Tissues and Primary Growth of Stem
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Parenchyma
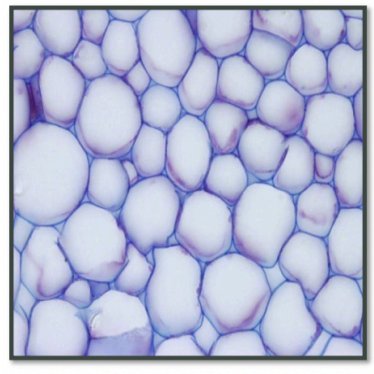
Collenchyma

Schlerenchyma
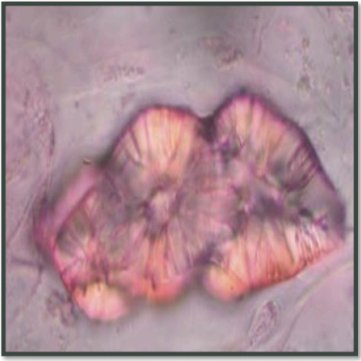
Specialized Parenchyma Cells
Chlorenchyma
Glandular cells
Transfer cells
Phloem
Glandular Cells
What parenchyma cells secrete nectar, fragrances, mucilage, resins and oils?
Resin Canal
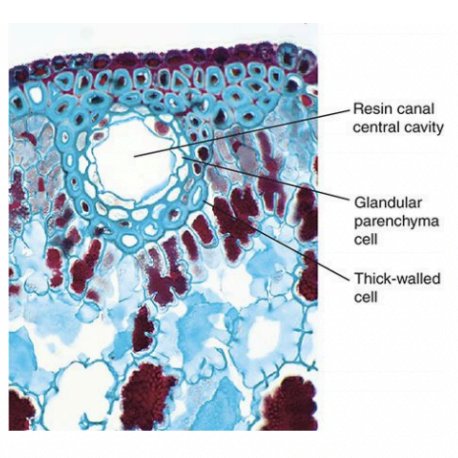
Phloem
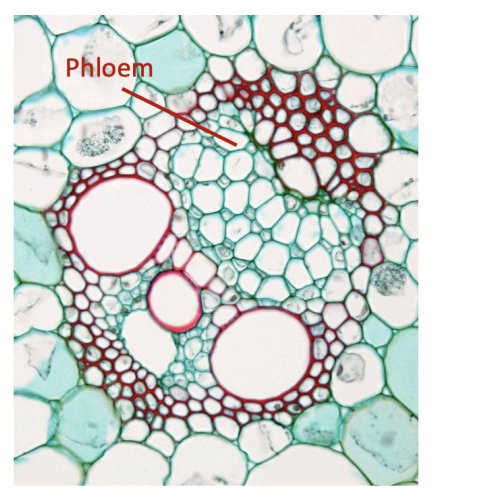
Schlerenchyma
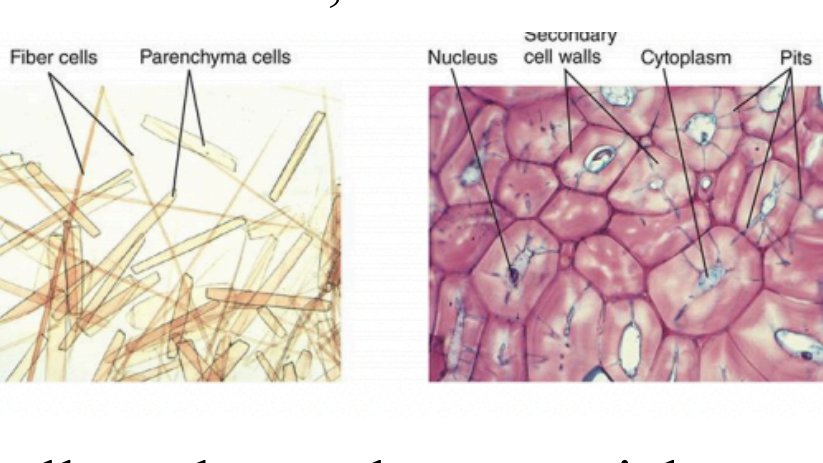
Mechanical (nonconducting) sclerenchyma
Fibers are long and flexible.
Sclereids are short, isodiametric (cuboidal), inflexible, and brittle.
Conducting sclerenchyma
transports water.
Tracheary elements of the xylem
Includes tracheids and vessel elements
shoot
stem with included leaves
leaf axil
stem area just above the point where a leaf attaches
Stolons / Runner
(stem modification)
have especially long and thin internodes allowing dispersal of daughter plants
Bulbs
(stem modification)
short shoots with thick, fleshy leaves
Corms
(stem modification)
vertical, thick stems with thin, papery leaves
Rhizomes
(stem modification)
fleshy horizontal stems that allow a plant to spread underground
Tubers
(stem modification)
horizontal, like rhizomes, but grow for a short period and are mainly a means of strong nutrients
Guard cells
pair of cells that border the stomatal pore
stomatal pore
hole between the guard cells through which gases can pass
Shoot Apical Meristem
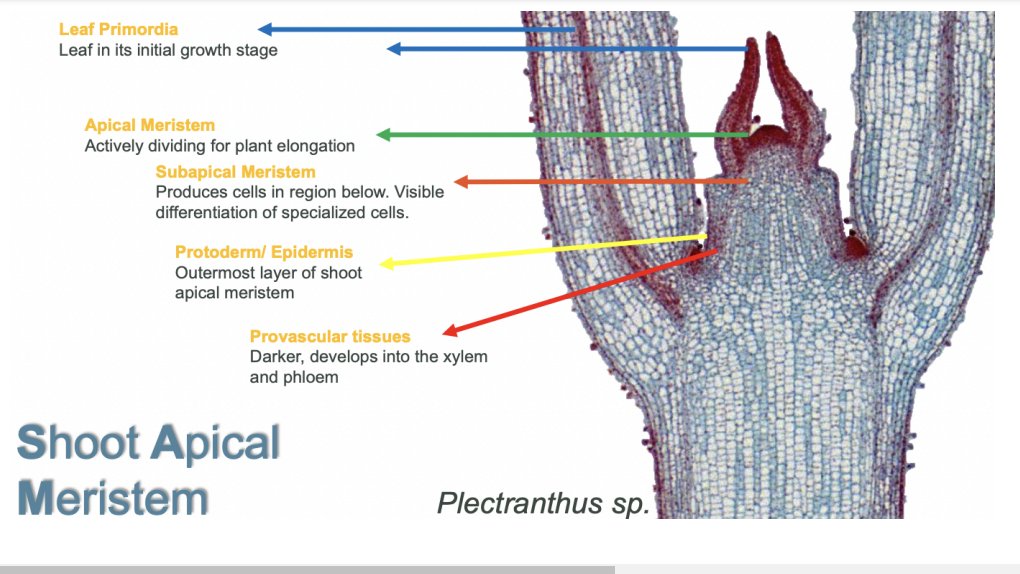
Leaf Primordia
leaf in its initial growth stage
Apical Meristem
Actively dividing for plant elongation
Produce an increase in girth especially for the secondary growth
Located at the tip of stems and roots
Subapical Meristem
produces cells in region below; visible differentiation of specialized cells
Protoderm
aka Epidermis; outermost layer of shoot apical meristem
Provascular Tissues
darker, develops into the xylem and phloem
Upper Tip
where young cells are found when growing up
Lower Tip
where young cells are found when growing down
True
T or F: Single cells of some plants can generate entire plants.
False
Parenchyma cells don’t easily propagate in dark plants
Protoderm
(type of primary meristem)
forms epidermis
Procambium
(type of primary meristem)
forms primary vascular tissue
Ground Meristem
(type of primary meristem)
differentiates into ground tissue
Apical Meristem
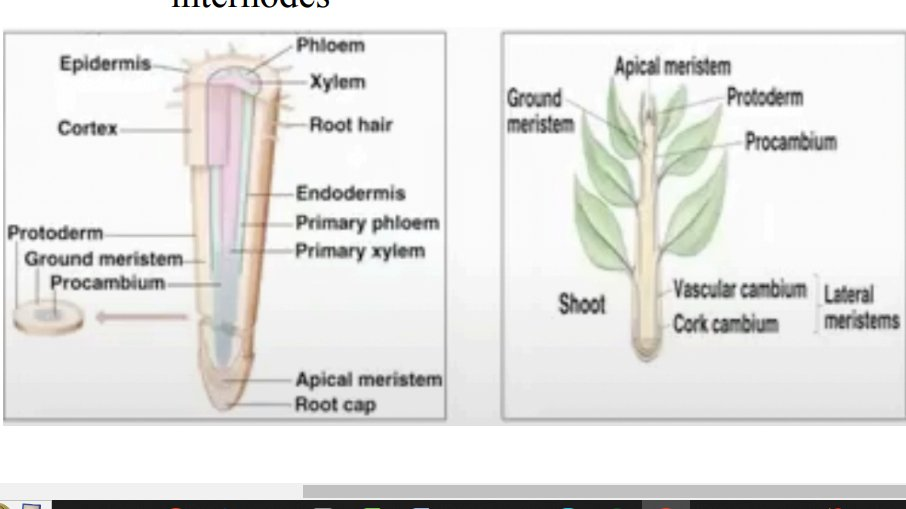
Cork cambium
Produces cork cells
Vascular cambium
Produces secondary vascular tissue
Root and Shoot System
2 components of vascular plants
Root System
system that anchors the plant
penetrates the soil to absorb water and nutrients
Shoot System
Stems: a framework for positioning leaves
Leaves: principle sites for photosynthesis
Vegetative shoot: comprised of the nodes, leaf, axillary buds
Ground Tissue
type of tissue that is made up of parenchymatous cells
ex : collenchyma and schlerenchyma
Dermal Tissue
type of tissue wherein epidermal cells originate from the protoderm cover all parts of the primary plant body
ex : Guard cells, Trichomes, Root hairs (increase surface area)
Vascular tissue
type of tissue that is mainly for conduction
ex : xylem and phloem
Tracheids
shape : long/narrow; with pointed ends
perforations : none
Vessel Elements
shape : short/wide; flat ends
perforations : usually two, one on each end wall
Fiber
schlerenchymatous tissue that supports internal structures
Sclereids
schlerenchymatous tissue that is also called as stone cells and are circular in shape
Apium graveolens
scientific name of celery
Pyrus sp
scientific name of pear
anthocyanin
present in Rhoeo discolor epidermis which is the purple pigmentation that comprises specialized pigments
Collenchyma
this type of tissue is present in the rib/ridges of celery
Sclereids
aka stone cells; cells that are bundled together and are found in pear
Totipotent Cells
type of cell that can develop into any type of cell
Pluripotent cells
type of cell that can develop into many, but not all different types of cells
Multipotent cells
type of cell that can develop into multiple types of cells, but not as many types as pluripotent cells
Height
primary meristem adds up to the plant’s ______
Girth
secondary meristem adds up to the plant’s ______