exchange rate for all countries, based on detailed studies of the prices and quantities of internationally tradable goods.
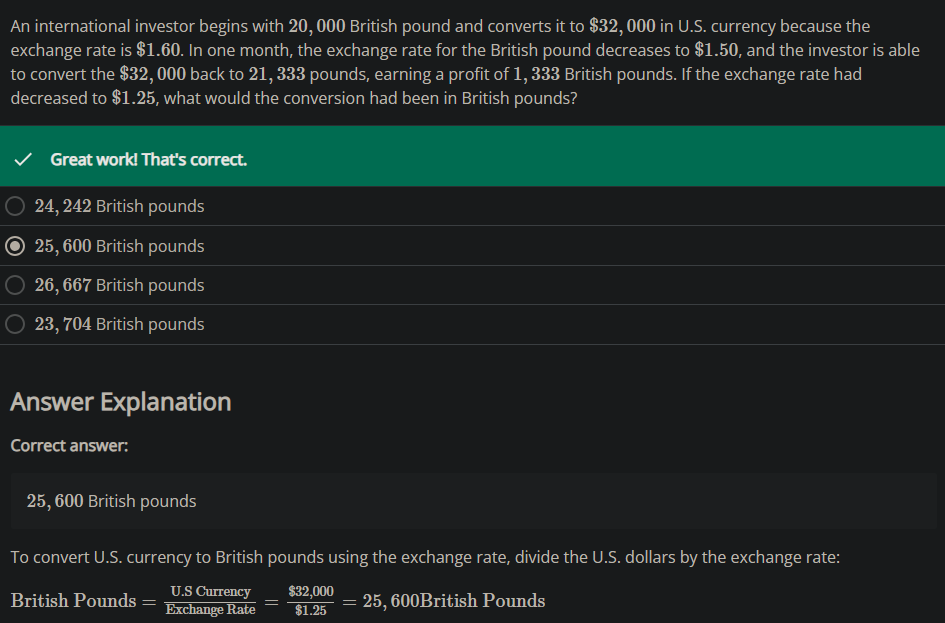
An international investor takes $30,000 in U.S. currency and converts it to 20,000 British pounds (the current exchange rate is $1.50). In one month, the exchange rate increases to $1.60 and the investor can convert the 20,000 British pounds to $32,000, earning a profit of $2,000. What is this a scenario of?
If an investor expects exchange rates to increase from 1British Pound=$1.50 to 1British Pound=$1.60, then the investor can earn a profit by ____________.
increasing their portfolio investment in British-denominated assets
Say that a British pound is currently worth $1.50 in U.S. currency. However, the investor believes that in a month, the British pound will be worth $1.60 in U.S. currency. This investor could change $24,000 for £16,000. In a month, if the pound is worth $1.60, then the portfolio investor can trade back to U.S. dollars at the new exchange rate, and have $25,600—a nice profit.
Which of the following best describes the price of a currency in the foreign exchange market?
equilibrium exchange rate
In a normal supply and demand graph, price is listed on the vertical axis. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is listed on the vertical axis. The exchange rate is the price of a specific currency in terms of another currency. That is, it is how many units of a foreign currency it takes to purchase one unit of a domestic currency. Or, atlernatively it is how many units of a foreign currency can be bought using one unit of a domestic currency.
True or false?
The Chinese yuan is one of the top three most frequently traded currencies.
False
The Chinese yuan accounts for less than 4% of daily foreign exchange transactions.
What is not true about arbitrage?
It involves central banks building up large reserves of their country's currency to stabilize its value.
Arbitrage is the buying and selling goods or currencies across markets at a profit.
Which group does not benefit from a weaker U.S dollar?
U.S. tourists abroad
A weaker U.S. dollar benefits U.S. exporting firms, foreign tourists in the United States, and U.S. investors abroad. A stronger U.S. dollar benefits foreign firms exporting to the United States, U.S. tourists abroad, and foreign investors in the United States.
How does the "supply" of U.S. dollars affect the dollar's exchange rate?
A higher supply of U.S. dollars will lower the exchange rate.
A larger supply of U.S. dollars will make for a "lower" exchange rate.
Supply for the U.S. dollar comes from __________.
U.S. investors who want to make portfolio investments in other countries
Supply for the U.S. dollar can be traced to four sources: foreign firms that have sold imported goods in the United States, earned U.S. dollars, and are trying to pay expenses incurred in their home countries; U.S. tourists leaving to visit other countries; U.S. investors who want to make foreign direct investments in other countries; and U.S. investors who want to make portfolio investments in other countries.
True or false?
The equilibrium exchange rate occurs at the intersection of the demand for currency and its supply curve in the foreign exchange market.
True
What is an "exchange rate"?
An exchange rate is is the price of a country's currency in terms of another currency or currencies.
Economists summarize the movement of exchange rates with a trade-weighted exchange rate, which is an index of exchange rates. The rates at which most currencies exchange for one another are determined by demand and supply.
Why might a country choose to let its currency float?
A floating exchange rate is self-regulating.
A floating exchange rate is an exchange rate determined by the foreign exchange market.
True or false?
Purchasing power parity determines exchange rates in the short term.
False
Exchange-rate movements in the short term are primarily driven by the news, such as reports or speculation about interest changes and people's optimism or pessimism about coming economic growth or recession. In contrast, PPP (purchasing power parity) describes the long-term behavior of exchange rates. The economic forces behind PPP eventually equalize the purchasing power of currencies, but it can take many years, typically from four to 10 years, to do so.
True or false?
One reason to sell a currency in the foreign exchange market is the expectation that the currency's value is about to increase.
False
One reason to demand a currency on the foreign exchange market is the belief that the currency's value is about to increase. One reason to supply a currency—that is, sell it on the foreign exchange market—is the expectation that the currency's value is about to decline.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to purchasing a firm (at least ten percent) in another country or starting up a new enterprise in a foreign country.
To be considered foreign direct invest, a firm must __________.
Purchase at least ten percent of a firm located in another country
start a new enterprise in a foreign country
We often divide financial investments that cross international boundaries and require exchanging currency into two categories. Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to purchasing a firm (at least ten percent) in another country or starting up a new enterprise in a foreign country. For example, in 2008 the Belgian beer-brewing company InBev bought the U.S. beer-maker Anheuser-Busch for $52 billion. To make this purchase, InBev would have to supply euros (the currency of Belgium) to the foreign exchange market and demand U.S. dollars.
Which of the following is not true of the foreign exchange market?
Each country has its own currency.
The foreign exchange market is the largest market in the world economy by far. It involves the buying and selling of currencies, mainly involving transactions with the U.S. dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen. The exchange rates in the foreign exchange market are usually determined by market forces. Because of the differing currencies used by countries, most of the international economy takes place in a situation of multiple currencies. However, not all countries have their own currency. Sometimes small economies use the currency of neighboring or larger countries.
True or false?
If the U.S. dollar is strong, then American exporters benefit.
False
When the U.S. dollar is strong, American importers benefit, because their money goes further. Exporters have trouble exporting their goods, which have higher relative prices in the international market.
What is the best definition for foreign direct investment?
A foreign direct investment is the purchase of more than ten percent of a firm or the creation of a new enterprise in another country.
A foreign direct investment is the purchase of more than ten percent of a firm or the creation of a new enterprise in another country.
Who is harmed by a weaker currency?
foreign investors in the home country
A weaker currency negatively affects foreign firms exporting to the home country, citizens of the home country as tourists abroad, and foreign investors in the home country. A stronger currency negatively affects home country exporting firms, foreign tourists in the home country, and investors from the home country abroad.
A result of a depreciating currency is __________.
a decrease in the amount of currency exchanged for a given amount of another currency
When a currency depreciates, the exchange rate decreases and the currency is weakened. A lower exchange rate means that the amount of currency needed to buy a given amount of another currency is greater. Equivalently, the amount of other currencies that can be bought with a given amount of the given currency is less.