Big Fat Nerves
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Recurrent Connections
feedback loops common in retina returning signals to presynaptic cells
Sympathetic Nervous System
“fight or flight”; uses norepinephrine; primary nucleus = superior cervical ganglion
Parasympathetic Nervous System
uses acetylcholine; ganglia close to target tissue (ciliary, pterygopalatine)
Autonomic Targets in Eye
iris & ciliary muscles, tarsal muscles, choroidal vessels, lacrimal and sweat glands
Optic Nerve (CN II)
main sensory nerve of eye, ~1 million RGC axons
Optic Chiasm
site where nasal retinal fibers cross and temporal fibers remain ipsilateral
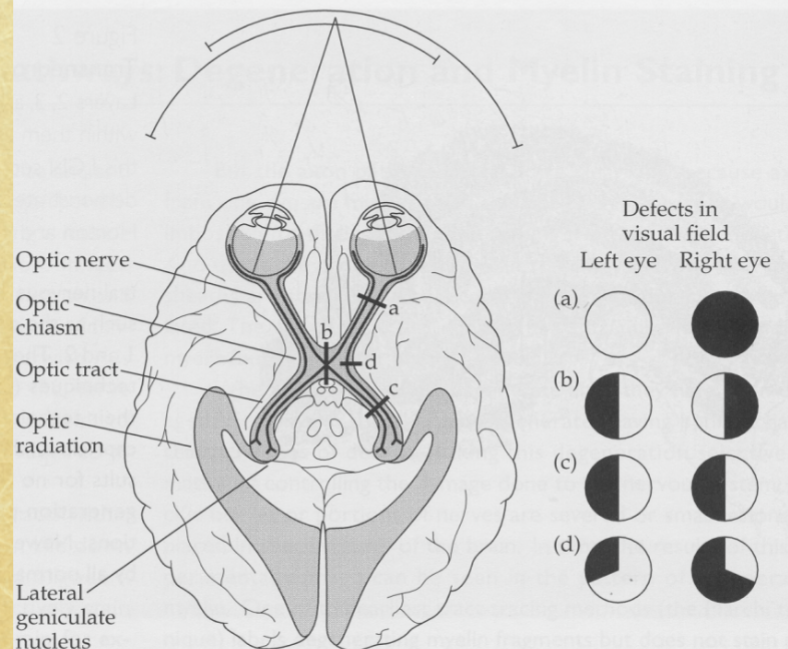
Contralateral Projection
nasal hemiretinal fibers crossing to opposite brain side
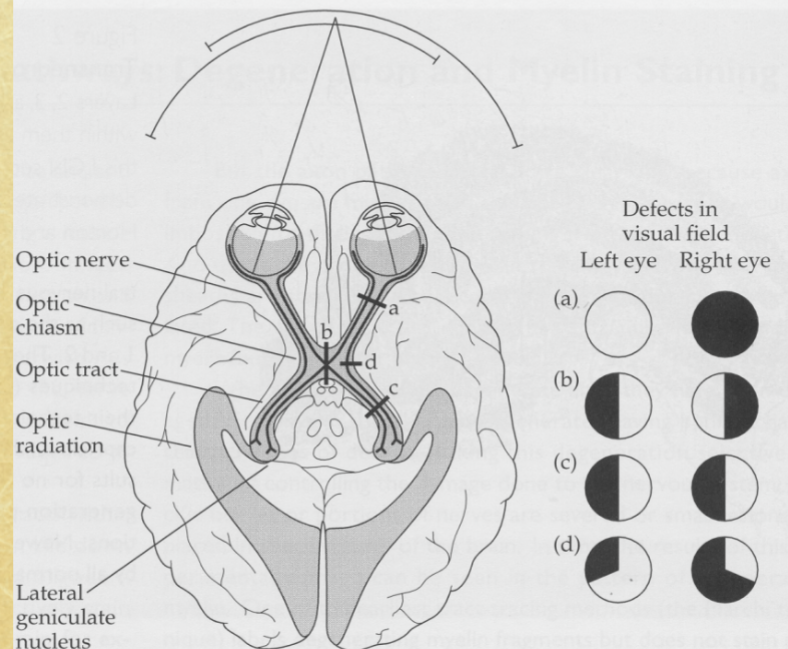
Ipsilateral Projection
temporal hemiretinal fibers staying on same side

Foveal Representation
bilateral projection to both optic tracts, high in LGN (house of representatives), low in superior colliculus (senate)
Optic Tracts
post-chiasmal pathways maintaining rough retinotopy
Retinotopic Projection
neighboring retinal regions map to neighboring areas in LGN and SC
LGN (Lateral Geniculate Nucleus)
main relay from retina to cortex; six-layered structure
LGN Contralateral Inputs
layers 1, 4, 6 (1, 4 and 6 cross the river styx), layer 1= magnocellular (parasol, periphery), layer 4+6= parvocellular (midgets, central)
LGN Ipsilateral Inputs
layers 2, 3, 5 (layers 2, 3 and 5 stay alive), layer 2= magnocellular (parasols, periphery), layer 3+5= parvocellular (midgets, central)
Left LGN Input
left temporal retina + right nasal retina (right visual field)
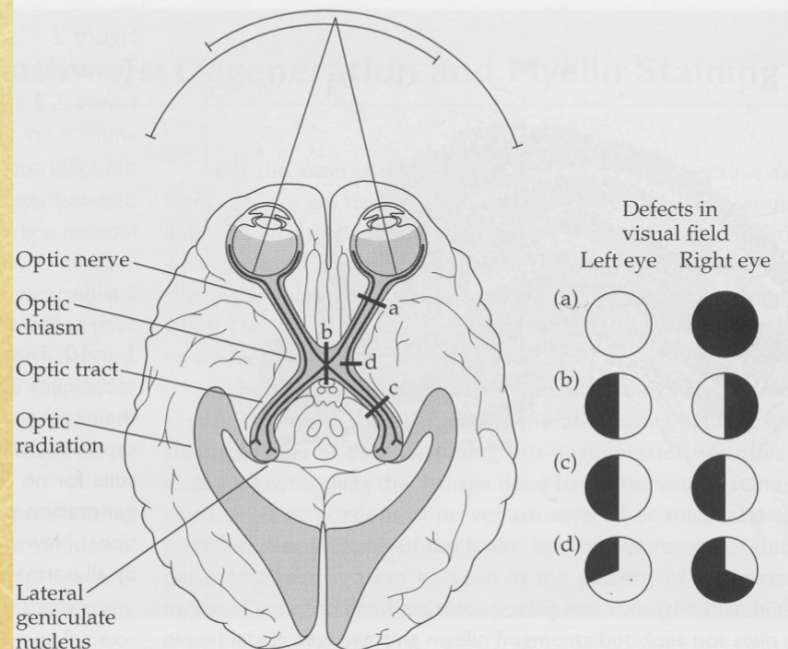
Right LGN Input
right temporal retina + left nasal retina (left visual field)
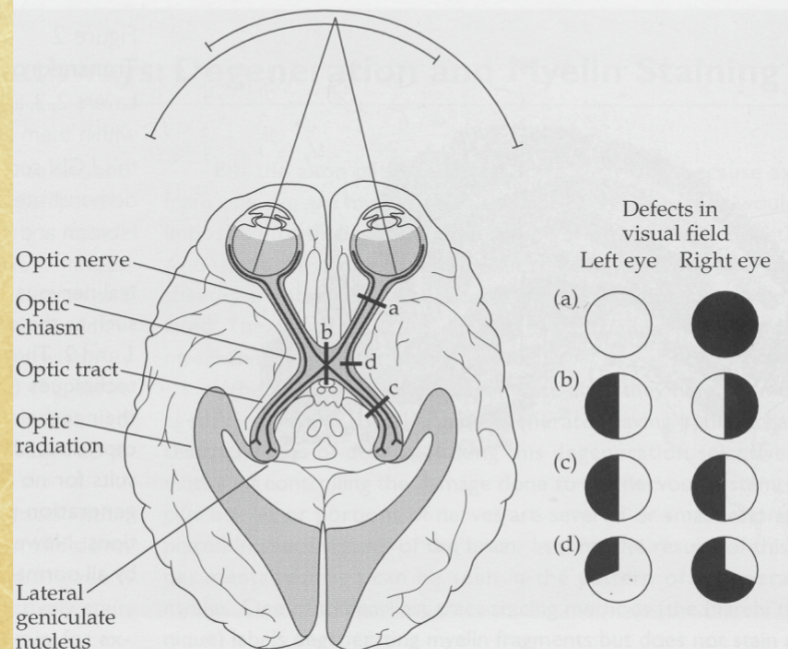
Optic Radiations
axon pathway from LGN to primary visual cortex

LGN Retinotopy
neighboring RGCs synapse in neighboring LGN regions
LGN Foveal Magnification
large representation of macular fibers due to high RGC density
Scotoma
visual field defect corresponding to damaged retinotopic area
Non-Visual Retinal Targets
Superior colliculus (eye movement, underrepresented fovea), Pretectal nuclei (pupillary reflex), Accessory optic nuclei (head-eye coordination), Suprachiasmatic nucleus (circadian rhythm)
Hemianopia
blindness in half of each visual field from optic tract lesions
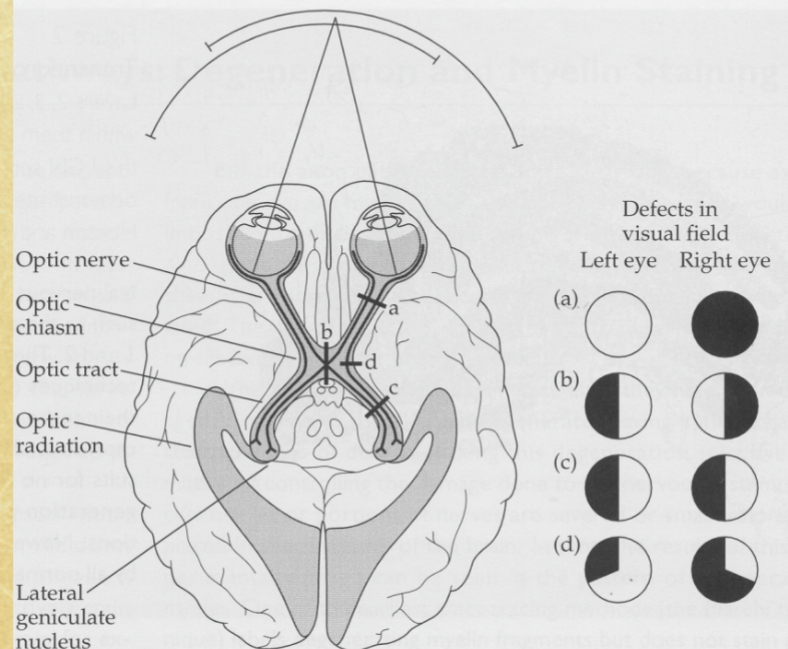
Primary vs Secondary Pathway Lesions
primary pathway lesions affect vision; secondary do not cause field loss but affect reflexes/movement
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V), cell body location
main sensory nerve of face; cell bodies in gasserian ganglion, forms opthalmic, mandibular and maxillary branches
Ophthalmic Division (V1)
sensory from eye and upper face, forms nasociliary, lacrimal and frontal divisions
Nasociliary Nerve
only V1 branch entering globe; receives long and short ciliary input (forms ethmoids, infratrochlear, long + short ciliary nerves)
Frontal Nerve
supratrochlear + supraorbital branches to forehead and upper lid
Lacrimal Nerve
carries parasympathetic fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion to lacrimal gland
Maxillary Division (V2)
forms zygomatic nerve, sensory for middle of the face
Zygomatic Nerve
branch of V2 entering orbit; skin of lower lid and cheek, carries lacrimal gland (communicating branch), facial and temporal branches
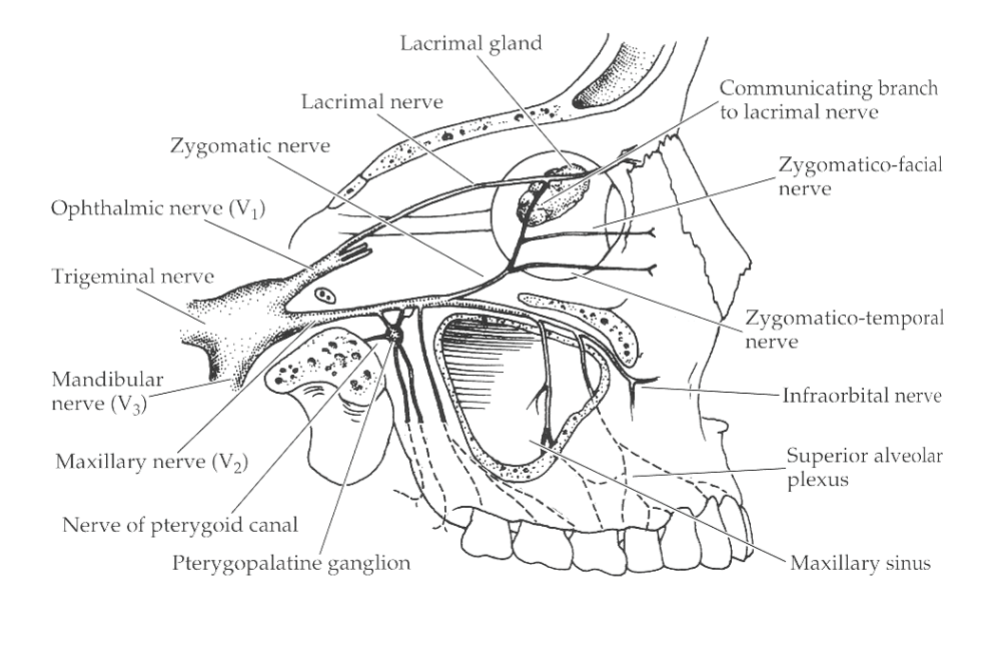
Mandibular Division (V3)
sensory & motor to lower jaw
Long Ciliary Nerves
sensory, mostly corneal fibers (also some iris and CB); join nasociliary nerve, activation leads to blink reflex via CN VII and tearing
Short Ciliary Nerves
mixed sensory (info from uvea), sympathetic, parasympathetic fibers passing through ciliary ganglion, 10-15 nerves down to 1 collection point (sensory root of ciliary ganglion)
Corneal Reflex
blink + lacrimation from corneal stimulation
Retrobulbar Block
injection behind eye producing anesthesia
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
innervates SR, MR, IR, IO, levator; nuclei= ipsilateral except SR, all nerves ipsilateral, also carries parasympathetic fibers to ciliary ganglion
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
innervates superior oblique; smallest + longest CN → trauma-prone, nuclei contralateral, nerves ipsilateral
Abducens Nerve (VI)
innervates lateral rectus; vulnerable to lateral head trauma, nerves and nuclei ipsilateral
Oculomotor Branches
superior division (levator, SR) and inferior division (MR, IR, IO)
Edinger-Westphal Nucleus
preganglionic parasympathetic source for sphincter & ciliary muscles
Cavernous Sinus
venous sinus traversed by CN III, IV, V1, V2, VI and carotid artery; optic nerve excluded
Orbicularis Oculi
muscle closing eyelids; innervated by facial nerve (VII)
Blepharospasm
excessive orbicularis activity from CN VII irritation
Ectropion
eversion of lower lid from CN VII dysfunction
Levator Palpebrae innervation and function
upper lid elevation; CN III
Tarsal Muscles
smooth muscle of eyelids; sympathetic innervation
Ptosis
drooping lid from CN III or sympathetic lesion
Sympathetic Pathway to Eye
superior cervical ganglion → internal carotid plexus → sympathetic root of ciliary ganglion (NO SYNAPSE) → short ciliary nerves → choroid to branch to targets
Iris Dilator Muscle
sympathetic; contraction causes mydriasis
Uveal Vasoconstriction
sympathetically controlled to regulate choroidal blood flow (constant blood flow while arterial pressure increases, inversely proportional to resistance)
Horner’s Syndrome
sympathetic lesion → ptosis (sympathetic tarsal muscle innervation), miosis, anhidrosis, possible low IOP and conjunctival vasodilation
Parasympathetic Pathway to Eye
Edinger-Westphal → travels with CN III → ciliary ganglion → short ciliary nerves
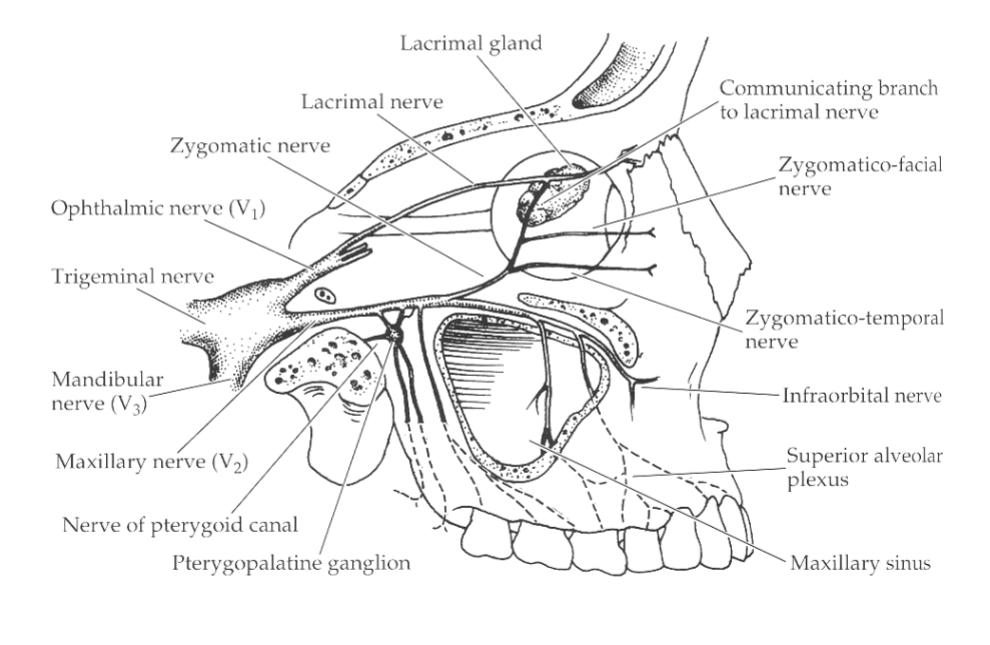
Rami Oculares
EW → postganglionic fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion to orbit
Pupillary Light Reflex
direct & consensual constriction via pretectal → EW nuclei → sphincter muscle
Argyll Robertson Pupil
constricted pupils lacking light reflex but able to accommodate; lesion between pretectal and EW nuclei
Lacrimal Gland Parasympathetic Pathway
lacrimal nucleus → pterygopalatine ganglion → zygomatic nerve → zygomaticotemporal → communicating branch → lacrimal nerve
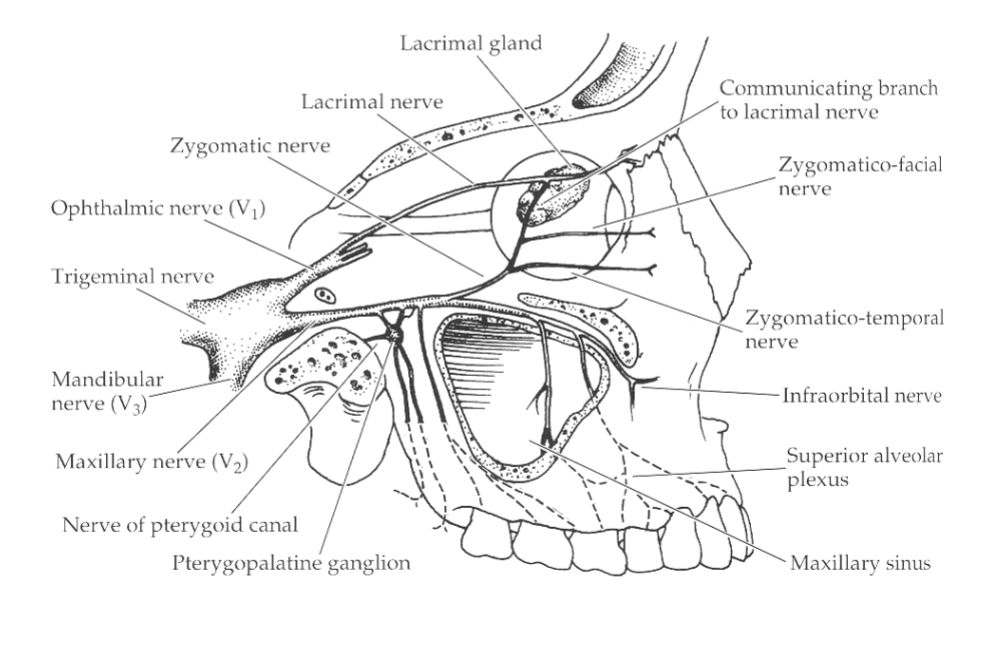
Lacrimal Stimulation
triggers from pain, emotion, bright light
Growth Cones
motile structures guiding developing axons/dendrites
Neuroglial Guidance
glial “adhesive” paths directing axon growth
Laminin
trophic signal directing axons to final targets
Ocular Albinism
pathfinding error causing abnormal optic chiasm crossing
Amblyopia
reduced acuity without refractive or pathological cause; synaptic development issue
Neuronal Regeneration
PNS neurons regenerate (but not the same as before damage); CNS neurons do not
Corneal Nerve Regeneration
occurs due to limited pathway complexity; damaged fibers regrow
Transneuronal Atrophy
degeneration of neurons due to loss of input source