Serology
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is tested in an antigen test?
Antigen in serum, exotoxins, endotoxins, mucotoxins, bacteria cell walls, viruses, protozoans, fungi, and endogenous cells that have been altered (like cancer)
What is an immunoglobulin?
Large protein molecule produced by specialized B lymphocytes in response to specific antigens
Innate immunity
First line immunity defense (Skin and MM)
Acquired immunity
Second line of defense after innate
Humoral immunity
Memory immunity, responds to specific antigens by producing plasma cells
B memory cells
Recognize antigens from previous exposure and clone to make huge numbers of specigic antibodies (immunoglobulins)
IgM
First responder immunoglobulin. Produces immune response to new antigens and is effective in neutralizing viruses
What is the second most common immunoglobulin?
IgM
IgG
Essential immunoglobulin that coats antigen and enables destruction of it by macrophages
What is the most common immunoglobulin?
IgG
IgA
Coats the RR and GI tract. Binds to antigens and prevents attachments of them to body
IgE
Allergy immunoglobulin. Release histamine and other substances to cause inflammation in response to allergy.
How do skin allergy tests work?
Detects specific IgE antibody by injected specific antigen ID and inflammation starts quickly if positive.
IgD
Immunoglobulin only seen in primates, rodents, and maybe dogs
What are compliment proteins?
Proteins in blood that assist in lysis of pathogens in the innate system.
What are type 1 hypersensitivity reactions?
Overreaction from IgE antibodies (allergy) which can cause as little as minor skin irritation to fatal anaphylactic shock
What are type 2 hypersensitivity reactions?
Antibodies attacking themselves
What can cause type 2 hypersensitivity reactions?
IMHA, incompatible blood transfusions, ITP, neonatal isoerytholysis
What are type 3 hypersensitivity reactions?
Antigen-antibody complexes are not phagocytized properly causing them to deposit into tissues which cause inflammation
What can cause type 3 hypersensitivity reactions?
SLE, glomerulonephritis, rheumatoid arthritis
What are type 4 hypersensitivity reactions?
Inflammatory reaction 24 hours or more after exposure, mediated byT-Lymphocytes
What form of hypersensitivity is also known as “delayed hypersensitivity”
Type 4
What does sensitivity mean?
A test’s ability to correctly identify a patient as positive
What does specificity mean?
A test’s ability to correctly identify a patient as negative
What does a False positive mean?
A test result that incorrectly states a patient is positive when they actually are not.
When a test result is a false positive that means that the test is not very ______
Specific
What does a False negative mean?
A test result that incorrectly states a patient is negative when they actually are.
When a test result is a false negative that means that the test is not very ______
Sensitive
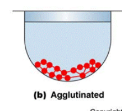
What is agglutination?
Cells in a well coated with antigens or antibodies. If a serum is positive for antigen or antibody, then they will link together creating a mat at the bottom.
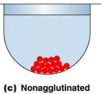
What does a negative agglutination test look like?
Not enough antibodies present in the test which cause the Antigens in the test to roll from the sides of the well to the center and form a mound at the bottom.
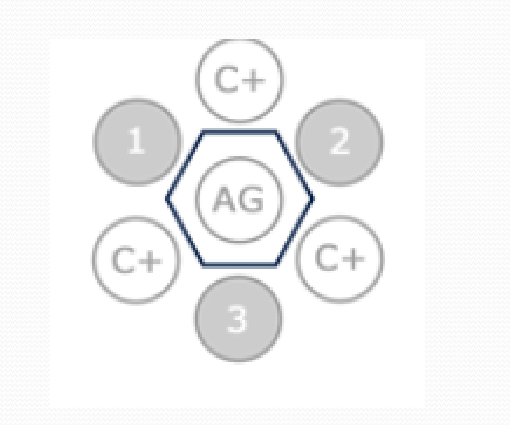
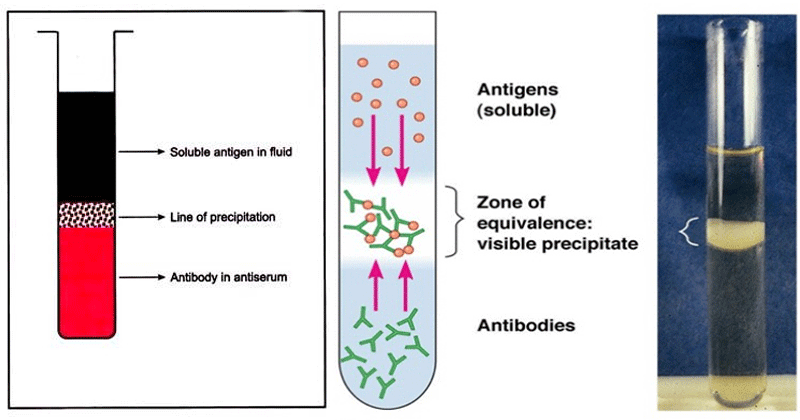
Immunodiffusion
Test that uses gel to detect reaction between antigen and antibodies in serum based on the line that is created
What does a positive agar gel immunodiffusion test look like?
Line is formed surrounding the control antigen in the middle well
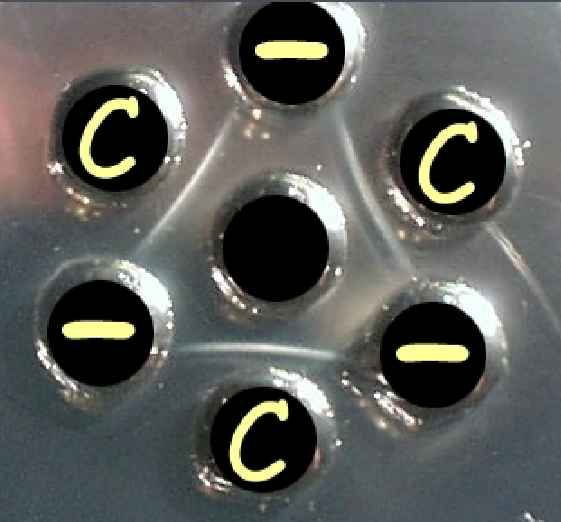
What does a negative agar gel immunodiffusion test look like?
Lines only form to serum
What disease is commonly immunodiffusion tests?
Coggins test, detects Equine Infectious Anemia (EIA)
What is a titer?
Indirect measurement of antibody present in serum. Determines strength of immunity towards the antigens
How is a titer performed?
Agglutination test with varying dilutions of antigen in each well. Serum is placed in each well. The highest dilution of serum that agglutinates indicates the strength of anitbodies in body.
Is a 1 to 10 titer stronger than a 1 to 200?
No, the more diluted the test, the less antigen present in the well. If the serum being tested can detect antigens in a highly diluted test that means the immunity is strong.
What are ELISA tests?
Tests monoclonal antibodies attached to membranes. Sample goes in, test looks for antibodies or antigen (depending on test).
What does a positive ELISA test look like?
Positive antigen or antibody in serum forms Ag-Ab complex on membrane in test. Test is then washed off to remove excess antigens. A specific antibody with an enzyme is added that binds to antibodies. Test is washed again to wash off excess enzymes. A third solution is added which changes color based on presence of enzymes.
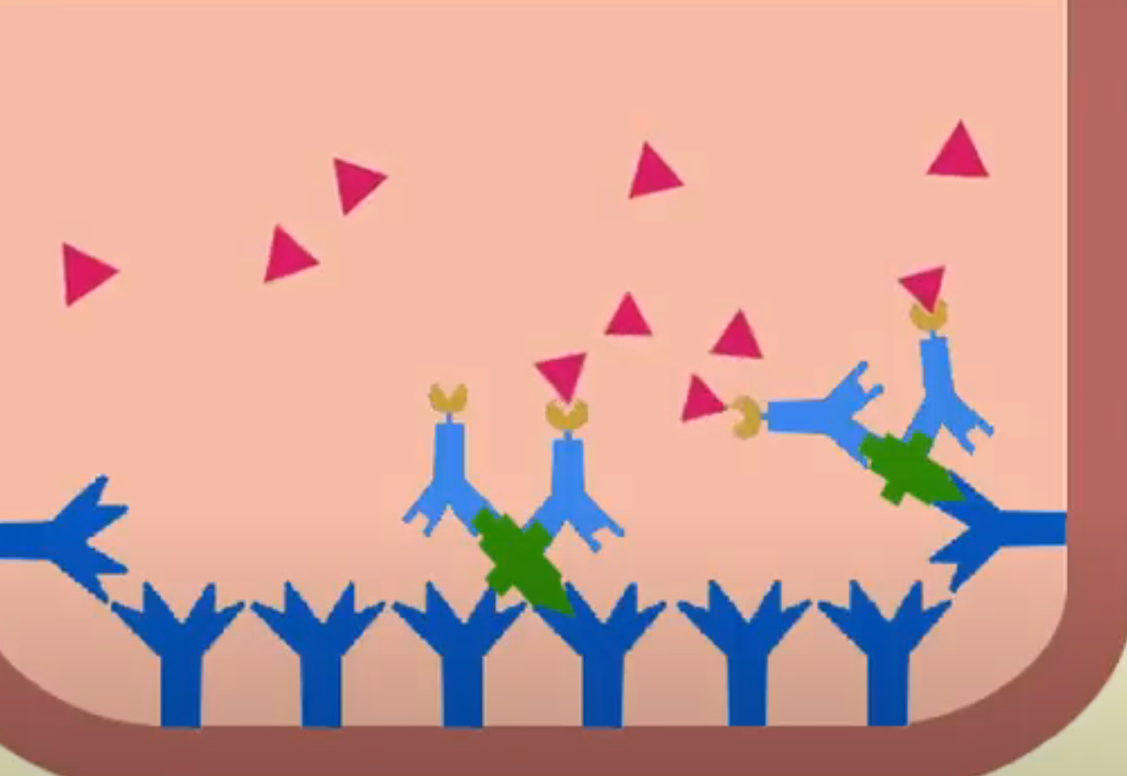
What are IFA tests? (Indirect fluorescent assay)
Samples are stained with fluorescent antibodies and then looked under a fluorescent microscope
What does a positive IFA test look like?
Antibodies bind to the antigen and become visible under a microscope, indicating a positive test.
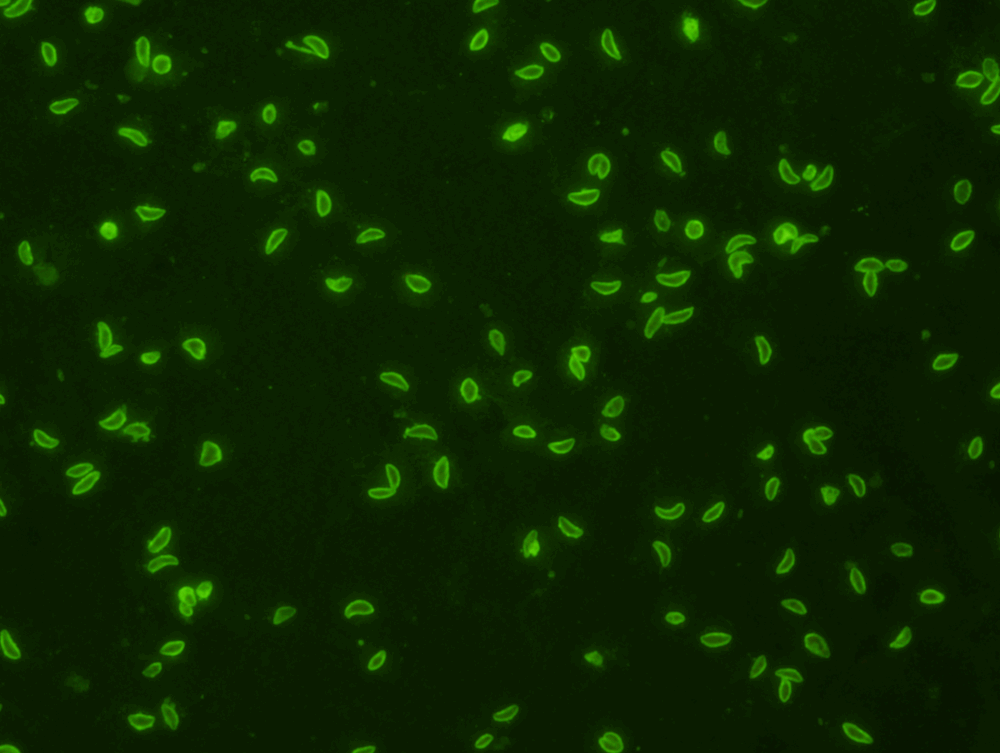
What are Rapid immunomigration tests (RIM)
Porous strips containing antibodies that show a colored band when a positive antigen flows through it.
What are tuberculin tests?
Tuberculin is injected intradermally in cattle. If positive swelling occurs in 72 hours