Feline retroviruses
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What are the feline retroviruses
Feline leukaemia (FeLV) - type c mammalian retrovirus
Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) - lentivirus
Feline synctium forming virus (FeSFV) - spumavirus
Endogenous viruses
What is virus classification based on
The geonome
Number and sense of RNA and DNA strands
Morphology
Genome sequence similarity
Ecology
What are the key properties of Retroviridae
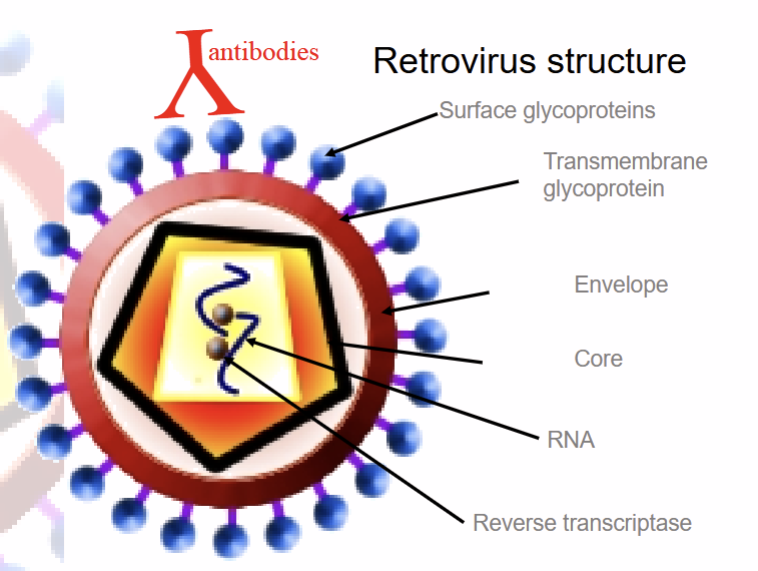
Enveloped ssRNA viruses with genone organisation 5’-gag-pro-pol-env-3’
What does the gag gene encode
Internal structure proteins matrix, capsid and nucleocapsid produced by proteolytic processing
What does the pro gene encode
Viral protesases which cleaves gag, pro, pol and env products
What doe the pol gene encode
Reverse transcriptase which contains DNA polymerase and integrase for geonome replication
What does the env gene encode
Surface glycoprotein and transmembrane protein forming the receptor binding complex
How does retroviridae replicate
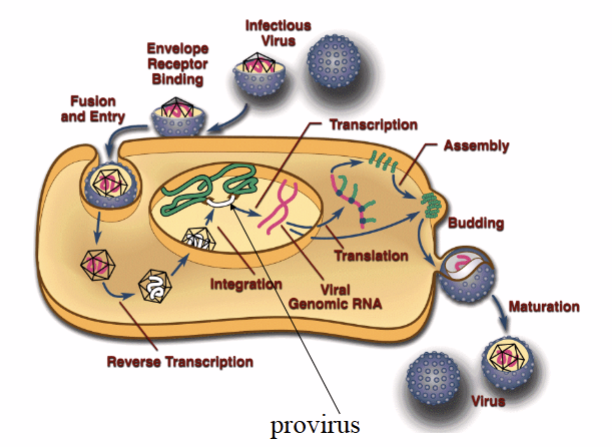
What are two unique features of Retroviridae replication
Their genome is made by host transcription machinery with no viral polymerase involved
Their positive sense RNA cannot act directly as mRNA after infection
What is the role of Reverse Transcriptase in Retroviridae
A viral RNA-dependent DNA polymerase that synthesises complementary DNA from the viral RNA genome
What is the role of Integrase in Retroviridae
Binds viral cDNA and host DNA to inset the viral genome into the host genome
What are endogenous retroviruses
Remnants if ancient retroviral insertions into germ cells that now make up 8% of human DNA
How are endogenous retroviruses transmitted
Vertically as permanent parts of the host genome
What diseases are endogenous retroviruses associated with
Various cancers
Autoimmune diseases
Neurological disorders
What biological roles do endogenous retroviruses play
Placentation
Early embryogenesis
Foetal development
What are the three subtypes of feline leukaemia virus
A, B and C distinguished by genome analysis and serology
What type of FeLV subtype is transmissable and most common
Type A
How do FeLV types B and C arise
As recombinants between type A and endoenous retroviruses or as mutants of type A
How is FeLV excreted
Saliva
Urine
Faeces
Milk
What type of contact is usually required for FeLV transmission
Close friendly contact
Does FeLV transmit vetically
yes vertical and transplacental transmission are common
What does PCR detect in PeLV diagnosis
Decects PeLV proviral DNA integrated into host cells
What does RT-PCR detect is FeLV diagnosis
Detects FeLV viral RNA in blood or tissues
What does a lateral flow test detect in FeLV diagnosis
Detects FeLV antigen circulating in blood
Where does FeLV first replicate after ingestion
Oropharynx and local lymph nodes
What follows primary viraemia in FeLV infection
Replication in other lymphoid tissues and bone marrow
What occurs after secondary viraemia in FeLV infection
Persistent viraemia
Clinical disease
Death or virus elimination
What are the possible outcomes of FeLV infection aside from persistent viraemia
Virus elimination or persistent latent infection with rare viraemia and shedding
What do test results show in primary viraemia
Provirus positive in PCR
Antigen positive
Antibody negative
Virus positive in RT-PCR
What do test results show in persistent latent infection
Provirus positive
Antigen negative
Virus negative in blood
Antibody positive
What do test results show in persistent viraemia
Provirus positive in PCR
Antigen positive
Antibody postive
Virus positive in RT-PCR
What are the main sources of FeLV virus exposure
Contact with persistently infected cats and in utero transmission
How does age affect FeLV susceptibility
It decreases with age
Only 1 in 5 cats over 16 weeks become persistently infected
What immune factors are protective against FeLV
VN antibody
Maternal derived antibody protects for 4 weeks
What disease syndromes can FeLV cause
Reproductive failure
Anaemia
Immunodeficiency
Neoplasia
How does FeLV A contribute to neoplasia
By sporadic insertion near cellular oncogenes activating proto-oncogenes or distributing tumour suppressor genes
What can common FeLV integration sites be used for
Studying oncogenesis
What are the four main types of FeLV-associated lymphoma
Mediastimal
Multicentric
Alimentary
Leukaemic
Besides major lymphoma types where else can FeLV neoplasia occur
Kidney
Nose
Eye
Skin
CNS
What are the clinical signs of alimentary lymphoma
ANorexia
Weight loss
Anaemic
How do you diagnose alimentary lymphoma
Radiography
Biopsy
What are the clinical signs of mediastinal lymphoma
Tachypnoea
Dyspnoea
Regurgitation
Weight loss
What is seen of a clinical exam on medialstinal lymphoma
Muffled heart sounds
Palpate increased thoracic resistance
How is mediastinal lymphoma diagnosed
Ultrasound
Radiography
Biopsy
What are the clinical signs of multicentric lymphoma
Posterior paralysis
Renal failure
What can be seen on a clinical exam of multicentric lymphoma
Peripheral gross lymphadenopathy
How is multicentric lymphoma diagnosed
Clinical signs
Biopsy
What are the clinical signs of leukaemia
Pyrexia
Weakness
Anorexia
What can be seen on a clinical exam of leukaemia
Haemorrhage
How is leukaemia diagnosed
Haemotology
Biopsy of bone marrow
What characterises primary FeLV anaemia
Red cell aplasia
Total marrow aplasia
Non-regenerative
Normocytic
Normochromic
What FeLV subtype is associated with primary anaemia
Subtype C as mutation allows infection of erythroid precursors
What characterises secondary FeLV anaemia
Regenerative anaemia due to myeloid tumours in bone barrow
Haemolytic anaemia is common but often milk and missed
What is the term for FeLV-associated immunosuppression
FAIDs
What clinical problems are associated with FAIDS
Secondary infections
Poor wound healing
Abscessation
Chronic respiratory or enteric infections
What are common clinical signs in FAIDS-affected cats
Thin
Persistently ill
Pyrexia
Gingivitis
Increased risk of haemobartonella
FIP
Panleukopnea-like enteritis
When does fetal resorption typically occur in FeLV-infected queens
At 3-5 weeks of pregnancy
What happens to kittens that survive to birth from FeLV-infected queens
They are persistently infected and may develop fading kitten syndrome
What is the purpose of a test-and-remove (T&R) programme for FeLV
To rehome or euthanise persistently viraemic cats essential in colonies
How is vaccination used in FeLV control
As part of colony management alongside T&R
What simple management measure helps reduce FeLV transmission
One food bowl per cat
What is the first step in a FeLV test-and-remove programme for colonies?
Test all cats with a lateral flow test and house all positives seperately
What cats can join the main colony after the 12-week retest
Cats that are negative twice or cats positive once then negative
What should be done with cats that were negative first and positive at the 12-week retest?
House separately and retest again in 12 weeks
What is the outcome for cats testing positive twice
They should be permanently removed from the colony
How often should all colony cats be retested
Every 6-12 months with all new entries being tested
What types of FeLV vaccines are available
Killed
Subunit
Recombinant canarypox
When is the FeLV vaccine given
First at 8-9 weeks old then a booster 3 weeks later
Are FeLV vaccines considered core
They are considered non-core but annual boosters are optional
What is the main approach to treating FeLV
Largely supportive care
Are there specific antivirals for FeLV
No drugs effective in cell culture are often toxic to cats
What treatment may prolong survival in FeLV cats
Interferon
Can lymphomas in FeLV cats be treated
Some can with cytotoxic drugs but other problems usually develop
What is feline immunodeficiency virus
A lentivirus related to HIV
What does FIV cause
Immunodeficiency and associated with a variety of lesions
Is FIV zoonotic
No it is not
What is the prevalence of FIV
Less then 5% in doemstic cats world wide
Which cats is FIV more common in
Males
Free roaming
Feral
Unstable colonies
How is FIV transmitted
Biting
Transplacental
Milk
What does FIV infect
CD4 T-cell lymphocytes
How does FIV gradually develop
Decreases CD4
Decreases mitogen and antigen proliferation assays
Decreased expression of MHC II
Where is FIV isolated from
Blood
CSF
Lymphoid organs
Saliva
How is FIV treated
Mainly supportive
How is FIV prevented and controlled
Prevent cats fighting
Keep indoors
Isolate infected cats
What vaccinations are there for FIV
Non in Europe
Fel-O-Vax FIV used on USA, Oz and NZ
Whole inactivated virus
What is the structure of rotraviruses
How is FIV and FeLV diagnosed
In house latent flow tests
IF
IFAT
Isolation
Western blot
PCR
RT-PCR
What types of in-house lateral flow tests (LFT) are used for FeLV/FIV diagnosis
SNAP - Idexx
DUO speed - biovet test
FASTest - Megacor
WITNESS - Synbiotics
One step - EVL
Why is FeLV testing based on antigen rather than antibody
Most seropositive cats have cleared viraemia
Vaccination can affect results
Antibody levels can fluctuate
Why is FIV testing based on antibody rather than antigen
Virus isolation is slow and expensive
Early virus levels fluctuate
No vaccine interferes
Antibodies remain high
Cats cannot clear infection
What happens in FeLV tests
Biological sample containing p27 antigen binds to antibody 1
Aqueous environment of membrane leads to migration of particles
p27 acts as a bridge to immobilise the particles by binding to antibody 1 and 2
Results in positive test
What do postive immunoflorescence FeLV tests look like
What happens in FIV tests
Biological sample containing FIV antibodies binds to FIV antigen in sample well
Aqueous environment of membrane leads to migration of particles
FIV antibody in test sample acts as a bridge to immobilise the particles by binding to both FIV antigens
Results in FIV positive test
What does an immunoflorescence antibody test in FIV look like
What happens in Western blot test for FIV
Viral proteins separated by gen electrophoresis
Transferred to membrane
Patient antibodies bind to specific FIV proteins
Detection confirms infection
What gives a false positive when measuring FIV antibodies
Maternally derived antibodies when younger then 6 months
What gives a false negative when measuring FIV antibodies
Seroconversion at less than 12 weeks
Decrease in serum antibody
What causes false positives in lateral flow tests
Cat anti-mouse antibody
What is sensitivity
Proportion of true positives picked up by the test
What is specificity
Proportion of true negatives picked up by the test